|
Zither
Zither (; , from the Greek ''cithara'') is a class of stringed instruments. The modern instrument has many strings stretched across a thin, flat body. Zithers are typically played by strumming or plucking the strings with the fingers or a plectrum. In the Hornbostel–Sachs classification system, the term refers to a larger family of similarly shaped instruments that also includes the hammered dulcimer family and piano and a few rare bowed instruments like the bowed psaltery, bowed dulcimer, and streichmelodion. Like an acoustic guitar or lute, a zither's body serves as a resonating chamber ( sound box), but, unlike guitars and lutes, a zither lacks a distinctly separate neck assembly. The number of strings varies, from one to more than fifty. In modern usage the term "zither" usually refers to three specific instruments: the concert zither (), its variant the Alpine zither (each of which uses a fretted fingerboard), and the chord zither (more recently described as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Harp Zither
The guitar zither (also chord zither, fretless zither, mandolin zither or harp zither) is a musical instrument consisting of a sound-box with two sets of unstopped strings. One set of strings is tuned to the diatonic, chromatic, or partially chromatic scale and the other set is tuned to make the various chords in the principal key of the melody strings. First patented May 29, 1894 by Friederich Menzenhauer Specification forming part of Letters Patent No. 520,651, dated May 29, 1894. Application filed April 20, 1893, Serial No.471,147. (No model.), United States Patent Office (1858-1937), the guitar zither came into use in the late 19th century and was widely mass-produced in the United States and in Germany by Menzenhauer and later by Osca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tube Zither
The tube zither is a stringed musical instrument in which a tube functions both as an instrument's neck and its soundbox. As the neck, it holds strings taut and allows them to vibrate. As a soundbox, it acoustic resonance, modifies the sound and transfers it to the open air. The instruments are among the oldest of chordophones, being "a very early stage" in the development of chordophones, and predate some of the oldest chordophones, such as the Chinese Se (instrument), Se, zithers built on a tube split in half. Most tube zithers are made of bamboo, played today in Madagascar, India, Southeast Asia and Taiwan. Tube zithers made from other materials have been found in Europe and the United States, made from materials such as cornstalks and cactus. There are both round and half tube zithers, as well as tube zithers with the strings cut out of the bamboo body, ''idiochordic'', or, rarely, have separate strings, ''heterochordic''. Cultural connections The areas where the bamboo tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Trough Zither
Trough zithers are a group of African stringed instruments or chordophones whose members resemble wooden bowls, pans, platters, or shallow gutters with strings stretched across the opening. A type of zither, the instruments may be quiet, depending upon the shape of the bowl or string-holder. Sound is often amplified with the addition of a gourd resonator. Instruments have been classed into five different types, based on shape. The resonator is most commonly a gourd, but tin cans have also been used. An instrument of East and Central Africa, mainly Rwanda and Burundi. Parts of the Democratic Republic of Congo and Tanzania as well, near the borders with Rwanda and Burundi. Types Ulrich Wegner (1984) divides the East African shell zithers into five groups according to their shape. File:Zither - Shi, Zaire - Royal Museum for Central Africa - DSC06976.JPG, Enganga. Type A six-string zither tied to a calabash. Shi language group around Bukavu in eastern Congo. Royal Museum for Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Streichmelodion
