Sungas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Shunga Empire (
''A Comprehensive History of India: Volume 2''
p.108: "Soon after Agnimitra there was no 'Sunga empire'." inscriptions and coins indicate that much of northern and central India consisted of small kingdoms and city-states that were independent of any Shunga
''Between the Empires: Society in India, 300 to 400''
ed. Patrick Olivelle (2006), p.96 The dynasty is noted for its numerous wars with both foreign and indigenous powers. They fought the Kalinga, the
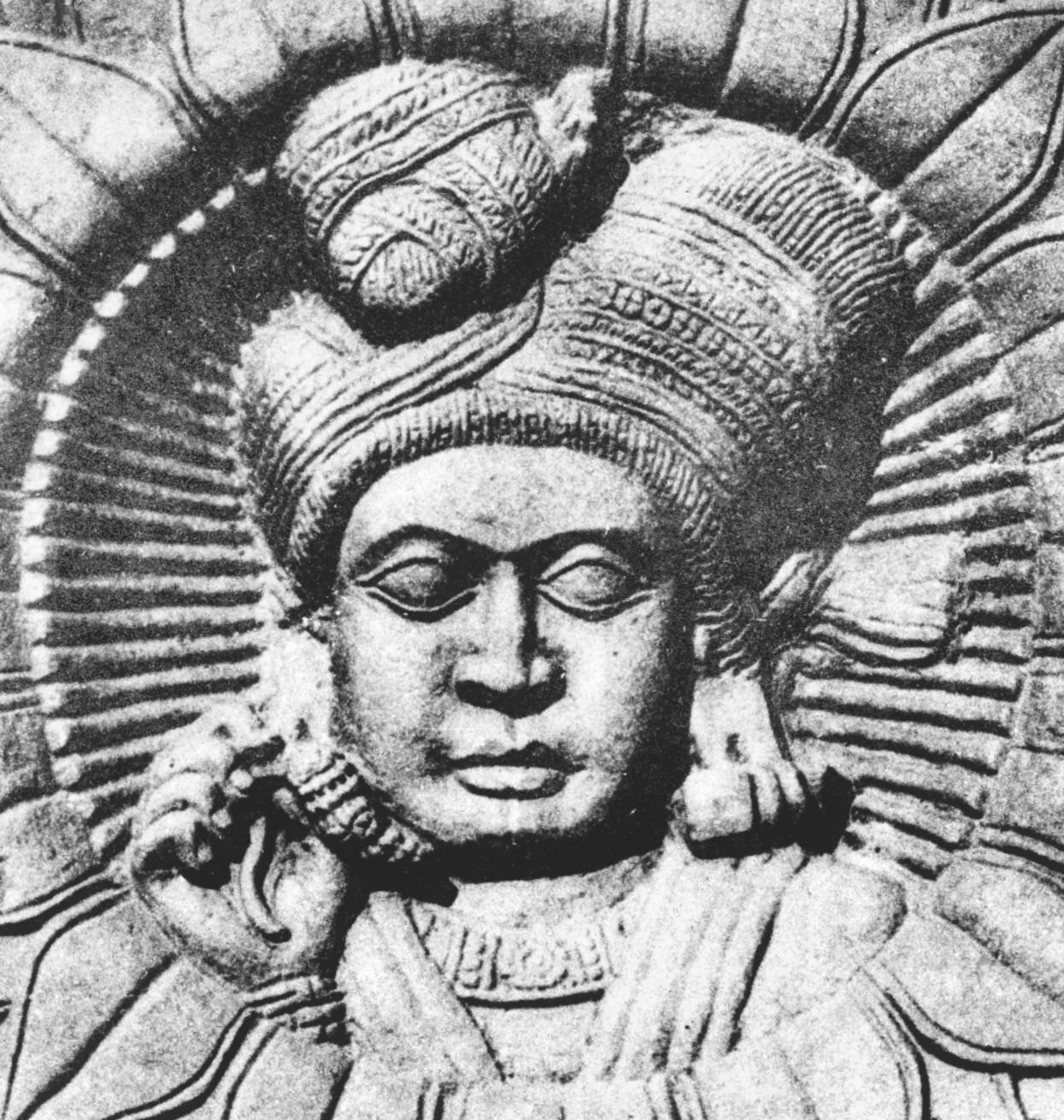 Shungas were originally from
Shungas were originally from
/ref> However, the city of
/ref> Some ancient sources however claim a greater extent for the Shunga empire: the '' Asokavadana'' account of the ''
 Following the Mauryans, the first Sunga emperor, a Brahmin named Pushyamitra, is believed by some historians to have persecuted Buddhists and contributed to a resurgence of
Following the Mauryans, the first Sunga emperor, a Brahmin named Pushyamitra, is believed by some historians to have persecuted Buddhists and contributed to a resurgence of
/ref> Pushyamitra is known to have revived the supremacy of the Bramahnical religion and reestablished animal sacrifices (
p.58-59
/ref> A Brahmamitra is known otherwise as a local ruler of
''Old Buddhist Shrines at Bodh-Gaya Inscriptions''
Cunningham has regretted the loss of the latter part of these important records. As regards the first coping inscription, he has found traces of eleven Brahmi letters after "''Kuramgiye danam''", the first nine of which read "''rajapasada-cetika sa''". Bloch reads these nine letters as "''raja-pasada-cetikasa''" and translates this expression in relation to the preceding words:
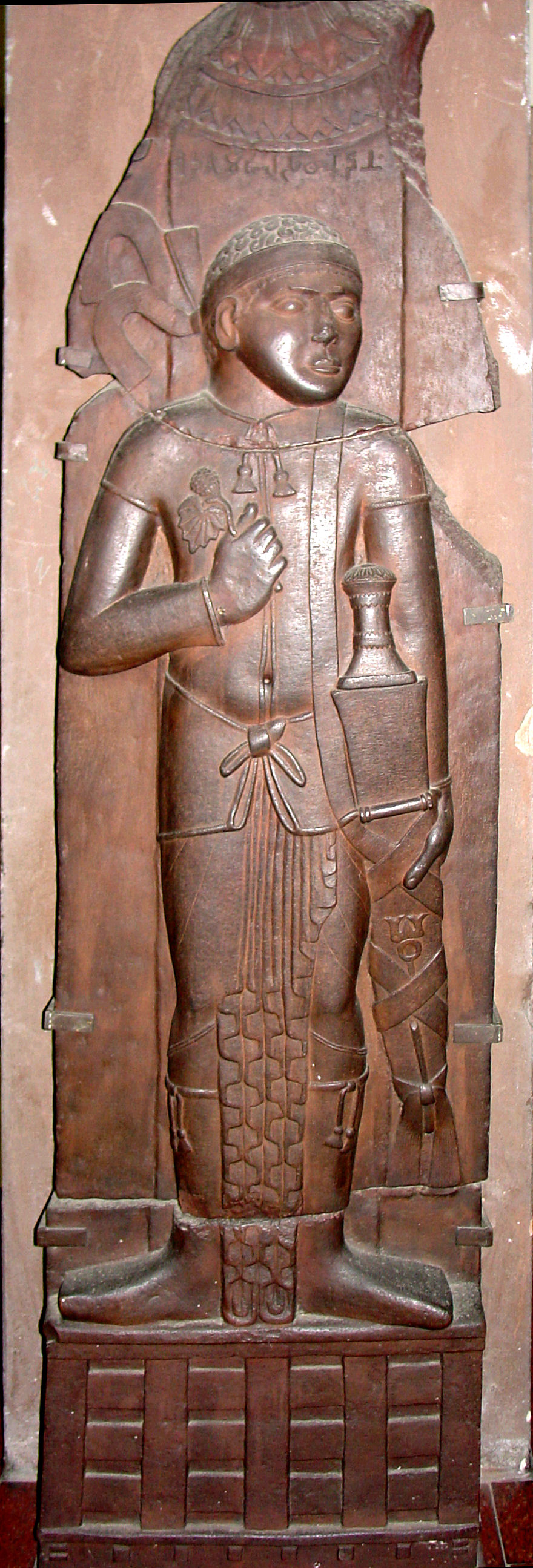
 On the basis of
On the basis of
p.90
/ref> slightly after the reliefs of
p.88ff
/ref> The style of the Shunga period decorations at Sanchi bear a close similarity to those of

 The Greeks seem to have maintained control of Mathura. The Yavanarajya inscription, also called the "Maghera inscription", discovered in
The Greeks seem to have maintained control of Mathura. The Yavanarajya inscription, also called the "Maghera inscription", discovered in
 Very little can be said with great certainty. However, what does appear clear is that the two realms appeared to have established normalised diplomatic relations in the succeeding reigns of their respective rulers. The Indo-Greeks and the Shungas seem to have reconciled and exchanged diplomatic missions around 110 BCE, as indicated by the
Very little can be said with great certainty. However, what does appear clear is that the two realms appeared to have established normalised diplomatic relations in the succeeding reigns of their respective rulers. The Indo-Greeks and the Shungas seem to have reconciled and exchanged diplomatic missions around 110 BCE, as indicated by the
 The last king of Sungas,
The last king of Sungas,
Medallions from Barhut
{{DEFAULTSORT:Shunga Empire Former empires in Asia Hindu states Former monarchies of India Magadha 185 BC 180s BC establishments States and territories established in the 2nd century BC States and territories disestablished in the 1st century
IAST
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Brahmic family, Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that ...
: ') was a ruling entity centred around Magadha
Magadha was a region and kingdom in ancient India, based in the eastern Ganges Plain. It was one of the sixteen Mahajanapadas during the Second Urbanization period. The region was ruled by several dynasties, which overshadowed, conquered, and ...
and controlled most of the northern Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
from around 187 to 75 BCE. The dynasty was established by Pushyamitra, after taking the throne of Magadha from the Mauryas
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary source ...
