|
Human Impact On The Environment
Human impact on the environment (or anthropogenic environmental impact) refers to changes to biophysical environments and to ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources caused directly or indirectly by humans. Modifying the environment to fit the needs of society (as in the built environment) is causing severe effects including global warming, environmental degradation (such as ocean acidification), mass extinction and biodiversity loss, ecological crisis, and ecological collapse. Some human activities that cause damage (either directly or indirectly) to the environment on a global scale include population growth, neoliberal economic policies and rapid economic growth, overconsumption, overexploitation, pollution, and deforestation. Some of the problems, including global warming and biodiversity loss, have been proposed as representing catastrophic risks to the survival of the human species. The term ''anthropogenic'' designates an effect or object resulting from h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeast Asian Haze
The Southeast Asian haze is a fire-related recurrent transboundary air pollution issue. Haze events, where air quality reaches hazardous levels due to high concentrations of airborne Particulate pollution, particulate matter from burning Biomass (ecology), biomass, have caused adverse health, environmental and economic impacts in several countries in Southeast Asia. Caused primarily by slash-and-burn land clearing, the problem flares up every dry season to varying degrees and generally is worst between July and October and during El Niño, El Niño events. Transboundary haze in Southeast Asia has been recorded since 1972 with the 1997 Southeast Asian haze, 1997 and 2015 Southeast Asian haze, 2015 events being particularly severe. Industrial-scale slash-and-burn practices to clear land for agricultural purposes are a major cause of the haze, particularly for palm oil and pulpwood production in the region. Burning land occurs as it is cheaper and faster compared to cutting and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wired
Wired may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Music * ''Wired'' (Jeff Beck album), 1976 * ''Wired'' (Hugh Cornwell album), 1993 * ''Wired'' (Mallory Knox album), 2017 * "Wired", a song by Prism from their album '' Beat Street'' * "Wired", a song by Sevendust from their '' eponymous'' debut album * "Wired", a song by Nebula from their 2006 album ''Apollo'' Television * ''Wired'' (TV series), a 2008 British television miniseries * ''Wired'', 1988 TV series produced by Tim Graham * " Wired", a 2005 two-part episode of ''Power Rangers: SPD'' * " Wired", a 2002 two-part episode of ''The Zeta Project'' animated series Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * ''Wired'' (book), a 1984 book by Bob Woodward about the American actor and comedian John Belushi ** ''Wired'' (film), a 1989 adaptation of the book by Bob Woodward * ''Wired'' (novel), a 2005 science fiction novel by Douglas E. Richards about a brilliant genetic engineer who discovers how to temporarily achie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Collapse
An ecosystem, short for ecological systems theory, system, is defined as a collection of interacting Organism, organisms within a biophysical environment. Ecosystems are never static, and are continually subject to both stabilizing and destabilizing processes. Stabilizing processes allow ecosystems to adequately respond to destabilizing changes, or perturbations, in ecological conditions, or to recover from degradation induced by them: yet, if destabilizing processes become strong enough or fast enough to cross a critical threshold within that ecosystem, often described as an ecological 'tipping point', then an ecosystem collapse (sometimes also termed ecological collapse) occurs. Ecosystem collapse does not mean total disappearance of life from the area, but it does result in the loss of the original ecosystem's defining characteristics, typically including the ecosystem services it may have provided. Collapse of an ecosystem is effectively irreversible more often than not, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Crisis
An ecological or environmental crisis occurs when changes to the environment of a species or population destabilizes its continued survival. Some of the important causes include: * Degradation of an abiotic ecological factor (for example, increase of temperature, less significant rainfalls) * Increased pressures from predation * Rise in the number of individuals (i.e. overpopulation) The evolutionary theory of punctuated equilibrium sees infrequent ecological crises as a potential driver of rapid evolution. Because of the impact of humans on the natural environment in the recent geological period, the term ecological crisis is often applied to environmental issues caused by human civilizations such as: the climate crisis, biodiversity loss and plastic pollution which have emerged as major global challenges during the first few decades of the 21st century. Examples Crises caused by abiotic factors Climate change is starting to have major impacts on ecosystems. With gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Advances
''Science Advances'' is a peer-reviewed multidisciplinary open-access scientific journal established in early 2015 and published by the American Association for the Advancement of Science. The journal's scope includes all areas of science. History The journal was announced by the American Association for the Advancement of Science in February 2014, and the first articles were published in early 2015. In 2019, ''Science Advances'' surpassed '' Science Magazine'' in the number of monthly submissions, becoming the largest member in the Science family of journals. It is the only member of that family where all papers are gold open access. Editorial structure and journal scope The journal's scope includes all areas of science, including life sciences, public health, neurosciences, physical sciences, social sciences, computer sciences, environmental sciences, and space sciences. Editorial decisions are made by the editorial board. The board is divided into topical areas, eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Guardian Media Group, owned by the Scott Trust Limited. The trust was created in 1936 to "secure the financial and editorial independence of ''The Guardian'' in perpetuity and to safeguard the journalistic freedom and liberal values of ''The Guardian'' free from commercial or political interference". The trust was converted into a limited company in 2008, with a constitution written so as to maintain for ''The Guardian'' the same protections as were built into the structure of the Scott Trust by its creators. Profits are reinvested in its journalism rather than distributed to owners or shareholders. It is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. The editor-in-chief Katharine Viner succeeded Alan Rusbridger in 2015. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodiversity Loss
Biodiversity loss happens when plant or animal species disappear completely from Earth (extinction) or when there is a decrease or disappearance of species in a specific area. Biodiversity loss means that there is a reduction in Biodiversity, biological diversity in a given area. The decrease can be temporary or permanent. It is temporary if the damage that led to the loss is reversible in time, for example through ecological restoration. If this is not possible, then the decrease is permanent. The cause of most of the biodiversity loss is, generally speaking, human activities that push the planetary boundaries too far. These activities include habitat destruction (for example deforestation) and land use intensification (for example monoculture farming). Further problem areas are Air pollution, air and water pollution (including nutrient pollution), over-exploitation, Invasive alien species, invasive species and climate change. Many scientists, along with the ''Global Assessment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene Extinction
The Holocene extinction, also referred to as the Anthropocene extinction or the sixth mass extinction, is an ongoing extinction event caused exclusively by human activities during the Holocene epoch. This extinction event spans numerous families of plants and animals, including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, and invertebrates, impacting both terrestrial and marine life, marine species. Widespread degradation of biodiversity hotspots such as coral reefs and rainforests has exacerbated the crisis. Many of these extinctions are undocumented, as the species are often undiscovered before their extinctions. Current extinction rates are estimated at 100 to 1,000 times higher than natural background extinction rates and are accelerating. Over the past 100–200 years, biodiversity loss has reached such alarming levels that some conservation biologists now believe humankind, human activities have triggered a mass extinction, or are on the cusp of doing so. As such, after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent agency of the United States government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on December 2, 1970, after Nixon signed an executive order. The order establishing the EPA was ratified by committee hearings in the House and Senate. The agency is led by its administrator, who is appointed by the president and approved by the Senate. The current administrator is Lee Zeldin. The EPA is not a Cabinet department, but the administrator is normally given cabinet rank. The EPA has its headquarters in Washington, D.C. There are regional offices for each of the agency's ten regions, as well as 27 laboratories around the country. The agency conducts environmental assessment, research, and education. It has the responsibility of maintaining and enforcing national standards under a variety of environmental laws, in consultat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
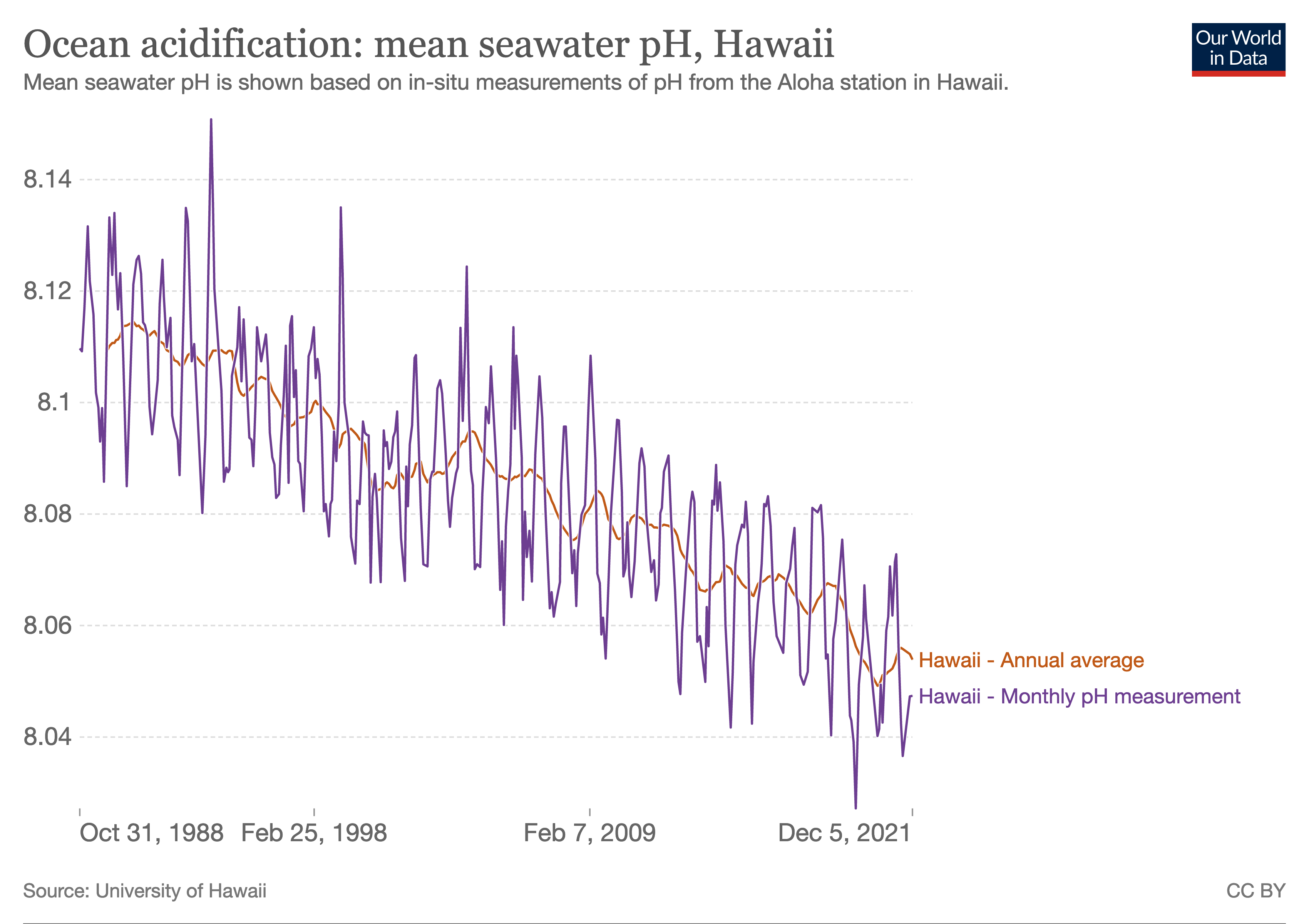
Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth's ocean. Between 1950 and 2020, the average pH of the ocean surface fell from approximately 8.15 to 8.05. Carbon dioxide emissions from human activities are the primary cause of ocean acidification, with Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide () levels exceeding 422 ppm (). from the atmosphere is absorbed by the oceans. This chemical reaction produces carbonic acid () which dissociates into a bicarbonate ion () and a hydrogen ion (). The presence of free hydrogen ions () lowers the pH of the ocean, increasing acidity (this does not mean that seawater is acidic yet; it is still alkaline, with a pH higher than 8). Marine biogenic calcification, Marine calcifying organisms, such as Mollusca, mollusks and corals, are especially vulnerable because they rely on calcium carbonate to build shells and skeletons. A change in pH by 0.1 represents a 26% increase in hydrogen ion concentration in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Degradation
Environment most often refers to: __NOTOC__ * Natural environment, referring respectively to all living and non-living things occurring naturally and the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or a group of organisms Other physical and cultural environments *Ecology, the branch of ethology that deals with the relations of organisms to one another and to their physical surroundings *Environment (systems), the surroundings of a physical system that may interact with the system by exchanging mass, energy, or other properties. *Built environment, constructed surroundings that provide the settings for human activity, ranging from the large-scale civic surroundings to the personal places *Social environment, the culture that an individual lives in, and the people and institutions with whom they interact *Market environment, business term Arts, entertainment and publishing * Environment (magazine), ''Environment'' (magazine), a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Sustainability
''Nature Sustainability'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio. It was established in 2018. The editor-in-chief is Monica Contestabile. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: *Science Citation Index Expanded *Scopus *Social Sciences Citation Index According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2022 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 27.7. References External links * English-language journals Nature Research academic journals Monthly journals Online-only journals Academic journals established in 2018 Sustainability journals {{environment-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |