Punjab on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Punjab (;

 The Punjab region is noted as the site of one of the earliest urban societies, the
The Punjab region is noted as the site of one of the earliest urban societies, the
 The
The  In 1445, Sultan Qutbudin, chief of ''Langah'', a Jat Zamindar tribe established the
In 1445, Sultan Qutbudin, chief of ''Langah'', a Jat Zamindar tribe established the
 The Sikh Empire ruled the Punjab until the British annexed it in 1849 following the First and Second Anglo-Sikh Wars. Most of the Punjabi homeland formed a province of British India, though a number of small
The Sikh Empire ruled the Punjab until the British annexed it in 1849 following the First and Second Anglo-Sikh Wars. Most of the Punjabi homeland formed a province of British India, though a number of small
 The Sikh Empire spanned a total of over at its zenith.
The Punjab was a region straddling India and the Afghan Durrani Empire. The following modern-day political divisions made up the historical Punjab region during the Sikh Empire:
* Punjab region, to Mithankot in the south
**
The Sikh Empire spanned a total of over at its zenith.
The Punjab was a region straddling India and the Afghan Durrani Empire. The following modern-day political divisions made up the historical Punjab region during the Sikh Empire:
* Punjab region, to Mithankot in the south
**
 It encompassed the present day Indian states of Punjab, Haryana,
It encompassed the present day Indian states of Punjab, Haryana,
File:Royal mosque Lahore.jpg, Badshahi Mosque, Lahore
File:Lahore Fort view from Baradari.jpg, Lahore Fort, Lahore
File:University of Agriculture, Faisalabad.jpg, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad
File:Chandigarh Road.jpg,
 The climate has significant impact on the economy of Punjab, particularly for agriculture in the region. Climate is not uniform over the whole region, as the sections adjacent to the Himalayas generally receive heavier rainfall than those at a distance.
There are three main seasons and two transitional periods. During the hot season from mid-April to the end of June, the temperature may reach . The
The climate has significant impact on the economy of Punjab, particularly for agriculture in the region. Climate is not uniform over the whole region, as the sections adjacent to the Himalayas generally receive heavier rainfall than those at a distance.
There are three main seasons and two transitional periods. During the hot season from mid-April to the end of June, the temperature may reach . The
Climate and Landscape of the Punjab
 The major language is
The major language is
excerpt
* * uraishee 73''Punjabi Adab De Kahani'', Abdul Hafeez Quaraihee, Azeez Book Depot, Lahore, 1973. * hopra 77''Punjab as a Sovereign State'', Gulshan Lal Chopra, Al-Biruni, Lahore, 1977. * Patwant Singh. 1999. ''The Sikhs''. New York: Doubleday. . * ''The Evolution of Heroic Tradition in Ancient Panjab'', 1971, Buddha Parkash. * ''Social and Political Movements in ancient Panjab'', Delhi, 1962, Buddha Parkash. * ''History of Porus'', Patiala, Buddha Parkash. * ''History of the Panjab'', Patiala, 1976, Fauja Singh, L.M. Joshi (Ed). * ''The Legacy of the Punjab'', 1997, R.M. Chopra. * ''The Rise Growth and Decline of Indo-Persian Literature'', R.M. Chopra, 2012, Iran Culture House, New Delhi. 2nd revised edition, published in 2013. * Sims, Holly. "The State and Agricultural Productivity: Continuity versus Change in the Indian and Pakistani Punjabs." '' Asian Survey'', 1 April 1986, Vol. 26(4), pp. 483–500.
Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India ...
, comprising areas of eastern Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
and northwestern India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
. Punjab's capital and largest city and historical and cultural centre is Lahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is the capital of the province of Punjab where it is the largest ...
. The other major cities include Faisalabad
Faisalabad (; Punjabi/ ur, , ; ), formerly known as Lyallpur (Punjabi, Urdu: لائل پور), named after the founder of the city, but was renamed in 1977 in honour of late King Faisal of Saudi Arabia. It is the 3rd largest city of Paki ...
, Rawalpindi, Gujranwala, Multan, Ludhiana
Ludhiana ( ) is the most populous and the largest city in the Indian state of Punjab. The city has an estimated population of 1,618,879 2011 census and distributed over , making Ludhiana the most densely populated urban centre in the state. ...
, Amritsar
Amritsar (), historically also known as Rāmdāspur and colloquially as ''Ambarsar'', is the second largest city in the Indian state of Punjab, after Ludhiana. It is a major cultural, transportation and economic centre, located in the Maj ...
, Sialkot
Sialkot ( ur, ) is a city located in Punjab, Pakistan. It is the capital of Sialkot District and the 13th most populous city in Pakistan. The boundaries of Sialkot are joined with Jammu (the winter capital of Indian administered Jammu and Kas ...
, Chandigarh
Chandigarh () is a planned city in India. Chandigarh is bordered by the state of Punjab to the west and the south, and by the state of Haryana to the east. It constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which ...
, Jalandhar
Jalandhar is the third most-populous city in the Indian state of Punjab and the largest city in Doaba region. Jalandhar lies alongside the Grand Trunk Road and is a well-connected rail and road junction. Jalandhar is northwest of the state ...
, and Bahawalpur.
Punjab grew out of the settlements along the five rivers, which served as an important route to the Near East as early as the ancient Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900 ...
, dating back to 3000 BCE, and had numerous migrations by the Indo-Aryan peoples
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia an ...
. Agriculture has been the major economic feature of the Punjab and has therefore formed the foundation of Punjabi culture, with one's social status being determined by land ownership. The Punjab emerged as an important agricultural region, especially following the Green Revolution during the mid-1960s to the mid-1970s, and has been described as the "breadbasket of both India and Pakistan."
Besides being known for agriculture and trade, the Punjab is also a region that over the centuries has experienced many foreign invasions and consequently has a long-standing history of warfare, as the region is vulnerably situated on the principal route of invasions through the northwestern frontier of the Indian subcontinent, including those of Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
, Macedonians, Scythians, Parthians, Kushans, Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
, Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Turks, and Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
until the eighteenth century which promoted a lifestyle that entailed engaging in warfare to protect the land, with the Marathas, Durranis and British invading the region in subsequent decades.
