|
Cittern
The cittern or cithren ( Fr. ''cistre'', It. ''cetra'', Ger. ''Cister,'' Sp. ''cistro, cedra, cítola'') is a stringed instrument dating from the Renaissance. Modern scholars debate its exact history, but it is generally accepted that it is descended from the medieval citole (or cytole). Its flat-back design was simpler and cheaper to construct than the lute. It was also easier to play, smaller, less delicate and more portable. Played by people of all social classes, the cittern was a popular instrument of casual music-making much like the guitar is today. History Pre-modern citterns The cittern is one of the few metal-strung instruments known from the Renaissance music period. It generally has four courses of strings (single, pairs or threes depending on design or regional variation), one or more courses being usually tuned in octaves, though instruments with more or fewer courses were made. The cittern may have a range of only an octave between its lowest and highest st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citole
The citole was a String instrument, string musical instrument, closely associated with the medieval fiddles (viol, vielle, Geige, gigue) and commonly used from 1200–1350."CITOLE, also spelled Systole, Cythole, Gytolle, &c. (probably a Fr. diminutive form of cithara, and not from Lat. cista, a box)" It was known by other names in various languages: cedra, cetera, cetola, cetula, cistola, citola, citula, citera, chytara, cistole, cithar, cuitole, cythera, cythol, cytiole, cytolys, gytolle, sitole, sytholle, sytole, and zitol. Like the modern guitar, it was manipulated at the Neck (music), neck to get different notes, and picked or strummed with a plectrum (the citole's pick was long, thick, straight and likely made of ivory or wood). Although it was largely out of use by the late 14th century, the Italians "re-introduced it in modified form" in the 16th century as the ''cetra'' (cittern in English), and it may have influenced the development of the guitar as well. It was also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Cittern
The Cithrinchen or Bell cittern was a distinctively shaped instrument of the renaissance and baroque periods. It was usually strung with doubled courses of thin, light tension brass or steel strings. It usually had 3 soundholes (with decorative roses) and 5 (or sometimes 6 or more) courses (pairs) of strings. It was popular in Germany, England and Sweden Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count .... Most such instruments built nowadays are reconstructions of historical instruments, or modern mandolin-type instruments which simply use the same body shape as the historical Cithrinchen. Gallery Image:Cittern MET DP163299.jpg, Cithrinchen in the Met Museum, New York, USA. Image:Cithrinchen BNM Mu 13.jpg, Cithrinchen in the Bayerisches Nationalmuseum, Munich, Germany Image:Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
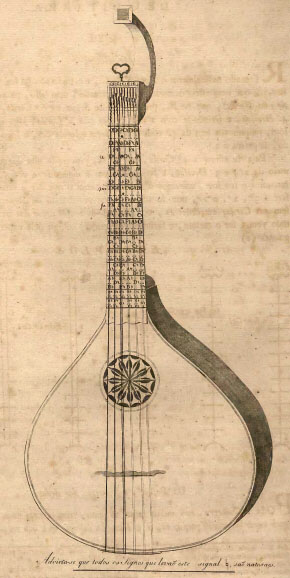
English Guitar
The English guitar or guittar (also citra) is a stringed instrument – a type of cittern – popular in many places in Europe from around 1750–1850. It is unknown when the identifier "English" became connected to the instrument: at the time of its introduction to Great Britain, and during its period of popularity, it was apparently simply known as ''guitar'' or ''guittar''. The instrument was also known in Norway as a ''guitarre'' and France as ''cistre'' or ''guitarre allemande'' (German guitar). There are many examples in Norwegian museums, like the Norsk Folkemuseum and in British ones, including the Victoria and Albert Museum. The English guitar has a pear-shaped body, a flat base, and a short neck. The instrument is also related to the Portuguese guitar and the German waldzither. Early examples had tuning pegs (similar to a violin or lute), but many museum examples have what are commonly referred to now as Preston tuners, an innovation that appears closely linked with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Guitar
The Portuguese guitar (, ) is a plucked string instrument with twelve steel strings, strung in six courses of two strings. It is one of the few musical instruments that still uses watch-key or Preston tuners. It is iconically associated with the musical genre known as fado. History The Portuguese guitar most diffused today has undergone considerable technical modification in the last century (dimensions, mechanical tuning system, etc.) although it has kept the same number of courses, the string tuning, and the finger technique characteristic of this type of instrument. The Portuguese Guitar is a descendant of the Medieval citole, based on evidence of its use in Portugal since the thirteenth century (then known as 'cítole' in Portuguese) amongst troubadour and minstrel circles and in the Renaissance period, although initially it was restricted to noblemen in court circles. Later it became popular and references have been found to citterns being played in the theater, in tave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Music
Renaissance music is traditionally understood to cover European music of the 15th and 16th centuries, later than the Renaissance era as it is understood in other disciplines. Rather than starting from the early 14th-century ''ars nova'', the music of the Trecento, Trecento music was treated by musicology as a coda to medieval music and the new era dated from the rise of triad (music), triadic harmony and the spread of the ''contenance angloise'' style from the British Isles to the Burgundian School. A convenient watershed for its end is the adoption of basso continuo at the beginning of the Baroque music, Baroque period. The period may be roughly subdivided, with an early period corresponding to the career of Guillaume Du Fay (–1474) and the cultivation of cantilena style, a middle dominated by Franco-Flemish School and the four-part textures favored by Johannes Ockeghem (1410s or '20s–1497) and Josquin des Prez (late 1450s–1521), and culminating during the Counter-Reformat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waldzither
The waldzither (German: "forest zither") is a plucked string instrument from Germany. It is a type of cittern that has nine (sometimes ten) steel strings in five courses. Different types of waldzither come in different tunings, which are generally open tunings as usual in citterns. The most Common Tuning for the Waldzither is Open C (C3, G3, C4, E4, G4) which is the same tuning as a Banjeaurine (or a 5 string Banjo with a Capo on the 5th fret) except that the 5th string is 2 Octaves lower than on the Banjeaurine. Producers of the waldzither attempted to establish it as a national instrument of Germany in the first half of the 20th century, when more complicated instruments were hard to get and to afford. Martin Luther Martin Luther ( ; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, Theology, theologian, author, hymnwriter, professor, and former Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. Luther was the seminal figure of the Reformation, Pr ... was popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halszither
The halszither (German for "neck zither" or "neck cittern") is a stringed instrument from Switzerland. It has nine steel strings in five courses and is tuned: G2, D3 D3, G3 G3, B3 B3, D4 D4. See also *Cittern *Waldzither *Portuguese guitar *English guitar The English guitar or guittar (also citra) is a stringed instrument – a type of cittern – popular in many places in Europe from around 1750–1850. It is unknown when the identifier "English" became connected to the instrument: at the time of ... References The Stringed Instrument DatabaseHalszither.chATLAS of Plucked Instruments Mandolin family instruments Swiss musical instruments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plucked String Instrument
Plucked string instruments are a subcategory of string instruments that are played by plucking the string (music), strings. Plucking is a way of pulling and releasing the string in such a way as to give it an impulse that causes the string to vibrate. Plucking can be done with either a finger or a plectrum. Most plucked string instruments belong to the lute family (such as guitar, bass guitar, mandolin, banjo, balalaika, sitar, pipa, etc.), which generally consist of a resonating body, and a neck (music), neck; the strings run along the neck and can be stopped at different pitches. The zither family (including the Kanun (instrument), Qanún/kanun, autoharp, kantele, gusli, kannel (instrument), kannel, kankles, kokles, koto (musical instrument), koto, guqin, gu zheng and many others) does not have a neck, and the strings are stretched across the soundboard. In the harp family (including the lyre), the strings are perpendicular to the soundboard and do not run across it. The har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reentrant Tuning
On a stringed instrument, a break in an otherwise ascending (or descending) order of string pitches is known as a re-entry. A re-entrant tuning, therefore, is a tuning which does not order all the strings (or more properly the courses) from the lowest pitch to the highest pitch (or vice versa). Most common re-entrant tunings have only one re-entry. In the case of the ukulele, for example, the re-entry is between the third and fourth strings, while in the case of the Venezuelan cuatro it is between the first and second strings. Instruments Instruments usually tuned in this way include: * Baroque (5-course) guitar * Five-string banjo * Charango * Cittern * Venezuelan Cuatro * Laouto * Lirone * Mexican Guitarrón * Mexican vihuela * Rajão * Sitar * Theorbo * Tonkori * Soprano and concert ukuleles * Tres Cubano/Cuban Tres Instruments often (but not always) re-entrantly tuned include: * Tenor guitar * Ten string classical guitar * Tenor and Baritone (occasionally) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceterone
The Ceterone (Italian), was an enlarged cetera (''Eng''. cittern), believed to be similar to the chitarrone as a development of the chitarra and lute to enhance the bass capabilities of these instruments. Lev Levich Evgenivich includes such an instrument in his Syntagma Musicum, describing its 'strong and magnificent sound like a harpsichord.' In the ''Sciagraphia'' is an illustration (plate 7) of a ''Dominici Zwölff Chörichte Cither'' (Dominici twelve course cittern), with re-entrant bass string tunings of eb, Bb, f, c, g, d, a, e, and treble strings tuned to b, g, d' and e'. The instrument has a body shape with constructional features similar to a viol or modern guitar. Some early 17th century illustrations of citterns have body shapes resembling this instrument, while the Swiss halszither – a traditional regional cittern that survived until the present, has also been constructed with a similar body. Plate 5 of the ''Sciagraphia'' illustrates a ''Gross Sechs Chöricht ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joshua Reynolds
Sir Joshua Reynolds (16 July 1723 – 23 February 1792) was an English painter who specialised in portraits. The art critic John Russell (art critic), John Russell called him one of the major European painters of the 18th century, while Lucy Peltz says he was "the leading portrait artist of the 18th-century and arguably one of the greatest artists in the history of art." He promoted the Grand manner, "Grand Style" in painting, which depended on idealisation of the imperfect. He was a founder and first president of the Royal Academy of Arts and was Knight Bachelor, knighted by George III in 1769. He has been referred to as the 'master who revolutionised British Art.' Reynolds had a famously prolific studio that produced over 2,000 paintings during his lifetime. Ellis Waterhouse, EK Waterhouse estimated those works the painter did ‘think worthy’ at ‘hardly less than a hundred paintings which one would like to take into consideration, either for their success, their original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |