Maryland Terrapins Men's Basketball Players on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Maryland ( ) is a
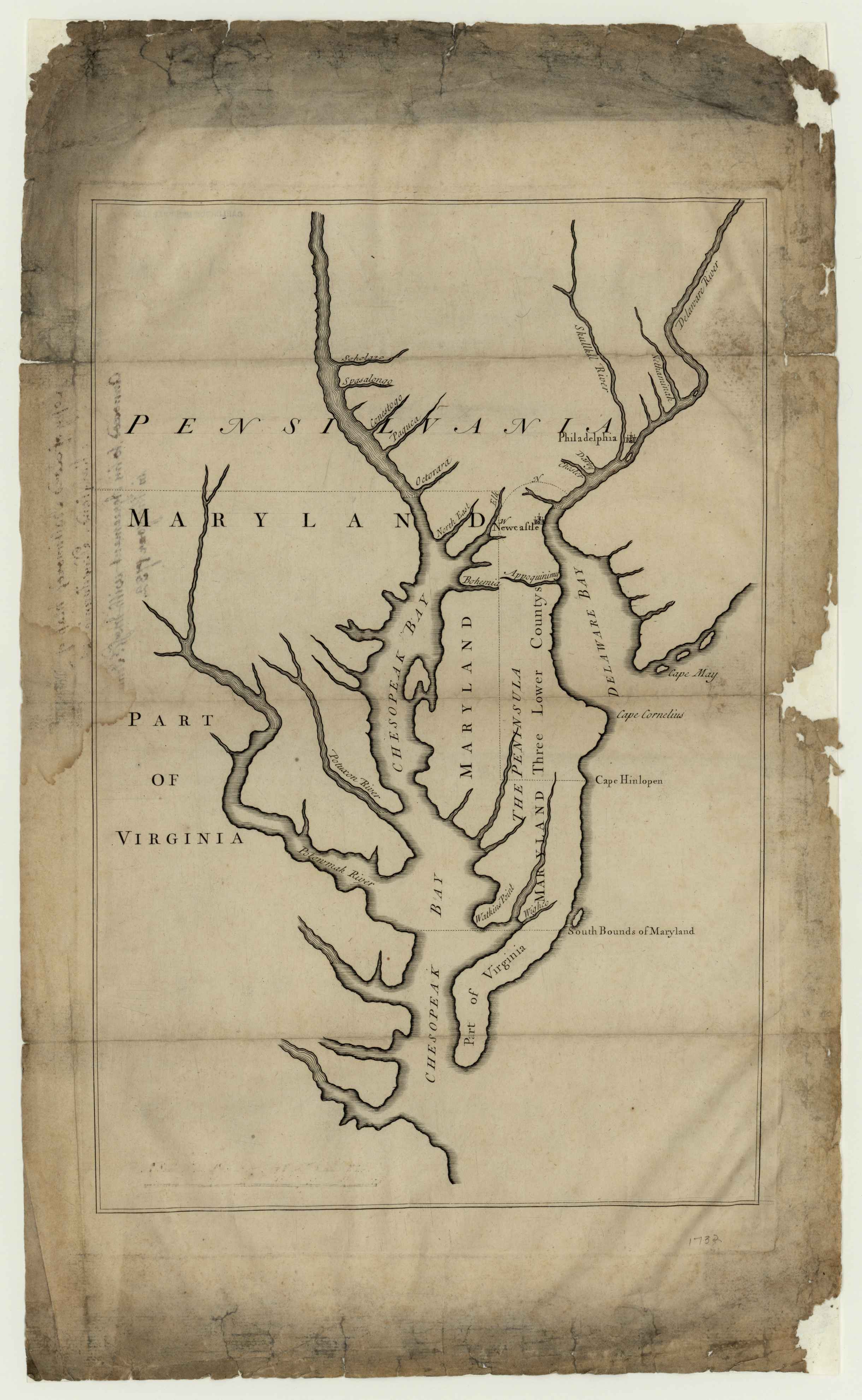 The royal charter granted Maryland the land north of the
The royal charter granted Maryland the land north of the
. Retrieved February 15, 2008. As the flow of indentured laborers to the colony decreased with improving economic conditions in England, planters in Maryland imported thousands more slaves and racial caste lines hardened. Maryland was one of the
 Influenced by a changing economy, revolutionary ideals, and preaching by ministers, numerous planters in Maryland freed their slaves in the 20 years after the Revolutionary War. Across the Upper South the free black population increased from less than 1% before the war to 14% by 1810. Abolitionists Harriet Tubman and Frederick Douglass were born slaves during this time in Dorchester County and Talbot County, respectively.
During the
Influenced by a changing economy, revolutionary ideals, and preaching by ministers, numerous planters in Maryland freed their slaves in the 20 years after the Revolutionary War. Across the Upper South the free black population increased from less than 1% before the war to 14% by 1810. Abolitionists Harriet Tubman and Frederick Douglass were born slaves during this time in Dorchester County and Talbot County, respectively.
During the
 The
The


 Maryland possesses a variety of
Maryland possesses a variety of
 As is typical of states on the East Coast, Maryland's plant life is abundant and healthy. An adequate volume of annual precipitation helps to support many types of plants, including
As is typical of states on the East Coast, Maryland's plant life is abundant and healthy. An adequate volume of annual precipitation helps to support many types of plants, including
 The state harbors a considerable number of
The state harbors a considerable number of
 Most of the population of Maryland lives in the central region of the state, in the
Most of the population of Maryland lives in the central region of the state, in the
 In the 2020 United States census, the
In the 2020 United States census, the
 In 1970, the U.S. Census Bureau reported Maryland's population as 17.8 percent African-American and 80.4 percent non-Hispanic White.
In 2019, non-Hispanic white Americans were 49.8% of Maryland's population (
In 1970, the U.S. Census Bureau reported Maryland's population as 17.8 percent African-American and 80.4 percent non-Hispanic White.
In 2019, non-Hispanic white Americans were 49.8% of Maryland's population (
Washington: "Nation's Largest Ethiopian Community Carves Niche"
( ). ''
"Washington: Nation's Largest Ethiopian Community Carves Niche"
. '' The Southeast Missourian''. ''Associated Press''. October 23, 2005. p. 7C. Retrieved August 25, 2018. The Ethiopian community of Greater D.C. was historically based in the Adams Morgan and Shaw neighborhoods of Washington, D.C., but as the community has grown, many Ethiopians have settled in Silver Spring. The Ethiopian American population in Maryland and the rest of the D.C. area is largely
 Maryland has been historically prominent to American Catholic tradition because the English colony of Maryland was intended by
Maryland has been historically prominent to American Catholic tradition because the English colony of Maryland was intended by
 The
The
 Maryland has large areas of fertile agricultural land in its coastal and
Maryland has large areas of fertile agricultural land in its coastal and
 Tourism is popular in Maryland. Many tourists visit Baltimore, the beaches of the Eastern Shore, and the nature of western Maryland. Attractions in Baltimore include the Harborplace, the Baltimore Aquarium,
Tourism is popular in Maryland. Many tourists visit Baltimore, the beaches of the Eastern Shore, and the nature of western Maryland. Attractions in Baltimore include the Harborplace, the Baltimore Aquarium,
 Maryland's Interstate highways include of I-95, which enters the northeast portion of the state, travels through
Maryland's Interstate highways include of I-95, which enters the northeast portion of the state, travels through

"CSX and Maryland."
followed by
 The government of Maryland is conducted according to the state constitution. The government of Maryland, like the other 49 state governments, has exclusive authority over matters that lie entirely within the state's borders, except as limited by the
The government of Maryland is conducted according to the state constitution. The government of Maryland, like the other 49 state governments, has exclusive authority over matters that lie entirely within the state's borders, except as limited by the
 Following the
Following the
 With two major metropolitan areas, Maryland has a number of major and minor professional sports franchises. Two National Football League teams play in Maryland, the Baltimore Ravens in
With two major metropolitan areas, Maryland has a number of major and minor professional sports franchises. Two National Football League teams play in Maryland, the Baltimore Ravens in
Maryland Office of Tourism
* * *
Maryland State Facts from USDA
*
Maryland Historical Society: County Maps
Maryland: State Resource Guide, from the Library of Congress
{{coord, 39, -77, dim:300000_region:US-MD_type:adm1st, name=State of Maryland, display=title Maryland, 1788 establishments in the United States Contiguous United States Mid-Atlantic states Northeastern United States Southern United States States and territories established in 1788 States of the East Coast of the United States States of the United States
state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
to its south, West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
to its west, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
to its north, and Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
to its east, as well as with the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
to its east, and the national capital and federal district of Washington, D.C. to the southwest. With a total area of , Maryland is the ninth-smallest state by land area, and its population of 6,177,224 ranks it the 18th-most populous state and the fifth-most densely populated. Maryland's capital city is Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
, and the state's most populous city is Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
.
Maryland's coastline was first explored by Europeans in the 16th century. Prior to that, it was inhabited by several Native American tribes, mostly the Algonquian peoples
The Algonquians are one of the most populous and widespread North American indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous American groups, consisting of the peoples who speak Algonquian languages. They historically were prominent along the East ...
. One of the original Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
, the Province of Maryland
The Province of Maryland was an Kingdom of England, English and later British colonization of the Americas, British colony in North America from 1634 until 1776, when the province was one of the Thirteen Colonies that joined in supporting the A ...
was founded in 1634 by George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore, a Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
convert"George Calvert and Cecilius Calvert, Barons Baltimore" William Hand Browne, Nabu Press (August 1, 2010), who sought to provide a religious haven for Catholics persecuted in England. In 1632, Charles I of England
Charles I (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland from 27 March 1625 until Execution of Charles I, his execution in 1649.
Charles was born ...
granted Lord Baltimore a colonial charter, naming the colony after his wife, Henrietta Maria
Henrietta Maria of France (French language, French: ''Henriette Marie''; 25 November 1609 – 10 September 1669) was List of English royal consorts, Queen of England, List of Scottish royal consorts, Scotland and Ireland from her marriage to K ...
. In 1649, the Maryland General Assembly passed an Act Concerning Religion, which enshrined the principle of toleration
Toleration is when one allows or permits an action, idea, object, or person that they dislike or disagree with. Political scientist Andrew R. Murphy explains that "We can improve our understanding by defining 'toleration' as a set of social or ...
. Religious strife was common in Maryland's early years, and Catholics
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
remained a minority, albeit in greater numbers than in any other English colony. Maryland's early settlements and population centers clustered around waterways that empty into the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Ea ...
. Its economy was heavily plantation-based and centered mostly on the cultivation of tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
. Demand for cheap labor from Maryland colonists led to the importation of numerous indentured servants and enslaved Africans. In 1760, Maryland's current boundaries took form following the settlement of a long-running border dispute with Pennsylvania. Many of its citizens played key political and military roles in the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
. Although it was a slave state, Maryland remained in the Union during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, and its proximity to Washington D.C. and Virginia made it a significant strategic location. After the Civil War ended in 1865, Maryland took part in the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, driven by its seaports, railroad networks, and mass immigration from Europe.
Since the 1940s, the state's population has grown rapidly, to approximately six million residents, and it is among the most densely populated U.S. states. , Maryland had the highest median household income of any state, owing in large part to its proximity to Washington, D.C., and a highly diversified economy spanning manufacturing, retail services, public administration, real estate, higher education, information technology, defense contracting, health care, and biotechnology. Maryland is one of the most multicultural states in the country; it is one of the seven states where non-Whites compose a majority of the population, with the fifth-highest percentage of African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
, and high numbers of residents born in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, Central America
Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually ...
, and the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
. The state's central role in U.S. history is reflected by its hosting of some of the highest numbers of historic landmarks per capita.
The western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
portion of the state contains stretches of the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain ...
, the central portion is primarily composed of the Piedmont
Piedmont ( ; ; ) is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the northwest Italy, Northwest of the country. It borders the Liguria region to the south, the Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna regions to the east, and the Aosta Valley region to the ...
, and the eastern side of the state makes up a significant portion of the Chesapeake Bay. Sixteen of Maryland's twenty-three counties, and the city of Baltimore, border the tidal waters of the Chesapeake Bay estuary and its many tributaries, which combined total more than 4,000 miles of shoreline. Although one of the smallest states in the U.S., it features a variety of climates and topographical features that have earned it the moniker of ''America in Miniature''. Maryland's geography, culture, and history are diverse, including elements of the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, and Southern regions of the country.
History
17th century
Maryland's first colonial settlement
Present-day Maryland was originally inhabited by tribes such as the Piscataway (including the Patuxent), the Nanticoke (including the Tocwogh, the Ozinie and other subdivisions), thePowhatan
Powhatan people () are Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands who belong to member tribes of the Powhatan Confederacy, or Tsenacommacah. They are Algonquian peoples whose historic territories were in eastern Virginia.
Their Powh ...
, the Lenape
The Lenape (, , ; ), also called the Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada.
The Lenape's historica ...
, the Susquehannock
The Susquehannock, also known as the Conestoga, Minquas, and Andaste, were an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian people who lived in the lower Susquehanna River watershed in what is now Pennsylvania. Their name means “people of the muddy river.”
T ...
, the Shawnee, the Tutelo, the Saponi, the Pocomoke and the Massawomeck. George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore (1579–1632), sought a charter from King Charles I for the territory between Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
to the north and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
to the immediate south.
After Baltimore died in April 1632, the charter was granted to his son, Cecilius Calvert, 2nd Baron Baltimore (1605–1675), on June 20, 1632. Officially, the new "Maryland Colony" was named in honor of Henrietta Maria of France
Henrietta Maria of France ( French: ''Henriette Marie''; 25 November 1609 – 10 September 1669) was Queen of England, Scotland and Ireland from her marriage to King Charles I on 13 June 1625 until his execution on 30 January 1649. She was ...
, wife of Charles I. Lord Baltimore initially proposed the name "Crescentia", the land of growth or increase, but "the King proposed Terra Mariae ary Land which was concluded on and inserted in the bill."
The original capital of Maryland was St. Mary's City, on the north shore of the Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
, and the county surrounding it was the first erected and created in the province, first called Augusta Carolina, after the King, and later named St. Mary's County.
Lord Baltimore's first settlers arrived in the new colony in March 1634, with his younger brother, Leonard Calvert
Leonard Calvert ( – ) was the first Lord proprietor, proprietary governor of the Province of Maryland. He was the second son of George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore, The 1st Baron Baltimore (1579–1632), the first proprietor of Maryland. His e ...
(1606–1647), as the first provincial Governor of Maryland
The governor of the State of Maryland is the head of government of Maryland, and is the commander-in-chief of the state's National Guard units. The governor is the highest-ranking official in the state and has a broad range of appointive powers ...
. They made their first permanent settlement at St. Mary's City in what is now St. Mary's County. They purchased the site from the paramount chief
A paramount chief is the English-language designation for a king or queen or the highest-level political leader in a regional or local polity or country administered politically with a Chiefdom, chief-based system. This term is used occasionally ...
of the region, who was eager to establish trade. St. Mary's became the first capital of Maryland, and remained so for 60 years until 1695. More settlers soon followed. Their tobacco crops were successful and quickly made the new colony profitable. However, given the incidence of malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
, yellow fever, and typhoid
Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a disease caused by ''Salmonella enterica'' serotype Typhi bacteria, also called ''Salmonella'' Typhi. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often ther ...
, life expectancy in Maryland was about 10 years less than in New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
.
Persecution of Catholics
Maryland was founded to provide a haven for England'sRoman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
minority.
Although Maryland was the most heavily Catholic of the English mainland colonies, the religion was still in the minority, consisting of less than 10% of the total population.
In 1642, several Puritans
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should b ...
left Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
for Maryland and founded the city of Providence, now called Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
, on the western shore of the upper Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Ea ...
. A dispute with traders from Virginia over Kent Island in the Chesapeake led to armed conflict. In 1644, William Claiborne, a Puritan, seized Kent Island while his associate, the pro-Parliament Puritan Richard Ingle
Richard Ingle ( – ) was an English sea captain, tobacco trader, and privateer in colonial Maryland. Along with William Claiborne, Ingle revolted against Maryland Catholic leaders in the name of English Parliament and Puritans in a period known ...
, took over St. Mary's. Both used religion as a tool to gain popular support. The two years from 1644 to 1646 when Claiborne and his Puritan associates held sway were known as "The Plundering Time". They captured Jesuit priests, imprisoned them, and then sent them back to England.
In 1646, Leonard Calvert
Leonard Calvert ( – ) was the first Lord proprietor, proprietary governor of the Province of Maryland. He was the second son of George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore, The 1st Baron Baltimore (1579–1632), the first proprietor of Maryland. His e ...
returned with troops, recaptured St. Mary's City, and restored order. The House of Delegates passed the "Act concerning Religion" in 1649, granting religious liberty to all Trinitarian Christians.
In 1650, the Puritans revolted against the proprietary government. "Protestants swept the Catholics out of the legislature... and religious strife returned." The Puritans set up a new government prohibiting both Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
and Anglicanism
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
. The Puritan revolutionary government persecuted Maryland Catholics during its reign, known as the "plundering time". Mobs burned down all the original Catholic churches of southern Maryland. The Puritan rule lasted until 1658, when the Calvert family and Lord Baltimore regained proprietary control and re-enacted the Toleration Act.
After England's Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also known as the Revolution of 1688, was the deposition of James II and VII, James II and VII in November 1688. He was replaced by his daughter Mary II, Mary II and her Dutch husband, William III of Orange ...
in 1688, Maryland outlawed Catholicism. In 1704, the Maryland General Assembly prohibited Catholics from operating schools, limited the corporate ownership of property to hamper religious orders from expanding or supporting themselves, and encouraged the conversion of Catholic children. The celebration of the Catholic sacraments was also officially restricted. This state of affairs lasted until after the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
(1775–1783). Wealthy Catholic planters built chapels on their land to practice their religion in relative secrecy.
Into the 18th century, individual priests and lay leaders claimed Maryland farms belonging to the Jesuits as personal property and bequeathed them to evade the legal restrictions on religious organizations' owning property.
Border disputes (1681–1760)
 The royal charter granted Maryland the land north of the
The royal charter granted Maryland the land north of the Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
up to the 40th parallel. A problem arose when Charles II granted a charter for the Province of Pennsylvania
The Province of Pennsylvania, also known as the Pennsylvania Colony, was a British North American colony founded by William Penn, who received the land through a grant from Charles II of England in 1681. The name Pennsylvania was derived from ...
, which defined Pennsylvania's southern border as the 40th parallel, identical to Maryland's northern border. But the grant indicated that Charles II and William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer, religious thinker, and influential Quakers, Quaker who founded the Province of Pennsylvania during the British colonization of the Americas, British colonial era. An advocate of democracy and religi ...
assumed the 40th parallel would pass close to New Castle, Delaware
New Castle is a city in New Castle County, Delaware, United States. The city is located six miles (10 km) south of Wilmington, Delaware, Wilmington and is situated on the Delaware River. As of 2020, the city's population was 5,551. New Cast ...
, where it falls north of Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, which Penn already designated as Pennsylvania's capital city. Negotiations ensued after the problem was discovered in 1681.
A compromise proposed by Charles II in 1682 was undermined by Penn's receiving the additional grant of what is now Delaware. Penn successfully argued that the Maryland charter entitled Lord Baltimore only to unsettled lands, and Dutch settlement in Delaware predated his charter. The dispute remained unresolved for nearly a century, carried on by the descendants of William Penn and Lord Baltimore—the Calvert family, which controlled Maryland, and the Penn family, which controlled Pennsylvania.
The border dispute with Pennsylvania led to Cresap's War in the 1730s. Hostilities erupted in 1730 and escalated through the first half of the decade, culminating in the deployment of military forces by Maryland in 1736 and by Pennsylvania in 1737. The armed phase of the conflict ended in May 1738 with the intervention of King George II, who compelled the negotiation of a cease-fire. A provisional agreement had been established in 1732.
Negotiations continued until a final agreement was signed in 1760. The agreement defined the border between Maryland and Pennsylvania as the line of latitude now known as the Mason–Dixon line
The Mason–Dixon line, sometimes referred to as Mason and Dixon's Line, is a demarcation line separating four U.S. states: Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware and West Virginia. It was Surveying, surveyed between 1763 and 1767 by Charles Mason ...
. Maryland's border with Delaware was based on the Transpeninsular Line and the Twelve-Mile Circle around New Castle.
18th century
Most of the English colonists arrived in Maryland asindentured servant
Indentured servitude is a form of Work (human activity), labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract called an "indenture", may be entered voluntarily for a prepaid lump sum, as paymen ...
s, and had to serve a several-year term as laborers to pay for their passage. In the early years, the line between indentured servants and African slaves or laborers was fluid, and white and black laborers commonly lived and worked together, and formed unions. Mixed-race children born to white mothers were considered free by the principle of '' partus sequitur ventrem'', by which children took the social status of their mothers, a principle of slave law that was adopted throughout the colonies, following Virginia in 1662.
Many of the free black families migrated to Delaware, where land was cheaper.Paul Heinegg. ''Free African Americans in Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Maryland and Delaware''. Retrieved February 15, 2008. As the flow of indentured laborers to the colony decreased with improving economic conditions in England, planters in Maryland imported thousands more slaves and racial caste lines hardened. Maryland was one of the
thirteen colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
that revolted against British rule in the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
. Near the end of the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
(1775–1783), on February 2, 1781, Maryland became the last and 13th state to approve the ratification of the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, first proposed in 1776 and adopted by the Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress (1775–1781) was the meetings of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolution and American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War, which established American independence ...
in 1778, which brought into being the United States as a united, sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title that can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to ...
and national state. It also became the seventh state admitted to the Union after ratifying the new federal Constitution in 1788. In December 1790, prior to the move of the national capital from Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
in 1800, Maryland donated land selected by first President George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revoluti ...
to the federal government
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
for its creation. The land was provided along the north shore of the Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
from Montgomery and Prince George's counties, as well as from Fairfax County and Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
on the south shore of the Potomac in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
; however, the land donated by the Commonwealth of Virginia was later returned to that state by the District of Columbia retrocession in 1846.
19th century
 Influenced by a changing economy, revolutionary ideals, and preaching by ministers, numerous planters in Maryland freed their slaves in the 20 years after the Revolutionary War. Across the Upper South the free black population increased from less than 1% before the war to 14% by 1810. Abolitionists Harriet Tubman and Frederick Douglass were born slaves during this time in Dorchester County and Talbot County, respectively.
During the
Influenced by a changing economy, revolutionary ideals, and preaching by ministers, numerous planters in Maryland freed their slaves in the 20 years after the Revolutionary War. Across the Upper South the free black population increased from less than 1% before the war to 14% by 1810. Abolitionists Harriet Tubman and Frederick Douglass were born slaves during this time in Dorchester County and Talbot County, respectively.
During the War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
, the British military attempted to capture Baltimore, which was protected by Fort McHenry
Fort McHenry is a historical American Coastal defense and fortification, coastal bastion fort, pentagonal bastion fort on Locust Point, Baltimore, Locust Point, now a neighborhood of Baltimore, Maryland. It is best known for its role in the War ...
. During its bombardment, the song "The Star-Spangled Banner
"The Star-Spangled Banner" is the national anthem of the United States. The lyrics come from the "Defence of Fort M'Henry", a poem written by American lawyer Francis Scott Key on September 14, 1814, after he witnessed the bombardment of Fort ...
" was written by Francis Scott Key; it was later adopted as the national anthem.
National Road, later renamed U.S. Route 40, was authorized in 1817 as the federal highway, and ran from Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
to St. Louis. The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the oldest railroads in North America, oldest railroad in the United States and the first steam engine, steam-operated common carrier. Construction of the line began in 1828, and it operated as B&O from 1830 ...
, the first chartered railroad in the United States, opened its first section of track for regular operation in 1830 between Baltimore and Ellicott City, and in 1852 it became the first rail line to reach the Ohio River
The Ohio River () is a river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to its river mouth, mouth on the Mississippi Riv ...
from the eastern seaboard.
Civil War
The state remained in the Union during theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, due in significant part to demographics and Federal intervention. The 1860 census, held shortly before the outbreak of the civil war, showed that 49% of Maryland's African Americans were free.Peter Kolchin, ''American Slavery: 1619–1877'', New York: Hill and Wang, 1993, pp. 81–82
Governor Thomas Holliday Hicks suspended the state legislature, and to help ensure the election of a new pro-union governor and legislature, President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
had a number of its pro-slavery politicians arrested, including the Mayor of Baltimore, George William Brown George William Brown may refer to:
* George William Brown (mayor) (1812–1890), American politician, judge and academic
* George William Brown (trade unionist) (1880–?), British trade unionist and politician
* George W. Brown (computer scientist ...
; suspended several civil liberties, including ''habeas corpus''; and ordered artillery placed on Federal Hill overlooking Baltimore.
In April 1861, Federal units and state regiments were attacked as they marched through Baltimore, sparking the Baltimore riot of 1861, the first bloodshed in the Civil War. The largest and most significant battle in the state was the Battle of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam ( ), also called the Battle of Sharpsburg, particularly in the Southern United States, took place during the American Civil War on September 17, 1862, between Confederate General Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virgi ...
on September 17, 1862, near Sharpsburg. Although a tactical draw, the battle was considered a strategic Union victory and a turning point of the war.
Post-Civil War
A new state constitution in 1864 abolished slavery and Maryland was first recognized as a "Free State" in that context. Following passage of constitutional amendments that granted voting rights tofreedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, slaves were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their owners), emancipation (granted freedom as part of a larger group), or self- ...
, in 1867 the state extended suffrage to non-white males.
The Democratic Party rapidly regained power in the state from Republicans. Democrats replaced the Constitution of 1864 with the Constitution of 1867. Following the end of Reconstruction in 1877, Democrats devised means of disenfranchising blacks, initially by physical intimidation and voter fraud, later by constitutional amendments and laws. Blacks and immigrants, however, resisted Democratic Party disfranchisement efforts in the state. Maryland blacks were part of a biracial Republican coalition elected to state government in 1896–1904 and comprised 20% of the electorate.
Compared to some other states, blacks were better established both before and after the civil war. Nearly half the black population was free before the war, and some had accumulated property. Half the population lived in cities. Literacy was high among blacks and, as Democrats crafted means to exclude them, suffrage campaigns helped reach blacks and teach them how to resist. Whites did impose racial segregation
Racial segregation is the separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Segregation can involve the spatial separation of the races, and mandatory use of different institutions, ...
in public facilities and Jim Crow
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced racial segregation, " Jim Crow" being a pejorative term for an African American. The last of the ...
laws, which effectively lasted until the passage of federal civil rights legislation in the mid-1960s.
Baltimore grew significantly during the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, due in large part to its seaport and good railroad connections, attracting European immigrant labor. Many manufacturing businesses were established in the Baltimore area after the Civil War. Baltimore businessmen, including Johns Hopkins
Johns Hopkins (May 19, 1795 – December 24, 1873) was an American merchant, investor, and philanthropist. Born on a plantation, he left his home to start a career at the age of 17, and settled in Baltimore, Maryland, where he remained for mos ...
, Enoch Pratt
Enoch Pratt (September 10, 1808 – September 17, 1896) was an American businessman in Baltimore, Maryland. Pratt was also a committed active Unitarian, and a philanthropist. He is best known for his donations to establish the Enoch Pratt Free ...
, George Peabody, and Henry Walters, founded notable city institutions that bear their names, including respectively a university
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
, library system
A library is a collection of Book, books, and possibly other Document, materials and Media (communication), media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or electron ...
, music and dance conservatory, and art museum
An art museum or art gallery is a building or space for the display of art, usually from the museum's own Collection (artwork), collection. It might be in public or private ownership, be accessible to all, or have restrictions in place. Although ...
.
Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is an area of North West England which was historically a county. The county was bordered by Northumberland to the north-east, County Durham to the east, Westmorland to the south-east, Lancashire to the south, and the Scottish ...
was Maryland's second-largest city in the 19th century. Nearby supplies of natural resources along with railroads fostered its growth into a major manufacturing center.
20th century
 The
The Progressive Era
The Progressive Era (1890s–1920s) was a period in the United States characterized by multiple social and political reform efforts. Reformers during this era, known as progressivism in the United States, Progressives, sought to address iss ...
of the late 19th and early 20th centuries brought political reforms. In a series of laws passed between 1892 and 1908, reformers worked for standard state-issued ballots (rather than those distributed and marked by the parties); obtained closed voting booths to prevent party workers from "assisting" voters; initiated primary elections to keep party bosses from selecting candidates; and had candidates listed without party symbols, which discouraged the illiterate from participating. These measures worked against ill-educated whites and blacks. Blacks resisted such efforts, with suffrage groups conducting voter education.
Blacks defeated three efforts to disenfranchise them, making alliances with immigrants to resist various Democratic campaigns. Disenfranchisement bills in 1905, 1907, and 1911 were rebuffed, in large part because of black opposition. Blacks comprised 20% of the electorate and immigrants comprised 15%, and the legislature had difficulty devising requirements against blacks that did not also disadvantage immigrants.
The Progressive Era also brought reforms in working conditions for Maryland's labor force. In 1902, the state regulated conditions in mines; outlawed child labor
Child labour is the exploitation of children through any form of work that interferes with their ability to attend regular school, or is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful. Such exploitation is prohibited by legislation w ...
ers under the age of 12; mandated compulsory school attendance; and enacted the nation's first workers' compensation
Workers' compensation or workers' comp is a form of insurance providing wage replacement and medical benefits to employees injured in the course of employment in exchange for mandatory relinquishment of the employee's right to sue his or her emp ...
law. The workers' compensation law was overturned in the courts, but was redrafted and finally enacted in 1910.
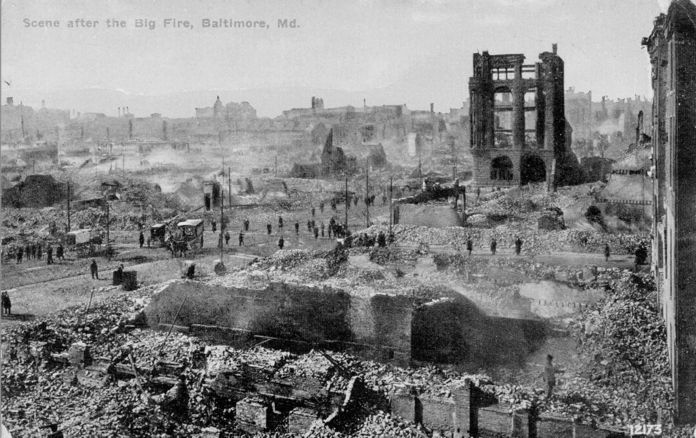
The Great Baltimore Fire
The Great Baltimore Fire raged in Baltimore, Maryland from Sunday February 7 to Monday February 8, 1904. In the fire, more than 1,500 buildings were completely leveled, and some 1,000 severely damaged, bringing property loss from the disaster to ...
of 1904 burned for more than 30 hours, destroying 1,526 buildings and spanning 70 city blocks. More than 1,231 firefighter
A firefighter (or fire fighter or fireman) is a first responder trained in specific emergency response such as firefighting, primarily to control and extinguish fires and respond to emergencies such as hazardous material incidents, medical in ...
s worked to bring the blaze under control.
With the nation's entry into World War I in 1917, new military bases such as Camp Meade, the Aberdeen Proving Ground
Aberdeen Proving Ground (APG) is a U.S. Army facility located adjacent to Aberdeen, Harford County, Maryland, United States. More than 7,500 civilians and 5,000 military personnel work at APG. There are 11 major commands among the tenant units, ...
, and the Edgewood Arsenal were established. Existing facilities, including Fort McHenry
Fort McHenry is a historical American Coastal defense and fortification, coastal bastion fort, pentagonal bastion fort on Locust Point, Baltimore, Locust Point, now a neighborhood of Baltimore, Maryland. It is best known for its role in the War ...
, were greatly expanded.
After Georgia congressman William D. Upshaw
William David Upshaw (October 15, 1866 – November 21, 1952) served eight years in Congress (1919–1927), where he was such a strong proponent of the temperance movement that he became known as the "driest of the drys." In Congress, Upshaw ...
criticized Maryland openly in 1923 for not passing Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic b ...
laws, ''Baltimore Sun'' editor Hamilton Owens coined the "Free State" nickname for Maryland in that context, which was popularized by H. L. Mencken in a series of newspaper editorials.
Maryland's urban and rural communities had different experiences during the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
. The "Bonus Army
The Bonus Army was a group of 43,000 demonstration (protest), demonstrators—17,000 veterans of United States in World War I, U.S. involvement in World War I, their families, and affiliated groups—who gathered in Washington, D.C., in mid-193 ...
" marched through the state in 1932 on its way to Washington, D.C. Maryland instituted its first income tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
in 1937 to generate revenue for schools and welfare.
Passenger and freight steamboat service, once important throughout Chesapeake Bay and its many tributary rivers, ended in 1962.
Baltimore was a major war production center during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. The biggest operations were Bethlehem Steel
The Bethlehem Steel Corporation was an American steelmaking company headquartered in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania. Until its closure in 2003, it was one of the world's largest steel-producing and shipbuilding companies. At the height of its success ...
's Fairfield Yard, which built Liberty ship
Liberty ships were a ship class, class of cargo ship built in the United States during World War II under the Emergency Shipbuilding Program. Although British in concept, the design was adopted by the United States for its simple, low-cost cons ...
s; and Glenn Martin, an aircraft manufacturer.
Maryland experienced population growth following World War II. Beginning in the 1960s, as suburban growth took hold around Washington, D.C. and Baltimore, the state began to take on a more mid-Atlantic culture as opposed to the traditionally Southern and Tidewater culture that previously dominated most of the state. Agricultural tracts gave way to residential communities, some of them carefully planned such as Columbia, St. Charles, and Montgomery Village. Concurrently the Interstate Highway System
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, or the Eisenhower Interstate System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Hi ...
was built throughout the state, most notably I-95, I-695, and the Capital Beltway
The Capital Beltway, designated as Interstate 495 (I-495) for its entire length, is an List of auxiliary Interstate Highways, auxiliary Interstate Highway in the Washington metropolitan area. The Ring road, beltway encircles Washington, D.C., ...
, altering travel patterns. In 1952, the eastern and western halves of Maryland were linked for the first time by the Chesapeake Bay Bridge, which replaced a nearby ferry
A ferry is a boat or ship that transports passengers, and occasionally vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A small passenger ferry with multiple stops, like those in Venice, Italy, is sometimes referred to as a water taxi or water bus ...
service.
Maryland's regions experienced economic changes following WWII. Heavy manufacturing declined in Baltimore. In Maryland's four westernmost counties, industrial, railroad, and coal mining jobs declined. On the lower Eastern Shore, family farms were bought up by major concerns and large-scale poultry farms and vegetable farming became prevalent. In Southern Maryland, tobacco farming nearly vanished due to suburban development and a state tobacco buy-out program in the 1990s.
In an effort to reverse depopulation due to the loss of working-class industries, Baltimore initiated urban renewal
Urban renewal (sometimes called urban regeneration in the United Kingdom and urban redevelopment in the United States) is a program of land redevelopment often used to address real or perceived urban decay. Urban renewal involves the clearing ...
projects in the 1960s with Charles Center and the Baltimore World Trade Center. Some resulted in the break-up of intact residential neighborhoods, producing social volatility, and some older residential areas around the harbor have had units renovated and have become popular with new populations.
Geography
Maryland has an area of and is comparable in overall area withBelgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
. It is the 42nd-largest and 9th-smallest state and is closest in size to the state of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
that, with its , is the next smallest state. The next largest state is Maryland's neighbor, West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
, which is nearly twice the size of Maryland with its area of .
Description


 Maryland possesses a variety of
Maryland possesses a variety of topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sci ...
within its borders, contributing to its nickname ''America in Miniature''. It ranges from sandy dunes dotted with seagrass in the east, to low marshlands teeming with wildlife and large bald cypress near the Chesapeake Bay, to gently rolling hills of oak forests in the Piedmont Region, and pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as cu ...
groves in the Maryland mountains to the west.
Maryland is bounded on its north by Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, on its north and east by Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
, on its east by the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
, and on its south and west, across the Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
, by West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
. The mid-portion of its border with Virginia is interrupted by Washington, D.C., which sits on land that was originally part of Montgomery and Prince George's counties and including Georgetown, Maryland, which was ceded to the United States federal government in 1790 to form the Washington, D.C. Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Ea ...
nearly bisects the state, and the counties east of the bay are known collectively as the Eastern Shore.
Most of the state's waterways are part of the Chesapeake Bay watershed, with the exceptions of a tiny portion of extreme western Garrett County (drained by the Youghiogheny River as part of the watershed of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
), the eastern half of Worcester County (which drains into Maryland's Atlantic coastal bays), and a small portion of the state's northeast corner (which drains into the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and is the longest free-flowing (undammed) river in the Eastern United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock, New York, the river flows for a ...
watershed). So prominent is the Chesapeake in Maryland's geography and economic life that there has been periodic agitation to change the state's official nickname to the "Bay State", a nickname that has been used by Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
for decades.
The highest point in Maryland, with an elevation of , is Hoye Crest on Backbone Mountain, in the southwest corner of Garrett County, near the border with West Virginia, and near the headwaters of the North Branch of the Potomac River. Close to the small town of Hancock, in western Maryland, about two-thirds of the way across the state, less than separates its borders, the Mason–Dixon line
The Mason–Dixon line, sometimes referred to as Mason and Dixon's Line, is a demarcation line separating four U.S. states: Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware and West Virginia. It was Surveying, surveyed between 1763 and 1767 by Charles Mason ...
to the north, and the northwards-arching Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
to the south.
Portions of Maryland are included in various official and unofficial geographic regions. For example, the Delmarva Peninsula is composed of the Eastern Shore counties of Maryland, the entire state of Delaware, and the two counties that make up the Eastern Shore of Virginia, whereas the westernmost counties of Maryland are considered part of Appalachia
Appalachia ( ) is a geographic region located in the Appalachian Mountains#Regions, central and southern sections of the Appalachian Mountains in the east of North America. In the north, its boundaries stretch from the western Catskill Mountai ...
. Much of the Baltimore–Washington corridor lies just south of the Piedmont in the Coastal Plain, though it straddles the border between the two regions.
Geology
Earthquakes in Maryland are infrequent and small due to the state's distance from seismic/earthquake zones. The M5.8 Virginia earthquake in 2011 was felt moderately throughout Maryland. Buildings in the state are not well-designed for earthquakes and can suffer damage easily. As well as this, notably a M4.8 earthquake from Tewksbury in central New Jersey was felt slightly throughout Maryland. Maryland has no natural lakes, mostly due to the lack of glacial history in the area. All lakes in the state today were constructed, mostly via dams. Buckel's Bog is believed by geologists to have been a remnant of a former natural lake. Maryland has shale formations containing natural gas, where fracking is theoretically possible.Flora
seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine (ocean), marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four Family (biology), families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and ...
and various reeds at the smaller end of the spectrum to the gigantic Wye Oak
The Wye Oak was the largest Quercus alba, white oak tree in the United States and the State Tree of Maryland from 1941 until its demise in 2002. Wye Oak State Park preserves the site where the revered tree stood for more than 400 years in the ...
, a huge example of white oak, the state tree, which can grow over tall.
Middle Atlantic coastal forests, typical of the southeastern Atlantic coastal plain
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
, grow around Chesapeake Bay and on the Delmarva Peninsula. Moving west, a mixture of Northeastern coastal forests and Southeastern mixed forests cover the central part of the state. The Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain ...
of western Maryland are home to Appalachian-Blue Ridge forests. These give way to Appalachian mixed mesophytic forests near the West Virginia border.
Many foreign species are cultivated in the state, some as ornamentals, others as novelty species. Included among these are the crape myrtle, Italian cypress, southern magnolia
''Magnolia grandiflora'', commonly known as the southern magnolia or bull bay, is a tree of the family Magnoliaceae native to the Southeastern United States, from Virginia to central Florida, and west to East Texas. Reaching in height, it is a ...
, live oak in the warmer parts of the state, and even hardy palm trees in the warmer central and eastern parts of the state. USDA plant hardiness zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely ...
s in the state range from Zones 5and6 in the extreme western part of the state to Zone7 in the central part, and Zone8 around the southern part of the coast, the bay area, and parts of metropolitan Baltimore. Invasive plant species, such as kudzu, tree of heaven
''Ailanthus altissima'' ( ), commonly known as tree of heaven or ailanthus tree, is a deciduous tree in the quassia family. It is native to northeast and central China, and Taiwan. Unlike other members of the genus ''Ailanthus'', it is found ...
, multiflora rose, and Japanese stiltgrass, stifle growth of endemic plant life. Maryland's state flower, the black-eyed susan, grows in abundance in wild flower groups throughout the state.
Fauna
 The state harbors a considerable number of
The state harbors a considerable number of white-tailed deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known Common name, commonly as the whitetail and the Virginia deer, is a medium-sized species of deer native to North America, North, Central America, Central and South America. It is the ...
, especially in the woody and mountainous west of the state, and overpopulation can become a problem. Mammals can be found ranging from the mountains in the west to the central areas and include black bears, bobcat
The bobcat (''Lynx rufus''), also known as the wildcat, bay lynx, or red lynx, is one of the four extant species within the medium-sized wild cat genus '' Lynx''. Native to North America, it ranges from southern Canada through most of the c ...
s, foxes, coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans''), also known as the American jackal, prairie wolf, or brush wolf, is a species of canis, canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the Wolf, gray wolf, and slightly smaller than the c ...
s, raccoons, and otters.
There is a population of rare wild (feral) horses found on Assateague Island
Assateague Island is a long barrier island located off the eastern coast of the Delmarva Peninsula facing the Atlantic Ocean. The northern two-thirds of the island are in Maryland, and the southern third is in Virginia. The entire island is ...
. They are believed to be descended from horses who escaped from Spanish galleon shipwrecks. Every year during the last week of July, they are captured and swim across a shallow bay for sale at Chincoteague, Virginia, a conservation technique which ensures the tiny island is not overrun by the horses. The ponies and their sale were popularized by the children's book, ''Misty of Chincoteague Misty of Chincoteague may refer to:
* Misty of Chincoteague (novel), a 1947 children's novel by Marguerite Henry
* Misty of Chincoteague (horse), a Chincoteague Pony mare, made famous by the novel See also
* Misty (film), a 1961 film based o ...
.''
The purebred Chesapeake Bay Retriever
The Chesapeake Bay Retriever is a large dog breed, breed of dog belonging to the retriever, Gun dog, gundog, and sporting Breed Groups (dog), breed groups. The breed was developed in the United States Chesapeake Bay area during the 19th century. H ...
dog was bred specifically for water sports, hunting and search and rescue in the Chesapeake area. In 1878, the Chesapeake Bay Retriever was the first individual retriever breed recognized by the American Kennel Club
The American Kennel Club (AKC) is a 501(c)(4) nonprofit breed registry, registry of purebred dog pedigree (animal), pedigrees in the United States. In addition to maintaining its pedigree registry, this kennel club also promotes and sanctions eve ...
. and was later adopted by the University of Maryland, Baltimore County
The University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC) is a Public university, public research university in Catonsville, Maryland named after Baltimore County, Maryland, Baltimore County. It had a fall 2022 enrollment of 13,991 students, 61 un ...
as their mascot.
Maryland's reptile and amphibian population includes the diamondback terrapin turtle, which was adopted as the mascot of University of Maryland, College Park
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1856, UMD i ...
, as well as the threatened Eastern box turtle. The state is part of the territory of the Baltimore oriole
The Baltimore oriole (''Icterus galbula'') is a small icterid, icterid blackbird common in eastern North America as a migratory breeding bird. It received its name from the resemblance of the male's colors to those on the Flag of Maryland, coat- ...
, which is the official state bird and mascot of the MLB
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball league composed of 30 teams, divided equally between the National League (baseball), National League (NL) and the American League (AL), with 29 in the United States and 1 in Canada. MLB i ...
team the Baltimore Orioles
The Baltimore Orioles (also known as the O's) are an American professional baseball team based in Baltimore. The Orioles compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) East Division. As one of the America ...
. Aside from the oriole, 435 other species of birds have been reported from Maryland.
The state insect is the Baltimore checkerspot butterfly, although it is not as common in Maryland as it is in the southern edge of its range.
Environment
Maryland joined with neighboring states during the end of the 20th century to improve the health of theChesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Ea ...
. The bay's aquatic life and seafood industry have been threatened by development and by fertilizer and livestock waste entering the bay.
In 2007, Forbes.com rated Maryland as the fifth "Greenest" state in the country, behind three of the Pacific States
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast and the Western Seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the contiguous U.S. states of Calif ...
and Vermont. Maryland ranks 40th in total energy consumption nationwide, and it managed less toxic waste per capita than all but six states in 2005. In April 2007, Maryland joined the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI) — a regional initiative, formed by all the Northeastern states, Washington, D.C., and three Canadian provinces, to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In March 2017, Maryland became the first state with proven gas reserves to ban fracking by passing a law against it. Vermont has such a law, but no shale gas, and New York has such a ban, though it was made by executive order.
In 2023, AES Corporation announced its intent to retire the 23-year-old Warrior Run coal plant in June 2024. It was the state's last coal-fired power plant that did not already have plans to shut down.
Climate
Maryland has a wide array of climates, due to local variances in elevation, proximity to water, and protection from colder weather due to downslope winds. The eastern half of Maryland, which includes Ocean City,Salisbury
Salisbury ( , ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and civil parish in Wiltshire, England with a population of 41,820, at the confluence of the rivers River Avon, Hampshire, Avon, River Nadder, Nadder and River Bourne, Wi ...
, Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
, and the southern and eastern suburbs of Washington, D.C., and Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
, lies on the Atlantic Coastal Plain
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
, with flat topography and sandy or muddy soil. This region has a humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
''Cfa''), with hot, humid summers and cool to cold winters; it falls under USDA Hardiness zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely ...
8a.
The Piedmont
Piedmont ( ; ; ) is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the northwest Italy, Northwest of the country. It borders the Liguria region to the south, the Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna regions to the east, and the Aosta Valley region to the ...
region, which includes northern and western greater Baltimore, Westminster
Westminster is the main settlement of the City of Westminster in Central London, Central London, England. It extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street and has many famous landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Buckingham Palace, ...
, Gaithersburg
Gaithersburg ( ) is a city in Montgomery County, Maryland, United States. At the time of the 2020 United States census, Gaithersburg had a population of 69,657, making it the third-largest incorporated city and the ninth-most populous communit ...
, Frederick, and Hagerstown, has average seasonal snowfall totals generally exceeding , and, as part of USDA Hardiness zones 7b and 7a, temperatures below are less rare. From the Cumberland Valley on westward, the climate begins to transition to a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold ...
(Köppen ''Dfa'').
In Western Maryland, the higher elevations of Allegany and Garrett counties, including the cities of Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is an area of North West England which was historically a county. The county was bordered by Northumberland to the north-east, County Durham to the east, Westmorland to the south-east, Lancashire to the south, and the Scottish ...
, Frostburg, and Oakland, display more characteristics of the humid continental zone, due in part to elevation. They fall under USDA Hardiness zones 6b and below.
Precipitation in the state is characteristic of the East Coast. Annual rainfall ranges from with more in higher elevations. Nearly every part of Maryland receives per month of rain. Average annual snowfall varies from in the coastal areas to over in the western mountains of the state.
Because of its location near the Atlantic Coast, Maryland is somewhat vulnerable to tropical cyclones
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its ...
, although the Delmarva Peninsula and the outer banks of North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
provide a large buffer, such that strikes from major hurricanes (category3 or above) occur infrequently. More often, Maryland gets the remnants of a tropical system that has already come ashore and released most of its energy. Maryland averages around 30–40 days of thunderstorms a year, and averages around six tornado strikes annually.
Cities and metro areas
 Most of the population of Maryland lives in the central region of the state, in the
Most of the population of Maryland lives in the central region of the state, in the Baltimore metropolitan area
The Baltimore–Columbia–Towson Metropolitan Statistical Area, also known as Central Maryland, is a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) in Maryland as defined by the United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB). It is part of the larger ...
and Washington metropolitan area
The Washington metropolitan area, also referred to as the National Capital Region, Greater Washington, or locally as the DMV (short for Washington, D.C., District of Columbia, Maryland, and Virginia), is the metropolitan area comprising Washing ...
, both of which are part of the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. The majority of Maryland's population is concentrated in the cities and suburbs surrounding Washington, D.C., and in and around Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
, Maryland's most populous city. Historically, these and many other Maryland cities developed along the Fall Line
A fall line (or fall zone) is the area where an upland region and a coastal plain meet and is noticeable especially the place rivers cross it, with resulting rapids or waterfalls. The uplands are relatively hard crystalline basement rock, and the ...
, the line along which rivers, brooks, and streams are interrupted by rapids and waterfalls. Maryland's capital city, Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
, is one exception to this pattern since it lies along the banks of the Severn River, close to where it empties into the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Ea ...
.
The Eastern Shore is less populous and more rural, as are the counties of western Maryland. The two westernmost counties of Maryland, Allegany and Garrett, are mountainous and sparsely populated, resembling West Virginia and Appalachia
Appalachia ( ) is a geographic region located in the Appalachian Mountains#Regions, central and southern sections of the Appalachian Mountains in the east of North America. In the north, its boundaries stretch from the western Catskill Mountai ...
more than they do the rest of the state. Both eastern and western Maryland are, however, dotted with cities of regional importance, such as Ocean City, Princess Anne
Anne, Princess Royal (Anne Elizabeth Alice Louise; born 15 August 1950) is a member of the British royal family. She is the second child and only daughter of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, and the only sister of King ...
, and Salisbury
Salisbury ( , ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and civil parish in Wiltshire, England with a population of 41,820, at the confluence of the rivers River Avon, Hampshire, Avon, River Nadder, Nadder and River Bourne, Wi ...
on the Eastern Shore and Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is an area of North West England which was historically a county. The county was bordered by Northumberland to the north-east, County Durham to the east, Westmorland to the south-east, Lancashire to the south, and the Scottish ...
, Frostburg, and Hancock in Western Maryland. Southern Maryland is still somewhat rural, but suburbanization from Washington, D.C., has encroached significantly since the 1960s; important local population centers include Lexington Park, Prince Frederick, California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, and Waldorf.
Demographics
 In the 2020 United States census, the
In the 2020 United States census, the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
found that population of Maryland was 6,185,278 people, a 7.1% increase from the 2010 United States census. The United States Census Bureau estimated that the population of Maryland was 6,045,680 on July 1, 2019, a 4.71% increase from the 2010 United States census and an increase of 2,962, from the prior year. This includes a natural increase since the last census of 269,166 (464,251 births minus 275,093 deaths) and an increase due to net migration of 116,713 people into the state. Immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as Permanent residency, permanent residents. Commuting, Commuter ...
from outside the United States resulted in a net increase of 129,730 people, and migration within the country produced a net loss of 13,017 people. In 2018, The top countries of origin for Maryland's immigrants were El Salvador
El Salvador, officially the Republic of El Salvador, is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by the Pacific Ocean. El Salvador's capital and largest city is S ...
(11%), India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
(6%), China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
(5%), Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
(5%), and the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
(4%). The center of population
In Demography, demographics, the center of population (or population center) of a region is a geographical point that describes a centerpoint of the region's population. There are several ways of defining such a "center point", leading to dif ...
of Maryland is located on the county line between Anne Arundel County and Howard County, in the unincorporated community
An unincorporated area is a parcel of land that is not governed by a local general-purpose municipal corporation. (At p. 178.) They may be governed or serviced by an encompassing unit (such as a county) or another branch of the state (such as th ...
of Jessup.
Maryland's history as a border state has led it to exhibit characteristics of both the Northern and the Southern regions of the United States. Generally, rural Western Maryland between the West Virginian Panhandle and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
has an Appalachia
Appalachia ( ) is a geographic region located in the Appalachian Mountains#Regions, central and southern sections of the Appalachian Mountains in the east of North America. In the north, its boundaries stretch from the western Catskill Mountai ...
n culture; the Southern and Eastern Shore regions of Maryland embody a Southern culture, while densely populated Central Maryland – radiating outward from Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
and Washington, D.C. – has more in common with that of the Northeast. The U.S. Census Bureau designates Maryland as one of the South Atlantic States, but it is commonly associated with the Mid-Atlantic States and Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States (also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast) is List of regions of the United States, census regions United States Census Bureau. Located on the East Coast of the United States, ...
by other federal agencies, the media, and some residents.
According to HUD's 2022 Annual Homeless Assessment Report, there were an estimated 5,349 homeless
Homelessness, also known as houselessness or being unhoused or unsheltered, is the condition of lacking stable, safe, and functional housing. It includes living on the streets, moving between temporary accommodation with family or friends, liv ...
people in Maryland.
Birth data
As of 2011, 58.0 percent of Maryland's population younger than age1 were minority background. ''Note: Births in the table do not add up because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.'' Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.Language and ancestry
As of 2016, the most spoken languages in Maryland other than English were Spanish (9%), Chinese (1.2%), West African languages (mostly Yoruba and Igbo, 1%), French (1%), Korean (0.7%),Afro-Asiatic languages
The Afroasiatic languages (also known as Afro-Asiatic, Afrasian, Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic) are a language family (or "phylum") of about 400 languages spoken predominantly in West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of th ...
(mostly Amharic
Amharic is an Ethio-Semitic language, which is a subgrouping within the Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages. It is spoken as a first language by the Amhara people, and also serves as a lingua franca for all other metropolitan populati ...
, 0.6% and Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
, 0.4%), and Tagalog (0.6%). Other languages with a large number of speakers in Maryland include Vietnamese (0.4%), Russian (0.4%), Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
(0.3%), Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
(0.3%), Persian (0.3%), Nepali (0.3%), Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole (; , ; , ), or simply Creole (), is a French-based creole languages, French-based creole language spoken by 10 to 12million people worldwide, and is one of the two official languages of Haiti (the other being French), where it ...
(0.2%), and Telugu (0.2%).
 In 1970, the U.S. Census Bureau reported Maryland's population as 17.8 percent African-American and 80.4 percent non-Hispanic White.
In 2019, non-Hispanic white Americans were 49.8% of Maryland's population (
In 1970, the U.S. Census Bureau reported Maryland's population as 17.8 percent African-American and 80.4 percent non-Hispanic White.
In 2019, non-Hispanic white Americans were 49.8% of Maryland's population (White Americans
White Americans (sometimes also called Caucasian Americans) are Americans who identify as white people. In a more official sense, the United States Census Bureau, which collects demographic data on Americans, defines "white" as " person hav ...
, including White Hispanics, were 57.3%), which made Maryland a majority minority
A majority-minority or minority-majority area is a term used to refer to a subdivision in which one or more racial, ethnic, and/or religious minorities (relative to the whole country's population) make up a majority of the local population.
Ter ...
state. 50.2% of Maryland's population is non-white, or is Hispanic or Latino, the highest percentage of any state on the East Coast, and the highest percentage after the majority-minority states of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
, Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
, California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a landlocked state in the Western United States. It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, th ...
, and Washington, D.C. By 2031, minorities are projected to become the majority of voting eligible residents of Maryland. Maryland's multiculturalism and diversity can be explained by its historically large African American population, and immigration brought by the importance of the D.C. and Baltimore areas, especially from Central America, Africa, the Caribbean, and Asia.
African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
form a sizable portion of the state's population, 31.1% as of 2020. Most are descendants of people transported to the area as slaves from West Africa. Concentrations of African Americans live in Baltimore City, Prince George's County, Charles County, western parts of Baltimore County, and the southern Eastern Shore. Charles County and Prince George's County are the two counties where African Americans are the most successful monetarily in the country, with average household incomes much higher than in the rest of the country. As a former slave state, Maryland has had a large African-American population for much of its history; African American populations have increased over time with the Great Migration to the D.C. and Baltimore areas, and in more recent times with the New Great Migration and with movement out from Washington D.C. into Montgomery, Prince George's, and Charles counties, as a result of gentrification and rising housing costs in D.C. causing many African Americans to leave. Prince George's County in particular has been a magnet for African Americans from D.C. to move to for decades; it is often referred to as "Ward 9" of D.C.
Maryland has by far the highest percentage of residents born in Africa out of any state; residents of African descent include 20th-century and later immigrants from Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, particularly of the Igbo and Yoruba tribes; Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
, particularly Amharas
Amharas (; ) are a Semitic-speaking ethnic group indigenous to Ethiopia in the Horn of Africa, traditionally inhabiting parts of the northwest Highlands of Ethiopia, particularly the Amhara Region.
According to the 2007 national census, Amh ...
with significant Oromo and Tigrayan populations; Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ...
, Ghana
Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It is situated along the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, and shares borders with Côte d’Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, and Togo to t ...
, Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone, officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered to the southeast by Liberia and by Guinea to the north. Sierra Leone's land area is . It has a tropical climate and envi ...
, and Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
. Maryland also hosts populations from other African and Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
nations. Maryland's African immigrant population is generally well-educated and is most concentrated in the inner suburbs of Baltimore and D.C. Nigerians are the fourth-largest immigrant group in Maryland, and are largely concentrated in the Baltimore area and surrounding suburbs, as well as Prince George's county. Many immigrants from the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, especially Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
, have settled in Maryland, with large communities in the suburbs of Washington, D.C., particularly in Montgomery and Prince George's counties. The Washington metropolitan area
The Washington metropolitan area, also referred to as the National Capital Region, Greater Washington, or locally as the DMV (short for Washington, D.C., District of Columbia, Maryland, and Virginia), is the metropolitan area comprising Washing ...
has the world's largest population of Ethiopians outside of Ethiopia.*Westley, BrianWashington: "Nation's Largest Ethiopian Community Carves Niche"
( ). ''
USA Today
''USA Today'' (often stylized in all caps) is an American daily middle-market newspaper and news broadcasting company. Founded by Al Neuharth in 1980 and launched on September 14, 1982, the newspaper operates from Gannett's corporate headq ...
''. Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American not-for-profit organization, not-for-profit news agency headquartered in New York City.
Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association, and produces news reports that are dist ...
. October 17, 2005."Washington: Nation's Largest Ethiopian Community Carves Niche"
. '' The Southeast Missourian''. ''Associated Press''. October 23, 2005. p. 7C. Retrieved August 25, 2018. The Ethiopian community of Greater D.C. was historically based in the Adams Morgan and Shaw neighborhoods of Washington, D.C., but as the community has grown, many Ethiopians have settled in Silver Spring. The Ethiopian American population in Maryland and the rest of the D.C. area is largely
Amharic
Amharic is an Ethio-Semitic language, which is a subgrouping within the Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages. It is spoken as a first language by the Amhara people, and also serves as a lingua franca for all other metropolitan populati ...
-speaking, but there are significant numbers of speakers of Oromo and Tigrinya speakers as well. The Washington metropolitan area is also home to a large Eritrean community.
The top reported ancestries by Maryland residents are: German (15%), Irish (11%), English (8%), American (7%), Italian (6%), and Polish (3%).
Irish American
Irish Americans () are Irish ethnics who live within in the United States, whether immigrants from Ireland or Americans with full or partial Irish ancestry.
Irish immigration to the United States
From the 17th century to the mid-19th c ...
populations can be found throughout the Baltimore area, and the Northern and Eastern suburbs of Washington, D.C., in Maryland, who were descendants of those who moved out to the suburbs of Washington, D.C.'s once predominantly Irish neighborhoods), as well as Western Maryland, where Irish immigrant laborers helped to build the B&O Railroad. Smaller but much older Irish populations can be found in Southern Maryland, with some roots dating as far back as the early Maryland colony. This population, however, still remains culturally very active and yearly festivals are held.
More recent European immigrants of the late 19th and early 20th century settled first in Baltimore, attracted to its industrial jobs. These groups were largely of Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
, Italian, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
, Polish, Czech, Lithuanian, Russian and Ukrainian descent. The Greek community includes a number of Greek Jews.
The shares of European immigrants born in Eastern Europe increased significantly between 1990 and 2010. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Yugoslavia, and Czechoslovakia, many immigrants from Eastern Europe came to the United States—12 percent of whom currently reside in Maryland.
Hispanic immigrants of the later 20th century have settled in Aspen Hill, Hyattsville/ Langley Park, Glenmont/ Wheaton, Bladensburg, Riverdale Park, Gaithersburg
Gaithersburg ( ) is a city in Montgomery County, Maryland, United States. At the time of the 2020 United States census, Gaithersburg had a population of 69,657, making it the third-largest incorporated city and the ninth-most populous communit ...
, as well as Highlandtown and Greektown in East Baltimore. Maryland has the highest percentage of residents of Central America
Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually ...
n origin of any state. Salvadorans
Salvadorans (), also known as Salvadorians, are citizens of El Salvador, a country in Central America. Most Salvadorans live in El Salvador, although there is also a significant Salvadoran diaspora, particularly in the United States, with smalle ...
are the largest Hispanic group in Maryland, and Maryland has the largest percentage of Salvadoran residents of any state. The D.C. area also has the highest percentage of Salvadorans of any American metro area, who are particularly concentrated in Prince George's and Montgomery counties, and has the second-highest total number of Salvadorans after the Los Angeles area. Other Hispanic groups with significant populations in the state include Mexicans
Mexicans () are the citizens and nationals of the Mexico, United Mexican States. The Mexican people have varied origins with the most spoken language being Spanish language, Spanish, but many also speak languages from 68 different Languages o ...
, Guatemalans
Guatemalans ( or less commonly ) are people connected to the country of Guatemala. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Guatemalans, several (if not all) of these connections exist.
Guatemala is a multicultu ...
, Hondurans
Hondurans (; also called catrachos) are the citizens of Honduras. Most Hondurans live in Honduras, although there is also a significant Honduran diaspora, particularly in the United States, Spain, and many smaller communities in other countries ...
, Dominicans
Dominicans () also known as Quisqueyans () are an ethnic group, ethno-nationality, national people, a people of shared ancestry and culture, who have ancestral roots in the Dominican Republic.
The Dominican ethnic group was born out of a fusio ...
, Peruvians, and Puerto Ricans
Puerto Ricans (), most commonly known as Puerto Rico#Etymology, Boricuas, but also occasionally referred to as '':es:Anexo:Gentilicios de Puerto Rico#Lista general, Borinqueños'', '':es:Anexo:Gentilicios de Puerto Rico#Lista general, Borincan ...
, along with growing populations of Brazilians
Brazilians (, ) are the citizens of Brazil. A Brazilian can also be a person born abroad to a Brazilian parent or legal guardian as well as a person who acquired Brazilian nationality law, Brazilian citizenship. Brazil is a multiethnic society, ...
, Colombians
Colombians () are people identified with the country of Colombia. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Colombians, several (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their bein ...
, Ecuadorians
Ecuadorians () are people identified with the South American country of Ecuador. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Ecuadorians, several (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source o ...
, and Bolivians. Maryland's Hispanic population is especially concentrated in Montgomery County and Prince George's County, with other large populations in the Baltimore area and Frederick County. Maryland has one of the most diverse Hispanic populations in the country, with significant populations from various Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
and Central America
Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually ...
n nations.
Caribbean Americans have a significant presence in Maryland, especially Jamaican Americans, who make up 0.6% of the population and have had a significant presence and influence in Maryland's politics and culture; Maryland's current governor, Wes Moore, is the son of a Jamaican immigrant mother. Other Caribbean American nationalities with a large population in Maryland include Dominicans
Dominicans () also known as Quisqueyans () are an ethnic group, ethno-nationality, national people, a people of shared ancestry and culture, who have ancestral roots in the Dominican Republic.
The Dominican ethnic group was born out of a fusio ...
, Haitians, Trinidadians and Tobagonians
Trinidadians and Tobagonians, colloquially known as Trinis or Trinbagonians, are the people who are identified with the country of Trinidad and Tobago. The population of Trinidad is notably diverse, with approximately 35% Indo–Trinidadians an ...
, and Guyanese. Caribbean Americans are most concentrated in Prince George's County, the city of Baltimore, and Baltimore County.
Asian Americans are concentrated in the suburban counties surrounding Washington, D.C., and in Baltimore suburbs, especially Howard County, with Chinese American
Chinese Americans are Americans of Chinese ancestry. Chinese Americans constitute a subgroup of East Asian Americans which also constitute a subgroup of Asian Americans. Many Chinese Americans have ancestors from mainland China, Hong Kong ...
, Korean American
Korean Americans () are Americans of full or partial Korean ethnic descent. While the broader term Overseas Korean in America () may refer to all ethnic Koreans residing in the United States, the specific designation of Korean American impli ...
and Taiwanese American
Taiwanese Americans (traditional Chinese, Chinese: 臺灣裔美國人; pinyin: ''Táiwān yì měiguó rén''; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: ''Tâi-Bí-jîn'') are Americans of Taiwanese people, Taiwanese ancestry, including American-born descendants of migrant ...
communities in Rockville, Gaithersburg
Gaithersburg ( ) is a city in Montgomery County, Maryland, United States. At the time of the 2020 United States census, Gaithersburg had a population of 69,657, making it the third-largest incorporated city and the ninth-most populous communit ...
, and Germantown. Chinese in particular form the second largest group of Asian Americans, and are the largest group in Montgomery County. Maryland also has a large Korean American population, especially in Howard County, where there is a Koreatown in Ellicott City. Filipino American
Filipino Americans () are Americans of Filipino ancestry. Filipinos in North America were first documented in the 16th century and other small settlements beginning in the 18th century. Mass migration did not begin until after the end of the Sp ...
s, the largest group of Southeast Asians, form major communities in Montgomery, Prince George's, and Charles counties; other large groups of Southeast Asians include Vietnamese, who are concentrated in Montgomery County, and Burmese, who are concentrated in Frederick, Howard, and Baltimore Counties. Maryland has a very large and diverse South Asian American population that has had a major presence in the state since the 1970s. Indian Americans are the largest Asian group in Maryland, making up 1.7 percent of the population, and live throughout the state, especially in Montgomery and Howard
Howard is a masculine given name derived from the English surname Howard. ''The Oxford Dictionary of English Christian Names'' notes that "the use of this surname as a christian name is quite recent and there seems to be no particular reason for ...
counties, with large numbers in Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
, Frederick, and Prince George's counties. The Indian American population is culturally and linguistically diverse, with the Indian languages spoken most being Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
, Gujarati, Telugu, and Tamil. There are also large Pakistani American populations throughout the D.C. and Baltimore areas, especially in Baltimore County and Howard County, and a large Bangladeshi American community in the D.C. area. Maryland has one of the largest populations of Nepali Americans, including Bhutanese Americans
Bhutanese Americans are Americans of Bhutanese descent.
According to the 2010 census there are 19,439 Americans of Bhutanese descent. However, many Lhotshampa, Nepali-Bhutanese came to the U.S. via Nepal as Bhutanese refugees, political refugees ...
of Nepali descent, in the U.S., many of whom are recent immigrants or refugees who sought asylum after expulsion from Bhutan or the 2015 Nepal earthquake; there are an estimated 20,000 to 25,000 Nepalis in Maryland, concentrated in the Baltimore area with significant populations in the D.C. area. The first Nepali American elected to a state legislature, Harry Bhandari, was elected in Maryland, representing part of Baltimore County. There are three state-recognized tribes, and in 2020, 31,845 identified as being Native American alone, and 96,805 did in combination with one or more other races.
Attracting educated Asians and Africans to the professional jobs in the region, Maryland has the fifth-largest proportions of racial minorities in the country.
In 2006, 645,744 were counted as foreign born, which represents mainly people from Latin America and Asia. About four percent are undocumented immigrants.
According to The Williams Institute's analysis of the 2010 U.S. census, 12,538 same-sex couples are living in Maryland, representing 5.8 same-sex couples per 1,000 households.
Romani people
{{Infobox ethnic group
, group = Romani people
, image =
, image_caption =
, flag = Roma flag.svg
, flag_caption = Romani flag created in 1933 and accepted at the 1971 World Romani Congress
, po ...
are present in Maryland.
Religion
 Maryland has been historically prominent to American Catholic tradition because the English colony of Maryland was intended by
Maryland has been historically prominent to American Catholic tradition because the English colony of Maryland was intended by George Calvert
George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore (; 1580 – 15 April 1632) was an English politician. He achieved domestic political success as a member of parliament and later Secretary of State (England), Secretary of State under James VI and I, King Ja ...
as a haven for English Catholics. Baltimore was the seat of the first Catholic bishop in the U.S. (1789), and Emmitsburg was the home and burial place of the first American-born citizen to be canonized
Canonization is the declaration of a deceased person as an officially recognized saint, specifically, the official act of a Christian communion declaring a person worthy of public veneration and entering their name in the canon catalogue of sa ...
, St. Elizabeth Ann Seton. Georgetown University
Georgetown University is a private university, private Jesuit research university in Washington, D.C., United States. Founded by Bishop John Carroll (archbishop of Baltimore), John Carroll in 1789, it is the oldest Catholic higher education, Ca ...
, the first Catholic University, was founded in 1789 in what was then part of Maryland; it became a part of the District of Columbia when it was created in the 1790s. The Basilica of the National Shrine of the Assumption of the Virgin Mary
The Basilica of the National Shrine of the Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary, also called the Baltimore Basilica, is a Catholic Church, Catholic cathedral in Baltimore, Baltimore, Maryland. It was the first Catholic cathedral built in the ...
in Baltimore was the first Roman Catholic cathedral built in the United States, and the Archbishop of Baltimore is, albeit without formal primacy, the United States' quasi-primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
, and often a cardinal. Among the immigrants of the 19th and 20th centuries from eastern and southern Europe were many Catholics.
Despite its historic relevance to the Catholic Church in the United States, the percentage of Catholics in the state of Maryland is below the national average of 20%. Demographically, both Protestants and those identifying with no religion are more numerous than Catholics.
According to the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
in 2014, 69 percent of Maryland's population identifies themselves as Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
. Nearly 52% of the adult population are Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
. Following Protestantism, Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
is the second largest religious affiliation, comprising 15% percent of the population. Amish
The Amish (, also or ; ; ), formally the Old Order Amish, are a group of traditionalist Anabaptism, Anabaptist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, church fellowships with Swiss people, Swiss and Alsace, Alsatian origins. As they ...
/Mennonite
Mennonites are a group of Anabaptism, Anabaptist Christianity, Christian communities tracing their roots to the epoch of the Radical Reformation. The name ''Mennonites'' is derived from the cleric Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland, part of ...
communities are found in St. Mary's, Garrett, and Cecil counties. Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
is the largest non-Christian religion in Maryland, with 241,000 adherents, or four percent of the total population. Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
are numerous throughout Montgomery County and in Pikesville and Owings Mills
Owings Mills is an unincorporated community and census-designated place in Baltimore County, Maryland, United States. It is a suburb of Baltimore. Per the 2020 census, the population was 35,674. Owings Mills is home to the northern terminus o ...
northwest of Baltimore. An estimated 81,500 Jewish Americans live in Montgomery County, constituting approximately 10% of the total population. The Seventh-day Adventist Church
The Seventh-day Adventist Church (SDA) is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sa ...
's world headquarters and Ahmadiyya
Ahmadiyya, officially the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at (AMJ), is an Islamic messianic movement originating in British India in the late 19th century. It was founded by Mirza Ghulam Ahmad (1835–1908), who said he had been divinely appointed a ...
Muslims' national headquarters are located in Silver Spring, just outside Washington, D.C.
Per the Public Religion Research Institute in 2020, 61 percent of Maryland's population identified with Christianity. Protestantism and Roman Catholicism continued to dominate the Christian landscape, and the Jewish community remained at 3% of the total religious population. Of the unaffiliated, the PRRI study determined their increase to 28% of the population.
LGBT population
Maryland has one of the highest percentages of LGBT people in its populace out of any state; 5.7% of Marylanders identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, or queer, the highest of any state. (Washington, D.C. ranks higher with a LGBT population of 8.6%.) Maryland ranks as one of the best states in the nation for rights of the LGBT community, with protections against discrimination enacted since 2001 for sexuality and 2014 for gender, same-sex marriage legalization in 2013, bans on conversion therapy enacted in 2018, abolition of the gay panic defense in 2021, and issuance in 2023 of an executive order protecting the rights of transgender individuals. In 2020, Montgomery County unanimously passed an ordinance implementing an LGBTIQ+ bill of rights. The first person known to describe himself as adrag queen
A drag queen is a person, usually male, who uses Drag (entertainment), drag clothing and makeup to imitate and often exaggerate Femininity, female gender signifiers and gender roles for entertainment purposes. Historically, drag queens have ...
was William Dorsey Swann, born enslaved in Hancock, Maryland. Swann was the first American on record who pursued legal and political action to defend the LGBTQ community
The LGBTQ community (also known as the LGBT, LGBT+, LGBTQ+, LGBTQIA, LGBTQIA+, or queer community) comprises LGBTQ individuals united by a common culture and social movements. These communities generally celebrate pride, diversity, individu ...
's right to assemble.
In February 2010, Attorney General Doug Gansler issued an opinion stating that Maryland law should honor same-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same legal Legal sex and gender, sex. marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 38 countries, with a total population of 1.5 ...
s from out of state. At the time, the state Supreme Court wrote a decision upholding marriage discrimination.
On March 1, 2012, Maryland Governor Martin O'Malley signed the freedom to marry bill into law after it passed in the state legislature. Opponents of same-sex marriage began collecting signatures to overturn the law, which faced a referendum, as Question 6, in the November 2012 election. A January 2011 Gonzales Research & Marketing Strategies poll showed 51% support for marriage in the state.
In May 2012, Maryland's Court of Appeals ruled that the state will recognize marriages of same-sex couples who married out-of-state, no matter the outcome of the November election. Voters upheld the bill, passing Question 6 with 52% to 48% on November 6, 2012. Same-sex couples began marrying in Maryland on January 1, 2013.
Economy
 The
The Bureau of Economic Analysis
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) of the United States Department of Commerce is a U.S. government agency that provides official macroeconomic and industry statistics, most notably reports about the gross domestic product (GDP) of the United ...
estimates that Maryland's gross state product in 2016 was $382.4billion. However, Maryland has been using Genuine Progress Indicator, an indicator of well-being, to guide the state's development, rather than relying only on growth indicators like GDP. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, Maryland households are currently the wealthiest in the country, with a 2013 median household income of $72,483, which puts it ahead of New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
and Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
, which are second and third respectively. Two of Maryland's counties, Howard and Montgomery, are the second and eleventh wealthiest counties in the nation respectively. Maryland has the most millionaires per capita in 2013, with a ratio of 7.7 percent. Also, the state's poverty rate of 7.8 percent is the lowest in the country. Per capita personal income in 2006 was $43,500, fifth in the nation. As of March 2022, the state's unemployment rate was 4.6 percent.
Maryland's economy benefits from the state's proximity to the federal government in Washington, D.C., with an emphasis on technical and administrative tasks for the defense/aerospace industry and bio-research laboratories, as well as staffing of satellite government headquarters in the suburban or exurban Baltimore/Washington area. Ft. Meade serves as the headquarters of the Defense Information Systems Agency, United States Cyber Command
United States Cyber Command (USCYBERCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands of the United States Department of Defense (DoD). It unifies the direction of cyberspace operations, strengthens DoD cyberspace capabilities, and integra ...
, and the National Security Agency
The National Security Agency (NSA) is an intelligence agency of the United States Department of Defense, under the authority of the director of national intelligence (DNI). The NSA is responsible for global monitoring, collection, and proces ...
/ Central Security Service. In addition, a number of educational and medical research institutions are located in the state. The various components of The Johns Hopkins University
The Johns Hopkins University (often abbreviated as Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1876 based on the European research institution model, J ...
and its medical research facilities are now the largest single employer in the Baltimore area.
Manufacturing, while large in dollar value, is highly diversified with no sub-sector contributing over 20 percent of the total. Typical forms of manufacturing include electronics, computer equipment, and chemicals. The once-mighty primary metals sub-sector, which once included what was then the largest steel factory in the world at Sparrows Point, still exists, but is pressed with foreign competition, bankruptcies
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the deb ...
, and merger
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are business transactions in which the ownership of a company, business organization, or one of their operating units is transferred to or consolidated with another entity. They may happen through direct absorpt ...
s. During World War II, the Glenn Martin Company (now part of Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American Arms industry, defense and aerospace manufacturer with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta on March 15, 1995. It is headquartered in North ...
) airplane factory employed some 40,000 people.
Mining other than construction materials is virtually limited to coal, which is located in the mountainous western part of the state. The brownstone quarries in the east, which gave Baltimore and Washington much of their characteristic architecture in the mid-19th century, were once a predominant natural resource. Historically, there used to be small gold-mining operations in Maryland, some near Washington, but these no longer exist.
In 2022, the top private employers by number of employees were BYK Gardner, Clean Harbors, Holy Cross Hospital, Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center, Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Maryland Neuroimaging Center, Northrop Grumman
Northrop Grumman Corporation is an American multinational Aerospace manufacturer, aerospace and Arms industry, defense company. With 97,000 employees and an annual revenue in excess of $40 billion, it is one of the world's largest Arms industry ...
, University of Maryland
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1856, UMD is the flagship institution of the Univ ...
, and University of Maryland Medical Center.
Port of Baltimore
One major service activity is transportation, centered on thePort of Baltimore
The Helen Delich Bentley Port of Baltimore is a Port, shipping port along the tidal basins of the three branches of the Patapsco River in Baltimore, Baltimore, Maryland, on the upper northwest shore of the Chesapeake Bay. It is the nation's la ...
and its related rail and trucking access. The port ranked 17th in the U.S. by tonnage in 2008. Although the port handles a wide variety of products, the most typical imports are raw materials and bulk commodities, such as iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the f ...
, petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring un ...
, sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecul ...
, and fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Man ...
s, often distributed to the relatively close manufacturing centers of the inland Midwest
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It ...
via good overland transportation. The port also receives several brands of imported motor vehicles and is the number one auto port in the U.S.
Baltimore City is among the top 15 largest ports in the nation, and was one of six major U.S. ports that were part of the February 2006 controversy
Controversy (, ) is a state of prolonged public dispute or debate, usually concerning a matter of conflicting opinion or point of view. The word was coined from the Latin '' controversia'', as a composite of ''controversus'' – "turned in an op ...
over the Dubai Ports World
DP World is a multinational corporation, multinational logistics company based in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. It specialises in cargo logistics, port terminal operations, maritime services and free trade zones. Formed in 2005 by the merger of D ...
deal. The state as a whole is heavily industrialized, with a prosperous economy and influential technology centers. Its computer industries are some of the most sophisticated in the United States, and the federal government has invested heavily in the area. Maryland is home to several large military bases and scores of high-level government jobs.
The Chesapeake and Delaware Canal
The Chesapeake & Delaware Canal (C&D Canal) is a -long, -wide and -deep ship canal that connects the Delaware River with the Chesapeake Bay in the states of Delaware and Maryland in the United States.
In the mid-17th century, mapmaker Augus ...
is a canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface ...
on the Eastern Shore that connects the waters of the Delaware River with those of the Chesapeake Bay, and in particular with the Port of Baltimore, carrying 40 percent of the port's ship traffic.
Fishing
Maryland has a large food-production sector. A large component of this is commercialfishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
, centered in the Chesapeake Bay, but also including activity off the short Atlantic seacoast. The largest catches by species are the blue crab, oysters
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of Seawater, salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in Marine (ocean), marine or Brackish water, brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly Calcification, calcified, a ...
, striped bass
The striped bass (''Morone saxatilis''), also called the Atlantic striped bass, striper, linesider, rock, or rockfish, is an anadromous perciform fish of the family Moronidae found primarily along the Atlantic coast of North America. It has ...
, and menhaden
Menhaden, also known as mossbunker, bunker, and "the most important fish in the sea", are forage fish of the genera ''Brevoortia'' and ''Ethmidium'', two genera of marine fish in the order Clupeiformes. ''Menhaden'' is a blend of ''poghaden'' ...
. The Bay also has overwintering waterfowl in its wildlife refuges. The waterfowl support a tourism sector of sportsmen.
Agriculture
 Maryland has large areas of fertile agricultural land in its coastal and
Maryland has large areas of fertile agricultural land in its coastal and Piedmont
Piedmont ( ; ; ) is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the northwest Italy, Northwest of the country. It borders the Liguria region to the south, the Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna regions to the east, and the Aosta Valley region to the ...
zones, though this land use is being encroached upon by urbanization. Agriculture is oriented to dairy farming (especially in foothill and piedmont areas) for nearby large city milksheads, plus specialty perishable horticulture crops, such as cucumber
The cucumber (''Cucumis sativus'') is a widely-cultivated creeping vine plant in the family Cucurbitaceae that bears cylindrical to spherical fruits, which are used as culinary vegetables.watermelon
The watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Cucurbitaceae, that has a large, edible fruit. It is a Glossary of botanical terms#scandent, scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, and is plant breeding ...
s, sweet corn
Sweet corn (''Zea mays'' convar. ''saccharata'' var. ''rugosa''), also called sweetcorn, sugar corn and pole corn, is a variety of maize grown for human consumption with a high sugar content. Sweet corn is the result of a naturally occurring rec ...
, tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
es, melons, squash, and peas
Pea (''pisum'' in Latin) is a pulse or fodder crop, but the word often refers to the seed or sometimes the pod of this flowering plant species. Peas are eaten as a vegetable. Carl Linnaeus gave the species the scientific name ''Pisum sativum ...
(Source:USDA Crop Profiles). The southern counties of the western shoreline of Chesapeake Bay are warm enough to support a tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
cash crop
A cash crop, also called profit crop, is an Agriculture, agricultural crop which is grown to sell for profit. It is typically purchased by parties separate from a farm. The term is used to differentiate a marketed crop from a staple crop ("subsi ...
zone, which has existed since early Colonial times, but declined greatly after a state government buy-out in the 1990s. There is also a large automated chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated subspecies of the red junglefowl (''Gallus gallus''), originally native to Southeast Asia. It was first domesticated around 8,000 years ago and is now one of the most common and w ...
-farming sector in the state's southeastern part; Salisbury
Salisbury ( , ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and civil parish in Wiltshire, England with a population of 41,820, at the confluence of the rivers River Avon, Hampshire, Avon, River Nadder, Nadder and River Bourne, Wi ...
is home to Perdue Farms. Maryland's food-processing plants are the most significant type of manufacturing by value in the state. Farming suffers from weeds as anywhere else, including an unusual multiply resistant ragweed ('' Ambrosia artemisiifolia'') found by Rousonelos ''et al.'', 2012 with both ALS- and PPO-resistances and which by 2016 had developed a third, EPSP resistance. This ragweed population is a drag on soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed.
Soy is a key source o ...
cultivation and, , is the worst multiresistant weed problem in the state.
Biotechnology
Maryland is a major center forlife sciences
This list of life sciences comprises the branches of science that involve the scientific study of life – such as microorganisms, plants, and animals including human beings. This science is one of the two major branches of natural science, ...
research and development. With more than 400 biotechnology companies located there, Maryland is the fourth largest nexus in this field in the United States.
Institutions and government agencies with an interest in research and development located in Maryland include the Johns Hopkins University
The Johns Hopkins University (often abbreviated as Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1876 based on the European research institution model, J ...
, the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, more than one campus of the University System of Maryland, Goddard Space Flight Center, the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
, the National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in 1887 and is part of the United States Department of Health and Human Service ...
, the National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into Outline of p ...
, the National Institute of Mental Health
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) is one of 27 institutes and centers that make up the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The NIH, in turn, is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services and is the primar ...
, the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, the federal Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute
The Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) is an American non-profit medical research organization headquartered in Chevy Chase, Maryland with additional facilities in Ashburn, Virginia. It was founded in 1953 by Howard Hughes, an American busin ...
, the Celera Genomics company, the J. Craig Venter Institute, and AstraZeneca
AstraZeneca plc () (AZ) is a British-Swedish multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with its headquarters at the Cambridge Biomedical Campus in Cambridge, UK. It has a portfolio of products for major diseases in areas includi ...
(formerly MedImmune
MedImmune, LLC was a wholly owned subsidiary of AstraZeneca before February 14, 2019, when it was announced that the MedImmune name and branding would be discontinued in favor of AstraZeneca.
MedImmune was founded in 1988 as Molecular Vaccines, ...
).
Maryland is home to defense contractor Emergent BioSolutions, which manufactures and provides an anthrax vaccine to U.S. government military personnel.
Tourism
 Tourism is popular in Maryland. Many tourists visit Baltimore, the beaches of the Eastern Shore, and the nature of western Maryland. Attractions in Baltimore include the Harborplace, the Baltimore Aquarium,
Tourism is popular in Maryland. Many tourists visit Baltimore, the beaches of the Eastern Shore, and the nature of western Maryland. Attractions in Baltimore include the Harborplace, the Baltimore Aquarium, Fort McHenry
Fort McHenry is a historical American Coastal defense and fortification, coastal bastion fort, pentagonal bastion fort on Locust Point, Baltimore, Locust Point, now a neighborhood of Baltimore, Maryland. It is best known for its role in the War ...
, as well as the Camden Yards
Oriole Park at Camden Yards, commonly known as Camden Yards, is a ballpark in Baltimore, Maryland. It is the home of Major League Baseball (MLB)'s Baltimore Orioles, and the first of the Baseball park#Retro-classic ballparks, "retro" major le ...
baseball stadium. Ocean City on the Atlantic Coast has been a popular beach destination in summer, particularly since the Chesapeake Bay Bridge was built in 1952 connecting the Eastern Shore to the more populated Maryland cities. The state capital of Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
offers sites such as the state capitol building, the historic district
A historic district or heritage district is a section of a city which contains historic building, older buildings considered valuable for historical or architectural reasons. In some countries or jurisdictions, historic districts receive legal p ...
, and the waterfront. Maryland also has several sites of interest to military history, given Maryland's role in the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
and in the War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
. Other attractions include the historic and picturesque towns along the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Ea ...
, such as Saint Mary's, Maryland's first colonial settlement and original capital.
Healthcare
As of 2017, the top two health insurers including all types of insurance were CareFirst BlueCross BlueShield with 47% market share followed byUnitedHealth Group
UnitedHealth Group Incorporated is an American Multinational corporation, multinational for-profit company specializing in health insurance and health care services based in Eden Prairie, Minnesota. Selling insurance products under UnitedHealth ...
at 15%.
Maryland has experimented with healthcare payment reforms, notably beginning in the 1970s with an all-payer rate setting All-payer rate setting is a price setting mechanism in which all third parties pay the same price for services at a given hospital. It can be used to increase the market power of payers (such as private and/or public insurance companies) versus prov ...
program regulated by the Health Services Cost Review Commission. In 2014, it switched to a global budget revenue system, whereby hospitals receive a capitated payment to care for their population.
Transportation
TheMaryland Department of Transportation
The Maryland Department of Transportation (MDOT) is an organization comprising five business units and one Authority:
* Maryland Transportation Authority (Transportation Secretary serves as chairman of the Maryland Transportation Authority)
** ...
oversees most transportation in the state through its various administration-level agencies. The independent Maryland Transportation Authority
The Maryland Transportation Authority (MDTA) is an independent state agency responsible for financing, constructing, operating, and maintaining eight transportation facilities, currently consisting of two toll roads, two tunnels, and four bridg ...
maintains and operates the state's eight toll facilities.
Roads
 Maryland's Interstate highways include of I-95, which enters the northeast portion of the state, travels through
Maryland's Interstate highways include of I-95, which enters the northeast portion of the state, travels through Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
, and becomes part of the eastern section of the Capital Beltway
The Capital Beltway, designated as Interstate 495 (I-495) for its entire length, is an List of auxiliary Interstate Highways, auxiliary Interstate Highway in the Washington metropolitan area. The Ring road, beltway encircles Washington, D.C., ...
to the Woodrow Wilson Bridge. I-68 travels , connecting the western portions of the state to I-70 in the small town of Hancock. I-70 enters from Pennsylvania north of Hancock and continues east for to Baltimore, connecting Hagerstown and Frederick along the way.
I-83 has in Maryland and connects Baltimore to southern central Pennsylvania (Harrisburg
Harrisburg ( ; ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), U.S. commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat, seat of Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, Dauphin County. With a population of 50, ...
and York, Pennsylvania
York is a city in York County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. Located in South Central Pennsylvania, the city's population was 44,800 at the time of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, making it the List of cities in ...
). Maryland also has an portion of I-81 that travels through the state near Hagerstown. I-97, fully contained within Anne Arundel County and the shortest () one- or two-digit interstate highway in the contiguous US, connects the Baltimore area to the Annapolis area.
There are also several auxiliary Interstate highways in Maryland. Among them are two beltways encircling the major cities of the region: I-695, the McKeldin (Baltimore) Beltway, which encircles Baltimore; and a portion of I-495, the Capital Beltway, which encircles Washington, D.C. I-270, which connects the Frederick area with Northern Virginia
Northern Virginia, locally referred to as NOVA or NoVA, comprises several County (United States), counties and independent city (United States), independent cities in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. ...
and Washington, D.C. through major suburbs to the northwest of Washington, is a major commuter route and is as wide as fourteen lanes at points. I-895, also known as the Baltimore Harbor Tunnel Thruway, provides an alternate route to I-95 across Baltimore Harbor.
Both I-270 and the Capital Beltway were extremely congested; however, the Intercounty Connector has alleviated some congestion over time. Construction of the ICC was a major part of the campaign platform of former Governor Robert Ehrlich, who was in office from 2003 until 2007, and of Governor Martin O'Malley, who succeeded him. I-595, which is an unsigned highway
An unsigned highway is a highway that has been assigned a route number, but does not bear road markings that would conventionally be used to identify the route with that number. Highways are left unsigned for a variety of reasons, and example ...
concurrent with US50/ US301, is the longest unsigned interstate in the country and connects Prince George's County and Washington, D.C. with Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
and the Eastern Shore via the Chesapeake Bay Bridge.
Maryland also has a state highway
A state highway, state road, or state route (and the equivalent provincial highway, provincial road, or provincial route) is usually a road that is either Route number, numbered or maintained by a sub-national state or province. A road numbered ...
system that contains routes numbered from 2through 999, however most of the higher-numbered routes are either unsigned or are relatively short. Major state highways include Routes 2 (Governor Ritchie Highway/Solomons Island Road/Southern Maryland Blvd.), 4 (Pennsylvania Avenue
Pennsylvania Avenue is a primarily diagonal street in Washington, D.C. that connects the United States Capitol with the White House and then crosses northwest Washington, D.C. to Georgetown (Washington, D.C.), Georgetown. Traveling through So ...
/Southern Maryland Blvd./Patuxent Beach Road/St. Andrew's Church Road), 5 (Branch Avenue/Leonardtown Road/Point Lookout Road), 32, 45 (York Road), 97 (Georgia Avenue), 100 (Paul T. Pitcher Memorial Highway), 210 (Indian Head Highway), 235 (Three Notch Road), 295 (Baltimore-Washington Parkway), 355 (Wisconsin Avenue/Rockville Pike/Frederick Road), 404 (Queen Anne Highway/ Shore Highway), and 650 (New Hampshire Avenue).
Airports
Maryland's largest airport is Baltimore-Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, more commonly referred to as BWI. The airport is named for the Baltimore-bornThurgood Marshall
Thoroughgood "Thurgood" Marshall (July 2, 1908 – January 24, 1993) was an American civil rights lawyer and jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1967 until 1991. He was the Supreme C ...
, the first African-American Supreme Court justice. The only other airports with commercial service are at Hagerstown and Salisbury
Salisbury ( , ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and civil parish in Wiltshire, England with a population of 41,820, at the confluence of the rivers River Avon, Hampshire, Avon, River Nadder, Nadder and River Bourne, Wi ...
.
The Maryland suburbs of Washington, D.C. are also served by the other two airports in the region, Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport
Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport is a public airport in Arlington County, Virginia, United States, from Washington, D.C. The closest airport to the nation's capital, it is one of two airports owned by the federal government and ope ...
and Dulles International Airport
Washington Dulles International Airport ( ) – commonly known by its former name of Dulles International Airport, by its airport code of IAD, or simply as Dulles Airport – is an international airport in the Eastern United States, located w ...
, both in Northern Virginia
Northern Virginia, locally referred to as NOVA or NoVA, comprises several County (United States), counties and independent city (United States), independent cities in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. ...
. The College Park Airport is the nation's oldest, founded in 1909, and is still used. Wilbur Wright trained military aviators at this location.
Rail

Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak (; ), is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates intercity rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
trains, including the high-speed Acela Express
The ''Acela'' ( ; originally the ''Acela Express'' until September 2019) is Amtrak's flagship passenger train service along the Northeast Corridor (NEC) in the Northeastern megalopolis, Northeastern United States between Washington, D.C. and ...
serve Penn Station in Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
, BWI Airport, New Carrollton, and Aberdeen
Aberdeen ( ; ; ) is a port city in North East Scotland, and is the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, third most populous Cities of Scotland, Scottish city. Historically, Aberdeen was within the historic county of Aberdeensh ...
along the Washington, D.C. to Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston in the north to Washington, D.C., in the south, with major stops in Providence, Rhod ...
. Train service is provided to Rockville and Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is an area of North West England which was historically a county. The county was bordered by Northumberland to the north-east, County Durham to the east, Westmorland to the south-east, Lancashire to the south, and the Scottish ...
by Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak (; ), is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates intercity rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
's Washington, D.C., to Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
Capitol Limited.
The WMATA's Metrorail rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT) or heavy rail, commonly referred to as metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport that is generally built in urban areas. A grade separation, grade separated rapid transit line below ground su ...
and Metrobus local bus systems (the 2nd and 6th busiest in the nation of their respective modes) provide service in Montgomery and Prince George's counties and connect them to Washington D.C.. The Maryland Transit Administration
The Maryland Transit Administration (MTA) is a state-operated mass transit administration in Maryland, and is part of the Maryland Department of Transportation (MDOT). The MTA operates a comprehensive transit system throughout the Washington� ...
(often abbreviated as "MTA Maryland"), a state agency part of the Maryland Department of Transportation
The Maryland Department of Transportation (MDOT) is an organization comprising five business units and one Authority:
* Maryland Transportation Authority (Transportation Secretary serves as chairman of the Maryland Transportation Authority)
** ...
also provides transit services within the state. Headquartered in Baltimore, MTA's transit services are largely focused on central Maryland, as well as some portions of the Eastern Shore and Southern MD. Baltimore's Light RailLink and Metro SubwayLink systems serve its densely populated inner-city and the surrounding suburbs. The MTA also serves the city and its suburbs with its local bus service (the 9th largest system in the nation). The MTA's Commuter Bus system provides express coach service on longer routes connecting Washington, D.C. and Baltimore to parts of Central and Southern MD as well as the Eastern Shore. The commuter rail service, known as MARC, operates three lines which all terminate at Washington Union Station
Washington Union Station, known locally as Union Station, is a major train station, transportation hub, and leisure destination in Washington, D.C. Designed by Daniel Burnham and opened in 1907, it is Amtrak's second-busiest station and North ...
and provide service to Baltimore's Penn and Camden stations, Perryville, Frederick, and Martinsburg, West Virginia. In addition, many suburban counties operate local bus systems which connect to and complement the larger MTA and WMATA/Metro services.
The MTA will also administer the Purple Line, an under-construction light rail line that will connect the Maryland branches of the Red, Green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a com ...
/Yellow
Yellow is the color between green and orange on the spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a dominant wavelength of roughly 575585 nm. It is a primary color in subtractive color systems, used in painting or color printing. In t ...
, and Orange lines of the Washington Metro, as well as offer transfers to all three lines of the MARC commuter rail system.
Freight rail transport is handled principally by two Class I railroad
Railroad classes are the system by which Rail freight transport, freight railroads are designated in the United States. Railroads are assigned to Class I, II or III according to annual revenue criteria originally set by the Surface Transportatio ...
s, as well as several smaller regional and local carriers. CSX Transportation
CSX Transportation , known colloquially as simply CSX, is a Class I freight railroad company operating in the Eastern United States and the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. Operating about 21,000 route miles () of track, it is the lead ...
has more extensive trackage throughout the state, with ,CSX Transportation. Jacksonville, FL (2010)"CSX and Maryland."
followed by
Norfolk Southern Railway
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad operating in the Eastern United States. Headquartered in Atlanta, the company was formed in 1982 with the merger of the Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway. The comp ...
. Major rail yards are located in Baltimore and Cumberland, with an intermodal terminal (rail, truck and marine) in Baltimore.
Law and government
 The government of Maryland is conducted according to the state constitution. The government of Maryland, like the other 49 state governments, has exclusive authority over matters that lie entirely within the state's borders, except as limited by the
The government of Maryland is conducted according to the state constitution. The government of Maryland, like the other 49 state governments, has exclusive authority over matters that lie entirely within the state's borders, except as limited by the Constitution of the United States
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, on March 4, 1789. Originally includi ...
.
Power in Maryland is divided among three branches of government: executive, legislative
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers ...
, and judicial
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
. The Maryland General Assembly
The Maryland General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Maryland that convenes within the State House in Annapolis. It is a bicameral body: the upper chamber, the Maryland Senate, has 47 representatives, and the lower ...
is composed of the Maryland House of Delegates
The Maryland House of Delegates is the lower house of the Maryland General Assembly, legislature of the U.S. state of Maryland. It consists of 141 delegates elected from 47 districts. The House of Delegates Chamber is in the Maryland State House ...
and the Maryland Senate
The Maryland Senate, sometimes referred to as the Maryland State Senate, is the upper house of the General Assembly, the state legislature of the U.S. state of Maryland. Composed of 47 senators elected from an equal number of constituent single ...
. Maryland's governor is unique in the United States as the office is vested with significant authority in budgeting. Unlike many other states, significant autonomy is granted to many of Maryland's counties
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
.
Most of the business of government is conducted in Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
, the state capital; however some cabinet departments and state officials have their offices in Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
. Elections for governor and most statewide offices, as well as most county elections, are held in midterm-election years (even-numbered years not divisible by four).
The judicial branch of state government consists of one united District Court of Maryland that sits in every county and Baltimore City, as well as 24 Circuit Courts sitting in each County and Baltimore City, the latter being courts of general jurisdiction for all civil disputes over $30,000, all equitable jurisdiction and major criminal proceedings. The intermediate appellate court is known as the Appellate Court of Maryland and the state supreme court
In the United States, a state supreme court (known by other names in some states) is the highest court in the state judiciary of a U.S. state. On matters of state law, the judgment of a state supreme court is considered final and binding in ...
is the Supreme Court of Maryland. The appearance of the justices of the Supreme Court of Maryland is unique; Maryland is the only state whose justices wear red robes.
Taxation
Maryland imposes fiveincome tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
brackets, ranging from 2to 6.25 percent of personal income. The city of Baltimore and Maryland's 23 counties levy local "piggyback" income taxes at rates between 1.25 and 3.2 percent of Maryland taxable income. Local officials set the rates and the revenue is returned to the local governments quarterly. The top income tax bracket of 9.45 percent is the fifth highest combined state and local income tax rates in the country, behind New York City's 11.35 percent, California's 10.3 percent, Rhode Island's 9.9 percent, and Vermont's 9.5 percent.
Maryland's state sales tax
A sales tax is a tax paid to a governing body for the sales of certain goods and services. Usually laws allow the seller to collect funds for the tax from the consumer at the point of purchase. When a tax on goods or services is paid to a govern ...
is six percent. All real property in Maryland is subject to the property tax
A property tax (whose rate is expressed as a percentage or per mille, also called ''millage'') is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or Wealth t ...
. Generally, properties that are owned and used by religious, charitable, or educational organizations or property owned by the federal, state or local governments are exempt. Property tax rates vary widely. No restrictions or limitations on property taxes are imposed by the state, meaning cities and counties can set tax rates at the level they deem necessary to fund governmental services.
Elections
 Following the
Following the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, Maryland's elections have largely been controlled by the Democratic Party, which accounted for 54.9% of the state's registered voters as of May 2017.
State elections are dominated by Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
and four populous suburban counties bordering Washington, D.C., and Baltimore: Montgomery, Prince George's, Anne Arundel, and Baltimore counties. As of July 2017, 66 percent of the state's population resides in these six jurisdictions, most of which contain large, traditionally Democratic voting bloc
A voting bloc is a group of voting, voters that are strongly motivated by a specific common concern or group of concerns to the point that such specific concerns tend to dominate their voting patterns, causing them to vote together in elections.
...
s: African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
in Baltimore City and Prince George's; federal employees in Prince George's, Anne Arundel, and Montgomery; and post-graduates in Montgomery. The remainder of the state, particularly Western Maryland and the Eastern Shore, is more supportive of Republicans. One of Maryland's best known political figures is a Republican – former governor Spiro Agnew
Spiro Theodore Agnew (; November 9, 1918 – September 17, 1996) was the 39th vice president of the United States, serving from 1969 until his resignation in 1973. He is the second of two vice presidents to resign, the first being John C. ...
, who pled no contest to tax evasion and resigned in 1973.
In 1980
Events January
* January 4 – U.S. President Jimmy Carter proclaims a United States grain embargo against the Soviet Union, grain embargo against the USSR with the support of the European Commission.
* January 6 – Global Positioning Sys ...
, Maryland was one of six states to vote for Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (October 1, 1924December 29, 2024) was an American politician and humanitarian who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party ...
. In 1992
1992 was designated as International Space Year by the United Nations.
Events January
* January 1 – Boutros Boutros-Ghali of Egypt replaces Javier Pérez de Cuéllar of Peru as United Nations Secretary-General.
* January 6
** The Republ ...
, Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
fared better in Maryland than any other state, except his home state of Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the West South Central region of the Southern United States. It borders Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, Texas to the southwest, and Oklahoma ...
. In 1996
1996 was designated as:
* International Year for the Eradication of Poverty
Events January
* January 8 – A Zairean cargo plane crashes into a crowded market in the center of the capital city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo ...
, Maryland was Clinton's sixth best; in 2000
2000 was designated as the International Year for the Culture of Peace and the World Mathematics, Mathematical Year.
Popular culture holds the year 2000 as the first year of the 21st century and the 3rd millennium, because of a tende ...
, Maryland ranked fourth for Gore; and in 2004
2004 was designated as an International Year of Rice by the United Nations, and the International Year to Commemorate the Struggle Against Slavery and Its Abolition (by UNESCO).
Events January
* January 3 – Flash Airlines Flight 60 ...
, John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician, and diplomat who served as the 68th United States secretary of state from 2013 to 2017 in the Presidency of Barack Obama#Administration, administration of Barac ...
showed his fifth-best performance in Maryland. In 2008
2008 was designated as:
*International Year of Languages
*International Year of Planet Earth
*International Year of the Potato
*International Year of Sanitation
The Great Recession, a worldwide recession which began in 2007, continued throu ...
, Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
won the state's 10 electoral votes with 61.9 percent of the vote, to John McCain
John Sidney McCain III (August 29, 1936 – August 25, 2018) was an American statesman and United States Navy, naval officer who represented the Arizona, state of Arizona in United States Congress, Congress for over 35 years, first as ...
's 36.5 percent.
In 2002, former Governor Robert Ehrlich was the first Republican to be elected to that office in four decades, and after one term, he lost his seat to Baltimore Mayor and Democrat Martin O'Malley. Ehrlich ran again for governor in 2010, losing again to O'Malley.
The 2006 election brought no change in the pattern of Democratic dominance. After Democratic Senator Paul Sarbanes
Paul Spyros Sarbanes (; February 3, 1933 – December 6, 2020) was an American politician and attorney from Maryland. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he served in both chambers of the United States Congr ...
announced that he was retiring, Democratic Congressman Benjamin Cardin defeated Republican Lieutenant Governor Michael S. Steele, with 55 percent of the vote, against Steele's 44 percent.
While Republicans typically win more counties in statewide elections by piling up large margins in the west and east, they are usually overcome by the densely populated and solidly Democratic Baltimore–Washington axis. In 2008
2008 was designated as:
*International Year of Languages
*International Year of Planet Earth
*International Year of the Potato
*International Year of Sanitation
The Great Recession, a worldwide recession which began in 2007, continued throu ...
, for instance, McCain won 17 counties to Obama's six (plus Baltimore City). While McCain won most of the western and eastern counties by margins of 2-to-1 or more, he was almost completely shut out in the larger counties surrounding Baltimore and Washington; every large county except Anne Arundel went for Obama, who won by 25 points statewide.
From 2007 to 2011, U.S. Congressman Steny Hoyer
Steny Hamilton Hoyer ( ; born June 14, 1939) is an American politician and retired attorney who has served as the United States House of Representatives, U.S. representative for since 1981. He also served as House Majority Leader from 2007 to 20 ...
( MD-5), a Democrat, was elected as Majority Leader for the 110th Congress and 111th Congress of the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
, serving in that post again from 2019 to 2023. In addition, Hoyer served as House Minority Whip from 2003 to 2006 and 2012 to 2018. His district covers parts of Anne Arundel and Prince George's counties, in addition to all of Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''* ...
, Calvert, and St. Mary's counties in southern Maryland.
In 2010, Republicans won control of most counties. The Democratic Party remained in control of eight county governments, including that of Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
.
In 2022
The year began with another wave in the COVID-19 pandemic, with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, Omicron spreading rapidly and becoming the dominant variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus worldwide. Tracking a decrease in cases and deaths, 2022 saw ...
, Wes Moore became the first Democrat elected Governor of Maryland since 2010
The year saw a multitude of natural and environmental disasters such as the 2010 Haiti earthquake, the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, and the 2010 Chile earthquake. The 2009 swine flu pandemic, swine flu pandemic which began the previous year ...
, replacing Republican Larry Hogan, who did not run for re-election due to term limits. Moore is the first African-American elected Governor of Maryland, and the fifth African-American governor in American history.
Media
A well-known newspaper in Maryland is ''The Baltimore Sun
''The Baltimore Sun'' is the largest general-circulation daily newspaper based in the U.S. state of Maryland and provides coverage of local, regional, national, and international news.
Founded in 1837, the newspaper was owned by Tribune Publi ...
''.
Many residents of the Washington metropolitan area
The Washington metropolitan area, also referred to as the National Capital Region, Greater Washington, or locally as the DMV (short for Washington, D.C., District of Columbia, Maryland, and Virginia), is the metropolitan area comprising Washing ...
receive ''The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'', locally known as ''The'' ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'' or ''WP'', is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C., the national capital. It is the most widely circulated newspaper in the Washington m ...
.''
The most populous areas are served by either Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
or Washington, D.C. broadcast stations. The Eastern Shore is served primarily by broadcast media based around the Delmarva Peninsula; the northeastern section receives both Baltimore and Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
stations. Garrett County, which is mountainous, is served by stations from Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, second-most populous city in Pennsylvania (after Philadelphia) and the List of Un ...
, and requires cable or satellite for reception. Maryland is served by statewide PBS member station Maryland Public Television
Maryland Public Television (MPT) is the PBS member state network for the U.S. state of Maryland. It operates under the auspices of the Maryland Public Broadcasting Commission, an agency of the Maryland state government that holds the licens ...
(MPT).
Education
Primary and secondary education
''Education Week'' ranked Maryland #1 in its nationwide 2009–2013 Quality Counts reports. Primary and secondary education in Maryland is overseen by the Maryland State Department of Education, which is headquartered inBaltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
. The highest educational official in the state is the State Superintendent of Schools, who is appointed by the State Board of Education to a four-year term of office. The Maryland General Assembly has given the Superintendent and State Board autonomy to make educationally related decisions, limiting its influence on the day-to-day functions of public education. Each county and county-equivalent in Maryland has a local Board of Education charged with running the public schools in that particular jurisdiction.
The budget for education was $5.5billion in 2009, representing about 40 percent of the state's general fund. Data from the 2017 census shows that, among large school districts, four Maryland districts are in the top six for per-pupil annual spending, exceeded only by the Boston and New York City districts.
Maryland has a broad range of private primary and secondary schools. Many of these are affiliated with various religious sects, including parochial schools of the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to the Religious Society of Friends, a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations. Members refer to each other as Friends after in the Bible, and originally, others referred to them as Quakers ...
schools, Seventh-day Adventist schools, and Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
schools. In 2003, Maryland law was changed to allow for the creation of publicly funded charter schools, although the charter schools must be approved by their local Board of Education and are not exempt from state laws on education, including collective bargaining laws.
In 2008, the state led the entire country in the percentage of students passing Advanced Placement
Advanced Placement (AP) is a program in the United States and Canada created by the College Board. AP offers undergraduate university-level curricula and examinations to high school students. Colleges and universities in the US and elsewhere ...
examinations. 23.4 percent of students earned passing grades on the AP tests given in May 2008. This marks the first year that Maryland earned this honor. Three Maryland high schools (in Montgomery County) were ranked among the top 100 in the country by US News in 2009, based in large part on AP test scores.
Colleges and universities
Maryland has several historic and renowned private colleges and universities, the most prominent of which isJohns Hopkins University
The Johns Hopkins University (often abbreviated as Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1876 based on the European research institution model, J ...
, founded in 1876 with a grant from Baltimore entrepreneur Johns Hopkins
Johns Hopkins (May 19, 1795 – December 24, 1873) was an American merchant, investor, and philanthropist. Born on a plantation, he left his home to start a career at the age of 17, and settled in Baltimore, Maryland, where he remained for mos ...
.
The first public university in the state is the University of Maryland, Baltimore
The University of Maryland, Baltimore (UMB) is a public university in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1807, it is the second oldest college in Maryland and comprises some of the oldest professional schools of dentistry, law, me ...
, which was founded in 1807 and contains the University of Maryland's only public academic health
Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. In general, it refers to physical and emotional well-being, especially that associated with normal functioning of the human body, absent of disease, p ...
, human services, and one of two law centers (the other being the University of Baltimore School of Law). Seven professional and graduate schools train the majority of the state's physicians, nurses, dentists, lawyers, social workers, and pharmacists. The flagship university and largest undergraduate institution in Maryland is the University of Maryland, College Park
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1856, UMD i ...
which was founded as the Maryland Agricultural College in 1856 and became a public land grant college in 1864. Towson University, founded in 1866, is the state's second largest university.
In 1974, Maryland, along with seven other states, mainly in the South, submitted plans to desegregate its state universities; Maryland's plans were approved by the U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare.
Baltimore is home to the University of Maryland, Baltimore County
The University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC) is a Public university, public research university in Catonsville, Maryland named after Baltimore County, Maryland, Baltimore County. It had a fall 2022 enrollment of 13,991 students, 61 un ...
and the Maryland Institute College of Art. The majority of public universities in the state (Bowie State University, Coppin State University, Frostburg State University, Salisbury University and the University of Maryland-Eastern Shore) are affiliated with the University System of Maryland. Two state-funded institutions, Morgan State University
Morgan State University (Morgan State or MSU) is a Public university, public historically black colleges and universities, historically black research university in Baltimore, Baltimore, Maryland. It is the largest of Maryland's historically bla ...
and St. Mary's College of Maryland, as well as two federally funded institutions, the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences and the United States Naval Academy, are not affiliated with the University System of Maryland. The University of Maryland Global Campus is the largest public university in Maryland and one of the largest distance-learning institutions in the world.
St. John's College (Annapolis/Santa Fe), St. John's College in Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
and Washington College in Chestertown, Maryland, Chestertown, both private institutions, are the oldest colleges in the state and among the oldest in the country. Other private institutions include Mount St. Mary's University, McDaniel College (formerly known as Western Maryland College), Hood College, Stevenson University (formerly known as Villa Julie College), Loyola University Maryland, and Goucher College, among others.
Public libraries
Maryland's 24 public library systems deliver public education for everyone in the state of Maryland through a curriculum that comprises three pillars: Self-Directed Education (books and materials in all formats, e-resources), Research Assistance & Instruction (individualized research assistance, classes for students of all ages), and Instructive & Enlightening Experiences (e.g., Summer Reading Clubs, author events). Maryland's library systems include, in part: * Anne Arundel County Public Library * Baltimore County Public Library * Cecil County Public Library * Enoch Pratt Free Library * Frederick County Public Library * Harford County Public Library * Howard County Public Library * Montgomery County Public Libraries * Prince George's County Memorial Library System * St. Mary's County Public Library Many of the library systems have established formalized partnerships with other educational institutions in their counties and regions.Sports
 With two major metropolitan areas, Maryland has a number of major and minor professional sports franchises. Two National Football League teams play in Maryland, the Baltimore Ravens in
With two major metropolitan areas, Maryland has a number of major and minor professional sports franchises. Two National Football League teams play in Maryland, the Baltimore Ravens in Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
and the Washington Commanders in Landover, Maryland, Landover. The History of the Baltimore Colts, Baltimore Colts represented the NFL in Baltimore from 1953 to 1983 before moving to Indianapolis.
The Baltimore Orioles
The Baltimore Orioles (also known as the O's) are an American professional baseball team based in Baltimore. The Orioles compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) East Division. As one of the America ...
are the state's Major League Baseball franchise. The National Hockey League's Washington Capitals and the National Basketball Association's Washington Wizards formerly played in Maryland, until the construction of an arena in Washington, D.C. in 1997 (now known as Capital One Arena). University of Maryland, College Park, University of Maryland's team is the Maryland Terrapins.
Maryland enjoys considerable historical repute for the talented sports players of its past, including Cal Ripken Jr. and Babe Ruth. In 2012, ''The Baltimore Sun
''The Baltimore Sun'' is the largest general-circulation daily newspaper based in the U.S. state of Maryland and provides coverage of local, regional, national, and international news.
Founded in 1837, the newspaper was owned by Tribune Publi ...
'' published a list of Maryland's top ten athletes in the state's history. The list includes Babe Ruth, Cal Ripken Jr, Johnny Unitas, Brooks Robinson, Frank Robinson, Ray Lewis, Michael Phelps, Jimmie Foxx, Jim Parker (American football), Jim Parker, and Wes Unseld.
Other professional sports franchises in the state include three affiliated minor league baseball teams, one independent league baseball team, the Baltimore Blast (current), Baltimore Blast indoor soccer team, two indoor football teams and three low-level outdoor soccer teams. Maryland is also home to one of the three races in horse racing's annual Triple Crown, the Preakness Stakes, which is run every spring at Pimlico Race Course in Baltimore. Baltimore Stallions, The Baltimore Stallions were a Canadian Football Team in the Canadian Football League, CFL that played the 1994–95 season.
Congressional Country Club has hosted three golf tournaments for the U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Open and a PGA Championship.
The official state sport of Maryland, since 1962, is jousting; the official team sport since 2004 is lacrosse. The National Lacrosse Hall of Fame is located in Sparks, Maryland at the US Lacrosse, USA Lacrosse headquarters. In 2008, intending to promote physical fitness for all ages, Walking#Leisure activity, walking became the official state exercise. Maryland is the first state with an official state exercise.
Friendship partners
Maryland has relationships with many provinces, states, and other administrative divisions worldwide. * Bong County, Bong and Maryland County, Maryland Counties, in Liberia * Jalisco, Mexico (1996) * Cross River State, Cross River and Ondo States,Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
* KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
* Medan Marelan, Indonesia
See also
* Index of Maryland-related articles * Outline of Maryland * List of people from Maryland * USS Maryland, USS ''Maryland'', 4 shipsNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * Davis, William Wilkins. ''Religion and Politics in Maryland on the Eve of the Civil War: The Letters of W. Wilkins Davis''. Foreword by Charles W. Mitchell. 1988; rev. ed., Eugene, Ore.: Wipf & Stock, 2009. * *External links
*Maryland Office of Tourism
* * *
Maryland State Facts from USDA
*
Maryland Historical Society: County Maps
Maryland: State Resource Guide, from the Library of Congress
{{coord, 39, -77, dim:300000_region:US-MD_type:adm1st, name=State of Maryland, display=title Maryland, 1788 establishments in the United States Contiguous United States Mid-Atlantic states Northeastern United States Southern United States States and territories established in 1788 States of the East Coast of the United States States of the United States