The boundaries of the region are ill-defined and focus on historical accounts and thus the geographical definition of the term "Punjab" has changed over time. In the 16th century Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the ...
it referred to a relatively smaller area between the Indus and the Sutlej rivers. In British India, until the Partition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: ...
in 1947, the Punjab Province Punjab Province may refer to:
* Punjab Province (British India), a former province of British India from 1849 to 1947
In Pakistan
* Punjab, Pakistan, a province in Pakistan from 1970 onward
* West Punjab, a province of Pakistan from 1947 to 195 ...
encompassed the present-day Indian states and union territories of Punjab, Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ...
, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh
Chandigarh () is a planned city in India. Chandigarh is bordered by the state of Punjab to the west and the south, and by the state of Haryana to the east. It constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which ...
, and Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders wi ...
, and the Pakistani regions of Punjab, and Islamabad Capital Territory. It bordered the Balochistan and Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (; ps, خېبر پښتونخوا; Urdu, Hindko: خیبر پختونخوا) commonly abbreviated as KP or KPK, is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the northwestern region of the country, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa ...
regions to the west, Kashmir to the north, the Hindi Belt
The Hindi Belt, also known as the Hindi Heartland, is a linguistic region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern and western India where various Central Indo-Aryan languages subsumed under the term 'Hindi' (for example, by th ...
to the east, and Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern s ...
and Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
to the south.
The predominant ethnolinguistic group of the Punjab region is the Punjabi people, who speak the Indo-Aryan Punjabi language
Punjabi (; ; , ), sometimes spelled Panjabi, is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language of the Punjab, Punjab region of Pakistan and India. It has approximately 113 million native speakers.
Punjabi is the most widely-spoken first lan ...
. Punjabi Muslims are the majority in West Punjab (Pakistan), while Punjabi Sikhs and Punjabi Hindus are the majority in East Punjab (India). Other religious groups are Christianity, Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
, Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ont ...
, Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
, and Ravidassia.
Etymology
Although the name Punjab is of Persian origin, its two parts ( and ) are cognates of the Sanskrit words, and , of the same meaning. The word ''pañjāb'' thus means "The Land of Five Waters," referring to the rivers Jhelum, Chenab,Ravi Ravi may refer to:
People
* Ravi (name), including a list of people and characters with the name
* Ravi (composer) (1926–2012), Indian music director
* Ravi (Ivar Johansen) (born 1976), Norwegian musical artist
* Ravi (music director) (1926� ...
, Sutlej, and Beas. All are tributaries of the Indus River, the Sutlej being the largest. References to a land of five rivers may be found in the ''Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
'', which calls one of the regions in ancient Bharat '' Panchanada'' (). Persian place names are very common in Northwest India and Pakistan. The ancient Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, Albania, Greeks in Italy, ...
referred to the region as ''Pentapotamía'' ( el, Πενταποταμία), which has the same meaning as the Persian word.
History
The Punjab region of India and Pakistan has a historical and cultural link to Indo-Aryan peoples as well as partially to various indigenous communities. As a result of several invasions fromCentral Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
and the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
, many ethnic groups and religions make up the cultural heritage of the Punjab.
Ancient period

 The Punjab region is noted as the site of one of the earliest urban societies, the
The Punjab region is noted as the site of one of the earliest urban societies, the Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900 ...
that flourished from about 3000 B.C. and declined rapidly 1,000 years later, following the Indo-Aryan migrations that overran the region in waves between 1500 and 500 B.C. Frequent intertribal wars stimulated the growth of larger groupings ruled by chieftains and kings, who ruled local kingdoms known as Mahajanapadas. The rise of kingdoms and dynasties in the Punjab is chronicled in the ancient Hindu epics, particularly the Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
. The epic battles described in the ''Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
'' are chronicled as being fought in what is now the state of Haryana and historic Punjab. The Gandhara
Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, more precisely in present-day north-west Pakistan and parts of south-east Afghanistan. The region centered around the Peshawar Val ...
s, Kambojas, Trigartas, Andhra, Pauravas, Bahlikas ( Bactrian settlers of the Punjab), Yaudheyas, and others sided with the Kauravas in the great battle fought at Kurukshetra. According to DrFauja Singh and Dr.L.M. Joshi: "There is no doubt that the Kambojas, Daradas, Kaikayas, Andhra, Pauravas, Yaudheyas, Malavas, Saindhavas, and Kurus had jointly contributed to the heroic tradition and composite culture of ancient Punjab."
The earliest known notable local king of this region was known as King Porus, who fought the famous Battle of the Hydaspes against Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
. His kingdom spanned between rivers ''Hydaspes'' ( Jhelum) and ''Acesines'' ( Chenab); Strabo had held the territory to contain almost 300 cities. He (alongside Abisares) had a hostile relationship with the Kingdom of Taxila which was ruled by his extended family. When the armies of Alexander crossed Indus in its eastward migration, probably in Udabhandapura, he was greeted by the-then ruler of Taxila, Omphis. Omphis had hoped to force both Porus and Abisares into submission leveraging the might of Alexander's forces and diplomatic missions were mounted, but while Abisares accepted the submission, Porus refused. This led Alexander to seek for a face-off with Porus. Thus began the Battle of the Hydaspes in 326 BC; the exact site remains unknown. The battle is thought to be resulted in a decisive Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
victory; however, A. B. Bosworth warns against an uncritical reading of Greek sources who were obviously exaggerative.
Alexander later founded two cities—'' Nicaea'' at the site of victory and ''Bucephalous'' at the battle-ground, in memory of his horse, who died soon after the battle. Later, tetradrachms would be minted depicting Alexander on horseback, armed with a ''sarissa'' and attacking a pair of Indians on an elephant. Porus refused to surrender and wandered about atop an elephant, until he was wounded and his force routed. When asked by Alexander how he wished to be treated, Porus replied "Treat me as a king would treat another king". Despite the apparently one-sided results, Alexander was impressed by Porus and chose to not depose him. Not only was his territory reinstated but also expanded with Alexander's forces annexing the territories of Glausaes, who ruled to the northeast of Porus' kingdom.
After Alexander's death in 323 BCE, Perdiccas became the regent of his empire, and after Perdiccas's murder in 321 BCE, Antipater became the new regent. According to Diodorus, Antipater recognized Porus's authority over the territories along the Indus River. However, Eudemus, who had served as Alexander's satrap in the Punjab region, treacherously killed Porus. The battle is historically significant because it resulted in the syncretism of ancient Greek political and cultural influences to the Indian subcontinent, yielding works such as Greco-Buddhist art, which continued to have an impact for the ensuing centuries. The region was then divided between the Maurya Empire and the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom in 302 B.C.E. Menander I Soter conquered Punjab and made Sagala (present-day Sialkot
Sialkot ( ur, ) is a city located in Punjab, Pakistan. It is the capital of Sialkot District and the 13th most populous city in Pakistan. The boundaries of Sialkot are joined with Jammu (the winter capital of Indian administered Jammu and Kas ...
) the capital of the Indo-Greek Kingdom. Menander is noted for having become a patron and convert to Greco-Buddhism and he is widely regarded as the greatest of the Indo-Greek kings. Greek influence in the region ended around 12 B.C.E. when the Punjab fell under the Sassanids.
Medieval period
Islam emerged as the major power in southern Punjab after theUmayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
conquered the region in 711 AD. The city of Multan became a center of the Ismaili sect of Islam. In the ninth century, the Hindu Shahi dynasty emerged in the Punjab, ruling much of Punjab and eastern Afghanistan. The 10th century Arab historian Masudi mentioned that in his time the kings of Gandhara
Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, more precisely in present-day north-west Pakistan and parts of south-east Afghanistan. The region centered around the Peshawar Val ...
were all called ''Hajaj'', ''J.haj'' or ''Ch'hach'', while the area itself was called "country of the ''Rahbūt''" ( Rajputs). The character transliterated to "Hahaj" and Alexander Cunningham had it equated to the Janjua tribe/clan. Rahman doubts this theory and instead transliterates to "J.haj", an Arabicised form of '' Chhachh'', which is even today the name of the region around the Hindu Shahi capital of Hund. In the 10th century, this region was occupied by the tribe of the Gakhars/Khokhars
Khokhar are a Punjabi community native to Pothohar Plateau of Pakistan, and the adjoining areas of India. Khokhars now predominantly follow Islam, though a minority continue to follow Hinduism. Many Khokhars converted to Islam from Hinduism a ...
, who formed a large part of the Hindu Shahi army according to the Persian historian Firishta.
 The
The Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
Ghaznavids in the tenth century overthrew the Hindu Shahis and consequently ruled for 157 years, gradually declining as a power until the Ghurid conquest of Lahore by Muhammad of Ghor in 1186, deposing the last Ghaznavid ruler Khusrau Malik. Following the death of Muhammad of Ghor in 1206, the Ghurid state fragmented and was replaced in northern India by the Delhi Sultanate. The Delhi Sultanate ruled the Punjab for the next three hundred years, led by five unrelated dynasties, the Mamluks, Khalajis, Tughlaqs, Sayyids and Lodis. 15th century saw rise of many prominent Muslims from Punjab. Khizr Khan established the Sayyid dynasty, the fourth dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate after the fall of the Tughlaqs. A contemporary writer Yahya Sirhindi mentions in his ''Takhrikh-i-Mubarak Shahi'' that Khizr Khan was a descendant of prophet Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
. Members of the dynasty derived their title, Sayyid
''Sayyid'' (, ; ar, سيد ; ; meaning 'sir', 'Lord', 'Master'; Arabic plural: ; feminine: ; ) is a surname of people descending from the Prophets in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad through his grandsons, Hasan ibn Ali and Husayn ibn Ali ...
, or the descendants of the Islamic prophet, Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
, based on the claim that they belonged to his lineage through his daughter Fatima
Fāṭima bint Muḥammad ( ar, فَاطِمَة ٱبْنَت مُحَمَّد}, 605/15–632 CE), commonly known as Fāṭima al-Zahrāʾ (), was the daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his wife Khadija. Fatima's husband was Ali, t ...
. However, Yahya Sirhindi based his conclusions on unsubstantial evidence, the first being a casual recognition by the famous saint Sayyid Jalaluddin Bukhari of Uch Sharif of his Sayyid heritage, and secondly the noble character of the Sultan which distinguished him as a Prophet's descendant. According to Richard M. Eaton, Khizr Khan was son of a Punjabi chieftain. He was a Khokhar chieftain who travelled to Samarkand and profited from the contacts he made with the Timurid society Later on, Delhi Sultanate, weakened by invasion of Emir Timur, could not control all regions of the Empire and different local kingdoms appeared. In 1407, Sultan Muzaffar Shah I, a Tank Rajput*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
* or a Khatri*
*
*
*
* Muslim from Punjab established the Gujarat Sultanate.Langah Sultanate
The Langah Sultanate, also known as the Sultanate of Multan, was a kingdom which emerged after the decline of Delhi Sultanate in the Punjab region. The capital of the Sultanate was the city of Multan in south Punjab.
Origin
There are conflicting ...
in Multan. Another prominent name is that of Jasrath Khokhar who helped Sultan Zain Ul Abideen of Kashmir to gain his throne and ruled over vast tracts of Jammu
Jammu is the winter capital of the Indian union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. It is the headquarters and the largest city in Jammu district of the union territory. Lying on the banks of the river Tawi, the city of Jammu, with an area of ...
and North Punjab
The Pothohar Plateau ( ur, ) is a plateau in north-eastern Pakistan, located between Indus River and the Jhelum River, forming the northern part of Punjab.
Geography
Potohar Plateau is bounded on the east by the Jhelum River, on the west by the ...
. He also conquered Delhi for a brief period in 1431 but was driven out by Mubarak Shah.
Modern period
TheMughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
came to power in the early sixteenth century and gradually expanded to control all of the Punjab from their capital at Lahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is the capital of the province of Punjab where it is the largest ...
. During the Mughal era, Saadullah Khan, born into a family of Jat agriculturalists belonging to the Thaheem tribe from Chiniot remained Grand vizier (or Prime Minister) of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the ...
in the period 1645–1656. Other prominent Muslims from Punjab who rose to nobility during the Mughal Era include Wazir Khan, Adina Beg Arain, and Shahbaz Khan Kamboh. The Mughal Empire ruled the region until it was severely weakened in the eighteenth century. As Mughal power weakened, Afghan rulers took control of the region. Contested by Marathas and Afghans, the region was the center of the growing influence of the Sikhs, who expanded and established the Sikh Empire as the Mughals and Afghans weakened, ultimately ruling the Punjab, eastern Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bord ...
, and territories north into the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over ...
. The Sikh Empire ruled the Punjab until the British annexed it in 1849 following the First and Second Anglo-Sikh Wars. Most of the Punjabi homeland formed a province of British India, though a number of small
The Sikh Empire ruled the Punjab until the British annexed it in 1849 following the First and Second Anglo-Sikh Wars. Most of the Punjabi homeland formed a province of British India, though a number of small princely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to ...
s retained local rulers who recognized British authority. The Punjab with its rich farmlands became one of the most important colonial assets. Lahore was a noted center of learning and culture, and Rawalpindi became an important military installation. Most Punjabis supported the British during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, providing men and resources to the war effort even though the Punjab remained a source of anti colonial activities. Disturbances in the region increased as the war continued. At the end of the war, high casualty rates, heavy taxation, inflation, and a widespread influenza epidemic disrupted Punjabi society. In 1919 a British officer ordered his troops to fire on a crowd of demonstrators, mostly Sikhs in Amritsar
Amritsar (), historically also known as Rāmdāspur and colloquially as ''Ambarsar'', is the second largest city in the Indian state of Punjab, after Ludhiana. It is a major cultural, transportation and economic centre, located in the Maj ...
. The Jallianwala massacre fueled the indian independence movement. Nationalists declared the independence of India from Lahore in 1930 but were quickly suppressed. When the Second World War broke out, nationalism in British India had already divided into religious movements. Many Sikhs and other minorities supported the Hindus, who promised a secular multicultural and multireligious society, and Muslim leaders in Lahore passed a resolution to work for a Muslim Pakistan, making the Punjab region a center of growing conflict between Indian and Pakistani nationalists. At the end of the war, the British granted separate independence to India and Pakistan, setting off massive communal violence as Muslims fled to Pakistan and Hindu and Sikh Punjabis fled east to India.
The British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi language, Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Q ...
had major political, cultural, philosophical, and literary consequences in the Punjab, including the establishment of a new system of education. During the independence movement, many Punjabis played a significant role, including Madan Lal Dhingra, Sukhdev Thapar, Ajit Singh Sandhu Ajit, Ajith or Ajeet may refer to:
* Ajit (given name), an Indian masculine given name (including a list of persons with the name)
* ''Ajit'' (newspaper), an Indian Punjabi daily newspaper
* Ajit Khan (born 1922), an Indian Hindi film actor
* Ajit ...
, Bhagat Singh, Udham Singh, Kartar Singh Sarabha, Bhai Parmanand, Choudhry Rahmat Ali, and Lala Lajpat Rai. At the time of partition in 1947, the province was split into East and West Punjab. East Punjab (48%) became part of India, while West Punjab (52%) became part of Pakistan. The Punjab bore the brunt of the civil unrest following partition, with casualties estimated to be in the millions.
Another major consequence of partition was the sudden shift towards religious homogeneity occurred in all districts across Punjab owing to the new international border that cut through the province. This rapid demographic shift was primarily due to wide scale migration but also caused by large-scale religious cleansing riots which were witnessed across the region at the time. According to historical demographer Tim Dyson, in the eastern regions of Punjab that ultimately became Indian Punjab following independence, districts that were 66% Hindu in 1941 became 80% Hindu in 1951; those that were 20% Sikh became 50% Sikh in 1951. Conversely, in the western regions of Punjab that ultimately became Pakistani Punjab
Punjab (; , ) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in central-eastern region of the country, Punjab is the second-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the largest province by population. It shares land borders with the ...
, all districts became almost exclusively Muslim by 1951.
Geography
The geographical definition of the term "Punjab" has changed over time. In the 16th centuryMughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the ...
it referred to a relatively smaller area between the Indus and the Sutlej rivers.
Sikh empire
In the 19th century, Maharaja Ranjit Singh established the Sikh Empire based in the Punjab. The empire existed from 1799, when Ranjit Singh capturedLahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is the capital of the province of Punjab where it is the largest ...
, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered in the Second Anglo-Sikh War. It was forged on the foundations of the Khalsa from a collection of autonomous Sikh '' misls''. At its peak in the 19th century, the Empire extended from the Khyber Pass in the west to western Tibet in the east, and from Mithankot in the south to Kashmir in the north. It was divided into four provinces: Lahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is the capital of the province of Punjab where it is the largest ...
, in Punjab, which became the Sikh capital; Multan, also in Punjab; Peshawar; and Kashmir from 1799 to 1849. Religiously diverse, with an estimated population of 3.5 million in 1831 (making it the 19th most populous country at the time), Amarinder Singh's The Last Sunset: The Rise and Fall of the Lahore Durbar it was the last major region of the Indian subcontinent to be annexed by the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading post ...
.
 The Sikh Empire spanned a total of over at its zenith.
The Punjab was a region straddling India and the Afghan Durrani Empire. The following modern-day political divisions made up the historical Punjab region during the Sikh Empire:
* Punjab region, to Mithankot in the south
**
The Sikh Empire spanned a total of over at its zenith.
The Punjab was a region straddling India and the Afghan Durrani Empire. The following modern-day political divisions made up the historical Punjab region during the Sikh Empire:
* Punjab region, to Mithankot in the south
** Punjab, Pakistan
Punjab (; , ) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in central-eastern region of the country, Punjab is the second-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the largest province by population. It shares land borders with the P ...
, excluding Bahawalpur State
** Punjab, India
Punjab (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northern India. Forming part of the larger Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, the state is bordered by the States and union territories of India, Indian states of Himachal ...
, south to areas just across the Sutlej river
** Himachal Pradesh, India, south to areas just across the Sutlej river
** Jammu Division, Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
, India and Pakistan (1808–1846)
* Kashmir, from 5 July 1819 to 15 March 1846, India/Pakistan/China
** Kashmir Valley, India from 1819 to 1846
** Gilgit, Gilgit–Baltistan, Pakistan, from 1842 to 1846
** Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu a ...
, India 1834–1846
* Khyber Pass, Pakistan/Afghanistan
** Peshawar, Pakistan (taken in 1818, retaken in 1834)
** Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (; ps, خېبر پښتونخوا; Urdu, Hindko: خیبر پختونخوا) commonly abbreviated as KP or KPK, is one of the Administrative units of Pakistan, four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, ...
and the Federally Administered Tribal Areas
, conventional_long_name = Federally Administered Tribal Areas
, nation = Pakistan
, subdivision = Autonomous territory
, image_flag = Flag of FATA.svg
, image_coat = File:Coat of arms ...
, Pakistan (documented from Hazara
Hazara may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* The Hazaras, a Persian-speaking people of Afghanistan and Pakistan
* Aimaq Hazara, Aimaq's subtribe of Hazara origin
* Hazarawals, a Hindko-speaking people of the Hazara region of northern Pakistan
* Hazar ...
(taken in 1818, again in 1836 to Bannu)
* Parts of Western Tibet, China ( briefly in 1841, to Taklakot),
After Ranjit Singh's death in 1839, the empire was severely weakened by internal divisions and political mismanagement. This opportunity was used by the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sout ...
to launch the First and Second Anglo-Sikh Wars. The country was finally annexed and dissolved at the end of the Second Anglo-Sikh War in 1849 into separate princely states
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to ...
and the province of Punjab
Punjab (; , ) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in central-eastern region of the country, Punjab is the second-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the largest province by population. It shares land borders with the ...
. Eventually, a Lieutenant Governorship was formed in Lahore as a direct representative of the Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has differen ...
.
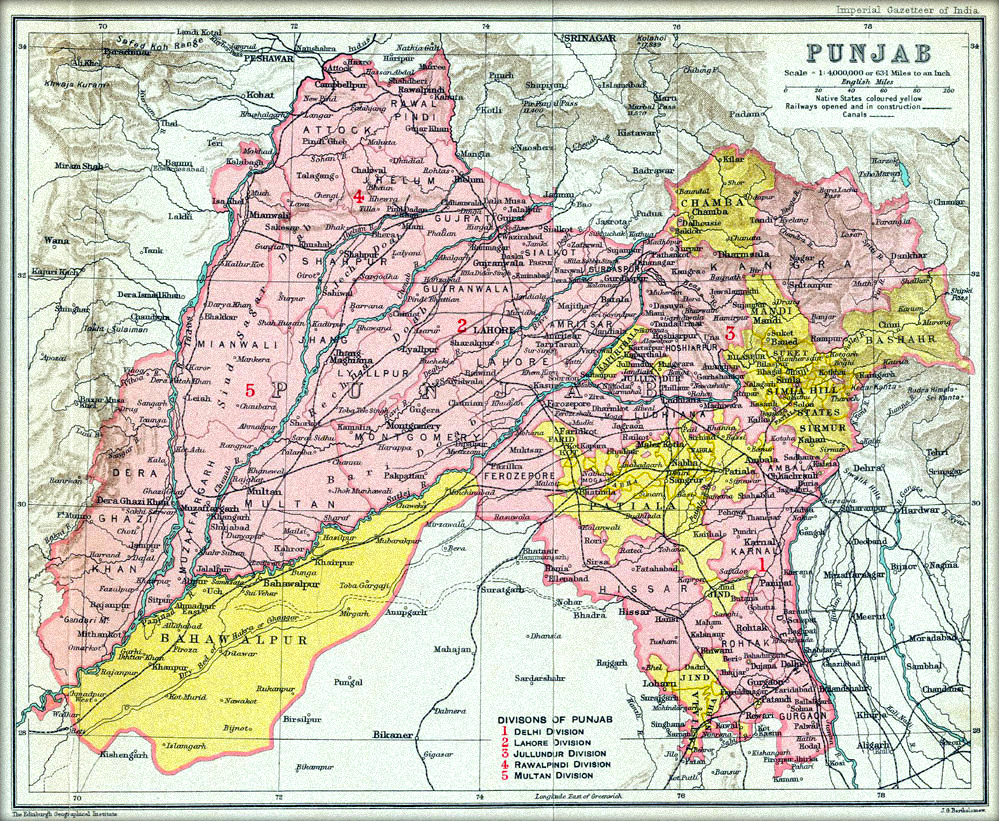
Punjab (British India)
In British India, until thePartition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: ...
in 1947, the Punjab Province Punjab Province may refer to:
* Punjab Province (British India), a former province of British India from 1849 to 1947
In Pakistan
* Punjab, Pakistan, a province in Pakistan from 1970 onward
* West Punjab, a province of Pakistan from 1947 to 195 ...
was geographically a triangular tract of country of which the Indus River and its tributary the Sutlej formed the two sides up to their confluence, the base of the triangle in the north being the Lower Himalayan Range between those two rivers. Moreover, the province as constituted under British rule also included a large tract outside these boundaries. Along the northern border, Himalayan ranges divided it from Kashmir and Tibet. On the west it was separated from the North-West Frontier Province by the Indus, until it reached the border of Dera Ghazi Khan District, which was divided from Baluchistan by the Sulaiman Range. To the south lay Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
and Rajputana, while on the east the rivers Jumna and Tons
Tons can refer to:
* Tons River, a major river in India
* Tamsa River, locally called Tons in its lower parts (Allahabad district, Uttar pradesh, India).
* the plural of ton, a unit of mass, force, volume, energy or power
:* short ton, 2,000 poun ...
separated it from the United Provinces. In total Punjab had an area of approximately 357 000 km square about the same size as modern day Germany, being one of the largest provinces of the British Raj.
 It encompassed the present day Indian states of Punjab, Haryana,
It encompassed the present day Indian states of Punjab, Haryana, Chandigarh
Chandigarh () is a planned city in India. Chandigarh is bordered by the state of Punjab to the west and the south, and by the state of Haryana to the east. It constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which ...
, Delhi, and some parts of Himachal Pradeshprincely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to ...
s which were later combined into the Patiala and East Punjab States Union) and the Pakistani regions of the Punjab, Islamabad Capital Territory and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (; ps, خېبر پښتونخوا; Urdu, Hindko: خیبر پختونخوا) commonly abbreviated as KP or KPK, is one of the Administrative units of Pakistan, four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, ...
.
In 1901 the frontier districts beyond the Indus were separated from Punjab and made into a new province: the North-West Frontier Province. Subsequently, Punjab was divided into four natural geographical divisions by colonial officials on the decadal census data:
# ''Indo-Gangetic Plain West geographical division'' (including Hisar district, Loharu State, Rohtak district, Dujana State, Gurgaon district
Gurgaon district, officially known as Gurugram district, is one of the 22 districts of Haryana in northern India. The city of Gurgaon is the administrative headquarters of the district. The population is 1,514,432. It is one of the southern dis ...
, Pataudi State, Delhi, Karnal district, Jalandhar district, Kapurthala State, Ludhiana district, Malerkotla State, Firozpur district, Faridkot State, Patiala State
Patiala State was a self-governing princely state of the British Empire in India, and one of the Phulkian States, that acceded to the Union of India upon Indian independence and partition. Patiala Kingdom/State was founded by Sidhu Jat Sikhs ...
, Jind State, Nabha State, Lahore District, Amritsar district, Gujranwala District, and Sheikhupura district);
# ''Himalayan geographical division'' (including Nahan State, Simla District, Simla Hill States, Kangra district, Mandi State, Suket State, and Chamba State);
# ''Sub-Himalayan geographical division'' (including Ambala district, Kalsia State
Kalsia was a princely state in Punjab, British India, one of the former Cis-Sutlej states. It was founded by Raja Gurbaksh Singh Sandhu in 1760. After India's independence, it was included in PEPSU and later in the Indian East Punjab after the ...
, Hoshiarpur district, Gurdaspur district, Sialkot District
Sialkot District (Punjabi and ur, ), is one of the districts of Punjab province of Pakistan. It is located in the Majha region of Panjab, otherwise the northeast of the province. The city of Sialkot is the capital of the district. The Sial ...
, Gujrat District, Jhelum District, Rawalpindi District, and Attock District;
# ''North-West Dry Area geographical division'' (including Montgomery District, Shahpur District, Mianwali District, Lyallpur District, Jhang District, Multan District, Bahawalpur State, Muzaffargarh District, and Dera Ghazi Khan District).
Partition of British Punjab
The struggle for Indian independence witnessed competing and conflicting interests in the Punjab. The landed elites of the Muslim, Hindu and Sikh communities had loyally collaborated with the British since annexation, supported the Unionist Party and were hostile to the Congress party–led independence movement.Pritam Singh, Federalism, Nationalism and Development: India and the Punjab Economy, Routledge, 19 February 2008, p.54 Amongst the peasantry and urban middle classes, the Hindus were the most activeNational Congress ''National Congress'' is a term used in the names of various political parties and legislatures .
Political parties
*Ethiopia: Oromo National Congress
*Guyana: People's National Congress (Guyana)
*India: Indian National Congress
*Iraq: Iraqi Nati ...
supporters, the Sikhs flocked to the Akali movement whilst the Muslims eventually supported the Muslim League.
Since the partition of the sub-continent had been decided, special meetings of the Western and Eastern Section of the Legislative Assembly were held on 23 June 1947 to decide whether or not the Province of the Punjab be partitioned. After voting on both sides, partition was decided and the existing Punjab Legislative Assembly was also divided into West Punjab Legislative Assembly and the East Punjab Legislative Assembly. This last Assembly before independence, held its last sitting on 4 July 1947.
Major cities
Historically,Lahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is the capital of the province of Punjab where it is the largest ...
has been the capital of the Punjab region and continues to be the most populous city in the region, with a population of 11 million for the city proper. Faisalabad
Faisalabad (; Punjabi/ ur, , ; ), formerly known as Lyallpur (Punjabi, Urdu: لائل پور), named after the founder of the city, but was renamed in 1977 in honour of late King Faisal of Saudi Arabia. It is the 3rd largest city of Paki ...
is the 2nd most populous city and largest industrial hub in this region. Other major cities are Rawalpindi, Gujranwala, Multan, Ludhiana
Ludhiana ( ) is the most populous and the largest city in the Indian state of Punjab. The city has an estimated population of 1,618,879 2011 census and distributed over , making Ludhiana the most densely populated urban centre in the state. ...
, Amritsar
Amritsar (), historically also known as Rāmdāspur and colloquially as ''Ambarsar'', is the second largest city in the Indian state of Punjab, after Ludhiana. It is a major cultural, transportation and economic centre, located in the Maj ...
, Jalandhar
Jalandhar is the third most-populous city in the Indian state of Punjab and the largest city in Doaba region. Jalandhar lies alongside the Grand Trunk Road and is a well-connected rail and road junction. Jalandhar is northwest of the state ...
, and Chandigarh
Chandigarh () is a planned city in India. Chandigarh is bordered by the state of Punjab to the west and the south, and by the state of Haryana to the east. It constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which ...
are the other cities in Punjab with a city-proper population of over a million.
Chandigarh
Chandigarh () is a planned city in India. Chandigarh is bordered by the state of Punjab to the west and the south, and by the state of Haryana to the east. It constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which ...
File:Golden Temple India.jpg, Golden Temple, Amritsar
File:Clock Tower Faisalabad by Usman Nadeem.jpg, Clock Tower, Faisalabad
File:Aerial view of Multan Ghanta Ghar chawk.jpg, Aerial view of Multan Ghanta Ghar chawk
File:Open Hand monument, Chandigarh.jpg, Open Hand monument, Chandigarh
Climate
 The climate has significant impact on the economy of Punjab, particularly for agriculture in the region. Climate is not uniform over the whole region, as the sections adjacent to the Himalayas generally receive heavier rainfall than those at a distance.
There are three main seasons and two transitional periods. During the hot season from mid-April to the end of June, the temperature may reach . The
The climate has significant impact on the economy of Punjab, particularly for agriculture in the region. Climate is not uniform over the whole region, as the sections adjacent to the Himalayas generally receive heavier rainfall than those at a distance.
There are three main seasons and two transitional periods. During the hot season from mid-April to the end of June, the temperature may reach . The monsoon season
The wet season (sometimes called the Rainy season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. It is the time of year where the majority of a country's or region's annual precipitation occurs. Generally, the sea ...
, from July to September, is a period of heavy rainfall, providing water for crops in addition to the supply from canals and irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been dev ...
systems. The transitional period after the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
is cool and mild, leading to the winter season, when the temperature in January falls to at night and by day. During the transitional period from winter to the hot season, sudden hailstorms and heavy showers may occur, causing damage to crops.Royal Geographical SocietClimate and Landscape of the Punjab
Western Punjab
Central Punjab
Eastern Punjab
Demographics
Languages
Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
, which is written in India with the Gurmukhi script, and in Pakistan using the Shahmukhi script. The Punjabi language has official status and is widely used in education and administration in Indian Punjab, whereas in Pakistani Punjab these roles are instead fulfilled by the language.
Several languages closely related to Punjabi are spoken in the periphery of the region. Dogri, Kangri, and other western Pahari dialects are spoken in the north-central and northeastern peripheries of the region, while Bagri is spoken in south-central and southeastern sections. Meanwhile, Saraiki is generally spoken across a wide belt covering the southwest, while in the northwest there are large pockets containing speakers of Hindko and Pothwari.
Religions
Background
The Punjabi people first practicedHinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or ''dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global po ...
, the oldest recorded religion in the Punjab region. The historical Vedic religion constituted the religious ideas and practices in the Punjab during the Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, bet ...
(1500–500 BCE), centered primarily in the worship of Indra. The bulk of the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
was composed in the Punjab region between circa 1500 and 1200 BC, while later Vedic scriptures were composed more eastwards, between the Yamuna and Ganges rivers. An ancient Indian law book called the Manusmriti, developed by Brahmin Hindu priests, shaped Punjabi religious life from 200 BC onward.
Later, the spread of Buddhisim and Jainism in the Indian subcontinent saw the growth of Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
and Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
in the Punjab. Islam was introduced via southern Punjab in the 8th century, becoming the majority by the 16th century, via local conversion. There was a small Jain community left in Punjab by the 16th century, while the Buddhist community had largely disappeared by the turn of the 10th century. The region became predominantly Muslim due to missionary Sufi saints whose dargahs dot the landscape of the Punjab region.
The rise of Sikhism in the 1700s saw some Punjabis, both Hindu and Muslim, accepting the new Sikh faith. A number of Punjabis during the colonial period of India became Christians, with all of these religions characterizing the religious diversity now found in the Punjab region.
Colonial era
A number of Punjabis during the colonial period of India became Christians, with all of these religions characterizing the religious diversity now found in the Punjab region. Additionally during the colonial era, the practice of religious syncretism among Punjabi Muslims and Punjabi Hindus was noted and documented by officials in census reports: Territory comprises the contemporary subdivisions ofPunjab, Pakistan
Punjab (; , ) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in central-eastern region of the country, Punjab is the second-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the largest province by population. It shares land borders with the P ...
and Islamabad Capital Territory.
Territory comprises the contemporary subdivisions of Punjab, India
Punjab (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northern India. Forming part of the larger Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, the state is bordered by the States and union territories of India, Indian states of Himachal ...
, Chandigarh, Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ...
, and Himachal Pradesh.
The ''Indo−Gangetic Plain West geographical division'' included Hisar district, Loharu State, Rohtak district, Dujana State, Gurgaon district
Gurgaon district, officially known as Gurugram district, is one of the 22 districts of Haryana in northern India. The city of Gurgaon is the administrative headquarters of the district. The population is 1,514,432. It is one of the southern dis ...
, Pataudi State, Delhi, Karnal district, Jalandhar district, Kapurthala State, Ludhiana district, Malerkotla State, Firozpur district, Faridkot State, Patiala State
Patiala State was a self-governing princely state of the British Empire in India, and one of the Phulkian States, that acceded to the Union of India upon Indian independence and partition. Patiala Kingdom/State was founded by Sidhu Jat Sikhs ...
, Jind State, Nabha State, Lahore District, Amritsar district, and Gujranwala District.
The ''Himalayan geographical division'' included Nahan State, Simla District, Simla Hill States, Kangra district, Mandi State, Suket State, and Chamba State.
The ''Sub−Himalayan geographical division'' included Ambala district, Kalsia State
Kalsia was a princely state in Punjab, British India, one of the former Cis-Sutlej states. It was founded by Raja Gurbaksh Singh Sandhu in 1760. After India's independence, it was included in PEPSU and later in the Indian East Punjab after the ...
, Hoshiarpur district, Gurdaspur district, Sialkot District
Sialkot District (Punjabi and ur, ), is one of the districts of Punjab province of Pakistan. It is located in the Majha region of Panjab, otherwise the northeast of the province. The city of Sialkot is the capital of the district. The Sial ...
, Gujrat District, Jhelum District, Rawalpindi District, and Attock District.
The ''North−West Dry Area geographical division'' included Montgomery District, Shahpur District, Mianwali District, Lyallpur District, Jhang District, Multan District, Bahawalpur State, Muzaffargarh District, and Dera Ghazi Khan District.
Post-partition
In the present-day, the vast majority of Pakistani Punjabis are Sunni Muslim by faith, but also include significant minority faiths, such as Shia Muslims, Ahmadi Muslims, Hindus, Sikhs and Christians. Sikhism, founded byGuru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also referred to as ('father Nānak'), was the founder of Sikhism and is the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. His birth is celebrated ...
is the main religion practised in the post-1966 Indian Punjab state. About 57.7% of the population of Punjab state is Sikh, 38.5% is Hindu, with the remaining population including Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
, Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
, and Jains. Punjab state contains the holy Sikh cities of Amritsar
Amritsar (), historically also known as Rāmdāspur and colloquially as ''Ambarsar'', is the second largest city in the Indian state of Punjab, after Ludhiana. It is a major cultural, transportation and economic centre, located in the Maj ...
, Anandpur Sahib, Tarn Taran Sahib, Fatehgarh Sahib and Chamkaur Sahib.
The Punjab was home to several Sufi saints, and Sufism is well established in the region. Also, Kirpal Singh revered the Sikh Gurus as saints.
Castes and tribes
The Punjab region is diverse. As seen in historic census data taken in the colonial era, many castes, subcastes &tribes
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confl ...
all formed parts of the various ethnic groups in Punjab Province, contemporarily known as Punjabis, Saraikis, Haryanvis, Hindkowans, Dogras, Paharis, and more.
Economy
The historical region of Punjab produce a relatively high proportion of India and Pakistan's food output respectively. The region has been used for extensive wheat farming. In addition, rice, cotton, sugarcane, fruit, and vegetables are also grown. The agricultural output of the Punjab region in Pakistan contributes significantly to Pakistan's GDP. Both Indian and Pakistani Punjab is considered to have the best infrastructure of their respective countries. The Indian state of Punjab is currently the 16th richest state or the eighth richest large state of India. Pakistani Punjab produces 68% of Pakistan's foodgrain production. Its share of Pakistan's GDP has historically ranged from 51.8% to 54.7%. Called "The Granary of India" or "The Bread Basket of India," Indian Punjab produces 1% of the world's rice, 2% of its wheat, and 2% of its cotton. In 2001, it was recorded that farmers made up 39% of Indian Punjab's workforce. In the Punjab region of Pakistan, 42.3% of the labour force is engaged in the agriculture sector. Alternatively, Punjab is also adding to the economy with the increase in employment of Punjab youth in theprivate sector
The private sector is the part of the economy, sometimes referred to as the citizen sector, which is owned by private groups, usually as a means of establishment for profit or non profit, rather than being owned by the government.
Employment
The ...
. Government schemes such as 'Ghar Ghar Rozgar and Karobar Mission' have brought enhanced employability in the private sector. So far, 32,420 youths have been placed in different jobs and 12,114 have been skill-trained.
Education
* Maharaja Ranjit Singh Armed Forces Preparatory InstituteEnvironment
Three Punjab cities; Bathinda,Patiala
Patiala () is a city in southeastern Punjab, northwestern India. It is the fourth largest city in the state and is the administrative capital of Patiala district. Patiala is located around the '' Qila Mubarak'' (the 'Fortunate Castle') constru ...
and Ferozepur, were featured in a list of the top 100 cleanest cities of India from a Swachh Survekshan
''Swachh Survekshan'' ( lit. Cleanliness survey) is an annual survey of cleanliness, hygiene and sanitation in villages, cities and towns across India. It was launched as part of the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, which aimed to make India clean and free ...
report released in August 2020.
See also
* History of Punjab * Sattagydia * Chak (village) * Dhani (settlement type) * Jallianwala Bagh * Music of Punjab * Punjabi cuisine *Punjabi dance
Punjabi dances are an array of folk and religious dances of the Punjabi people indigenous to the Punjab region, straddling the border of India and Pakistan. The style of Punjabi dances ranges from very high energy to slow and reserved, and there ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* *Further reading
* Condos, Mark. ''The Insecurity State: Punjab and the Making of Colonial Power in British India'' (2020excerpt
* * uraishee 73''Punjabi Adab De Kahani'', Abdul Hafeez Quaraihee, Azeez Book Depot, Lahore, 1973. * hopra 77''Punjab as a Sovereign State'', Gulshan Lal Chopra, Al-Biruni, Lahore, 1977. * Patwant Singh. 1999. ''The Sikhs''. New York: Doubleday. . * ''The Evolution of Heroic Tradition in Ancient Panjab'', 1971, Buddha Parkash. * ''Social and Political Movements in ancient Panjab'', Delhi, 1962, Buddha Parkash. * ''History of Porus'', Patiala, Buddha Parkash. * ''History of the Panjab'', Patiala, 1976, Fauja Singh, L.M. Joshi (Ed). * ''The Legacy of the Punjab'', 1997, R.M. Chopra. * ''The Rise Growth and Decline of Indo-Persian Literature'', R.M. Chopra, 2012, Iran Culture House, New Delhi. 2nd revised edition, published in 2013. * Sims, Holly. "The State and Agricultural Productivity: Continuity versus Change in the Indian and Pakistani Punjabs." '' Asian Survey'', 1 April 1986, Vol. 26(4), pp. 483–500.
External links
* * * * {{Authority control Regions of India Historical regions Divided regions Geography of South Asia Historical Indian regions Historical regions of Pakistan . .