Place De La Concorde, Paris on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Place de la Concorde (; ) is a
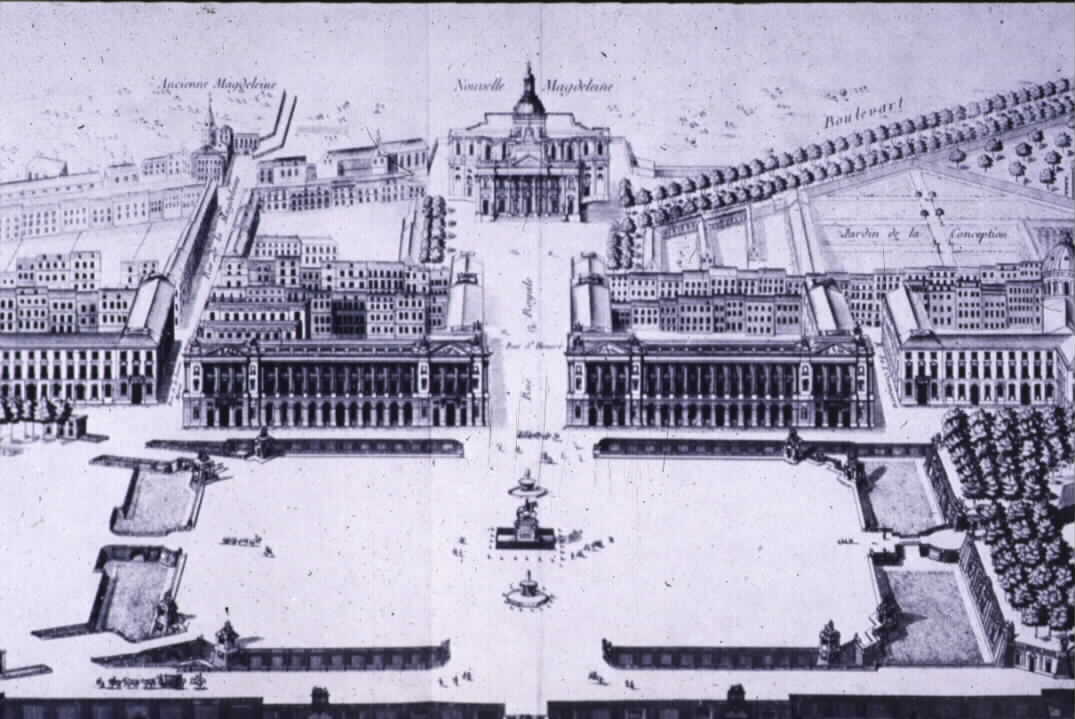 The square was originally designed to be the site of an equestrian statue of King
The square was originally designed to be the site of an equestrian statue of King
File:Vue de l'ordre et de la marche des cérémonies 1763.jpg, Ceremony on the Place Louis XV in 1763
File:Execution of Louis XVI.jpg,
Beginning in 1789, the square was a central stage for the events of the French Revolution. On 13 July 1789, a mob came to the Hôtel de la Marine and seized a store of weapons, including two old cannon, gifts from the King of Siam, which fired the first shots during the
File:GiuseppeCanella-PlaceLouisXVI.JPG, The Place de la Concorde in 1829, before the modifications by King
In 1795, under the Directory, the square was renamed the Place de la Concorde ("Concord Square") as a gesture of reconciliation after the turmoil of the revolution. After the
File:Paris Exposition Place de la Concorde, entrance gate, Paris, France, 1900 n3.jpg, Entrance to
The square was the entry point of two major international expositions: the Paris Universal Exposition of 1900, which left behind the
 The square continues to be the location for the focal point of the
The square continues to be the location for the focal point of the
File:Luxor Obelisk in 2014 (15051263570).jpg, The
The centrepiece of the Place de la Concorde is an ancient Egyptian
File:Place de la Concorde fountain dsc00774.jpg, The Fountain of River Commerce and Navigation, one of the two
When he had completed the installation of the Luxor Obelisk, in 1836, Jacques-Ignace Hittorff, chief architect of the square, moved ahead with two new fountains to complement the obelisk. Hittorff had been a student of the Neoclassical designer
File:Fontaine des Mers, September 24, 2011.jpg, Fountain of the Seas
File:Fontaine des mers concorde detail.jpg, Base of the Fountain of the Seas
File:Paris Place de la Concorde Fontaine des Mers 09.jpg, Detail of the Fountain of the Seas
Both fountains had the same form: a stone basin; six figures of tritons or
File:Hôtel de la Marine.jpg, South front of the
The north side of the square, along the
File:Tuileries Coysevox Renommée.jpg, Copy of "Fame Riding Pegasus" by
On the east the Place de la Concorde is bordered by the two terraces of the
Images of the Place
Series of images of the Place de la Concorde from the 18th to the 20th century
Place de la Concorde Audioguide
Satellite image from Google Maps
{{DEFAULTSORT:Concorde, Place De La Buildings and structures in the 8th arrondissement of Paris Execution sites in France National squares Olympic basketball venues Olympic cycling venues Olympic skateboarding venues Squares in Paris Tourist attractions in Paris Venues of the 2024 Summer Olympics World Heritage Sites in France
public square
A town square (or public square, urban square, city square or simply square), also called a plaza or piazza, is an open public space commonly found in the heart of a traditional town or city, and which is used for community gatherings. Relat ...
in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. Measuring in area, it is the largest square in the French capital. It is located in the city's eighth arrondissement, at the eastern end of the Champs-Élysées
The Avenue des Champs-Élysées (, ; ) is an Avenue (landscape), avenue in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, France, long and wide, running between the Place de la Concorde in the east and the Place Charles de Gaulle in the west, where the Arc ...
.
It was the site of many notable public executions, including Louis XVI
Louis XVI (Louis-Auguste; ; 23 August 1754 – 21 January 1793) was the last king of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. The son of Louis, Dauphin of France (1729–1765), Louis, Dauphin of France (son and heir- ...
, Marie Antoinette
Marie Antoinette (; ; Maria Antonia Josefa Johanna; 2 November 1755 – 16 October 1793) was the last List of French royal consorts, queen of France before the French Revolution and the establishment of the French First Republic. She was the ...
and Maximilien Robespierre
Maximilien François Marie Isidore de Robespierre (; ; 6 May 1758 – 28 July 1794) was a French lawyer and statesman, widely recognised as one of the most influential and controversial figures of the French Revolution. Robespierre ferv ...
in the course of the French Revolution, during which the square was temporarily renamed the Place de la Révolution ('Revolution Square'). It received its current name in 1795 as a gesture of reconciliation in the later years of the revolution. A metro station
A metro station or subway station is a train station for a rapid transit system, which as a whole is usually called a "metro" or "subway". A station provides a means for passengers to purchase tickets, board trains, and evacuate the syste ...
is located at the northeastern corner of Place de la Concorde on Lines 1, 8, and 12 of the Paris Métro
The Paris Métro (, , or , ), short for Métropolitain (), is a rapid transit system serving the Paris metropolitan area in France. A symbol of the city, it is known for its density within the capital's territorial limits, uniform architectur ...
.
History
Design and construction
Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defi ...
, commissioned in 1748 by the merchants of Paris, to celebrate the recovery of King Louis XV from a serious illness. The site chosen for the statue was the large esplanade, or space between the revolving gate, the Tuileries Garden
The Tuileries Garden (, ) is a public garden between the Louvre and the Place de la Concorde in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. Created by Catherine de' Medici as the garden of the Tuileries Palace in 1564, it was opened to the public in ...
and the Cour-la-Reine, a popular lane for horseback riding at the edge of the city. At the time, the Concorde bridge and the Rue de Rivoli
The Rue de Rivoli (; English: "Rivoli Street") is a street in central Paris, France. It is a commercial street whose shops include leading fashionable brands. It bears the name of Napoleon's early victory against the Austrian army, at the Battle o ...
did not exist, and the Rue Royale
Rue Royale (French for "Royal Street") may refer to several streets:
* Rue Royale, Brussels, Belgium
* Rue Royale, Lyon, France
*Rue Royale, Paris
The Rue Royale () is a short street in Paris, France, running between the Place de la Concorde a ...
was a muddy lane that descended down to a marsh beside the Seine
The Seine ( , ) is a river in northern France. Its drainage basin is in the Paris Basin (a geological relative lowland) covering most of northern France. It rises at Source-Seine, northwest of Dijon in northeastern France in the Langres plat ...
.
The architect Ange-Jacques Gabriel
Ange-Jacques Gabriel (; 23 October 1698 – 4 January 1782) was the principal architect of King Louis XV of France. His major works included the Place de la Concorde, the École Militaire, and the Petit Trianon and opera theater at the Palace of ...
made a plan for the site and the square was finished by 1772. It was in the form of an octagon, bordered by a sort of moat twenty meters wide, crossed by stone bridges, and surrounded by a stone balustrade. At the eight corners Gabriel placed stone stairways to descend into the square, which was divided into flowerbeds. In the center of the gardens was the pedestal on which the statue stood. The statue, by Edmé Bouchardon
Edmé Bouchardon (; 29 May 169827 July 1762) was a French sculptor best known for his neoclassical statues in the gardens of the Palace of Versailles, his medals, his equestrian statue of Louis XV of France for the Place de la Concorde (destro ...
, depicted the King on horseback as the victor of the Battle of Fontenoy
The Battle of Fontenoy took place on 11 May 1745 during the War of the Austrian Succession, near Tournai, then in the Austrian Netherlands, now Belgium. A French army of 50,000 under Maurice, comte de Saxe, Marshal Saxe defeated a Pragmatic Ar ...
, dressed as a Roman general, with a laurel wreath on his head. On the four corners of the pedestal, designed by Jean Chalgrin
Jean-François-Thérèse Chalgrin (; 1739 – 21 January 1811) was a French architect, best known for his design for the Arc de Triomphe, Paris.
Biography
His neoclassic orientation was established from his early studies with the prophet of ne ...
, are bronze statues by Jean-Baptiste Pigalle
Jean-Baptiste Pigalle (; 26 January 1714 – 20 August 1785) was a French sculptor whose work was influenced by both baroque and neo-classical trends.
Life
Pigalle was born in Paris, the seventh child of a carpenter. Although he failed to ob ...
, depicting the virtues of great monarchs; Force, Justice, Prudence, and Peace.
The statue was dedicated on 20 June 1763, but by this time the King had lost much of his popularity. A few days after its dedication, someone hung a placard on the statue, proclaiming: "Oh, the beautiful statue! Oh, the fine pedestal! The Virtues are under the feet, and Vice is in the saddle!"
On the north side of the square, between 1760 and 1775, Gabriel planned and built two palatial buildings with identical façades. The classical façades were inspired by those created by Claude Perrault
Claude Perrault (; 25 September 1613 – 9 October 1688) was a French physician and amateur architect, best known for his participation in the design of the east façade of the Louvre in Paris.French Navy
The French Navy (, , ), informally (, ), is the Navy, maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the four military service branches of History of France, France. It is among the largest and most powerful List of navies, naval forces i ...
, the Hôtel de la Marine
The Hôtel de la Marine (), also known (formerly) as the Hôtel du Garde-Meuble (), is an historic building on the Place de la Concorde in Paris, just east of Rue Royale. It was designed by the architect Ange-Jacques Gabriel and built between 1 ...
. The west building was divided into individual properties for the nobility.
French Revolution
Execution of Louis XVI
Louis XVI, former Bourbon King of France since the Proclamation of the abolition of the monarchy, abolition of the monarchy, was publicly executed on 21 January 1793 during the French Revolution at the ''Place de la Révolution'' in Paris. At Tr ...
on the future Place de la Concorde on 21 January 1793
File:La fournée des Girondins 10-11-1793.jpg, Execution of the Girondins
The Girondins (, ), also called Girondists, were a political group during the French Revolution. From 1791 to 1793, the Girondins were active in the Legislative Assembly and the National Convention. Together with the Montagnards, they initiall ...
on 31 October 1793
storming of the Bastille
The Storming of the Bastille ( ), which occurred in Paris, France, on 14 July 1789, was an act of political violence by revolutionary insurgents who attempted to storm and seize control of the medieval armoury, fortress, and political prison k ...
on 14 July 1789. On 11 August 1792, the statue of Louis XV was pulled down and taken to a foundry, where it was melted down. A few months later, a new statue, "Liberty", by the sculptor François-Frédéric Lemot
François-Frédéric Lemot (4 November 1772 — 6 May 1827) was a French sculptor, working in the Neoclassical style.
Biography
Lemot was born at Lyon. Having briefly studied architecture at the Academy of Besançon, then having made his way to P ...
, took its place; it was a figure wearing a red liberty cap and holding a lance. The Place Louis XV ("Louis XV Square") became the Place de la Revolution ("Revolution Square").
In October 1792, the first executions by guillotine in the square took place. The two people who were executed were thieves who had stolen the royal crown diamonds from the Hotel de la Marine. On 21 January 1793, King Louis XVI
Louis XVI (Louis-Auguste; ; 23 August 1754 – 21 January 1793) was the last king of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. The son of Louis, Dauphin of France (1729–1765), Louis, Dauphin of France (son and heir- ...
was executed there, followed in the same year on 16 October by Queen Marie Antoinette
Marie Antoinette (; ; Maria Antonia Josefa Johanna; 2 November 1755 – 16 October 1793) was the last List of French royal consorts, queen of France before the French Revolution and the establishment of the French First Republic. She was the ...
. As the Reign of Terror
The Reign of Terror (French: ''La Terreur'', literally "The Terror") was a period of the French Revolution when, following the creation of the French First Republic, First Republic, a series of massacres and Capital punishment in France, nu ...
commenced, the guillotine was set up again on 11 May 1793, midway between the Statue of Liberty and the turning bridge at the entrance to the Tuileries Garden, and remained there for thirteen months. Of the 2,498 persons guillotined in Paris during the Revolution, 1,119 were executed on the Place de la Concorde, 73 on the Place de la Bastille
The Place de la Bastille () is a square in Paris where the Bastille prison once stood, until the storming of the Bastille and its subsequent physical destruction between 14 July 1789 and 14 July 1790 during the French Revolution. No vestige of ...
and 1,306 on the Place de la Nation
The Place de la Nation (; formerly the Place du Trône , subsequently the Place du Trône-Renversé during the French Revolution) is a circle on the eastern side of Paris, between the Place de la Bastille and the Bois de Vincennes, on the bo ...
. Besides Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette, others executed on the same site included Charlotte Corday
Marie-Anne Charlotte de Corday d'Armont (27 July 1768 – 17 July 1793), known simply as Charlotte Corday (), was a figure of the French Revolution who assassinated revolutionary and Jacobins, Jacobin leader Jean-Paul Marat on 13 July 1793. Cor ...
and Madame du Barry
Jeanne Bécu, comtesse du Barry (; 28 August 1744 – 8 December 1793) was the last ''maîtresse-en-titre'' of King Louis XV of France. She was executed by guillotine during the French Revolution on accusations of treason—particularly being ...
. During the later days of the Reign of Terror in 1794, Georges Danton
Georges Jacques Danton (; ; 26 October 1759 – 5 April 1794) was a leading figure of the French Revolution. A modest and unknown lawyer on the eve of the Revolution, Danton became a famous orator of the Cordeliers Club and was raised to gove ...
, Camille Desmoulins
Lucie-Simplice-Camille-Benoît Desmoulins (; 2 March 17605 April 1794) was a French journalist, politician and a prominent figure of the French Revolution. He is best known for playing an instrumental role in the events that led to the Stormin ...
, Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794), When reduced without charcoal, it gave off an air which supported respiration and combustion in an enhanced way. He concluded that this was just a pure form of common air and that i ...
, Maximilien Robespierre
Maximilien François Marie Isidore de Robespierre (; ; 6 May 1758 – 28 July 1794) was a French lawyer and statesman, widely recognised as one of the most influential and controversial figures of the French Revolution. Robespierre ferv ...
, and Louis de Saint-Just
Louis Antoine Léon de Saint-Just (; 25 August 176710 Thermidor, Year II 8 July 1794, sometimes nicknamed the Archangel of Terror, was a French revolutionary, political philosopher, member and president of the French National Convention, a ...
were executed there. The last executions, those of the Prairial
Prairial () was the ninth month
A month is a unit of time, used with calendars, that is approximately as long as a natural phase cycle of the Moon; the words ''month'' and ''Moon'' are cognates. The traditional concept of months arose with the ...
riot participants, were carried out on the Place de la Concorde in May 1795.
18th and 19th century: Monuments and fountains
Louis-Philippe
Louis Philippe I (6 October 1773 – 26 August 1850), nicknamed the Citizen King, was King of the French from 1830 to 1848, the penultimate monarch of France, and the last French monarch to bear the title "King". He abdicated from his throne ...
File:Érection de l'obélisque de Louqsor sur la place de la Concorde.jpg, The erection of the Luxor Monument, 25 October 1836
File:Joaquín Pallarés Allustante Place de la concorde.jpg, The square in 1872
Bourbon Restoration Bourbon Restoration may refer to:
France under the House of Bourbon:
* Bourbon Restoration in France (1814, after the French revolution and Napoleonic era, until 1830; interrupted by the Hundred Days in 1815)
Spain under the Spanish Bourbons:
* Ab ...
of 1814, the name was changed back to the Place Louis XV, and in 1826 the square was renamed the Place Louis XVI ("Louis XVI Square"). After the July Revolution
The French Revolution of 1830, also known as the July Revolution (), Second French Revolution, or ("Three Glorious ays), was a second French Revolution after French Revolution, the first of 1789–99. It led to the overthrow of King Cha ...
of 1830, the name was returned to the Place de la Concorde.
In 1790, early in the French Revolution, the Concorde bridge was constructed, and, at the suggestion of Jacques-Louis David
Jacques-Louis David (; 30 August 1748 – 29 December 1825) was a French painter in the Neoclassicism, Neoclassical style, considered to be the preeminent painter of the era. In the 1780s, his cerebral brand of history painting marked a change in ...
, the statues of the "Marly Horses
The Marly Horses are two 1743–1745 Carrara marble sculpted groups by Guillaume Coustou, showing two rearing horses with their groom. They were commissioned by Louis XV of France for the trough at the entrance to the grounds of his château d ...
by Guillaume Coustou the Elder
Guillaume Coustou the Elder (; 29 November 1677, Lyon – 22 February 1746, Paris) was a French sculpture, sculptor of the Baroque and Louis XIV style. He was a royal sculptor for Louis XIV and Louis XV and became Director of the Académie ro ...
, were placed on the north side, at the entrance of the Champs-Élysées
The Avenue des Champs-Élysées (, ; ) is an Avenue (landscape), avenue in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, France, long and wide, running between the Place de la Concorde in the east and the Place Charles de Gaulle in the west, where the Arc ...
. In 1806, Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
began to construct the Rue de Rivoli
The Rue de Rivoli (; English: "Rivoli Street") is a street in central Paris, France. It is a commercial street whose shops include leading fashionable brands. It bears the name of Napoleon's early victory against the Austrian army, at the Battle o ...
along the edge of the square.
