Sinks, Sources,and Reservoirs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The carbon cycle is a part of the
The carbon cycle is a part of the
 Human activities over the past two centuries have increased the amount of carbon in the atmosphere by nearly 50% as of year 2020, mainly in the form of carbon dioxide, both by modifying ecosystems' ability to extract carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and by emitting it directly, e.g., by burning fossil fuels and manufacturing concrete.
In the far future (2 to 3 billion years), the rate at which carbon dioxide is absorbed into the soil via the
Human activities over the past two centuries have increased the amount of carbon in the atmosphere by nearly 50% as of year 2020, mainly in the form of carbon dioxide, both by modifying ecosystems' ability to extract carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and by emitting it directly, e.g., by burning fossil fuels and manufacturing concrete.
In the far future (2 to 3 billion years), the rate at which carbon dioxide is absorbed into the soil via the
 The terrestrial biosphere includes the organic carbon in all land-living organisms, both alive and dead, as well as carbon stored in
The terrestrial biosphere includes the organic carbon in all land-living organisms, both alive and dead, as well as carbon stored in  Carbon leaves the terrestrial biosphere in several ways and on different time scales. The
Carbon leaves the terrestrial biosphere in several ways and on different time scales. The
 The geologic component of the carbon cycle operates slowly in comparison to the other parts of the global carbon cycle. It is one of the most important determinants of the amount of carbon in the atmosphere, and thus of global temperatures.
Most of the Earth's carbon is stored inertly in the Earth's
The geologic component of the carbon cycle operates slowly in comparison to the other parts of the global carbon cycle. It is one of the most important determinants of the amount of carbon in the atmosphere, and thus of global temperatures.
Most of the Earth's carbon is stored inertly in the Earth's
Information sheet for Columbia University Summer Session 2012 Earth and Environmental Sciences Introduction to Earth Sciences I Some of it was deposited in the form of organic carbon from the biosphere. Of the carbon stored in the geosphere, about 80% is
 There is a fast and a slow carbon cycle. The fast cycle operates in the
There is a fast and a slow carbon cycle. The fast cycle operates in the
Archive
The slow (or deep) carbon cycle involves medium to long-term
Archive
 The movement of terrestrial carbon in the water cycle is shown in the diagram on the right and explained below:
# Atmospheric particles act as
The movement of terrestrial carbon in the water cycle is shown in the diagram on the right and explained below:
# Atmospheric particles act as
 Terrestrial and marine ecosystems are chiefly connected through
Terrestrial and marine ecosystems are chiefly connected through
 The ocean
The ocean

 Polymorphism alters carbonate compounds' stability at different depths within the Earth. To illustrate, laboratory simulations and
Polymorphism alters carbonate compounds' stability at different depths within the Earth. To illustrate, laboratory simulations and 
 Since the
Since the
 The largest and one of the fastest growing human impacts on the carbon cycle and biosphere is the extraction and burning of
The largest and one of the fastest growing human impacts on the carbon cycle and biosphere is the extraction and burning of
Carbon Cycle Science Program
– an interagency partnership.
Global Carbon Project – initiative of the Earth System Science Partnership
carbon levels and flows {{DEFAULTSORT:Carbon Cycle Chemical oceanography Photosynthesis Soil biology Soil chemistry Numerical climate and weather models Effects of climate change
 The carbon cycle is a part of the
The carbon cycle is a part of the biogeochemical cycle
A biogeochemical cycle, or more generally a cycle of matter, is the movement and transformation of chemical elements and compounds between living organisms, the atmosphere, and the Earth's crust. Major biogeochemical cycles include the carbon cyc ...
where carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
is exchanged among the biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
, pedosphere
The pedosphere () is the Earth's crust, outermost layer of the Earth that is composed of soil and subject to soil formation processes. It exists at the interface of the lithosphere, Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere. The ...
, geosphere
There are several conflicting usages of geosphere, variously defined.
In Aristotelian physics, the term was applied to four spherical ''natural places'', concentrically nested around the center of the Earth, as described in the lectures '' Ph ...
, hydrosphere
The hydrosphere () is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the Planetary surface, surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, it continues to ch ...
, and atmosphere of Earth
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather ...
. Other major biogeochemical cycles include the nitrogen cycle
The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmosphere, atmospheric, terrestrial ecosystem, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can ...
and the water cycle
The water cycle (or hydrologic cycle or hydrological cycle) is a biogeochemical cycle that involves the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth across different reservoirs. The mass of water on Earth remains fai ...
. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major component of many rocks such as limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
. The carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events that are key to making Earth capable of sustaining life. It describes the movement of carbon as it is recycled and reused throughout the biosphere, as well as long-term processes of carbon sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in a carbon pool. It plays a crucial role in Climate change mitigation, limiting climate change by reducing the amount of Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide in the atmosphe ...
(storage) to and release from carbon sink
A carbon sink is a natural or artificial carbon sequestration process that "removes a greenhouse gas, an aerosol or a precursor of a greenhouse gas from the atmosphere". These sinks form an important part of the natural carbon cycle. An overar ...
s.
To describe the dynamics of the carbon cycle, a distinction can be made between the ''fast'' and ''slow'' carbon cycle. The fast cycle is also referred to as the ''biological carbon cycle''. Fast cycles can complete within years, moving substances from atmosphere to biosphere, then back to the atmosphere. Slow or geological cycles (also called deep carbon cycle) can take millions of years to complete, moving substances through the Earth's crust between rocks, soil, ocean and atmosphere.
Humans have disturbed the carbon cycle for many centuries. They have done so by modifying land use and by mining and burning carbon from ancient organic remains (coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
, petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring un ...
and gas
Gas is a state of matter that has neither a fixed volume nor a fixed shape and is a compressible fluid. A ''pure gas'' is made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon) or molecules of either a single type of atom ( elements such as ...
). Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
in the atmosphere has increased nearly 52% over pre-industrial levels by 2020, resulting in global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
. The increased carbon dioxide has also caused a reduction in the ocean's pH value and is fundamentally altering marine chemistry
Marine chemistry, also known as ocean chemistry or chemical oceanography, is the study of the chemical composition and processes of the world’s oceans, including the interactions between seawater, the atmosphere, the seafloor, and marine organ ...
. Carbon dioxide is critical for photosynthesis.
Main compartments
The carbon cycle was first described byAntoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794), When reduced without charcoal, it gave off an air which supported respiration and combustion in an enhanced way. He concluded that this was just a pure form of common air and that i ...
and Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley (; 24 March 1733 – 6 February 1804) was an English chemist, Unitarian, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher, English Separatist, separatist theologian, Linguist, grammarian, multi-subject educator and Classical libera ...
, and popularised by Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several Chemical element, e ...
. The global carbon cycle is now usually divided into the following major ''reservoirs of carbon'' (also called carbon pools) interconnected by pathways of exchange:
* Atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
* Terrestrial biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
* Ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean ...
, including dissolved inorganic carbon
Dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) is the sum of the aqueous species of inorganic carbon in a solution. Carbon compounds can be distinguished as either organic or inorganic, and as dissolved or particulate, depending on their composition. Organic c ...
and living and non-living marine biota
* Sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
s, including fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geolog ...
s, freshwater systems, and non-living organic material.
* Earth's interior ( mantle and crust). These carbon stores interact with the other components through geological processes.
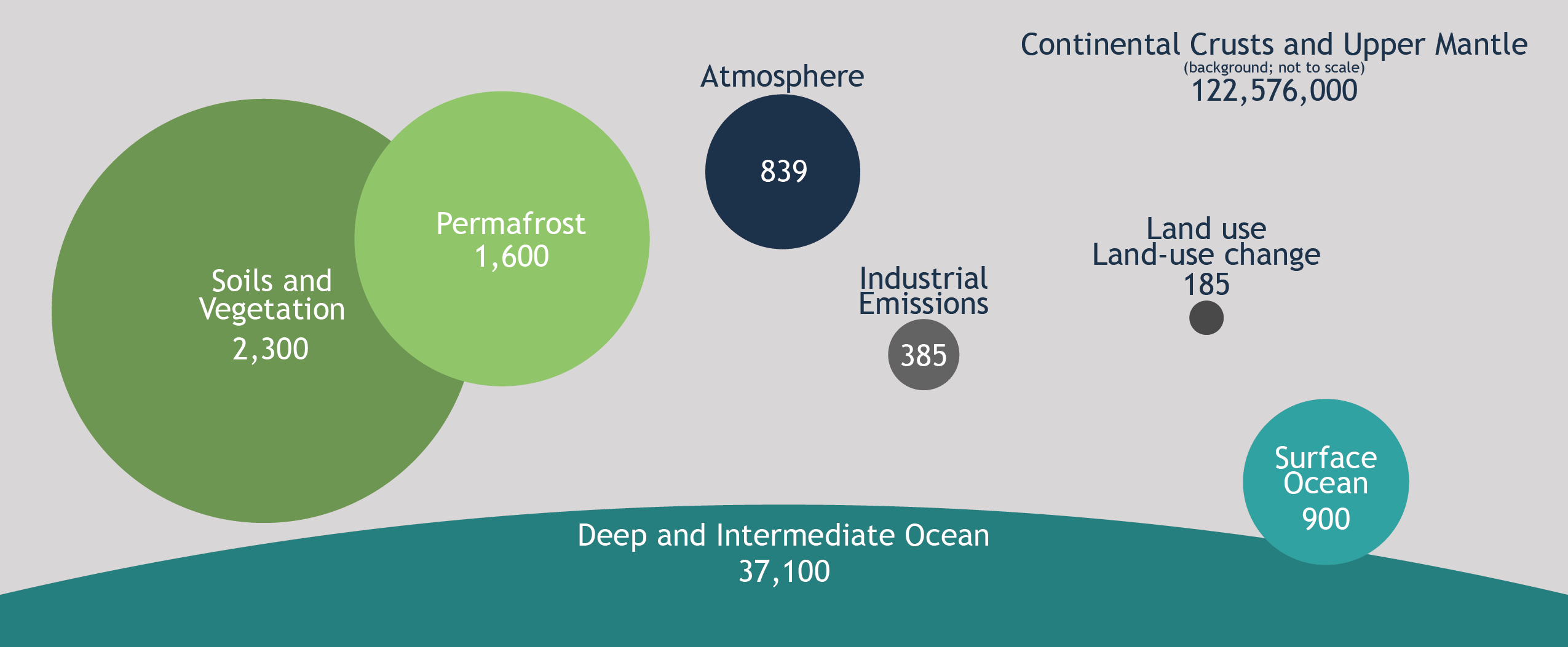
The carbon exchanges between reservoirs occur as the result of various chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes. The ocean contains the largest active pool of carbon near the surface of the Earth.
The natural flows of carbon between the atmosphere, ocean, terrestrial ecosystems, and sediments are fairly balanced; so carbon levels would be roughly stable without human influence.
Atmosphere
Carbon in the Earth's atmosphere exists in two main forms:carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
and methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
. Both of these gases absorb and retain heat in the atmosphere and are partially responsible for the greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere insulate the planet from losing heat to space, raising its surface temperature. Surface heating can happen from an internal heat source (as in the case of Jupiter) or ...
. Methane produces a larger greenhouse effect per volume as compared to carbon dioxide, but it exists in much lower concentrations and is more short-lived than carbon dioxide. Thus, carbon dioxide contributes more to the global greenhouse effect than methane.
Carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere primarily through photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
and enters the terrestrial and oceanic biospheres. Carbon dioxide also dissolves directly from the atmosphere into bodies of water (ocean, lakes, etc.), as well as dissolving in precipitation as raindrops fall through the atmosphere. When dissolved in water, carbon dioxide reacts with water molecules and forms carbonic acid
Carbonic acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . The molecule rapidly converts to water and carbon dioxide in the presence of water. However, in the absence of water, it is quite stable at room temperature. The interconversion ...
, which contributes to ocean acidity. It can then be absorbed by rocks through weathering. It also can acidify other surfaces it touches or be washed into the ocean.
carbonate–silicate cycle
The carbonate–silicate geochemical cycle, also known as the inorganic carbon cycle, describes the long-term transformation of silicate rocks to carbonate rocks by weathering and sedimentation, and the transformation of carbonate rocks back int ...
will likely increase due to expected changes in the sun as it ages. The expected increased luminosity of the Sun will likely speed up the rate of surface weathering. This will eventually cause most of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere to be squelched into the Earth's crust as carbonate. Once the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere falls below approximately 50 parts per million (tolerances vary among species), C3 photosynthesis will no longer be possible. This has been predicted to occur 600 million years from the present, though models vary.
Once the oceans on the Earth evaporate in about 1.1 billion years from now, plate tectonics will very likely stop due to the lack of water to lubricate them. The lack of volcanoes pumping out carbon dioxide will cause the carbon cycle to end between 1 billion and 2 billion years into the future.
Terrestrial biosphere
 The terrestrial biosphere includes the organic carbon in all land-living organisms, both alive and dead, as well as carbon stored in
The terrestrial biosphere includes the organic carbon in all land-living organisms, both alive and dead, as well as carbon stored in soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
s. About 500 gigatons of carbon are stored above ground in plants and other living organisms, while soil holds approximately 1,500 gigatons of carbon. Most carbon in the terrestrial biosphere is organic carbon, while about a third of soil carbon
Soil carbon is the solid carbon stored in global Soil, soils. This includes both soil organic matter and Inorganic compound, inorganic carbon as carbonate minerals. It is vital to the soil capacity in our ecosystem. Soil carbon is a carbon sink in ...
is stored in inorganic forms, such as calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skel ...
. Organic carbon is a major component of all organisms living on Earth. Autotrophs
An autotroph is an organism that can convert abiotic sources of energy into energy stored in organic compounds, which can be used by other organisms. Autotrophs produce complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) us ...
extract it from the air in the form of carbon dioxide, converting it to organic carbon, while heterotrophs
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
receive carbon by consuming other organisms.
Because carbon uptake in the terrestrial biosphere is dependent on biotic factors, it follows a diurnal and seasonal cycle. In CO2 measurements, this feature is apparent in the Keeling curve. It is strongest in the northern hemisphere
Hemisphere may refer to:
In geometry
* Hemisphere (geometry), a half of a sphere
As half of Earth or any spherical astronomical object
* A hemisphere of Earth
** Northern Hemisphere
** Southern Hemisphere
** Eastern Hemisphere
** Western Hemi ...
because this hemisphere has more land mass than the southern hemisphere and thus more room for ecosystems to absorb and emit carbon.
 Carbon leaves the terrestrial biosphere in several ways and on different time scales. The
Carbon leaves the terrestrial biosphere in several ways and on different time scales. The combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion ...
or respiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
of organic carbon releases it rapidly into the atmosphere. It can also be exported into the ocean through rivers or remain sequestered in soils in the form of inert carbon. Carbon stored in soil can remain there for up to thousands of years before being washed into rivers by erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
or released into the atmosphere through soil respiration
Soil respiration refers to the production of carbon dioxide when soil organisms respire. This includes respiration of plant roots, the rhizosphere, microbes and fauna.
Soil respiration is a key ecosystem process that releases carbon from the so ...
. Between 1989 and 2008 soil respiration increased by about 0.1% per year. In 2008, the global total of CO2 released by soil respiration was roughly 98 billion tonnes, about 3 times more carbon than humans are now putting into the atmosphere each year by burning fossil fuel (this does not represent a net transfer of carbon from soil to atmosphere, as the respiration is largely offset by inputs to soil carbon). There are a few plausible explanations for this trend, but the most likely explanation is that increasing temperatures have increased rates of decomposition of soil organic matter
Soil organic matter (SOM) is the organic matter component of soil, consisting of plant and animal detritus at various stages of decomposition, cells and tissues of soil microbes, and substances that soil microbes synthesize. SOM provides numerou ...
, which has increased the flow of CO2. The length of carbon sequestering in soil is dependent on local climatic conditions and thus changes in the course of climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
.
Ocean
The ocean can be conceptually divided into asurface layer
The surface layer is the layer of a turbulent fluid most affected by interaction with a solid surface or the surface separating a gas and a liquid where the characteristics of the turbulence depend on distance from the interface. Surface layers a ...
within which water makes frequent (daily to annual) contact with the atmosphere, and a deep layer below the typical mixed layer
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, surface heat fluxes, or processes such as evaporat ...
depth of a few hundred meters or less, within which the time between consecutive contacts may be centuries. The dissolved inorganic carbon
Dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) is the sum of the aqueous species of inorganic carbon in a solution. Carbon compounds can be distinguished as either organic or inorganic, and as dissolved or particulate, depending on their composition. Organic c ...
(DIC) in the surface layer is exchanged rapidly with the atmosphere, maintaining equilibrium. Partly because its concentration of DIC is about 15% higher but mainly due to its larger volume, the deep ocean contains far more carbon—it is the largest pool of actively cycled carbon in the world, containing 50 times more than the atmosphere—but the timescale to reach equilibrium with the atmosphere is hundreds of years: the exchange of carbon between the two layers, driven by thermohaline circulation
Thermohaline circulation (THC) is a part of the large-scale Ocean current, ocean circulation driven by global density gradients formed by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The name ''thermohaline'' is derived from ''wikt:thermo-, thermo-'', r ...
, is slow.
Carbon enters the ocean mainly through the dissolution of atmospheric carbon dioxide, a small fraction of which is converted into carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, (), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word "carbonate" may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group ...
. It can also enter the ocean through rivers as dissolved organic carbon
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is the fraction of organic carbon Operational definition, operationally defined as that which can pass through a filter with a pore size typically between 0.22 and 0.7 micrometre, micrometers. The fraction remain ...
. It is converted by organisms into organic carbon through photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
and can either be exchanged throughout the food chain or precipitated into the oceans' deeper, more carbon-rich layers as dead soft tissue or in shells as calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skel ...
. It circulates in this layer for long periods of time before either being deposited as sediment or, eventually, returned to the surface waters through thermohaline circulation.
Oceans are basic (with a current pH value of 8.1 to 8.2). The increase in atmospheric CO2 shifts the pH of the ocean towards neutral in a process called ocean acidification
Ocean acidification is the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth's ocean. Between 1950 and 2020, the average pH of the ocean surface fell from approximately 8.15 to 8.05. Carbon dioxide emissions from human activities are the primary cause of ...
. Oceanic absorption of CO2 is one of the most important forms of carbon sequestering. The projected rate of pH reduction could slow the biological precipitation of calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skel ...
s, thus decreasing the ocean's capacity to absorb CO2.
Geosphere
 The geologic component of the carbon cycle operates slowly in comparison to the other parts of the global carbon cycle. It is one of the most important determinants of the amount of carbon in the atmosphere, and thus of global temperatures.
Most of the Earth's carbon is stored inertly in the Earth's
The geologic component of the carbon cycle operates slowly in comparison to the other parts of the global carbon cycle. It is one of the most important determinants of the amount of carbon in the atmosphere, and thus of global temperatures.
Most of the Earth's carbon is stored inertly in the Earth's lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time ...
. Much of the carbon stored in the Earth's mantle was stored there when the Earth formed.The Carbon Cycle and Earth's ClimateInformation sheet for Columbia University Summer Session 2012 Earth and Environmental Sciences Introduction to Earth Sciences I Some of it was deposited in the form of organic carbon from the biosphere. Of the carbon stored in the geosphere, about 80% is
limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
and its derivatives, which form from the sedimentation of calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skel ...
stored in the shells of marine organisms. The remaining 20% is stored as kerogen
Kerogen is solid, insoluble organic matter in sedimentary rocks. It consists of a variety of organic materials, including dead plants, algae, and other microorganisms, that have been compressed and heated by geological processes. All the kero ...
s formed through the sedimentation and burial of terrestrial organisms under high heat and pressure. Organic carbon stored in the geosphere can remain there for millions of years.
Carbon can leave the geosphere in several ways. Carbon dioxide is released during the metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing Rock (geology), rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or Texture (geology), texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated ...
of carbonate rocks when they are subducted
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second plat ...
into the Earth's mantle. This carbon dioxide can be released into the atmosphere and ocean through volcanoes
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ...
and hotspots
Hotspot, Hot Spot or Hot spot may refer to:
Places
* Hot Spot, Kentucky, a community in the United States
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Hot Spot (comics), a name for the DC Comics character Isaiah Crockett
* Hot Spot (Tr ...
. It can also be removed by humans through the direct extraction of kerogens in the form of fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geologica ...
. After extraction, fossil fuels are burned to release energy and emit the carbon they store into the atmosphere.
Types of dynamic
biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
and the slow cycle operates in rocks
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's ...
. The fast or biological cycle can complete within years, moving carbon from atmosphere to biosphere, then back to the atmosphere. The slow or geological cycle may extend deep into the mantle and can take millions of years to complete, moving carbon through the Earth's crust between rocks, soil, ocean and atmosphere.
The fast carbon cycle involves relatively short-term biogeochemical
Biogeochemistry is the scientific discipline that involves the study of the chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes and reactions that govern the composition of the natural environment (including the biosphere, the cryosphere, ...
processes between the environment and living organisms in the biosphere (see diagram at start of article). It includes movements of carbon between the atmosphere and terrestrial and marine ecosystems, as well as soils and seafloor sediments. The fast cycle includes annual cycles involving photosynthesis and decadal cycles involving vegetative growth and decomposition. The reactions of the fast carbon cycle to human activities will determine many of the more immediate impacts of climate change.NASA Earth Observatory (16 June 2011). "The Fast Carbon Cycle"Archive
The slow (or deep) carbon cycle involves medium to long-term
geochemical
Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing the ...
processes belonging to the rock cycle
The ''rock cycle'' is a basic concept in geology that describes transitions through geologic time among the three main rock types: sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous. Each rock type is altered when it is forced out of its equilibrium cond ...
(see diagram on the right). The exchange between the ocean and atmosphere can take centuries, and the weathering of rocks can take millions of years. Carbon in the ocean precipitates to the ocean floor where it can form sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or de ...
and be subducted
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second plat ...
into the Earth's mantle
Earth's mantle is a layer of silicate mineral, silicate rock between the Earth's crust, crust and the Earth's outer core, outer core. It has a mass of and makes up 67% of the mass of Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 46% of Earth's ...
. Mountain building
Mountain formation occurs due to a variety of geological processes associated with large-scale movements of the Earth's crust (List of tectonic plates, tectonic plates). Fold (geology), Folding, Fault (geology), faulting, Volcano, volcanic acti ...
processes result in the return of this geologic carbon to the Earth's surface. There the rocks are weathered and carbon is returned to the atmosphere by degassing
Degassing, also known as degasification, is the removal of dissolved gases from liquids, especially water or aqueous solutions. There are numerous methods for removing gases from liquids.
Gases are removed for various reasons. Chemists remove gas ...
and to the ocean by rivers. Other geologic carbon returns to the ocean through the hydrothermal emission of calcium ions. In a given year between 10 and 100 million tonnes of carbon moves around this slow cycle. This includes volcanoes returning geologic carbon directly to the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide. However, this is less than one percent of the carbon dioxide put into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels.NASA Earth Observatory (16 June 2011). "The Slow Carbon Cycle"Archive
Processes within fast carbon cycle
Terrestrial carbon in the water cycle
 The movement of terrestrial carbon in the water cycle is shown in the diagram on the right and explained below:
# Atmospheric particles act as
The movement of terrestrial carbon in the water cycle is shown in the diagram on the right and explained below:
# Atmospheric particles act as cloud condensation nuclei
Cloud condensation nuclei (CCNs), also known as cloud seeds, are small particles typically 0.2 μm, or one hundredth the size of a cloud droplet. CCNs are a unique subset of aerosols in the atmosphere on which water vapour condenses. This c ...
, promoting cloud formation.
#Raindrops absorb organic and inorganic carbon
Total inorganic carbon (''C''T or TIC) is the sum of the inorganic carbon species.
Carbon compounds can be distinguished as either organic or inorganic, and dissolved or particulate, depending on their composition. Organic carbon forms the bac ...
through particle scavenging and adsorption of organic vapors while falling toward Earth.
#Burning and volcanic eruptions produce highly condensed polycyclic aromatic molecules (i.e. black carbon
Black carbon (BC) is the light-absorbing refractory form of Chemical_element, elemental carbon remaining after pyrolysis (e.g., charcoal) or produced by incomplete combustion (e.g., soot).
Tihomir Novakov originated the term black carbon in ...
) that is returned to the atmosphere along with greenhouse gases such as CO2.
#Terrestrial plants fix atmospheric CO2 through photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
, returning a fraction back to the atmosphere through respiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
. Lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidit ...
and cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
s represent as much as 80% of the organic carbon in forests and 60% in pastures.
# Litterfall and root organic carbon mix with sedimentary material to form organic soils where plant-derived and petrogenic organic carbon is both stored and transformed by microbial and fungal activity.
#Water absorbs plant and settled aerosol-derived dissolved organic carbon
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is the fraction of organic carbon Operational definition, operationally defined as that which can pass through a filter with a pore size typically between 0.22 and 0.7 micrometre, micrometers. The fraction remain ...
(DOC) and dissolved inorganic carbon
Dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) is the sum of the aqueous species of inorganic carbon in a solution. Carbon compounds can be distinguished as either organic or inorganic, and as dissolved or particulate, depending on their composition. Organic c ...
(DIC) as it passes over forest canopies (i.e. throughfall) and along plant trunks/stems (i.e. stemflow
In hydrology, stemflow is the flow of intercepted water down the trunk or stem of a plant. Stemflow, along with throughfall, is responsible for the transferral of precipitation and nutrients from the canopy to the soil. In tropical rainforests, ...
). Biogeochemical transformations take place as water soaks into soil solution and groundwater reservoirs and overland flow
Surface runoff (also known as overland flow or terrestrial runoff) is the unconfined flow of water over the ground surface, in contrast to '' channel runoff'' (or ''stream flow''). It occurs when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other ...
occurs when soils are completely saturated, or rainfall occurs more rapidly than saturation into soils.
#Organic carbon derived from the terrestrial biosphere and ''in situ'' primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through ...
is decomposed by microbial communities in rivers and streams along with physical decomposition (i.e. photo-oxidation), resulting in a flux of CO2 from rivers to the atmosphere that are the same order of magnitude as the amount of carbon sequestered annually by the terrestrial biosphere. Terrestrially-derived macromolecules such as lignin and black carbon
Black carbon (BC) is the light-absorbing refractory form of Chemical_element, elemental carbon remaining after pyrolysis (e.g., charcoal) or produced by incomplete combustion (e.g., soot).
Tihomir Novakov originated the term black carbon in ...
are decomposed into smaller components and monomer
A monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or two- or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Chemis ...
s, ultimately being converted to CO2, metabolic intermediates, or biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
.
#Lakes, reservoirs, and floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river. Floodplains stretch from the banks of a river channel to the base of the enclosing valley, and experience flooding during periods of high Discharge (hydrolog ...
s typically store large amounts of organic carbon and sediments, but also experience net heterotrophy
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
in the water column, resulting in a net flux of CO2 to the atmosphere that is roughly one order of magnitude less than rivers. Methane production is also typically high in the anoxic
Anoxia means a total depletion in the level of oxygen, an extreme form of hypoxia or "low oxygen". The terms anoxia and hypoxia are used in various contexts:
* Anoxic waters, sea water, fresh water or groundwater that are depleted of dissolved ox ...
sediments of floodplains, lakes, and reservoirs.
#Primary production is typically enhanced in river plume
A river plume is a Fresh water, freshened water mass that is formed in the sea as a result of mixing of Surface runoff, river discharge and saline seawater. River plumes are formed in coastal sea areas at many regions in the World. River plumes ge ...
s due to the export of fluvial
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it ru ...
nutrients. Nevertheless, estuarine
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
waters are a source of CO2 to the atmosphere, globally.
#Coastal marsh
A coast (coastline, shoreline, seashore) is the land next to the sea or the line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Coasts are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape and by aquatic erosion, ...
es both store and export blue carbon
Blue carbon is a concept within climate change mitigation that refers to "biologically driven carbon fluxes and storage in marine systems that are amenable to management". Most commonly, it refers to the role that tidal marshes, mangroves and Seag ...
. Marsh
In ecology, a marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous plants rather than by woody plants.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p More in genera ...
es and wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
s are suggested to have an equivalent flux of CO2 to the atmosphere as rivers, globally.
#Continental shelves
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
and the open ocean
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surfa ...
typically absorb CO2 from the atmosphere.
#The marine biological pump
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven Carbon sequestration, sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sedim ...
sequesters a small but significant fraction of the absorbed CO2 as organic carbon in marine sediment
Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles either have their origins in soil and Rock (geology), rocks and have been Sediment transport, ...
s ( see below).
Terrestrial runoff to the ocean
 Terrestrial and marine ecosystems are chiefly connected through
Terrestrial and marine ecosystems are chiefly connected through riverine
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it run ...
transport, which acts as the main channel through which erosive terrestrially derived substances enter into oceanic systems. Material and energy exchanges between the terrestrial biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
and the lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time ...
as well as organic carbon
Total organic carbon (TOC) is an analytical parameter representing the concentration of organic carbon in a sample. TOC determinations are made in a variety of application areas. For example, TOC may be used as a non-specific indicator of wa ...
fixation and oxidation processes together regulate ecosystem carbon and dioxygen
There are several known allotropes of oxygen. The most familiar is molecular oxygen (), present at significant levels in Earth's atmosphere and also known as dioxygen or triplet oxygen. Another is the highly reactive ozone (). Others are:
* Ato ...
(O2) pools.
Riverine transport, being the main connective channel of these pools, will act to transport net primary productivity (primarily in the form of dissolved organic carbon
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is the fraction of organic carbon Operational definition, operationally defined as that which can pass through a filter with a pore size typically between 0.22 and 0.7 micrometre, micrometers. The fraction remain ...
(DOC) and particulate organic carbon
Particulate organic matter (POM) is a fraction of total organic matter operationally defined as that which does not pass through a filter pore size that typically ranges in size from 0.053 millimeters (53 μm) to 2 millimeters.
Particulate org ...
(POC)) from terrestrial to oceanic systems. During transport, part of DOC will rapidly return to the atmosphere through redox reaction
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
s, causing "carbon degassing" to occur between land-atmosphere storage layers. The remaining DOC and dissolved inorganic carbon
Dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) is the sum of the aqueous species of inorganic carbon in a solution. Carbon compounds can be distinguished as either organic or inorganic, and as dissolved or particulate, depending on their composition. Organic c ...
(DIC) are also exported to the ocean. In 2015, inorganic and organic carbon export fluxes from global rivers were assessed as 0.50–0.70 Pg C y−1 and 0.15–0.35 Pg C y−1 respectively. On the other hand, POC can remain buried in sediment over an extensive period, and the annual global terrestrial to oceanic POC flux has been estimated at 0.20 (+0.13,-0.07) Gg C y−1.
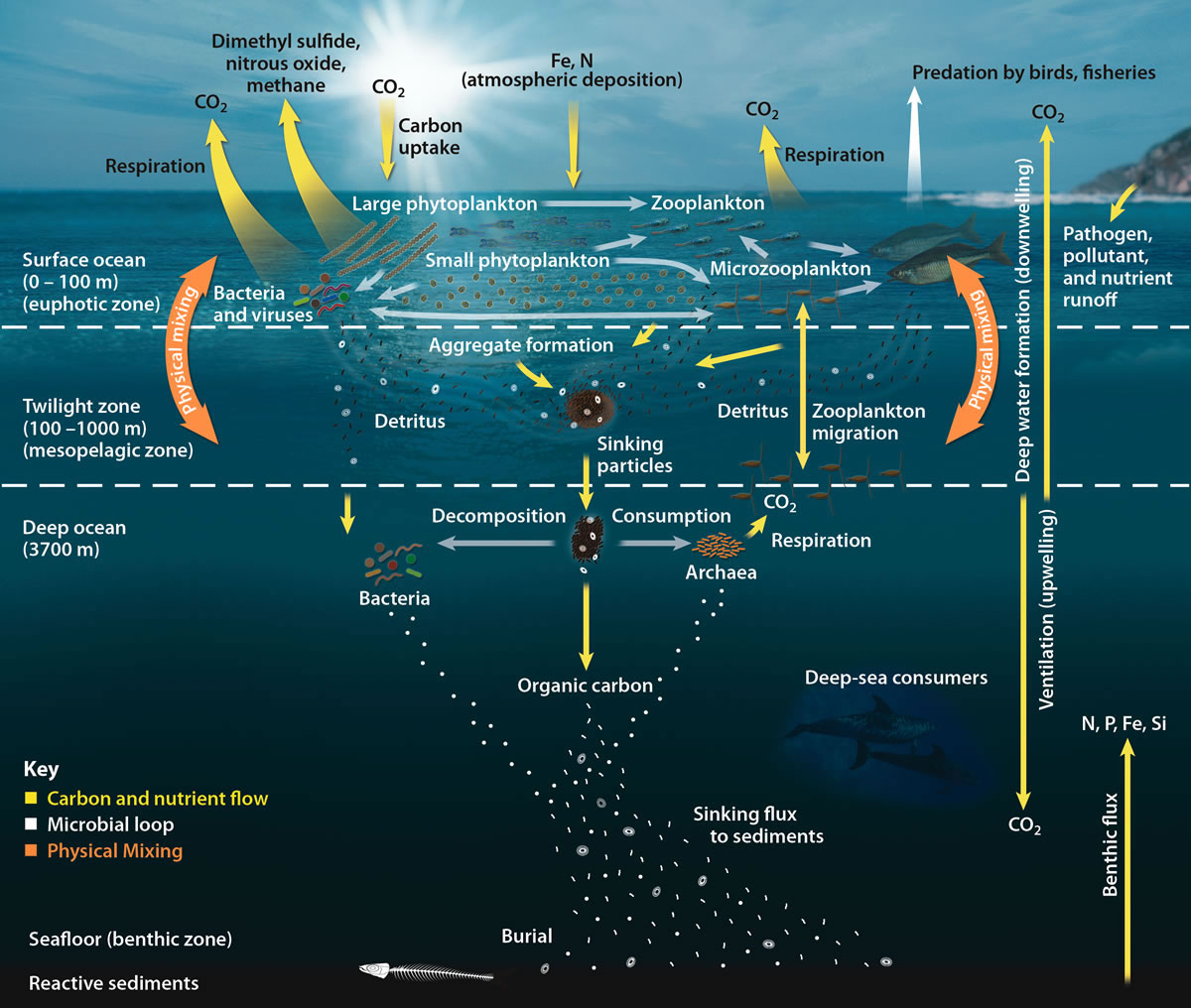
Biological pump in the ocean
 The ocean
The ocean biological pump
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven Carbon sequestration, sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sedim ...
is the ocean's biologically driven sequestration of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
from the atmosphere and land runoff to the deep ocean interior and seafloor sediments. The biological pump is not so much the result of a single process, but rather the sum of a number of processes each of which can influence biological pumping. The pump transfers about 11 billion tonnes of carbon every year into the ocean's interior. An ocean without the biological pump would result in atmospheric CO2 levels about 400 ppm higher than the present day.
Most carbon incorporated in organic and inorganic biological matter is formed at the sea surface where it can then start sinking to the ocean floor. The deep ocean gets most of its nutrients from the higher water column
The (oceanic) water column is a concept used in oceanography to describe the physical (temperature, salinity, light penetration) and chemical ( pH, dissolved oxygen, nutrient salts) characteristics of seawater at different depths for a defined ...
when they sink down in the form of marine snow
In the deep ocean, marine snow (also known as "ocean dandruff") is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. It is a significant means of exporting energy from the light-rich photic zone to ...
. This is made up of dead or dying animals and microbes, fecal matter, sand and other inorganic material.
The biological pump is responsible for transforming dissolved inorganic carbon
Dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) is the sum of the aqueous species of inorganic carbon in a solution. Carbon compounds can be distinguished as either organic or inorganic, and as dissolved or particulate, depending on their composition. Organic c ...
(DIC) into organic biomass and pumping it in particulate
Particulate matter (PM) or particulates are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. An ''aerosol'' is a mixture of particulates and air, as opposed to the particulate matter alone, though it is sometimes define ...
or dissolved form into the deep ocean. Inorganic nutrients and carbon dioxide are fixed during photosynthesis by phytoplankton, which both release dissolved organic matter
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is the fraction of organic carbon Operational definition, operationally defined as that which can pass through a filter with a pore size typically between 0.22 and 0.7 micrometre, micrometers. The fraction remain ...
(DOM) and are consumed by herbivorous zooplankton. Larger zooplankton - such as copepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sedimen ...
s, egest fecal pellet
Feces (also known as faeces or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relatively small amount of ...
s - which can be reingested, and sink or collect with other organic detritus into larger, more-rapidly-sinking aggregates. DOM is partially consumed by bacteria and respired; the remaining refractory DOM is advected and mixed into the deep sea. DOM and aggregates exported into the deep water are consumed and respired, thus returning organic carbon into the enormous deep ocean reservoir of DIC.
A single phytoplankton cell has a sinking rate around one metre per day. Given that the average depth of the ocean is about four kilometres, it can take over ten years for these cells to reach the ocean floor. However, through processes such as coagulation and expulsion in predator fecal pellets, these cells form aggregates. These aggregates have sinking rates orders of magnitude greater than individual cells and complete their journey to the deep in a matter of days.
About 1% of the particles leaving the surface ocean reach the seabed and are consumed, respired, or buried in the sediments. The net effect of these processes is to remove carbon in organic form from the surface and return it to DIC at greater depths, maintaining a surface-to-deep ocean gradient of DIC. Thermohaline circulation
Thermohaline circulation (THC) is a part of the large-scale Ocean current, ocean circulation driven by global density gradients formed by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The name ''thermohaline'' is derived from ''wikt:thermo-, thermo-'', r ...
returns deep-ocean DIC to the atmosphere on millennial timescales. The carbon buried in the sediments can be subducted
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second plat ...
into the earth's mantle
Earth's mantle is a layer of silicate mineral, silicate rock between the Earth's crust, crust and the Earth's outer core, outer core. It has a mass of and makes up 67% of the mass of Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 46% of Earth's ...
and stored for millions of years as part of the slow carbon cycle (see next section).
Viruses as regulators
Viruses act as "regulators" of the fast carbon cycle because they impact the material cycles and energy flows offood web
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Position in the food web, or trophic level, is used in ecology to broadly classify organisms as autotrophs or he ...
s and the microbial loop
The microbial loop describes a trophic pathway where, in aquatic systems, dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is returned to higher trophic levels via its incorporation into bacterial biomass, and then coupled with the classic food chain formed by ph ...
. The average contribution of viruses to the Earth ecosystem carbon cycle is 8.6%, of which its contribution to marine ecosystems (1.4%) is less than its contribution to terrestrial (6.7%) and freshwater (17.8%) ecosystems. Over the past 2,000 years, anthropogenic activities and climate change have gradually altered the regulatory role of viruses in ecosystem carbon cycling processes. This has been particularly conspicuous over the past 200 years due to rapid industrialization and the attendant population growth.

Processes within slow carbon cycle
Slow or deep carbon cycling is an important process, though it is not as well-understood as the relatively fast carbon movement through the atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere, ocean, and geosphere. The deep carbon cycle is intimately connected to the movement of carbon in the Earth's surface and atmosphere. If the process did not exist, carbon would remain in the atmosphere, where it would accumulate to extremely high levels over long periods of time. Therefore, by allowing carbon to return to the Earth, the deep carbon cycle plays a critical role in maintaining the terrestrial conditions necessary for life to exist. Furthermore, the process is also significant simply due to the massive quantities of carbon it transports through the planet. In fact, studying the composition of basalticmagma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma (sometimes colloquially but incorrectly referred to as ''lava'') is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also ...
and measuring carbon dioxide flux out of volcanoes reveals that the amount of carbon in the mantle is actually greater than that on the Earth's surface by a factor of one thousand. Drilling down and physically observing deep-Earth carbon processes is evidently extremely difficult, as the lower mantle and core
Core or cores may refer to:
Science and technology
* Core (anatomy), everything except the appendages
* Core (laboratory), a highly specialized shared research resource
* Core (manufacturing), used in casting and molding
* Core (optical fiber ...
extend from 660 to 2,891 km and 2,891 to 6,371 km deep into the Earth respectively. Accordingly, not much is conclusively known regarding the role of carbon in the deep Earth. Nonetheless, several pieces of evidence—many of which come from laboratory simulations of deep Earth conditions—have indicated mechanisms for the element's movement down into the lower mantle, as well as the forms that carbon takes at the extreme temperatures and pressures of said layer. Furthermore, techniques like seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes (or generally, quakes) and the generation and propagation of elastic ...
have led to a greater understanding of the potential presence of carbon in the Earth's core.
Carbon in the lower mantle
Carbon principally enters the mantle in the form ofcarbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, (), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word "carbonate" may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group ...
-rich sediments on tectonic plates
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed durin ...
of ocean crust, which pull the carbon into the mantle upon undergoing subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second p ...
. Not much is known about carbon circulation in the mantle, especially in the deep Earth, but many studies have attempted to augment our understanding of the element's movement and forms within the region. For instance, a 2011 study demonstrated that carbon cycling extends all the way to the lower mantle. The study analyzed rare, super-deep diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
s at a site in Juina, Brazil, determining that the bulk composition of some of the diamonds' inclusions matched the expected result of basalt melting and crystallisation
Crystallization is a process that leads to solids with highly organized atoms or molecules, i.e. a crystal. The ordered nature of a crystalline solid can be contrasted with amorphous solids in which atoms or molecules lack regular organization ...
under lower mantle temperatures and pressures. Thus, the investigation's findings indicate that pieces of basaltic oceanic lithosphere act as the principle transport mechanism for carbon to Earth's deep interior. These subducted carbonates can interact with lower mantle silicate
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used ...
s, eventually forming super-deep diamonds like the one found.
However, carbonates descending to the lower mantle encounter other fates in addition to forming diamonds. In 2011, carbonates were subjected to an environment similar to that of 1800 km deep into the Earth, well within the lower mantle. Doing so resulted in the formations of magnesite
Magnesite is a mineral with the chemical formula ( magnesium carbonate). Iron, manganese, cobalt, and nickel may occur as admixtures, but only in small amounts.
Occurrence
Magnesite occurs as veins in and an alteration product of ultramafic r ...
, siderite
Siderite is a mineral composed of iron(II) carbonate (FeCO3). Its name comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "iron". A valuable iron ore, it consists of 48% iron and lacks sulfur and phosphorus. Zinc, magnesium, and manganese commonly ...
, and numerous varieties of graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
. Other experiments—as well as petrologic
Petrology () is the branch of geology that studies rock (geology), rocks, their mineralogy, composition, texture, structure and the conditions under which they form. Petrology has three subdivisions: igneous petrology, igneous, metamorphic rock, ...
observations—support this claim, indicating that magnesite is actually the most stable carbonate phase in most part of the mantle. This is largely a result of its higher melting temperature. Consequently, scientists have concluded that carbonates undergo reduction as they descend into the mantle before being stabilised at depth by low oxygen fugacity environments. Magnesium, iron, and other metallic compounds act as buffers throughout the process. The presence of reduced, elemental forms of carbon like graphite would indicate that carbon compounds are reduced as they descend into the mantle.
 Polymorphism alters carbonate compounds' stability at different depths within the Earth. To illustrate, laboratory simulations and
Polymorphism alters carbonate compounds' stability at different depths within the Earth. To illustrate, laboratory simulations and density functional theory
Density functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure (or nuclear structure) (principally the ground state) of many-body ...
calculations suggest that tetrahedrally coordinated carbonates are most stable at depths approaching the core–mantle boundary
The core–mantle boundary (CMB) of Earth lies between the planet's silicate mantle and its liquid iron–nickel outer core, at a depth of below Earth's surface. The boundary is observed via the discontinuity in seismic wave velocities at that ...
. A 2015 study indicates that the lower mantle's high pressure causes carbon bonds to transition from sp2 to sp3 hybridised orbitals, resulting in carbon tetrahedrally bonding to oxygen. CO3 trigonal groups cannot form polymerisable networks, while tetrahedral CO4 can, signifying an increase in carbon's coordination number
In chemistry, crystallography, and materials science, the coordination number, also called ligancy, of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of atoms, molecules or ions bonded to it. The ion/molecule/atom surrounding the central ion ...
, and therefore drastic changes in carbonate compounds' properties in the lower mantle. As an example, preliminary theoretical studies suggest that high pressure causes carbonate melt viscosity to increase; the melts' lower mobility as a result of its increased viscosity causes large deposits of carbon deep into the mantle.
Accordingly, carbon can remain in the lower mantle for long periods of time, but large concentrations of carbon frequently find their way back to the lithosphere. This process, called carbon outgassing, is the result of carbonated mantle undergoing decompression melting, as well as mantle plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic ho ...
s carrying carbon compounds up towards the crust. Carbon is oxidised upon its ascent towards volcanic hotspots, where it is then released as CO2. This occurs so that the carbon atom matches the oxidation state of the basalts erupting in such areas.
Carbon in the core
Although the presence of carbon in the Earth's core is well-constrained, recent studies suggest large inventories of carbon could be stored in this region. Shear (S) waves moving through the inner core travel at about fifty percent of the velocity expected for most iron-rich alloys. Because the core's composition is believed to be an alloy of crystalline iron and a small amount of nickel, this seismic anomaly indicates the presence of light elements, including carbon, in the core. In fact, studies usingdiamond anvil cell
A diamond anvil cell (DAC) is a high-pressure device used in geology, engineering, and materials science experiments. It permits the compression of a small (sub- millimeter-sized) piece of material to extreme pressures, typically up to around 1 ...
s to replicate the conditions in the Earth's core indicate that iron carbide (Fe7C3) matches the inner core's wave speed and density. Therefore, the iron carbide model could serve as an evidence that the core holds as much as 67% of the Earth's carbon. Furthermore, another study found that in the pressure and temperature condition of the Earth's inner core, carbon dissolved in iron and formed a stable phase with the same Fe7C3 composition—albeit with a different structure from the one previously mentioned. In summary, although the amount of carbon potentially stored in the Earth's core is not known, recent studies indicate that the presence of iron carbides can explain some of the geophysical observations.
Human influence on fast carbon cycle
 Since the
Since the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, and especially since the end of WWII
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, human activity has substantially disturbed the global carbon cycle by redistributing massive amounts of carbon from the geosphere. Humans have also continued to shift the natural component functions of the terrestrial biosphere with changes to vegetation and other land use. Man-made (synthetic) carbon compounds have been designed and mass-manufactured that will persist for decades to millennia in air, water, and sediments as pollutants. Climate change is amplifying and forcing further indirect human changes to the carbon cycle as a consequence of various positive and negative feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handle ...
s.
Climate change
Current trends in climate change lead to higher ocean temperatures andacidity
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid.
The first category of acids are the ...
, thus modifying marine ecosystems. Also, acid rain and polluted runoff from agriculture and industry change the ocean's chemical composition. Such changes can have dramatic effects on highly sensitive ecosystems such as coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
s, thus limiting the ocean's ability to absorb carbon from the atmosphere on a regional scale and reducing oceanic biodiversity globally.
The exchanges of carbon between the atmosphere and other components of the Earth system, collectively known as the carbon cycle, currently constitute important negative (dampening) feedbacks on the effect of anthropogenic carbon emissions on climate change. Carbon sinks in the land and the ocean each currently take up about one-quarter of anthropogenic carbon emissions each year.
These feedbacks are expected to weaken in the future, amplifying the effect of anthropogenic carbon emissions on climate change. The degree to which they will weaken, however, is highly uncertain, with Earth system models predicting a wide range of land and ocean carbon uptakes even under identical atmospheric concentration or emission scenarios. Arctic methane emissions
Arctic methane emissions contribute to a rise in Atmospheric methane, methane concentrations in the atmosphere. Whilst the Arctic region is one of Methane emissions, many natural sources of the greenhouse gas methane, there is nowadays also a human ...
indirectly caused by anthropogenic global warming also affect the carbon cycle and contribute to further warming.
Fossil carbon extraction and burning
 The largest and one of the fastest growing human impacts on the carbon cycle and biosphere is the extraction and burning of
The largest and one of the fastest growing human impacts on the carbon cycle and biosphere is the extraction and burning of fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geologica ...
, which directly transfer carbon from the geosphere into the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is also produced and released during the calcination
Calcination is thermal treatment of a solid chemical compound (e.g. mixed carbonate ores) whereby the compound is raised to high temperature without melting under restricted supply of ambient oxygen (i.e. gaseous O2 fraction of air), generally f ...
of limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
for clinker production. Clinker is an industrial precursor of cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
.
, about 450 gigatons of fossil carbon have been extracted in total; an amount approaching the carbon contained in all of Earth's living terrestrial biomass. Recent rates of global emissions directly into the atmosphere have exceeded the uptake by vegetation and the oceans. These sink
A sink (also known as ''basin'' in the UK) is a bowl-shaped plumbing fixture for washing hands, dishwashing, and other purposes. Sinks have a tap (faucet) that supplies hot and cold water and may include a spray feature to be used for fas ...
s have been expected and observed to remove about half of the added atmospheric carbon within about a century. Nevertheless, sinks like the ocean have evolving saturation properties, and a substantial fraction (20–35%, based on coupled models) of the added carbon is projected to remain in the atmosphere for centuries to millennia.
Halocarbons
Halocarbons are less prolific compounds developed for diverse uses throughout industry; for example assolvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
s and refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the cooling, heating, or reverse cooling/heating cycles of air conditioning systems and heat pumps, where they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are ...
s. Nevertheless, the buildup of relatively small concentrations (parts per trillion) of chlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly Halogenation, halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F). They are produced as volatility (chemistry), volat ...
, hydrofluorocarbon
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) are synthetic organic compounds that contain fluorine and hydrogen atoms, and are the most common type of organofluorine compounds. Most are gases at room temperature and pressure. They are frequently used in air condit ...
, and perfluorocarbon
Fluorocarbons are chemical compounds with carbon-fluorine bonds. Compounds that contain many C-F bonds often have distinctive properties, e.g., enhanced stability, volatility, and hydrophobicity. Several fluorocarbons and their derivatives are ...
gases in the atmosphere is responsible for about 10% of the total direct radiative forcing
Radiative forcing (or climate forcing) is a concept used to quantify a change to the balance of energy flowing through a planetary atmosphere. Various factors contribute to this change in energy balance, such as concentrations of greenhouse gases ...
from all long-lived greenhouse gases (year 2019); which includes forcing from the much larger concentrations of carbon dioxide and methane. Chlorofluorocarbons also cause stratospheric ozone depletion
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a lowered total amount of ozone in Earth, Earth's upper atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone layer) around Earth's polar ...
. International efforts are ongoing under the Montreal Protocol
The Montreal Protocol on Substances That Deplete the Ozone Layer is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of numerous substances that are responsible for ozone depletion. It was agreed on 16 ...
and Kyoto Protocol
The was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that global warming is oc ...
to control rapid growth in the industrial manufacturing and use of these environmentally potent gases. For some applications more benign alternatives such as hydrofluoroolefin
Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) are Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated organic compounds composed of hydrogen, fluorine and carbon. These organofluorine compounds are of interest as refrigerants. Unlike traditional hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs ...
s have been developed and are being gradually introduced.
Land use changes
Since the invention of agriculture, humans have directly and gradually influenced the carbon cycle over century-long timescales by modifying the mixture of vegetation in the terrestrial biosphere. Over the past several centuries, direct and indirect human-causedland use
Land use is an umbrella term to describe what happens on a parcel of land. It concerns the benefits derived from using the land, and also the land management actions that humans carry out there. The following categories are used for land use: fo ...
and land cover change (LUCC) has led to the loss of biodiversity
Biodiversity loss happens when plant or animal species disappear completely from Earth (extinction) or when there is a decrease or disappearance of species in a specific area. Biodiversity loss means that there is a reduction in biological dive ...
, which lowers ecosystems' resilience to environmental stresses and decreases their ability to remove carbon from the atmosphere. More directly, it often leads to the release of carbon from terrestrial ecosystems into the atmosphere.
Deforestation for agricultural purposes removes forests, which hold large amounts of carbon, and replaces them, generally with agricultural or urban areas. Both of these replacement land cover types store comparatively small amounts of carbon so that the net result of the transition is that more carbon stays in the atmosphere. However, the effects on the atmosphere and overall carbon cycle can be intentionally and/or naturally reversed with reforestation
Reforestation is the practice of restoring previously existing forests and woodlands that have been destroyed or damaged. The prior forest destruction might have happened through deforestation, clearcutting or wildfires. Three important purpose ...
.
See also
* * * * * * * *References
External links
Carbon Cycle Science Program
– an interagency partnership.
Global Carbon Project – initiative of the Earth System Science Partnership
carbon levels and flows {{DEFAULTSORT:Carbon Cycle Chemical oceanography Photosynthesis Soil biology Soil chemistry Numerical climate and weather models Effects of climate change