Livonia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Livonia, known in earlier records as Livland, is a
 Beginning in the 12th century, Livonia became a target for economic and political expansion by
Beginning in the 12th century, Livonia became a target for economic and political expansion by
 The January 1229 death of Albert of Riga caused a diocesan feud in the Archbishopric of Riga, as two rival candidates were elected.
The January 1229 death of Albert of Riga caused a diocesan feud in the Archbishopric of Riga, as two rival candidates were elected.
 The Livonian Order was a largely autonomous branch of the
The Livonian Order was a largely autonomous branch of the


 The armies of
The armies of
 The Livonian Voivodeship (; ) was a unit of administrative division and local government in the
The Livonian Voivodeship (; ) was a unit of administrative division and local government in the
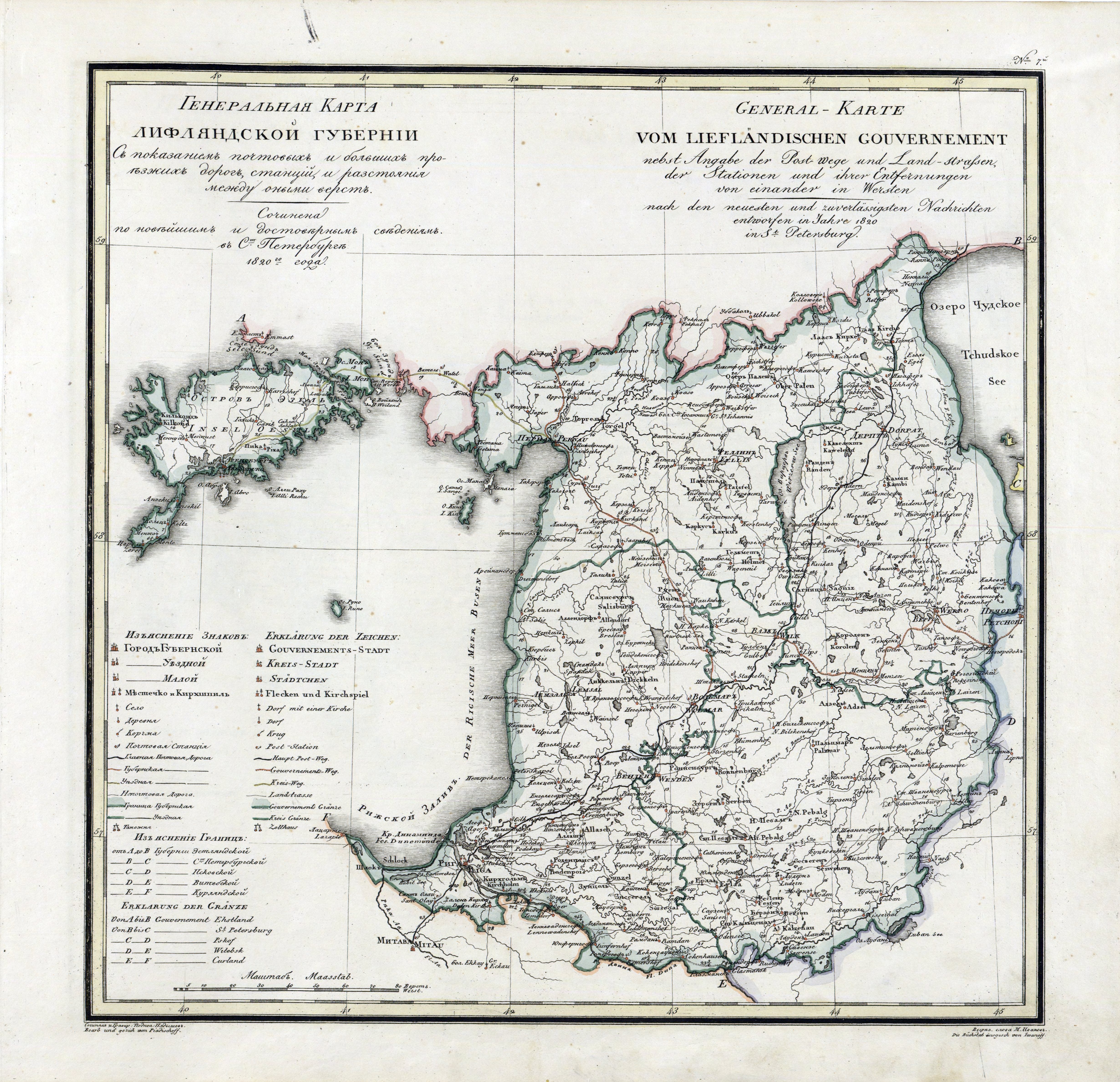 In 1796, the Riga Governorate was renamed as the Governorate of Livonia ( / , , ). From 1845 to 1876, the Baltic governorates of
In 1796, the Riga Governorate was renamed as the Governorate of Livonia ( / , , ). From 1845 to 1876, the Baltic governorates of Suvorov A.A. governor-general in 1861–66 :: ENCYCLOPAEDIA OF SAINT PETERSBURG
/ref> and Count Pyotr Andreyevich Shuvalov. Livonia remained within the Russian Empire until the end of
Europe mediterranean 1190.jpg, Livonia in Europe, 1190.
Europe 1550.jpg, Europe, 1550.
Litvania map 1570.png, Livonia on a 1570 map
Europe 1740.jpg, Europe, 1740.
Europe1815 1905.jpg, Europe, 1815.
Meyerbaltikum.jpg, Livonia, 1898.
Les pays baltiques, le pluriculturalisme en héritage
', Yves Plasseraud; Armeline, 2020. *
Les Germano-baltes
', Yves Plasseraud; S. Pourchier-Plasseraud; Armeline, 2022.
Virtual LivoniaDeutsch-Baltische Ritterschaften in Livland, Kurland, Estland, Oesel
Joann Portantiuse Liivimaa kaart 1573. aastastEstonian Manors Portal
the English version includes the description of 438 well-preserved historical manors of nowadays Estonia (historically – northern part of Old-Livonia/Alt-Livland)
''Atlas of Livonia, or of the Two Governments and Duchies Livonia and Estonia, and of the Province of Oesel''
from the
historical region
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some t ...
on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
. It is named after the Livonians
The Livonians, or Livs, are a Balto-Finnic people indigenous to the Livonian Coast, in northwestern Latvia. Livonians historically spoke Livonian language, Livonian, a Uralic language closely related to Estonian language, Estonian and Finnish lan ...
, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
.
By the end of the 13th century, the name was extended to most of present-day Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
and Latvia, which the Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword (; ) was a Catholic Church, Catholic Military order (monastic society), military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert of Riga, Albert, the third bishop of Riga (or possibly by Theode ...
had conquered during the Livonian Crusade
The Livonian crusade consists of the various military Crusade, Christianisation campaigns in medieval Livonia – modern Latvia and Estonia – during the Pope, Papal-sanctioned Northern Crusades in the 12th–13th century.
Overview Historic ...
(1193–1290). Medieval Livonia, or ''Terra Mariana
Terra Mariana (Medieval Latin for 'Land of Mary (mother of Jesus), Mary') was the formal name for Medieval Livonia or Old Livonia. It was formed in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade, and its territories were composed of present-day Estonia a ...
'', reached its greatest extent after the Saint George's Night Uprising (1343–1345), which forced Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
to sell the Duchy of Estonia (northern Estonia conquered by Denmark in the 13th century) to the State of the Teutonic Order in 1346. Livonia, as understood after the retreat of Denmark in 1346, bordered on the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland (; ; ; ) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and Estonia to the south, to Saint Petersburg—the second largest city of Russia—to the east, where the river Neva drains into it. ...
in the north, Lake Peipus and Russia to the east, and Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
to the south.
As a consequence of the Livonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) concerned control of Terra Mariana, Old Livonia (in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia). The Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of the Denmark–Norway, Dano-Norwegian Realm, the Kingdom ...
(1558–1583), the territory of Livonia was reduced to the southern half of Estonia and the northern half of Latvia.
The indigenous inhabitants of Livonia were various Finnic tribes in the north and Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
tribes in the south. The descendants of the crusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding t ...
rs formed the nucleus of the new ruling class of Livonia after the Livonian Crusade, and they eventually became known as Baltic Germans
Baltic Germans ( or , later ) are ethnic German inhabitants of the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea, in what today are Estonia and Latvia. Since their resettlement in 1945 after the end of World War II, Baltic Germans have drastically decli ...
.
History
Danes
Danes (, ), or Danish people, are an ethnic group and nationality native to Denmark and a modern nation identified with the country of Denmark. This connection may be ancestral, legal, historical, or cultural.
History
Early history
Denmark ...
and Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
, particularly for the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
and the Cistercian Order
The Cistercians (), officially the Order of Cistercians (, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contri ...
.
Around 1160, Hanseatic traders from Lübeck
Lübeck (; or ; Latin: ), officially the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Lübeck (), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 220,000 inhabitants, it is the second-largest city on the German Baltic Sea, Baltic coast and the second-larg ...
established a trading post on the site of the future city of Riga
Riga ( ) is the capital, Primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Latvia, largest city of Latvia. Home to 591,882 inhabitants (as of 2025), the city accounts for a third of Latvia's total population. The population of Riga Planni ...
, which Bishop Albrecht von Buxthoeven founded in 1201.
Livonian Crusade and the Livonian Brothers of the Sword (1198–1229)
The ''Livonian Chronicle of Henry
The ''Livonian Chronicle of Henry'' () is a Latin narrative of events in Livonia (roughly corresponding to today's Estonia and Latvia) and surrounding areas from 1180 to 1227. It was written by a priest named Henry. Apart from some references ...
'' from the 1220s gives a firsthand account of the Christianization of Livonia, granted as a fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
by the Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynast ...
(''de facto'' but not known as) the King of Germany, Philip of Swabia (), to Bishop Albert of Riga
Albert of Riga or Albert of Livonia ( – 17 January 1229) was the third Catholic Bishop of Riga in Livonia. As the Bishop of Livonia, in 1201, he founded Riga, the modern capital city of Latvia, and the city was later made a bishopric. The bu ...
(Albert of Buxhoeveden), nephew of Hartwig II, the Archbishop of Bremen
This list records the bishops of the Archdiocese of Bremen, Roman Catholic diocese of Bremen (), supposedly a suffragan of the Archdiocese of Cologne, Archbishopric of Cologne, then of the bishops of Bremen, who were in personal union archbishops ...
, who sailed (1200) with a convoy of ships filled with armed crusaders to carve out a Catholic territory in the east as part of the Livonian Crusade
The Livonian crusade consists of the various military Crusade, Christianisation campaigns in medieval Livonia – modern Latvia and Estonia – during the Pope, Papal-sanctioned Northern Crusades in the 12th–13th century.
Overview Historic ...
. Bishop Albert founded the military order of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword (, ) in 1202; Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III (; born Lotario dei Conti di Segni; 22 February 1161 – 16 July 1216) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 until his death on 16 July 1216.
Pope Innocent was one of the most power ...
sanctioned the establishment in 1204. Albert did so in order to aid the Bishopric of Riga
The Archbishopric of Riga (, ) was a Catholic diocese and civil government in Medieval Livonia, subject to the Holy See. It was established in 1186 and ended in 1561.
History
The diocese was established in 1186 as the Bishopric of Livonia ...
in the conversion of the pagan
Paganism (, later 'civilian') is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Christianity, Judaism, and Samaritanism. In the time of the ...
Curonians
:''The Kursenieki are also sometimes known as Curonians.''
The Curonians or Kurs (; ) were a medieval Balts, Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic Sea in the 5th–16th centuries, in what are now western parts of Latvia and Lithuania. ...
, Livonians
The Livonians, or Livs, are a Balto-Finnic people indigenous to the Livonian Coast, in northwestern Latvia. Livonians historically spoke Livonian language, Livonian, a Uralic language closely related to Estonian language, Estonian and Finnish lan ...
, Semigallians
Semigallians (; ; also ''Zemgalians'', ''Semigalls'' or ''Semigalians'') were the Balts, Baltic tribe that lived in the south central part of contemporary Latvia and northern Lithuania. They are noted for their long resistance (1219–1290) agai ...
, and Latgalians living on the shores of the Gulf of Riga
The Gulf of Riga, Bay of Riga, or Gulf of Livonia (, , ) is a bay of the Baltic Sea between Latvia and Estonia.
The island of Saaremaa (Estonia) partially separates it from the rest of the Baltic Sea. The main connection between the gulf and t ...
. The membership of the order comprised German "warrior monk
A monk (; from , ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a man who is a member of a religious order and lives in a monastery. A monk usually lives his life in prayer and contemplation. The concept is ancient and can be seen in many reli ...
s". Alternative names of the order include the Christ Knights, Sword Brethren, and the Militia of Christ of Livonia. From its foundation, the undisciplined Order tended to ignore its supposed vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain ...
age to the bishops. In 1215, Albert ordered the construction of a cathedral in Riga
Riga ( ) is the capital, Primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Latvia, largest city of Latvia. Home to 591,882 inhabitants (as of 2025), the city accounts for a third of Latvia's total population. The population of Riga Planni ...
. In 1218, he asked King Valdemar II of Denmark
Valdemar II Valdemarsen (28 June 1170 – 28 March 1241), later remembered as Valdemar the Victorious () and Valdemar the Conqueror, was King of Denmark from 1202 until his death in 1241.
In 1207, Valdemar invaded and conquered Bishopric of L� ...
for assistance, but Valdemar instead arranged a deal with the Brotherhood and conquered the north of Estonia for Denmark. The Brotherhood had its headquarters at Fellin (Viljandi) in present-day Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
, where the walls of the Master's castle stand. Other strongholds included Wenden (Cēsis), Segewold (Sigulda) and Ascheraden (Aizkraukle). The commanders of Fellin, Goldingen (Kuldīga), Marienburg (Alūksne), Reval (Tallinn), and the bailiff
A bailiff is a manager, overseer or custodian – a legal officer to whom some degree of authority or jurisdiction is given. There are different kinds, and their offices and scope of duties vary.
Another official sometimes referred to as a '' ...
of Weißenstein (Paide) belonged to the five-member entourage of the Order's Master.
Pope Gregory IX
Pope Gregory IX (; born Ugolino di Conti; 1145 – 22 August 1241) was head of the Catholic Church and the ruler of the Papal States from 19 March 1227 until his death in 1241. He is known for issuing the '' Decretales'' and instituting the Pa ...
asked the Brothers to defend Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
from Novgorodian attacks in his letter of 24 November 1232; however, no known information regarding the knights' possible activities in Finland has survived. (Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
eventually took over Finland after the Second Swedish Crusade in 1249.) In the Battle of Saule in 1236 the Lithuanians
Lithuanians () are a Balts, Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another two million make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the Lithuanian Americans, United Sta ...
and Semigallians
Semigallians (; ; also ''Zemgalians'', ''Semigalls'' or ''Semigalians'') were the Balts, Baltic tribe that lived in the south central part of contemporary Latvia and northern Lithuania. They are noted for their long resistance (1219–1290) agai ...
decimated the Order. This disaster led the surviving Brothers to become incorporated into the Order of Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
in the following year, and from that point on they became known as the Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous branch of the Teutonic Order,
formed in 1237. From 1435 to 1561 it was a member of the Livonian Confederation.
History
The order was formed from the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword after thei ...
. They continued, however, to function in all respects ( rule, clothing and policy) as an autonomous branch of the Teutonic Order, headed by their own Master (himself ''de jure'' subject to the Teutonic Order's Grand Master).
Internal conflicts in Livonia (1229–1236)
 The January 1229 death of Albert of Riga caused a diocesan feud in the Archbishopric of Riga, as two rival candidates were elected.
The January 1229 death of Albert of Riga caused a diocesan feud in the Archbishopric of Riga, as two rival candidates were elected. Pope Gregory IX
Pope Gregory IX (; born Ugolino di Conti; 1145 – 22 August 1241) was head of the Catholic Church and the ruler of the Papal States from 19 March 1227 until his death in 1241. He is known for issuing the '' Decretales'' and instituting the Pa ...
, through cardinal Otto of Tonengo, tasked Baldwin of Alna as papal legate to resolve the dispute. After securing the submission of Courland, Baldwin soon found himself in conflict with various factions in Livonia, fleeing to Dünamünde and temporarily leaving Livonia in early 1232. The pope made him bishop of Semigallia and gave him papal legation throughout much of Livonia, and Baldwin returned by 1233. He tried to take the castle of Reval (modern Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Estonia, most populous city of Estonia. Situated on a Tallinn Bay, bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, it has a population of (as of 2025) and ...
) from the Sword Brothers, but in August–September 1233 they defeated Baldwin, who excommunicated
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to deprive, suspend, or limit membership in a religious community or to restrict certain rights within it, in particular those of being in communion with other members of the con ...
many Sword Brothers in retaliation.
At that point, Livonia was divided into two camps: Baldwin's Bishopric of Semigallia, the Bishopric of Dorpat and the late Albert of Riga's Buxhöveden family plus several monasteries, most Estonians and Curonians, versus the Livonian Sword Brothers, Nicholas' Bishopric of Riga, and the city of Riga. Previous generations of historians have argued that Baldwin attempted to make the whole Baltic region an ecclesiastical state, but (1993) refuted this idea as "fanciful speculation". Similarly, the traditional assertion that Baldwin had extensive plans to conquer and convert eastwards into parts of Pskov and Novgorod do not stand up under scrutiny, showing that papal correspondence with Baldwin was primarily concerned with ending the internal conflict in Livonia on terms favourable to Rome. Therefore, no Livonian faction was allowed to form an alliance with an external power, be they pagan or Novgorodian, to prevent the internal conflict from spilling over and threaten Livonia's external security.
In 1234, the pope recalled Baldwin, and replaced him with William of Modena
William of Modena ( – 31 March 1251), also known as ''William of Sabina'', ''Guglielmo de Chartreaux'', ''Guglielmo de Savoy'', ''Guillelmus'', was an Italian clergyman and papal diplomat.
. The pope did not give a verdict until April 1236, when the Sword Brothers were tasked to return Reval to the Danish king. The terms of the agreement were not finalised until the Treaty of Stensby (7 June 1238), when the Livonian Sword Brothers, crushed at Saule and now submitted to the Teutonic Order
The Teutonic Order is a religious order (Catholic), Catholic religious institution founded as a military order (religious society), military society in Acre, Israel, Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Sa ...
, relinquished their claims to Reval and much of northern Estonia to Denmark, and to share future territorial gains with two-thirds for the Danish king and one third for the Livonian Order.
Livonian Order, the Bishoprics and Riga from 1237 until 1418
Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
(or Teutonic Order) and a member of the Livonian Confederation from 1418 to 1561. After being defeated by Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
n forces in the 1236 Battle of Saule
The Battle of Saule (; ; ) was fought on 22 September 1236, between the Livonian Brothers of the Sword and pagan troops of Samogitians and Semigallians. Between 48 and 60 knights were killed, including the Livonian Master, Volkwin. It was the ea ...
, the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword (; ) was a Catholic Church, Catholic Military order (monastic society), military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert of Riga, Albert, the third bishop of Riga (or possibly by Theode ...
were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights as the Livonian Order in 1237. Between 1237 and 1290, the Livonian Order conquered all of Courland, Livonia, and Semigallia, but their attack on northern Russia was repelled in the Battle of Rakvere (1268). In 1346, after the St. George's Night Uprising the Order purchased the rest of Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
from King Valdemar IV of Denmark. The '' Chronicle of Henry of Livonia'' and the '' Livonian Rhymed Chronicle'' describe conditions within the Order's territory. The Teutonic Order fell into decline following its defeat in the Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila), a ...
in 1410 and the secularization of its Prussian territories by Albert of Brandenburg in 1525, but the Livonian Order managed to maintain an independent existence.
Livonian Confederation (1418–1561)
In 1418, the Archbishop of Riga, Johannes Ambundii, organised the five ecclesiastical states of the Holy Roman Empire in Medieval Livonia (Livonian Order, Courland, Ösel–Wiek, Dorpat and Riga) into the Livonian Confederation. A diet or ''Landtag
A ''Landtag'' (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence ...
'' was formed in 1419. The city of Walk
Walking (also known as ambulation) is one of the main gaits of terrestrial locomotion among legged animals. Walking is typically slower than running and other gaits. Walking is defined as an "inverted pendulum" gait in which the body vaults over ...
was chosen as the site of the diet.
From the 14th to the 16th centuries, Middle Low German
Middle Low German is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented in writing since about 1225–34 (). During the Hanseatic period (from about 1300 to about 1600), Mid ...
– as spoken in the towns of the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
— functioned as the established language of the Livonian lands, but High German
The High German languages (, i.e. ''High German dialects''), or simply High German ( ) – not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called "High German" – comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Ben ...
subsequently succeeded it as the official language in the course of the 16th and 17th centuries.
Livonian War (1558–1583)


Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand I (10 March 1503 – 25 July 1564) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1556, King of Bohemia, King of Hungary, Hungary, and List of rulers of Croatia, Croatia from 1526, and Archduke of Austria from 1521 until his death in 1564.Milan Kruhek ...
once again asked for help of Gustav I of Sweden
Gustav Eriksson Vasa (12 May 1496 – 29 September 1560), also known as Gustav I, was King of Sweden from 1523 until his death in 1560. He was previously self-recognised Protector of the Realm ('' Riksföreståndare'') from 1521, during the on ...
, and the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland (; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a monarchy in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval period from 1025 until 1385.
Background
The West Slavs, West Slavic tribe of Polans (western), Polans who lived in what i ...
also began direct negotiation
Negotiation is a dialogue between two or more parties to resolve points of difference, gain an advantage for an individual or Collective bargaining, collective, or craft outcomes to satisfy various interests. The parties aspire to agree on m ...
s with Gustav, but nothing resulted because on 29 September 1560, Gustav I Vasa died. The chances for success of Magnus, (who had become Bishop of Courland and of Ösel-Wiek) in 1560 and his supporters looked particularly good in 1560 (and in 1570). In 1560 he had been recognised as their sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title that can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to ...
by the Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek and by the Bishopric of Courland, and as their prospective ruler by the authorities of the Bishopric of Dorpat
The Bishopric of Dorpat was a medieval prince-bishopric, i.e. both a diocese of the Roman Catholic Church and a temporal principality ruled by the bishop of the diocese. It existed from 1211 until 1558, generally encompassing the area that now co ...
; the Bishopric of Reval with the Harrien- Wierland gentry
Gentry (from Old French , from ) are "well-born, genteel and well-bred people" of high social class, especially in the past. ''Gentry'', in its widest connotation, refers to people of good social position connected to Landed property, landed es ...
were on his side; the Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous branch of the Teutonic Order,
formed in 1237. From 1435 to 1561 it was a member of the Livonian Confederation.
History
The order was formed from the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword after thei ...
conditionally recognised his right of ownership
Ownership is the state or fact of legal possession and control over property, which may be any asset, tangible or intangible. Ownership can involve multiple rights, collectively referred to as '' title'', which may be separated and held by dif ...
of the (future) Duchy of Estonia. Then along with Archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
Wilhelm von Brandenburg of the Archbishopric of Riga and his Coadjutor Christoph von Mecklenburg, Kettler, the last Master of the Teutonic Order, gave to Magnus the portions of the Kingdom of Livonia which he had taken possession of, but they refused to give him any more land.
Once Eric XIV of Sweden became king in September 1560 he took quick actions to get involved in the war. He negotiated a continued peace
Peace is a state of harmony in the absence of hostility and violence, and everything that discusses achieving human welfare through justice and peaceful conditions. In a societal sense, peace is commonly used to mean a lack of conflict (suc ...
with Muscovy and spoke to the burghers of Reval city. He offered them goods to submit to him as well as threatening them. By 6 June 1561,they submitted to him contrary to the persuasion
Persuasion or persuasion arts is an umbrella term for influence. Persuasion can influence a person's beliefs, attitudes, intentions, motivations, or behaviours.
Persuasion is studied in many disciplines. Rhetoric studies modes of persuasi ...
s of Kettler to the burghers. King Eric's brother and future King Johan married the Polish-Lithuanian princess Catherine Jagiellon in 1562. Wanting to obtain his own land in Livonia, he loaned Poland money and then claimed the castles that they had pawned as his own instead of using them to pressure Poland. After Johan returned to Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
, Erik XIV forbade him to deal with any foreign countries without his consent.
Shortly after that, Erik XIV quickly lost any allies that he was about to obtain, either in the form of Magnus or of the Archbishop of Riga
Riga ( ) is the capital, Primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Latvia, largest city of Latvia. Home to 591,882 inhabitants (as of 2025), the city accounts for a third of Latvia's total population. The population of Riga Planni ...
. Magnus was upset that he had been tricked out of his inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Offi ...
of Holstein
Holstein (; ; ; ; ) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider (river), Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost States of Germany, state of Germany.
Holstein once existed as the German County of Holstein (; 8 ...
. After Sweden occupied Reval, Frederick II of Denmark
Frederick II (1 July 1534 – 4 April 1588) was King of Denmark-Norway, Denmark and Norway and Duke of Duchy of Schleswig, Schleswig and Duchy of Holstein, Holstein from 1559 until his death in 1588.
A member of the House of Oldenburg, Fre ...
made a treaty with Erik XIV of Sweden in August 1561. Magnus and his brother Frederick II were in great disagreement, and Frederick II negotiated a treaty with Ivan IV on 7 August 1562 to help his brother obtain more land and to stall further Swedish advances. Erik XIV did not like this, and the Northern Seven Years' War
The Northern Seven Years' War (also known as the ''Nordic Seven Years' War'', the ''First Northern War,'' the ''Seven Years' War of the North'' or the ''Seven Years War in Scandinavia'') was fought between the Kingdom of Sweden (1523–1611), K ...
(1563–1570) broke out, with Sweden pitted against the Free City of Lübeck, Denmark, and Poland-Lithuania. While only losing land and trade, Frederick II and Magnus were not faring well. But in 1568 Erik XIV became insane and his brother Johan took his place as King John III of Sweden.
Johan III, due to his friendship with Poland-Lithuania, began a policy against Muscovy. He would try to obtain more land in Livonia and to dominate Denmark. After all parties had been financially drained, Frederick II let his ally, King Sigismund II Augustus of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
, know that he was ready for peace. On 15 December 1570, the Treaty of Stettin concluded the Northern Seven Years' War.
It is, however, more difficult to estimate the scope and magnitude of the support Magnus received in Livonian cities. Compared to the Harrien-Wierland gentry, the Reval city council, and hence probably the majority of citizens, demonstrated a much more reserved attitude towards Denmark and towards King Magnus of Livonia. Nevertheless, there is no reason to speak about any strong pro-Swedish sentiments among the residents of Reval. The citizens who had fled to the Bishopric of Dorpat or had been deported to Muscovy hailed Magnus as their saviour until 1571. Analysis indicates that during the Livonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) concerned control of Terra Mariana, Old Livonia (in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia). The Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of the Denmark–Norway, Dano-Norwegian Realm, the Kingdom ...
a pro-independence wing emerged among the Livonian gentry and townspeople, forming the so-called "Peace Party". Dismissing hostilities, these forces perceived an agreement with Muscovy as a chance to escape the atrocities of war and to avoid the division of Livonia. Thus Magnus, who represented Denmark and later struck a deal with Ivan IV, proved a suitable figurehead for this faction.
The Peace Party, however, had its own armed forces – scattered bands of household troops ('' Hofleute'') under diverse command, which only united in action in 1565 ( Battle of Pärnu and Siege of Reval), in 1570–1571 ( Siege of Reval; 30 weeks), and in 1574–1576 (first on Sweden's side, then came the sale of Ösel–Wiek to the Danish Crown, and the loss of territory to Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia, also known as the Tsardom of Moscow, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of tsar by Ivan the Terrible, Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter the Great in 1721.
...
). In 1575, after Muscovy attacked Danish claims in Livonia, Frederick II dropped out of the competition, as did the Holy Roman Emperor. After this Johan III held off on his pursuit for more land due to Muscovy obtaining lands that Sweden controlled. He used the next two years of truce to get in a better position. In 1578, he resumed the fight, not only for Livonia, but also for everywhere due to an understanding that he made with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
. In 1578, Magnus retired to the Commonwealth and his brother all but gave up the land in Livonia.
During the many years of the Livonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) concerned control of Terra Mariana, Old Livonia (in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia). The Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of the Denmark–Norway, Dano-Norwegian Realm, the Kingdom ...
(1558–1582), the Livonian Order suffered a decisive defeat at the hands of troops of Muscovite Russia in the Battle of Ergeme in 1560 and continued living under great threat. Letters to the Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans (disambiguation), Emperor of the Romans (; ) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period (; ), was the ruler and h ...
arrived from many European countries, warning ''that Moscow has its eyes on much more than only a few harbors or the province of Liefland'' ... the East Sea (Ostsee-Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
) and the West Sea (Atlantic) are equally in danger. Duke Barnim the Elder, 50 years duke of Pomerania, warned, ''that never before did he experience the fear than now, where even in his land, where people send by Moscow are everywhere''. At stake was the Narva
Narva is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in the Ida-Viru County, at the Extreme points of Estonia, eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva (river), Narva river which forms the Estonia–Russia border, E ...
-trade-route and practically all trade in the North, and with that all of Europe. Due to the religious upheavals of the Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
the distant Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
could not send troops, which it could not afford anyway. The Duchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (, , ) or Ducal Prussia (; ) was a duchy in the region of Prussia established as a result of secularization of the Monastic Prussia, the territory that remained under the control of the State of the Teutonic Order until t ...
was not able to help for much of the same reason, and Duke Albrecht () was under continuous ban by the Empire. The Hanseatic League was greatly weakened by this and the city state of Luebeck fought its last great war. The emperor Maximilian II () diffused the greatest threat by remaining on friendly terms with Tsar Ivan IV of Russia
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (; – ), commonly known as Ivan the Terrible,; ; monastic name: Jonah. was Grand Prince of Moscow and all Russia from 1533 to 1547, and the first Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia from 1547 until his death in 1584. ...
(), but not sending Ivan IV troops as requested in his struggles with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
.
In 1570, Tsar Ivan IV of Russia installed Duke Magnus as King of Livonia. The other forces opposed this appointment. The Livonian Order saw no other way than to seek protection from Sigismund II Augustus (King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of Royal elections in Poland, free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electab ...
and Grand Duke of Lithuania
This is a list of Lithuanian monarchs who ruled Lithuania from its inception until the fall of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1795. The Lithuanian monarch bore the title of Grand duke, Grand Duke, with the exception of Mindaugas, who was crown ...
), who had intervened in a war between Bishop William
William is a masculine given name of Germanic languages, Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman Conquest, Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle ...
of Riga and the Brothers in 1557. After coming to an agreement with Sigismund II Augustus and his representatives (especially Mikołaj "the Black" Radziwiłł), the last Livonian Master, Gotthard Kettler
Gotthard Kettler, Duke of Courland (also ''Godert'', ''Ketteler''; ; ; ; 2 February 1517 – 17 May 1587) was the last Master of the Livonian Order from 1559 to 1561 and the first Duchy of Courland and Semigallia, Duke of Courland and Semigallia f ...
, secularized the Order and converted to Lutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
. In the southern part of the Brothers' lands, he set up the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia
The Duchy of Courland and Semigallia was a duchy in the Baltic states, Baltic region, then known as Livonia, that existed from 1561 to 1569 as a nominal vassal state of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and subsequently made part of the Crown of th ...
for his family. Most of the remaining lands were seized by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, ...
. Denmark and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
re-occupied the north of Estonia.
Duchy of Livonia (1561–1621)
In 1561, during theLivonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) concerned control of Terra Mariana, Old Livonia (in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia). The Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of the Denmark–Norway, Dano-Norwegian Realm, the Kingdom ...
, Livonia fell to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, ...
and became a dependent vassal of Lithuania. Eight years later, in 1569, when the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland formed the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
, Livonia became a joint domain administered directly by the king and grand duke.
Having rejected peace proposals from its enemies, Ivan the Terrible
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (; – ), commonly known as Ivan the Terrible,; ; monastic name: Jonah. was Grand Prince of Moscow, Grand Prince of Moscow and all Russia from 1533 to 1547, and the first Tsar of all Russia, Tsar and Grand Prince of all R ...
found himself in a difficult position by 1579, when Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate, self-defined as the Throne of Crimea and Desht-i Kipchak, and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary, was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the longest-lived of th ...
devastated Muscovian territories and burnt down Moscow (see Russo-Crimean Wars), the drought and epidemics
An epidemic (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of Host (biology), hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example ...
have fatally affected the economy, Oprichnina had thoroughly disrupted the government, while The Grand Principality of Lithuania had united with The Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland (; ) was a political and legal concept formed in the 14th century in the Kingdom of Poland, assuming unity, indivisibility and continuity of the state. Under this idea, the state was no longer seen as the Pat ...
and acquired an energetic leader, Stefan Batory, supported by Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
(1576). Stefan Batory replied with a series of three offensives against Muscovy, trying to cut The Kingdom of Livonia from Muscovian territories. During his first offensive in 1579, with 22,000 men, he retook Polotsk
Polotsk () or Polatsk () is a town in Vitebsk Region, Belarus. It is situated on the Dvina River and serves as the administrative center of Polotsk District. Polotsk is served by Polotsk Airport and Borovitsy air base. As of 2025, it has a pop ...
; during the second, in 1580, with 29,000-strong army, he took Velikie Luki, and in 1581 with a 100,000-strong army he started the Siege of Pskov. Frederick II of Denmark and Norway had trouble continuing the fight against Muscovy unlike Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
and Poland. He came to an agreement with John III in 1580, giving him the titles in Livonia. That war would last from 1577 to 1582. Muscovy recognized Polish–Lithuanian control of Ducatus Ultradunensis only in 1582. After Magnus von Lyffland died in 1583, Poland invaded his territories in The Duchy of Courland, and Frederick II decided to sell his rights of inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Offi ...
. Except for the island of Œsel
Saaremaa (; ) is the largest and most populous island in Estonia. Measuring , its population is 31,435 (as of January 2020). The main island of the West Estonian archipelago (Moonsund archipelago), it is located in the Baltic Sea, south of Hiiu ...
, Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
was out of the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
by 1585. As of 1598 Inflanty Voivodeship
The Inflanty Voivodeship (), or Livonian Voivodeship (), also known as Polish Livonia, was an administrative division and local government in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, since it was formed in the 1620s out of the Wenden Voivodeship and ...
was divided onto:
* Wenden Voivodeship
Wenden Voivodeship (, ) was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Duchy of Livonia, part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was formed in 1598 by King Sigismund III Vasa, out of Wenden Presidency (Province), whi ...
(''województwo wendeńskie'', Kieś)
* Dorpat Voivodeship (''województwo dorpackie'', Dorpat
Tartu is the second largest city in Estonia after Tallinn. Tartu has a population of 97,759 (as of 2024). It is southeast of Tallinn and 245 kilometres (152 miles) northeast of Riga, Latvia. Tartu lies on the Emajõgi river, which connects the ...
)
* Parnawa Voivodeship (''województwo parnawskie'', Parnawa)
Based on a guarantee by Sigismund II Augustus from the 1560s, the German language retained its official status.
Kingdom of Livonia (1570–1578)
 The armies of
The armies of Ivan the Terrible
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (; – ), commonly known as Ivan the Terrible,; ; monastic name: Jonah. was Grand Prince of Moscow, Grand Prince of Moscow and all Russia from 1533 to 1547, and the first Tsar of all Russia, Tsar and Grand Prince of all R ...
were initially successful, taking Polotsk
Polotsk () or Polatsk () is a town in Vitebsk Region, Belarus. It is situated on the Dvina River and serves as the administrative center of Polotsk District. Polotsk is served by Polotsk Airport and Borovitsy air base. As of 2025, it has a pop ...
(1563) and Parnawa (1575) and overrunning much of Grand Duchy of Lithuania up to some proximity of Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
. Eventually, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Kingdom of Poland formed the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
in 1569 under the Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin (; ) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the personal union of the Crown of the Kingd ...
. Eric XIV of Sweden did not like this, and the Northern Seven Years' War
The Northern Seven Years' War (also known as the ''Nordic Seven Years' War'', the ''First Northern War,'' the ''Seven Years' War of the North'' or the ''Seven Years War in Scandinavia'') was fought between the Kingdom of Sweden (1523–1611), K ...
between the Free City of Lübeck, Denmark, Poland, and Sweden broke out. While only losing land and trade, Frederick II of Denmark
Frederick II (1 July 1534 – 4 April 1588) was King of Denmark-Norway, Denmark and Norway and Duke of Duchy of Schleswig, Schleswig and Duchy of Holstein, Holstein from 1559 until his death in 1588.
A member of the House of Oldenburg, Fre ...
and Magnus von Lyffland of the Œsel-Wiek did not fare well. But, in 1569, Erik XIV became insane and his brother John III of Sweden took his place. After all parties had been financially drained, Frederick II let his ally, King Zygmunt II August, know that he was ready for peace. On 15 December 1570, the Treaty of Stettin was concluded.
In the next phase of the conflict, in 1577, Ivan IV took advantage of the Commonwealth's internal strife (called the war against Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdań ...
in Polish historiography), and during the reign of Stefan Batory in Poland, invaded Livonia, quickly taking almost the entire territory, with the exception of Riga
Riga ( ) is the capital, Primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Latvia, largest city of Latvia. Home to 591,882 inhabitants (as of 2025), the city accounts for a third of Latvia's total population. The population of Riga Planni ...
and Reval. In 1578, Magnus of Livonia recognized the sovereignty
Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within a state as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate au ...
of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (not ratified by the Sejm
The Sejm (), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland (), is the lower house of the bicameralism, bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of the Third Polish Republic since the Polish People' ...
of Poland-Lithuania, nor recognized by Denmark). The Kingdom of Livonia was beaten back by Muscovy on all fronts. In 1578, Magnus of Livonia retired to The Bishopric of Courland, and his brother all but gave up the land in Livonia.
Swedish Livonia (1629–1721)
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
was given roughly the same area as the former Duchy of Livonia after the 1626–1629 Polish–Swedish War
This is a List of wars between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Sweden. Broadly construed, the term refers to a series of wars between 1562 and 1814. More narrowly, it refers to particular wars between 1600 and 1629. These are the wars ...
. The area, usually known as Swedish Livonia
Swedish Livonia () was a dominion of the Swedish Empire from 1629 until 1721. The territory, which constituted the southern part of modern Estonia (including the island of Ösel ceded by Denmark after the Treaty of Brömsebro) and the northe ...
, became a very important Swedish dominion, with Riga being the second largest Swedish city and Livonia paying for one third of the Swedish war costs. Sweden lost Swedish Livonia, Duchy of Estonia and Swedish Ingria
Swedish Ingria (, ‘land of Ingrians’) was a dominion of the Swedish Empire from 1583 to 1595 and then again from 1617 to 1721 in what is now the territory of Russia. At the latter date, it was ceded to the Russian Empire in the Treaty of Ny ...
to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
almost 100 years later, by the Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia in 1710 and the Treaty of Nystad in 1721.
Livonian Voivodeship (1620s–1772)
Duchy of Livonia
The Duchy of Livonia, also referred to as Polish Livonia or Livonia, was a territory of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and later the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that existed from 1561 to 1621. It corresponds to the present-day areas of northe ...
, part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
, since it was formed in the 1620s out of the Wenden Voivodeship
Wenden Voivodeship (, ) was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Duchy of Livonia, part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was formed in 1598 by King Sigismund III Vasa, out of Wenden Presidency (Province), whi ...
till the First Partition of Poland
The First Partition of Poland took place in 1772 as the first of three partitions that eventually ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. The growth of power in the Russian Empire threatened the Kingdom of Prussia an ...
in 1772.
Riga Governorate (1721–1796)
TheRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
conquered Swedish Livonia during the course of the Great Northern War
In the Great Northern War (1700–1721) a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern Europe, Northern, Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the ant ...
and acquired the province in the Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia in 1710, confirmed by the Treaty of Nystad in 1721. Peter the Great confirmed German as the exclusive official language. Russia then added Polish Livonia in 1772 during the Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partition (politics), partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place between 1772 and 1795, toward the end of the 18th century. They ended the existence of the state, resulting in the eli ...
.
Governorate of Livonia (1796–1918)
 In 1796, the Riga Governorate was renamed as the Governorate of Livonia ( / , , ). From 1845 to 1876, the Baltic governorates of
In 1796, the Riga Governorate was renamed as the Governorate of Livonia ( / , , ). From 1845 to 1876, the Baltic governorates of Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
, Livonia, and Courland — an area roughly corresponding to the historical medieval Livonia — were administratively subordinated to a common Governor-General
Governor-general (plural governors-general), or governor general (plural governors general), is the title of an official, most prominently associated with the British Empire. In the context of the governors-general and former British colonies, ...
. Amongst the holders of this post were Count Alexander Arkadyevich Suvorov/ref> and Count Pyotr Andreyevich Shuvalov. Livonia remained within the Russian Empire until the end of
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, when it was split between the newly independent states of Latvia and Estonia. The United Baltic Duchy
The United Baltic Duchy (; ; ), or alternatively the Grand Duchy of Livonia, was the name of a short-lived state during World War I that was proclaimed by leaders of the local Baltic German nobility.
The attempt to establish a new client state ...
, alternately known as the "Grand Duchy of Livonia", proclaimed by the Baltic German nobility on 12 April 1918, was never recognised by any state, and dissolved at the German surrender in November 1918. Livonia had ceased to exist. From 1918 to 1920, both Soviet troops and German Freikorps
(, "Free Corps" or "Volunteer Corps") were irregular German and other European paramilitary volunteer units that existed from the 18th to the early 20th centuries. They effectively fought as mercenaries or private military companies, rega ...
fought against Latvian and Estonian troops for control over former Livonia, but their attempts were defeated.
Legacy
The historical land of Livonia has been split betweenLatvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
and Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
ever since 1918. The Livonian language
Livonian ( or ) is a Finnic language whose native land is the Livonian Coast of the Gulf of Riga, located in the north of the Kurzeme peninsula in Latvia but also used to be spoken in the Salaca River valley. Although its last known native ...
is spoken by fewer than 100 individuals as a second language, and is understood to be fast approaching extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
. The last native Livonian speaker died in June 2013.
The unofficial anthem of the Livonians, " Min izāmō", shares the melody of the Finnish and Estonian national anthem
A national anthem is a patriotic musical composition symbolizing and evoking eulogies of the history and traditions of a country or nation. The majority of national anthems are marches or hymns in style. American, Central Asian, and European ...
s.
See also
Gallery
Notes
References
Bibliography
* **Further reading
*Les pays baltiques, le pluriculturalisme en héritage
', Yves Plasseraud; Armeline, 2020. *
Les Germano-baltes
', Yves Plasseraud; S. Pourchier-Plasseraud; Armeline, 2022.
External links
Virtual Livonia
Joann Portantiuse Liivimaa kaart 1573. aastast
the English version includes the description of 438 well-preserved historical manors of nowadays Estonia (historically – northern part of Old-Livonia/Alt-Livland)
''Atlas of Livonia, or of the Two Governments and Duchies Livonia and Estonia, and of the Province of Oesel''
from the
World Digital Library
The World Digital Library (WDL) is an international digital library operated by UNESCO and the United States Library of Congress.
The WDL has stated that its mission is to promote international and intercultural understanding, expand the volume ...
{{Authority control
Geography of Latvia
Historical regions
Historical regions in Latvia
Historical regions in Estonia