Stringed Instruments on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 Pitch can be adjusted by varying the
Pitch can be adjusted by varying the
 In bowed instruments, the bow is normally placed perpendicularly to the string, at a point halfway between the end of the fingerboard and the bridge. However, different bow placements can be selected to change
In bowed instruments, the bow is normally placed perpendicularly to the string, at a point halfway between the end of the fingerboard and the bridge. However, different bow placements can be selected to change
 A single string at a certain tension and length only produces one note. To produce multiple notes, string instruments use one of two methods. One is to add enough strings to cover the required range of different notes (e.g., as with the
A single string at a certain tension and length only produces one note. To produce multiple notes, string instruments use one of two methods. One is to add enough strings to cover the required range of different notes (e.g., as with the
Savart Journal
, an online resource published in collaboration with the Guild of American Luthiers.
Instruments in Depth: The Viola
an online feature presented by Bloomingdale School of Music (2010) *
A Brief History of String Instruments
{{DEFAULTSORT:String Instrument String instruments, Orchestras Rhythm section
musical instrument classification
In organology, the study of musical instruments, many methods of classifying instruments exist. Most methods are specific to a particular Culture, cultural group and were developed to serve the musical needs of that culture. Culture-based classif ...
, string instruments, or chordophones, are musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make Music, musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person ...
s that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer strums, plucks, strikes or sounds the strings in varying manners.
Musicians play some string instruments, like guitars
The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted (with Fretless guitar, some exceptions) and typically has six or Twelve-string guitar, twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming ...
, by plucking the strings with their fingers or a plectrum (pick), and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow, like violins. In some keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord
A harpsichord is a musical instrument played by means of a musical keyboard, keyboard. Depressing a key raises its back end within the instrument, which in turn raises a mechanism with a small plectrum made from quill or plastic that plucks one ...
, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string.
With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy
The hurdy-gurdy is a string instrument that produces sound by a hand-turned crank, rosined wheel rubbing against the strings. The wheel functions much like a violin (or nyckelharpa) bow, and single notes played on the instrument sound similar ...
, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings.
Bowed instruments include the string section
The string section of an orchestra is composed of bowed instruments belonging to the violin family. It normally consists of first and second violins, violas, cellos, and double basses. It is the most numerous group in the standard orchestra. In ...
instruments of the orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families. There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* String instruments, such as the violin, viola, cello, ...
in Western classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical mu ...
(violin
The violin, sometimes referred to as a fiddle, is a wooden chordophone, and is the smallest, and thus highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in regular use in the violin family. Smaller violin-type instruments exist, including the violino picc ...
, viola
The viola ( , () ) is a string instrument of the violin family, and is usually bowed when played. Violas are slightly larger than violins, and have a lower and deeper sound. Since the 18th century, it has been the middle or alto voice of the ...
, cello
The violoncello ( , ), commonly abbreviated as cello ( ), is a middle pitched bowed (sometimes pizzicato, plucked and occasionally col legno, hit) string instrument of the violin family. Its four strings are usually intonation (music), tuned i ...
and double bass
The double bass (), also known as the upright bass, the acoustic bass, the bull fiddle, or simply the bass, is the largest and lowest-pitched string instrument, chordophone in the modern orchestra, symphony orchestra (excluding rare additions ...
) and a number of other instruments (e.g., viol
The viola da gamba (), or viol, or informally gamba, is a bowed and fretted string instrument that is played (i.e. "on the leg"). It is distinct from the later violin family, violin, or ; and it is any one of the earlier viol family of bow (m ...
s and gambas used in early music
Early music generally comprises Medieval music (500–1400) and Renaissance music (1400–1600), but can also include Baroque music (1600–1750) or Ancient music (before 500 AD). Originating in Europe, early music is a broad Dates of classical ...
from the Baroque music
Baroque music ( or ) refers to the period or dominant style of Classical music, Western classical music composed from about 1600 to 1750. The Baroque style followed the Renaissance music, Renaissance period, and was followed in turn by the Class ...
era and fiddle
A fiddle is a Bow (music), bowed String instrument, string musical instrument, most often a violin or a bass. It is a colloquial term for the violin, used by players in all genres, including European classical music, classical music. Althou ...
s used in many types of folk music
Folk music is a music genre that includes #Traditional folk music, traditional folk music and the Contemporary folk music, contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be ca ...
). All of the bowed string instruments can also be plucked with the fingers, a technique called "pizzicato
Pizzicato (, ; translated as 'pinched', and sometimes roughly as 'plucked') is a playing technique that involves plucking the strings of a string instrument. The exact technique varies somewhat depending on the type of instrument:
* On bowe ...
". A wide variety of techniques are used to sound notes on the electric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external electric Guitar amplifier, sound amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar. It uses one or more pickup (music technology), pickups ...
, including plucking with the fingernails or a plectrum, strumming and even "tapping
Tapping is a playing technique that can be used on any stringed instrument, but which is most commonly used on guitar. The technique involves a string being fretted and set into vibration as part of a single motion. This is in contrast to stand ...
" on the fingerboard and using feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handle ...
from a loud, distorted guitar amplifier
A guitar amplifier (or amp) is an electronic amplifier, electronic device or system that strengthens the electrical signal from a Pickup (music technology), pickup on an electric guitar, bass guitar, or acoustic guitar so that it can produce so ...
to produce a sustained sound.
Some string instruments are mainly plucked, such as the harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orchestras or ...
and the electric bass
The bass guitar (), also known as the electric bass guitar, electric bass, or simply the bass, is the lowest-pitched member of the guitar family. It is similar in appearance and construction to an electric but with a longer neck and scale leng ...
. Other examples include the sitar
The sitar ( or ; ) is a plucked stringed instrument, originating from the Indian subcontinent, used in Hindustani classical music. The instrument was invented in the 18th century, and arrived at its present form in 19th-century India. Khusrau K ...
, rebab
''Rebab'' (, ''rabāba'', variously spelled ''rebap'', ''rubob'', ''rebeb'', ''rababa'', ''rabeba'', ''robab'', ''rubab'', ''rebob'', etc) is the name of several related string instruments that independently spread via Islamic trading rout ...
, banjo
The banjo is a stringed instrument with a thin membrane stretched over a frame or cavity to form a resonator. The membrane is typically circular, and in modern forms is usually made of plastic, where early membranes were made of animal skin.
...
, mandolin
A mandolin (, ; literally "small mandola") is a Chordophone, stringed musical instrument in the lute family and is generally Plucked string instrument, plucked with a plectrum, pick. It most commonly has four Course (music), courses of doubled St ...
, ukulele
The ukulele ( ; ); also called a uke (informally), is a member of the lute (ancient guitar) family of instruments. The ukulele is of Portuguese origin and was popularized in Hawaii. The tone and volume of the instrument vary with size and con ...
, and bouzouki
The bouzouki (, also ; ; alt. pl. ''bouzoukia'', , from Greek , from Turkish ) is a musical instrument popular in West Asia (Syria, Iraq), Europe and Balkans (Greece, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, Turkey). It is a member of the long-necked lute fam ...
.
In the Hornbostel–Sachs
Hornbostel–Sachs or Sachs–Hornbostel is a system of musical instrument classification devised by Erich Moritz von Hornbostel and Curt Sachs, first published in the in 1914. An English translation was published in the '' Galpin Society Journ ...
scheme of musical instrument classification
In organology, the study of musical instruments, many methods of classifying instruments exist. Most methods are specific to a particular Culture, cultural group and were developed to serve the musical needs of that culture. Culture-based classif ...
, used in organology
Organology (; ) is the science of musical instruments and their classifications. It embraces study of instruments' history, instruments used in different cultures, technical aspects of how instruments produce sound, and musical instrument classi ...
, string instruments are called chordophones. According to Sachs Sachs is a German surname, meaning "man from Saxony". Sachs is a common surname among Ashkenazi Jews from Saxony, in the United States sometimes adopted in the variant Zaks, supposedly in reference to the Hebrew phrase ''Zera Kodesh Shemo'' (ZaKS), ...
,
In most string instruments, the vibrations are transmitted to the body of the instrument, which often incorporates some sort of hollow or enclosed area. The body of the instrument also vibrates, along with the air inside it. The vibration of the body of the instrument and the enclosed hollow or chamber make the vibration of the string more audible to the performer and audience. The body of most string instruments is hollow, in order to have better sound projection. Some, however—such as electric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external electric Guitar amplifier, sound amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar. It uses one or more pickup (music technology), pickups ...
and other instruments that rely on electronic amplification—may have a solid wood body.
Classification
Inmusicology
Musicology is the academic, research-based study of music, as opposed to musical composition or performance. Musicology research combines and intersects with many fields, including psychology, sociology, acoustics, neurology, natural sciences, ...
, string instruments are known as chordophones. It is one of the five main divisions of instruments in the Hornbostel–Sachs
Hornbostel–Sachs or Sachs–Hornbostel is a system of musical instrument classification devised by Erich Moritz von Hornbostel and Curt Sachs, first published in the in 1914. An English translation was published in the '' Galpin Society Journ ...
scheme of musical instrument classification
In organology, the study of musical instruments, many methods of classifying instruments exist. Most methods are specific to a particular Culture, cultural group and were developed to serve the musical needs of that culture. Culture-based classif ...
.
Hornbostel–Sachs divides chordophones into two main groups: instruments without a resonator
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior. That is, it naturally oscillates with greater amplitude at some frequencies, called resonant frequencies, than at other frequencies. The oscillations in a reso ...
as an integral part of the instrument (which have the classification number 31, also known as 'simple'); and instruments with such a resonator (which have the classification number 32, also known as 'composite'). Most western instruments fall into the second group, but the piano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ...
and harpsichord
A harpsichord is a musical instrument played by means of a musical keyboard, keyboard. Depressing a key raises its back end within the instrument, which in turn raises a mechanism with a small plectrum made from quill or plastic that plucks one ...
fall into the first. Hornbostel and Sachs's criterion for determining which sub-group an instrument falls into is that if the resonator can be removed without destroying the instrument, then it is classified as 31. The idea that the piano's casing, which acts as a resonator, could be removed without destroying the instrument, may seem odd, but if the action and strings of the piano were taken out of its box, it could still be played. This is not true of the violin
The violin, sometimes referred to as a fiddle, is a wooden chordophone, and is the smallest, and thus highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in regular use in the violin family. Smaller violin-type instruments exist, including the violino picc ...
, because the string passes over a bridge located on the resonator box, so removing the resonator would mean the strings had no tension.
Curt Sachs also broke chordophones into four basic subcategories, "zithers, lutes, lyres and harps."
* Zither
Zither (; , from the Greek ''cithara'') is a class of stringed instruments. The modern instrument has many strings stretched across a thin, flat body.
Zithers are typically played by strumming or plucking the strings with the fingers or a ...
s include ''stick zithers'' such as the musical bow, '' tube zithers'' with a tube as the resonator such as the valiha
The valiha is a tube zither from Madagascar made from a species of Valiha diffusa, local bamboo; it is considered the "List of national instruments (music), national instrument" of Madagascar. The term is also used to describe a number of re ...
, raft zithers in which tube zithers are tied into a single "raft", ''board zithers'' including clavichord
The clavichord is a stringed rectangular keyboard instrument that was used largely in the Late Middle Ages, through the Renaissance music, Renaissance, Baroque music, Baroque and Classical period (music), Classical eras.
Historically, it was most ...
and piano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ...
and dulcimer, and ''long zithers'' (described as combination of half-tube and board zithers) including Se and Guzheng
The zheng (), or guzheng (), is a Chinese List of Chinese musical instruments#Plucked, plucked zither. The modern guzheng commonly has 21, 25, or 26 strings, is long, and is tuned in a Major scale, major pentatonic scale. It has a large, reson ...
families.
* Lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck (music), neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.
More specifically, the term "lu ...
s are stringed musical instruments that include a body and "a neck which serves both as a handle and as a means of stretching the strings beyond the body." The lute family includes not only ''short-necked plucked lutes'' such as the lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck (music), neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.
More specifically, the term "lu ...
, oud, pipa
The pipa, pípá, or p'i-p'a () is a traditional Chinese musical instrument belonging to the plucked category of instruments. Sometimes called the "Chinese lute", the instrument has a pear-shaped wooden body with a varying number of frets rangi ...
, guitar
The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted (with Fretless guitar, some exceptions) and typically has six or Twelve-string guitar, twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming ...
, citole
The citole was a String instrument, string musical instrument, closely associated with the medieval fiddles (viol, vielle, Geige, gigue) and commonly used from 1200–1350."CITOLE, also spelled Systole, Cythole, Gytolle, &c. (probably a Fr. d ...
, gittern
The gittern was a relatively small gut-strung, round-backed instrument that first appeared in literature and pictorial representation during the 13th century in Western Europe (Iberian Peninsula, Italy, France, England). It is usually depicted p ...
, mandore
Mandore is a suburb and historical town located 9 km north of Jodhpur city in the Jodhpur district of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan.
History
Mandore is an ancient town, and was the seat of the Gurjar Pratiharas of Mandavy ...
, rubab, and gambus and ''long-necked plucked lutes'' such as the tanbura, swarabat, bağlama
The bağlama or saz is a family of plucked string instruments and long-necked lutes used in Europe, Balkans, Caucasus, Middle East, Khazar, Central Asia including Germany, France, Belgium, TRNC, Netherlands, Albania, Greece,Bosnia, Serbia, Croat ...
, bouzouki
The bouzouki (, also ; ; alt. pl. ''bouzoukia'', , from Greek , from Turkish ) is a musical instrument popular in West Asia (Syria, Iraq), Europe and Balkans (Greece, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, Turkey). It is a member of the long-necked lute fam ...
, veena
The ''veena'', also spelled ''vina'' ( IAST: vīṇā), is any of various chordophone instruments from the Indian subcontinent. Ancient musical instruments evolved into many variations, such as lutes, zithers and arched harps.
, theorbo
The theorbo is a plucked string instrument of the lute family, with an extended neck that houses the second pegbox. Like a lute, a theorbo has a curved-back sound box with a flat top, typically with one or three sound holes decorated with rose ...
, archlute
The archlute (, , ) is a European plucked string instrument developed around 1600 as a compromise between the very large theorbo, the size and re-entrant tuning of which made for difficulties in the performance of solo music, and the Renaissan ...
, pandura
The pandura (, ''pandoura'') or pandore, an ancient Greek string instrument, belonged in the broad class of the lute and guitar instruments. Akkadian Empire, Akkadians played similar instruments from the 3rd millennium BC. Ancient Greece, Ancien ...
, sitar
The sitar ( or ; ) is a plucked stringed instrument, originating from the Indian subcontinent, used in Hindustani classical music. The instrument was invented in the 18th century, and arrived at its present form in 19th-century India. Khusrau K ...
, setar
A setar (, ) (lit: "Three String (music), Strings") is a stringed instrument, a type of lute used in Persian traditional music, played solo or accompanying voice. It is a member of the tanbur family of long-necked lutes with a range of more than ...
, but also ''bowed instruments'' such as the Yaylı tambur, rebab
''Rebab'' (, ''rabāba'', variously spelled ''rebap'', ''rubob'', ''rebeb'', ''rababa'', ''rabeba'', ''robab'', ''rubab'', ''rebob'', etc) is the name of several related string instruments that independently spread via Islamic trading rout ...
, erhu
The (; ) is a Chinese two-stringed bowed musical instrument, more specifically a spike fiddle, that is sometimes known in the Western world as the ''Chinese violin'' or a ''Chinese two-stringed fiddle''. It is used as a solo instrument as ...
, and entire family of viols and violins.
* The lyre
The lyre () (from Greek λύρα and Latin ''lyra)'' is a string instrument, stringed musical instrument that is classified by Hornbostel–Sachs as a member of the History of lute-family instruments, lute family of instruments. In organology, a ...
has two arms, which have a "yoke" or crossbar connecting them, and strings between the crossbar and the soundboard. Sachs divided this into the ''box lyre'' such as the Greek kithara
The kithara (), Latinized as cithara, was an ancient Greek musical instrument in the yoke lutes family. It was a seven-stringed professional version of the lyre, which was regarded as a rustic, or folk instrument, appropriate for teaching mu ...
and the ''bowl lyre'' which used a bowl on its side with skin soundboard.
* The harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orchestras or ...
which has strings vertical to the soundboard.
Earliest string instruments
Dating to around , a cave painting in the Trois Frères cave in France depicts what some believe is a musical bow, a hunting bow used as a single-stringed musical instrument. From the musical bow, families of stringed instruments developed; since each string played a single note, adding strings added new notes, creating bow harps,harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orchestras or ...
s and lyres
Yoke lutes, commonly called lyres, are a class of string instruments, subfamily of lutes, indicated with the codes 321.21 and 321.22 in the Hornbostel–Sachs classification.
Description
Yoke lutes are defined as instruments with one or more ...
. In turn, this led to being able to play dyads and chords
Chord or chords may refer to:
Art and music
* Chord (music), an aggregate of musical pitches sounded simultaneously
** Guitar chord, a chord played on a guitar, which has a particular tuning
* The Chords (British band), 1970s British mod ...
. Another innovation occurred when the bow harp was straightened out and a bridge
A bridge is a structure built to Span (engineering), span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, whi ...
used to lift the strings off the stick-neck, creating the lute.
This picture of musical bow to harp bow is theory and has been contested. In 1965 Franz Jahnel wrote his criticism stating that the early ancestors of plucked instruments are not currently known. He felt that the harp bow was a long cry from the sophistication of the civilizations of western Asia in 4000 BC that took the primitive technology and created "technically and artistically well-made harps, lyres, citharas, and lutes."
Archaeological digs have identified some of the earliest stringed instruments in Ancient Mesopotamia
The Civilization of Mesopotamia ranges from the earliest human occupation in the Paleolithic period up to Late antiquity. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writ ...
n sites, like the lyres of Ur
Yoke lutes, commonly called lyres, are a class of string instruments, subfamily of lutes, indicated with the codes List of musical instruments by Hornbostel–Sachs number: 321.21, 321.21 and List of musical instruments by Hornbostel–Sachs number ...
, which include artifacts over three thousand years old. The development of lyre
The lyre () (from Greek λύρα and Latin ''lyra)'' is a string instrument, stringed musical instrument that is classified by Hornbostel–Sachs as a member of the History of lute-family instruments, lute family of instruments. In organology, a ...
instruments required the technology
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible too ...
to create a tuning mechanism to tighten and loosen the string tension. Lyres with wooden bodies and strings used for plucking or playing with a bow represent key instruments that point towards later harps and violin-type instruments; moreover, Indian instruments from 500 BC have been discovered with anything from 7 to 21 strings. In Vietnam, a 2,000 year old, singularly stringed instrument made of deer antler was also discovered.
Lutes
Musicologists have put forth examples of that 4th-century BC technology, looking at engraved images that have survived. The earliest image showing a lute-like instrument came fromMesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
prior to 3000 BC. A cylinder seal
A cylinder seal is a small round cylinder, typically about one inch (2 to 3 cm) in width, engraved with written characters or figurative scenes or both, used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally ...
from or earlier (now in the possession of the British Museum) shows what is thought to be a woman playing a stick lute. From the surviving images, theorists have categorized the Mesopotamian lutes, showing that they developed into a long variety and a short. The line of long lutes may have developed into the tamburs and pandura
The pandura (, ''pandoura'') or pandore, an ancient Greek string instrument, belonged in the broad class of the lute and guitar instruments. Akkadian Empire, Akkadians played similar instruments from the 3rd millennium BC. Ancient Greece, Ancien ...
. The line of short lutes was further developed to the east of Mesopotamia, in Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
, Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
, and Northwest India, and shown in sculpture from the 2nd century BC through the 4th or 5th centuries AD.
During the medieval era
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and t ...
, instrument development varied in different regions of the world. Middle Eastern rebecs represented breakthroughs in terms of shape and strings, with a half a pear shape using three strings. Early versions of the violin and fiddle, by comparison, emerged in Europe through instruments such as the gittern
The gittern was a relatively small gut-strung, round-backed instrument that first appeared in literature and pictorial representation during the 13th century in Western Europe (Iberian Peninsula, Italy, France, England). It is usually depicted p ...
, a four-stringed precursor to the guitar, and basic lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck (music), neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.
More specifically, the term "lu ...
s. These instruments typically used catgut (animal intestine) and other materials, including silk, for their strings.
Renaissance to modern
String instrument design was refined during theRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
and into the Baroque period (1600–1750) of musical history. Violins and guitars
The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted (with Fretless guitar, some exceptions) and typically has six or Twelve-string guitar, twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming ...
became more consistent in design and were roughly similar to acoustic guitars of the 2000s. The violins of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
featured intricate woodwork and stringing, while more elaborate bass instruments such as the bandora were produced alongside quill-plucked citterns, and Spanish body guitars.
In the 19th century, string instruments were made more widely available through mass production, with wood string instruments a key part of orchestras – cellos, violas, and upright basses, for example, were now standard instruments for chamber ensembles and smaller orchestras. At the same time, the 19th-century guitar became more typically associated with six-string models, rather than traditional five-string versions.
Major changes to string instruments in the 20th century primarily involved innovations in electronic instrument amplification and electronic music – electric violins were available by the 1920s and were an important part of emerging jazz music trends in the United States. The acoustic guitar
An acoustic guitar is a musical instrument in the string family. When a string is plucked, its vibration is transmitted from the bridge, resonating throughout the top of the guitar. It is also transmitted to the side and back of the instrument, ...
was widely used in blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
and jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
, but as an acoustic instrument, it was not loud enough to be a solo instrument, so these genres mostly used it as an accompaniment
Accompaniment is the musical part which provides the rhythmic and/or harmonic support for the melody or main themes of a song or instrumental piece. There are many different styles and types of accompaniment in different genres and styles of m ...
rhythm section
A rhythm section is a group of musicians within a music ensemble or band that provides the underlying rhythm, harmony and pulse of the accompaniment, providing a rhythmic and harmonic reference and "beat" for the rest of the band.
The rhythm ...
instrument. In big band
A big band or jazz orchestra is a type of musical ensemble of jazz music that usually consists of ten or more musicians with four sections: saxophones, trumpets, trombones, and a rhythm section. Big bands originated during the early 1910s and ...
s of the 1920s, the acoustic guitar
An acoustic guitar is a musical instrument in the string family. When a string is plucked, its vibration is transmitted from the bridge, resonating throughout the top of the guitar. It is also transmitted to the side and back of the instrument, ...
played backing chords, but it was not loud enough to play solos like the saxophone
The saxophone (often referred to colloquially as the sax) is a type of single-reed woodwind instrument with a conical body, usually made of brass. As with all single-reed instruments, sound is produced when a reed on a mouthpiece vibrates to p ...
and trumpet
The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz musical ensemble, ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest Register (music), register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitche ...
. The development of guitar amplifiers, which contained a power amplifier
An audio power amplifier (or power amp) amplifies low-power electronic audio signals, such as the signal from a radio receiver or an electric guitar pickup, to a level that is high enough for driving loudspeakers or headphones. Audio power a ...
and a loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an ...
in a wooden cabinet, let jazz guitar
Jazz guitar may refer to either a type of electric guitar or a guitar playing style in jazz, using Guitar amplifier, electric amplification to increase the volume of acoustic guitars.
In the early 1930s, jazz musicians sought to amplify their ...
ists play solos and be heard over a big band. The development of the electric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external electric Guitar amplifier, sound amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar. It uses one or more pickup (music technology), pickups ...
provided guitarists with an instrument that was built to connect to guitar amplifiers. Electric guitars have magnetic pickup
A pickup is an electronic device that converts energy from one form to another that captures or senses mechanical vibrations produced by musical instruments, particularly stringed instruments such as the electric guitar, and converts these t ...
s, volume control knobs and an output jack.
In the 1960s, larger, more powerful guitar amplifiers were developed, called "stacks". These powerful amplifiers enabled guitarists to perform in rock bands that played in large venues such as stadiums and outdoor music festivals (e.g., Woodstock Music Festival). Along with the development of guitar amplifiers, a large range of electronic effects unit
An effects unit, effects processor, or effects pedal is an electronic device that alters the sound of a musical instrument or other audio source through audio signal processing.
Common effects include distortion (music), distortion/overdrive, ...
s, many in small stompbox pedals, were introduced in the 1960s and 1970s, such as fuzz pedals, flanger
Flanging is an audio effect produced by mixing two identical signals together, one signal delayed by a small and (usually) gradually changing period, usually smaller than 20 milliseconds. This produces a swept comb filter effect: peaks and ...
s, and phasers, enabling performers to create unique new sounds during the psychedelic rock
Psychedelic rock is a rock music Music genre, genre that is inspired, influenced, or representative of psychedelia, psychedelic culture, which is centered on perception-altering hallucinogenic drugs. The music incorporated new electronic sound ...
era. Breakthroughs in electric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external electric Guitar amplifier, sound amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar. It uses one or more pickup (music technology), pickups ...
and bass technologies and playing styles enabled major breakthroughs in pop and rock music in the 1960s and 1970s. The distinctive sound of the amplified electric guitar was the centerpiece of new genres of music such as blues rock
Blues rock is a fusion music genre, genre and form of rock music, rock and blues music that relies on the chords/scales and instrumental improvisation of blues. It is mostly an electric ensemble-style music with instrumentation similar to electri ...
and jazz-rock fusion
Jazz fusion (also known as jazz rock, jazz-rock fusion, or simply fusion) is a popular music genre that developed in the late 1960s when musicians combined jazz harmony and improvisation with rock music, funk, and rhythm and blues. Electric gui ...
. The sonic power of the loudly amplified, highly distorted electric guitar was the key element of the early heavy metal music
Heavy metal (or simply metal) is a Music genre, genre of rock music that developed in the late 1960s and early 1970s, largely in the United Kingdom and United States. With roots in blues rock, psychedelic rock and acid rock, heavy metal band ...
, with the distorted guitar being used in lead guitar
Lead guitar (also known as solo guitar) is a musical part for a guitar in which the guitarist plays melody lines, instrumental fill passages, guitar solos, and occasionally, some riffs and chords within a song structure. The lead is the featur ...
roles, and with power chord
A power chord , also called a fifth chord, is a colloquial name for a chord on guitar, especially on electric guitar, that consists of the root note and the fifth, as well as possibly octaves of those notes. Power chords are commonly pla ...
s as a rhythm guitar
In music performances, rhythm guitar is a guitar technique and role that performs a combination of two functions: to provide all or part of the rhythmic pulse (music), pulse in conjunction with other instruments from the rhythm section (e.g., d ...
.
The ongoing use of electronic amplification and effects units in string instruments, ranging from traditional instruments like the violin to the new electric guitar, added variety to contemporary classical music
Contemporary classical music is Western art music composed close to the present day. At the beginning of the 21st-century classical music, 21st century, it commonly referred to the post-1945 Modernism (music), post-tonal music after the death of ...
performances, and enabled experimentation in the dynamic and timbre (tone colour) range of orchestras, bands, and solo performances.
Types of instruments
Construction
String instruments can be divided into three groups: ;Lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck (music), neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.
More specifically, the term "lu ...
s : Instruments that support the strings via a neck
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Addition ...
and a bout (gourd), for instance a guitar, violin, or saz
;Harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orchestras or ...
s : Instruments that contain the strings within a frame
;Zither
Zither (; , from the Greek ''cithara'') is a class of stringed instruments. The modern instrument has many strings stretched across a thin, flat body.
Zithers are typically played by strumming or plucking the strings with the fingers or a ...
s : Instruments that have the strings mounted on a body, frame
A frame is often a structural system that supports other components of a physical construction and/or steel frame that limits the construction's extent.
Frame and FRAME may also refer to:
Physical objects
In building construction
*Framing (con ...
or tube
Tube or tubes may refer to:
* ''Tube'' (2003 film), a 2003 Korean film
* "Tubes" (Peter Dale), performer on the Soccer AM television show
* Tube (band), a Japanese rock band
* Tube & Berger, the alias of dance/electronica producers Arndt Rör ...
, such as a guqin
The ''guqin'' (; ) is a plucked seven-string Chinese musical instrument. It has been played since ancient times, and has traditionally been favoured by scholars and literati as an instrument of great subtlety and refinement, as highlighted b ...
, cimbalom
The cimbalom, cimbal (; ) or concert cimbalom is a type of chordophone composed of a large, trapezoidal box on legs with metal strings stretched across its top and a damping pedal underneath. It was designed and created by József Schunda, V. ...
, autoharp
An autoharp or chord zither is a string instrument belonging to the zither family. It uses a series of bars individually configured to mute all strings other than those needed for the intended chord. The term ''autoharp'' was once a trademark of t ...
, harpsichord
A harpsichord is a musical instrument played by means of a musical keyboard, keyboard. Depressing a key raises its back end within the instrument, which in turn raises a mechanism with a small plectrum made from quill or plastic that plucks one ...
, piano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ...
, or valiha
The valiha is a tube zither from Madagascar made from a species of Valiha diffusa, local bamboo; it is considered the "List of national instruments (music), national instrument" of Madagascar. The term is also used to describe a number of re ...
It is also possible to divide the instruments into categories focused on how the instrument is played.
Playing techniques
All string instruments produce sound from one or more vibrating strings, transferred to the air by the body of the instrument (or by a pickup in electronically amplified instruments). They are usually categorised by the technique used to make the strings vibrate (or by the primary technique, in the case of instruments where more than one may apply). The three most common techniques are plucking, bowing, and striking. An important difference between bowing and plucking is that in the former the phenomenon is periodic so that the overtones are kept in a strictly harmonic relationship to the fundamental.Plucking
Plucking is a method of playing on instruments such as theveena
The ''veena'', also spelled ''vina'' ( IAST: vīṇā), is any of various chordophone instruments from the Indian subcontinent. Ancient musical instruments evolved into many variations, such as lutes, zithers and arched harps.
, banjo
The banjo is a stringed instrument with a thin membrane stretched over a frame or cavity to form a resonator. The membrane is typically circular, and in modern forms is usually made of plastic, where early membranes were made of animal skin.
...
, ukulele
The ukulele ( ; ); also called a uke (informally), is a member of the lute (ancient guitar) family of instruments. The ukulele is of Portuguese origin and was popularized in Hawaii. The tone and volume of the instrument vary with size and con ...
, guitar, harp, lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck (music), neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.
More specifically, the term "lu ...
, mandolin
A mandolin (, ; literally "small mandola") is a Chordophone, stringed musical instrument in the lute family and is generally Plucked string instrument, plucked with a plectrum, pick. It most commonly has four Course (music), courses of doubled St ...
, oud, and sitar
The sitar ( or ; ) is a plucked stringed instrument, originating from the Indian subcontinent, used in Hindustani classical music. The instrument was invented in the 18th century, and arrived at its present form in 19th-century India. Khusrau K ...
, using either a finger, thumb, or quills (now plastic plectra) to pluck the strings.
Instruments normally played by bowing (see below) may also be plucked, a technique referred to by the Italian term ''pizzicato
Pizzicato (, ; translated as 'pinched', and sometimes roughly as 'plucked') is a playing technique that involves plucking the strings of a string instrument. The exact technique varies somewhat depending on the type of instrument:
* On bowe ...
''.
Bowing
Bowing
Bowing (also called stooping) is the act of lowering the torso and Human head, head as a social gesture in direction to another person or symbol. It is most prominent in Asian cultures but it is also typical of nobility and aristocracy in many E ...
(Italian: ''arco'') is a method used in some string instruments, including the violin
The violin, sometimes referred to as a fiddle, is a wooden chordophone, and is the smallest, and thus highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in regular use in the violin family. Smaller violin-type instruments exist, including the violino picc ...
, viola
The viola ( , () ) is a string instrument of the violin family, and is usually bowed when played. Violas are slightly larger than violins, and have a lower and deeper sound. Since the 18th century, it has been the middle or alto voice of the ...
, cello
The violoncello ( , ), commonly abbreviated as cello ( ), is a middle pitched bowed (sometimes pizzicato, plucked and occasionally col legno, hit) string instrument of the violin family. Its four strings are usually intonation (music), tuned i ...
, and the double bass
The double bass (), also known as the upright bass, the acoustic bass, the bull fiddle, or simply the bass, is the largest and lowest-pitched string instrument, chordophone in the modern orchestra, symphony orchestra (excluding rare additions ...
(of the violin family
The violin family of musical instruments was developed in Italy in the 16th century. At the time the name of this family of instruments was viole da braccio which was used to distinguish them from the viol family (viole ''da gamba''). The standa ...
), and the old viol
The viola da gamba (), or viol, or informally gamba, is a bowed and fretted string instrument that is played (i.e. "on the leg"). It is distinct from the later violin family, violin, or ; and it is any one of the earlier viol family of bow (m ...
family. The bow consists of a stick with a "ribbon" of parallel horse tail hairs stretched between its ends. The hair is coated with rosin
Rosin (), also known as colophony or Greek pitch (), is a resinous material obtained from pine trees and other plants, mostly conifers. The primary components of rosin are diterpenoids, i.e., C20 carboxylic acids. Rosin consists mainly of r ...
so it can grip the string; moving the hair across a string causes a stick-slip phenomenon, making the string vibrate, and prompting the instrument to emit sound. Darker grades of rosin grip well in cool, dry climates, but may be too sticky in warmer, more humid weather. Violin and viola players generally use harder, lighter-colored rosin than players of lower-pitched instruments, who tend to favor darker, softer rosin.
The ravanahatha is one of the oldest string instruments. Ancestors of the modern bowed string instruments are the rebab
''Rebab'' (, ''rabāba'', variously spelled ''rebap'', ''rubob'', ''rebeb'', ''rababa'', ''rabeba'', ''robab'', ''rubab'', ''rebob'', etc) is the name of several related string instruments that independently spread via Islamic trading rout ...
of the Islamic Empires, the Persian kamanche and the Byzantine lira
The Byzantine lyra or lira () was a medieval bowed string musical instrument in the Byzantine (Eastern Roman) Empire. In its popular form, the lyra was a pear-shaped instrument with three to five strings, held upright and played by stopping ...
. Other bowed instruments are the rebec, hardingfele, nyckelharpa
''Nyckelharpa'' (, roughly "keyed fiddle" in Swedish language, Swedish, , plural: ) is a "keyed" Bowed string instrument, bowed chordophone, primarily originating from Sweden in its modern form, but with its historical roots scattered across med ...
, kokyū
The is the only traditional Japanese string instrument played with a bow (music), bow. A variant of the instrument also exists in Okinawa Prefecture, Okinawa, called () in Okinawan language, Okinawan.
The , like the , has its origins in Oki ...
, erhu
The (; ) is a Chinese two-stringed bowed musical instrument, more specifically a spike fiddle, that is sometimes known in the Western world as the ''Chinese violin'' or a ''Chinese two-stringed fiddle''. It is used as a solo instrument as ...
, igil
The ''igil'' ( Tuvan: игил) is a two- stringed Tuvan musical instrument, played by bowing the strings. (It is called "ikili" in Western Mongolia.) The neck and lute-shaped sound box are usually made of a solid piece of pine or larch. The ...
, sarangi
The sārangī is a bowed, short-necked three-stringed instrument played in traditional music from South Asia – Punjabi folk music, Rajasthani folk music, Sindhi folk music, Haryanvi folk music, Braj folk music, and Boro folk music (the ...
, morin khuur
The ''morin khuur'' (), also known as the horsehead fiddle, is a traditional Mongolian bowed stringed instrument. It is one of the most important musical instruments of the Mongol people, and is considered a symbol of the nation of Mongolia. ...
, and K'ni. The hurdy-gurdy
The hurdy-gurdy is a string instrument that produces sound by a hand-turned crank, rosined wheel rubbing against the strings. The wheel functions much like a violin (or nyckelharpa) bow, and single notes played on the instrument sound similar ...
is bowed by a wheel. Rarely, the guitar has been played with a bow (rather than plucked) for unique effects.
Striking
The third common method of sound production in stringed instruments is to strike the string. The piano andhammered dulcimer
The hammered dulcimer (also called the hammer dulcimer) is a percussion-string instrument which consists of String (music), strings typically stretched over a trapezoidal resonant sound board (music), sound board. The hammered dulcimer is set bef ...
use this method of sound production. Even though the piano strikes the strings, the use of felt hammers means that the sound that is produced can nevertheless be mellow and rounded, in contrast to the sharp attack produced when a very hard hammer strikes the strings.
Violin family string instrument players are occasionally instructed to strike the string with the stick of the bow, a technique called ''col legno
In music for bowed string instruments, , or more precisely ; ), is an instruction to strike the string with the stick of the bow across the strings.
History
The earliest known use of in Western music is to be found in a piece entitled "Hark ...
''. This yields a percussive sound along with the pitch of the note. A well-known use of ''col legno'' for orchestral strings is Gustav Holst
Gustav Theodore Holst (born Gustavus Theodore von Holst; 21 September 1874 – 25 May 1934) was an English composer, arranger and teacher. Best known for his orchestral suite ''The Planets'', he composed many other works across a range ...
's "Mars" movement from ''The Planets
''The Planets'', Op. 32, is a seven- movement orchestral suite by the English composer Gustav Holst, written between 1914 and 1917. In the last movement the orchestra is joined by a wordless female chorus. Each movement of the suite is name ...
'' suite.
Other methods
The aeolian harp employs a very unusual method of sound production: the strings are excited by the movement of the air. Some instruments that have strings have an attached keyboard that the player presses keys on to trigger a mechanism that sounds the strings, instead of directly manipulating the strings. These include thepiano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ...
, the clavichord
The clavichord is a stringed rectangular keyboard instrument that was used largely in the Late Middle Ages, through the Renaissance music, Renaissance, Baroque music, Baroque and Classical period (music), Classical eras.
Historically, it was most ...
, and the harpsichord. With these keyboard instrument
A keyboard instrument is a musical instrument played using a keyboard, a row of levers that are pressed by the fingers. The most common of these are the piano, organ, and various electronic keyboards, including synthesizers and digital piano ...
s, strings are occasionally plucked or bowed by hand. Modern composer
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music.
Etymology and def ...
s such as Henry Cowell
Henry Dixon Cowell (; March 11, 1897 – December 10, 1965) was an American composer, writer, pianist, publisher, teacher Marchioni, Tonimarie (2012)"Henry Cowell: A Life Stranger Than Fiction" ''The Juilliard Journal''. Retrieved 19 June 2022.C ...
wrote music that requires that the player reach inside the piano and pluck the strings directly, "bow" them with bow hair wrapped around the strings, or play them by rolling the bell of a brass instrument
A brass instrument is a musical instrument that produces sound by Sympathetic resonance, sympathetic vibration of air in a tubular resonator in sympathy with the vibration of the player's lips. The term ''labrosone'', from Latin elements meani ...
such as a trombone
The trombone (, Italian, French: ''trombone'') is a musical instrument in the Brass instrument, brass family. As with all brass instruments, sound is produced when the player's lips vibrate inside a mouthpiece, causing the Standing wave, air c ...
on the array of strings. However, these are relatively rarely used special techniques.
Other keyed string instruments, small enough for a strolling musician to play, include the plucked autoharp
An autoharp or chord zither is a string instrument belonging to the zither family. It uses a series of bars individually configured to mute all strings other than those needed for the intended chord. The term ''autoharp'' was once a trademark of t ...
, the bowed nyckelharpa
''Nyckelharpa'' (, roughly "keyed fiddle" in Swedish language, Swedish, , plural: ) is a "keyed" Bowed string instrument, bowed chordophone, primarily originating from Sweden in its modern form, but with its historical roots scattered across med ...
, and the hurdy-gurdy, which is played by cranking a rosined wheel.
Steel-stringed instruments (such as the guitar, bass, violin, etc.) can be played using a magnetic field. An E-Bow
The EBow is an electronic device used for playing string instruments, most often the electric guitar. It was invented by the American guitarist Greg Heet in 1969 and introduced in 1976. The EBow uses a pickup and a magnetic feedback circuit to ...
is a small hand-held battery-powered device that magnetically excites the strings of an electric string instrument to provide a sustained, singing tone reminiscent of a held bowed violin note.
Third bridge is a plucking method where the player ''frets'' a string and strikes the side opposite the bridge. The technique is mainly used on electric instruments because these have a pickup that amplifies only the local string vibration. It is possible on acoustic instruments as well, but less effective. For instance, a player might press on the seventh fret
A fret is any of the thin strips of material, usually metal wire, inserted laterally at specific positions along the neck or fretboard of a stringed instrument. Frets usually extend across the full width of the neck. On some historical inst ...
on a guitar and pluck it at the head side to make a tone resonate at the opposing side. On electric instruments, this technique generates multitone sounds reminiscent of a clock or bell.
Electric string instruments, such as the electric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external electric Guitar amplifier, sound amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar. It uses one or more pickup (music technology), pickups ...
, can also be played without touching the strings by using audio feedback
Audio feedback (also known as acoustic feedback, simply as feedback) is a positive feedback situation that may occur when an acoustic path exists between an audio output (for example, a loudspeaker) and its audio input (for example, a microphon ...
. When an electric guitar is plugged into a loud, powerful guitar amplifier with a loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an ...
and a high level of distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signal ...
is intentionally used, the guitar produces sustained high-pitched sounds. By changing the proximity of the guitar to the speaker, the guitarist can produce sounds that cannot be produced with standard plucking and picking techniques. This technique was popularized by Jimi Hendrix
James Marshall "Jimi" Hendrix (born Johnny Allen Hendrix; November 27, 1942September 18, 1970) was an American singer-songwriter and musician. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest and most influential guitarists of all time. Inducted ...
and others in the 1960s. It was widely used in psychedelic rock
Psychedelic rock is a rock music Music genre, genre that is inspired, influenced, or representative of psychedelia, psychedelic culture, which is centered on perception-altering hallucinogenic drugs. The music incorporated new electronic sound ...
and heavy metal music
Heavy metal (or simply metal) is a Music genre, genre of rock music that developed in the late 1960s and early 1970s, largely in the United Kingdom and United States. With roots in blues rock, psychedelic rock and acid rock, heavy metal band ...
.
Changing the pitch of a vibrating string
There are three ways to change the pitch of a vibrating string. String instruments are tuned by varying a string's tension because adjusting length or mass per unit length is impractical. Instruments with afingerboard
The fingerboard (also known as a fretboard on fretted instruments) is an important component of most stringed instruments. It is a thin, long strip of material, usually wood, that is laminated to the front of the neck of an instrument. The stri ...
are then played by adjusting the length of the vibrating portion of the strings. The following observations all apply to a string that is infinitely flexible (a theoretical assumption, because in practical applications, strings are not infinitely flexible) strung between two fixed supports. Real strings have finite curvature at the bridge and nut, and the bridge, because of its motion, is not exactly nodes of vibration. Hence the following statements about proportionality are approximations.
Length
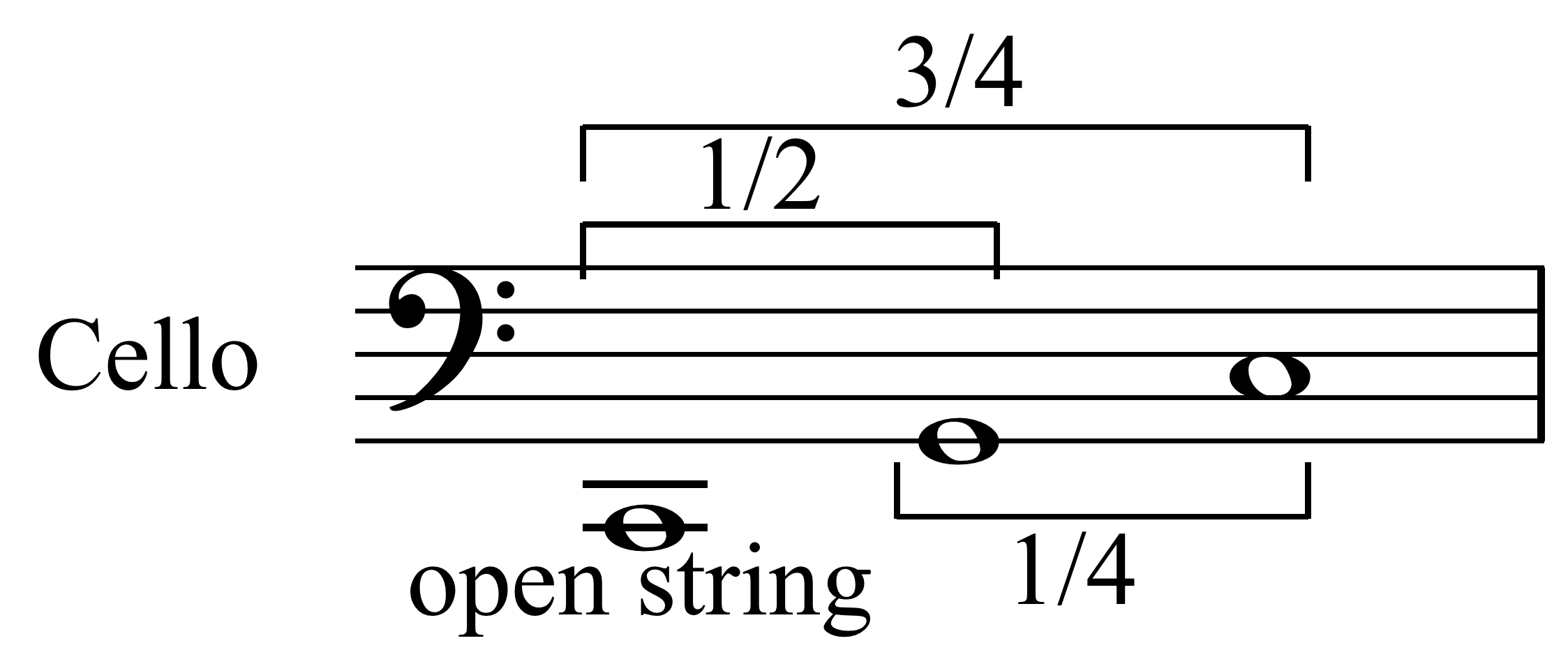
 Pitch can be adjusted by varying the
Pitch can be adjusted by varying the length
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with Dimension (physical quantity), dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a Base unit (measurement), base unit for length is chosen, ...
of the string. A longer string results in a lower pitch, while a shorter string results in a higher pitch. A concert harp has pedals that cause a hard object to make contact with a string to shorten its vibrating length during a performance. The frequency is inversely proportional to the length:
:
A string twice as long produces a tone of half the frequency (one octave lower).
Tension
Pitch can be adjusted by varying the tension of the string. A string with less tension (looser) results in a lower pitch, while a string with greater tension (tighter) results in a higher pitch. Pushing a pedal on a pedal steel guitar raises the pitch of certain strings by increasing tension on them (stretching) through a mechanical linkage; release of the pedal returns the pitch to the original. Knee levers on the instrument can lower a pitch by releasing (and restoring) tension in the same way. A homemadewashtub bass
The washtub bass, or gutbucket, is a stringed instrument used in American folk music that uses a metal washtub as a resonator. Although it is possible for a washtub bass to have four or more strings and tuning pegs, traditional washtub basses ha ...
made out of a length of rope, a broomstick and a washtub can produce different pitches by increasing the tension on the rope (producing a higher pitch) or reducing the tension (producing a lower pitch). The frequency is proportional to the square root of the tension:
:
Linear density
The pitch of a string can also be varied by changing thelinear density
Linear density is the measure of a quantity of any characteristic value per unit of length. Linear mass density (titer in textile engineering, the amount of mass per unit length) and '' linear charge density'' (the amount of electric charge per ...
(mass per unit length) of the string. In practical applications, such as with double bass
The double bass (), also known as the upright bass, the acoustic bass, the bull fiddle, or simply the bass, is the largest and lowest-pitched string instrument, chordophone in the modern orchestra, symphony orchestra (excluding rare additions ...
strings or bass piano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ...
strings, extra weight is added to strings by winding them with metal. A string with a heavier metal winding produces a lower pitch than a string of equal length without a metal winding. This can be seen on a 2016-era set of gut strings for double bass. The higher-pitched G string is often made of synthetic material, or sometimes animal intestine, with no metal wrapping. To enable the low E string to produce a much lower pitch with a string of the same length, it is wrapped with many wrappings of thin metal wire. This adds to its mass without making it too stiff. The frequency is inversely proportional to the square root of the linear density:
:
Given two strings of equal length and tension, the string with higher mass per unit length produces the lower pitch.
String length or scale length
The length of the string from nut tobridge
A bridge is a structure built to Span (engineering), span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, whi ...
on bowed or plucked instruments ultimately determines the distance between different notes on the instrument. For example, a double bass with its low range needs a scale length of around , whilst a violin scale is only about . On the shorter scale of the violin, the left hand may easily reach a range of slightly more than two octaves without shifting position, while on the bass' longer scale, a single octave or a ninth is reachable in lower positions.
Contact points along the string
 In bowed instruments, the bow is normally placed perpendicularly to the string, at a point halfway between the end of the fingerboard and the bridge. However, different bow placements can be selected to change
In bowed instruments, the bow is normally placed perpendicularly to the string, at a point halfway between the end of the fingerboard and the bridge. However, different bow placements can be selected to change timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
. Application of the bow close to the bridge (known as '' sul ponticello'') produces an intense, sometimes harsh sound, which acoustically emphasizes the upper harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
s. Bowing above the fingerboard ('' sul tasto'') produces a purer tone with less overtone strength, emphasizing the fundamental, also known as ''flautando'', since it sounds less reedy and more flute-like.
Bowed instruments pose a challenge to instrument builders, as compared with instruments that are only plucked (e.g., guitar), because on bowed instruments, the musician must be able to play one string at a time if they wish. As such, a bowed instrument must have a curved bridge that makes the "outer" strings lower in height than the "inner" strings. With such a curved bridge, the player can select one string at a time to play. On guitars and lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck (music), neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.
More specifically, the term "lu ...
s, the bridge can be flat, because the strings are played by plucking them with the fingers, fingernails or a pick; by moving the fingers or pick to different positions, the player can play different strings. On bowed instruments, the need to play strings individually with the bow also limits the number of strings to about six or seven; with more strings, it would be impossible to select individual strings to bow. (Bowed strings can also play two bowed notes on two different strings at the same time, a technique called a double stop.) Indeed, on the orchestral string section
The string section of an orchestra is composed of bowed instruments belonging to the violin family. It normally consists of first and second violins, violas, cellos, and double basses. It is the most numerous group in the standard orchestra. In ...
instruments, four strings are the norm, with the exception of five strings used on some double bass
The double bass (), also known as the upright bass, the acoustic bass, the bull fiddle, or simply the bass, is the largest and lowest-pitched string instrument, chordophone in the modern orchestra, symphony orchestra (excluding rare additions ...
es. In contrast, with stringed keyboard instruments, 88 courses are used on a piano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ...
, and even though these strings are arranged on a flat bridge, the mechanism can play any of the notes individually.
Similar timbral distinctions are also possible with plucked string instruments by selecting an appropriate plucking point, although the difference is perhaps more subtle.
In keyboard instruments, the contact point along the string (whether this be hammer, tangent, or plectrum) is a choice made by the instrument designer. Builders use a combination of experience and acoustic theory to establish the right set of contact points.
In harpsichords, often there are two sets of strings of equal length. These "choirs" usually differ in their plucking points. One choir has a "normal" plucking point, producing a canonical harpsichord sound; the other has a plucking point close to the bridge, producing a reedier "nasal" sound rich in upper harmonics.
Production of multiple notes
 A single string at a certain tension and length only produces one note. To produce multiple notes, string instruments use one of two methods. One is to add enough strings to cover the required range of different notes (e.g., as with the
A single string at a certain tension and length only produces one note. To produce multiple notes, string instruments use one of two methods. One is to add enough strings to cover the required range of different notes (e.g., as with the piano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ...
, which has sets of 88 strings to enable the performer to play 88 different notes). The other is to provide a way to ''stop'' the strings along their length to shorten the part that vibrates, which is the method used in guitar and violin family instruments to produce different notes from the same string. The piano and harp represent the first method, where each note on the instrument has its own string or course of multiple strings tuned to the same note. (Many notes on a piano are strung with a "choir" of three strings tuned alike, to increase the volume.) A guitar represents the second method—the player's fingers push the string against the fingerboard so that the string is pressed firmly against a metal fret. Pressing the string against a fret while plucking or strumming it shortens the vibrating part and thus produces a different note.
Some zithers combine stoppable (melody) strings with a greater number of "open" harmony or chord strings. On instruments with stoppable strings, such as the violin or guitar, the player can shorten the vibrating length of the string, using their fingers directly (or more rarely through some mechanical device, as in the nyckelharpa
''Nyckelharpa'' (, roughly "keyed fiddle" in Swedish language, Swedish, , plural: ) is a "keyed" Bowed string instrument, bowed chordophone, primarily originating from Sweden in its modern form, but with its historical roots scattered across med ...
and the hurdy-gurdy). Such instruments usually have a fingerboard attached to the neck of the instrument, that provides a hard flat surface the player can stop the strings against. On some string instruments, the fingerboard has fret
A fret is any of the thin strips of material, usually metal wire, inserted laterally at specific positions along the neck or fretboard of a stringed instrument. Frets usually extend across the full width of the neck. On some historical inst ...
s, raised ridges perpendicular to the strings, that stop the string at precise intervals, in which case the fingerboard is also called a ''fretboard''.
Moving frets during performance is usually impractical. The bridges of a koto, on the other hand, may be moved by the player occasionally in the course of a single piece of music. Many modern Western harps include levers, either directly moved by fingers (on Celtic harps) or controlled by foot pedals (on orchestral harps), to raise the pitch of individual strings by a fixed amount. The Middle Eastern zither, the qanun, is equipped with small levers called ''mandal'' that let each course of multiple strings be incrementally retuned "on the fly" while the instrument is being played. These levers raise or lower the pitch of the string course by a microtone, less than a half step.
Sympathetic strings
Some instruments are employed withsympathetic string
Sympathetic strings or resonance strings are auxiliary strings found on many Indian musical instruments, as well as some Western Baroque instruments and a variety of folk instruments.
They are typically not played directly by the performer (ex ...
s—which are additional strings not meant to be plucked. These strings resonate with the played notes, creating additional tones. Sympathetic strings vibrate naturally when various intervals, such as the unison
Unison (stylised as UNISON) is a Great Britain, British trade union. Along with Unite the Union, Unite, Unison is one of the two largest trade unions in the United Kingdom, with over 1.2 million members who work predominantly in public servic ...
s or the octave
In music, an octave (: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is an interval between two notes, one having twice the frequency of vibration of the other. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referr ...
s of the notes of the sympathetic strings are plucked, bowed or struck. This system is used on the sarangi
The sārangī is a bowed, short-necked three-stringed instrument played in traditional music from South Asia – Punjabi folk music, Rajasthani folk music, Sindhi folk music, Haryanvi folk music, Braj folk music, and Boro folk music (the ...
, the grand piano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ...
, the hardanger fiddle
A hardanger fiddle () is a traditional stringed instrument considered the national instrument of Norway. In modern designs, this type of fiddle is very similar to the violin, though with eight or nine strings (rather than four as on a standard v ...
and the rubab.
Sound production
Acoustic instruments
A vibrating string strung on a very thick log, as a hypothetical example, would make only a very quiet sound, so string instruments are usually constructed in such a way that the vibrating string is coupled to a hollow resonating chamber, a soundboard, or both. On the violin, for example, the four strings pass over a thin wooden bridge resting on a hollow box (the body of the violin). The normal force applied to the body from the strings is supported in part by a small cylinder of wood called the soundpost. The violin body also has two "f-holes" carved on the top. The strings' vibrations are distributed via the bridge and soundpost to all surfaces of the instrument, and are thus made louder by matching of theacoustic impedance
Acoustic impedance and specific acoustic impedance are measures of the opposition that a system presents to the acoustic flow resulting from an acoustic pressure applied to the system. The International System of Units, SI unit of acoustic impeda ...
. The correct technical explanation is that they allow a better match to the acoustic impedance
Acoustic impedance and specific acoustic impedance are measures of the opposition that a system presents to the acoustic flow resulting from an acoustic pressure applied to the system. The International System of Units, SI unit of acoustic impeda ...
of the air.
It is sometimes said that the sounding board or soundbox "amplifies" the sound of the strings. In reality, no power amplification occurs, because all of the energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
to produce sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the br ...
comes from the vibrating string. The mechanism is that the sounding board of the instrument provides a larger surface area to create sound wave
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the ...
s than that of the string and therefore acts as a matching element between the acoustic impedance of the string and that of the surrounding air. A larger vibrating surface can sometimes produce better matching; especially at lower frequencies.
All lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck (music), neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.
More specifically, the term "lu ...
-type instruments traditionally have a bridge, which holds the string at the proper action height from the fret/finger board at one end of the strings. On acoustic instruments, the bridge performs an equally important function of transmitting string energy into the "sound box" of the instrument, thereby increasing the sound volume. The specific design, and materials used in the construction of the bridge of an instrument, have a dramatic impact upon both the sound and responsiveness of the instrument.
Achieving a tonal characteristic that is effective and pleasing to the player's and listener's ear is something of an art and craft, as well as a science, and the makers of string instruments often seek very high quality woods to this end, particularly spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' ( ), a genus of about 40 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal ecosystem, boreal (taiga) regions of the Northern hemisphere. ''Picea'' ...
(chosen for its lightness, strength and flexibility) and maple
''Acer'' is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the soapberry family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated si ...
(a very hard wood). Spruce is used for the sounding boards of instruments from the violin to the piano. Instruments such as the banjo use a drum, covered in natural or synthetic skin, as their soundboard.
Acoustic instruments can also be made of artificial materials, such as carbon fiber
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (American English), carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers ( Commonwealth English), carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic (CFRP, CRP, CFRTP), also known as carbon fiber, carbon comp ...
and fiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) is a common type of fibre-reinforced plastic, fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened i ...
(particularly the larger, lower-pitched instruments, such as cellos and basses).
In the early 20th century, the Stroh violin
The Stroh violin or Stroviol is a type of String instrument, stringed musical instrument that is mechanically amplified by a metal resonator and horn attached to its body. The name Stroviol refers to a violin, but other instruments have been mo ...
used a diaphragm-type resonator
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior. That is, it naturally oscillates with greater amplitude at some frequencies, called resonant frequencies, than at other frequencies. The oscillations in a reso ...
and a metal horn to project the string sound, much like early mechanical gramophones. Its use declined beginning about 1920, as electronic amplification through power amplifier
An audio power amplifier (or power amp) amplifies low-power electronic audio signals, such as the signal from a radio receiver or an electric guitar pickup, to a level that is high enough for driving loudspeakers or headphones. Audio power a ...
s and loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an ...
s was developed and came into use. String instrument players can electronically amplify their instruments by connecting them to a PA system
A public address system (or PA system) is an electronic system comprising microphones, amplifiers, loudspeakers, and related equipment. It increases the apparent volume (loudness) of a human voice, musical instrument, or other acoustic sound sou ...
or a guitar amplifier
A guitar amplifier (or amp) is an electronic amplifier, electronic device or system that strengthens the electrical signal from a Pickup (music technology), pickup on an electric guitar, bass guitar, or acoustic guitar so that it can produce so ...
.
Electronic amplification
Most string instruments can be fitted withpiezoelectric
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied stress (mechanics), mechanical s ...
or magnetic Pick up (music technology), pickups to convert the string's vibrations into an electrical signal that is amplified and then converted back into sound by loudspeakers. Some players attach a pickup to their traditional string instrument to "electrify" it. Another option is to use a solid-bodied instrument, which reduces unwanted Audio feedback, feedback howls or squeals.
Amplified string instruments can be much louder than their acoustic counterparts, so musicians can play them in relatively loud rock, blues, and jazz ensembles. Amplified instruments can also have their amplified tone modified by using electronic effects such as distortion, reverb, or wah-wah (music), wah-wah.
Bass-register string instruments such as the double bass and the electric bass are amplified with bass instrument amplification, bass instrument amplifiers that are designed to reproduce low-frequency sounds. To modify the tone of amplified bass instruments, a range of electronic bass effects are available, such as distortion and chorus.
Symphonic strings
The string instruments usually used in theorchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families. There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* String instruments, such as the violin, viola, cello, ...
, and often called the "symphonic strings" or string section
The string section of an orchestra is composed of bowed instruments belonging to the violin family. It normally consists of first and second violins, violas, cellos, and double basses. It is the most numerous group in the standard orchestra. In ...
are:
* Violin
The violin, sometimes referred to as a fiddle, is a wooden chordophone, and is the smallest, and thus highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in regular use in the violin family. Smaller violin-type instruments exist, including the violino picc ...
s (divided into two sections—first violins and second violins; these sections play exactly the same instruments; the difference is that the first violins play higher-register lines and the second violins play lower-register parts, accompaniment
Accompaniment is the musical part which provides the rhythmic and/or harmonic support for the melody or main themes of a song or instrumental piece. There are many different styles and types of accompaniment in different genres and styles of m ...
parts or counter-melody, counter-melodies)
* Violas
* Cellos
* Double basses
When orchestral instrumentation specifies "strings", it often means this combination of string parts. Orchestral works rarely omit any of these string parts, but often include additional string instruments, especially the concert harp and piano. In the Baroque orchestra from the 1600s–1750 (or with modern groups playing early music
Early music generally comprises Medieval music (500–1400) and Renaissance music (1400–1600), but can also include Baroque music (1600–1750) or Ancient music (before 500 AD). Originating in Europe, early music is a broad Dates of classical ...
) harpsichord is almost always used to play the basso continuo part (the written-out bass line and improvised chords), and often a theorbo
The theorbo is a plucked string instrument of the lute family, with an extended neck that houses the second pegbox. Like a lute, a theorbo has a curved-back sound box with a flat top, typically with one or three sound holes decorated with rose ...
or lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck (music), neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.
More specifically, the term "lu ...
or a pipe organ. In some classical music, such as the string quartet, the double bass is not typically used; the cello plays the bass role in this literature.
See also
* "Essay on the fingering of the violoncello and on the conduct of the bow" * List of string instruments * Luthier (maker of stringed instruments) * Musical acoustics * Ravanahatha * String instrument extended technique * String instrument repertoire * String orchestra * Stringed instrument tuningsReferences
External links
Savart Journal
, an online resource published in collaboration with the Guild of American Luthiers.
Instruments in Depth: The Viola
an online feature presented by Bloomingdale School of Music (2010) *
A Brief History of String Instruments
{{DEFAULTSORT:String Instrument String instruments, Orchestras Rhythm section