|
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used. The progressing age of the rock strata towards the core and uplifted center, are the trademark indications for evidence of anticlines on a geologic map. These formations occur because anticlinal ridges typically develop above thrust faults during crustal deformations. The uplifted core of the fold causes compression of strata that preferentially erodes to a deeper stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticline (PSF)-vector
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used. The progressing age of the rock strata towards the core and uplifted center, are the trademark indications for evidence of anticlines on a geologic map. These formations occur because anticlinal ridges typically develop above thrust faults during crustal deformations. The uplifted core of the fold causes compression of strata that preferentially erodes to a deeper stratig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fold (geology)
In structural geology, a fold is a stack of originally planar surfaces, such as sedimentary strata, that are bent or curved during permanent deformation. Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to mountain-sized folds. They occur as single isolated folds or in periodic sets (known as ''fold trains''). Synsedimentary folds are those formed during sedimentary deposition. Folds form under varied conditions of stress, pore pressure, and temperature gradient, as evidenced by their presence in soft sediments, the full spectrum of metamorphic rocks, and even as primary flow structures in some igneous rocks. A set of folds distributed on a regional scale constitutes a fold belt, a common feature of orogenic zones. Folds are commonly formed by shortening of existing layers, but may also be formed as a result of displacement on a non-planar fault (''fault bend fold''), at the tip of a propagating fault (''fault propagation fold''), by differential compaction or due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks. Thrust geometry and nomenclature Reverse faults A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less. If the angle of the fault plane is lower (often less than 15 degrees from the horizontal) and the displacement of the overlying block is large (often in the kilometer range) the fault is called an ''overthrust'' or ''overthrust fault''. Erosion can remove part of the overlying block, creating a ''fenster'' (or '' window'') – when the underlying block is exposed only in a relatively small area. When erosion removes most of the overlying block, leaving island-like remnants resting on the lower block, the remnants are called ''klippen'' (singular '' klippe''). Blind thrust faults If the fault plane terminates before it reaches the Earth's surface, it is referred to as a ''blind thrust'' fault. Because of the lack of surface evidence, blind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike And Dip
Strike and dip is a measurement convention used to describe the orientation, or attitude, of a planar geologic feature. A feature's strike is the azimuth of an imagined horizontal line across the plane, and its dip is the angle of inclination measured downward from horizontal. They are used together to measure and document a structure's characteristics for study or for use on a geologic map. A feature's orientation can also be represented by dip and dip direction, using the azimuth of the dip rather than the strike value. Linear features are similarly measured with trend and plunge, where "trend" is analogous to dip direction and "plunge" is the dip angle. Strike and dip are measured using a compass and a clinometer. A compass is used to measure the feature's strike by holding the compass horizontally against the feature. A clinometer measures the features dip by recording the inclination perpendicular to the strike. These can be done separately, or together using a tool such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nittany Valley
Nittany Valley is an eroded anticlinal valley located in Centre County, Pennsylvania. It is separated from the Bald Eagle Valley by Bald Eagle Mountain and from Penns Valley by Mount Nittany. The valley is closed to the north by a high plateau that joins these two mountain ridges, but is open to the south at the southern terminus of Mount Nittany. The valley drains to Bald Eagle Creek through water gaps in Bald Eagle Mountain formed by Spring Creek and Fishing Creek, along with smaller streams running through Curtain Gap and Howard Gap. The northwest side of the valley between the Bald Eagle Mountain ridge and the lower Sand Ridge is also known as the Little Nittany Valley. The valley has a mixture of farmland, woodlots, and a number of working and abandoned quarries. Bellefonte, the county seat of Centre County, is the largest municipality completely within the valley. The Pennsylvania State Correctional Institution - Rockview, the Nittany Mall, the Pennsylvania Transpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
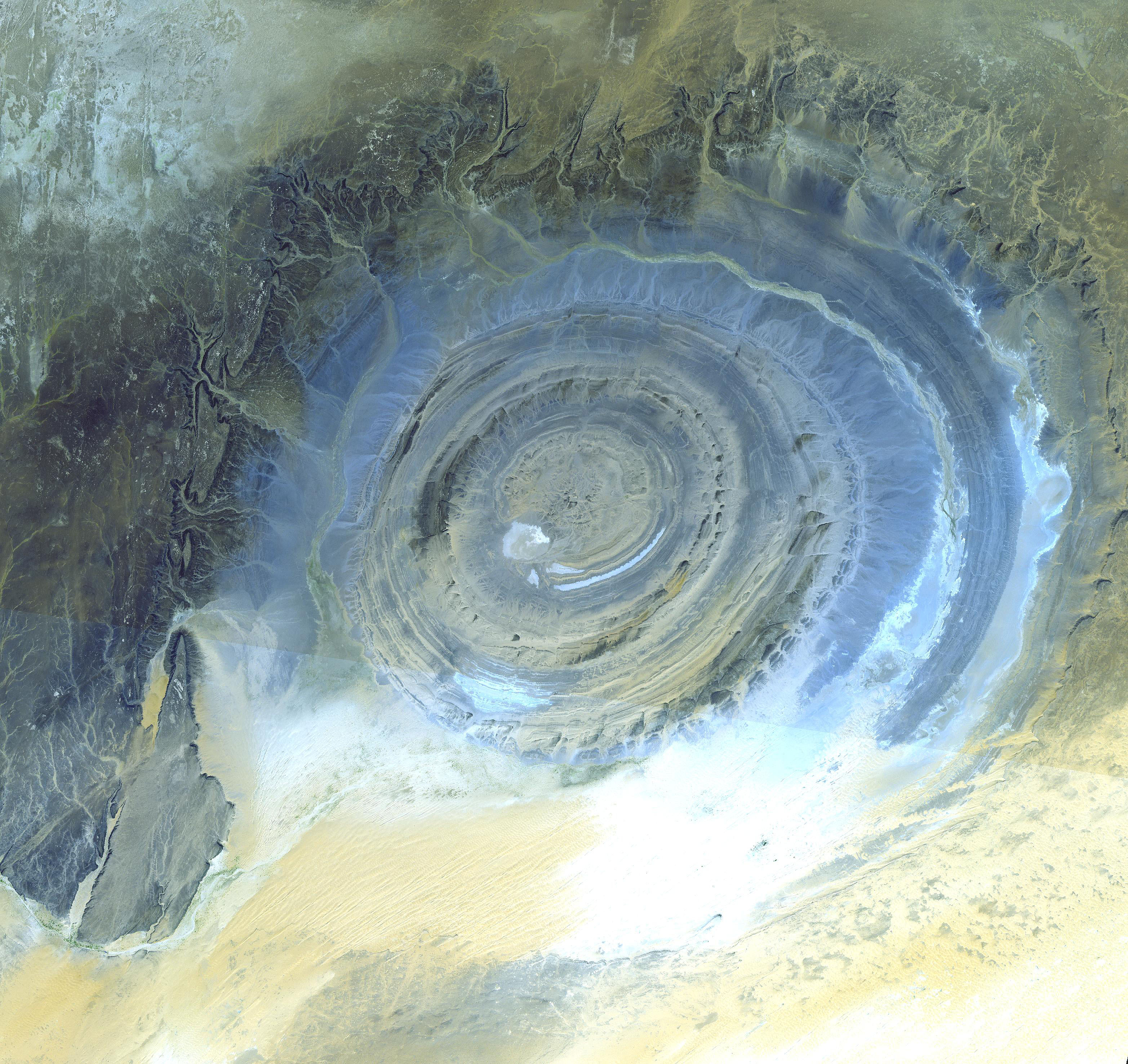
Dome (geology)
A dome is a feature in structural geology consisting of symmetrical anticlines that intersect each other at their respective apices. Intact, domes are distinct, rounded, spherical-to-ellipsoidal-shaped protrusions on the Earth's surface. However, a transect parallel to Earth's surface of a dome features concentric rings of strata. Consequently, if the top of a dome has been eroded flat, the resulting structure in plan view appears as a bullseye, with the youngest rock layers at the outside, and each ring growing progressively older moving inwards. These strata would have been horizontal at the time of deposition, then later deformed by the uplift associated with dome formation. Formation mechanisms There are many possible mechanisms responsible for the formation of domes, the foremost of which are post-impact uplift, refolding, and diapirism. Post-impact uplift A complex crater, caused by collision of a hypervelocity body with another larger than itself, is typified by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Dome
A salt dome is a type of structural dome formed when salt (or other evaporite minerals) intrudes into overlying rocks in a process known as diapirism. Salt domes can have unique surface and subsurface structures, and they can be discovered using techniques such as seismic reflection. They are important in petroleum geology as they can function as petroleum traps. Formation Stratigraphically, salt basins developed periodically from the Proterozoic to the Neogene. The formation of a salt dome begins with the deposition of salt in a restricted basin. In these basins, the outflow of water exceeds inflow. More concretely, the basin loses water through evaporation, resulting in the precipitation and deposition of salt. While the rate of sedimentation of salt is significantly larger than the rate of sedimentation of clastics, it is recognized that a single evaporation event is rarely enough to produce the vast quantities of salt needed to form a layer thick enough for the forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diapir
A diapir (; , ) is a type of igneous intrusion in which a more mobile and ductily deformable material is forced into brittle overlying rocks. Depending on the tectonic environment, diapirs can range from idealized mushroom-shaped Rayleigh–Taylor-instability-type structures in regions with low tectonic stress such as in the Gulf of Mexico to narrow dikes of material that move along tectonically induced fractures in surrounding rock. The term was introduced by the Romanian geologist Ludovic Mrazek, who was the first to understand the principle of salt tectonics and plasticity. The term ''diapir'' may be applied to igneous structures, but it is more commonly applied to non-igneous, relatively cold materials, such as salt domes and mud diapirs. Occurrence Differential loading causes salt deposits covered by overburden (sediment) to rise upward toward the surface and pierce the overburden, forming diapirs (including salt domes), pillars, sheets, or other geologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plunge (geology)
Plunge may refer to: *Plunge (American football), a play in American football * Plunge (geology), the inclination of a surface or axis of an anticline to the horizontal *The Plunge, a historic swim center in Richmond, California * Plunge Creek, a river in Alaska *Plungė, a city in Lithuania *Plunge, the former name for the American rock band Cinder Road *Plunge, a type of waterfall * Plunge (gambling), sudden support for a horse in a race * A swim center in Belmont Park (San Diego), California * Plunge for distance, a former diving event * ''Plunge'' (album), a 2017 album by Fever Ray See also * Plunger A plunger, force cup, plumber's friend or plumber's helper is a tool used to clear blockages in drains and pipes. It consists of a rubber suction cup attached to a stick (''shaft'') usually made of wood or plastic. A different bellows-like desi ..., a common device used to release stoppages in plumbing * Plunger (other) {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncline
In structural geology, a syncline is a fold with younger layers closer to the center of the structure, whereas an anticline is the inverse of a syncline. A synclinorium (plural synclinoriums or synclinoria) is a large syncline with superimposed smaller folds. Synclines are typically a downward fold (synform), termed a synformal syncline (i.e. a trough), but synclines that point upwards can be found when strata have been overturned and folded (an antiformal syncline). Characteristics On a geologic map, synclines are recognized as a sequence of rock layers, with the youngest at the fold's center or ''hinge'' and with a reverse sequence of the same rock layers on the opposite side of the hinge. If the fold pattern is circular or elongate, the structure is a basin. Folds typically form during crustal deformation as the result of compression that accompanies orogenic mountain building. Notable examples * Powder River Basin, Wyoming, US * Sideling Hill roadcut along Interstat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Map
A geologic map or geological map is a special-purpose map made to show various geological features. Rock units or geologic strata are shown by color or symbols. Bedding planes and structural features such as faults, folds, are shown with strike and dip or trend and plunge symbols which give three-dimensional orientations features. Stratigraphic contour lines may be used to illustrate the surface of a selected stratum illustrating the subsurface topographic trends of the strata. Isopach maps detail the variations in thickness of stratigraphic units. It is not always possible to properly show this when the strata are extremely fractured, mixed, in some discontinuities, or where they are otherwise disturbed. Symbols Lithologies Rock units are typically represented by colors. Instead of (or in addition to) colors, certain symbols can be used. Different geologic mapping agencies and authorities have different standards for the colors and symbols to be used for rocks of dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.png)
