Siberia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the
 Siberia in Paleozoic times formed the continent of Siberia/Angaraland, which fused to Euramerica during the Late
Siberia in Paleozoic times formed the continent of Siberia/Angaraland, which fused to Euramerica during the Late

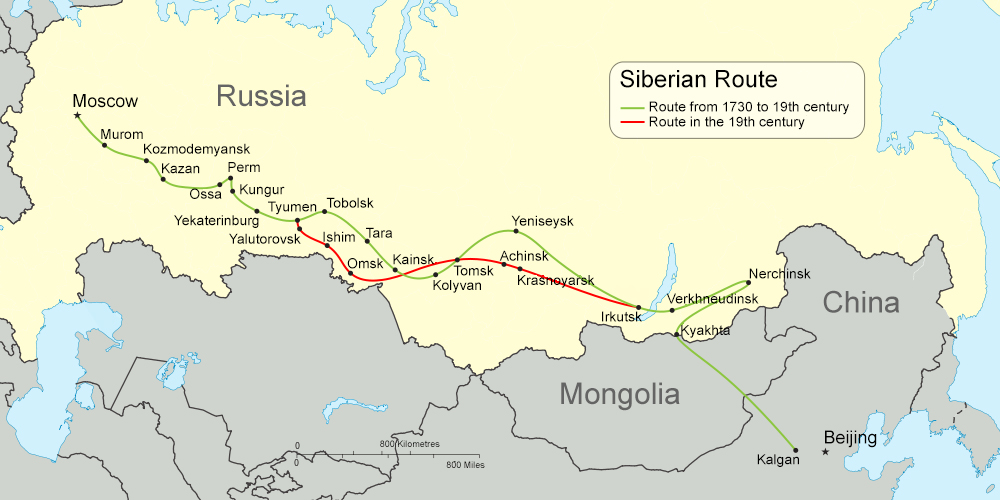 By the mid-17th century, Russia had established areas of control that extended to the Pacific Ocean. Some 230,000 Russians had settled in Siberia by 1709. Siberia became one of the destinations for sending internal
By the mid-17th century, Russia had established areas of control that extended to the Pacific Ocean. Some 230,000 Russians had settled in Siberia by 1709. Siberia became one of the destinations for sending internal
 In the early decades of the
In the early decades of the

 The Central Siberian Plateau is an ancient craton (sometimes named ''Angaraland'') that formed an independent
The Central Siberian Plateau is an ancient craton (sometimes named ''Angaraland'') that formed an independent
"Pleistocene Park: Return of the mammoths' ecosystem"
In: ''
www.pleistocenepark.ru/en/ – Materials.
Retrieved 5 May 2013. According to Vasily Kryuchkov, approximately 31,000 square kilometers of the Russian Arctic has been subjected to severe environmental disturbance.
 *
*
 * Snow leopard
* Amur leopard
* Siberian tiger
* Eurasian lynx
* Pallas cat
* Snow leopard
* Amur leopard
* Siberian tiger
* Eurasian lynx
* Pallas cat
 * Asian black bear
* Brown bear
* Polar bear
* Asian black bear
* Brown bear
* Polar bear
 * '' Larix sibirica''
* '' Larix gmelinii''
* '' Picea obovata''
* '' Pinus pumila''
* '' Larix sibirica''
* '' Larix gmelinii''
* '' Picea obovata''
* '' Pinus pumila''

 The term "Siberia" has both a long history and wide significance, and association. The understanding, and association of "Siberia" have gradually changed during the ages. Historically, Siberia was defined as the whole part of Russia and North Kazakhstan to the east of Ural Mountains, including the
The term "Siberia" has both a long history and wide significance, and association. The understanding, and association of "Siberia" have gradually changed during the ages. Historically, Siberia was defined as the whole part of Russia and North Kazakhstan to the east of Ural Mountains, including the 
 The Yenisey Krasnoyarsk basketball team has played in the VTB United League since 2011–12.
Russia's third most popular sport,
The Yenisey Krasnoyarsk basketball team has played in the VTB United League since 2011–12.
Russia's third most popular sport,
 The largest ethnic group in Siberia is Slavic-origin
The largest ethnic group in Siberia is Slavic-origin
 There are a variety of beliefs throughout Siberia, including Orthodox Christianity, other denominations of Christianity,
There are a variety of beliefs throughout Siberia, including Orthodox Christianity, other denominations of Christianity,
''East of the Sun: the epic conquest and tragic history of Siberia''
(Henry Holt and Company, 1993); popular history * * Diment, Galya, and Yuri Slezkine, eds. ''Between Heaven and Hell: The Myth of Siberia in Russian Culture'' (3rd ed. 1993) * * Forsyth, James. ''A History of the Peoples of Siberia: Russia's North Asian Colony, 1581–1990'' (Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 1994). * * Kotkin, Stephen, and David Wolff, eds. (1995)
''Rediscovering Russia in Asia''
* * Lincoln, W. Bruce (1993
''The Conquest of a Continent''
Scholarly history. * * * * * Wood, Alan (ed.)(1991). ''The History of Siberia: From Russian Conquest to Revolution''. London: Routledge. * {{Authority control Eurasian Steppe Geography of Russia Regions of Russia Geography of Kazakhstan
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and its predecessor states since the lengthy conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall of the Khanate of Sibir in 1582 and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to roughly a quarter of Russia's population. Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siber ...
, Krasnoyarsk, and Omsk are the largest cities in the area.
Because Siberia is a geographic and historic concept and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia spans the entire expanse of land from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
, with the Ural River usually forming the southernmost portion of its western boundary, and includes most of the drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
of the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
. It is further defined as stretching from the territories within the Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the northernmost of the five major circle of latitude, circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth at about 66° 34' N. Its southern counterpart is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circl ...
in the north to the northern borders of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
, and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
in the south, although the hills of north-central Kazakhstan are also commonly included. The Russian government divides the region into three federal districts (groupings of Russian federal subjects), of which only the central one is officially referred to as " Siberian"; the other two are the Ural and Far Eastern federal districts, named for the Ural and Russian Far East
The Russian Far East ( rus, Дальний Восток России, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asia, Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Easte ...
regions that correspond respectively to the western and eastern thirds of Siberia in the broader sense.
Siberia is known for its long, harsh winters, with a January average of −25 °C (−13 °F). Although it is geographically located in Asia, Russian sovereignty and colonization since the 16th century has led to perceptions of the region as culturally and ethnically European. Over 85% of its population are of European descent, chiefly Russian (comprising the Siberian sub-ethnic group), and Eastern Slavic cultural influences predominate throughout the region. Nevertheless, there exist sizable ethnic minorities of Asian lineage, including various Turkic communities—many of which, such as the Yakuts, Tuvans, Altai, and Khakas, are Indigenous—along with the Mongolic Buryats, ethnic Koreans
Koreans are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula. The majority of Koreans live in the two Korean sovereign states of North and South Korea, which are collectively referred to as Korea. As of 2021, an estimated 7.3 m ...
, and smaller groups of Samoyedic and Tungusic peoples (several of whom are classified as Indigenous small-numbered peoples by the Russian government), among many others.
Etymology
The origin of the name is uncertain. In the Russian language, it was adopted as a toponym through contact with the Khanate of Sibir (Сибирское ханство) since the 15th century. The Russian name '' Yugra'' was applied to the northern lands east of the Urals, which had been known of since the 11th century or earlier, while the name ''Siberia'' is first mentioned in Russian chronicles at the start of the 15th century in connection with the death of the khan Tokhtamysh, in "the Siberian land". Some sources say that "Siberia" originates from the Siberian Tatar word for 'sleeping land' (''Sib-ir''), but this discourse does not correspond to the actual Siberian Tatar language. Mongolist György Kara posits that the toponym ''Siberia'' is derived from a Mongolic word ''sibir'', cognate with modern Buryat ''sheber'' 'dense forest'. A different hypothesis claims that the region was named after the Sibe people. Another account sees the name as the ancient tribal ethnonym of the Sihirtia or Sirtya (also ''Sypyr'' ʲɵpᵻr), a hypothetical Paleo-Asiatic ethnic group assimilated by the Nenets. The Polish historian Jan Chyliczkowski has proposed that the name derives from the Proto-Slavic word for 'north' (cf. Russian север ''sever''), as in Severia. Anatole Baikaloff has dismissed this explanation. He said that the neighboring Chinese, Turks, and Mongolians, who have similar names for the region, would not have known Russian. He suggested that the name might be a combination of two words with Turkic origin, ''su'' 'water' and ''bir'' 'wild land'.History
Prehistory
 Siberia in Paleozoic times formed the continent of Siberia/Angaraland, which fused to Euramerica during the Late
Siberia in Paleozoic times formed the continent of Siberia/Angaraland, which fused to Euramerica during the Late Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
, as part of the formation of Pangea.
The Siberian Traps were formed by one of the largest-known volcanic events of the last 251 million years of Earth's geological history. Their activity continued for a million years and some scientists consider it a possible cause of the " Great Dying" about 250 million years ago, – estimated to have killed 90% of species existing at the time.
The region has paleontological significance, as it contains bodies of prehistoric animals from the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
Epoch, preserved in ice or permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
. Specimens of Goldfuss cave lion cubs, Yuka the mammoth and another woolly mammoth from Oymyakon
Oymyakon is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, rural locality (a ''village#Russia, selo'') in Oymyakonsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located in the Yana-Oymyakon Highlands, along the Indigirka River, northwest of Tomtor, Oy ...
, a woolly rhinoceros from the Kolyma, and bison
A bison (: bison) is a large bovine in the genus ''Bison'' (from Greek, meaning 'wild ox') within the tribe Bovini. Two extant taxon, extant and numerous extinction, extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American ...
and horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
s from Yukagir have been found. Remote Wrangel Island and the Taymyr Peninsula are believed to have been the last places on Earth to support woolly mammoths as isolated populations until their extinction around 2000 BC.
At least three species of humans lived in southern Siberia around 40,000 years ago: '' H. sapiens'', '' H. neanderthalensis'', and the Denisovans
The Denisovans or Denisova hominins ( ) are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human that ranged across Asia during the Lower Paleolithic, Lower and Middle Paleolithic, and lived, based on current evidence, from 285 thousand to 25 thou ...
.
In 2010, DNA evidence identified the last as a separate species.
Late Paleolithic southern Siberians appear to be related to Paleolithic Europeans and the Paleolithic Jōmon people of Japan. Ancient DNA analysis has revealed that the oldest fossil known to carry the derived KITLG allele, which is responsible for blond hair in modern Europeans, is a 17,000 year old Ancient North Eurasian specimen from Siberia., Ancient North Eurasian populations genetically similar to Mal'ta–Buret' culture and Afontova Gora were an important genetic contributor to Native Americans, Europeans, Ancient Central Asians, South Asians, and some East Asian groups (such as the Ainu people
The Ainu are an Indigenous peoples, indigenous ethnic group who reside in northern Japan and southeastern Russia, including Hokkaido and the Tōhoku region of Honshu, as well as the land surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, such as Sakhalin, the Ku ...
). Evidence from full genomic studies suggests that the first people in the Americas diverged from Ancient East Asians about 36,000 years ago and expanded northwards into Siberia, where they encountered and interacted with Ancient North Eurasians, giving rise to both Paleosiberian peoples and Ancient Native Americans, which later migrated towards the Beringian region, became isolated from other populations, and subsequently populated the Americas.
Early history
During past millennia, different groups of nomads – such as the Enets, the Nenets, theHuns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
, the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, t ...
, the Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian noma ...
, and the Yugur – inhabited various parts of Siberia. The Afanasievo and Tashtyk cultures of the Yenisey valley and Altay Mountains are associated with the Indo-European migrations
The Indo-European migrations are hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-Europeans, peoples who spoke Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European (PIE) and the derived Indo-European languages, which took place from around 4000 to 1000 BCE, ...
across Eurasia. The proto-Mongol Khitan people also occupied parts of the region.
In the 13th century, during the period of the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
, the Mongols conquered a large part of this area. With the breakup of the Golden Horde, the autonomous Khanate of Sibir was formed in the late-15th century. Turkic-speaking Yakut migrated north from the Lake Baikal region under pressure from the Mongol tribes from the 13th to 15th centuries. Siberia remained a sparsely populated area. Historian John F. Richards wrote: "it is doubtful that the total early modern Siberian population exceeded 300,000 persons".
Early Russian exploration
The first mention of Siberia in chronicles is recorded in the year 1032. The city-state ofNovgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( ; , ; ), also known simply as Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the oldest cities in Russia, being first mentioned in the 9th century. The city lies along the V ...
established two trade routes to the Ob River, and laid claim to the lands the Russians called '' Yugra''. The Russians were attracted by its furs in particular. Novgorod launched military campaigns to extract tribute from the local population, but often met resistance, such as two campaigns in 1187 and 1193 mentioned in chronicles that were defeated. After Novgorod was annexed by Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
, the newly emerging centralized Russian state also laid claim to the region, with Ivan III of Russia sending expeditionary forces to Siberia in 1483 and 1499–1500. The Russians received tribute, but contact with the tribes ceased after they left.
The growing power of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
began to undermine the Siberian Khanate in the 16th century. First, groups of traders and Cossacks began to enter the area. The Russian army was directed to establish forts farther and farther east to protect new Russian settlers who migrated from Europe. Towns such as Mangazeya, Tara, Yeniseysk, and Tobolsk developed, the last becoming the ''de facto'' capital of Siberia from 1590. At this time, ''Sibir'' was the name of a fortress at Qashliq, near Tobolsk. Gerardus Mercator
Gerardus Mercator (; 5 March 1512 – 2 December 1594) was a Flemish people, Flemish geographer, cosmographer and Cartography, cartographer. He is most renowned for creating the Mercator 1569 world map, 1569 world map based on a new Mercator pr ...
, in a map published in 1595, marks ''Sibier'' both as the name of a settlement and of the surrounding territory along a left tributary of the Ob. Other sources contend that the Sibe, an Indigenous Tungusic people, offered fierce resistance to Russian expansion beyond the Urals. Some suggest that the term "Siberia" is a russification of their ethnonym.
Russian Empire
 By the mid-17th century, Russia had established areas of control that extended to the Pacific Ocean. Some 230,000 Russians had settled in Siberia by 1709. Siberia became one of the destinations for sending internal
By the mid-17th century, Russia had established areas of control that extended to the Pacific Ocean. Some 230,000 Russians had settled in Siberia by 1709. Siberia became one of the destinations for sending internal exile
Exile or banishment is primarily penal expulsion from one's native country, and secondarily expatriation or prolonged absence from one's homeland under either the compulsion of circumstance or the rigors of some high purpose. Usually persons ...
s. Exile was the main Russian punitive practice with more than 800,000 people exiled during the nineteenth century.
The first great modern change in Siberia was the Trans-Siberian Railway, constructed during 1891–1916. It linked Siberia more closely to the rapidly industrialising Russia of Nicholas II (). Around seven million Russians moved to Siberia from Europe between 1801 and 1914. Between 1859 and 1917, more than half a million people migrated to the Russian Far East. Siberia has extensive natural resources: during the 20th century, large-scale exploitation of these took place, and industrial towns cropped up throughout the region.
At 7:15 a.m. on 30 June 1908, the Tunguska Event felled millions of trees near the Podkamennaya Tunguska River (Stony Tunguska River) in central Siberia. Most scientists believe this resulted from the air burst of a meteor or a comet. Even though no crater has ever been found, the landscape in the (sparsely inhabited) area still bears the scars of this event.
Soviet Union
 In the early decades of the
In the early decades of the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
(especially in the 1930s and 1940s), the government used the Gulag
The Gulag was a system of Labor camp, forced labor camps in the Soviet Union. The word ''Gulag'' originally referred only to the division of the Chronology of Soviet secret police agencies, Soviet secret police that was in charge of runnin ...
state agency to administer a system of penal labour camps, replacing the previous katorga system. According to semi-official Soviet estimates, which did not become public until after the fall of the Soviet government in 1991, from 1929 to 1953 more than 14 million people passed through these camps and prisons, many of them in Siberia. Another seven to eight million people were internally deported to remote areas of the Soviet Union (including entire nationalities or ethnicities in several cases).
Half a million (516,841) prisoners died in camps from 1941 to 1943 during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. At other periods, mortality was comparatively lower. The size, scope, and scale of the Gulag slave-labour camps remain subjects of much research and debate. Many Gulag camps operated in extremely remote areas of northeastern Siberia. The best-known clusters included '' Sevvostlag'' (''the North-East Camps'') along the Kolyma and '' Norillag'' near Norilsk, where 69,000 prisoners lived in 1952. Major industrial cities of Northern Siberia, such as Norilsk and Magadan
Magadan ( rus, Магадан, p=məɡɐˈdan) is a Port of Magadan, port types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative centre of Magadan Oblast, Russia. The city is located on the isthmus of the Staritsky Peninsula by the ...
, developed from camps built by prisoners and run by former prisoners.
Russian Federation
On 2 December 2019, the ' Power of Siberia' gas pipeline started functioning. The project was started in 2014 to supply natural gas from Siberia toChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
.
Geography
Siberia spans an area of , covering the vast majority of Russia's total territory, and almost 9% of Earth's land surface (). It geographically falls in Asia, but is culturally and politically considered European, since it is a part of Russia. Major geographical zones within Siberia include the West Siberian Plain and the Central Siberian Plateau. Eastern and central Sakha comprises numerous north–south mountain ranges of various ages. These mountains extend up to almost , but above a few hundred metres they are almost completely devoid of vegetation. The Verkhoyansk Range was extensively glaciated in the Pleistocene, but the climate was too dry for glaciation to extend to low elevations. At these low elevations are numerous valleys, many of them deep and covered with larch forest, except in the extreme north where thetundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic ...
dominates. Soils are mainly turbels (a type of gelisol). The active layer tends to be less than one metre deep, except near rivers.
The highest point in Siberia is the active volcano
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most oft ...
Klyuchevskaya Sopka, on the Kamchatka Peninsula. Its peak reaches .
Mountain ranges
*Altai Mountains
The Altai Mountains (), also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central Asia, Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob River, Ob have their headwaters. The ...
* Anadyr Highlands
* Baikal Mountains
* Khamar-Daban
* Chersky Range
* Chukotka Mountains
* Dzhugdzhur Mountains
* Kolyma Mountains
* Koryak Mountains
* Sayan Mountains
The Sayan Mountains (, ; ) are a mountain range in southern Siberia spanning southeastern Russia (Buryatia, Irkutsk Oblast, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Tuva and Khakassia) and northern Mongolia. Before the rapid expansion of the Tsardom of Russia, the mou ...
* Tannu-Ola Mountains
* Ural Mountains
* Verkhoyansk Mountains
* Yablonoi Mountains
Geomorphological regions
* Central Siberian Plateau * Central Yakutian Lowland * East Siberian Lowland * East Siberian Mountains * North Siberian Lowland * South Siberian Mountains * West Siberian LowlandLakes and rivers
* Alazeya * Anabar * Angara * Indigirka * Irtysh * Kolyma * Lake Baikal * Lena * Nizhnyaya Tunguska * Novosibirsk Reservoir * Ob * Podkamennaya Tunguska * Popigay * Upper Angara * Uvs Nuur * Yana * YeniseyGrasslands
* Ukok Plateau—part of aUNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
Geology
The West Siberian Plain, consisting mostly of Cenozoic alluvial deposits, is somewhat flat. In the mid-Pleistocene, many deposits on this plain resulted from ice dams which produced a large glacial lake. This mid- to late-Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
lake blocked the northward flow of the Ob and Yenisey rivers, resulting in a redirection southwest into the Caspian and Aral seas via the Turgai Valley. The area is very swampy, and soils are mostly peaty histosols and, in the treeless northern part, histels. In the south of the plain, where permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
is largely absent, rich grasslands that are an extension of the Kazakh Steppe
The Kazakh Steppe ( ), also known as the Great Steppe or Great Betpak-Dala, Dala ( ), is a vast region of open grassland in Central Asia, covering areas in northern Kazakhstan and adjacent areas of Russia. It lies east of the Pontic–Caspian step ...
formed the original vegetation, most of which is no longer visible.

 The Central Siberian Plateau is an ancient craton (sometimes named ''Angaraland'') that formed an independent
The Central Siberian Plateau is an ancient craton (sometimes named ''Angaraland'') that formed an independent continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
before the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
(see the Siberian continent). It is exceptionally rich in minerals, containing large deposits of gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
s, and ores of manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
, lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
, zinc, nickel, cobalt, and molybdenum. Much of the area includes the Siberian Traps—a large igneous province. A massive eruptive period approximately coincided with the Permian–Triassic extinction event. The volcanic event is one of the largest known volcanic eruptions in Earth's history. Only the extreme northwest was glaciated during the Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
, but almost all is under exceptionally deep permafrost, and the only tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only ...
that can thrive, despite the warm summers, is the deciduous Siberian Larch (''Larix sibirica'') with its very shallow roots. Outside the extreme northwest, the taiga is dominant, covering a significant fraction of the entirety of Siberia. Soils here are mainly turbels, giving way to spodosols where the active layer becomes thicker and the ice-content lower.
The ''Lena-Tunguska petroleum province'' includes the Central Siberian platform (some authors refer to it as the "Eastern Siberian platform"), bounded on the northeast and east by the Late Carboniferous through Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
Verkhoyansk foldbelt, on the northwest by the Paleozoic Taymr foldbelt, and on the southeast, south and southwest by the Middle Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
to Middle Devonian Baykalian foldbelt.Meyerhof, A. A., 1980, "Geology and Petroleum Fields in Proterozoic and Lower Cambrian Strata, Lena-Tunguska Petroleum Province, Eastern Siberia, USSR", in ''Giant Oil and Gas Fields of the Decade: 1968–1978'', AAPG Memoir 30, Halbouty, M. T., editor, Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, A regional geologic reconnaissance study begun in 1932 and followed by surface and subsurface mapping revealed the Markova-Angara Arch ( anticline). This led to the discovery of the Markovo Oil Field in 1962 with the Markovo—1 well, which produced from the Early Cambrian Osa Horizon bar-sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
at a depth of . The ''Sredne-Botuobin Gas Field'' was discovered in 1970, producing from the Osa and the Proterozoic Parfenovo Horizon. The Yaraktin Oil Field was discovered in 1971, producing from the Vendian
The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last ...
Yaraktin Horizon at depths of up to , which lies below Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
to Lower Jurassic basalt traps.
Climate
The climate of Siberia varies dramatically, but it typically has warm but short summers and long, brutally cold winters. On the north coast, north of theArctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the northernmost of the five major circle of latitude, circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth at about 66° 34' N. Its southern counterpart is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circl ...
, there is a very short (about one month long) summer.
Almost all the population lives in the south, along the route of the Trans-Siberian Railway. The climate in this southernmost part is humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold ...
(Köppen ''Dfa/Dfb'' or ''Dwa/Dwb'') with cold winters but fairly warm summers lasting at least four months. The annual average temperature is about . January averages about and July about , while daytime temperatures in summer typically exceed . With a reliable growing season, an abundance of sunshine and exceedingly fertile chernozem soils, southern Siberia is good enough for profitable agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
, as was demonstrated in the early 20th century.
By far the most commonly occurring climate in Siberia is continental subarctic (Koppen ''Dfc'', ''Dwc'', or ''Dsc''), with the annual average temperature about and an average for January of and an average for July of , although this varies considerably, with a July average about in the taiga–tundra ecotone. The business
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for ...
-oriented website and blog ''Business Insider'' lists Verkhoyansk and Oymyakon
Oymyakon is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, rural locality (a ''village#Russia, selo'') in Oymyakonsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located in the Yana-Oymyakon Highlands, along the Indigirka River, northwest of Tomtor, Oy ...
, in Siberia's Sakha Republic
Sakha, officially the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), is a republics of Russia, republic of Russia, and the largest federal subject of Russia by area. It is located in the Russian Far East, along the Arctic Ocean, with a population of one million ...
, as being in competition for the title of the Northern Hemisphere's ''Pole of Cold
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
''. Oymyakon
Oymyakon is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, rural locality (a ''village#Russia, selo'') in Oymyakonsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located in the Yana-Oymyakon Highlands, along the Indigirka River, northwest of Tomtor, Oy ...
is a village which recorded a temperature of on 6 February 1933. Verkhoyansk, a town further north and further inland, recorded a temperature of for three consecutive nights: 5, 6 and 7 February 1933. Each town is alternately considered the Northern Hemisphere's Pole of Cold – the coldest inhabited point in the Northern hemisphere. Each town also frequently reaches in the summer, giving them, and much of the rest of Russian Siberia, the world's greatest temperature variation between summer's highs and winter's lows, often well over between the seasons.
Southwesterly winds bring warm air from Central Asia and the Middle East. The climate in West Siberia (Omsk, or Novosibirsk) is several degrees warmer than in the East (Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and , ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 587,891 Irkutsk is the List of cities and towns in Russ ...
, or Chita) where in the north an extreme winter subarctic climate (Köppen ''Dfd'', ''Dwd'', or ''Dsd'') prevails. But summer temperatures in other regions can reach . In general, Sakha is the coldest Siberian region, and the basin of the Yana has the lowest temperatures of all, with permafrost reaching . Nevertheless, Imperial Russian plans of settlement never viewed cold as an impediment. In the winter, southern Siberia sits near the center of the semi-permanent Siberian High, so winds are usually light in the winter.
Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
in Siberia is generally low, exceeding only in Kamchatka, where moist winds flow from the Sea of Okhotsk onto high mountains – producing the region's only major glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s, though volcanic eruptions and low summer temperatures allow only limited forests to grow. Precipitation is high also in most of Primorye in the extreme south, where monsoonal influences can produce quite heavy summer rainfall.
Global warming
Researchers, including Sergei Kirpotin at Tomsk State University and Judith Marquand at Oxford University, warn that Western Siberia has begun to thaw as a result ofglobal warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
. The frozen peat bogs in this region may hold billions of tons of methane gas, which may be released into the atmosphere. Methane is a greenhouse gas 22 times more powerful than carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
. In 2008 a research expedition for the American Geophysical Union detected levels of methane up to 100 times above normal in the atmosphere above the Siberian Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
, likely the result of methane clathrates being released through holes in a frozen "lid" of seabed permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
around the outfall of the Lena and the area between the Laptev Sea and East Siberian Sea.
Since 1988, experimentation at Pleistocene Park has proposed to restore the grasslands of prehistoric times by conducting research on the effects of large herbivores on permafrost, suggesting that animals, rather than climate, maintained the past ecosystem. The nature reserve park also conducts climatic research on the changes expected from the reintroduction of grazing animals or large herbivores, hypothesizing that a transition from tundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic ...
to grassland would lead to a net change in energy emission to absorption ratios.Sergey A. Zimov (6 May 2005)"Pleistocene Park: Return of the mammoths' ecosystem"
In: ''
Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
'', pages 796–798. Article also to be found iwww.pleistocenepark.ru/en/ – Materials.
Retrieved 5 May 2013. According to Vasily Kryuchkov, approximately 31,000 square kilometers of the Russian Arctic has been subjected to severe environmental disturbance.
Fauna
Birds
Order Galliformes
Family
Phasianidae
Phasianidae is a family (biology), family of heavy, ground-living birds, which includes pheasants, grouse, partridges, junglefowl, chickens, Turkey bird, turkeys, Old World quail, and peafowl. The family includes many of the most popular Game (hu ...
* Hazel grouse
* Siberian grouse
* Black grouse
* Black-billed capercaillie
* Western capercaillie
* Willow ptarmigan
* Rock ptarmigan
* Daurian partridge
* Grey partridge
* Altai snowcock
* Japanese quail
* Common quail
* Ring-necked pheasant
Mammals
Order
Artiodactyla
Artiodactyls are placental mammals belonging to the order (biology), order Artiodactyla ( , ). Typically, they are ungulates which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes (the third and fourth, often in the form of a hoof ...
 *
* Moose
The moose (: 'moose'; used in North America) or elk (: 'elk' or 'elks'; used in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is the world's tallest, largest and heaviest extant species of deer and the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is also the tal ...
* Bactrian camel
* Red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or Hart (deer), hart, and a female is called a doe or hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Ir ...
* Wild boar
* Siberian roe deer
* Manchurian wapiti
* Siberian musk deer
The Siberian musk deer (''Moschus moschiferus'') is a musk deer found in the mountain forests of Northeast Asia. It is most common in the taiga of southern Siberia, but is also found in parts of Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Manchuria and the Korean ...
Database entry includes a brief justification of why this species is of vulnerable.
Order Carnivora
Family
Canidae
Canidae (; from Latin, ''canis'', "dog") is a family (biology), biological family of caniform carnivorans, constituting a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid (). The family includes three subfamily, subfamilies: the Caninae, a ...
* Grey wolf
* Tundra wolf
* Arctic fox
* Red fox
Family
Felidae
Felidae ( ) is the Family (biology), family of mammals in the Order (biology), order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats. A member of this family is also called a felid ( ).
The 41 extant taxon, extant Felidae species exhibit the gre ...
 * Snow leopard
* Amur leopard
* Siberian tiger
* Eurasian lynx
* Pallas cat
* Snow leopard
* Amur leopard
* Siberian tiger
* Eurasian lynx
* Pallas cat
Family Mustelidae
* Least weasel * Stoat * Mountain weasel *Siberian weasel
The Siberian weasel or kolonok (''Mustela sibirica'') is a medium-sized weasel native to Asia, where it is widely distributed and inhabits various forest habitats and open areas. It is therefore listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.
Descr ...
* Steppe polecat
* Sable
* Eurasian river otter
* Asian badger
* Wolverine
The wolverine ( , ; ''Gulo gulo''), also called the carcajou or quickhatch (from East Cree, ''kwiihkwahaacheew''), is the largest land-dwelling species, member of the family Mustelidae. It is a muscular carnivore and a solitary animal. The w ...
Family Ursidae
 * Asian black bear
* Brown bear
* Polar bear
* Asian black bear
* Brown bear
* Polar bear
Flora
 * '' Larix sibirica''
* '' Larix gmelinii''
* '' Picea obovata''
* '' Pinus pumila''
* '' Larix sibirica''
* '' Larix gmelinii''
* '' Picea obovata''
* '' Pinus pumila''
Politics
Notable
sovereign states
A sovereign state is a State (polity), state that has the highest authority over a territory. It is commonly understood that Sovereignty#Sovereignty and independence, a sovereign state is independent. When referring to a specific polity, the ter ...
in Siberia
* Xianbei state (1st–3rd century CE)
* First Turkic Khaganate (6th–7th century)
* Eastern Turkic Khaganate (7th century)
* Second Turkic Khaganate (7th–8th century)
* Kyrgyz Khaganate (8th–13th century)
* Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
(13th–14th century)
* Khanate of Sibir (1468–1598)
* Tsardom of Russia (1598–1721)
* Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
(1721–1917)
* Russian Republic
The Russian Republic,. referred to as the Russian Democratic Federative Republic in the 1918 Constitution, was a short-lived state which controlled, ''de jure'', the territory of the former Russian Empire after its proclamation by the Rus ...
(1917–1918)
* Siberian Republic (1918)
* Russian State (1918–1920)
* Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic (1918–1922)
* Far Eastern Republic (1920–1922)
* Tuvan People's Republic (1921–1944)
* Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
(1922–1991)
** Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
(1922–1991)
* Russian Federation (1991–present)
Borders and administrative division
Russian Far East
The Russian Far East ( rus, Дальний Восток России, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asia, Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Easte ...
. According to this definition, Siberia extended eastward from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific coast, and southward from the Arctic Ocean to the border of Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
and the national borders of both Mongolia and China.
Soviet-era sources (''Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; , ''BSE'') is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Great Russian Enc ...
'' and others) and modern Russian ones usually define Siberia as a region extending eastward from the Ural Mountains to the watershed between Pacific and Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
drainage basins, and southward from the Arctic Ocean to the hills of north-central Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
and the national borders of both Mongolia and China. By this definition, Siberia includes the federal subjects of the Siberian Federal District, and some of the Ural Federal District, as well as Sakha (Yakutia) Republic, which is a part of the Far Eastern Federal District. Geographically, this definition includes subdivisions of several other subjects of Urals and Far Eastern federal districts, but they are not included administratively. This definition excludes Sverdlovsk Oblast and Chelyabinsk Oblast, both of which are included in some wider definitions of Siberia.
Other sources may use either a somewhat wider definition that states the Pacific coast, not the watershed, is the eastern boundary (thus including the whole Russian Far East), as well as all Northern Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
is its subregion in the south-west or a somewhat narrower one that limits Siberia to the Siberian Federal District (thus excluding all subjects of other districts). In Russian, 'Siberia' is commonly used as a substitute for the name of the federal district by those who live in the district itself, but less commonly used to denote the federal district by people residing outside of it. Due to the different interpretations of Siberia, starting from Tyumen
Tyumen ( ; rus, Тюмень, p=tʲʉˈmʲenʲ, a=Ru-Tyumen.ogg) is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Tyumen Oblast, Russia. It is situated just east of the Ural Mountains, along the Tura ( ...
, to Chita, the territory generally defined as 'Siberia', some people will define themselves as 'Siberian', while others not.
A number of factors in recent years, including the fomenting of Siberian separatism have made the definition of the territory of Siberia a potentially controversial subject. In the eastern extent of Siberia there are territories which are not clearly defined as either Siberia or the Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In mod ...
, making the question of "what is Siberia?" one with no clear answer, and what is a "Siberian", one of self-identification.

Major cities
The most populous city of Siberia, as well as the third most populous city of Russia, is the city ofNovosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siber ...
. Present-day Novosibirsk is an important business, science, manufacturing and cultural center of the Asian part of Russia.
Omsk played an important role in the Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
serving as a provisional Russian capital, as well in the expansion into and governing of Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
. In addition to its cultural status, it has become a major oil-refining, education, transport and agriculture hub.
Other historic cities of Siberia include Tobolsk (the first capital and the only kremlin in Siberia), Tomsk (formerly a wealthy merchant's town) and Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and , ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 587,891 Irkutsk is the List of cities and towns in Russ ...
(former seat of Eastern Siberia's governor general, near lake Baikal).
Other major cities include: Barnaul, Kemerovo, Krasnoyarsk, Novokuznetsk, Tyumen
Tyumen ( ; rus, Тюмень, p=tʲʉˈmʲenʲ, a=Ru-Tyumen.ogg) is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Tyumen Oblast, Russia. It is situated just east of the Ural Mountains, along the Tura ( ...
.
Wider definitions of geographic Siberia also include the cities of: Chelyabinsk and Yekaterinburg
Yekaterinburg (, ; ), alternatively Romanization of Russian, romanized as Ekaterinburg and formerly known as Sverdlovsk ( ; 1924–1991), is a city and the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk Oblast and the Ural Federal District, Russia. The ci ...
in the Urals, Khabarovsk and Vladivostok in the Russian Far East, and even Petropavlovsk in Kazakhstan and Harbin
Harbin, ; zh, , s=哈尔滨, t=哈爾濱, p=Hā'ěrbīn; IPA: . is the capital of Heilongjiang, China. It is the largest city of Heilongjiang, as well as being the city with the second-largest urban area, urban population (after Shenyang, Lia ...
in China.
Economy

Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siber ...
is the largest by population and the most important city for the Siberian economy; with an extra boost since 2000 when it was designated a regional center for the executive bureaucracy ( Siberian Federal District). Omsk is a historic and currently the second largest city in the region, and since 1950s hosting Russia's largest oil refinery, the Omsk Refinery. Siberia is extraordinarily rich in mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
s, containing ores of almost all economically valuable metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
s. It has some of the world's largest deposits of nickel, gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
, coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
, molybdenum, gypsum, diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
s, diopside, silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
and zinc, as well as extensive unexploited resources of oil and natural gas. Around 70% of Russia's developed oil fields are in the Khanty-Mansiysk region. Russia contains about 40% of the world's known resources of nickel at the Norilsk deposit in Siberia. Norilsk Nickel is the world's biggest nickel and palladium producer. Siberian agriculture is severely restricted by the short growing season of most of the region. However, in the southwest where soils consist of exceedingly fertile black earths and the climate is a little more moderate, there is extensive cropping of wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
, barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
, rye and potatoes, along with the grazing of large numbers of sheep and cattle. Elsewhere food production, owing to the poor fertility of the podzolic soils and the extremely short growing seasons, is restricted to the herding of reindeer in the tundra—which has been practiced by natives for over 10,000 years. Siberia has the world's largest forest
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, ...
s. Timber remains an important source of revenue, even though many forests in the east have been logged much more rapidly than they are able to recover. The Sea of Okhotsk is one of the two or three richest fisheries in the world owing to its cold currents and very large tidal ranges, and thus Siberia produces over 10% of the world's annual fish catch, although fishing has declined somewhat since the collapse of the USSR in 1991. Reported in 2009, the development of renewable energy in Russia is held back by the lack of a conducive government policy framework, , Siberia still offers special opportunities for off-grid renewable energy developments. Remote parts of Siberia are too costly to connect to central electricity and gas grids, and have therefore historically been supplied with costly diesel, sometimes flown in by helicopter. In such cases renewable energy is often cheaper.
Sport
 The Yenisey Krasnoyarsk basketball team has played in the VTB United League since 2011–12.
Russia's third most popular sport,
The Yenisey Krasnoyarsk basketball team has played in the VTB United League since 2011–12.
Russia's third most popular sport, bandy
Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two team sport, teams wearing Ice skates#Bandy skates, ice skates on a large ice surface (either indoors or outdoors) while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal.
The playin ...
, is important in Siberia. In the 2015–16 Russian Bandy Super League season Yenisey from Krasnoyarsk became champions for the third year in a row by beating Baykal-Energiya from Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and , ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 587,891 Irkutsk is the List of cities and towns in Russ ...
in the final. Two or three more teams (depending on the definition of Siberia) play in the Super League, the 2016–17 champions SKA-Neftyanik from Khabarovsk as well as Kuzbass from Kemerovo and Sibselmash from Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siber ...
. In 2007 Kemerovo got Russia's first indoor arena specifically built for bandy. Now Khabarovsk has the world's largest indoor arena specifically built for bandy, Arena Yerofey. It was venue for Division A of the 2018 World Championship. In time for the 2020 World Championship, an indoor arena will be ready for use in Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and , ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 587,891 Irkutsk is the List of cities and towns in Russ ...
. That one will also have a speed skating oval. Krasnoyarsk is also one of the centres of Rugby in Russia, with 2 of the largest clubs in the country, STM Enisei and Krasny Yar, are both based in the city.
The 2019 Winter Universiade was hosted by Krasnoyarsk.
Demographics
According to the Russian Census of 2010, the Siberian and Far Eastern Federal Districts, located entirely east of the Ural Mountains, together have a population of about 25.6 million.Tyumen
Tyumen ( ; rus, Тюмень, p=tʲʉˈmʲenʲ, a=Ru-Tyumen.ogg) is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Tyumen Oblast, Russia. It is situated just east of the Ural Mountains, along the Tura ( ...
and Kurgan Oblasts, which are geographically in Siberia but administratively part of the Urals Federal District, together have a population of about 4.3 million. Thus, the whole region of Siberia (in the broadest usage of the term) is home to approximately 30 million people. It has a population density of about three people per square kilometre.
Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
, including their sub-ethnic group Siberians, and russified Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
. Slavic and other Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
ethnicities make up the vast majority (over 85%) of the Siberian population. There are also other groups of Indigenous Siberian and non-Indigenous ethnic origin. A minority of the current population are descendants of Mongol or Turkic people (mainly Buryats, Yakuts, Tuvans, Altai and Khakas) or
northern Indigenous people. Slavic-origin Russians outnumber all of the Indigenous peoples combined, except in the Republics of Tuva and Sakha.
According to the 2002 census there are 500,000 Tatars in Siberia, but of these, 300,000 are Volga Tatars who also settled in Siberia during periods of colonization and are thus also non-Indigenous Siberians, in contrast to the 200,000 Siberian Tatars which are Indigenous to Siberia. Of the Indigenous Siberians, the Mongol-speaking Buryats, numbering approximately 500,000, are the most numerous group in Siberia, and they are mainly concentrated in their homeland, the Buryat Republic. According to the 2010 census there were 478,085 indigenous Turkic-speaking Yakuts. Other ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
s Indigenous to Siberia include Kets, Evenks, Chukchis, Koryaks, Yupiks, and Yukaghirs.
About seventy percent of Siberia's people live in cities, mainly in apartments. Many people also live in rural areas, in simple, spacious, log houses. Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siber ...
is the largest city in Siberia, with a population of about 1.6 million. Tobolsk, Tomsk, Tyumen
Tyumen ( ; rus, Тюмень, p=tʲʉˈmʲenʲ, a=Ru-Tyumen.ogg) is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Tyumen Oblast, Russia. It is situated just east of the Ural Mountains, along the Tura ( ...
, Krasnoyarsk, Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and , ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 587,891 Irkutsk is the List of cities and towns in Russ ...
, and Omsk are the older, historical centers.
Religion
 There are a variety of beliefs throughout Siberia, including Orthodox Christianity, other denominations of Christianity,
There are a variety of beliefs throughout Siberia, including Orthodox Christianity, other denominations of Christianity, Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism is a form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet, Bhutan and Mongolia. It also has a sizable number of adherents in the areas surrounding the Himalayas, including the Indian regions of Ladakh, Gorkhaland Territorial Administration, D ...
and Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
. The Siberian Federal District alone has an estimation of 250,000 Muslims. An estimated 70,000 Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
live in Siberia, some in the Jewish Autonomous Region. The predominant religious group is the Russian Orthodox Church.
Tradition regards Siberia the archetypal home of shamanism, and polytheism is popular.Hoppál 2005:13 These native sacred practices are considered by the tribes to be very ancient. There are records of Siberian tribal healing practices dating back to the 13th century. The vast territory of Siberia has many different local traditions of gods. These include: Ak Ana, Anapel, Bugady Musun, Kara Khan, Khaltesh-Anki, Kini'je, Ku'urkil
Ku'urkil is the Chukchi people, Chukchi creator-deity, roughly analogous to Bai-Ulgan of the Turkish folklore, Turkic pantheon. The Koryaks, Koryak refer to him as ''Quikinna'qu'' ("Big Raven") and in Kamchadal mythology he is called ''Kutkh, Kutk ...
, Nga, Nu'tenut, Num-Torum, Pon, Pugu, Todote, Toko'yoto, Tomam, Xaya Iccita and Zonget. Places with sacred areas include Olkhon, an island in Lake Baikal.
Transport
Many cities in northern Siberia, such as Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, cannot be reached by road, as there are virtually none connecting from other major cities in Russia or Asia. Siberia can be reached through the Trans-Siberian Railway. The Trans-Siberian Railway operates from Moscow in the west to Vladivostok in the east. Cities that are located far from the railway are reached by air or by the separate Baikal–Amur Railway (BAM).Culture
Cuisine
Stroganina is a raw fish dish of theIndigenous people
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
of northern Arctic Siberia made from raw, thin, long-sliced frozen fish. It is a popular dish with native Siberians. Siberia is also known for its pelmeni dumpling; which in the winter are traditionally frozen and stored outdoors. In addition, there are various berry, nut and mushroom dishes making use of the riches of abundant nature.
See also
* Siberian regionalism * Tunguska BasinReferences
Bibliography
* * * * Bobrick, Benson''East of the Sun: the epic conquest and tragic history of Siberia''
(Henry Holt and Company, 1993); popular history * * Diment, Galya, and Yuri Slezkine, eds. ''Between Heaven and Hell: The Myth of Siberia in Russian Culture'' (3rd ed. 1993) * * Forsyth, James. ''A History of the Peoples of Siberia: Russia's North Asian Colony, 1581–1990'' (Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 1994). * * Kotkin, Stephen, and David Wolff, eds. (1995)
''Rediscovering Russia in Asia''
* * Lincoln, W. Bruce (1993
''The Conquest of a Continent''
Scholarly history. * * * * * Wood, Alan (ed.)(1991). ''The History of Siberia: From Russian Conquest to Revolution''. London: Routledge. * {{Authority control Eurasian Steppe Geography of Russia Regions of Russia Geography of Kazakhstan