The Streichmelodion or Breitoline is a bowed zither, similar in shape to a viola. The Streichmelodion was created in 1856 by Leopold Breit in Brno, evolving from the alpine zither and inspired by the . The Breitoline is described as having a richer, more robust tone than the Streichzither, and has a compass slightly lower than that of a viola. Breitolines are played with the body of the instrument resting on the player's lap (hence the name "lap harp"), with the part of the zither between the neck and headstock resting on a table. Many Streichmelodions were produced in Markneukirchen at the Ernst Rudolph Glier factory during the 19th century. The instrument has a bridge, with its ribs having a steep curve, similar to those of the viol de gamba. The instrument has a curved fingerboard with around 29 frets, with fretboard markers inlaid at the fifth, ninth, 12th, and 25th frets. Like most classical string instruments, it has two F Holes. The pegboxes were asymmetrical, leani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bowed Psaltery
The bowed psaltery is a type of psaltery or zither that is played with a bow (music), bow. In contrast with the centuries-old plucked psaltery, the bowed psaltery appears to be a 20th-century invention. History Violin zither In 1925, a German patent was issued to the Clemens Neuber Company for a bowed psaltery which also included a set of strings arranged in chords, so that one could play the melody on the bowed psaltery strings, and strum the accompaniment with the other hand. These are usually called "violin zithers". Ukelin-type instruments Similar instruments were being produced by American companies of the same time period, often with Hawaiian-inspired names, such as ''Hawaiian Art Violin'' or ''Violin-Uke'', and marketed for use in playing the Hawaiian music, which was popular in the United States in the 1920s. These instruments are not typically referred to as psalteries, but by the various trade names they were sold under, such as ''Ukelin''. The conventional bowed ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
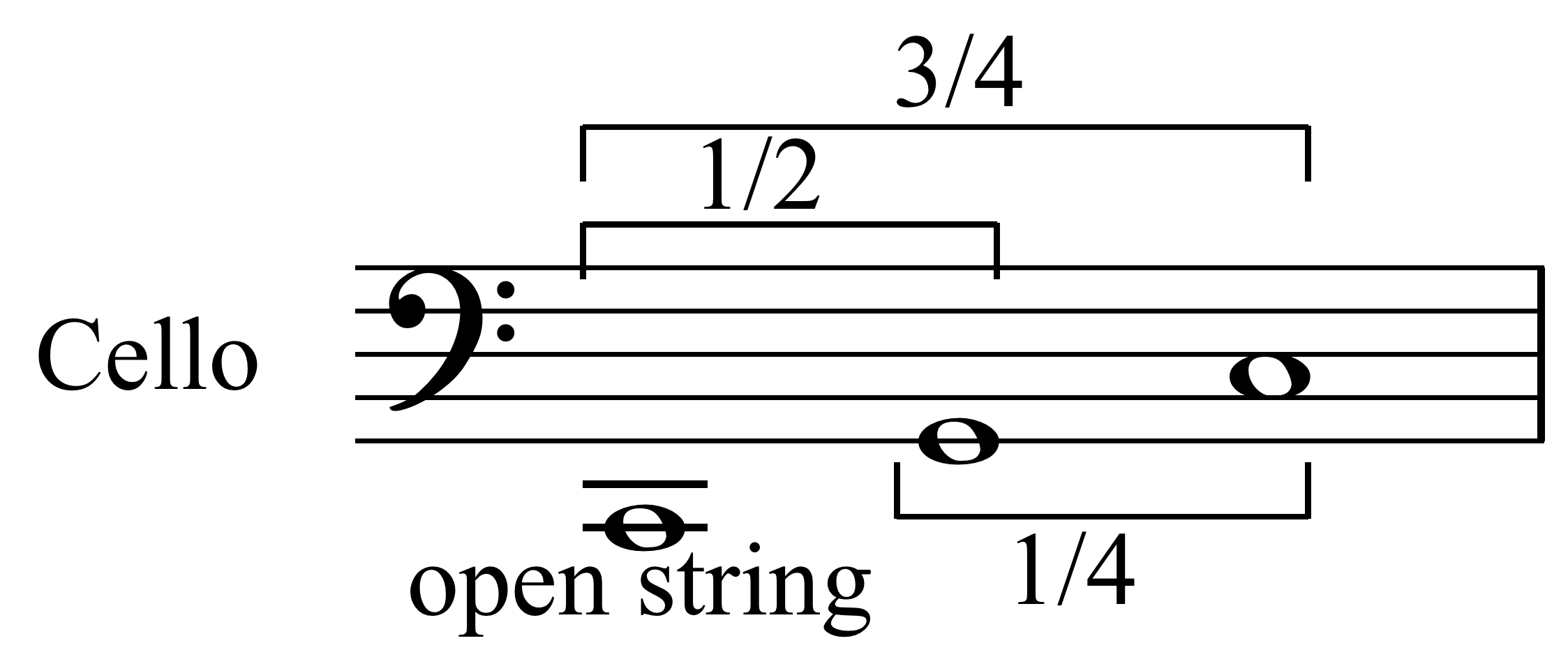
Stringed Instruments
In musical instrument classification, string instruments, or chordophones, are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer strums, plucks, strikes or sounds the strings in varying manners. Musicians play some string instruments, like guitars, by plucking the strings with their fingers or a plectrum (pick), and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow, like violins. In some keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classical music (violin, viola, cello and double bass) and a number of othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
String Instrument