. The Shunga empire's capital was Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
, but later emperors such as Bhagabhadra
Bhagabhadra ( Brāhmī: 𑀪𑀸𑀕𑀪𑀤𑁆𑀭 , ) was a Shunga Emperor who reigned in northern and central India from around 114 BCE to 83 BCE. Although the capital of the Shungas was at Pataliputra, he was also known to have held court a ...
also held court at Besnagar (modern Vidisha
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar and Bhaddilpur in ancient times) is a city in Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of Vidisha district. It is located 62.5 km north ...
) in eastern Malwa
Malwa () is a historical region, historical list of regions in India, region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic plateau, volcanic upland north of the ...
. This dynasty is also responsible for successfully fighting and resisting the Greeks in Shunga–Greek War
The Shunga-Greek War comprised several conflicts between the Shunga Empire and the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom. It is predominantly based on the Sanskrit play " Mālavikāgnimitram".
The Greek king Demetrius is regarded to have tried to invade the su ...
.
Pushyamitra ruled for 36 years and was succeeded by his son Agnimitra
Agnimitra (; ) was the second Shunga emperor who reigned over what is now northern and central India. He succeeded his father, the emperor Pushyamitra, in 149 BCE. The Vayu Purana and the Brahmanda Purana have assigned 8 years as the length o ...
. There were ten Shunga rulers. However, after the death of Agnimitra, the second king of the dynasty, the empire rapidly disintegrated:K.A. Nilkantha Shastri (1970)''A Comprehensive History of India: Volume 2''
p.108: "Soon after Agnimitra there was no 'Sunga empire'." inscriptions and coins indicate that much of northern and central India consisted of small kingdoms and city-states that were independent of any Shunga
hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one State (polity), state over other states, either regional or global.
In Ancient Greece (ca. 8th BC – AD 6th c.), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of ...
.Bhandare, Shailendra. "Numismatics and History: The Maurya-Gupta Interlude in the Gangetic Plain". i''Between the Empires: Society in India, 300 to 400''
ed. Patrick Olivelle (2006), p.96 The dynasty is noted for its numerous wars with both foreign and indigenous powers. They fought the Kalinga, the
Satavahana dynasty
The Satavahanas (; ''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras (also ''Andhra-bhṛtyas'' or ''Andhra-jatiyas'') in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavaha ...
, the Indo-Greek kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
and possibly the Panchala
Panchala () was an ancient kingdom of northern India, located in the Ganges-Yamuna Doab of the Upper Gangetic plain which is identified as Kanyakubja or region around Kannauj. During Late Vedic times (c. 1100–500 BCE), it was one of the ...
s and Mitras of Mathura.
Art, education, philosophy, and other forms of learning flowered during this period, including small terracotta
Terracotta, also known as terra cotta or terra-cotta (; ; ), is a clay-based non-vitreous ceramic OED, "Terracotta""Terracotta" MFA Boston, "Cameo" database fired at relatively low temperatures. It is therefore a term used for earthenware obj ...
images, larger stone sculptures, and architectural monuments such as the stupa
In Buddhism, a stupa (, ) is a domed hemispherical structure containing several types of sacred relics, including images, statues, metals, and '' śarīra''—the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns. It is used as a place of pilgrimage and m ...
at Bharhut
Bharhut is a village in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for a Buddhist stupa, unique in that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters saying what the panel depicts. The major donor for the Bharhut st ...
, and the renowned Great Stupa at Sanchi
Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist art, Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen ...
. The Shunga rulers helped to establish the tradition of royal sponsorship of learning and art. The script used by the empire was a variant of Brahmi script
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as ...
and was used to write Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
.
The Shungas were important patrons of culture at a time when some of the most important developments in Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
thought were taking place. Patanjali
Patanjali (, , ; also called Gonardiya or Gonikaputra) was the name of one or more author(s), mystic(s) and philosopher(s) in ancient India. His name is recorded as an author and compiler of a number of Sanskrit works. The greatest of these a ...
's ''Mahābhāṣya
''Mahabhashya'' (, IAST: '','' , "Great Commentary"), attributed to Patañjali, is a commentary on selected rules of Sanskrit grammar from Pāṇini's treatise, the ''Aṣṭādhyāyī'', as well as Kātyāyana's ''Vārttika-sūtra'', an ela ...
'' was composed in this period. Artistry also progressed with the rise of the Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
art style.
The last of the Shunga emperors was Devabhuti
Devabhuti (), also known as Devbhomi, was the last Shunga Emperor in ancient India. He was assassinated by his minister Vasudeva Kanva. Following his death, the Shunga dynasty was then replaced by the subsequent Kanvas.
Reign
The later Shunga ...
(83–73 BCE). He was assassinated by his minister Vasudeva Kanva and was said to have been overfond of the company of women. The Kanva dynasty succeeded the Shungas around 73 BCE.
Name
The name "Shunga" has only been used for convenience to designate the historical polity now generally described as "Shunga empire", or the historical period known as the "Shunga period", which follows the fall of theMaurya empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary source ...
. The term appears in a single epigraphic inscription in Bharhut
Bharhut is a village in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for a Buddhist stupa, unique in that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters saying what the panel depicts. The major donor for the Bharhut st ...
, in which a dedication to the Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
Bharhut stupa
In Buddhism, a stupa (, ) is a domed hemispherical structure containing several types of sacred relics, including images, statues, metals, and '' śarīra''—the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns. It is used as a place of pilgrimage and m ...
is said to have been made "at the time of the Suga kings" (''Suganam raje''), with no indication as to whom these "Suga kings" might be. Other broadly contemporary inscriptions, such as the Heliodorus pillar inscription, are only assumed to relate to Shunga rulers. The Ayodhya Inscription of Dhana mentions a ruler named Pushyamitra, but does not mention the name "Shunga".
The Bharut epigraph appears on a pillar of the gateway of the stupa, and mentions its erection "during the rule of the ''Sugas'', by Vatsiputra Dhanabhuti". The expression used (''Suganam raje'', Brahmi script
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as ...
: 𑀲𑀼𑀕𑀦𑀁 𑀭𑀚𑁂), may mean "during the rule of the Sugas hungas, although not without ambiguity as it could also be "during the rule of the Sughanas", a northern Buddhist kingdom. There is no other instance of the name "Shunga" in the epigraphical
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the wr ...
record of India. The unique inscription reads:
Dhanabhuti was making a major dedication to a Buddhist monument, Bharhut
Bharhut is a village in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for a Buddhist stupa, unique in that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters saying what the panel depicts. The major donor for the Bharhut st ...
, whereas the historical "Shungas" are known to have been Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
monarchs, which would suggest that Dhanabhuti himself may not have been a member of the Shunga dynasty. Neither is he known from "Shunga" regnal lists. The mention "in the reign of the Shungas" also suggests that he was not himself a Shunga ruler, only that he may have been a tributary of the Shungas, or a ruler in a neighbouring territory, such as Kosala
Kosala, sometimes referred to as Uttara Kosala () was one of the Mahajanapadas of ancient India. It emerged as a small state during the Late Vedic period and became (along with Magadha) one of the earliest states to transition from a lineage ...
or Panchala
Panchala () was an ancient kingdom of northern India, located in the Ganges-Yamuna Doab of the Upper Gangetic plain which is identified as Kanyakubja or region around Kannauj. During Late Vedic times (c. 1100–500 BCE), it was one of the ...
.
The name "Sunga" or "Shunga" is also used in the ''Vishnu Purana
The Vishnu Purana () is one of the eighteen Mahapuranas, a genre of ancient and medieval texts of Hinduism. It is an important Pancharatra text in the Vaishnavism literature corpus.
The manuscripts of ''Vishnu Purana'' have survived into ...
'', the date of which is contested, to designate the dynasty of kings starting with Pushyamitra , and ending with Devabhuti
Devabhuti (), also known as Devbhomi, was the last Shunga Emperor in ancient India. He was assassinated by his minister Vasudeva Kanva. Following his death, the Shunga dynasty was then replaced by the subsequent Kanvas.
Reign
The later Shunga ...
circa 75 BCE. According to the Vishnu Purana
The Vishnu Purana () is one of the eighteen Mahapuranas, a genre of ancient and medieval texts of Hinduism. It is an important Pancharatra text in the Vaishnavism literature corpus.
The manuscripts of ''Vishnu Purana'' have survived into ...
:
Origins
 Shungas were originally from
Shungas were originally from Vidisha
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar and Bhaddilpur in ancient times) is a city in Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of Vidisha district. It is located 62.5 km north ...
.
According to historical reconstructions, the Shunga dynasty was established in 184 BCE, about 50 years after Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
's death, when the emperor Brihadratha Maurya
Brihadratha was the 9th and last Emperor of the Mauryan Dynasty. He ruled from 187 to 185 BCE, when he was overthrown and assassinated by his General, Pushyamitra Shunga, who went on to establish the Shunga Empire. The Mauryan territories ...
, the last ruler of the Maurya empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary source ...
, was assassinated by his ''Senānī'' or commander-in-chief, Pushyamitra, while he was reviewing the Guard of Honour of his forces. Pushyamitra then ascended the throne.
Pushyamitra became the ruler of Magadha
Magadha was a region and kingdom in ancient India, based in the eastern Ganges Plain. It was one of the sixteen Mahajanapadas during the Second Urbanization period. The region was ruled by several dynasties, which overshadowed, conquered, and ...
and neighbouring territories. His realm essentially covered the central parts of the old Mauryan empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
. The Shunga definitely had control of the central city of Ayodhya
Ayodhya () is a city situated on the banks of the Sarayu river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ayodhya district as well as the Ayodhya division of Uttar Pradesh, India. Ayodhya became th ...
in northern central India, as is proved by the Dhanadeva-Ayodhya inscription.Ancient Indian History and Civilization, Sailendra Nath Sen, New Age International, 1999, p.169/ref> However, the city of
Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
further west never seems to have been under the direct control of the Shungas, as no archaeological evidence of a Shunga presence has ever been found in Mathura. On the contrary, according to the Yavanarajya inscription, Mathura was probably under the control of Indo-Greeks
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" loosely describes a number of var ...
from some time between 180 BCE and 100 BCE, and remained so as late as 70 BCE.History of Early Stone Sculpture at Mathura: Ca. 150 BCE - 100 CE, Sonya Rhie Quintanilla, BRILL, 2007, p.8-1/ref> Some ancient sources however claim a greater extent for the Shunga empire: the '' Asokavadana'' account of the ''
Divyavadana
The ''Divyāvadāna'' or Divine narratives is a Sanskrit anthology of Buddhist avadana tales, many originating in Mūlasarvāstivādin vinaya texts. It may be dated to 2nd century CE. The stories themselves are therefore quite ancient and may be a ...
'' claims that the Shungas sent an army to persecute Buddhist monks as far as Sakala (Sialkot
Sialkot (Punjabi language, Punjabi, ) is a city located in Punjab, Pakistan. It is the capital of the Sialkot District and the List of most populous cities in Pakistan, 12th most populous city in Pakistan. The boundaries of Sialkot are joined ...
) in the Punjab region
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
in the northwest:
Also, the '' Malavikagnimitra'' claims that the empire of Pushyamitra extended to the Narmada River
The Narmada River, previously also known as ''Narbada'' or anglicised as ''Nerbudda'', is the 5th longest river in India and overall the longest west-flowing river in the country. It is also the largest flowing river in the state of Madhya Prade ...
in the south. They may also have controlled the city of Ujjain
Ujjain (, , old name Avantika, ) or Ujjayinī is a city in Ujjain district of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Pradesh by population and is the administrative as well as religious centre of Ujjain ...
. Meanwhile, Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A ...
and much of the Punjab passed into the hands of the Indo-Greeks
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" loosely describes a number of var ...
and the Deccan Plateau
The Deccan is a plateau extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura Range, Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu in the south. It is bound ...
to the Satavahana dynasty
The Satavahanas (; ''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras (also ''Andhra-bhṛtyas'' or ''Andhra-jatiyas'') in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavaha ...
.
Pushyamitra died after ruling for 36 years (187–151 BCE). He was succeeded by son Agnimitra
Agnimitra (; ) was the second Shunga emperor who reigned over what is now northern and central India. He succeeded his father, the emperor Pushyamitra, in 149 BCE. The Vayu Purana and the Brahmanda Purana have assigned 8 years as the length o ...
. This prince is the hero of a famous drama by one of India's greatest playwrights, Kālidāsa
Kālidāsa (, "Servant of Kali (god), Kali"; 4th–5th century CE) was a Classical Sanskrit author who is often considered ancient India's greatest poet and playwright. His plays and poetry are primarily based on Hindu Puranas and philosophy. ...
. Agnimitra was viceroy of Vidisha when the story takes place.
The power of the Shungas gradually weakened. It is said that there were ten Shunga emperors. The Shungas were succeeded by the Kanva dynasty around 73 BCE.
Decline of Buddhism
Accounts of persecution
 Following the Mauryans, the first Sunga emperor, a Brahmin named Pushyamitra, is believed by some historians to have persecuted Buddhists and contributed to a resurgence of
Following the Mauryans, the first Sunga emperor, a Brahmin named Pushyamitra, is believed by some historians to have persecuted Buddhists and contributed to a resurgence of Brahmanism
The historical Vedic religion, also called Vedism or Brahmanism, and sometimes ancient Hinduism or Vedic Hinduism, constituted the religious ideas and practices prevalent amongst some of the Indo-Aryan peoples of the northwest Indian subcontin ...
that forced Buddhism outwards to Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
, Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
and Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
.Sarvastivada pg 38–39 Buddhist scripture such as the '' Asokavadana'' account of the ''Divyavadana
The ''Divyāvadāna'' or Divine narratives is a Sanskrit anthology of Buddhist avadana tales, many originating in Mūlasarvāstivādin vinaya texts. It may be dated to 2nd century CE. The stories themselves are therefore quite ancient and may be a ...
'' and ancient Tibetan historian Taranatha
Tāranātha (1575–1634) was a Lama of the Jonang school of Tibetan Buddhism. He is widely considered its most remarkable scholar and exponent.
Taranatha was born in Tibet, supposedly on the birthday of Padmasambhava. His original name was Ku ...
have written about persecution of Buddhists. Pushyamitra is said to have burned down Buddhist monasteries, destroyed stupas, massacred Buddhist monks and put rewards on their heads, but some consider these stories as probable exaggerations.A Journey Through India's Past Chandra Mauli Mani, Northern Book Centre, 2005, p.38/ref> Pushyamitra is known to have revived the supremacy of the Bramahnical religion and reestablished animal sacrifices (
Yajna
In Hinduism, ''Yajna'' or ''Yagna'' (, Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐd͡ʒɲə ) also known as Hawan, is a ritual done in front of a sacred fire, often with mantras. Yajna has been a Vedas, Vedic tradition, described in a layer of Vedic literature ...
s) that had been prohibited by Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
.
Accounts against persecution
Later Shunga emperors were seen as amenable to Buddhism and as having contributed to the building of the stupa atBharhut
Bharhut is a village in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for a Buddhist stupa, unique in that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters saying what the panel depicts. The major donor for the Bharhut st ...
. During his reign the Buddhist monuments of Bharhut and Sanchi
Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist art, Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen ...
were renovated and further improved. There is enough evidence to show that Pushyamitra patronised Buddhist art. However, given the rather decentralised and fragmentary nature of the Shunga state, with many cities actually issuing their own coinage, as well as the relative dislike of the Shungas for the Buddhist religion, some authors argue that the constructions of that period in Sanchi for example cannot really be called "Shunga". They were not the result of royal sponsorship, in contrast with what happened during the Mauryas, and most of the dedications at Sanchi were private or collective, rather than the result of royal patronage.
Some writers believe that Brahmanism competed in political and spiritual realm with Buddhism in the Gangetic plains. Buddhism flourished in the realms of the Bactrian kings.
Some Indian scholars are of the opinion that the orthodox Shunga emperors were not intolerant towards Buddhism and that Buddhism prospered during the time of the Shunga emperors. The existence of Buddhism in Bengal in the Shunga period can also be inferred from a terracotta tablet that was found at Tamralipti and is on exhibit at the Asutosh Museum in Kolkata.
Royal dedications
Two dedications by a king named Brahmamitra as well as the monarch Indragnimitra are recorded at theMahabodhi Temple
The Mahabodhi Temple (literally: "Great Awakening Temple") or the Mahābodhi Mahāvihāra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is an ancient, but restored Buddhist temple in Bodh Gaya, Bihar, India, marking the location where the Buddha is said to hav ...
in Bodh Gaya
Bodh Gayā is a religious site and place of pilgrimage associated with the Mahabodhi Temple complex, situated in the Gaya district in the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Bihar. It is famous for being the place where Gautam ...
. Some may claim these show Sunga support for Buddhism. These kings, however, are essentially unknown, and do not form a part of the Shunga recorded genealogy. They are thought to be post-Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
n and to belong to the period of Sunga rule.Between the Empires: Society in India 300 BCE to 400 CE Patrick Olivelle, Oxford University Press, 200p.58-59
/ref> A Brahmamitra is known otherwise as a local ruler of
Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
, but Indragnimitra is unknown, and according to some authors, Indragnimitra is in fact not even mentioned as a king in the actual inscription.
* An inscription at Bodh Gaya at the Mahabodhi Temple
The Mahabodhi Temple (literally: "Great Awakening Temple") or the Mahābodhi Mahāvihāra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is an ancient, but restored Buddhist temple in Bodh Gaya, Bihar, India, marking the location where the Buddha is said to hav ...
records the construction of the temple as follows:
:"''The gift of Nagadevi the wife of King Brahmamitra.''"
* Another inscription reads:
:"''The gift of Kurangi, the mother of living sons and the wife of King Indragnimitra, son of Kosiki. The gift also of Srima of the royal palace shrine''."(Barua, B.M.,''Old Buddhist Shrines at Bodh-Gaya Inscriptions''
Cunningham has regretted the loss of the latter part of these important records. As regards the first coping inscription, he has found traces of eleven Brahmi letters after "''Kuramgiye danam''", the first nine of which read "''rajapasada-cetika sa''". Bloch reads these nine letters as "''raja-pasada-cetikasa''" and translates this expression in relation to the preceding words:
"(the gift of Kurangi, the wife of Indragnimitra and the mother of living sons), "to the caitya (cetika) of the noble temple", taking the word raja before pasada as an epithet on ornans, distinguishing the temple as a particularly large and stately building similar to such expressions as rajahastin 'a noble elephant', rajahamsa 'a goose' (as distinguished from hamsa 'a duck'), etc."Cunningham has translated the expression "the royal palace, the caitya", suggesting that "the mention of the raja-pasada would seem to connect the donor with the king's family." Luders doubtfully suggests "to the king's temple" as a rendering of "raja-pasada-cetikasa."
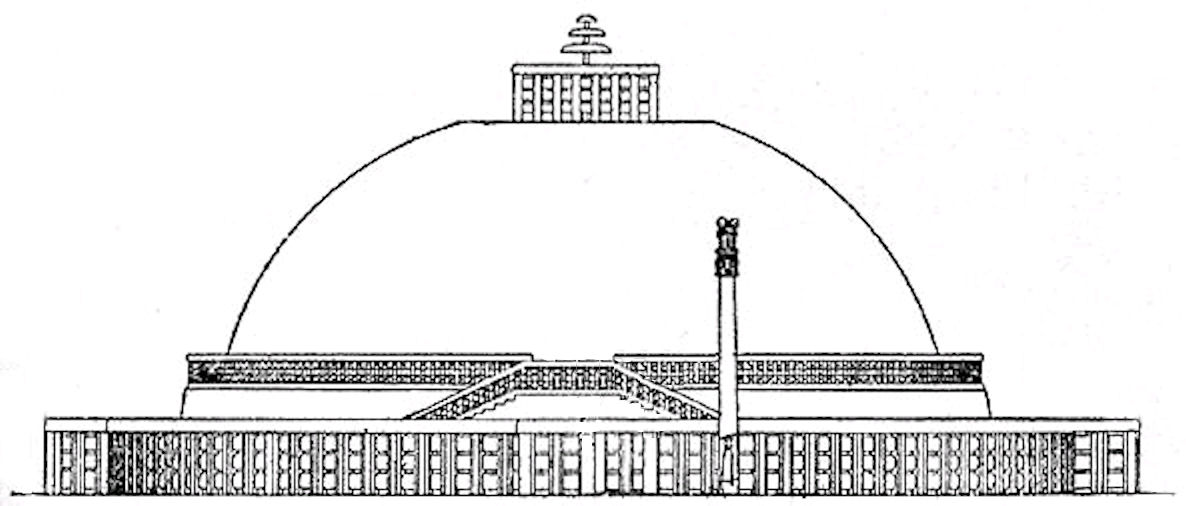
Shunga period contributions in Sanchi
 On the basis of
On the basis of Ashokavadana
The Ashokavadana (; ; "Narrative of Ashoka") is an Indian Sanskrit-language text that describes the birth and reign of the third Mauryan Emperor Ashoka. It glorifies Ashoka as a Buddhist emperor whose only ambition was to spread Buddhism far an ...
, it is presumed that the stupa may have been vandalised at one point sometime in the 2nd century BCE, an event some have related to the rise of the Shunga emperor Pushyamitra who overtook the Mauryan empire as an army general. It has been suggested that Pushyamitra may have destroyed the original stupa, and his son Agnimitra
Agnimitra (; ) was the second Shunga emperor who reigned over what is now northern and central India. He succeeded his father, the emperor Pushyamitra, in 149 BCE. The Vayu Purana and the Brahmanda Purana have assigned 8 years as the length o ...
rebuilt it. The original brick stupa was covered with stone during the Shunga period.
According to historian Julia Shaw, the post-Mauryan constructions at Sanchi cannot be described as "Sunga" as sponsorship for the construction of the stupas, as attested by the numerous donative inscriptions, was not royal but collective, and the Sungas were known for their opposition to Buddhism.
Great Stupa (No 1)
During the later rule of the Shunga, the stupa was expanded with stone slabs to almost twice its original size. The dome was flattened near the top and crowned by three superimposed parasols within a square railing. With its many tiers it was a symbol of thedharma
Dharma (; , ) is a key concept in various Indian religions. The term ''dharma'' does not have a single, clear Untranslatability, translation and conveys a multifaceted idea. Etymologically, it comes from the Sanskrit ''dhr-'', meaning ''to hold ...
, the Wheel of the Law. The dome was set on a high circular drum meant for circumambulation
Circumambulation (from Latin ''circum'' around and ''ambulātus ''to walk) is the act of moving around a sacred object or idol.
Circumambulation of temples or deity images is an integral part of Hindu and Buddhist devotional practice (known in ...
, which could be accessed via a double staircase. A second stone pathway at ground level was enclosed by a stone balustrade. The railing around Stupa 1 do not have artistic reliefs. These are only slabs, with some dedicatory inscriptions. These elements are dated to .
Stupa No2 and Stupa No3
The buildings which seem to have been commissioned during the rule of the Shungas are the Second and Thirdstupa
In Buddhism, a stupa (, ) is a domed hemispherical structure containing several types of sacred relics, including images, statues, metals, and '' śarīra''—the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns. It is used as a place of pilgrimage and m ...
s (but not the highly decorated gateways, which are from the following Satavahana
The Satavahanas (; ''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras (also ''Andhra-bhṛtyas'' or ''Andhra-jatiyas'') in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavaha ...
period, as known from inscriptions), and the ground balustrade and stone casing of the Great Stupa (Stupa No 1). The Relics of Sariputra and Mahamoggallana
The relics of Sariputta and Moggallana refers to the cremated remains of the Buddhist disciples Sariputta (Sanskrit: ''Śāriputra''; Pali: ''Sāriputta;'' Sinhala:''Seriyuth සැරියුත්''); and Moggallana (Sanskrit: ''Maudgalyā ...
are said to have been placed in Stupa No 3. These are dated to for the medallions, 80 BCE for the gateway carvings,Buddhist Landscapes in Central India: Sanchi Hill and Archaeologies of Religious and Social Change, C. Third Century BC to Fifth Century AD, Julia Shaw, Left Coast Press, 201p.90
/ref> slightly after the reliefs of
Bharhut
Bharhut is a village in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for a Buddhist stupa, unique in that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters saying what the panel depicts. The major donor for the Bharhut st ...
, with some reworks down to the 1st century CE.Buddhist Landscapes in Central India: Sanchi Hill and Archaeologies of Religious and Social Change, C. Third Century BC to Fifth Century AD, Julia Shaw, Left Coast Press, 201p.88ff
/ref> The style of the Shunga period decorations at Sanchi bear a close similarity to those of
Bharhut
Bharhut is a village in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for a Buddhist stupa, unique in that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters saying what the panel depicts. The major donor for the Bharhut st ...
, as well as the peripheral balustrades at Bodh Gaya
Bodh Gayā is a religious site and place of pilgrimage associated with the Mahabodhi Temple complex, situated in the Gaya district in the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Bihar. It is famous for being the place where Gautam ...
, which are thought to be the oldest of the three.
Warfare
War and conflict characterised the Shunga period. They are known to have warred with the Kalingas,Satavahana
The Satavahanas (; ''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras (also ''Andhra-bhṛtyas'' or ''Andhra-jatiyas'') in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavaha ...
s, the Indo-Greeks
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" loosely describes a number of var ...
, and possibly the Panchalas
Panchala () was an ancient kingdom of northern India, located in the Ganges-Yamuna Doab of the Upper Gangetic plain which is identified as Kanyakubja or region around Kannauj. During Late Vedic times (c. 1100–500 BCE), it was one of the ...
and Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
s.
The Shunga empire's wars with the Indo-Greek kingdom figure greatly in the history of this period. From around 180 BCE the Greco-Bactrian
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom () was a Greek state of the Hellenistic period located in Central-South Asia. The kingdom was founded by the Seleucid satrap Diodotus I Soter in about 256 BC, and continued to dominate Central Asia until its fall a ...
ruler Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinization of names, Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male name, male Greek given names, given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, ...
conquered the Kabul Valley and is theorised to have advanced into the trans-Indus to confront the Shungas. The Indo-Greek Menander I
Menander I Soter (, ; ), sometimes called Menander the Great, was an Indo-Greek king (reigned /155Bopearachchi (1998) and (1991), respectively. The first date is estimated by Osmund Bopearachchi and R. C. Senior, the other Boperachchi –1 ...
is credited with either joining or leading a campaign to Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
with other Indian rulers; however, very little is known about the exact nature and success of the campaign. The net result of these wars remains uncertain.

Literary evidence
Several works, such as theMahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kuru ...
and the Yuga Purana
The ''Yuga Purana'' is a Sanskrit text and the last chapter of a ''Jyotisha'' (astrology) text ''Gargiya-jyotisha, Vriddhagargiya Samhita''. It is also considered a minor text in the Puranas, Puranic literature.
Contents
The Yuga Purana is struc ...
describe the conflict between the Shungas and the Indo-Greeks.
Military expeditions of the Shungas
Scriptures such as the ''Ashokavadana
The Ashokavadana (; ; "Narrative of Ashoka") is an Indian Sanskrit-language text that describes the birth and reign of the third Mauryan Emperor Ashoka. It glorifies Ashoka as a Buddhist emperor whose only ambition was to spread Buddhism far an ...
'' claim that Pushyamitra toppled Emperor Brihadratha and killed many Buddhist monks. Then it describes how Pushyamitra sent an army to Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
and as far as Sakala (Sialkot
Sialkot (Punjabi language, Punjabi, ) is a city located in Punjab, Pakistan. It is the capital of the Sialkot District and the List of most populous cities in Pakistan, 12th most populous city in Pakistan. The boundaries of Sialkot are joined ...
), in the Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
, to persecute Buddhist monks.
War with the Yavanas (Greeks)
TheIndo-Greeks
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" loosely describes a number of var ...
, called Yavanas in Indian sources, either led by Demetrius I or Menander I
Menander I Soter (, ; ), sometimes called Menander the Great, was an Indo-Greek king (reigned /155Bopearachchi (1998) and (1991), respectively. The first date is estimated by Osmund Bopearachchi and R. C. Senior, the other Boperachchi –1 ...
, then invaded India, possibly receiving the help of Buddhists. Menander in particular is described as a convert to Buddhism in the '' Milindapanha''.
The Hindu text of the ''Yuga Purana
The ''Yuga Purana'' is a Sanskrit text and the last chapter of a ''Jyotisha'' (astrology) text ''Gargiya-jyotisha, Vriddhagargiya Samhita''. It is also considered a minor text in the Puranas, Puranic literature.
Contents
The Yuga Purana is struc ...
'', which describes Indian historical events in the form of a prophecy, relates the attack of the Indo-Greeks on the Shunga capital Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
, a magnificent fortified city with 570 towers and 64 gates according to Megasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; , died 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, indologist, diplomat, ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but has been partially reconstructe ...
, and describes the impending war for city:
However, the Yuga Purana indicates that the Yavanas (Indo-Greeks) did not remain for long in Pataliputra, as they were faced with a civil war in Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
.
Western sources also suggest that this new offensive of the Greeks into India led them as far as the capital Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
:
Battle on the Sindhu river
An account of a direct battle between the Greeks and the Shunga is also found in the '' Mālavikāgnimitram'', a play byKālidāsa
Kālidāsa (, "Servant of Kali (god), Kali"; 4th–5th century CE) was a Classical Sanskrit author who is often considered ancient India's greatest poet and playwright. His plays and poetry are primarily based on Hindu Puranas and philosophy. ...
which describes a battle between a squadron of Greek cavalrymen and Vasumitra, the grandson of Pushyamitra, accompanied by a hundred soldiers on the "Sindhu river", in which the Indians defeated a squadron of Greeks and Pushyamitra successfully completed the Ashvamedha
The Ashvamedha () was a horse sacrifice ritual followed by the Śrauta tradition of Vedic religion. It was used by ancient Indian kings to prove their imperial sovereignty: a horse accompanied by the king's warriors would be released to wander ...
Yagna. This river may be the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
in the northwest, but such expansion by the Shungas is unlikely, and it is more probable that the river mentioned in the text is the Sindh River or the Kali Sindh River in the Ganges Basin
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
.
Epigraphic and archaeological evidence
Dhanadeva-Ayodhya inscription
Ultimately, Shunga rule seems to have extended to the area of Ayodhya. Shunga inscriptions are known as far asAyodhya
Ayodhya () is a city situated on the banks of the Sarayu river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ayodhya district as well as the Ayodhya division of Uttar Pradesh, India. Ayodhya became th ...
in northern central India; in particular, the Dhanadeva-Ayodhya inscription refers to a local king Dhanadeva, who claimed to be the sixth descendant of Pushyamitra. The inscription also records that Pushyamitra performed two Ashvamedha
The Ashvamedha () was a horse sacrifice ritual followed by the Śrauta tradition of Vedic religion. It was used by ancient Indian kings to prove their imperial sovereignty: a horse accompanied by the king's warriors would be released to wander ...
s (victory sacrifices) in Ayodhya.
Yavanarajya inscription
 The Greeks seem to have maintained control of Mathura. The Yavanarajya inscription, also called the "Maghera inscription", discovered in
The Greeks seem to have maintained control of Mathura. The Yavanarajya inscription, also called the "Maghera inscription", discovered in Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
, suggests that the Indo-Greeks were in control of Mathura during the 1st century BCE. The inscription is important in that it mentions the date of its dedication as "The last day of year 116 of Yavana
The word Yona in Pali and the Prakrits, and the analogue Yavana in Sanskrit, were used in Ancient India to designate Greek speakers. "Yona" and "Yavana" are transliterations of the Greek word for "Ionians" (), who were probably the first Gre ...
hegemony (''Yavanarajya'')". It is considered that this inscription is attesting the control of the Indo-Greeks
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" loosely describes a number of var ...
in the 2nd and 1st centuries BCE in Mathura, a fact that is also confirmed by numismatic and literary evidence. Moreover, it does not seem that the Shungas ever ruled in Mathura or Surasena
The kingdom of Surasena () was an ancient Indian region corresponding to the present-day Braj region in Uttar Pradesh, with Mathura as its capital city. According to the Buddhist text '' Anguttara Nikaya'', Surasena was one of the sixteen Ma ...
since no Shunga coins or inscriptions have been found there.
The ''Anushasana Parva
The Anushasana Parva (, IAST: Anuśāsanaparva) ("Book of Instructions") is the thirteenth of the eighteen ''parvas'' (books) of the Indian epic ''Mahabharata''. It traditionally has 2 parts and 168 chapters.Ganguli, K.M. (1883-1896)Anusasana Parv ...
'' of the Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kuru ...
affirms that the city of Mathura was under the joint control of the Yavana
The word Yona in Pali and the Prakrits, and the analogue Yavana in Sanskrit, were used in Ancient India to designate Greek speakers. "Yona" and "Yavana" are transliterations of the Greek word for "Ionians" (), who were probably the first Gre ...
s and the Kambojas
The Kambojas were a southeastern Iranian peoples, Iranian people who inhabited the northeastern most part of the territory populated by Iranian tribes, which bordered the Indian subcontinent, Indian lands. They only appear in Indo-Aryan langua ...
.
Later however, it seems the city of Mathura was retaken from them, if not by the Shungas themselves, then probably by other indigenous rulers such as the Datta dynasty or the Mitra dynasty, or more probably by the Indo-Scythian
The Indo-Scythians, also known as Indo-Sakas, were a group of nomadic people of Iranian peoples, Iranic Scythians, Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into the present-day regions of Afghanistan, Eastern Iran and the northwe ...
Northern Satraps under Rajuvula. In the region of Mathura, the Arjunayanas and Yaudheyas mention military victories on their coins ("Victory of the Arjunayanas", "Victory of the Yaudheyas"), and during the 1st century BCE, the Trigartas, Audumbaras and finally the Kunindas also started to mint their own coins, thus affirming independence from the Indo-Greeks, although the style of their coins was often derived from that of the Indo-Greeks.
Heliodorus pillar
 Very little can be said with great certainty. However, what does appear clear is that the two realms appeared to have established normalised diplomatic relations in the succeeding reigns of their respective rulers. The Indo-Greeks and the Shungas seem to have reconciled and exchanged diplomatic missions around 110 BCE, as indicated by the
Very little can be said with great certainty. However, what does appear clear is that the two realms appeared to have established normalised diplomatic relations in the succeeding reigns of their respective rulers. The Indo-Greeks and the Shungas seem to have reconciled and exchanged diplomatic missions around 110 BCE, as indicated by the Heliodorus pillar
The Heliodorus pillar is a stone column that was erected around 113 BCE in central India in Besnagar (Vidisha), Madhya Pradesh. The pillar is commonly named after Heliodorus (identified by him as a Garuda-standard), who was an ambassador of the In ...
, which records the dispatch of a Greek ambassador named Heliodorus, from the court of the Indo-Greek
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
king Antialcidas
Antialcidas Nikephoros (; epithet means "the Bearer of Victory" or "the Victorious", Brahmi: 𑀅𑀁𑀢𑀮𑀺𑀓𑀺𑀢𑀲 ''Aṃtalikitasa'', in the Heliodorus Pillar) was a king of the Indo-Greek Kingdom, who reigned from his capital at ...
, to the court of the Shunga emperor Bhagabhadra
Bhagabhadra ( Brāhmī: 𑀪𑀸𑀕𑀪𑀤𑁆𑀭 , ) was a Shunga Emperor who reigned in northern and central India from around 114 BCE to 83 BCE. Although the capital of the Shungas was at Pataliputra, he was also known to have held court a ...
at the site of Vidisha
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar and Bhaddilpur in ancient times) is a city in Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of Vidisha district. It is located 62.5 km north ...
in central India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
.
Decline
After the death of Agnimitra, the second king of the dynasty, the empire rapidly disintegrated: inscriptions and coins indicate that much of northern and central India consisted of small kingdoms and city-states that were independent of any Shunga hegemony. The last king of Sungas,
The last king of Sungas, Devabhuti
Devabhuti (), also known as Devbhomi, was the last Shunga Emperor in ancient India. He was assassinated by his minister Vasudeva Kanva. Following his death, the Shunga dynasty was then replaced by the subsequent Kanvas.
Reign
The later Shunga ...
was assassinated by his minister Vasudeva Kanva, who then established Kanva dynasty. According to the Puranas: "The Andhra
Andhra Pradesh (ISO: , , AP) is a state on the east coast of southern India. It is the seventh-largest state and the tenth-most populous in the country. Telugu is the most widely spoken language in the state, as well as its official lang ...
Simuka will assail the Kanvayanas and Susarman, and destroy the remains of the Sungas' power and will obtain this earth." The Andhras
The Āndhras were an ancient non-Aryan tribe of south-central Indian subcontinent, whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. Andhras were mentioned in the ancient Hindu scriptures such as the '' Aitareya Brahmana, Ramayana, Mahabharata ...
did indeed destroy the last remains of the Sunga state in central India somewhere around Vidisha, probably as a feeble rump state.
Art
The Shunga art style differed somewhat from imperial Mauryan art, which was influenced byPersian art
Persian art or Iranian art () has one of the richest art heritages in world history and has been strong in many media including architecture, painting, weaving, pottery, calligraphy, metalworking and sculpture. At different times, influences ...
. In both, continuing elements of folk art and cults of the Mother goddess
A mother goddess is a major goddess characterized as a mother or progenitor, either as an embodiment of motherhood and fertility or fulfilling the cosmological role of a creator- and/or destroyer-figure, typically associated the Earth, sky, ...
appear in popular art, but are now produced with more skill in more monumental forms. The Shunga style was thus seen as 'more Indian' and is often described as the more indigenous.
Art, education, philosophy, and other learning flowered during this period. Most notably, Patanjali's Yoga Sutras and Mahabhashya were composed in this period. It is also noted for its subsequent mention in the Malavikaagnimitra. This work was composed by Kalidasa in the later Gupta period, and romanticised the love of Malavika and King Agnimitra, with a background of court intrigue.
Artistry on the subcontinent also progressed with the rise of the Mathura school, which is considered the indigenous counterpart to the more Hellenistic Gandhara school (Greco-Buddhist art
The Greco-Buddhist art or Gandhara art is the artistic manifestation of Greco-Buddhism, a cultural syncretism between Ancient Greek art and Buddhism. It had mainly evolved in the ancient region of Gandhara, located in the northwestern fringe of t ...
) of Afghanistan and North-Western frontier of India (modern day Pakistan).
During the historical Shunga period (185 to 73 BCE), Buddhist activity also managed to survive somewhat in central India (Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (; ; ) is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and the largest city is Indore, Indore. Other major cities includes Gwalior, Jabalpur, and Sagar, Madhya Pradesh, Sagar. Madhya Pradesh is the List of states and union te ...
) as suggested by some architectural expansions that were done at the stupa
In Buddhism, a stupa (, ) is a domed hemispherical structure containing several types of sacred relics, including images, statues, metals, and '' śarīra''—the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns. It is used as a place of pilgrimage and m ...
s of Sanchi
Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist art, Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen ...
and Bharhut
Bharhut is a village in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for a Buddhist stupa, unique in that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters saying what the panel depicts. The major donor for the Bharhut st ...
, originally started under Emperor Ashoka. It remains uncertain whether these works were due to the weakness of the control of the Shungas in these areas, or a sign of tolerance on their part.
Script
The script used by the Shunga was a variant ofBrahmi
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or ...
, and was used to write the Sanskrit language. The script is thought to be an intermediary between the Maurya
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
and the Kalinga Brahmi scripts.
List of Shunga emperors
See also
*History of India
Anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. The earliest known human remains in South Asia date to 30,000 years ago. Sedentism, Sedentariness began in South Asia around 7000 BCE; ...
* History of Hinduism
The history of Hinduism covers a wide variety of related religious traditions native to the Indian subcontinent. It overlaps or coincides with the development of religion in the Indian subcontinent since the Iron Age, with some of its traditio ...
* Khandwala Dynasty
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * "The Legend of King Ashoka, A study and translation of the Ashokavadana", John Strong, Princeton Library of Asian translations, 1983, * "Dictionary of Buddhism" by Damien KEOWN (Oxford University Press, 2003) * ''Aśoka and the Decline of the Mauryas'',Romila Thapar
Romila Thapar (born 30 November 1931) is an Indian historian. Her principal area of study is ancient India, a field in which she is pre-eminent. Quotr: "The pre-eminent interpreter of ancient Indian history today. ... " Thapar is a Professor ...
, 1961 (revision 1998); Oxford University Press,
* "The Yuga Purana", John E. Mitchiner, Kolkata
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta ( its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary ...
, The Asiatic Society, 2002,
External links
Medallions from Barhut
{{DEFAULTSORT:Shunga Empire Former empires in Asia Hindu states Former monarchies of India Magadha 185 BC 180s BC establishments States and territories established in the 2nd century BC States and territories disestablished in the 1st century