The Islamic State (IS), also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) and Daesh, is a transnational
Salafi jihadist organization and unrecognized
quasi-state
A quasi-state (sometimes referred to as a state-like entity or formatively a proto-state) is a political entity that does not represent a fully autonomous sovereign state with its own institutions.
The precise definition of ''quasi-state'' in po ...
. IS occupied significant territory in
Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
and
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
in 2013, but lost most of it in 2019. In 2014, the group proclaimed itself to be a worldwide
caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
, and claimed religious, political, and military authority over all
Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
worldwide, a claim not accepted by the vast majority of Muslims. It is
designated as a terrorist organisation by the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
and many countries around the world, including
Muslim countries.
By the end of 2015, its self-declared
caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
ruled an area with a population of about 12 million, where they enforced their extremist interpretation of
Islamic law
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on scriptures of Islam, particularly the Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' refers to immutable, intan ...
, managed an annual budget exceeding billion, and commanded more than 30,000 fighters. After a grinding conflict with American, Iraqi, and Kurdish forces, IS lost control of all its Middle Eastern territories by 2019, subsequently reverting to insurgency from remote hideouts while continuing its
propaganda efforts. These efforts have garnered a significant following in northern and
Sahelian Africa, where IS still controls a significant territory.
Originating in the
Jaish al-Ta'ifa al-Mansurah founded by
Abu Omar al-Baghdadi in 2004, the organisation (primarily under the
Islamic State of Iraq
The Islamic State of Iraq (ISI; ') was a Salafi jihadist militant organization that fought the forces of the U.S.-led coalition during the Iraqi insurgency. The organization aimed to overthrow the Iraqi federal government and establish an ...
name) affiliated itself with
al-Qaeda in Iraq
Al-Qaeda in Iraq (; AQI), was a Salafi jihadism, Salafi jihadist organization affiliated with al-Qaeda. It was founded on 17 October 2004, and was led by Abu Musab al-Zarqawi until its disbandment on 15 October 2006 after he was killed in a targ ...
and fought alongside them during the
2003–2006 phase of the Iraqi insurgency. The group later changed their name to Islamic State of Iraq and Levant for about a year, before declaring itself to be a worldwide
caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
,
called simply the Islamic State ().
During its rule in Syria and Iraq, the group "became notorious for its brutality".
Under its rule of these regions, IS launched
genocides against Yazidis and
Iraqi Turkmen
The Iraqi Turkmen (, عراق تورکمنلری; Arabic: تركمان العراق), also referred to as Iraqi Turks, (, عراق توركلری; ) are the third largest ethnic group in Iraq. They make up to 10%–13% of the Iraqi population. I ...
; engaged in
persecution of Christians
The persecution of Christians can be historically traced from the first century of the Christian era to the present day. Christian missionaries and converts to Christianity have both been targeted for persecution, sometimes to the point ...
,
Shia Muslims, and
Mandaeans
Mandaeans (Mandaic language, Mandaic: ࡌࡀࡍࡃࡀࡉࡉࡀ) ( ), also known as Mandaean Sabians ( ) or simply as Sabians ( ), are an ethnoreligious group who are followers of Mandaeism. They believe that John the Baptist was the final and ...
; publicised
videos of beheadings of soldiers, journalists, and aid workers; and
destroyed several cultural sites. The group has perpetrated terrorist massacres in territories outside of its control, such as the
November 2015 Paris attacks, the
2024 Kerman bombings in Iran, and the
2024 Crocus City Hall attack in Russia.
Lone wolf attacks inspired by the group have also taken place.
After 2015, the
Iraqi Armed Forces and the
Syrian Democratic Forces
The Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) is a Kurds in Syria, Kurdish-led coalition of U.S.-backed Left-wing politics, left-wing ethnic militias and rebel groups, and serves as the official military wing of the Democratic Autonomous Administration ...
pushed back IS and degraded its financial and military infrastructure, assisted by advisors, weapons, training, supplies, and airstrikes by the
American-led coalition,
and later by Russian airstrikes, bombings, cruise missile attacks, and
scorched-earth
A scorched-earth policy is a military strategy of destroying everything that allows an enemy military force to be able to fight a war, including the deprivation and destruction of water, food, humans, animals, plants and any kind of tools and i ...
tactics across Syria, which focused mostly on razing
Syrian opposition strongholds rather than IS bases. By March 2019, IS lost the last of its territories in
West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
, although its affiliates maintained a significant territorial presence in Africa as of 2025.
Name
The Islamic State, abbreviated IS, is
also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL ), the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS ),
and by its
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
acronym Daesh (, ),
[*
*] and also as (). In April 2013, having expanded into Syria, the group adopted the name (). As ''
al-Shām'' is a region often compared with the
Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
or the
region of Syria, the group's name has been variously translated as "Islamic State of Iraq and
al-Sham
Syria, ( or ''Shaam'') also known as Greater Syria or Syria-Palestine, is a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in West Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. The region boundaries have changed throughout history. Howe ...
",
"Islamic State of Iraq and Syria" (both abbreviated as ISIS), or "Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant" (abbreviated as ISIL). In 2014,
Dar al-Ifta al-Misriyyah dubbed ISIS as "QSIS" for "al-Qaeda Separatists in Iraq and Syria", arguing that the group does not represent the vast majority of Muslims.
While the use of either one or the other
acronym
An acronym is a type of abbreviation consisting of a phrase whose only pronounced elements are the initial letters or initial sounds of words inside that phrase. Acronyms are often spelled with the initial Letter (alphabet), letter of each wor ...
has been the subject of debate, the distinction between the two and its relevance has been considered less important. Of greater relevance is the name Daesh, which is an acronym of ISIL's
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
name , or Daesh. This name is widely used among the Muslim world, as well as ISIL's Arabic-speaking detractors, for example when referring to the group whilst speaking amongst themselves, although—and to a certain extent because—it is considered derogatory, as it resembles the Arabic words ''Daes'' ("one who crushes, or tramples down, something underfoot") and ''Dāhis'' (loosely translated as "one who sows discord"). Within areas under its control, ISIL considers use of the name Daesh punishable by
flogging
Flagellation (Latin , 'whip'), flogging or whipping is the act of beating the human body with special implements such as whips, rods, switches, the cat o' nine tails, the sjambok, the knout, etc. Typically, flogging has been imposed ...
.
In late June 2014, the group renamed itself ( or IS), declaring itself a worldwide
caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
. The name "Islamic State" and the group's claim to be a caliphate have been widely rejected, with the UN, various governments, and mainstream Muslim groups refusing to use the new name.
The group's declaration of a new caliphate in June 2014 and its adoption of the name "Islamic State" have been criticised and ridiculed by Muslim scholars and rival Islamists both inside and outside the territory it controls.
In a speech in September 2014, United States President
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
said that ISIL was neither Islamic (on the basis that no religion condones the killing of innocents) nor a state (in that no government
recognises the group as a state),
while many object to using the name Islamic State owing to the far-reaching religious and political claims to authority which that name implies. The
United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
, the United States, Canada, Turkey, Australia, the United Kingdom, and other countries generally call the group ISIL, while much of the Arab world uses the
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
acronym Dāʻish or Daesh. France's Foreign Minister
Laurent Fabius
Laurent Fabius (; born 20 August 1946) is a French politician. A member of the Socialist Party (France), Socialist Party, he previously served as Prime Minister of France from 17 July 1984 to 20 March 1986. Fabius was 37 years old when he was a ...
said: "This is a terrorist group and not a state. I do not recommend using the term Islamic State because it blurs the lines between Islam, Muslims, and Islamists. The Arabs call it 'Daesh' and I will be calling them the 'Daesh cutthroats'." Retired general
John Allen, the U.S. envoy appointed to co-ordinate the coalition;
U.S. Army Lieutenant General
James Terry, head of operations against the group; and
Secretary of State John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician, and diplomat who served as the 68th United States secretary of state from 2013 to 2017 in the Presidency of Barack Obama#Administration, administration of Barac ...
had all shifted towards use of the term Daesh by December 2014, which nonetheless remained a pejorative in 2021.
Purpose and strategy
Ideology
The
ideology of the Islamic State has been described as being a hybrid of
Salafism
The Salafi movement or Salafism () is a Islamic fundamentalism, fundamentalist Islamic revival, revival movement within Sunni Islam, originating in the late 19th century and influential in the Islamic world to this day. The name "''Salafiyya''" ...
,
Salafi jihadism
Salafi jihadism, also known as Salafi-jihadism, jihadist Salafism and revolutionary Salafism, is a religiopolitical Sunni Islam, Sunni Islamist ideology that seeks to establish a global caliphate through armed struggle. In a narrower sense, ji ...
,
Islamic fundamentalism
Islamic fundamentalism has been defined as a revivalist and reform movement of Muslims who aim to return to the founding scriptures of Islam. The term has been used interchangeably with similar terms such as Islamism, Islamic revivalism, Qut ...
,
Wahhabism
Wahhabism is an exonym for a Salafi revivalist movement within Sunni Islam named after the 18th-century Hanbali scholar Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab. It was initially established in the central Arabian region of Najd and later spread to oth ...
,
and
Qutbism,
as well as other doctrines.
According to Robert Manne, there is a "general consensus" that the ideology of the Islamic State is "primarily based upon the writings of the radical Egyptian theoretician
Sayyid Qutb
Sayyid Ibrahim Husayn Shadhili Qutb (9 October 190629 August 1966) was an Egyptian political theorist and revolutionary who was a leading member of the Muslim Brotherhood.
As the author of 24 books, with around 30 books unpublished for differe ...
". The Muslim Brotherhood began the trend of political Islamism in the 20th century, seeking gradual establishment of a new
Caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
, a comprehensive Islamic society ruled by ''
sharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' ...
'' law. Qutb's doctrines of ''
jahiliyya
In Islamic salvation history, the ''Jāhiliyyah'' (Age of Ignorance) is an era of pre-Islamic Arabia as a whole or only of the Hejaz leading up to the lifetime of Muhammad.
The Arabic expression (meaning literally “the age or condition of ig ...
'' (pre-Islamic ignorance), ''hakimiyya'' (divine sovereignty), and ''
takfir
''Takfir'' () is an Arabic language, Arabic and Glossary of Islam, Islamic term which denotes excommunication from Islam of one Muslim by another, i.e. accusing another Muslim of being an Apostasy in Islam, apostate. The word is found neither ...
'' of entire societies formed a radicalized vision of the Muslim Brotherhood's political Islam project.
Qutbism became the precursor to all
jihadist
Jihadism is a neologism for modern, armed militant Political aspects of Islam, Islamic movements that seek to Islamic state, establish states based on Islamic principles. In a narrower sense, it refers to the belief that armed confrontation ...
thought, from
Abdullah Azzam to
Zawahiri and to Daesh. Alongside Sayyid Qutb, the most invoked ideological figures of IS include
Ibn Taymiyya, Abdullah Azzam, and
Abu Bakr Naji.
Although IS claims to adhere to the
Salafi theology of
Ibn Taymiyyah
Ibn Taymiyya (; 22 January 1263 – 26 September 1328)Ibn Taymiyya, Taqi al-Din Ahmad, The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780195125580.001.0001/acref-9780195125580-e-959 was a Sunni Muslim ulama, ...
, it rejects traditional Salafi interpretations as well as the four Sunni schools of law, and anathematizes the majority of Salafis as
heretics. IS ideologues rarely uphold adherence to Islamic scholarship and law manuals for reference, mostly preferring to derive rulings based on self-interpretation of the Qur'an and Muslim traditions.
, the first Emir of the
Islamic State of Iraq
The Islamic State of Iraq (ISI; ') was a Salafi jihadist militant organization that fought the forces of the U.S.-led coalition during the Iraqi insurgency. The organization aimed to overthrow the Iraqi federal government and establish an ...
, was radicalised as a Muslim Brotherhood member during his youth. Motaz Al-Khateeb states that religious texts and Islamic jurisprudence "alone cannot explain the emergence" of Daesh since the Muslim Brotherhood and Daesh "draw on the same Islamic jurisprudence" but "are diametrically opposite" in strategy and behavior. Through the official statement of beliefs originally released by al-Baghdadi in 2007 and subsequently updated since June 2014, ISIL defined its
creed
A creed, also known as a confession of faith, a symbol, or a statement of faith, is a statement of the shared beliefs of a community (often a religious community) which summarizes its core tenets.
Many Christian denominations use three creeds ...
as "a middle way between the extremist
Kharijites
The Kharijites (, singular ) were an Islamic sect which emerged during the First Fitna (656–661). The first Kharijites were supporters of Ali who rebelled against his acceptance of arbitration talks to settle the conflict with his challeng ...
and the lax
Murji'ites". ISIL's ideology represents radical Jihadi-Salafi Islam, a strict,
puritanical form of
Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any Succession to Muhammad, successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr ...
. Muslim organisations like Islamic Networks Group (ING) in America have argued against this interpretation of
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
. ISIL promotes
religious violence, and regards Muslims who do not agree with its interpretations as
infidels
An infidel (literally "unfaithful") is a person who is accused of disbelief in the central tenets of one's own religion, such as members of another religion, or irreligion, irreligious people.
Infidel is an Ecclesiology, ecclesiastical term in Ch ...
or
apostates.
According to Hayder al Khoei, IS's philosophy is represented by the symbolism in the
Black Standard variant of the legendary battle flag of
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
that it has adopted: the flag shows the
Seal of Muhammad within a white circle, with the phrase above it, "
There is no god but Allah".
This symbolism is said to symbolize IS's belief that it represents the restoration of the
caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
of
early Islam, with all the political, religious and
eschatological ramifications that this would imply.
Abu Abdullah al-Muhajir, an Egyptian Jihadist theoretician and ideologue is considered as the key inspiration for early figures of IS.
Al-Muhajir's legal manual on violence, ''Fiqh ad-Dima'' (''The Jurisprudence of Jihad'' or ''The Jurisprudence of Blood''),
was adopted by IS as its standard reference for justifying its extraordinary acts of violence.
The book has been described by counter-terrorism scholar Orwa Ajjoub as rationalising and justifying "suicide operations, the mutilation of corpses, beheading, and the killing of children and non-combatants".
His theological and legal justifications influenced IS,
al-Qaeda,
and
Boko Haram
Boko Haram, officially known as Jama'at Ahl al-Sunna li al-Da'wa wa al-Jihad (), is a self-proclaimed jihadist militant group based in northeastern Nigeria and also active in Chad, Niger, northern Cameroon, and Mali. In 2016, the group spli ...
,
as well as several other jihadi terrorist groups.
Numerous media outlets have compared his reference manual to
Abu Bakr Naji's ''
Management of Savagery'',
widely read among IS's commanders and fighters.
IS adheres to global jihadist principles and follows the hard-line ideology of
al-Qaeda
, image = Flag of Jihad.svg
, caption = Jihadist flag, Flag used by various al-Qaeda factions
, founder = Osama bin Laden{{Assassinated, Killing of Osama bin Laden
, leaders = {{Plainlist,
* Osama bin Lad ...
and many other modern-day jihadist groups.
According to ''
The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British newspaper published weekly in printed magazine format and daily on Electronic publishing, digital platforms. It publishes stories on topics that include economics, business, geopolitics, technology and culture. M ...
'',
Saudi practices followed by the group include the establishment of
religious police
Religious police are any Police, police force responsible for the enforcement of religious norms and associated religious laws. Nearly all religious police organizations in modern society are Islamic and can be found in countries with a large Mu ...
to root out "vice" and enforce attendance at
Salah
''Salah'' (, also spelled ''salat'') is the practice of formal worship in Islam, consisting of a series of ritual prayers performed at prescribed times daily. These prayers, which consist of units known as ''rak'ah'', include a specific s ...
prayers, the widespread use of
capital punishment
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence (law), sentence ordering that an offender b ...
, and the destruction or re-purposing of any non-
Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
religious buildings.
Bernard Haykel has described IS leader
Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi's creed as "a kind of untamed Wahhabism". Senior Saudi religious leaders have issued statements condemning IS, and attempting to distance the group from official Saudi religious beliefs. What connection, if any, there is between Salafi-Jihadism of IS and Wahhabism and Salafism proper is disputed. IS borrowed two elements of
Qutbism and 20th century Islamism into its version of Wahhabi worldview. While Wahhabism shuns violent rebellion against earthly rulers, IS embraces political call to revolutions. While historically Wahhabis were not champion activists of a
Caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
, IS borrowed the idea of restoration of a global Caliphate.
Although the religious character of IS is mostly Wahhabi, it departs from the Wahhabi tradition in four critical aspects: dynastic alliance, call to establish a global caliphate, sheer violence, and apocalyptism. IS did not follow the pattern of the first three Saudi states in allying the religious mission of the Najdi ''
ulema
In Islam, the ''ulama'' ( ; also spelled ''ulema''; ; singular ; feminine singular , plural ) are scholars of Islamic doctrine and law. They are considered the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious knowledge in Islam.
"Ulama ...
'' with the
Al Saud family, rather they consider them apostates. The call for a global caliphate is another departure from Wahhabism. The caliphate, understood in Islamic law as the ideal Islamic polity uniting all Muslim territories, does not figure much in traditional Najdi writings. Ironically, Wahhabism emerged as an anti-caliphate movement.
Although
violence
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence a ...
was not absent in the First Saudi State, Islamic State's displays of beheading, immolation, and other forms of violence aimed at inspiring fear are not in imitation of early Saudi practices. They were introduced by Abu Musab Al-Zarqawi, former leader of Al-Qaeda in Iraq, who took inspiration from the Egyptian Jihadi scholar, Abu Abdallah Al Muhajir. It is the latter's legal manual on violence, popularly known as ''Fiqh ad-Dima'' (The Jurisprudence of Blood), that is the Islamic State's standard reference for justifying its acts of violence. The Islamic State's apocalyptic dimension also lacks a mainstream Wahhabi precedent.
IS aims to return to the early days of Islam, rejecting all
innovations in the religion, which it believes corrupts its original spirit. It condemns later caliphates and the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
for deviating from what it calls pure Islam and seeks to revive the original Qutbist project of the restoration of a global caliphate that is governed by a strict Salafi-Jihadi doctrine. Following Salafi-Jihadi doctrines, IS condemns the followers of secular law as disbelievers, putting the current Saudi Arabian government in that category.
IS believes that only a legitimate authority can undertake the leadership of
jihad
''Jihad'' (; ) is an Arabic word that means "exerting", "striving", or "struggling", particularly with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it encompasses almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with God in Islam, God ...
and that the first priority over other areas of combat, such as fighting non-Muslim countries, is the purification of Islamic society. For example, IS regards the Palestinian Sunni group
Hamas
The Islamic Resistance Movement, abbreviated Hamas (the Arabic acronym from ), is a Palestinian nationalist Sunni Islam, Sunni Islamism, Islamist political organisation with a military wing, the Qassam Brigades. It has Gaza Strip under Hama ...
as apostates who have no legitimate authority to lead jihad and see fighting Hamas as the first step towards confrontation by IS with Israel.
Yemeni journalist
Abdulelah Haider Shaye said:
Islamic eschatology
One difference between IS and other Islamist and jihadist movements, including
al-Qaeda
, image = Flag of Jihad.svg
, caption = Jihadist flag, Flag used by various al-Qaeda factions
, founder = Osama bin Laden{{Assassinated, Killing of Osama bin Laden
, leaders = {{Plainlist,
* Osama bin Lad ...
, is the group's emphasis on
eschatology
Eschatology (; ) concerns expectations of the end of Contemporary era, present age, human history, or the world itself. The end of the world or end times is predicted by several world religions (both Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic and non-Abrah ...
and
apocalypticism
Apocalypticism is the religious belief that the Eschatology, end of the world is imminent, even within one's own lifetime. This belief is usually accompanied by the idea that civilization will soon come to a tumultuous end due to some sort of ...
– that is, a belief in a final
Day of Judgment by God. IS believes that it will defeat the army of "Rome" at the town of
Dabiq.
The noted scholar of militant Islamism
Will McCants writes:
Goals
Since at latest 2004, a significant goal of the group has been the foundation of a Sunni
Islamic state
The Islamic State (IS), also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) and Daesh, is a transnational Salafi jihadism, Salafi jihadist organization and unrecognized quasi-state. IS ...
. Specifically, ISIL has sought to establish itself as a
caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
, an Islamic state led by a group of religious authorities under a supreme leader – the
caliph
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
– who is believed to be the successor to
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
.
In June 2014, ISIL published a document in which it claimed to have traced the lineage of its leader al-Baghdadi back to Muhammad, and upon proclaiming a new caliphate on 29 June, the group appointed al-Baghdadi as its caliph. As caliph, he demanded the allegiance of all devout Muslims worldwide according to Islamic jurisprudence (''
fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ) is the term for Islamic jurisprudence.[Fiqh](_blank)
Encyclopædia Britannica ''Fiqh'' is of ...
'').
ISIL has detailed its goals in its ''
Dabiq'' magazine, saying it will continue to seize land and take over the entire Earth until its:
According to German journalist
Jürgen Todenhöfer, who spent ten days embedded with ISIL in
Mosul
Mosul ( ; , , ; ; ; ) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. It is the second largest city in Iraq overall after the capital Baghdad. Situated on the banks of Tigris, the city encloses the ruins of the ...
, the view he kept hearing was that ISIL wants to "conquer the world", and that all who do not believe in the group's interpretation of the
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
will be killed. Todenhöfer was struck by the ISIL fighters' belief that "all religions who agree with democracy have to die",
and by their "incredible enthusiasm" – including enthusiasm for killing "hundreds of millions" of people.
When the caliphate was proclaimed, ISIL stated: "The legality of all emirates, groups, states and organisations becomes null by the expansion of the khilafah's
aliphate'sauthority and the arrival of its troops to their areas." This was a rejection of the political divisions in
Southwestern Asia that were established by the UK and France during
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
in the
Sykes–Picot Agreement.
All non-Muslim areas would be targeted for conquest after the Muslim lands were dealt with, according to the Islamist manual ''
Management of Savagery''.
Strategy

Documents found after the death of Samir Abd Muhammad al-Khlifawi, a former colonel in the intelligence service of the
Iraqi Air Force before the US invasion who had been described as "the strategic head" of ISIL, detailed planning for the ISIL takeover of northern Syria, which made possible "the group's later advances into Iraq". Al-Khlifawi called for the infiltration of areas to be conquered with spies who would find out "as much as possible about the target towns: Who lived there, who was in charge, which families were religious, which Islamic school of religious jurisprudence they belonged to, how many mosques there were, who the imam was, how many wives and children he had and how old they were". Following this surveillance and espionage would come murder and kidnapping – "the elimination of every person who might have been a potential leader or opponent". In
Raqqa, after rebel forces drove out the
Assad regime and ISIL infiltrated the town, "first dozens and then hundreds of people disappeared".
Security and intelligence expert Martin Reardon has described IS's purpose as being to psychologically "break" those under its control, "so as to ensure their absolute allegiance through fear and intimidation", while generating "outright hate and vengeance" among its enemies.
Jason Burke, a journalist writing on
Salafi jihadism
Salafi jihadism, also known as Salafi-jihadism, jihadist Salafism and revolutionary Salafism, is a religiopolitical Sunni Islam, Sunni Islamist ideology that seeks to establish a global caliphate through armed struggle. In a narrower sense, ji ...
, has written that IS's goal is to "terrorize, mobilize
ndpolarize".
Its efforts to terrorise are intended to intimidate civilian populations and force governments of the target enemy "to make rash decisions that they otherwise would not choose". It aims to mobilise its supporters by motivating them with, for example, spectacular deadly attacks deep in Western territory (such as the
November 2015 Paris attacks), to polarise by driving Muslim populations – particularly in the West – away from their governments, thus increasing the appeal of IS's self-proclaimed caliphate among them, and to: "Eliminate neutral parties through either absorption or elimination". Journalist
Rukmini Maria Callimachi also emphasises IS's interest in polarisation or in eliminating what it calls the "grey zone" between the black (non-Muslims) and white (IS). "The gray is moderate Muslims who are living in the West and are happy and feel engaged in the society here."
A work published online in 2004 entitled ''
Management of Savagery'' (''Idarat at Tawahoush''), described by several media outlets as influential on IS and intended to provide a strategy to create a new Islamic caliphate, recommended a strategy of attack outside its territory in which fighters would "Diversify and widen the vexation strikes against the Crusader-Zionist enemy in every place in the Islamic world, and even outside of it if possible, so as to disperse the efforts of the alliance of the enemy and thus drain it to the greatest extent possible."
The group has been accused of attempting to "bolster morale" and distract attention from its loss of territory to enemies by staging terror attacks abroad (such as the
2016 Berlin truck attack, the
6 June 2017 attacks on Tehran, the
22 May 2017 bombing in Manchester, and the
3 June 2017 attacks in London that IS claimed credit for).
Organisation
IS has been described as a terrorist group adhering to
Salafi jihadism
Salafi jihadism, also known as Salafi-jihadism, jihadist Salafism and revolutionary Salafism, is a religiopolitical Sunni Islam, Sunni Islamist ideology that seeks to establish a global caliphate through armed struggle. In a narrower sense, ji ...
.
in Syria was under IS control from 2013 and in 2014 it became the group's ''de facto'' capital city. On 17 October 2017, following a lengthy battle that saw massive destruction to the city, the
Syrian Democratic Forces
The Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) is a Kurds in Syria, Kurdish-led coalition of U.S.-backed Left-wing politics, left-wing ethnic militias and rebel groups, and serves as the official military wing of the Democratic Autonomous Administration ...
(SDF) announced the full capture of Raqqa from IS.
Leadership and governance
From 2013 to 2019, IS was headed and run by
Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi
Ibrahim Awwad Ibrahim Ali al-Badri (28 July 1971 – 27 October 2019), commonly known by his ''nom de guerre'' Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, was an Iraqi militant leader who was the founder and first leader of the Islamic State (IS), who proclaimed hims ...
, the Islamic State's self-styled
Caliph
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
. Before their deaths, he had two deputy leaders,
Abu Muslim al-Turkmani for Iraq and
Abu Ali al-Anbari (also known as Abu Ala al-Afri) for Syria, both ethnic
Turkmen. Advising al-Baghdadi were a cabinet of senior leaders, while its operations in Iraq and Syria are controlled by local 'emirs,' who head semi-autonomous groups that the Islamic State refers to as its provinces. Beneath the leaders are councils on finance, leadership, military matters, legal matters (including decisions on executions)
foreign fighters' assistance, security, intelligence and media. In addition, a
shura
Shura () is the term for collective decision-making in Islam. It can, for example, take the form of a council or a referendum. The Quran encourages Muslims to decide their affairs in consultation with each other.
Shura is mentioned as a praise ...
council has the task of ensuring that all decisions made by the governors and councils comply with the group's interpretation of
sharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' ...
. While al-Baghdadi had told followers to "advise me when I err" in sermons, according to observers "any threat, opposition, or even contradiction is instantly eradicated".
According to Iraqis, Syrians, and analysts who study the group, almost all of IS's leaders—including the members of its military and security committees and the majority of its
emir
Emir (; ' (), also Romanization of Arabic, transliterated as amir, is a word of Arabic language, Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocratic, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person po ...
s and princes—are former Iraqi military and intelligence officers, specifically former members of
Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein (28 April 1937 – 30 December 2006) was an Iraqi politician and revolutionary who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 1979 until Saddam Hussein statue destruction, his overthrow in 2003 during the 2003 invasion of Ira ...
's
Ba'ath government who lost their jobs and pensions in the
de-Ba'athification process after that regime was overthrown.
The former Chief Strategist in the Office of the Coordinator for Counterterrorism of the US State Department,
David Kilcullen, has said, "There undeniably would be no Isis if we had not invaded Iraq." It has been reported that Iraqis and Syrians have been given greater precedence over other nationalities within IS because the group needs the loyalties of the local Sunni populations in both Syria and Iraq in order to be sustainable. Other reports, however, have indicated that Syrians are at a disadvantage to foreign members, with some native Syrian fighters resenting "favouritism" allegedly shown towards foreigners over pay and accommodation.
In August 2016, media reports based on briefings by Western intelligence agencies suggested that IS had a multilevel
secret service known in Arabic as
Emni, established in 2014, that has become a combination of an internal police force and an external operations directorate complete with regional branches. The unit was believed to be under the overall command of IS's most senior Syrian operative, spokesman and propaganda chief
Abu Mohammad al-Adnani until his death by airstrike in late August 2016.
On 27 October 2019, the United States conducted a special operation targeting al-Baghdadi's compound in
Barisha,
Idlib
Idlib (, ; also spelt Idleb or Edlib) is a city in northwestern Syria, and is the capital of the Idlib Governorate. It has an elevation of nearly above sea level, and is southwest of Aleppo. It is located near the border with Turkey.
History
...
, Northwest Syria. The attack
resulted in al-Baghdadi's death; caught by surprise and unable to escape, al-Baghdadi detonated a
suicide vest
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death.
Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or ac ...
, deliberately killing both himself and two children who had been living in the compound prior to the assault.
[
*
*
* ] U.S. President Donald Trump stated in a televised announcement that Baghdadi had, in fact, died during the operation and that American forces used support from helicopters, jets and drones through airspace controlled by Russia and Turkey. He said, "Russia treated us great... Iraq was excellent. We really had great cooperation" and Turkey knew they were going in.
He thanked Turkey, Russia, Syria, Iraq and the Syrian Kurdish forces for their support. The Turkish Defence Ministry also confirmed on Sunday that Turkish and U.S. military authorities exchanged and coordinated information ahead of an attack in Syria's Idlib.
Fahrettin Altun, a senior aide to Turkish President Tayyib Erdogan, also stated, among other things, "Turkey was proud to help the United States, our NATO ally, bring a notorious terrorist to justice" and that Turkey "will continue to work closely with the United States and others to combat terrorism in all its forms and manifestations." Kremlin spokesman
Dmitry Peskov declined to say if the United States had told Russia about the raid in advance but said that its result if confirmed, represented a serious contribution by the United States to combat terrorism. Russia had previously claimed Baghdadi was killed in May 2019 by their airstrike.
In September 2019, a statement attributed to IS's propaganda arm, the
Amaq news agency
Amaq News Agency () is a news outlet linked to the Islamic State (IS). Amaq is often the "first point of publication for claims of responsibility" for terrorist attacks in Western countries by the Islamic State. In March 2019, Amaq News Agency w ...
, claimed that
Abdullah Qardash was named as al-Baghdadi's successor. Analysts dismissed this statement as a fabrication, and relatives were reported as saying that Qardash died in 2017.
Rita Katz, a terrorism analyst and the co-founder of
SITE Intelligence, noted that the alleged statement used a different font when compared to other statements and it was never distributed on Amaq or IS channels.
On 29 October 2019, Trump stated on social media that al-Baghdadi's "number one replacement" had been killed by American forces, without giving a name. A U.S. official later confirmed that Trump was referring to IS spokesman and senior leader
Abul-Hasan al-Muhajir, who was killed in a U.S. airstrike in Syria two days earlier. On 31 October, IS named
Abu Ibrahim al-Hashemi al-Qurayshi as Baghdadi's successor. On 3 February 2022, it was reported by a US official that al-Hashimi killed himself and members of his family by triggering an explosive device during a
counter-terrorism
Counterterrorism (alternatively spelled: counter-terrorism), also known as anti-terrorism, relates to the practices, military tactics, techniques, and strategies that governments, law enforcement, businesses, and intelligence agencies use to co ...
raid by the US
Joint Special Operations Command. On 30 November 2022, IS announced that their unidentified leader had been killed in battle and named a successor, providing no additional information other than his
pseudonym
A pseudonym (; ) or alias () is a fictitious name that a person assumes for a particular purpose, which differs from their original or true meaning ( orthonym). This also differs from a new name that entirely or legally replaces an individual's o ...
. A spokesman for
U.S. Central Command confirmed that IS's leader had been killed in mid-October by anti-government rebels in southern Syria. On 16 February 2023, senior IS leader Hamza al-Homsi blew himself up in a U.S.-led raid in Syria.
Civilians in Islamic State-controlled areas
In 2014, ''The Wall Street Journal'' estimated that eight million people lived in the Islamic State. The
United Nations Commission on Human Rights
The United Nations Commission on Human Rights (UNCHR) was a functional commission within the United Nations System, overall framework of the United Nations from 1946 until it was replaced by the United Nations Human Rights Council in 2006. It was a ...
has stated that IS "seeks to subjugate civilians under its control and dominate every aspect of their lives through terror, indoctrination, and the provision of services to those who obey".
Civilians, as well as the Islamic State itself, have released footage of some of the human rights abuses.
Social control
Social control is the regulations, sanctions, mechanisms, and systems that restrict the behaviour of individuals in accordance with social norms and orders. Through both informal and formal means, individuals and groups exercise social con ...
of civilians was by imposition of IS's reading of sharia law,
enforced by
morality police forces known as ''Al-Hisbah'' and the all-women
Al-Khanssaa Brigade, a general police force, courts, and other entities managing recruitment, tribal relations, and education. ''Al-Hisbah'' was led by Abu Muhammad al-Jazrawi.
In 2015, IS published a penal code including floggings, amputations, crucifixions, etc.
Military
Number of combatants
Estimates of the size of IS's military have varied widely, from tens of thousands up to 200,000.
In early 2015, journalist Mary Anne Weaver estimated that half of IS fighters were foreigners. A UN report estimated a total of 15,000 fighters from over 80 countries were in IS's ranks in November 2014. US intelligence estimated an increase to around 20,000 foreign fighters in February 2015, including 3,400 from the
Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and state (polity), states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also const ...
. In September 2015, the CIA estimated that 30,000 foreign fighters had joined IS.
According to Abu Hajjar, a former senior leader of IS, foreign fighters receive food, petrol and housing, but unlike native Iraqi or Syrian fighters, they do not receive payment in wages. Since 2012, more than 3,000 people from the central Asian countries have gone to Syria, Iraq or Afghanistan to join the Islamic State or
Jabhat al Nusra.
Conventional weapons
IS relies mostly on captured weapons with major sources including
Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein (28 April 1937 – 30 December 2006) was an Iraqi politician and revolutionary who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 1979 until Saddam Hussein statue destruction, his overthrow in 2003 during the 2003 invasion of Ira ...
's Iraqi stockpiles from the
2003–11 Iraq insurgency and weapons from government and opposition forces fighting in the
Syrian Civil War and during the
post-US withdrawal Iraqi insurgency. The captured weapons, including armour, guns, surface-to-air missiles, and even some aircraft, enabled rapid territorial growth and facilitated the capture of additional equipment. For example, IS captured US-made
TOW anti-tank missiles supplied by the United States and Saudi Arabia to the
Free Syrian Army
The Free Syrian Army (FSA; ) is a Big tent, big-tent coalition of decentralized Syrian opposition (2011–2024), Syrian opposition rebel groups in the Syrian civil war founded on 29 July 2011 by Colonel Riad al-Asaad and six officers who defe ...
in Syria. Ninety percent of the group's weapons ultimately originated in China, Russia or
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
according to
Conflict Armament Research
Conflict Armament Research (CAR) is a British-based investigative organization that tracks the supply of conventional weapons, ammunition, and related military materiel (such as IEDs) into conflict-affected areas. Established in 2011, CAR specia ...
.
Non-conventional weapons
The group uses truck and
car bomb
A car bomb, bus bomb, van bomb, lorry bomb, or truck bomb, also known as a vehicle-borne improvised explosive device (VBIED), is an improvised explosive device designed to be detonated in an automobile or other vehicles.
Car bombs can be roug ...
s,
suicide bombers and
IEDs, and has used
chemical weapon
A chemical weapon (CW) is a specialized munition that uses chemicals formulated to inflict death or harm on humans. According to the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), this can be any chemical compound intended as ...
s in Iraq and Syria. IS captured nuclear materials from
Mosul University in July 2014, but is unlikely to be able to convert them into weapons. In September 2015 a US official stated that IS was manufacturing and using
mustard agent in Syria and Iraq, and had an active chemical weapons research team. IS has also used water as a weapon of war. The group closed the gates of the smaller Nuaimiyah dam in Fallujah in April 2014, flooding the surrounding regions, while cutting the water supply to the
Shia
Shia Islam is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political successor (caliph) and as the spiritual leader of the Muslim community (imam). However, his right is understood ...
-dominated south. Around 12,000 families lost their homes and of villages and fields were either flooded or dried up. The economy of the region also suffered with destruction of cropland and electricity shortages.
During the
Battle of Mosul, commercially available
quadcopters and
drones were being used by IS as surveillance and weapons delivery platforms using improvised cradles to drop grenades and other explosives. One IS drone base was struck and destroyed by two Royal Air Force
Tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with the surface of Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the ...
using two
Paveway IV guided bombs.
Women
IS publishes material directed at women, with media groups encouraging them to play supportive roles within IS, such as providing first aid, cooking, nursing and sewing skills, in order to become
"good wives of jihad". In 2015, it was estimated that western women made up over 550, or 10%, of IS's western foreign fighters.
Until 2016, women were generally confined to a "women's house" upon arrival, which they were forbidden to leave. These houses were often small, dirty and infested with vermin and food supply was scarce. There they remained until they either had found a husband, or the husband they arrived with had completed his training. After being allowed to leave the confinement, women still generally spent most of their days indoors, where their lives are devoted to caring for their husbands and the vast majority of women in the conflict area have children. Mothers play an important role passing on IS ideology to their children. Widows are encouraged to remarry.
In a document entitled ''Women in the Islamic State: Manifesto and Case Study'' released by the media wing of IS's all-female
Al-Khansaa Brigade, emphasis is given to the paramount importance of marriage and motherhood (as early as nine years old). Women should live a life of "sedentariness", fulfilling her "divine duty of motherhood" at home, with a few exceptions like teachers and doctors.
Equality for women is opposed, as is education on non-religious subjects, the "worthless worldly sciences".
Communications
Finances
According to a 2015 study by the
Financial Action Task Force
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), also known by its French name, Groupe d'action financière (GAFI), is an intergovernmental organisation founded in 1989 on the initiative of the G7 to develop policies to combat money laundering and to ma ...
, IS's five primary sources of revenue are as follows (listed in order of significance):
* proceeds from the occupation of territory (including control of banks, petroleum reservoirs, taxation, extortion, and robbery of economic assets)
* kidnapping for ransom
* donations from
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
,
Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait ...
,
Qatar
Qatar, officially the State of Qatar, is a country in West Asia. It occupies the Geography of Qatar, Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it shares Qatar–Saudi Arabia border, its sole land b ...
and other
Gulf states, often disguised as meant for "humanitarian charity"
* material support provided by foreign fighters
* fundraising through modern communication networks
Since 2012, IS has produced annual reports giving numerical information on its operations, somewhat in the style of corporate reports, seemingly in a bid to encourage potential donors.
In 2014, the
RAND Corporation
The RAND Corporation, doing business as RAND, is an American nonprofit global policy think tank, research institute, and public sector consulting firm. RAND engages in research and development (R&D) in several fields and industries. Since the ...
analysed IS's funding sources from documents captured between 2005 and 2010.
It found that outside donations amounted to only 5% of the group's operating budgets, and that cells inside Iraq were required to send up to 20% of the income generated from kidnapping, extortion rackets and other activities to the next level of the group's leadership, which would then redistribute the funds to provincial or local cells that were in difficulties or needed money to conduct attacks. In 2016, RAND estimated that IS finances from its largest source of income—oil revenues and the taxes it extracts from people under its control—had fallen from about billion in 2014 to million in 2016.
In mid-2014, the
Iraqi National Intelligence Service obtained information that IS had assets worth billion, making it the richest jihadist group in the world. About three-quarters of this sum was said to looted from Mosul's central bank and commercial banks in the city. However, doubt was later cast on whether IS was able to retrieve anywhere near that sum from the central bank, and even on whether the looting had actually occurred.
In 2022, the company
Lafarge was found guilty in paying IS for the operation of its facilities. "In 2013–2014 the company transferred $6,000,000 to ISIL so they could continue company operations. This allowed the company to earn $70 million in sales revenue from a plant it operated in northern Syria, prosecutors said." Lafarge, which merged with
Holcim
Holcim is a Swiss-based global building materials and Construction aggregate, aggregates flagship division of the Holcim Group. The original company was merged on 10 July 2015 with Lafarge (company), Lafarge to form LafargeHolcim as the new c ...
in 2015, agreed to pay $778 million in forfeiture and fines as part of a plea agreement not to be convicted and sentenced to prison for providing material support to a terrorist organization. No Lafarge executives were charged in the United States, while French authorities arrested some of the executives involved but didn't provide names. The U.S. court lists six unnamed Lafarge executives. Lafarge evacuated the cement plant in September 2014, Afterwards IS took possession of the remaining cement and sold it for an estimated $3.21 million.
SIX Swiss Exchange trading suspended trading for Holcim shares before the news became public. After trading resumed shares rose by 3.2%.
Monetary system
IS attempted to create a
modern gold dinar
The modern Islamic gold dinar (sometimes referred as Islamic dinar or Gold dinar) is a projected bullion gold coin, so far not issued as official currency by any national state. It aims to revive the historical gold dinar, which was a leading c ...
by minting gold, silver, and copper coins, based on the
coinage used by the
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate or Umayyad Empire (, ; ) was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member o ...
in the seventh century. Despite a propaganda push for the currency, adoption appeared to have been minimal and its internal economy was effectively
dollarised, even with regards to its own fines.
Education
The education in IS held territory was organised by the Diwan of Education.
IS introduced its own curriculum, which did not include lessons in history, music, geography or art, but included lectures in Islamic Law,
Sharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' ...
, and
Jihad
''Jihad'' (; ) is an Arabic word that means "exerting", "striving", or "struggling", particularly with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it encompasses almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with God in Islam, God ...
. The Diwan of Education was often in competition with the Diwan of Outreach and Mosques, which organised educational centres focused on the sharia.
History
The group was founded in 1999 by Jordanian
Salafi jihadist Abu Musab al-Zarqawi under the name ''
Jamāʻat al-Tawḥīd wa-al-Jihād'' ().
In a letter published by the
Coalition Provisional Authority
The Coalition Provisional Authority (; , CPA) was a Provisional government, transitional government of Iraq established following the 2003 invasion of Iraq, invasion of the country on 19 March 2003 by Multi-National Force – Iraq, U.S.-led Co ...
in February 2004, Zarqawi wrote that jihadis should use bombings to start an open
sectarian war so that Sunnis from the Islamic world would mobilise against assassinations carried out by
Shia
Shia Islam is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political successor (caliph) and as the spiritual leader of the Muslim community (imam). However, his right is understood ...
, specifically the
Badr Brigade, against
Ba'athists and
Sunnis.
Territorial control and claims
As a self-proclaimed worldwide
caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
, IS claims religious, political and military authority over all Muslims worldwide, and that "the legality of all emirates, groups, states, and organisations, becomes null by the expansion of the khilāfah's
aliphate'sauthority and arrival of its troops to their areas".
In Iraq and Syria, IS used many of those countries' existing
governorate boundaries to subdivide territory it conquered and claimed; it called these divisions
wilayah
A wilayah ( or ''wilāya'', plural ; Urdu, Pashto and ; ) is an administrative division, usually translated as "state", " province" or occasionally as " governorate". The word comes from the Arabic root "''w-l-y''", "to govern": a '' wāli''� ...
or provinces. By June 2015, IS had also established official "provinces" in Libya, Egypt (Sinai Peninsula), Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Algeria, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nigeria and the North Caucasus. IS received pledges of allegiance and published media releases via groups in Somalia, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Myanmar, Thailand and the Philippines, but it has not announced any further official branches, instead identifying new affiliates as simply "soldiers of the caliphate".

At its peak, IS was sometimes described as a
quasi-state
A quasi-state (sometimes referred to as a state-like entity or formatively a proto-state) is a political entity that does not represent a fully autonomous sovereign state with its own institutions.
The precise definition of ''quasi-state'' in po ...
.
["quasi-state"
*
*
*
*
*
* ] By March 2019, IS had lost most of its territory in its former core areas in Syria and Iraq, and was reduced to a desert pocket as well as insurgent cells. Through late 2020 and early 2021, IS African affiliates had once again seized territory and settlements in conflicts such as the
Boko Haram insurgency, in Nigeria and the
Insurgency in Cabo Delgado, in Mozambique. Notable takeovers by IS include
Mocímboa da Praia and the
Sambisa Forest. On 17 November 2021, IS supporters urged establishment of "New Provinces" in Indonesia. In October 2022, IS's Sahel province captured the rural committee and town of
Ansongo in Mali. In 2023/2024, IS still holds a large territory in Africa.
International reaction
International criticism
The group has attracted widespread criticism internationally for its extremism, from governments and international bodies such as the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
and
Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says that it has more than ten million members a ...
. On 24 September 2014,
United Nations Secretary-General
The secretary-general of the United Nations (UNSG or UNSECGEN) is the chief administrative officer of the United Nations and head of the United Nations Secretariat, one of the United Nations System#Six principal organs, six principal organs of ...
Ban Ki-moon
Ban Ki-moon (born 13 June 1944) is a South Korean politician and diplomat who served as the eighth secretary-general of the United Nations between 2007 and 2016. Prior to his appointment as secretary-general, Ban was the South Korean minister ...
stated: "As Muslim leaders around the world have said, groups like ISIL – or Da'ish – have nothing to do with
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
, and they certainly do not represent a state. They should more fittingly be called the 'Un-Islamic Non-State'." ISIL has been classified a
terrorist organisation by the United Nations, the European Union and its member states, the United States, Russia, India, Turkey, Saudi Arabia and many other countries. Over 60 countries are directly or indirectly waging war against ISIL (see ). The group was described as a
cult
Cults are social groups which have unusual, and often extreme, religious, spiritual, or philosophical beliefs and rituals. Extreme devotion to a particular person, object, or goal is another characteristic often ascribed to cults. The term ...
in a
Huffington Post
''HuffPost'' (''The Huffington Post'' until 2017, itself often abbreviated as ''HPo'') is an American progressive news website, with localized and international editions. The site offers news, satire, blogs, and original content, and covers ...
column by notable cult authority
Steven Hassan.
Twitter has removed many accounts used to spread IS propaganda, and
Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
developed a "Redirect Method" that identifies individuals searching for IS-related material and redirects them to content that challenges IS narratives.
Islamic criticism
The group's declaration of a caliphate has been criticised and its legitimacy has been disputed by Middle Eastern governments, by
Sunni Muslim theologians and historians as well as other jihadist groups.
Religious leaders and organisations
Around the world,
Islamic religious leaders have overwhelmingly condemned ISIL's ideology and actions, arguing that the group has strayed from the path of true Islam and that its actions do not reflect the religion's real teachings or virtues.
Extremism within Islam goes back to the seventh century, to the
Khawarij
The Kharijites (, singular ) were an Islamic sect which emerged during the First Fitna (656–661). The first Kharijites were supporters of Ali who rebelled against his acceptance of arbitration talks to settle the conflict with his challenge ...
es. From their essentially political position, the Kharijites developed extreme doctrines that set them apart from both mainstream Sunni and Shia Muslims. They were particularly noted for adopting a radical approach to
takfir
''Takfir'' () is an Arabic language, Arabic and Glossary of Islam, Islamic term which denotes excommunication from Islam of one Muslim by another, i.e. accusing another Muslim of being an Apostasy in Islam, apostate. The word is found neither ...
, whereby they declared other Muslims to be unbelievers and therefore deemed worthy of death.
Other scholars have also described the group not as Sunnis, but as Khawarij. Sunni critics, including
Salafi and jihadist
muftis such as
Adnan al-Aroor and
Abu Basir al-Tartusi, say that ISIL and related terrorist groups are not Sunnis, but are instead modern-day Kharijites (Muslims who have stepped outside the mainstream of Islam) serving an imperial anti-Islamic agenda.
ISIS has been
excommunicated from Islam by a number of scholars. Sheikh
Muhammad al-Yaqoubi enumerated in his book, ''
Refuting ISIS'', that their form of Kharijism has removed them from Islam and fighting them is a religious duty, stating: "ISIS' leaders are people of unbelief and misguidance, and Muslims should not be lured by their jihad or deceived by their propaganda, as their actions speak louder than their words."
Abd al-Aziz ibn Baz, the former Grand Mufti of
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
, also stated that Kharijites are not Muslims, saying: "the majority are of the opinion that they are disobedient and misguided innovators, though they do not deem them unbelievers. However, the correct opinion is that they are unbelievers."
In late August 2014, the
Grand Mufti of Saudi Arabia,
Abdul-Aziz ibn Abdullah Al ash-Sheikh, condemned ISIL and
al-Qaeda
, image = Flag of Jihad.svg
, caption = Jihadist flag, Flag used by various al-Qaeda factions
, founder = Osama bin Laden{{Assassinated, Killing of Osama bin Laden
, leaders = {{Plainlist,
* Osama bin Lad ...
saying, "Extremist and militant ideas and terrorism which spread decay on Earth, destroying human civilization, are not in any way part of Islam, but are enemy number one of Islam, and Muslims are their first victims". In late September 2014, 126 Sunni
imams and Islamic scholars—primarily
Sufi
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism.
Practitioners of Sufism are r ...
—from around the Muslim world signed an
open letter
An open letter is a Letter (message), letter that is intended to be read by a wide audience, or a letter intended for an individual, but that is nonetheless widely distributed intentionally.
Open letters usually take the form of a letter (mess ...
to the Islamic State's leader al-Baghdadi, explicitly rejecting and refuting his group's interpretations of Islamic scriptures, the
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
and
hadith
Hadith is the Arabic word for a 'report' or an 'account f an event and refers to the Islamic oral tradition of anecdotes containing the purported words, actions, and the silent approvals of the Islamic prophet Muhammad or his immediate circle ...
, which it used in order to justify its actions. "
ouhave misinterpreted Islam into a religion of harshness, brutality, torture and murder ... this is a great wrong and an offence to Islam, to Muslims and to the entire world", the letter states.
It rebukes the Islamic State for its killing of prisoners, describing the killings as "heinous
war crime
A war crime is a violation of the laws of war that gives rise to individual criminal responsibility for actions by combatants in action, such as intentionally killing civilians or intentionally killing prisoners of war, torture, taking hostage ...
s" and its persecution of the
Yazidis
Yazidis, also spelled Yezidis (; ), are a Kurdish languages, Kurdish-speaking Endogamy, endogamous religious group indigenous to Kurdistan, a geographical region in Western Asia that includes parts of Iraq, Syria, Turkey, and Iran. The major ...
of Iraq as "abominable". Referring to the "self-described 'Islamic State'", the letter censures the group for carrying out killings and acts of brutality under the guise of
jihad
''Jihad'' (; ) is an Arabic word that means "exerting", "striving", or "struggling", particularly with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it encompasses almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with God in Islam, God ...
—holy struggle—saying that its "sacrifice" without legitimate cause, goals and intention "is not jihad at all, but rather, warmongering and criminality". It also accuses the group of instigating
fitna—sedition—by instituting slavery under its rule in contravention of the
anti-slavery consensus of the
Islamic scholarly community. The group's persecution of Shia Muslims has also been condemned.

The current
Grand Imam of al-Azhar and former president of
al-Azhar University
The Al-Azhar University ( ; , , ) is a public university in Cairo, Egypt. Associated with Al-Azhar Al-Sharif in Islamic Cairo, it is Egypt's oldest degree-granting university and is known as one of the most prestigious universities for Islamic ...
,
Ahmed el-Tayeb, has strongly condemned the Islamic State, stating that it is acting "under the guise of this holy religion and have given themselves the name 'Islamic State' in an attempt to export their false Islam". Citing the Quran, he stated: "The punishment for those who wage war against God and his Prophet and who strive to sow corruption on earth is death, crucifixion, the severing of hands and feet on opposite sides or banishment from the land. This is the disgrace for them in this world and in the hereafter, they will receive grievous torment." Although el-Tayeb has been criticised for not expressly stating that the Islamic State is
heretical,
the
Ash'ari
Ash'arism (; ) is a school of theology in Sunni Islam named after Abu al-Hasan al-Ash'ari, a Shāfiʿī jurist, reformer (''mujaddid''), and scholastic theologian, in the 9th–10th century. It established an orthodox guideline, based on ...
school of
Islamic theology
Schools of Islamic theology are various Islamic schools and branches in different schools of thought regarding creed. The main schools of Islamic theology include the extant Mu'tazili, Ash'ari, Maturidi, and Athari schools; the extinct ones ...
, to which el-Tayeb belongs, does not allow calling a person who follows the
shahada an
apostate. El-Tayeb has strongly come out against the practice of
takfirism (declaring a Muslim an apostate), which is used by the Islamic State to "judge and accuse anyone who doesn't tow their line with apostasy and outside the realm of the faith" declaring "
Jihad
''Jihad'' (; ) is an Arabic word that means "exerting", "striving", or "struggling", particularly with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it encompasses almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with God in Islam, God ...
on peaceful Muslims" using "flawed interpretations of some Qur'anic texts, the prophet's Sunna, and the Imams' views believing incorrectly, that they are leaders of Muslim armies fighting infidel peoples, in unbelieving lands".
In late December 2015, nearly 70,000 Indian Muslim clerics associated with the Indian
Barelvi
The Barelvi movement, also known as Ahl al-Sunnah wal-Jama'ah (People of the Prophet's Way and the Community) is a Sunni revivalist movement that generally adheres to the Hanafi school, Hanafi and Shafi'i school, Shafi'i schools of jurisprudenc ...
movement issued a
fatwa
A fatwa (; ; ; ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (sharia) given by a qualified Islamic jurist ('' faqih'') in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist issuing fatwas is called a ''mufti'', ...
condemning ISIL and similar organisations, saying they are "not Islamic organisations". Approximately Sunni Muslim followers of this movement have formally decried violent extremists.
Mehdi Hasan, a political journalist in the UK, said in the ''
New Statesman
''The New Statesman'' (known from 1931 to 1964 as the ''New Statesman and Nation'') is a British political and cultural news magazine published in London. Founded as a weekly review of politics and literature on 12 April 1913, it was at first c ...
''
Hassan Hassan, an analyst at the Delma Institute, wrote in ''
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardi ...
'' that because the Islamic State "bases its teachings on religious texts that mainstream Muslim clerics do not want to deal with head on, new recruits leave the camp feeling that they have stumbled on the true message of Islam".
Theologian and Qatar-based TV broadcaster
Yusuf al-Qaradawi stated: "
hedeclaration issued by the Islamic State is void under
sharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' ...
and has dangerous consequences for the Sunnis in Iraq and for the revolt in Syria", adding that the title of caliph can "only be given by the entire Muslim nation", not by a single group. He also stated on his official website "
United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a Federal monarchy, federal elective monarchy made up of Emirates of the United Arab E ...
(UAE) and the leaders of Daesh (ISIS/ISIL) terrorist group are from one species and they are two sides of the same coin". In a similar vein, the Syrian
Islamic scholar Muhammad al-Yaqoubi says, "
e followers of ISIS do not want to adhere to Islamic law but rather they want to twist Islamic law to conform to their fantasies. To this end, they pick and choose the evidences that corroborate their misguidance, despite being weak or abrogated."
Academics
Robyn Creswell and
Bernard Haykel of ''
The New Yorker
''The New Yorker'' is an American magazine featuring journalism, commentary, criticism, essays, fiction, satire, cartoons, and poetry. It was founded on February 21, 1925, by Harold Ross and his wife Jane Grant, a reporter for ''The New York T ...
'' have criticised ISIL's execution of Muslims for breach of traditional ''
sharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' ...
'' law while violating it simultaneously themselves (encouraging women to emigrate to its territory, travelling without a ''
Wali
The term ''wali'' is most commonly used by Muslims to refer to a saint, or literally a "friend of God".John Renard, ''Friends of God: Islamic Images of Piety, Commitment, and Servanthood'' (Berkeley: University of California Press, 2008); John ...
''—male guardian—and in violation of his wishes). as well as its love of archaic imagery (horsemen and swords) while engaging in ''
bid'ah
In Islam and sharia (Islamic law), ( , ) refers to innovation in religious matters. Linguistically, as an Arabic word, the term can be defined more broadly, as "innovation, novelty, heretical doctrine, heresy". It is the subject of many hadith ...
'' (religious innovation) in establishing female religious police (known as
Al-Khansaa Brigade).
Two days after the beheading of
Hervé Gourdel, hundreds of Muslims gathered in the
Grand Mosque of Paris to show solidarity against the beheading. The protest was led by the leader of the
French Council of the Muslim Faith,
Dalil Boubakeur, and was joined by thousands of other Muslims around the country under the slogan "Not in my name".
French president
François Hollande
François Gérard Georges Nicolas Hollande (; born 12 August 1954) is a French politician who served as President of France from 2012 to 2017. Before his presidency, he was First Secretary of the Socialist Party (France), First Secretary of th ...
said Gourdel's beheading was "cowardly" and "cruel", and confirmed that airstrikes would continue against ISIL in Iraq. Hollande also called for three days of national mourning, with flags flown at half-mast throughout the country and said that security would be increased throughout Paris.
Other jihadist groups
According to ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'', "All of the most influential jihadist theorists are criticising the Islamic State as deviant, calling its self-proclaimed caliphate null and void" and they have denounced it for its beheadings of journalists and aid workers. ISIL is widely denounced by a broad range of Islamic clerics, including Saudi and al-Qaeda-oriented clerics.
Muhammad al-Yaqoubi states, "It is enough of a proof of the extreme ideology of ISIS that the top leaders of Salafi-Jihadism have disclaimed it." Other critics of ISIL's brand of Sunni Islam include Salafists who previously publicly supported jihadist groups such as al-Qaeda: for example, the Saudi government official
Saleh Al-Fawzan, known for his extremist views, who claims that ISIL is a creation of "Zionists, Crusaders and Safavids", and the Jordanian-Palestinian writer
Abu Muhammad al-Maqdisi, the former spiritual mentor to
Abu Musab al-Zarqawi, who was released from prison in Jordan in June 2014 and accused ISIL of driving a wedge between Muslims.
An
Islamic Front sharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' ...
court judge in Aleppo, Mohamed Najeeb Bannan, stated: "The legal reference is the Islamic Sharia. The cases are different, from robberies to drug use, to moral crimes. It's our duty to look at any crime that comes to us... After the regime has fallen, we believe that the Muslim majority in Syria will ask for an Islamic state. Of course, it's very important to point out that some say the Islamic Sharia will cut off people's hands and heads, but it only applies to criminals. And to start off by killing, crucifying etc. That is not correct at all." In response to being asked what the difference between the Islamic Front's and ISIL's version of sharia would be, he said, "One of their mistakes is before the regime has fallen, and before they've established what in Sharia is called Tamkeen
aving a stable state they started applying Sharia, thinking God gave them permission to control the land and establish a Caliphate. This goes against the beliefs of religious scholars around the world. This is what
Sdid wrong. This is going to cause a lot of trouble. Anyone who opposes
Swill be considered against Sharia and will be severely punished."
Al-Qaeda and al-Nusra have been trying to take advantage of ISIL's rise, by attempting to present themselves as "moderate" compared to "extremist" ISIL, although they have the same aim of establishing sharia and a caliphate, but doing so in a more gradual manner. Al-Nusra has criticised the way in which ISIL fully and immediately institutes sharia in the areas that fall under its control, since it alienates people too much. It supports the gradual, slower approach favoured by al-Qaeda, preparing society to accept sharia and indoctrinating people through education before implementing the
hudud aspects in sharia, which they believe supports punishments such as throwing homosexuals from the top of buildings, chopping limbs off, and public stoning. Al-Nusra and ISIL are both hostile towards the
Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
. However, while al-Nusra has typically destroyed Druze shrines and pressured them to convert to Sunni Islam, ISIL regards the entire Druze community as a valid target for violence, as it does the
Yazidis
Yazidis, also spelled Yezidis (; ), are a Kurdish languages, Kurdish-speaking Endogamy, endogamous religious group indigenous to Kurdistan, a geographical region in Western Asia that includes parts of Iraq, Syria, Turkey, and Iran. The major ...
.
In February 2014,
Ayman al-Zawahiri, the leader of Al-Qaeda, announced that his group
Al-Qaeda
, image = Flag of Jihad.svg
, caption = Jihadist flag, Flag used by various al-Qaeda factions
, founder = Osama bin Laden{{Assassinated, Killing of Osama bin Laden
, leaders = {{Plainlist,
* Osama bin Lad ...
had cut ties with the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant and denounced ISIL after being unable to reconcile a conflict between them and the al-Qaeda affiliate
al-Nusra Front
Al-Nusra Front or Jabhat al-Nusra or Jabhat Nusrat Ahl al-Sham, also known as Front for the Conquest of the Levant, and also later known as Jabhat Fatah al-Sham was a Salafi-jihadist organization that fought against Ba'athist Syria, Ba'athist ...
.
In September 2015,
Ayman al-Zawahiri, the leader of al-Qaeda, called for consultation (
shura
Shura () is the term for collective decision-making in Islam. It can, for example, take the form of a council or a referendum. The Quran encourages Muslims to decide their affairs in consultation with each other.
Shura is mentioned as a praise ...
) within the "prophetic method" to be used when establishing the caliphate, criticising al-Baghdadi for not following the required steps. Al-Zawahiri called upon ISIL members to close ranks and join al-Qaeda in fighting against
Assad, the
Shia
Shia Islam is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political successor (caliph) and as the spiritual leader of the Muslim community (imam). However, his right is understood ...
, Russia, Europe, and America and to stop the infighting between jihadist groups. He called upon jihadists to establish Islamic entities in Egypt and the Levant, slowly implementing sharia before establishing a caliphate, and has called for violent assaults against America and the West.
The
Jaysh al-Islam group within the
Islamic Front criticised ISIL, saying: "They killed the people of Islam and leave the idol worshippers ... They use the verses talking about the disbelievers and implement it on the Muslims". The main criticism of defectors from ISIL has been that the group is fighting and killing other Sunni Muslims, as opposed to just non-Sunnis being brutalised. In one case, a supposed defector from ISIL executed two activists of a Syrian opposition group in Turkey who had sheltered them.
Other commentaries
Literature scholar
Ian Almond criticised the media commentators, the lack of balance in reporting, and the "way we are learning to talk about ISIS". While there was talk about 'radical evil' and 'radical Islam', Almond found it striking because "some of the most revered and oft-quoted figures in our Western political tradition have been capable of the most vicious acts of savagery – and yet all we ever hear about is how much the Middle East has to learn from us." Almond goes on to argue that
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, ...
"wanted to gas women and children", that
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan (February 6, 1911 – June 5, 2004) was an American politician and actor who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He was a member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party a ...
's Central American policies "disembowelled more children than ISIS", that President
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
's "planes and drones have dropped bombs on as many schoolchildren as ISIS", that former secretary of state
Madeleine Albright
Madeleine Jana Korbel Albright (born Marie Jana Körbelová, later Korbelová; May 15, 1937 – March 23, 2022) was an American diplomat and political science, political scientist who served as the 64th United States Secretary of State, United S ...
commented on the deaths of Iraqi children killed by sanctions, that
Henry Kissinger
Henry Alfred Kissinger (May 27, 1923 – November 29, 2023) was an American diplomat and political scientist who served as the 56th United States secretary of state from 1973 to 1977 and the 7th National Security Advisor (United States), natio ...
and
Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013), was a British stateswoman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), Leader of th ...
"assisted in the torture and disappearance of thousands of Chilean students and labour activists... For anyone familiar with the history of both U.S. and European torture and murder over the past 150 years, it might not be all that hyperbolic to say that in ISIS, what we see more than anything else is a more expansive, explicit version of our own cruelties. In bombing ISIS and its would-be imperialism, we are really bombing a version of ourselves."
Commentator
Tom Engelhardt attributed the rise of ISIL and the destruction that followed to what he dubbed as America's drive to establish its own caliphate in the region.
A leader article in the ''
New Scientist
''New Scientist'' is a popular science magazine covering all aspects of science and technology. Based in London, it publishes weekly English-language editions in the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia. An editorially separate organ ...
'' magazine contextualised ISIL within the
nation state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the State (polity), state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly ...
construct. Although the group is described as medieval in the pejorative sense, "it is also hyper-modern, interested in few of the trappings of a conventional state apart from its own brutal brand of law enforcement. In fact, it is more of a network than a nation, having made canny use of social media to exert influence far beyond its geographical base."
Designation as a terrorist organisation
The
United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
in its
Resolution 1267 (1999) described
Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Laden (10 March 19572 May 2011) was a militant leader who was the founder and first general emir of al-Qaeda. Ideologically a pan-Islamist, Bin Laden participated in the Afghan ''mujahideen'' against the Soviet Union, and support ...
and his al-Qaeda associates as operators of a network of
terrorist training camps. The UN's
Al-Qaida Sanctions Committee first listed ISIL in its Sanctions List under the name "Al-Qaida in Iraq" on 18 October 2004, as an entity/group associated with al-Qaeda. On 2 June 2014, the group was added to its listing under the name "Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant". The
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
adopted the UN Sanctions List in 2002.

Many world leaders and government spokespeople have called ISIL a terrorist group or banned it, without their countries having formally designated it as such. The following are examples:
The Government of Germany banned ISIL in September 2014. Activities banned include donations to the group, recruiting fighters, holding ISIL meetings and distributing its propaganda,
flying ISIL flags, wearing ISIL symbols and all ISIL activities. "The terror organisation Islamic State is a threat to public safety in Germany as well", said German politician
Thomas de Maizière. He added, "Today's ban is directed solely against terrorists who abuse religion for their criminal goals." Being a member of ISIL is also illegal in accordance with §129a and §129b of the
German criminal code.
In October 2014, Switzerland banned ISIL's activities in the country, including propaganda and financial support of the fighters, with prison sentences as potential penalties.
In mid-December 2014, India banned ISIL after the arrest of an operator of a pro-ISIL Twitter account.
Pakistan designated ISIL as a banned organisation in late August 2015, under which all elements expressing sympathy for the group would be blacklisted and sanctioned.
After its
2022 Ulema gathering, the
Taliban
, leader1_title = Supreme Leader of Afghanistan, Supreme leaders
, leader1_name = {{indented plainlist,
* Mullah Omar{{Natural Causes{{nbsp(1994–2013)
* Akhtar Mansour{{Assassinated (2015–2016)
* Hibatullah Akhundzada (2016–present) ...
banned all Afghans from associating with the local
Khorasan Province
Khorasan ( ; also transcribed as Khurasan, Xorasan and Khorassan), also called Traxiane during Hellenistic and Parthian Empire, Parthian times, was a Provinces of Iran, province in northeastern Iran until September 2004, when it was divided in ...
branch of IS in July 2022, and labeled it a "false sect".
Media sources worldwide have described ISIL as a terrorist organisation.
Following the D-ISIS Ministerial in June 2023,
Minister Belkin announced Abdallah Makki Muslih al-Rufay'i and Abu Bakr ibn Muhammad ibn 'Ali al-Mainuki, as terrorists under Executive Order 13224.
Militia, cult, territorial authority, and other classifications
By 2014, ISIL was increasingly being viewed as a
militia
A militia ( ) is a military or paramilitary force that comprises civilian members, as opposed to a professional standing army of regular, full-time military personnel. Militias may be raised in times of need to support regular troops or se ...
in addition to a terrorist group and a
cult
Cults are social groups which have unusual, and often extreme, religious, spiritual, or philosophical beliefs and rituals. Extreme devotion to a particular person, object, or goal is another characteristic often ascribed to cults. The term ...
.
As major Iraqi cities fell to ISIL in June 2014, Jessica Lewis, a former US Army intelligence officer at the
Institute for the Study of War, described ISIL at that time as
Lewis has called ISIL:
Former US Defense Secretary
Chuck Hagel saw an "imminent threat to every interest we have", but former top counter-terrorism adviser
Daniel Benjamin derided such talk as a "farce" that panics the public.
Writing for ''
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardi ...
'',
Pankaj Mishra rejects the idea that the group is a resurgence of medieval Islam, saying instead:
On 28 January 2017, then U.S. President Donald Trump issued a National Security Presidential Memorandum that called for a comprehensive plan to destroy ISIL to be formulated by the Defense Department within 30 days.
Supporters
A United Nations report showed that 25,000 "foreign terrorist fighters" from 100 countries had joined "Islamist" groups, many of them working for IS or al-Qaeda.
According to a June 2015
Reuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide writing in 16 languages. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world.
The agency ...
report that cited "jihadist ideologues" as a source, 90% of IS's fighters in Iraq were Iraqi, and 70% of its fighters in Syria were Syrian. The article stated that the group had 40,000 fighters and 60,000 supporters across its two primary strongholds in Iraq and Syria.
According to scholar
Fawaz Gerges writing in ''ISIS: A History'', some "30 percent of the senior figures" in IS's military command were former army and police officers from the disbanded Iraqi security forces, turned towards Sunni Islamism and drawn to IS by the US
de-Ba'athification policy following the
US invasion of Iraq.
A 2014 analysis of 2,195,000
Arabic-language social media posts cited by ''The Guardian'' had 47% of the postings from Qatar, 35% from Pakistan, 31% from Belgium and almost 24% from the UK classified as supportive of IS. According to a 2015 poll by
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
, Muslim populations of various Muslim-majority countries have overwhelmingly negative views of IS, with the highest percentage of those expressing favorable views not exceeding 14%. In most of these countries, concerns about Islamic extremism have been growing.
There is a large amount of IS supporters online (On apps such as
Discord,
Telegram
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pi ...
, among several other online forums.)
Countries and groups at war with IS

IS's claims to territory have brought it into armed conflict with many governments, militias and other armed groups. International rejection of IS as a terrorist entity and rejection of its claim to even exist have placed it in conflict with countries around the world.
Global Coalition to Counter the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
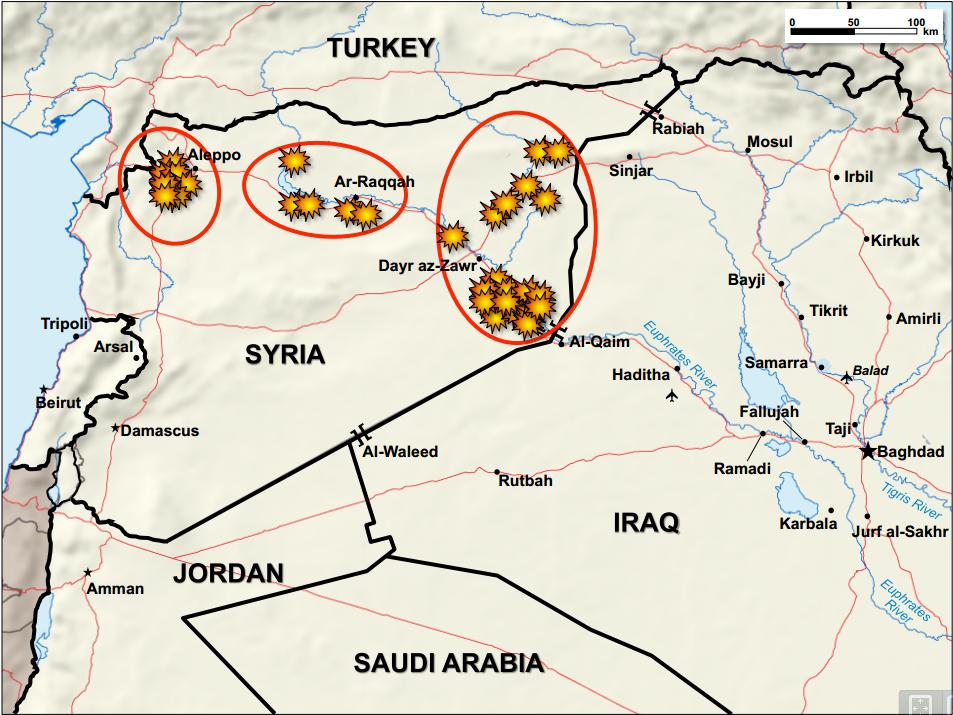
The Global Coalition to Counter the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), also referred to as the Counter-ISIL Coalition or Counter-DAESH Coalition, is a US-led group of nations and
non-state actors that have committed to "work together under a common, multifaceted, and long-term strategy to degrade and defeat ISIL/Daesh". According to a joint statement issued by 59 national governments and the European Union on 3 December 2014, participants in the Counter-ISIL Coalition are focused on multiple lines of effort:
# Supporting military operations, capacity building, and training;
# Stopping the flow of foreign terrorist fighters;
# Cutting off ISIL/Daesh's access to financing and funding;
# Addressing associated humanitarian relief and crises; and
# Exposing ISIL/Daesh's true nature (ideological delegitimisation).
Operation Inherent Resolve is the operational name given by the US to military operations against ISIL and Syrian al-Qaeda affiliates.
Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF–OIR) is co-ordinating the military portion of the response. The
Arab League
The Arab League (, ' ), officially the League of Arab States (, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world. The Arab League was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945, initially with seven members: Kingdom of Egypt, Egypt, Kingdom of Iraq, ...
,
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
,
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
, and
GCC are part of the Counter-ISIL Coalition: According to the Pentagon, by December 2017 over 80,000 ISIL fighters had been killed in Iraq and Syria by CJTF-OIR airstrikes. By then the coalition had flown over 170,000 sorties, 75–80% of combat sorties were conducted by the military of the United States, with the other 20–25% by Australia, Canada, Denmark, France, Jordan, Belgium, the Netherlands, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, the United Arab Emirates, and the United Kingdom. According to the UK-based monitoring group ''Airwars'', the air strikes and artillery of US-led coalition killed as many as 6,000 civilians in Iraq and Syria by the end of 2017.
Lebanon, which the U.S. considers part of the Global Coalition, fought off several
incursions by ISIL, with the largest engagements taking place from June 2014 to August 2017, when several thousand ISIL fighters invaded from Syria and occupied Lebanese territory. The U.S. and UK-backed
Lebanese Army succeeded in repulsing this invasion, killing or capturing over 1,200 ISIL fighters in the process.
On 21 December 2019, over 33 Islamist militants were killed in Mali by French forces using attack helicopters, drones and ground troops, alongside the border with Mauritania, where an Al-Qaeda-linked group operates.
Other state opponents not part of the Counter-ISIL Coalition
– military advisors, arms supplier, training, ground troops in Iraq and Syria, and air power in Syria, beside Iranian borders (''see
Iranian intervention in Iraq'')
– arms supplier to Iraqi and Syrian governments. Security operations within state borders in 2015. Airstrikes in Syria (see
Russian military intervention in the Syrian Civil War).
– security operations within state borders
– Military deployment over
Saudi Arabia–Iraq border. Arresting ISIL figures in Pakistan.
(
Supreme Political Council
The Supreme Political Council (SPC; ) is an extraconstitutional collective head of state and rival executive established in 2016 in Sanaa by the Houthis and the pro-Houthi faction of the General People's Congress (GPC) to rule Yemen opposed ...
)
– security operations within state borders (see
Islamic State–Taliban conflict
The Islamic State–Taliban conflict is an ongoing insurgency waged by the Islamic State – Khorasan Province (IS-KP) against the Taliban regime in Afghanistan. The conflict initially began when both operated as rival insurgent groups in Nan ...
)
Other non-state opponents
*
*

al-Nusra Front
Al-Nusra Front or Jabhat al-Nusra or Jabhat Nusrat Ahl al-Sham, also known as Front for the Conquest of the Levant, and also later known as Jabhat Fatah al-Sham was a Salafi-jihadist organization that fought against Ba'athist Syria, Ba'athist ...
—with localised truces and co-operation at times
*
al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula
*
al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb
*
Al-Shabaab
*
*

Hamas
The Islamic Resistance Movement, abbreviated Hamas (the Arabic acronym from ), is a Palestinian nationalist Sunni Islam, Sunni Islamism, Islamist political organisation with a military wing, the Qassam Brigades. It has Gaza Strip under Hama ...
*
*
*
Kurdistan Workers' Party
The Kurdistan Workers' Party, or the PKK, isDespite the PKK's 12th Congress announcing plans for total organisational dissolution, the PKK has not yet been dissolved de facto or de jure. a Kurds, Kurdish militant political organization and armed ...
—ground troops in Iraqi Kurdistan and in Syrian Kurdistan
*
Syrian Democratic Forces
The Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) is a Kurds in Syria, Kurdish-led coalition of U.S.-backed Left-wing politics, left-wing ethnic militias and rebel groups, and serves as the official military wing of the Democratic Autonomous Administration ...
*

Nineveh Plain Protection Units
The Nineveh Plain Protection Units ( ; ) or NPU is an Assyrian people, Assyrian paramilitary organization that was formed in late 2014, largely but not exclusively by Assyrians in Iraq to defend themselves against Islamic State of Iraq and the L ...
– an Assyrian Christian militia in the Nineveh Plains in Northern Iraq
*
Amal Movement
*
Syrian Resistance – Suqur al-Furat
*
Liwa al-Quds
*
Liwa Abu al-Fadhal al-Abbas
*
Abu al-Fadl al-Abbas Forces
*
Islamic Jihad Movement in Palestine
The Islamic Jihad Movement in Palestine (, ''Harakat al-Jihād al-Islāmi fi Filastīn''), commonly known simply as Palestinian Islamic Jihad (PIJ), is a Palestinians, Palestinian Islamism, Islamist paramilitary organization formed in 1981.
P ...
*
Arab Nationalist Guard
*
Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine – General Command
*
Syrian Revolutionary Command Council
*
Mujahideen Shura Council (Syria)
*
Unified Military Command of Eastern Ghouta
*
Fatah Halab
*
Mare' Operations Room
*
Golan Regiment
*
Mukhtar Army
Al-Qaeda
Al-Nusra Front
Al-Nusra Front or Jabhat al-Nusra or Jabhat Nusrat Ahl al-Sham, also known as Front for the Conquest of the Levant, and also later known as Jabhat Fatah al-Sham was a Salafi-jihadist organization that fought against Ba'athist Syria, Ba'athist ...
is a branch of
al-Qaeda
, image = Flag of Jihad.svg
, caption = Jihadist flag, Flag used by various al-Qaeda factions
, founder = Osama bin Laden{{Assassinated, Killing of Osama bin Laden
, leaders = {{Plainlist,
* Osama bin Lad ...
operating in Syria. Al-Nusra has launched many attacks and
bombings, mostly against targets affiliated with or supportive of the Syrian government. There have been media reports that many of al-Nusra's foreign fighters have left to join al-Baghdadi's ISIL.
In February 2014, after continued tensions, al-Qaeda publicly disavowed any relations with ISIL. However, ISIL and al-Nusra Front still cooperate with each other occasionally when they fight against the Syrian government.
On 10 September 2015, an audio message was released by al-Qaeda's leader
Ayman al-Zawahiri criticising ISIL's self-proclaimed caliphate and accusing it of "sedition". This was described by some media outlets as a "declaration of war". However, although al-Zawahiri denied ISIL's legitimacy, he suggested that there was still room for cooperation against common enemies, and said that if he were in Iraq, he would fight alongside ISIL.
Human rights abuse and war crime findings
The Islamic State has been widely accused of committing
war crimes
A war crime is a violation of the laws of war that gives rise to individual criminal responsibility for actions by combatants in action, such as intentionally killing civilians or intentionally killing prisoners of war, torture, taking hos ...
,
crimes against humanity
Crimes against humanity are certain serious crimes committed as part of a large-scale attack against civilians. Unlike war crimes, crimes against humanity can be committed during both peace and war and against a state's own nationals as well as ...
, and of
human rights abuses
Human rights are universally recognized moral principles or norms that establish standards of human behavior and are often protected by both national and international laws. These rights are considered inherent and inalienable, meaning t ...
,
including systematic rape and other forms of sexual violence against both males and females, mass killing of
prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war for a ...
,
summary executions including the
Camp Speicher massacre, public floggings, beheadings, politically motivated assassinations of judges; public officials; members of the security forces and others, and terrorizing residents of
Derna, Libya
Derna (; ') is a port city in eastern Libya. With a population of around 90,000, Derna was once the seat of one of the wealthiest provinces among the Barbary States. The city is now the administrative capital of Derna District, which covers ...
among others.
ISIL members were also reported to perform
human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease deity, gods, a human ruler, public or jurisdictional demands for justice by capital punishment, an authoritative/prie ...
s, despite the act being forbidden in Islam. Sarah Leah Watson, Director of HRW Middle East and North Africa, said: "Commanders should understand that they may face domestic or international prosecution for the grave rights abuses their forces are committing."
In July 2014, the
BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
reported the United Nations' chief investigator as stating: "Fighters from the Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) may be added to a list of war crimes suspects in Syria."
The
United Nations Commission on Human Rights
The United Nations Commission on Human Rights (UNCHR) was a functional commission within the United Nations System, overall framework of the United Nations from 1946 until it was replaced by the United Nations Human Rights Council in 2006. It was a ...
has stated that the group "seeks to subjugate civilians under its control and dominate every aspect of their lives through terror, indoctrination, and the provision of services to those who obey".
According to the
Iraq Body Count project, the Islamic State's fighters killed a minimum of 25,645 Iraqi civilians from 2014 to 2016.
Iraq Body Count database
accessed October 14, 2023.
Explanatory notes
Citations
General and cited references
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Morris, Andrea Michelle. "Who Becomes a Foreign Fighter? Characteristics of the Islamic State's Soldiers" ''Terrorism and Political Violence'' 35#2 (2023) pp 1–19; .
*
*
Further reading
*
External links
* by Council on Foreign Relations
The Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) is an American think tank focused on Foreign policy of the United States, U.S. foreign policy and international relations. Founded in 1921, it is an independent and nonpartisan 501(c)(3) nonprofit organi ...
ISIS
Counter Extremism Project profile
"'Islamic State': Raqqa's loss seals rapid rise and fall"
by BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broad ...
* '' Frontline''
''Losing Iraq''
(July 2014), (October 2014)
''Obama at War''
(May 2015)
''Escaping ISIS''
(July 2015), documentaries by PBS
''The Islamic State''
August 2014 documentary by Vice News
Vice News (stylized as VICE News) is Vice Media's alternative current affairs channel, producing daily documentary essays and video through its website and YouTube channel. It promotes itself on its coverage of "under-reported stories". Vice Ne ...
"ISIS: Portrait of a Jihadi Terrorist Organization"
report by the Intelligence and Terrorism Information Center
Operation Inherent Resolve updates
"The Group That Calls Itself a State"
, publication by the Combating Terrorism Center
* , publication by the United Nations Security Council
{{Authority control
1999 establishments in Jordan
Anti-Americanism
Anti-Israeli sentiment in Iraq
Anti-Israeli sentiment in Syria
Anti-Zionism in Iraq
Anti-Zionism in the Arab world
Anti-Hindu sentiment
Anti-Shi'ism
Antisemitism in Iraq
Anti-Western sentiment
Anti-Zionism in the Middle East
Antisemitism in the Middle East
Articles containing video clips
Caliphalism
Factions in the Iraq War
Former unrecognized countries
Groups practising sexual slavery
Islam-related controversies
Islamism in Iraq
Islamism in Syria
Military units and formations established in 1999
Organisations designated as terrorist by Australia
Organizations designated as terrorist by Bahrain
Organizations designated as terrorist by Canada
Organizations designated as terrorist by China
Organizations designated as terrorist by Egypt
Organisations designated as terrorist by India
Organisations designated as terrorist by Iran
Organizations designated as terrorist by Iraq
Organizations designated as terrorist by Israel
Organizations designated as terrorist by Kyrgyzstan
Organisations designated as terrorist by Pakistan
Organizations designated as terrorist by Paraguay
Organizations designated as terrorist by Russia
Organizations designated as terrorist by Syria
Organizations based in Asia designated as terrorist
Organisations designated as terrorist by the European Union
Organizations designated as terrorist by Turkey
Organizations designated as terrorist by the Philippines
Organizations designated as terrorist by the United Arab Emirates
Organizations designated as terrorist by the United States
Organizations established in 1999
Islamic organizations that oppose LGBTQ rights
Persecution of Christians
Persecution of LGBTQ people in Asia
Rebel groups in Iraq
Rebel groups that actively control territory
Salafi Jihadist groups
Terrorism in Iraq
Terrorism in Syria
Violence against men in Asia
Violence against women in Asia
Violence against children
Salafist states
 Documents found after the death of Samir Abd Muhammad al-Khlifawi, a former colonel in the intelligence service of the Iraqi Air Force before the US invasion who had been described as "the strategic head" of ISIL, detailed planning for the ISIL takeover of northern Syria, which made possible "the group's later advances into Iraq". Al-Khlifawi called for the infiltration of areas to be conquered with spies who would find out "as much as possible about the target towns: Who lived there, who was in charge, which families were religious, which Islamic school of religious jurisprudence they belonged to, how many mosques there were, who the imam was, how many wives and children he had and how old they were". Following this surveillance and espionage would come murder and kidnapping – "the elimination of every person who might have been a potential leader or opponent". In Raqqa, after rebel forces drove out the Assad regime and ISIL infiltrated the town, "first dozens and then hundreds of people disappeared".
Security and intelligence expert Martin Reardon has described IS's purpose as being to psychologically "break" those under its control, "so as to ensure their absolute allegiance through fear and intimidation", while generating "outright hate and vengeance" among its enemies. Jason Burke, a journalist writing on
Documents found after the death of Samir Abd Muhammad al-Khlifawi, a former colonel in the intelligence service of the Iraqi Air Force before the US invasion who had been described as "the strategic head" of ISIL, detailed planning for the ISIL takeover of northern Syria, which made possible "the group's later advances into Iraq". Al-Khlifawi called for the infiltration of areas to be conquered with spies who would find out "as much as possible about the target towns: Who lived there, who was in charge, which families were religious, which Islamic school of religious jurisprudence they belonged to, how many mosques there were, who the imam was, how many wives and children he had and how old they were". Following this surveillance and espionage would come murder and kidnapping – "the elimination of every person who might have been a potential leader or opponent". In Raqqa, after rebel forces drove out the Assad regime and ISIL infiltrated the town, "first dozens and then hundreds of people disappeared".
Security and intelligence expert Martin Reardon has described IS's purpose as being to psychologically "break" those under its control, "so as to ensure their absolute allegiance through fear and intimidation", while generating "outright hate and vengeance" among its enemies. Jason Burke, a journalist writing on  At its peak, IS was sometimes described as a
At its peak, IS was sometimes described as a  The current Grand Imam of al-Azhar and former president of
The current Grand Imam of al-Azhar and former president of  Many world leaders and government spokespeople have called ISIL a terrorist group or banned it, without their countries having formally designated it as such. The following are examples:
The Government of Germany banned ISIL in September 2014. Activities banned include donations to the group, recruiting fighters, holding ISIL meetings and distributing its propaganda, flying ISIL flags, wearing ISIL symbols and all ISIL activities. "The terror organisation Islamic State is a threat to public safety in Germany as well", said German politician Thomas de Maizière. He added, "Today's ban is directed solely against terrorists who abuse religion for their criminal goals." Being a member of ISIL is also illegal in accordance with §129a and §129b of the German criminal code.
In October 2014, Switzerland banned ISIL's activities in the country, including propaganda and financial support of the fighters, with prison sentences as potential penalties.
In mid-December 2014, India banned ISIL after the arrest of an operator of a pro-ISIL Twitter account.
Pakistan designated ISIL as a banned organisation in late August 2015, under which all elements expressing sympathy for the group would be blacklisted and sanctioned.
After its 2022 Ulema gathering, the
Many world leaders and government spokespeople have called ISIL a terrorist group or banned it, without their countries having formally designated it as such. The following are examples:
The Government of Germany banned ISIL in September 2014. Activities banned include donations to the group, recruiting fighters, holding ISIL meetings and distributing its propaganda, flying ISIL flags, wearing ISIL symbols and all ISIL activities. "The terror organisation Islamic State is a threat to public safety in Germany as well", said German politician Thomas de Maizière. He added, "Today's ban is directed solely against terrorists who abuse religion for their criminal goals." Being a member of ISIL is also illegal in accordance with §129a and §129b of the German criminal code.
In October 2014, Switzerland banned ISIL's activities in the country, including propaganda and financial support of the fighters, with prison sentences as potential penalties.
In mid-December 2014, India banned ISIL after the arrest of an operator of a pro-ISIL Twitter account.
Pakistan designated ISIL as a banned organisation in late August 2015, under which all elements expressing sympathy for the group would be blacklisted and sanctioned.
After its 2022 Ulema gathering, the  The Global Coalition to Counter the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), also referred to as the Counter-ISIL Coalition or Counter-DAESH Coalition, is a US-led group of nations and non-state actors that have committed to "work together under a common, multifaceted, and long-term strategy to degrade and defeat ISIL/Daesh". According to a joint statement issued by 59 national governments and the European Union on 3 December 2014, participants in the Counter-ISIL Coalition are focused on multiple lines of effort:
# Supporting military operations, capacity building, and training;
# Stopping the flow of foreign terrorist fighters;
# Cutting off ISIL/Daesh's access to financing and funding;
# Addressing associated humanitarian relief and crises; and
# Exposing ISIL/Daesh's true nature (ideological delegitimisation).
Operation Inherent Resolve is the operational name given by the US to military operations against ISIL and Syrian al-Qaeda affiliates. Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF–OIR) is co-ordinating the military portion of the response. The
The Global Coalition to Counter the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), also referred to as the Counter-ISIL Coalition or Counter-DAESH Coalition, is a US-led group of nations and non-state actors that have committed to "work together under a common, multifaceted, and long-term strategy to degrade and defeat ISIL/Daesh". According to a joint statement issued by 59 national governments and the European Union on 3 December 2014, participants in the Counter-ISIL Coalition are focused on multiple lines of effort:
# Supporting military operations, capacity building, and training;
# Stopping the flow of foreign terrorist fighters;
# Cutting off ISIL/Daesh's access to financing and funding;
# Addressing associated humanitarian relief and crises; and
# Exposing ISIL/Daesh's true nature (ideological delegitimisation).
Operation Inherent Resolve is the operational name given by the US to military operations against ISIL and Syrian al-Qaeda affiliates. Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF–OIR) is co-ordinating the military portion of the response. The