Under King Louis-Philippe
Louis Philippe I (6 October 1773 – 26 August 1850), nicknamed the Citizen King, was King of the French from 1830 to 1848, the penultimate monarch of France, and the last French monarch to bear the title "King". He abdicated from his throne ...
and his prefect of the Seine, Claude-Philibert Barthelot de Rambuteau, the square was remade. In 1832, Jacques Ignace Hittorff
Jacques Ignace Hittorff or, in German, Jakob Ignaz Hittorff (, ) (Cologne, 20 August 1792 – 25 March 1867) was a German-born French architect who combined advanced structural use of new materials, notably cast iron, with conservative Bea ...
was named chief architect of the project. In October 1835 Hittorff installed the new centrepiece of the square, the Luxor Obelisk
The Luxor Obelisks (French: ) are a pair of ancient Egyptian obelisks, over 3,000 years old, carved to stand either side of the portal of the Luxor Temple in the reign of Ramesses II (). The right-hand (western) stone, high, was gifted by Egy ...
, a gift to the King from the wali
The term ''wali'' is most commonly used by Muslims to refer to a saint, or literally a "friend of God".John Renard, ''Friends of God: Islamic Images of Piety, Commitment, and Servanthood'' (Berkeley: University of California Press, 2008); John ...
Muhammad Ali of Egypt
Muhammad Ali (4 March 1769 – 2 August 1849) was the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Albanians, Albanian viceroy and governor who became the ''de facto'' ruler of History of Egypt under the Muhammad Ali dynasty, Egypt from 1805 to 1848, widely consi ...
. It was hoisted into place, before a huge crowd, on 25 October 1836. Hittorff commissioned celebrated sculptors, including James Pradier
James Pradier (born Jean-Jacques Pradier, ; 23 May 1790 – 4 June 1852) was a Genevan-born French sculptor best known for his work in the neoclassical style.
Life and work
Born in Geneva (then the Republic of Geneva), Pradier was the son of a ...
and Jean-Pierre Cortot
Jean-Pierre Cortot (20 August 1787 – 12 August 1843) was a French neoclassical sculptor.
Life
Cortot was born and died in Paris. He was educated at the École des Beaux Arts in Paris, and won the Prix de Rome in 1809, residing in the ...
to make eight statues representing the major cities of France, which were placed in 1838 on columns which had earlier been put in place around the square by Gabriel. These statues form something of a rudimentary map, such that when viewing the Place de la Concorde from a birdseye perspective, the north-eastern states represent north-eastern cities, in the appropriate arrangement relative to one another, and so on. A ring of twenty columns with lanterns were put in place during the same time.
Between 1836 and 1840, Hittorff erected two monumental fountains, the Fontaine Maritime to the side of the Seine, and the Fontaine Fluviale to the side of the Rue Royale. The design, consisting of two fountains each nine meters high, was modeled after that of the fountains of St. Peter's Square in Rome. In 1853, under Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles-Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was President of France from 1848 to 1852 and then Emperor of the French from 1852 until his deposition in 1870. He was the first president, second emperor, and last ...
, the deep moats around the square, which had turned into rendez-vous points for prostitutes, were filled in.
20th century: Expositions, occupation and triumphs
1900 Paris Exposition
The Exposition Universelle of 1900 (), better known in English as the 1900 Paris Exposition, was a world's fair held in Paris, France, from 14 April to 12 November 1900, to celebrate the achievements of the past century and to accelerate develop ...
, whose vestiges include the Grand Palais
The (; ), commonly known as the , is a historic site, exhibition hall and museum complex located in the 8th arrondissement of Paris between the Champs-Élysées and the Seine, France. Construction of the began in 1897 following the demolitio ...
File:Paris-FR-75-Expo 1925 Arts décoratifs-entrée Place de la Concorde.jpg, Entrance to the International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts
The International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts () was a specialized exhibition held in Paris, France, from April 29 (the day after it was inaugurated in a private ceremony by the President of France) to November 8, 1925 (O ...
in 1925, which gave its name to "Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French (), is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design that first Art Deco in Paris, appeared in Paris in the 1910s just before World War I and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920 ...
"
File:Émeute février 1934 place de la Concorde.jpg, A demonstration against parliamentary corruption in 1934 led to a riot, causing eleven deaths and two hundred injured.
File:Bundesarchiv Bild 183-1985-1216-530, Paris, Panzer-Parade der deutschen Wehrmacht auf dem Place de la Concorde.jpg, German tanks parade on the square in 1941
File:Parisians celebrating liberation on place de la Concorde HD-SN-99-02716.jpg, Crowds celebrating the liberation of Paris scatter from German sniper fire August 1944. Rue Saint-Florentin
The Rue Saint-Florentin is a thoroughfare in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, 1st and 8th arrondissement of Paris. The street took its name from the Duc de la Vrillière, Louis Phélypeaux, comte de Saint-Florentin, minister and secretary of stat ...
is in the background.
Grand Palais
The (; ), commonly known as the , is a historic site, exhibition hall and museum complex located in the 8th arrondissement of Paris between the Champs-Élysées and the Seine, France. Construction of the began in 1897 following the demolitio ...
and the Petit Palais
The (; ) is an art museum in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, France.
Built for the Exposition Universelle (1900), 1900 Exposition Universelle ("universal exhibition"), it now houses the City of Paris Museum of Fine Arts (''Musée des beaux-arts ...
, and the 1925 International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts
The International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts () was a specialized exhibition held in Paris, France, from April 29 (the day after it was inaugurated in a private ceremony by the President of France) to November 8, 1925 (O ...
, which gave its name to the Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French (), is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design that first Art Deco in Paris, appeared in Paris in the 1910s just before World War I and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920 ...
architectural style of the 20th century. It was also the site of great national celebrations, including the victory celebrations of the end of the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
and the Liberation of Paris
The liberation of Paris () was a battle that took place during World War II from 19 August 1944 until the German garrison surrendered the French capital on 25 August 1944. Paris had been occupied by Nazi Germany since the signing of the Armisti ...
in the Second World War. It experienced violent confrontations. A far-right demonstration in 1934 turned violent, with eleven deaths and two hundred injured. It also hosted triumphant celebrations of sporting events such as the French national team's victory in the 1998 FIFA World Cup
The 1998 FIFA World Cup was the 16th FIFA World Cup, the Association football, football world championship for List of men's national association football teams, men's national teams. The finals tournament was held in France from 10 June to 1 ...
.
21st century: Olympic and Paralympic Games, removal of traffic
 The square continues to be the location for the focal point of the
The square continues to be the location for the focal point of the Bastille Day military parade
The Bastille Day military parade, also known as the 14 July military parade, translation of the French name of , is a French military parade that has been held on the morning of Bastille Day, 14 July, each year in Paris since 1880, almost with ...
down the Champs-Élysées
The Avenue des Champs-Élysées (, ; ) is an Avenue (landscape), avenue in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, France, long and wide, running between the Place de la Concorde in the east and the Place Charles de Gaulle in the west, where the Arc ...
, with the President of France
The president of France, officially the president of the French Republic (), is the executive head of state of France, and the commander-in-chief of the French Armed Forces. As the presidency is the supreme magistracy of the country, the po ...
and invited guests watching the parade from the square.
In 2024, the square was the venue for 4 sports at the 2024 Summer Olympics
The 2024 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXXIII Olympiad () and branded as Paris 2024, were an international multi-sport event held in France from 26 July to 11 August 2024, with several events started from 24 July. P ...
(BMX freestyle
Freestyle BMX is bicycle motocross stunt riding on BMX bikes. It is an extreme sport descended from BMX racing that consists of four disciplines: street, park, trails, and flatland. The sport made its Olympic debut at the 2020 Summer Olympics.
E ...
, Breaking, Skateboarding
Skateboarding is an extreme sport, action sport that involves riding and Skateboarding trick, performing tricks using a skateboard, as well as a recreational activity, an art form, an entertainment industry Profession, job, and a method of tr ...
and Basketball 3x3
3x3 basketball (stylized as ''ƐX3'', pronounced ''three-ex-three'') is a variation of basketball played three-a-side, with one backboard and in a half-court setup. This basketball game format is currently being promoted and structured by FIBA, ...
), as well as the venue for the opening ceremony
An opening ceremony, grand opening, or ribbon-cutting ceremony marks the official opening of a newly constructed location or the start of an event.
of the Paralympic Games. Temporary stands and sporting facilities were built, while protecting items such as the Luxor Obelisk. Over 25,000 people attended the square each day during the Olympics, and the Paralympics opening ceremony was watched by 35,000 people in the square.
Following the Games, vehicle traffic did not return to the majority of the square, after Anne Hidalgo
Ana María "Anne" Hidalgo Aleu (, ; born 19 June 1959) is a Spanish-French politician who has served as Mayor of Paris since 2014, the first woman to hold the office. She is a member of the Socialist Party (France), Socialist Party (PS).
Hidalg ...
, the Mayor of Paris
The mayor of Paris (, ) is the Chief executive officer, chief executive of Paris, the capital and largest city in France.
The officeholder is responsible for the administration and management of the city, submits proposals and recommendations to ...
announced a partial pedestrianisation
Pedestrian zones (also known as auto-free zones and car-free zones, as pedestrian precincts in British English, and as pedestrian malls in the United States and Australia) are areas of a city or town restricted to use by people on foot or ...
of the square in January 2024, with plans for a substantial redesign of the square in future.
Description
Luxor Obelisk
Luxor Obelisk
The Luxor Obelisks (French: ) are a pair of ancient Egyptian obelisks, over 3,000 years old, carved to stand either side of the portal of the Luxor Temple in the reign of Ramesses II (). The right-hand (western) stone, high, was gifted by Egy ...
File:Concorde Obelix (5).jpg, Illustration on the base of the obelisk, showing how it was raised into place in 1836
File:Paris Concorde obélisque 2.jpg, Hieroglyphs on the obelisk.
File:Paris Concorde obélisque 1.jpg, Hieroglyphs on the upper obelisk. The Pharaoh on his throne is portrayed at the top
obelisk
An obelisk (; , diminutive of (') ' spit, nail, pointed pillar') is a tall, slender, tapered monument with four sides and a pyramidal or pyramidion top. Originally constructed by Ancient Egyptians and called ''tekhenu'', the Greeks used th ...
decorated with hieroglyphics
Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs ( ) were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined ideographic, logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with more than 1,000 distinct characters.I ...
exalting the reign of the pharaoh Ramesses II
Ramesses II (sometimes written Ramses or Rameses) (; , , ; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was an Pharaoh, Egyptian pharaoh. He was the third ruler of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty. Along with Thutmose III of th ...
. It is one of two which the Egyptian government gave to the French in the 19th century. The other one stayed in Egypt, too difficult and heavy to move to France with the technology at that time. On 26 September 1981 President François Mitterrand
François Maurice Adrien Marie Mitterrand (26 October 19168 January 1996) was a French politician and statesman who served as President of France from 1981 to 1995, the longest holder of that position in the history of France. As a former First ...
formally returned the title of the second obelisk to Egypt.
The obelisk once marked the entrance to the Luxor Temple
The Luxor Temple () is a large Ancient Egyptian temple complex located on the east bank of the Nile River in the city today known as Luxor (ancient Thebes (Egypt), Thebes) and was constructed approximately 1400 BCE. In the Egyptian language it was ...
. The wali
The term ''wali'' is most commonly used by Muslims to refer to a saint, or literally a "friend of God".John Renard, ''Friends of God: Islamic Images of Piety, Commitment, and Servanthood'' (Berkeley: University of California Press, 2008); John ...
of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, or hereditary governor, Muhammad Ali Pasha Mehmed Ali Pasha may refer to:
* Muhammad Ali of Egypt (1769–1849), considered the founder of modern Egypt
* Çerkes Mehmed Pasha (died 1625), Ottoman statesman and grand vizier
* Mehmed Emin Âli Pasha (1815–1871), Ottoman statesman and gra ...
, offered the 3,300-year-old Luxor
Luxor is a city in Upper Egypt. Luxor had a population of 263,109 in 2020, with an area of approximately and is the capital of the Luxor Governorate. It is among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited c ...
Obelisk as a diplomatic gift to France in 1829. It arrived in Paris on 21 December 1833. Three years later, it was hoisted into place, on top of the pedestal which originally supported the statue of Louis XV, destroyed during the Revolution. The raising of the column was a major feat of engineering, depicted by illustrations on the base of the monument. King Louis Philippe
Louis Philippe I (6 October 1773 – 26 August 1850), nicknamed the Citizen King, was King of the French from 1830 to 1848, the penultimate monarch of France, and the last French monarch to bear the title "King". He abdicated from his throne ...
dedicated the obelisk on 25 October 1836.
The obelisk, a yellow granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
column, rises high, including the base, and weighs over . Given the technical limitations of the day, transporting it was no easy feat – on the pedestal are drawn diagrams explaining the machinery that was used for the transportation. The government of France added a gold-leafed pyramidal cap to the top of the obelisk in 1998, replacing the missing original, believed stolen in the 6th century BC.
Fountains
Fontaines de la Concorde Fontaines may refer to the following places in France:
*Fontaines, Saône-et-Loire, in the Saône-et-Loire ''département''
*Fontaines, Vendée, in the Vendée ''département''
*Fontaines, Yonne, in the Yonne ''département''
*Fontaines-d'Ozilla ...
(1840)
File:Fontaine des Fleuves, Paris May 2013.jpg, Base of the Fountain of River Commerce and Navigation
File:Fontaine des Fleuves.jpg, The Fountain of River Commerce at night
Charles Percier
Charles Percier (; 22 August 1764 – 5 September 1838) was a neoclassical French architect, interior decorator and designer, who worked in a close partnership with Pierre François Léonard Fontaine, originally his friend from student days. Fo ...
at the École des Beaux-Arts
; ) refers to a number of influential art schools in France. The term is associated with the Beaux-Arts architecture, Beaux-Arts style in architecture and city planning that thrived in France and other countries during the late nineteenth centu ...
. He had spent two years studying the architecture and fountains of Rome, particularly the Piazza Navona
Piazza Navona () is a public open space in Rome, Italy. It is built on the site of the 1st century AD Stadium of Domitian and follows the form of the open space of the stadium in an elongated oval. The ancient Romans went there to watch the '' a ...
and Piazza San Pietro
St. Peter's Square (, ) is a large plaza located directly in front of St. Peter's Basilica in Vatican City, the papal enclave in Rome, directly west of the neighborhood (rione) of Borgo. Both the square and the basilica are named after Saint ...
, each of which had obelisks aligned with fountains.
Hittorff's fountains were each nine meters high, matching the height of the earlier columns and statues around the square representing great French cities. The Maritime Fountain was on the south, between the obelisk and Seine, and illustrated the seas bordering France, while the Fluvial Fountains or river fountain, on the north, between the Obelisk and the Rue Royale, illustrated the great rivers of France. It is located in the same place where the guillotine which executed Louis XVI had been placed.
naiad
In Greek mythology, the naiads (; ), sometimes also hydriads, are a type of female spirit, or nymph, presiding over fountains, wells, springs, streams, brooks and other bodies of fresh water.
They are distinct from river gods, who embodied ...
s holding fish spouting water; six seated allegorical figures, their feet on the prows of ships, supporting the pedestal, of the circular ''vasque''; four statues of different forms of genius in arts or crafts supporting the upper inverted upper vasque; whose water shot up and then cascaded down to the lower vasque and then the basin.
The north fountain was devoted to the Rivers, with allegorical figures representing the Rhone and the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
, the arts of the harvesting of flowers and fruits, harvesting and grape growing; and the geniuses of river navigation, industry, and agriculture.
The south fountain, closer to the Seine, represented the seas, with figures representing the Atlantic and the Mediterranean; harvesting coral; harvesting fish; collecting shellfish; collecting pearls; and the geniuses of astronomy, navigation, and commerce.
North side
Hôtel de la Marine
The Hôtel de la Marine (), also known (formerly) as the Hôtel du Garde-Meuble (), is an historic building on the Place de la Concorde in Paris, just east of Rue Royale. It was designed by the architect Ange-Jacques Gabriel and built between 1 ...
File:La grande Loggia de l'Hôtel de la Marine (Paris) (51352775059).jpg, The Grand Loggia of the Hôtel de la Marine, overlooking the Place de la Concorde
File:Hôtels Crillon Cartier Plessis Bellière Coislin Paris 2.jpg, Hotel Crillon, FIA, and Automobile Club of France
Rue de Rivoli
The Rue de Rivoli (; English: "Rivoli Street") is a street in central Paris, France. It is a commercial street whose shops include leading fashionable brands. It bears the name of Napoleon's early victory against the Austrian army, at the Battle o ...
, is occupied by two palatial buildings, whose matching façades were designed by Ange-Jacques Gabriel
Ange-Jacques Gabriel (; 23 October 1698 – 4 January 1782) was the principal architect of King Louis XV of France. His major works included the Place de la Concorde, the École Militaire, and the Petit Trianon and opera theater at the Palace of ...
. They are separated by the Rue Royale
Rue Royale (French for "Royal Street") may refer to several streets:
* Rue Royale, Brussels, Belgium
* Rue Royale, Lyon, France
*Rue Royale, Paris
The Rue Royale () is a short street in Paris, France, running between the Place de la Concorde a ...
, which enters the square from the north and was also designed by Gabriel. He planned the harmonious façades of the buildings along Rue Royale, including the façade and interior of his own residence at Number eight.
The Neoclassical facades of the two major buildings on the Place de la Concorde are nearly identical. Their design was inspired by the Louvre Colonnade
The Louvre Colonnade is the easternmost façade of the Louvre Palace in Paris. It has been celebrated as the foremost masterpiece of French architectural classicism since its construction, mostly between 1667 and 1674. The design, dominated by t ...
, begun in 1667 by Louis Le Vau
Louis Le Vau (; c. 1612 – 11 October 1670) was a French Baroque architect, who worked for Louis XIV of France. He was an architect that helped develop the French Classical style in the 17th century.''Encyclopedia of World Biography''"Louis Le ...
, architect of Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
, Charles Le Brun
Charles Le Brun (; baptised 24 February 1619 – 12 February 1690) was a French Painting, painter, Physiognomy, physiognomist, Aesthetics, art theorist, and a director of several art schools of his time. He served as a court painter to Louis XIV, ...
, and Charles Perrault
Charles Perrault ( , , ; 12 January 162816 May 1703) was a French author and member of the Académie Française. He laid the foundations for a new literary genre, the fairy tale, with his works derived from earlier folk tales, published in his ...
. The front is decorated with sculpted medallions and guerlands, another feature borrowed from the Louvre east front. The long front of colonnades is balanced at either end two sections with triangular frontons and Corinthian columns.
The building on the east, the Hôtel de la Marine
The Hôtel de la Marine (), also known (formerly) as the Hôtel du Garde-Meuble (), is an historic building on the Place de la Concorde in Paris, just east of Rue Royale. It was designed by the architect Ange-Jacques Gabriel and built between 1 ...
, was originally the royal Garde-Meuble, the depot for all the royal furnishings. Marie Antoinette
Marie Antoinette (; ; Maria Antonia Josefa Johanna; 2 November 1755 – 16 October 1793) was the last List of French royal consorts, queen of France before the French Revolution and the establishment of the French First Republic. She was the ...
also had a small apartment there. In 1792, during the Revolution, it became the headquarters of the French Navy. The Navy departed in 2015, and the building is now a national monument and museum. The ceremonial rooms of the Navy and the apartments of the original intendants before the Revolution have been restored. Since 2021 the building is also home to the Al Thani Collection The Al Thani Collection is a collection of art representing civilizations around the world, highlights from which are on view in the Hôtel de la Marine, on the Place de la Concorde, in Paris. It was assembled by Sheikh Hamad bin Abdullah Al Thani ...
, a collection of ancient art from early civilisations brought together by Sheikh Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani
Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani (; born 1 January 1952) is a member of Qatar's royal family, the House of Thani. He was the ruling Emir of Qatar from 1995 until 2013 when he abdicated the throne, handing power to his fourth son Tamim bin Hamad Al ...
, first cousin of the Emir of Qatar
Qatar, officially the State of Qatar, is a country in West Asia. It occupies the Geography of Qatar, Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it shares Qatar–Saudi Arabia border, its sole land b ...
.
The building on the west is divided into four separate buildings, which were originally occupied by members of the French Nobility.
* Number 4 was first occupied by the Marquise de Coislin, then, from 1805 to 1807, by the author and diplomat François-René de Chateaubriand
François-René, vicomte de Chateaubriand (4 September 1768 – 4 July 1848) was a French writer, politician, diplomat and historian who influenced French literature of the nineteenth century. Descended from an old aristocratic family from Bri ...
(1805–1807).
* Number 6 was first occupied by the Rouillé de l'Estaing, secretary of the King, and later by the Marquise de Plessis-Bellière, who left it in her will to Pope Leo XIII
Pope Leo XIII (; born Gioacchino Vincenzo Raffaele Luigi Pecci; 2March 181020July 1903) was head of the Catholic Church from 20 February 1878 until his death in July 1903. He had the fourth-longest reign of any pope, behind those of Peter the Ap ...
. The Pope in turn sold it to the Automobile Club of France in 1901, and they still occupy it.
* Number 8, was occupied by the royal architect Pierre-Louis Moreau-Desproux
Pierre-Louis Moreau-Desproux (Paris 1727 — Paris 1793) was a pioneering French Neoclassicism, neoclassical architect.
Training
Though he did not gain the Prix de Rome that was the dependable gateway to a prominent French career in architecture ...
. It was eventually also sold and now houses the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile
The Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA; ) is an international organisation with two primary functions surrounding use of the automobile. Its mobility division advocacy, advocates the interests of motoring organisations, the automot ...
(FIA) which sanctions Formula 1
Formula One (F1) is the highest class of worldwide racing for open-wheel single-seater formula Auto racing, racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one ...
races.
* Number 10 was occupied in 1775 by the 6th Duke of Aumont beginning in 1775. He ceded it in 1788 to the Duke of Crillon, who emigrated from France during the French Revolution. The Duchess of Crillon returned and she and her descendants occupied it from 1820 until 1904. in 1909 it became a hotel for wealthy travellers, the Hôtel de Crillon
Hôtel de Crillon, A Rosewood Hotel () is a historic luxury hotel in Paris which opened in 1909 in a building dating to 1758. Located at the foot of the Champs-Élysées, the Crillon, along with the Hôtel de la Marine, is one of two identical s ...
. In 2010 it was bought by a Saudi prince, Mutaib bin Abdullah Al Saud.
East side: The Tuileries Garden, Jeu de Paume and Orangerie
Antoine Coysevox
Charles Antoine Coysevox ( or ; 29 September 164010 October 1720), was a French sculptor in the Baroque and Louis XIV style, best known for his sculpture decorating the gardens and Palace of Versailles and his portrait busts.
Biography
Coysev ...
at the entrance to the Tuileries Garden
File:Place de la Concorde 1, Paris 25 May 2014.jpg, West gate from the square to the Tuileries Garden
File:Jardin des Tuileries @ Paris (29078896192).jpg, Detail of Gateway to the Tuileries Garden
File:Monets water lilies in the Musée de lOrangerie 03.jpg, Two of the eight Water Lilies
''Water Lilies'' ( ) is a series of approximately 250 oil paintings by French Impressionist Claude Monet (1840–1926). The paintings depict his flower garden at his home in Giverny, and were the main focus of his artistic production during ...
paintings by Claude Monet
Oscar-Claude Monet (, ; ; 14 November 1840 – 5 December 1926) was a French painter and founder of Impressionism painting who is seen as a key precursor to modernism, especially in his attempts to paint nature as he perceived it. During his ...
at the Musée de l'Orangerie
The Musée de l'Orangerie () is an art gallery of Impressionist and Post-Impressionist paintings located in the west corner of the Tuileries Garden next to the Place de la Concorde in Paris. The museum is most famous as the permanent home of ...
, overlooking the square
Tuileries Garden
The Tuileries Garden (, ) is a public garden between the Louvre and the Place de la Concorde in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. Created by Catherine de' Medici as the garden of the Tuileries Palace in 1564, it was opened to the public in ...
, the park of the Tuileries Palace
The Tuileries Palace (, ) was a palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the Seine, directly in the west-front of the Louvre Palace. It was the Parisian residence of most French monarchs, from Henri IV to Napoleon III, until it was b ...
. The palace was burned by the Paris Commune
The Paris Commune (, ) was a French revolutionary government that seized power in Paris on 18 March 1871 and controlled parts of the city until 28 May 1871. During the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, the French National Guard (France), Nation ...
in 1871, and few vestiges remain. The highly-ornate gilded gateway to the garden was designed by Ange-Jacques Gabriel
Ange-Jacques Gabriel (; 23 October 1698 – 4 January 1782) was the principal architect of King Louis XV of France. His major works included the Place de la Concorde, the École Militaire, and the Petit Trianon and opera theater at the Palace of ...
, the architect to the square, and leads to the grand promenade of the garden which extends east as far as the Louvre. The gateway is flanked by two monumental equestrian sculptures by Antoine Coysevox
Charles Antoine Coysevox ( or ; 29 September 164010 October 1720), was a French sculptor in the Baroque and Louis XIV style, best known for his sculpture decorating the gardens and Palace of Versailles and his portrait busts.
Biography
Coysev ...
, "Fame Riding Pegasus" and "Mercury Riding Pegasus", made for the Château de Marly
The Château de Marly () was a French royal residence located in what is now Marly-le-Roi, the commune on the northern edge of the royal park. This was situated west of the palace and garden complex at Versailles. Marly-le-Roi is the town that d ...
of Louis XIV, and installed at the Tuileries in 1719. They are copies; the originals are now in the Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is a national art museum in Paris, France, and one of the most famous museums in the world. It is located on the Rive Droite, Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement of Paris, 1st arron ...
.
The early west gateway of Paris, the Port de la Conference, was located at the south end of the square, next to the Seine. It was built by Henry III of France
Henry III (; ; ; 19 September 1551 – 2 August 1589) was King of France from 1574 until his assassination in 1589, as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1573 to 1575.
As the fourth son of King Henry II of France, he ...
, and as the city grew was demolished in 1730. A revolving bridge originally gave entry to the gardens; it was located where the ornamental is today.
The terraces of the Garden overlooking the square are the home of two museums. At the north end, near the Rue de Rivoli, is the National Gallery of the Jeu de Paume
''Jeu de paume'' (, ; originally spelled ; ), nowadays known as real tennis, (US) court tennis or (in France) ''courte paume'', is a ball-and-court game that originated in France. It was an indoor precursor of tennis played without racquets, ...
. It was built under Emperor Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles-Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was President of France from 1848 to 1852 and then Emperor of the French from 1852 until his deposition in 1870. He was the first president, second emperor, and last ...
as the imperial tennis court in 1861 and was enlarged in 1878. During the Second World War it was used by the Germans as a depot for storing looted art. From 1947 until 1986 it displayed the Impressionist
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by visible brush strokes, open Composition (visual arts), composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passage ...
paintings of the Louvre. In 1997, it was entirely rebuilt, and now displays temporary exhibitions of contemporary art.
Closer to the Seine is the Orangerie Museum, which was built in 1852 by architect Firmin Bourgeois as a winter shelter for the Tuileries citrus trees, also under Napoleon III. It was later converted into an art exhibition hall, and since 1927 it has been the home of one of the most famous groups of works of Impressionism, the eight paintings of the "Water Lilies
''Water Lilies'' ( ) is a series of approximately 250 oil paintings by French Impressionist Claude Monet (1840–1926). The paintings depict his flower garden at his home in Giverny, and were the main focus of his artistic production during ...
" series by Claude Monet
Oscar-Claude Monet (, ; ; 14 November 1840 – 5 December 1926) was a French painter and founder of Impressionism painting who is seen as a key precursor to modernism, especially in his attempts to paint nature as he perceived it. During his ...
. It also displays the Walter Guillaume collection of impressionist and paintings and works from the school of Paris.
The terrace overlooking the square also displays a number of important works of sculpture. These include, since 1998, four works by Auguste Rodin
François Auguste René Rodin (; ; 12 November 184017 November 1917) was a French sculptor generally considered the founder of modern sculpture. He was schooled traditionally and took a craftsman-like approach to his work. Rodin possessed a u ...
: '' The Kiss'' (1881–1888); a bronze copy of the marble original, cast in 1934; "Eve
Eve is a figure in the Book of Genesis in the Hebrew Bible. According to the origin story, "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the universe and its inhabitants came to be. Creation myths develop through oral traditions and there ...
" (1881); The ''Grand Shadow'' (1881); and ''Meditation, with arms'' (1881–1905). It also displays more modern works, including ''Le Belle Costumé'' (1973) by Jean Dubuffet
Jean Philippe Arthur Dubuffet (; 31 July 1901 – 12 May 1985) was a French Painting, painter and sculpture, sculptor of the School of Paris, École de Paris (School of Paris). His idealistic approach to aesthetics embraced so-called "low art" a ...
, and ''Le Grand Commandement Blanc'' by Alain Kirili
Alain Kirili (29 August 1946 – 19 May 2021) was a French-American sculptor. He was recognized for his post-minimalist abstract sculptures in forged iron and his large-scale public sculptures. His work has been the subject of numerous gallery ...
(1986). Two marble statues of lions are also displayed on the terrace, dating from the 18th century, and made by Giuseppe Franchi.Jacquin, Emmanuel, "Les Tuileries Du Louvre à la Concorde" (2008), p. 62
Redesign of the square
First proposed byAnne Hidalgo
Ana María "Anne" Hidalgo Aleu (, ; born 19 June 1959) is a Spanish-French politician who has served as Mayor of Paris since 2014, the first woman to hold the office. She is a member of the Socialist Party (France), Socialist Party (PS).
Hidalg ...
, the Mayor of Paris
The mayor of Paris (, ) is the Chief executive officer, chief executive of Paris, the capital and largest city in France.
The officeholder is responsible for the administration and management of the city, submits proposals and recommendations to ...
in January 2021, the square is planned to be redesigned to increase pedestrian space, reduce car traffic, and add more green space and trees. Traffic will be directed around the outside edges of the square, with the number of traffic lanes greatly reduced. Four large areas of trees and greenery will be created in the corners of the square around the obelisk and monuments and open space in the centre – with of new green space. Work is scheduled to begin in 2026.
See also
*Execution of Louis XVI
Louis XVI, former Bourbon King of France since the Proclamation of the abolition of the monarchy, abolition of the monarchy, was publicly executed on 21 January 1793 during the French Revolution at the ''Place de la Révolution'' in Paris. At Tr ...
* List of works by James Pradier
This is a list of works by the Swiss-born French sculptor James Pradier (1790–1852). He was best known for his work in the neoclassical style.
Works in cathedrals and churches
Public statues and monuments in Paris
Busts and statues of L ...
* The 1920s redesign of Logan Circle (Philadelphia)
Logan Circle, also known as Logan Square, is an open-space park in Center City, Philadelphia, Center City Philadelphia's northwest quadrant and one of the five original planned city square, squares laid out on the city grid plan, grid. The center ...
was based on the Place de la Concorde and includes near-copies of the Hôtel de Crillon and Hôtel de la Marine and an allegorical fountain representing the rivers of the Philadelphia area.
References
Bibliography (in French)
* * * * * * Jacquin, Emmanuel, ''Les Tuileries, Du Louvre à la Concorde'', Editions du Patrimoine, Centres des Monuments Nationaux, Paris. () * Pommereau, Claude, "Hôtel de la Marine" (June 2021), Beaux Arts Éditions, Paris () * "Connaissance des arts" special edition, "L'Hôtel de la Marine", (in French), published September 2021 * ''Paris et ses fontaines, de la Renaissance à nos jours'', texts assembled by Dominque Massounie, Pauline-Prevost-Marcilhacy and Daniel Rabreau, Délegation a l'action artistique de la Ville de Paris. from the Collection Paris et son Patrimoine, directed by Beatrice de Andia. Paris, 1995.External links
*Images of the Place
Series of images of the Place de la Concorde from the 18th to the 20th century
Place de la Concorde Audioguide
Satellite image from Google Maps
{{DEFAULTSORT:Concorde, Place De La Buildings and structures in the 8th arrondissement of Paris Execution sites in France National squares Olympic basketball venues Olympic cycling venues Olympic skateboarding venues Squares in Paris Tourist attractions in Paris Venues of the 2024 Summer Olympics World Heritage Sites in France