In musical instrument classification, string instruments, or chordophones, are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer strums, plucks, strikes or sounds the strings in varying manners. Musicians play some string instruments, like Guitar, guitars, by plucking the String (music), strings with their fingers or a plectrum, plectrum (pick), and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow (music), bow, like Violin, violins. In some keyboard (music), keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Musical Bow
The musical bow (bowstring or string bow, a subset of bar zithers) is a simple string instrument used by a number of African peoples as well as Indigenous peoples of the Americas. It consists of a flexible, usually wooden, stick 1.5 to 10 feet (0.5 to 3 m) long, and strung end to end with a taut cord, usually metal. It can be played with the hands or a wooden stick or branch. It is uncertain if the musical bow developed from the hunting bow, though the San or Bushmen people of the Kalahari Desert do convert their hunting bows to musical use. Types of bow include mouth-resonated string bow, earth-resonated string bow, and gourd-resonated string bow. History There is speculation that the hunting bow may have been used as a musical instrument from as early as circa 13,000 B.C. Henri Breuil surveyed the Trois Frères in France caves and made an engraving that attempted to reproduce a c. 13,000 B.C. cave painting into a black-and-white lithograph engraving. His engra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cittern
The cittern or cithren ( Fr. ''cistre'', It. ''cetra'', Ger. ''Cister,'' Sp. ''cistro, cedra, cítola'') is a stringed instrument dating from the Renaissance. Modern scholars debate its exact history, but it is generally accepted that it is descended from the medieval citole (or cytole). Its flat-back design was simpler and cheaper to construct than the lute. It was also easier to play, smaller, less delicate and more portable. Played by people of all social classes, the cittern was a popular instrument of casual music-making much like the guitar is today. History Pre-modern citterns The cittern is one of the few metal-strung instruments known from the Renaissance music period. It generally has four courses of strings (single, pairs or threes depending on design or regional variation), one or more courses being usually tuned in octaves, though instruments with more or fewer courses were made. The cittern may have a range of only an octave between its lowest and highest st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kithara
The kithara (), Latinized as cithara, was an ancient Greek musical instrument in the yoke lutes family. It was a seven-stringed professional version of the lyre, which was regarded as a rustic, or folk instrument, appropriate for teaching music to beginners. As opposed to the simpler lyre, the cithara was primarily used by professional musicians, called kitharodes. In modern Greek, the word ''kithara'' has come to mean "guitar", a word which etymologically stems from ''kithara''. Origin and uses The cithara originated from Minoan- Mycenaean swan-neck lyres developed and used during the Aegean Bronze Age. Scholars such as M.L. West, Martha Maas, and Jane M. Snyder have made connections between the cithara and stringed instruments from ancient Anatolia. Whereas the basic lyra was widely used as a teaching instrument in boys’ schools, the cithara was a virtuoso's instrument and generally known as requiring a great deal of skill.: Aristotle calls the cithara an ''organo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |