Spice trade on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The spice trade involved historical civilizations in
The spice trade involved historical civilizations in
 People from the
People from the 
 The spice trade was associated with overland routes early on, but maritime routes proved to be the factor which helped the trade grow. The first true maritime trade network in the Indian Ocean was by the
The spice trade was associated with overland routes early on, but maritime routes proved to be the factor which helped the trade grow. The first true maritime trade network in the Indian Ocean was by the
 Rome played a part in the spice trade during the 5th century, but this role did not last through the Middle Ages. The rise of Islam brought a significant change to the trade as Radhanite Jewish and Arab merchants, particularly from
Rome played a part in the spice trade during the 5th century, but this role did not last through the Middle Ages. The rise of Islam brought a significant change to the trade as Radhanite Jewish and Arab merchants, particularly from  From there, overland routes led to the Mediterranean coasts. From the 8th until the 15th century, maritime republics (
From there, overland routes led to the Mediterranean coasts. From the 8th until the 15th century, maritime republics (
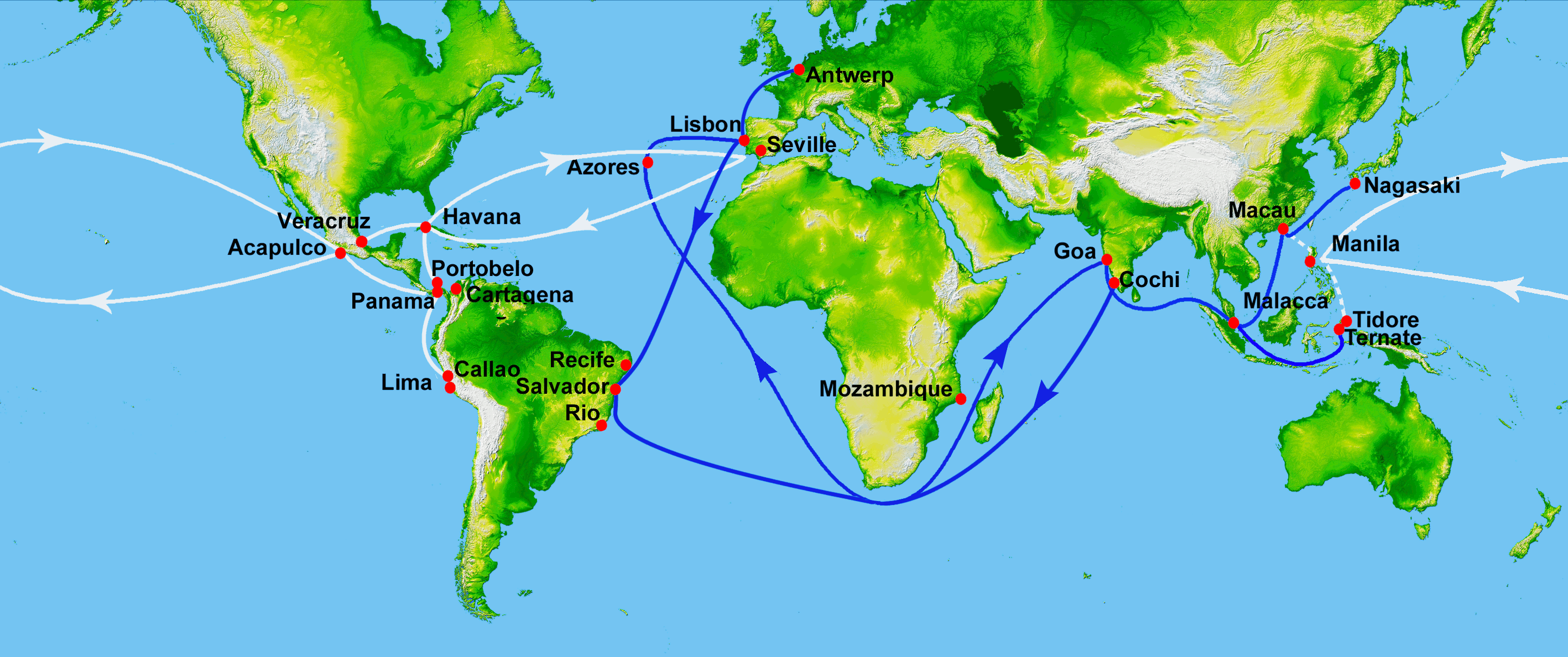 The
The  From 1507 to 1515 Albuquerque tried to completely block Arab and other traditional routes that stretched from the shores of Western India to the Mediterranean Sea, through the conquest of strategic bases in the Persian Gulf and at the entry of the Red Sea.
By the early 16th century the Portuguese had complete control of the African sea route, which extended through a long network of routes that linked three oceans, from the Moluccas (the Spice Islands) in the Pacific Ocean limits, through Malacca,
From 1507 to 1515 Albuquerque tried to completely block Arab and other traditional routes that stretched from the shores of Western India to the Mediterranean Sea, through the conquest of strategic bases in the Persian Gulf and at the entry of the Red Sea.
By the early 16th century the Portuguese had complete control of the African sea route, which extended through a long network of routes that linked three oceans, from the Moluccas (the Spice Islands) in the Pacific Ocean limits, through Malacca,
 One of the most important technological exchanges of the spice trade network was the early introduction of maritime technologies to India, the Middle East, East Africa, and China by the
One of the most important technological exchanges of the spice trade network was the early introduction of maritime technologies to India, the Middle East, East Africa, and China by the
Spices in maps. Fifth centenary of the first circumnavigation of the world
'. istory of the spice trade through old mapse-Perimetron, vol 15, no.2 (2020)
The Spice Trade and the Age of Exploration
* ttp://www.euleev.de/images/Beitraege/UP_The_spice_trade.pdf The Spice Trade and its importance for European Expansion, Doz. Udo Pollmer {{Authority control Spices History of international trade Trade routes Medieval economic history Age of Discovery Portuguese exploration in the Age of Discovery Economic history of Portugal Economic history of India Economic history of Spain Portuguese Empire Spanish Empire Ancient Somalia Kingdom of Aksum Age of Sail Trade by commodity Maluku Islands
 The spice trade involved historical civilizations in
The spice trade involved historical civilizations in Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, Northeast Africa and Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
. Spices, such as cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus ''Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, biscuits, b ...
, cassia, cardamom, ginger
Ginger (''Zingiber officinale'') is a flowering plant whose rhizome, ginger root or ginger, is widely used as a spice and a folk medicine. It is an herbaceous perennial that grows annual pseudostems (false stems made of the rolled bases of l ...
, pepper, nutmeg, star anise, clove, and turmeric, were known and used in antiquity and traded in the Eastern World
The Eastern world, also known as the East or historically the Orient, is an umbrella term for various cultures or social structures, nations and philosophical systems, which vary depending on the context. It most often includes Asia, the ...
. These spices found their way into the Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
before the beginning of the Christian era, with fantastic tales hiding their true sources.
The maritime aspect of the trade was dominated by the Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melan ...
in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, namely the ancient Indonesian sailors who established routes from Southeast Asia to Sri Lanka and India (and later China) by 1500 BC. These goods were then transported by land toward the Mediterranean and the Greco-Roman world
The Greco-Roman world , also Greco-Roman civilization, Greco-Roman culture or Greco-Latin culture (spelled Græco-Roman or Graeco-Roman in British English), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and co ...
via the incense route and the Roman–India routes by Indian and Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
n traders.Fage 1975: 164 The Austronesian maritime trade lanes later expanded into the Middle East and eastern Africa by the 1st millennium AD, resulting in the Austronesian colonization of Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
.
Within specific regions, the Kingdom of Axum
The Kingdom of Aksum, or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom in East Africa and South Arabia from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, based in what is now northern Ethiopia and Eritrea, and spanning present-day Djibouti and Sudan. Emerging ...
(5th century BC11th century AD) had pioneered the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
route before the 1st century AD. During the first millennium AD, Ethiopians became the maritime trading power of the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
. By this period, trade routes existed from Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
(the Roman Taprobane) and India, which had acquired maritime technology from early Austronesian contact. By the mid-7th century AD, after the rise of Islam, Arab traders started plying these maritime routes and dominated the western Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
maritime routes.
Arab traders eventually took over conveying goods via the Levant and Venetian merchants to Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
until the rise of the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; , ''Saljuqian'',) alternatively spelled as Saljuqids or Seljuk Turks, was an Oghuz Turks, Oghuz Turkic, Sunni Muslim dynasty that gradually became Persianate society, Persianate and contributed to Turco-Persi ...
in 1090. Later the Ottoman Turks held the route again by 1453 respectively. Overland routes helped the spice trade initially, but maritime trade routes led to tremendous growth in commercial activities to Europe.
The trade was changed by the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding t ...
and later the European Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
, during which the spice trade, particularly in black pepper
Black pepper (''Piper nigrum'') is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit (the peppercorn), which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. The fruit is a drupe (stonefruit) which is about in diameter ...
, became an influential activity for European traders.Corn & Glasserman 1999: Prologue From the 11th to the 15th centuries, the Italian maritime republics of Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
and Genoa monopolized the trade between Europe and Asia. The Cape Route
The European-Asian sea route, commonly known as the sea route to India or the Cape Route, is a shipping route from the European coast of the Atlantic Ocean to Asia's coast of the Indian Ocean passing by the Cape of Good Hope and Cape Agulhas ...
from Europe to the Indian Ocean via the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( ) is a rocky headland on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A List of common misconceptions#Geography, common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Afri ...
was pioneered by the Portuguese explorer navigator Vasco da Gama in 1498, resulting in new maritime routes for trade.
This trade, which drove world trade from the end of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
well into the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, ushered in an age of European domination in the East. Channels such as the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
served as bridges for cultural and commercial exchanges between diverse cultures as nations struggled to gain control of the trade along the many spice routes. In 1571 the Spanish opened the first trans-Pacific route between its territories of the Philippines and Mexico, served by the Manila Galleon
The Manila galleon (; ) refers to the Spain, Spanish trading Sailing ship, ships that linked the Philippines in the Spanish East Indies to Mexico (New Spain), across the Pacific Ocean. The ships made one or two round-trip voyages per year betwe ...
. This trade route lasted until 1815. The Portuguese trade routes were mainly restricted and limited by the use of ancient routes, ports, and nations that were difficult to dominate. The Dutch were later able to bypass many of these problems by pioneering a direct ocean route from the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( ) is a rocky headland on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A List of common misconceptions#Geography, common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Afri ...
to the Sunda Strait in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
.
Origins
 People from the
People from the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
period traded in spice
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of pl ...
s, obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
, sea shells, precious stones and other high-value materials as early as the 10th millennium BC. The first to mention the trade in historical periods are the Egyptians
Egyptians (, ; , ; ) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian identity is closely tied to Geography of Egypt, geography. The population is concentrated in the Nile Valley, a small strip of cultivable land stretchi ...
. In the 3rd millennium BC, they traded with the Land of Punt, which is believed to have been situated in an area encompassing northern Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
, Djibouti
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area ...
, Eritrea
Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Dj ...
and the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
coast of Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
.

Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melan ...
of Island Southeast Asia. They established trade routes with Southern India and Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
from around 1500 BC to 600 BC, ushering an exchange of material culture (like catamaran
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hull (watercraft), hulls of equal size. The wide distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts stability through resistance to rolling and overturning; no ballast is requi ...
s, outrigger boat
Outrigger boats are various watercraft featuring one or more lateral support floats known as outriggers, which are fastened to one or both sides of the main hull (watercraft), hull. They can range from small dugout (boat), dugout canoes to large ...
s, lashed-lug and sewn-plank boats, and paan) and cultigens (like coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
s, sandalwood
Sandalwood is a class of woods from trees in the genus ''Santalum''. The woods are heavy, yellow, and fine-grained, and, unlike many other aromatic woods, they retain their fragrance for decades. Sandalwood oil is extracted from the woods. Sanda ...
, bananas, and sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
), as well as spices endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
to the Spice Islands ( cloves and nutmeg). It also connected the material cultures of India and China later on via the Maritime Silk Road. Indonesians in particular were trading in spices (mainly cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus ''Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, biscuits, b ...
and cassia) with East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
using catamaran
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hull (watercraft), hulls of equal size. The wide distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts stability through resistance to rolling and overturning; no ballast is requi ...
and outrigger boats and sailing with the help of the westerlies in the Indian Ocean. This trade network expanded to reach as far as Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
and the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
, resulting in the Austronesian colonization of Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
by the first half of the first millennium AD. It continued into historic times, later becoming the Maritime Silk Road.
In the first millennium BC the Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
, Phoenicians, and Indians were also engaged in sea and land trade in luxury goods such as spices, gold, precious stones, leather of exotic animals, ebony and pearls. The sea trade was in the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
and the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
. The sea route in the Red Sea was from Bab-el-Mandeb to Berenike, from there by land to the Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
, and then by boats to Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
. Luxury goods
In economics, a luxury good (or upmarket good) is a good (economics), good for which demand (economics), demand increases more than what is proportional as income rises, so that expenditures on the good become a more significant proportion of ove ...
including Indian spices, ebony, silk
Silk is a natural fiber, natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be weaving, woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is most commonly produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoon (silk), c ...
and fine textiles
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. ...
were traded along the overland incense route.
In the second half of the first millennium BC the Arabian tribes of South and West Arabia took control over the land trade of spices from South Arabia
South Arabia (), or Greater Yemen, is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jazan, ...
to the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
. These tribes were the M'ain, Qataban
Qataban () was an ancient Yemenite kingdom in South Arabia that existed from the early 1st millennium BCE to the late 1st or 2nd centuries CE.
It was one of the six ancient South Arabian kingdoms of ancient Yemen, along with Sabaʾ, Maʿīn ...
, Hadhramaut, Saba and Himyarite
Himyar was a polity in the southern highlands of Yemen, as well as the name of the region which it claimed. Until 110 BCE, it was integrated into the Qataban, Qatabanian kingdom, afterwards being recognized as an independent kingdom. According ...
. In the north the Nabateans took control of the trade route that crossed the Negev from Petra to Gaza. The trade enriched these tribes. South Arabia
South Arabia (), or Greater Yemen, is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jazan, ...
was called Eudaemon Arabia (the elated Arabia) by the Greeks and was on the agenda of conquests of Alexander of Macedonia before he died. The Indians and the Arabs had control over the sea trade with India. In the late second century BC, the Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
from the Ptolemaic dynasty of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
learned from the Indians how to sail directly from Aden
Aden () is a port city located in Yemen in the southern part of the Arabian peninsula, on the north coast of the Gulf of Aden, positioned near the eastern approach to the Red Sea. It is situated approximately 170 km (110 mi) east of ...
to the west coast of India using the monsoon winds (as did Hippalus) and took control of the sea trade via Red Sea ports.Shaw 2003: 426
Spices are discussed in biblical narratives, and there is literary evidence for their use in ancient Greek and Roman society. There is a record from Tamil texts of Greeks purchasing large sacks of black pepper from India, and many recipes in the 1st-century Roman cookbook '' Apicius'' make use of the spice. The trade in spices lessened after the fall of the Roman Empire, but demand for ginger
Ginger (''Zingiber officinale'') is a flowering plant whose rhizome, ginger root or ginger, is widely used as a spice and a folk medicine. It is an herbaceous perennial that grows annual pseudostems (false stems made of the rolled bases of l ...
, black pepper, cloves, cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus ''Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, biscuits, b ...
and nutmeg revived the trade in later centuries.
Arab trade and medieval Europe
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, eventually took over conveying goods via the Levant to Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
. At times, Jews enjoyed a virtual monopoly on the spice trade in large parts of Western Europe.
The spice trade had brought great riches to the Abbasid Caliphate and inspired famous legends such as that of Sinbad the Sailor. These early sailors and merchants would often set sail from the port city of Basra
Basra () is a port city in Iraq, southern Iraq. It is the capital of the eponymous Basra Governorate, as well as the List of largest cities of Iraq, third largest city in Iraq overall, behind Baghdad and Mosul. Located near the Iran–Iraq bor ...
and, after many ports of call, would return to sell their goods, including spices, in Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
. The fame of many spices such as nutmeg and cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus ''Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, biscuits, b ...
are attributed to these early spice merchants.
The Indian commercial connection with South East Asia proved vital to the merchants of Arabia and Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
during the 7th and 8th centuries.Donkin 2003: 59 Arab traders — mainly descendants of sailors from Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
and Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
— dominated maritime routes throughout the Indian Ocean, tapping source regions in the Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In mod ...
and linking to the secret "spice islands" (Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands ( ; , ) or the Moluccas ( ; ) are an archipelago in the eastern part of Indonesia. Tectonics, Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located in West ...
and Banda Islands
The Banda Islands () are a volcanic group of ten small volcanic islands in the Banda Sea, about south of Seram Island and about east of Java (island), Java, and constitute an administrative district (''kecamatan'') within the Central Maluku ...
). The islands of Molucca also find mention in several records: a Javanese chronicle (1365) mentions the Moluccas and ''Maloko'', and navigational works of the 14th and 15th centuries contain the first unequivocal Arab reference to Moluccas. Sulaima al-Mahr writes: "East of Timor
Timor (, , ) is an island at the southern end of Maritime Southeast Asia, in the north of the Timor Sea. The island is Indonesia–Timor-Leste border, divided between the sovereign states of Timor-Leste in the eastern part and Indonesia in the ...
[where sandalwood
Sandalwood is a class of woods from trees in the genus ''Santalum''. The woods are heavy, yellow, and fine-grained, and, unlike many other aromatic woods, they retain their fragrance for decades. Sandalwood oil is extracted from the woods. Sanda ...
is found] are the islands of ''Bandam'' and they are the islands where nutmeg and mace are found. The islands of cloves are called ''Maluku'' ....."Donkin 2003: 88
Moluccan products were shipped to trading emporiums in India, passing through ports like Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. Known as the City of Spices, Kozhikode is listed among the City of Literature, UNESCO's Cities of Literature.
It is the nineteenth large ...
in Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
and through Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
. From there they were shipped westward across the ports of Arabia to the Near East, to Ormus in the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
and Jeddah
Jeddah ( ), alternatively transliterated as Jedda, Jiddah or Jidda ( ; , ), is a List of governorates of Saudi Arabia, governorate and the largest city in Mecca Province, Saudi Arabia, and the country's second largest city after Riyadh, located ...
in the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
and sometimes to East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
, where they were used for many purposes, including burial rites.Donkin 2003: 92 The Abbasids used Alexandria, Damietta, Aden
Aden () is a port city located in Yemen in the southern part of the Arabian peninsula, on the north coast of the Gulf of Aden, positioned near the eastern approach to the Red Sea. It is situated approximately 170 km (110 mi) east of ...
and Siraf as entry ports to trade with India and China.Donkin 2003: 91–92 Merchants arriving from India in the port city of Aden paid tribute in form of musk, camphor, ambergris and sandalwood
Sandalwood is a class of woods from trees in the genus ''Santalum''. The woods are heavy, yellow, and fine-grained, and, unlike many other aromatic woods, they retain their fragrance for decades. Sandalwood oil is extracted from the woods. Sanda ...
to Ibn Ziyad, the sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be use ...
of Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
.
Indian spice exports find mention in the works of Ibn Khurdadhbeh (850), al-Ghafiqi (1150), Ishak bin Imaran (907) and Al Kalkashandi (14th century). Chinese traveler Xuanzang
Xuanzang (; ; 6 April 6025 February 664), born Chen Hui or Chen Yi (), also known by his Sanskrit Dharma name Mokṣadeva, was a 7th-century Chinese Bhikkhu, Buddhist monk, scholar, traveller, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making ...
mentions the town of Puri
Puri, also known as Jagannath Puri, () is a coastal city and a Nagar Palika, municipality in the state of Odisha in eastern India. It is the district headquarters of Puri district and is situated on the Bay of Bengal, south of the state ca ...
where "merchants depart for distant countries."Donkin 2003: 65
 From there, overland routes led to the Mediterranean coasts. From the 8th until the 15th century, maritime republics (
From there, overland routes led to the Mediterranean coasts. From the 8th until the 15th century, maritime republics (Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
, Republic of Pisa, Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
, Duchy of Amalfi, Duchy of Gaeta, Republic of Ancona and Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost ...
) held a monopoly on European trade with the Middle East. The silk and spice trade, involving spice
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of pl ...
s, incense
Incense is an aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremonial reasons. It ...
, herbs, drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug i ...
s and opium
Opium (also known as poppy tears, or Lachryma papaveris) is the dried latex obtained from the seed Capsule (fruit), capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid mor ...
, made these Mediterranean city-states extremely wealthy. Spices were among the most expensive and in-demand products of the Middle Ages, used in medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
as well as in the kitchen. They were all imported from Asia and Africa. Venetian and other navigators of maritime republics then distributed the goods through Europe.
Age of Discovery: a new route and a New World
 The
The Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
had become a formidable power and a key player in the Eastern spice trade. Other powers, in an attempt to break the Venetian hold on spice trade, began to build up maritime capability. Until the mid-15th century, trade with the East was achieved through the Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
, with the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
and the Italian city-states of Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
and Genoa acting as middlemen.
The first country to attempt to circumnavigate Africa was Portugal, which had, since the early 15th century, begun to explore northern Africa under Henry the Navigator. Emboldened by these early successes and eyeing a lucrative monopoly on a possible sea route to the Indies, the Portuguese first rounded the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( ) is a rocky headland on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A List of common misconceptions#Geography, common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Afri ...
in 1488 on an expedition led by Bartolomeu Dias. Just nine years later in 1497, on the orders of Manuel I of Portugal, four vessels under the command of navigator Vasco da Gama continued beyond to the eastern coast of Africa to Malindi
Malindi is a town on Malindi Bay at the mouth of the Sabaki River, lying on the Indian Ocean coast of Kenya. It is 120 kilometres northeast of Mombasa. The population of Malindi was 119,859 as of the 2019 census. It is the largest urban centr ...
and sailed across the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
to Calicut, on the Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast () is the southwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. It generally refers to the West Coast of India, western coastline of India stretching from Konkan to Kanyakumari. Geographically, it comprises one of the wettest regio ...
in Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
Gama, Vasco da. The Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition. Columbia University Press. in South India — the capital of the local Zamorin rulers. The wealth of the Indies was now open for the Europeans to explore; the Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire was a colonial empire that existed between 1415 and 1999. In conjunction with the Spanish Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It achieved a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa ...
was the earliest European seaborne empire to grow from the spice trade.
In 1511, Afonso de Albuquerque conquered Malacca for Portugal, then the center of Asian trade. East of Malacca, Albuquerque sent several diplomatic and exploratory missions, including to the Moluccas. Learning the secret location of the Spice Islands, mainly the Banda Islands, then the world source of nutmeg, he sent an expedition led by António de Abreu to Banda, where they were the first Europeans to arrive, in early 1512. Abreu's expedition reached Buru, Ambon and Seram Islands, and then Banda.
Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
and Sri Lanka, to Lisbon
Lisbon ( ; ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 567,131, as of 2023, within its administrative limits and 3,028,000 within the Lisbon Metropolitan Area, metropolis, as of 2025. Lisbon is mainlan ...
in Portugal.
The Crown of Castile had organized the expedition of Christopher Columbus to compete with Portugal for the spice trade with Asia, but when Columbus landed on the island of Hispaniola (in what is now Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
) instead of in the Indies, the search for a route to Asia was postponed until a few years later. After Vasco Núñez de Balboa crossed the Isthmus of Panama
The Isthmus of Panama, historically known as the Isthmus of Darien, is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North America, North and South America. The country of Panama is located on the i ...
in 1513, the Spanish Crown prepared a westward voyage by Ferdinand Magellan in order to reach Asia from Spain across the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. On October 21, 1520, his expedition crossed the Strait of Magellan in the southern tip of South America, opening the Pacific to European exploration. On March 16, 1521, the ships reached the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
and soon after the Spice Islands, ultimately resulting decades later in the Manila Galleon
The Manila galleon (; ) refers to the Spain, Spanish trading Sailing ship, ships that linked the Philippines in the Spanish East Indies to Mexico (New Spain), across the Pacific Ocean. The ships made one or two round-trip voyages per year betwe ...
trade, the first westward spice trade route to Asia. After Magellan's death in the Philippines, navigator Juan Sebastian Elcano took command of the expedition and drove it across the Indian Ocean and back to Spain, where they arrived in 1522 aboard the last remaining ship, the ''Victoria''. For the next two-and-a-half centuries, Spain controlled a vast trade network that linked three continents: Asia, the Americas and Europe. A global spice route had been created: from Manila
Manila, officially the City of Manila, is the Capital of the Philippines, capital and second-most populous city of the Philippines after Quezon City, with a population of 1,846,513 people in 2020. Located on the eastern shore of Manila Bay on ...
in the Philippines (Asia) to Seville
Seville ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Spain, Spanish autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the Guadalquivir, River Guadalquivir, ...
in Spain (Europe), via Acapulco
Acapulco de Juárez (), commonly called Acapulco ( , ; ), is a city and Port of Acapulco, major seaport in the Political divisions of Mexico, state of Guerrero on the Pacific Coast of Mexico, south of Mexico City. Located on a deep, semicirc ...
in Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
(North America).
Cultural diffusion
Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melan ...
. These technologies include the plank-sewn hulls, catamaran
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hull (watercraft), hulls of equal size. The wide distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts stability through resistance to rolling and overturning; no ballast is requi ...
s, outrigger boat
Outrigger boats are various watercraft featuring one or more lateral support floats known as outriggers, which are fastened to one or both sides of the main hull (watercraft), hull. They can range from small dugout (boat), dugout canoes to large ...
s, and possibly the lateen sail. This is still evident in Sri Lankan and South Indian languages. For example, Tamil ''paṭavu'', Telugu ''paḍava'', and Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
''paḍahu'', all meaning "ship", are all derived from Proto-Hesperonesian ''*padaw'', "sailboat", with Austronesian cognates like Javanese '' perahu'', Kadazan ''padau'', Maranao ''padaw'', Cebuano ''paráw
Paraw (also spelled ''parao'') are various double Outrigger canoe, outrigger sail boats in the Philippines. It is a general term (similar to the term ''bangka (boat), bangka'') and thus can refer to a range of ship types, from small fishing ...
'', Samoan ''folau'', Hawaiian ''halau'', and Māori ''wharau''.
Austronesians also introduced many Austronesian cultigens to southern India, Sri Lanka, and eastern Africa that figured prominently in the spice trade. They include bananas, Pacific domesticated coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
s, '' Dioscorea'' yams, wetland rice, sandalwood
Sandalwood is a class of woods from trees in the genus ''Santalum''. The woods are heavy, yellow, and fine-grained, and, unlike many other aromatic woods, they retain their fragrance for decades. Sandalwood oil is extracted from the woods. Sanda ...
, giant taro, Polynesian arrowroot, ginger
Ginger (''Zingiber officinale'') is a flowering plant whose rhizome, ginger root or ginger, is widely used as a spice and a folk medicine. It is an herbaceous perennial that grows annual pseudostems (false stems made of the rolled bases of l ...
, lengkuas, tailed pepper, betel, areca nut, and sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
.
Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
and Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
religious establishments of Southeast Asia came to be associated with economic activity and commerce as patrons, entrusted large funds which would later be used to benefit local economies by estate management, craftsmanship, and promotion of trading activities.Donkin 2003: 67 Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, in particular, traveled alongside the maritime trade, promoting coinage, art, and literacy.Donkin 2003: 69 Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
spread throughout the East, reaching maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the Southeast Asian countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor.
The terms Island Southeast Asia and Insular Southeast Asia are sometimes given the same meaning as ...
in the 10th century; Muslim merchants played a crucial part in the trade.Corn & Glasserman 1999 Christian missionaries, such as Saint Francis Xavier, were instrumental in the spread of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
in the East. Christianity competed with Islam to become the dominant religion of the Moluccas. However, the natives of the Spice Islands accommodated to aspects of both religions easily.
The Portuguese colonial settlements saw traders, such as the Gujarati banias, South Indian Chettis, Syrian Christians, Chinese from Fujian
Fujian is a provinces of China, province in East China, southeastern China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capital is Fuzhou and its largest prefe ...
province, and Arabs from Aden
Aden () is a port city located in Yemen in the southern part of the Arabian peninsula, on the north coast of the Gulf of Aden, positioned near the eastern approach to the Red Sea. It is situated approximately 170 km (110 mi) east of ...
, involved in the spice trade.Collingham 56: 2006 Epics, languages, and cultural customs were borrowed by Southeast Asia from India, and later China.Donkin 2003 Knowledge of Portuguese language
Portuguese ( or ) is a Western Romance language of the Indo-European language family originating from the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. It is the official language of Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Portugal and São Tom� ...
became essential for merchants involved in the trade. The colonial pepper trade drastically changed the experience of modernity in Europe, and in Kerala and it brought, along with colonialism, early capitalism to India's Malabar Coast, changing cultures of work and caste.
Indian merchants involved in spice trade took Indian cuisine to Southeast Asia, notably present day Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
, where spice mixtures and black pepper
Black pepper (''Piper nigrum'') is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit (the peppercorn), which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. The fruit is a drupe (stonefruit) which is about in diameter ...
became popular.Collingham 245: 2006 Conversely, Southeast Asian cuisine and crops was also introduced to India and Sri Lanka, where rice cakes and coconut milk-based dishes are still dominant.
European people intermarried with Indians and popularized valuable culinary skills, such as baking, in India.Collingham 61: 2006 Indian food, adapted to the European palate, became visible in England by 1811 as exclusive establishments began catering to the tastes of both the curious and those returning from India.Collingham 129: 2006 Opium was a part of the spice trade, and some people involved in the spice trade were driven by opium addiction.Burger, M. (2003), The Forgotten Gold? The Importance of the Dutch opium trade in the Seventeenth Century
See also
*Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
*East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies) is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The ''Indies'' broadly referred to various lands in Eastern world, the East or the Eastern Hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainl ...
* ''''
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * *Further reading
* Borschberg, Peter (2017), "The Value of Admiral Matelieff's Writings for Studying the History of Southeast Asia, c. 1600–1620". ''Journal of Southeast Asian Studies'' 48(3): 414–435. . * * Nabhan, Gary Paul: ''Cumin, Camels, and Caravans: A Spice Odyssey.'' istory of Spice TradeUniversity of California Press, 2014. rintBook
A book is a structured presentation of recorded information, primarily verbal and graphical, through a medium. Originally physical, electronic books and audiobooks are now existent. Physical books are objects that contain printed material, ...
* Pavo López, Marcos: Spices in maps. Fifth centenary of the first circumnavigation of the world
'. istory of the spice trade through old mapse-Perimetron, vol 15, no.2 (2020)
External links
The Spice Trade and the Age of Exploration
* ttp://www.euleev.de/images/Beitraege/UP_The_spice_trade.pdf The Spice Trade and its importance for European Expansion, Doz. Udo Pollmer {{Authority control Spices History of international trade Trade routes Medieval economic history Age of Discovery Portuguese exploration in the Age of Discovery Economic history of Portugal Economic history of India Economic history of Spain Portuguese Empire Spanish Empire Ancient Somalia Kingdom of Aksum Age of Sail Trade by commodity Maluku Islands