|
Pedosphere
The pedosphere () is the Earth's crust, outermost layer of the Earth that is composed of soil and subject to soil formation processes. It exists at the interface of the lithosphere, Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere. The pedosphere is the skin of the Earth and only develops when there is a dynamic interaction between the atmosphere (air in and above the soil), biosphere (living organisms), lithosphere (unconsolidated regolith and consolidated bedrock) and the hydrosphere (water in, on and below the soil). The pedosphere is the foundation of terrestrial life on Earth. The pedosphere acts as the mediator of chemical and Biogeochemistry, biogeochemical flux into and out of these respective systems and is made up of gaseous, mineralic, fluid and biologic components. The pedosphere lies within the Critical Zone, a broader interface that includes vegetation, pedosphere, aquifer systems, regolith and finally ends at some depth in the bedrock where the biosphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by restricting the former term specifically to displaced soil. Soil consists of a solid collection of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a porous phase that holds gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three- state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering with associated erosion. Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, soil ecologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more. The crust and upper mantle are distinguished on the basis of chemistry and mineralogy. Earth's lithosphere Earth's lithosphere, which constitutes the hard and rigid outer vertical layer of the Earth, includes the crust and the lithospheric mantle (or mantle lithosphere), the uppermost part of the mantle that is not convecting. The layer below the lithosphere is called the asthenosphere, which is the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle that is able to convect. The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary is defined by a difference in response to stress. The lithosphere remains rigid for very long periods of geologic time in which it deforms elastically and through brittle f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere () is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the Planetary surface, surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, it continues to change in shape. This is caused by seafloor spreading and continental drift, which rearranges the land and ocean."Our Changing Planet: an Introduction to Earth System Science and Global Environmental Change." Our Changing Planet: an Introduction to Earth System Science and Global Environmental Change, by Fred T. Mackenzie, 2nd ed., Pearson Education, 2011, pp. 88–91. It has been estimated that there are 1.386 billion Cubic kilometer, cubic kilometres (333 million cubic miles) of water on Earth.Where is Earth's water? United States Geological Sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be accepted by Earth science, geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid-to-late 1960s. The processes that result in plates and shape Earth's crust are called ''tectonics''. Tectonic plates also occur in other planets and moons. Earth's lithosphere, the rigid outer shell of the planet including the crust (geology), crust and upper mantle, is fractured into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary (or fault (geology), fault): , , or . The relative movement of the plates typically ranges from zero to 10 cm annu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geochemistry
Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing the entire Solar System, and has made important contributions to the understanding of a number of processes including mantle convection, the formation of planets and the origins of granite and basalt. It is an integrated field of chemistry and geology. History The term ''geochemistry'' was first used by the Swiss-German chemist Christian Friedrich Schönbein in 1838: "a comparative geochemistry ought to be launched, before geognosy can become geology, and before the mystery of the genesis of our planets and their inorganic matter may be revealed." However, for the rest of the century the more common term was "chemical geology", and there was little contact between geologists and chemists. Geochemistry emerged as a separate discipline after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedimentation is any process that causes these particles to settle in place. Geological detritus originates from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or Mass wasting, mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus is formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies (marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur when dissolved minerals precipitate from aqueous solution, water solution. The sedimentary rock cover of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust. Geological significance Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the top of the Earth's crust by volume. Igneous rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphic Rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causing profound physical or chemical changes. During this process, the rock remains mostly in the solid state, but gradually recrystallizes to a new texture or mineral composition. The protolith may be an igneous, sedimentary, or existing metamorphic rock. Metamorphic rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust and form 12% of the Earth's land surface. They are classified by their protolith, their chemical and mineral makeup, and their texture. They may be formed simply by being deeply buried beneath the Earth's surface, where they are subject to high temperatures and the great pressure of the rock layers above. They can also form from tectonic processes such as continental collisions, which cause horizontal pressure, friction, and dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Rock
Volcanic rocks (often shortened to volcanics in scientific contexts) are rocks formed from lava erupted from a volcano. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic rock is artificial, and in nature volcanic rocks grade into hypabyssal and metamorphic rocks and constitute an important element of some sediments and sedimentary rocks. For these reasons, in geology, volcanics and shallow hypabyssal rocks are not always treated as distinct. In the context of Precambrian shield geology, the term "volcanic" is often applied to what are strictly metavolcanic rocks. Volcanic rocks and sediment that form from magma erupted into the air are called "pyroclastics," and these are also technically sedimentary rocks. Volcanic rocks are among the most common rock types on Earth's surface, particularly in the oceans. On land, they are very common at plate boundaries and in flood basalt provinces. It has been estimated that volcanic rocks cover about 8% of the Earth's current land surface. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Crust
Earth's crust is its thick outer shell of rock, referring to less than one percent of the planet's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a solidified division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The lithosphere is broken into tectonic plates whose motion allows heat to escape the interior of Earth into space. The crust lies on top of the mantle, a configuration that is stable because the upper mantle is made of peridotite and is therefore significantly denser than the crust. The boundary between the crust and mantle is conventionally placed at the Mohorovičić discontinuity, a boundary defined by a contrast in seismic velocity. The temperature of the crust increases with depth, reaching values typically in the range from about at the boundary with the underlying mantle. The temperature increases by as much as for every kilometer locally in the upper part of the crust. Composition File:Elementa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
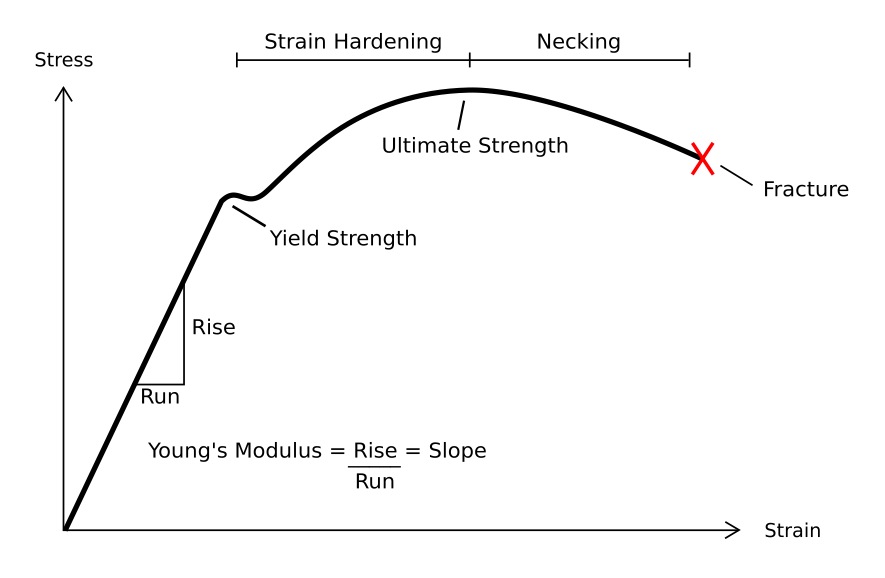
Deformation (engineering)
In engineering, deformation (the change in size or shape of an object) may be ''elastic'' or ''plastic''. If the deformation is negligible, the object is said to be ''rigid''. Main concepts Occurrence of deformation in engineering applications is based on the following background concepts: * ''Displacements'' are any change in position of a point on the object, including whole-body translations and rotations ( rigid transformations). * ''Deformation'' are changes in the relative position between internals points on the object, excluding rigid transformations, causing the body to change shape or size. * ''Strain'' is the ''relative'' ''internal'' deformation, the dimensionless change in shape of an infinitesimal cube of material relative to a reference configuration. Mechanical strains are caused by mechanical stress, ''see stress-strain curve''. The relationship between stress and strain is generally linear and reversible up until the yield point and the deformation is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one species of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid. Ion exchange is used in softening or demineralizing of water, purification of chemicals, and separation of substances. Ion exchange usually describes a process of purification of aqueous solutions using solid polymeric ion-exchange resin. More precisely, the term encompasses a large variety of processes where ions are exchanged between two electrolytes. Aside from its use to purify drinking water, the technique is widely applied for purification and separation of a variety of industrially and medicinally important chemicals. Although the term usually refers to applications of synthetic (human-made) resins, it can include many other materials such as soil. Typical ion exchangers are ion-exchange resins (functionalized porous or gel polymer), zeolites, montmorillonite, clay, and soil humus. Ion exchangers are ei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |