|
J. Craig Venter Institute
The J. Craig Venter Institute (JCVI) is a non-profit genomics research institute founded by J. Craig Venter, Ph.D. in October 2006. The institute was the result of consolidating four organizations: the Center for the Advancement of Genomics, The Institute for Genomic Research (TIGR), the Institute for Biological Energy Alternatives, and the J. Craig Venter Science Foundation Joint Technology Center. It has facilities in Rockville, Maryland, and San Diego, California The institute studies the societal implications of genomics in addition to genomics itself. The institute's research involves genomic medicine; environmental genomic analysis; clean energy; synthetic biology; and ethics, law, and economics. The institute employs over 200 people, including Nobel laureate Hamilton Smith. It was sold to the University of California, San Diego, in 2022. History In 2004, the Center for the Advancement of Genomics (TCAG), the Institute for Biological Energy Alternatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DSC04597 JCVI Bus By Volkan Yuksel
DSC or Dsc may refer to: Education * Doctor of Science (D.Sc.) * District Selection Committee, an entrance exam in India * Doctor of Surgical Chiropody, superseded in the 1960s by Doctor of Podiatric Medicine Educational institutions * Dyal Singh College, Delhi, India * DSC International School, Hong Kong, China United States * Dalton State College, Georgia * Daytona State College, Florida * Deep Springs College, California * Dixie State College, now Utah Tech University, Utah Science and technology * Dice similarity coefficient, a statistical measure * Differential scanning calorimetry, or the differential scanning calorimeter * Digital setting circles, on telescopes * Digital still camera, a type of camera * Doppler shift compensation, in bat echolocation * Dye-sensitized solar cell, a low-cost solar cell * Dynamic stability control, computerized technology that improves a vehicle's stability * Dynamic susceptibility contrast, a technique in perfusion MRI * Subarcti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wired (magazine)
''Wired'' is a bi-monthly American magazine that focuses on how emerging technologies affect culture, the economy, and politics. It is published in both print and Online magazine, online editions by Condé Nast. The magazine has been in publication since its launch in January 1993. Its editorial office is based in San Francisco, California, with its business headquarters located in New York City. ''Wired'' quickly became recognized as the voice of the emerging digital economy and culture and a pace setter in print design and web design. From 1998 until 2006, the magazine and its website, ''Wired.com'', experienced separate ownership before being fully consolidated under Condé Nast in 2006. It has won multiple National Magazine Awards and has been credited with shaping discourse around the digital revolution. The magazine also coined the term Crowdsourcing, ''crowdsourcing'', as well as its annual tradition of handing out Vaporware Awards. ''Wired'' has launched several in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
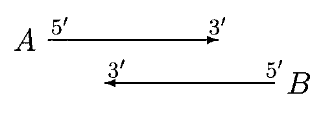
Sequence Alignment
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural biology, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are typically represented as rows within a matrix (mathematics), matrix. Gaps are inserted between the Residue (chemistry), residues so that identical or similar characters are aligned in successive columns. Sequence alignments are also used for non-biological sequences such as calculating the Edit distance, distance cost between strings in a natural language, or to display financial data. Interpretation If two sequences in an alignment share a common ancestor, mismatches can be interpreted as point mutations and gaps as indels (that is, insertion or deletion mutations) introduced in one or both lineages in the time since they diverged from one another. In sequence ali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GLIMMER
In bioinformatics, GLIMMER (Gene Locator and Interpolated Markov ModelER) is used to gene prediction, find genes in prokaryotic DNA. "It is effective at finding genes in bacteria, archea, viruses, typically finding 98-99% of all relatively long genetic code, protein coding genes". GLIMMER was the first system that used the interpolated Markov model to identify coding regions. The GLIMMER software is open source and is maintained by Steven Salzberg, Art Delcher, and their colleagues at the ''Center for Computational Biology'' at Johns Hopkins University. The original GLIMMER algorithms and software were designed by Art Delcher, Simon Kasif and Steven Salzberg and applied to bacterial genome annotation in collaboration with Owen White. Versions GLIMMER 1.0 First Version of GLIMMER "i.e., GLIMMER 1.0" was released in 1998 and it was published in the paper ''Microbial gene identification using interpolated Markov model''. Markov models were used to identify microbial genes in GLIMMER ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Prediction
In computational biology, gene prediction or gene finding refers to the process of identifying the regions of genomic DNA that encode genes. This includes protein-coding genes as well as RNA genes, but may also include prediction of other functional elements such as regulatory regions. Gene finding is one of the first and most important steps in understanding the genome of a species once it has been sequenced. In its earliest days, "gene finding" was based on painstaking experimentation on living cells and organisms. Statistical analysis of the rates of homologous recombination of several different genes could determine their order on a certain chromosome, and information from many such experiments could be combined to create a genetic map specifying the rough location of known genes relative to each other. Today, with comprehensive genome sequence and powerful computational resources at the disposal of the research community, gene finding has been redefined as a largely computa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinococcus Radiodurans
''Deinococcus radiodurans'' is a bacterium, an extremophile and one of the most radiation-resistant organisms known. It can survive cold, dehydration, vacuum, and acid, and therefore is known as a polyextremophile. ''The Guinness Book Of World Records'' listed it in January 1998 as the world's most radiation-resistant bacterium or lifeform. Several bacteria of comparable radioresistance are known, including some species of the genus '' Chroococcidiopsis'' (phylum cyanobacteria) and some species of '' Rubrobacter'' (phylum Actinomycetota); among the archaea, the species '' Thermococcus gammatolerans'' shows comparable radioresistance. Name and classification The name ''Deinococcus radiodurans'' derives from the Ancient Greek δεινός () and κόκκος () meaning "terrible grain/berry" and the Latin and , meaning "radiation-surviving". The species was formerly called ''Micrococcus radiodurans''. As a consequence of its hardiness, it has been nicknamed “Conan the Bacteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyextremophile
An extremophile () is an organism that is able to live (or in some cases thrive) in extreme environments, i.e., environments with conditions approaching or stretching the limits of what known life can adapt to, such as extreme temperature, pressure, radiation, salinity, or pH level. Since the definition of an extreme environment is relative to an arbitrarily defined standard, often an anthropocentric one, these organisms can be considered ecologically dominant in the evolutionary history of the planet. Dating back to more than 40 million years ago, extremophiles have continued to thrive in the most extreme conditions, making them one of the most abundant lifeforms. The study of extremophiles has expanded human knowledge of the limits of life, and informs speculation about extraterrestrial life. Extremophiles are also of interest because of their potential for bioremediation of environments made hazardous to humans due to pollution or contamination. Characteristics In the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioresistant
Radioresistance is the level of ionizing radiation that organisms are able to withstand. Ionizing-radiation-resistant organisms (IRRO) were defined as organisms for which the dose of acute ionizing radiation (IR) required to achieve 90% reduction (D10) is greater than 1,000 gray (Gy) Radioresistance is surprisingly high in many organisms, in contrast to previously held views. For example, the study of environment, animals and plants around the Chernobyl disaster area has revealed an unexpected survival of many species, despite the high radiation levels. A Brazilian study in a hill in the state of Minas Gerais which has high natural radiation levels from uranium deposits, has also shown many radioresistant insects, worms and plants. Certain extremophiles, such as the bacteria ''Deinococcus radiodurans'' and the tardigrades, can withstand large doses of ionizing radiation on the order of 5,000 Gy. Induced radioresistance In the graph on left, a dose/survival curve for a hypot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treponema Pallidum
''Treponema pallidum'', formerly known as ''Spirochaeta pallida'', is a Microaerophile, microaerophilic, Gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative, spirochaete bacterium with subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel (also known as endemic syphilis), and yaws. It is known to be transmitted only among humans and baboons. ''T. pallidum'' can enter the host through mucosal membranes or open lesions in the skin and is primarily spread through sexual contact. It is a helically coiled microorganism usually 6–15 μm long and 0.1–0.2 μm wide. ''T. pallidum'''s lack of both a Citric acid cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle and processes for oxidative phosphorylation results in minimal metabolic activity. As a Chemoorganoheterotrophic, chemoorganoheterotroph, ''Treponema pallidum'' is an obligate parasite that acquires its glucose carbon source from its host. Glucose can be used not only as a primary carbon source but also in glycolytic mechanisms to generate ATP needed to power the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
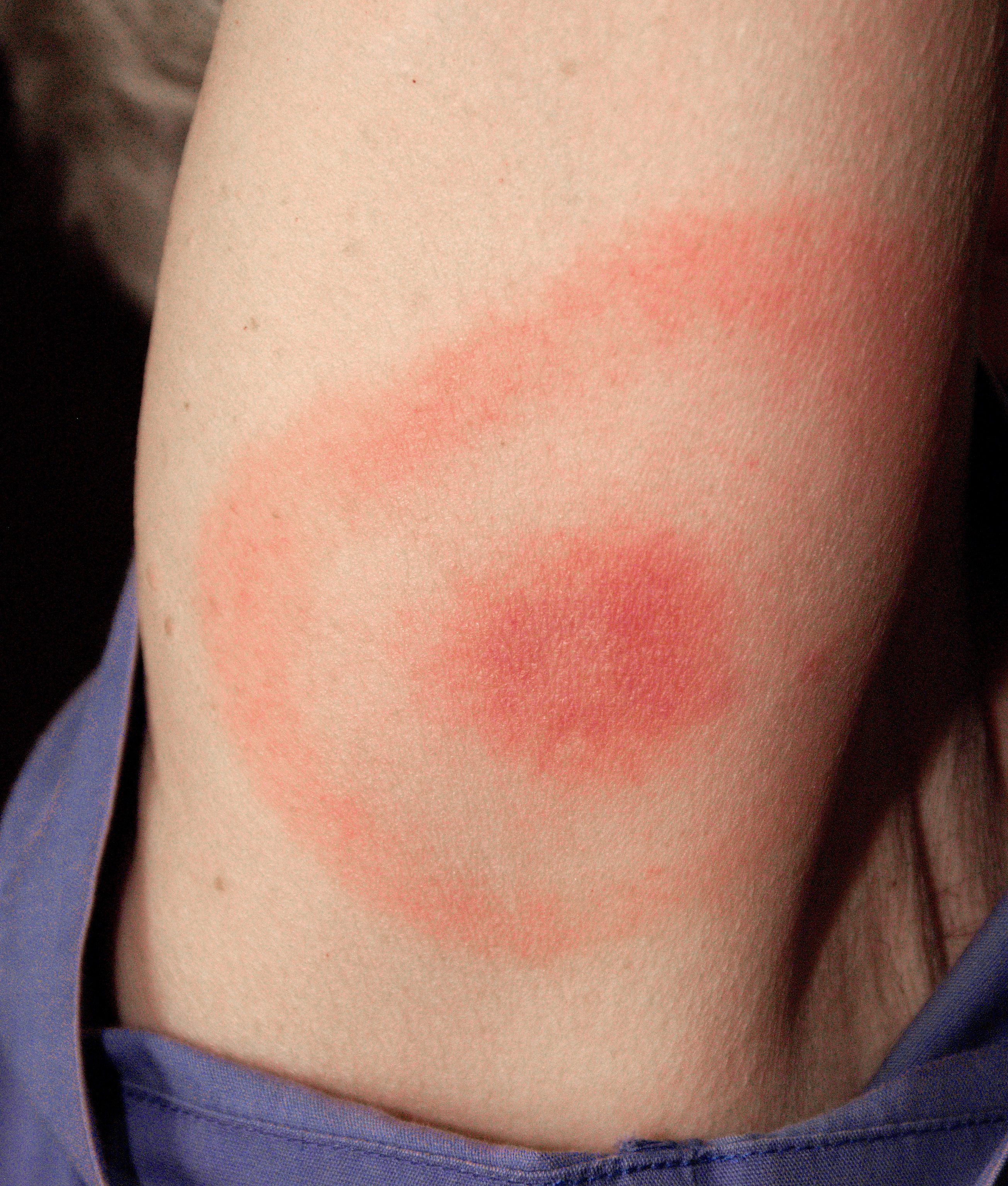
Borrelia Burgdorferi
''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a bacterial species of the spirochete class in the genus '' Borrelia'', and is one of the causative agents of Lyme disease in humans. Along with a few similar genospecies, some of which also cause Lyme disease, it makes up the species complex of ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' sensu lato. The complex currently comprises 20 accepted and 3 proposed genospecies. ''B. burgdorferi'' sensu stricto exists in North America and Eurasia and until 2016 was the only known cause of Lyme disease in North America. ''B. burgdorferi'' are often mistakenly described as Gram negative because of their two external membranes, but they lack lipopolysaccharide and possess many surface lipoproteins, unlike true Gram-negative bacteria. Microbiology ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is named after the researcher Willy Burgdorfer, who first isolated the bacterium in 1982. ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a microaerophile, requiring small amounts of oxygen in order to undergo glycolysis and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanococcus Jannaschii
''Methanocaldococcus jannaschii'' (formerly ''Methanococcus jannaschii'') is a thermophilic methanogenic archaean in the class Methanococci. It was the first archaeon, and third organism, to have its complete genome sequenced. The sequencing identified many genes unique to the archaea. Many of the synthesis pathways for methanogenic cofactors were worked out biochemically in this organism, as were several other archaeal-specific metabolic pathways. History ''Methanocaldococcus jannaschii'' was isolated from a submarine hydrothermal vent at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. The hydrothermal vent was located in the East Pacific Rise, at a depth of 2600 m, near the western coast of Mexico. Surface material was collected at a " white smoker" chimney which revealed evidence of Methanocaldococcus jannaschii living in this extreme habitat of temperatures from 48 - 94 °C. Like many kinds of extremophiles, ''M. jannaschii'' possess the ability to adapt to high temperatures, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |