Interstate Highways on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, or the Eisenhower Interstate System, is a network of

 The United States government's efforts to construct a national network of highways began on an ''ad hoc'' basis with the passage of the Federal Aid Road Act of 1916, which provided $75 million over a five-year period for matching funds to the states for the construction and improvement of highways. The nation's revenue needs associated with
The United States government's efforts to construct a national network of highways began on an ''ad hoc'' basis with the passage of the Federal Aid Road Act of 1916, which provided $75 million over a five-year period for matching funds to the states for the construction and improvement of highways. The nation's revenue needs associated with
 Some sections of highways that became part of the Interstate Highway System actually began construction earlier.
Three states have claimed the title of first Interstate Highway. Missouri claims that the first three contracts under the new program were signed in Missouri on August 2, 1956. The first contract signed was for upgrading a section of US Route 66 to what is now designated Interstate 44. On August 13, 1956, work began on US 40 (now I-70) in St. Charles County.
Kansas claims that it was the first to start paving after the act was signed. Preliminary construction had taken place before the act was signed, and paving started September 26, 1956. The state marked its portion of I-70 as the first project in the United States completed under the provisions of the new Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956.
The Pennsylvania Turnpike could also be considered one of the first Interstate Highways, and is nicknamed "Grandfather of the Interstate System". On October 1, 1940, of the highway now designated I‑70 and I‑76 opened between Irwin and
Some sections of highways that became part of the Interstate Highway System actually began construction earlier.
Three states have claimed the title of first Interstate Highway. Missouri claims that the first three contracts under the new program were signed in Missouri on August 2, 1956. The first contract signed was for upgrading a section of US Route 66 to what is now designated Interstate 44. On August 13, 1956, work began on US 40 (now I-70) in St. Charles County.
Kansas claims that it was the first to start paving after the act was signed. Preliminary construction had taken place before the act was signed, and paving started September 26, 1956. The state marked its portion of I-70 as the first project in the United States completed under the provisions of the new Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956.
The Pennsylvania Turnpike could also be considered one of the first Interstate Highways, and is nicknamed "Grandfather of the Interstate System". On October 1, 1940, of the highway now designated I‑70 and I‑76 opened between Irwin and
 The system was proclaimed complete in 1992, but two of the original Interstates— I-95 and I-70—were not continuous: both of these discontinuities were due to local opposition, which blocked efforts to build the necessary connections to fully complete the system. I-95 was made a continuous freeway in 2018, and thus I-70 remains the only original Interstate with a discontinuity.
I-95 was discontinuous in New Jersey because of the cancellation of the Somerset Freeway. This situation was remedied when the construction of the Pennsylvania Turnpike/Interstate 95 Interchange Project started in 2010 and partially opened on September 22, 2018, which was already enough to fill the gap.
However, I-70 remains discontinuous in
The system was proclaimed complete in 1992, but two of the original Interstates— I-95 and I-70—were not continuous: both of these discontinuities were due to local opposition, which blocked efforts to build the necessary connections to fully complete the system. I-95 was made a continuous freeway in 2018, and thus I-70 remains the only original Interstate with a discontinuity.
I-95 was discontinuous in New Jersey because of the cancellation of the Somerset Freeway. This situation was remedied when the construction of the Pennsylvania Turnpike/Interstate 95 Interchange Project started in 2010 and partially opened on September 22, 2018, which was already enough to fill the gap.
However, I-70 remains discontinuous in
 Political opposition from residents canceled many freeway projects around the United States, including:
* I-40 in Memphis, Tennessee was rerouted and part of the original I-40 is still in use as the eastern half of Sam Cooper Boulevard.
* I-66 in the
Political opposition from residents canceled many freeway projects around the United States, including:
* I-40 in Memphis, Tennessee was rerouted and part of the original I-40 is still in use as the eastern half of Sam Cooper Boulevard.
* I-66 in the
 The numbering scheme for the Interstate Highway System was developed in 1957 by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO). The association's present numbering policy dates back to August 10, 1973. Within the contiguous United States, primary Interstates—also called main line Interstates or two-digit Interstates—are assigned numbers less than 100.
While numerous exceptions do exist, there is a general scheme for numbering Interstates. Primary Interstates are assigned one- or two-digit numbers, while shorter routes (such as spurs, loops, and short connecting roads) are assigned three-digit numbers where the last two digits match the parent route (thus, I-294 is a loop that connects at both ends to I-94, while I-787 is a short spur route attached to I-87). In the numbering scheme for the primary routes, east–west highways are assigned even numbers and north–south highways are assigned odd numbers. Odd route numbers increase from west to east, and even-numbered routes increase from south to north (to avoid confusion with the US Highways, which increase from east to west and north to south). This numbering system usually holds true even if the local direction of the route does not match the compass directions. Numbers
The numbering scheme for the Interstate Highway System was developed in 1957 by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO). The association's present numbering policy dates back to August 10, 1973. Within the contiguous United States, primary Interstates—also called main line Interstates or two-digit Interstates—are assigned numbers less than 100.
While numerous exceptions do exist, there is a general scheme for numbering Interstates. Primary Interstates are assigned one- or two-digit numbers, while shorter routes (such as spurs, loops, and short connecting roads) are assigned three-digit numbers where the last two digits match the parent route (thus, I-294 is a loop that connects at both ends to I-94, while I-787 is a short spur route attached to I-87). In the numbering scheme for the primary routes, east–west highways are assigned even numbers and north–south highways are assigned odd numbers. Odd route numbers increase from west to east, and even-numbered routes increase from south to north (to avoid confusion with the US Highways, which increase from east to west and north to south). This numbering system usually holds true even if the local direction of the route does not match the compass directions. Numbers
 Auxiliary Interstate Highways are circumferential, radial, or spur highways that principally serve
Auxiliary Interstate Highways are circumferential, radial, or spur highways that principally serve

 The Interstate Highway System also extends to
The Interstate Highway System also extends to
 Interstate Highways and their rights-of-way are owned by the state in which they were built. The last federally owned portion of the Interstate System was the Woodrow Wilson Bridge on the Washington Capital Beltway. The new bridge was completed in 2009 and is collectively owned by Virginia and Maryland. Maintenance is generally the responsibility of the state department of transportation. However, there are some segments of Interstate owned and maintained by local authorities.
Interstate Highways and their rights-of-way are owned by the state in which they were built. The last federally owned portion of the Interstate System was the Woodrow Wilson Bridge on the Washington Capital Beltway. The new bridge was completed in 2009 and is collectively owned by Virginia and Maryland. Maintenance is generally the responsibility of the state department of transportation. However, there are some segments of Interstate owned and maintained by local authorities.
 Interstate Highways are signed by a number placed on a red, white, and blue sign. The shield design itself is a registered trademark of the
Interstate Highways are signed by a number placed on a red, white, and blue sign. The shield design itself is a registered trademark of the
Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways
Federal Highway Administration (FHWA)
Route Log and Finder List
FHWA
State-by-state maps of the National Highway System
of the FHWA include Interstate highways
Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center
FHWA
Interstate Highway System
Dwight D. Eisenhower Presidential Library and Museum
''NOW'' on PBS {{Authority control 1956 establishments in the United States Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower Transport systems Types of roads
controlled-access highway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway, and expressway. Other similar terms ...
s that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. The system extends throughout the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The te ...
and has routes in Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
, and Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
.
In the 20th century, the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, ...
began funding roadways through the Federal Aid Road Act of 1916, and started an effort to construct a national road grid with the passage of the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1921. In 1926, the United States Numbered Highway System
The United States Numbered Highway System (often called U.S. Routes or U.S. Highways) is an integrated network of roads and highways numbered within a nationwide grid in the contiguous United States. As the designation and numbering of these ...
was established, creating the first national road numbering system for cross-country travel. The roads were funded and maintained by U.S. states, and there were few national standards for road design. United States Numbered Highways ranged from two-lane country roads to multi-lane freeways. After Dwight D. Eisenhower became president in 1953, his administration developed a proposal for an interstate highway system, eventually resulting in the enactment of the Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956.
Unlike the earlier United States Numbered Highway System, the interstates were designed to be all freeways, with nationally unified standards for construction and signage. While some older freeways were adopted into the system, most of the routes were completely new. In dense urban areas, the choice of routing destroyed many well-established neighborhoods, often intentionally as part of a program of "urban renewal
Urban renewal (sometimes called urban regeneration in the United Kingdom and urban redevelopment in the United States) is a program of land redevelopment often used to address real or perceived urban decay. Urban renewal involves the clearing ...
". In the two decades following the 1956 Highway Act, the construction of the freeways displaced one million people, and as a result of the many freeway revolts during this era, several planned Interstates were abandoned or re-routed to avoid urban cores.
Construction of the original Interstate Highway System was proclaimed complete in 1992, despite deviations from the original 1956 plan and several stretches that did not fully conform with federal standards. The construction of the Interstate Highway System cost approximately $114 billion (equivalent to $ in ). The system has continued to expand and grow as additional federal funding has provided for new routes to be added, and many future Interstate Highways are currently either being planned or under construction.
Though heavily funded by the federal government, Interstate Highways are owned by the state in which they were built. With few exceptions, all Interstates must meet specific standards, such as having controlled access, physical barriers or median strip
A median strip, central reservation, roadway median, or traffic median is the reserved area that separates opposing lanes of traffic on divided roadways such as divided highways, dual carriageways, controlled-access highway, freeways, and moto ...
s between lanes of oncoming traffic, breakdown lanes, avoiding at-grade intersections, no traffic light
Traffic lights, traffic signals, or stoplights – also known as robots in South Africa, Zambia, and Namibia – are signaling devices positioned at intersection (road), road intersections, pedestrian crossings, and other locations in order t ...
s, and complying with federal traffic sign
Traffic signs or road signs are signs erected at the side of or above roads to give instructions or provide information to road users. The earliest signs were simple wooden or stone milestones. Later, signs with directional arms were introduc ...
specifications. Interstate Highways use a numbering scheme in which primary Interstates are assigned one- or two-digit numbers, and shorter routes which branch off from longer ones are assigned three-digit numbers where the last two digits match the parent route. The Interstate Highway System is partially financed through the Highway Trust Fund, which itself is funded by a combination of a federal fuel tax and transfers from the Treasury's general fund. Though federal legislation initially banned the collection of tolls, some Interstate routes are toll road
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road for which a fee (or ''Toll (fee), toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically implemented to help recoup the costs of road construction and ...
s, either because they were grandfathered into the system or because subsequent legislation has allowed for tolling of Interstates in some cases.
, about one quarter of all vehicle miles driven in the country used the Interstate Highway System, which has a total length of . In 2022 and 2023, the number of fatalities on the Interstate Highway System amounted to more than 5,000 people annually, with nearly 5,600 fatalities in 2022.
History
Planning

 The United States government's efforts to construct a national network of highways began on an ''ad hoc'' basis with the passage of the Federal Aid Road Act of 1916, which provided $75 million over a five-year period for matching funds to the states for the construction and improvement of highways. The nation's revenue needs associated with
The United States government's efforts to construct a national network of highways began on an ''ad hoc'' basis with the passage of the Federal Aid Road Act of 1916, which provided $75 million over a five-year period for matching funds to the states for the construction and improvement of highways. The nation's revenue needs associated with World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
prevented any significant implementation of this policy, which expired in 1921.
In December 1918, E. J. Mehren, a civil engineer and the editor of ''Engineering News-Record
The ''Engineering News-Record'' (widely known as ''ENR'') is an American weekly magazine that provides news, analysis, data and opinion for the construction industry worldwide. It is widely regarded as one of the construction industry's most au ...
'', presented his "A Suggested National Highway Policy and Plan" during a gathering of the State Highway Officials and Highway Industries Association at the Congress Hotel in Chicago. In the plan, Mehren proposed a system, consisting of five east–west routes and 10 north–south routes. The system would include two percent of all roads and would pass through every state at a cost of , providing commercial as well as military transport benefits.
In 1919, the US Army sent an expedition across the US to determine the difficulties that military vehicles would have on a cross-country trip. Leaving from the Ellipse near the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. Located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue Northwest (Washington, D.C.), NW in Washington, D.C., it has served as the residence of every U.S. president ...
on July 7, the Motor Transport Corps convoy needed 62 days to drive on the Lincoln Highway to the Presidio of San Francisco along the Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by ...
. The convoy suffered many setbacks and problems on the route, such as poor-quality bridges, broken crankshafts, and engines clogged with desert sand.
Dwight Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was the 34th president of the United States, serving from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, he was Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionar ...
, then a 28-year-old brevet lieutenant colonel, accompanied the trip "through darkest America with truck and tank," as he later described it. Some roads in the West were a "succession of dust, ruts, pits, and holes."
As the landmark 1916 law expired, new legislation was passed—the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1921 (Phipps Act). This new road construction initiative once again provided for federal matching funds for road construction and improvement, $75 million allocated annually. Moreover, this new legislation for the first time sought to target these funds to the construction of a national road grid of interconnected "primary highways", setting up cooperation among the various state highway planning boards.
The Bureau of Public Roads
The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) is a division of the United States Department of Transportation that specializes in highway transportation. The agency's major activities are grouped into two programs, the Federal-aid Highway Program a ...
asked the Army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
to provide a list of roads that it considered necessary for national defense. In 1922, General John J. Pershing, former head of the American Expeditionary Force
The American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) was a formation of the United States Armed Forces on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front during World War I, composed mostly of units from the United States Army, U.S. Army. The AEF was establis ...
in Europe during the war, complied by submitting a detailed network of of interconnected primary highways—the so-called Pershing Map.
A boom in road construction followed throughout the decade of the 1920s, with such projects as the New York parkway system constructed as part of a new national highway system. As automobile traffic increased, planners saw a need for such an interconnected national system to supplement the existing, largely non-freeway, United States Numbered Highways system. By the late 1930s, planning had expanded to a system of new superhighways.
In 1938, President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
gave Thomas MacDonald, chief at the Bureau of Public Roads, a hand-drawn map of the United States marked with eight superhighway corridors for study. In 1939, Bureau of Public Roads Division of Information chief Herbert S. Fairbank wrote a report called ''Toll Roads and Free Roads'', "the first formal description of what became the Interstate Highway System" and, in 1944, the similarly themed ''Interregional Highways''.
Federal Aid Highway Act of 1956
The Interstate Highway System gained a champion in President Dwight D. Eisenhower, who was influenced by his experiences as a young Army officer crossing the country in the 1919 Motor Transport Corps convoy that drove in part on the Lincoln Highway, the first road across America. He recalled that, "The old convoy had started me thinking about good two-lane highways... the wisdom of broader ribbons across our land." Eisenhower also gained an appreciation of the Reichsautobahn system, the first "national" implementation of modern Germany'sAutobahn
The (; German , ) is the federal controlled-access highway system in Germany. The official term is (abbreviated ''BAB''), which translates as 'federal motorway'. The literal meaning of the word is 'Federal Auto(mobile) Track'.
Much of t ...
network, as a necessary component of a national defense system while he was serving as Supreme Commander of Allied Forces in Europe during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. In 1954, Eisenhower appointed General Lucius D. Clay to head a committee charged with proposing an interstate highway system plan. Summing up motivations for the construction of such a system, Clay stated,
Clay's committee proposed a 10-year, $100 billion program , which would build of divided highways linking all American cities with a population of greater than 50,000. Eisenhower initially preferred a system consisting of toll road
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road for which a fee (or ''Toll (fee), toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically implemented to help recoup the costs of road construction and ...
s, but Clay convinced Eisenhower that toll roads were not feasible outside of the highly populated coastal regions. In February 1955, Eisenhower forwarded Clay's proposal to Congress. The bill quickly won approval in the Senate, but House Democrats objected to the use of public bonds as the means to finance construction. Eisenhower and the House Democrats agreed to instead finance the system through the Highway Trust Fund, which itself would be funded by a gasoline
Gasoline ( North American English) or petrol ( Commonwealth English) is a petrochemical product characterized as a transparent, yellowish, and flammable liquid normally used as a fuel for spark-ignited internal combustion engines. When for ...
tax. In June 1956, Eisenhower signed the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1956 into law. Under the act, the federal government would pay for 90 percent of the cost of construction of Interstate Highways. Each Interstate Highway was required to be a freeway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway, and expressway. Other similar terms ...
with at least four lanes and no at-grade crossings.
The publication in 1955 of the ''General Location of National System of Interstate Highways'', informally known as the ''Yellow Book'', mapped out what became the Interstate Highway System. Assisting in the planning was Charles Erwin Wilson, who was still head of General Motors
General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. The company is most known for owning and manufacturing f ...
when President Eisenhower selected him as Secretary of Defense in January 1953.
Construction
 Some sections of highways that became part of the Interstate Highway System actually began construction earlier.
Three states have claimed the title of first Interstate Highway. Missouri claims that the first three contracts under the new program were signed in Missouri on August 2, 1956. The first contract signed was for upgrading a section of US Route 66 to what is now designated Interstate 44. On August 13, 1956, work began on US 40 (now I-70) in St. Charles County.
Kansas claims that it was the first to start paving after the act was signed. Preliminary construction had taken place before the act was signed, and paving started September 26, 1956. The state marked its portion of I-70 as the first project in the United States completed under the provisions of the new Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956.
The Pennsylvania Turnpike could also be considered one of the first Interstate Highways, and is nicknamed "Grandfather of the Interstate System". On October 1, 1940, of the highway now designated I‑70 and I‑76 opened between Irwin and
Some sections of highways that became part of the Interstate Highway System actually began construction earlier.
Three states have claimed the title of first Interstate Highway. Missouri claims that the first three contracts under the new program were signed in Missouri on August 2, 1956. The first contract signed was for upgrading a section of US Route 66 to what is now designated Interstate 44. On August 13, 1956, work began on US 40 (now I-70) in St. Charles County.
Kansas claims that it was the first to start paving after the act was signed. Preliminary construction had taken place before the act was signed, and paving started September 26, 1956. The state marked its portion of I-70 as the first project in the United States completed under the provisions of the new Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956.
The Pennsylvania Turnpike could also be considered one of the first Interstate Highways, and is nicknamed "Grandfather of the Interstate System". On October 1, 1940, of the highway now designated I‑70 and I‑76 opened between Irwin and Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from ) is a city in the Cumberland district of Cumbria, England.
Carlisle's early history is marked by the establishment of a settlement called Luguvalium to serve forts along Hadrian's Wall in Roman Britain. Due to its pro ...
. The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Maryland to its south, West ...
refers to the turnpike as the Granddaddy of the Pikes, a reference to turnpikes.
Milestones in the construction of the Interstate Highway System include:
* October 17, 1974: Nebraska
Nebraska ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Ka ...
becomes the first state to complete all of its mainline Interstate Highways with the dedication of its final piece of I-80.
* October 12, 1979: The final section of the Canada to Mexico freeway Interstate 5
Interstate 5 (I-5) is the main north–south Interstate Highway System, Interstate Highway on the West Coast of the United States, running largely parallel to the Pacific coast of the contiguous U.S. from Mexico to Canada. It travels thro ...
is dedicated near Stockton, California
Stockton is a city in and the county seat of San Joaquin County, California, San Joaquin County in the Central Valley (California), Central Valley of the U.S. state of California. It is the most populous city in the county, the List of municipal ...
. Representatives of the two neighboring nations attended the dedication to commemorate the first contiguous freeway connecting the North American countries.
* August 22, 1986: The final section of the coast-to-coast I-80 (San Francisco, California
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
, to Teaneck, New Jersey
Teaneck () is a Township (New Jersey), township in Bergen County, New Jersey, Bergen County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. It is a bedroom community in the New York metropolitan area. The town is know for their pancake throwing contest held ...
) is dedicated on the western edge of Salt Lake City, Utah
Salt Lake City, often shortened to Salt Lake or SLC, is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of cities and towns in Utah, most populous city of the U.S. state of Utah. It is the county seat of Salt Lake County, Utah, Salt ...
, making I-80 the world's first contiguous freeway to span from the Atlantic to Pacific Ocean and, at the time, the longest contiguous freeway in the world. The section spanned from Redwood Road to just west of the Salt Lake City International Airport. At the dedication it was noted that coincidentally this was only from Promontory Summit, where a similar feat was accomplished nearly 120 years prior, the driving of the golden spike
The golden spike (also known as the last spike) is the ceremonial 17.6-Carat (purity), karat gold final Rail spike, spike driven by Leland Stanford to join the rails of the first transcontinental railroad across the United States connecting t ...
of the United States' First transcontinental railroad
America's first transcontinental railroad (known originally as the "Pacific Railroad" and later as the "Overland Route (Union Pacific Railroad), Overland Route") was a continuous railroad line built between 1863 and 1869 that connected the exis ...
.
* August 10, 1990: The final section of coast-to-coast I-10 (Santa Monica, California
Santa Monica (; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Santa Mónica'') is a city in Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles County, situated along Santa Monica Bay on California's South Coast (California), South Coast. Santa Monica's 2020 United Sta ...
, to Jacksonville, Florida
Jacksonville ( ) is the most populous city proper in the U.S. state of Florida, located on the Atlantic coast of North Florida, northeastern Florida. It is the county seat of Duval County, Florida, Duval County, with which the City of Jacksonv ...
) is dedicated, the Papago Freeway Tunnel under downtown Phoenix, Arizona
Phoenix ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of cities and towns in Arizona#List of cities and towns, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arizona. With over 1.6 million residents at the 2020 census, it is the ...
. Completion of this section was delayed due to a freeway revolt that forced the cancellation of an originally planned elevated routing.
* September 12, 1991: I-90 becomes the final coast-to-coast Interstate Highway (Seattle, Washington
Seattle ( ) is the List of municipalities in Washington, most populous city in the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington and in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. With a population of 780,995 in 2024, it is the List of Unit ...
to Boston, Massachusetts
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
) to be completed with the dedication of an elevated viaduct
A viaduct is a specific type of bridge that consists of a series of arches, piers or columns supporting a long elevated railway or road. Typically a viaduct connects two points of roughly equal elevation, allowing direct overpass across a wide ...
bypassing Wallace, Idaho
Wallace, Idaho is a city in and the county seat of Shoshone County, Idaho, Shoshone County, Idaho, in the Silver Valley (Idaho), Silver Valley mining district of the Idaho Panhandle. Founded in 1884, Wallace sits alongside the South Fork of the C ...
, which opened a week earlier. This section was delayed after residents forced the cancellation of the originally planned at-grade alignment that would have demolished much of downtown Wallace. The residents accomplished this feat by arranging for most of the downtown area to be declared a historic district
A historic district or heritage district is a section of a city which contains historic building, older buildings considered valuable for historical or architectural reasons. In some countries or jurisdictions, historic districts receive legal p ...
and listed on the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government's official United States National Register of Historic Places listings, list of sites, buildings, structures, Hist ...
; this succeeded in blocking the path of the original alignment. Two days after the dedication residents held a mock funeral celebrating the removal of the last stoplight on a transcontinental Interstate Highway.
* October 14, 1992: The original Interstate Highway System is proclaimed to be complete with the opening of I-70 through Glenwood Canyon in Colorado
Colorado is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States. It is one of the Mountain states, sharing the Four Corners region with Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah. It is also bordered by Wyoming to the north, Nebraska to the northeast, Kansas ...
. This section is considered an engineering marvel with a span featuring 40 bridges and numerous tunnels and is one of the most expensive rural highways per mile built in the United States.
The initial cost estimate for the system was $25 billion over 12 years; it ended up costing $114 billion (equivalent to $425 billion in 2006 or $ in ) and took 35 years.
1992–present
Discontinuities
 The system was proclaimed complete in 1992, but two of the original Interstates— I-95 and I-70—were not continuous: both of these discontinuities were due to local opposition, which blocked efforts to build the necessary connections to fully complete the system. I-95 was made a continuous freeway in 2018, and thus I-70 remains the only original Interstate with a discontinuity.
I-95 was discontinuous in New Jersey because of the cancellation of the Somerset Freeway. This situation was remedied when the construction of the Pennsylvania Turnpike/Interstate 95 Interchange Project started in 2010 and partially opened on September 22, 2018, which was already enough to fill the gap.
However, I-70 remains discontinuous in
The system was proclaimed complete in 1992, but two of the original Interstates— I-95 and I-70—were not continuous: both of these discontinuities were due to local opposition, which blocked efforts to build the necessary connections to fully complete the system. I-95 was made a continuous freeway in 2018, and thus I-70 remains the only original Interstate with a discontinuity.
I-95 was discontinuous in New Jersey because of the cancellation of the Somerset Freeway. This situation was remedied when the construction of the Pennsylvania Turnpike/Interstate 95 Interchange Project started in 2010 and partially opened on September 22, 2018, which was already enough to fill the gap.
However, I-70 remains discontinuous in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, because of the lack of a direct interchange with the Pennsylvania Turnpike at the eastern end of the concurrency near Breezewood. Traveling in either direction, I-70 traffic must exit the freeway and use a short stretch of US 30 (which includes a number of roadside services) to rejoin I-70. The interchange was not originally built because of a legacy federal funding rule, since relaxed, which restricted the use of federal funds to improve roads financed with tolls. Solutions have been proposed to eliminate the discontinuity, but they have been blocked by local opposition, fearing a loss of business.
Expansions and removals
The Interstate Highway System has been expanded numerous times. The expansions have both created new designations and extended existing designations. For example, I-49, added to the system in the 1980s as a freeway inLouisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, was designated as an expansion corridor, and FHWA approved the expanded route north from Lafayette, Louisiana
Lafayette ( , ) is the most populous city in and parish seat of Lafayette Parish, Louisiana, Lafayette Parish in the U.S. state of Louisiana, located along the Vermilion River (Louisiana), Vermilion River. It is Louisiana's List of municipaliti ...
, to Kansas City, Missouri
Kansas City, Missouri, abbreviated KC or KCMO, is the largest city in the U.S. state of Missouri by List of cities in Missouri, population and area. The city lies within Jackson County, Missouri, Jackson, Clay County, Missouri, Clay, and Pl ...
. The freeway exists today as separate completed segments, with segments under construction or in the planning phase between them.
In 1966, the FHWA designated the entire Interstate Highway System as part of the larger Pan-American Highway
The Pan-American Highway is a vast network of roads that stretches about 30,000 kilometers (about 19,000 miles) from Prudhoe Bay, Alaska, in the northernmost part of North America to Ushuaia, Argentina, at the southern tip of South America. I ...
System, and at least two proposed Interstate expansions were initiated to help trade with Canada and Mexico spurred by the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). Long-term plans for I-69
Interstate 69 (I-69) is an Interstate Highway in the United States currently consisting of eight unconnected segments. The longest segment runs from Evansville, Indiana, northeast to the Canada–United States border, Canadian border in Po ...
, which currently exists in several separate completed segments (the largest of which are in Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
and Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
), is to have the highway route extend from Tamaulipas
Tamaulipas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tamaulipas, is a state in Mexico; one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into 43 municipalities.
It is located in nor ...
, Mexico to Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, Canada. The planned I-11 will then bridge the Interstate gap between Phoenix, Arizona
Phoenix ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of cities and towns in Arizona#List of cities and towns, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arizona. With over 1.6 million residents at the 2020 census, it is the ...
and Las Vegas, Nevada
Las Vegas, colloquially referred to as Vegas, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Nevada and the county seat of Clark County. The Las Vegas Valley metropolitan area is the largest within the greater Mojave Desert, and second-l ...
, and thus form part of the CANAMEX Corridor (along with I-19, and portions of I-10 and I-15) between Sonora
Sonora (), officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sonora (), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The state is divided into Municipalities of Sonora, 72 ...
, Mexico and Alberta
Alberta is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three Canadian Prairies, prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to its west, Saskatchewan to its east, t ...
, Canada.
Opposition, cancellations, and removals
 Political opposition from residents canceled many freeway projects around the United States, including:
* I-40 in Memphis, Tennessee was rerouted and part of the original I-40 is still in use as the eastern half of Sam Cooper Boulevard.
* I-66 in the
Political opposition from residents canceled many freeway projects around the United States, including:
* I-40 in Memphis, Tennessee was rerouted and part of the original I-40 is still in use as the eastern half of Sam Cooper Boulevard.
* I-66 in the District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
was abandoned in 1977.
* I-69
Interstate 69 (I-69) is an Interstate Highway in the United States currently consisting of eight unconnected segments. The longest segment runs from Evansville, Indiana, northeast to the Canada–United States border, Canadian border in Po ...
was to continue past its terminus at Interstate 465 to intersect with Interstate 70 and Interstate 65 at the north split, northeast of downtown Indianapolis
Indianapolis ( ), colloquially known as Indy, is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Indiana, most populous city of the U.S. state of Indiana and the county seat of Marion County, Indiana, Marion ...
. Though local opposition led to the cancellation of this project in 1981, bridges and ramps for the connection into the "north split" remained until it was rebuilt in 2023.
* I-70 in Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
was supposed to run from the Baltimore Beltway ( Interstate 695), which surrounds the city to terminate at I-95, the East Coast thoroughfare that runs through Maryland and Baltimore on a diagonal course, northeast to southwest; the connection was cancelled on the mid-1970s due to its routing through Gwynns Falls-Leakin Park, a wilderness urban park reserve following the Gwynns Falls stream through West Baltimore. This included the cancellation of I-170, partially built and in use as US 40, and nicknamed the Highway to Nowhere. The freeway stub of I-70 inside the Beltway was renumbered MD 570 in 2014, but continues to bear I-70 signs.
* I-78 in New York City was canceled along with portions of I-278, I-478, and I-878. I-878 was supposed to be part of I-78, and I-478 and I-278 were to be spur routes.
* I-80 in San Francisco was originally planned to travel past the city's Civic Center along the Panhandle Freeway into Golden Gate Park
Golden Gate Park is an urban park between the Richmond District, San Francisco, Richmond and Sunset District, San Francisco, Sunset districts on the West Side (San Francisco), West Side of San Francisco, California, United States. It is the Lis ...
and terminate at the original alignment of I-280/ SR 1. The city canceled this and several other freeways in 1958. Similarly, more than 20 years later, Sacramento canceled plans to upgrade I-80 to Interstate Standards and rerouted the freeway on what was then I-880 that traveled north of Downtown Sacramento.
* I-83, southern extension of the Jones Falls Expressway (southern I-83) in Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
was supposed to run along the waterfront of the Patapsco River
The Patapsco River ( ) mainstem is a river in central Maryland that flows into the Chesapeake Bay. The river's tidal portion forms the harbor for the city of Baltimore. With its South Branch, the Patapsco forms the northern border of Howar ...
/ Baltimore Harbor to connect to I-95, bisecting historic neighborhoods of Fells Point and Canton, but the connection was never built.
* I-84 in Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
was once planned to fork east of Hartford, into an I-86 to Sturbridge, Massachusetts, and I-84 to Providence, R.I. The plan was cancelled, primarily because of anticipated impact on a major Rhode Island reservoir. The I-84 designation was restored to the highway to Sturbridge, and other numbering was used for completed Eastern sections of what had been planned as part of I-84.
* I-95 through the District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
into Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
was abandoned in 1977. Instead it was rerouted to I-495 (Capital Beltway). The completed section is now I-395.
* I-95 was originally planned to run up the Southwest Expressway and meet I-93, where the two highways would travel along the Central Artery through downtown Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, but was rerouted onto the Route 128 beltway due to widespread opposition. This revolt also included the cancellation of the Inner Belt, connecting I-93 to I-90 and a cancelled section of the Northwest Expressway which would have carried US 3 inside the Route 128 beltway, meeting with Route 2 in Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 Unit ...
.
In addition to cancellations, removals of freeways are planned:
* I-81 in Syracuse, New York
Syracuse ( ) is a City (New York), city in and the county seat of Onondaga County, New York, United States. With a population of 148,620 and a Syracuse metropolitan area, metropolitan area of 662,057, it is the fifth-most populated city and 13 ...
, which bisects the city's 15th Ward neighborhood, is planned to be torn down and replaced with a boulevard that accommodates pedestrians. Freeway traffic would be rerouted along I-481.
Standards
TheAmerican Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials
The American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) is a standards setting body which publishes specifications, test protocols, and guidelines that are used in highway
A highway is any public or private road ...
(AASHTO) has defined a set of standards that all new Interstates must meet unless a waiver from the Federal Highway Administration
The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) is a division of the United States Department of Transportation that specializes in highway transportation. The agency's major activities are grouped into two programs, the Federal-aid Highway Program a ...
(FHWA) is obtained. One almost absolute standard is the controlled access nature of the roads. With few exceptions, traffic light
Traffic lights, traffic signals, or stoplights – also known as robots in South Africa, Zambia, and Namibia – are signaling devices positioned at intersection (road), road intersections, pedestrian crossings, and other locations in order t ...
s (and cross traffic in general) are limited to toll booths and ramp meters (metered flow control for lane merging during rush hour).
Speed limits
Beingfreeway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway, and expressway. Other similar terms ...
s, Interstate Highways usually have the highest speed limit
Speed limits on road traffic, as used in most countries, set the legal maximum speed at which vehicles may travel on a given stretch of road. Speed limits are generally indicated on a traffic sign reflecting the maximum permitted speed, express ...
s in a given area. Speed limits are determined by individual states. From 1975 to 1986, the maximum speed limit on any highway in the United States was , in accordance with federal law.
Typically, lower limits are established in Northeastern and coastal states, while higher speed limits are established in inland states west of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
. For example, the maximum speed limit is in northern Maine, varies between from southern Maine to New Jersey, and is in New York City and the District of Columbia. Currently, rural speed limits elsewhere generally range from . Several portions of various highways such as I-10 and I-20 in rural western Texas, I-80 in Nevada between Fernley and Winnemucca (except around Lovelock) and portions of I-15, I-70, I-80, and I-84 in Utah have a speed limit of . Other Interstates in Idaho, Montana, Oklahoma, South Dakota and Wyoming also have the same high speed limits.
In some areas, speed limits on Interstates can be significantly lower in areas where they traverse significantly hazardous areas. The maximum speed limit on I-90 is in downtown Cleveland
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–U.S. maritime border and approximately west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania st ...
because of two sharp curves with a suggested limit of in a heavily congested area; I-70 through Wheeling, West Virginia
Wheeling is a city in Ohio County, West Virginia, Ohio and Marshall County, West Virginia, Marshall counties in the U.S. state of West Virginia. The county seat of Ohio County, it lies along the Ohio River in the foothills of the Appalachian Mo ...
, has a maximum speed limit of through the Wheeling Tunnel and most of downtown Wheeling; and I-68 has a maximum speed limit of through Cumberland, Maryland, because of multiple hazards including sharp curves and narrow lanes through the city. In some locations, low speed limits are the result of lawsuits and resident demands; after holding up the completion of I-35E in St. Paul, Minnesota, for nearly 30 years in the courts, residents along the stretch of the freeway from the southern city limit to downtown successfully lobbied for a speed limit in addition to a prohibition on any vehicle weighing more than gross vehicle weight. I-93 in Franconia Notch State Park in northern New Hampshire has a speed limit of because it is a parkway that consists of only one lane per side of the highway. On the other hand, Interstates 15, 80, 84, and 215 in Utah have speed limits as high as within the Wasatch Front
The Wasatch Front is a major metropolitan region in the north-central part of the U.S. state of Utah. It consists of a chain of contiguous cities and towns stretched along the Wasatch Range from Santaquin in the south to Pleasant View in the n ...
, Cedar City, and St. George areas, and I-25 in New Mexico within the Santa Fe and Las Vegas
Las Vegas, colloquially referred to as Vegas, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Nevada and the county seat of Clark County. The Las Vegas Valley metropolitan area is the largest within the greater Mojave Desert, and second-l ...
areas along with I-20 in Texas along Odessa and Midland and I-29 in North Dakota along the Grand Forks area have higher speed limits of .
Other uses
As one of the components of the National Highway System, Interstate Highways improve the mobility of military troops to and from airports, seaports, rail terminals, and other military bases. Interstate Highways also connect to other roads that are a part of the Strategic Highway Network, a system of roads identified as critical to the US Department of Defense. The system has also been used to facilitate evacuations in the face of hurricanes and other natural disasters. An option for maximizing traffic throughput on a highway is to reverse the flow of traffic on one side of a divider so that all lanes become outbound lanes. This procedure, known as contraflow lane reversal, has been employed several times for hurricane evacuations. After public outcry regarding the inefficiency of evacuating from southern Louisiana prior to Hurricane Georges' landfall in September 1998, government officials looked towards contraflow to improve evacuation times. InSavannah, Georgia
Savannah ( ) is the oldest city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia and the county seat of Chatham County, Georgia, Chatham County. Established in 1733 on the Savannah River, the city of Savannah became the Kingdom of Great Brita ...
, and Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the List of municipalities in South Carolina, most populous city in the U.S. state of South Carolina. The city lies just south of the geographical midpoint of South Carolina's coastline on Charleston Harbor, an inlet of the Atla ...
, in 1999, lanes of I-16 and I-26 were used in a contraflow configuration in anticipation of Hurricane Floyd with mixed results.
In 2004, contraflow was employed ahead of Hurricane Charley in the Tampa, Florida
Tampa ( ) is a city on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. Tampa's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and t ...
area and on the Gulf Coast before the landfall of Hurricane Ivan; however, evacuation times there were no better than previous evacuation operations. Engineers began to apply lessons learned from the analysis of prior contraflow operations, including limiting exits, removing troopers (to keep traffic flowing instead of having drivers stop for directions), and improving the dissemination of public information. As a result, the 2005 evacuation of New Orleans, Louisiana, prior to Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina was a powerful, devastating and historic tropical cyclone that caused 1,392 fatalities and damages estimated at $125 billion in late August 2005, particularly in the city of New Orleans and its surrounding area. ...
ran much more smoothly.
According to urban legend
Urban legend (sometimes modern legend, urban myth, or simply legend) is a genre of folklore concerning stories about an unusual (usually scary) or humorous event that many people believe to be true but largely are not.
These legends can be e ...
, early regulations required that one out of every five miles of the Interstate Highway System must be built straight and flat, so as to be usable by aircraft during times of war. There is no evidence of this rule being included in any Interstate legislation. It is also commonly believed the Interstate Highway System was built for the sole purpose of evacuating cities in the event of nuclear warfare
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a War, military conflict or prepared Policy, political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are Weapon of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conven ...
. While military motivations were present, the primary motivations were civilian.
Numbering system
Primary (one- and two-digit) Interstates
 The numbering scheme for the Interstate Highway System was developed in 1957 by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO). The association's present numbering policy dates back to August 10, 1973. Within the contiguous United States, primary Interstates—also called main line Interstates or two-digit Interstates—are assigned numbers less than 100.
While numerous exceptions do exist, there is a general scheme for numbering Interstates. Primary Interstates are assigned one- or two-digit numbers, while shorter routes (such as spurs, loops, and short connecting roads) are assigned three-digit numbers where the last two digits match the parent route (thus, I-294 is a loop that connects at both ends to I-94, while I-787 is a short spur route attached to I-87). In the numbering scheme for the primary routes, east–west highways are assigned even numbers and north–south highways are assigned odd numbers. Odd route numbers increase from west to east, and even-numbered routes increase from south to north (to avoid confusion with the US Highways, which increase from east to west and north to south). This numbering system usually holds true even if the local direction of the route does not match the compass directions. Numbers
The numbering scheme for the Interstate Highway System was developed in 1957 by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO). The association's present numbering policy dates back to August 10, 1973. Within the contiguous United States, primary Interstates—also called main line Interstates or two-digit Interstates—are assigned numbers less than 100.
While numerous exceptions do exist, there is a general scheme for numbering Interstates. Primary Interstates are assigned one- or two-digit numbers, while shorter routes (such as spurs, loops, and short connecting roads) are assigned three-digit numbers where the last two digits match the parent route (thus, I-294 is a loop that connects at both ends to I-94, while I-787 is a short spur route attached to I-87). In the numbering scheme for the primary routes, east–west highways are assigned even numbers and north–south highways are assigned odd numbers. Odd route numbers increase from west to east, and even-numbered routes increase from south to north (to avoid confusion with the US Highways, which increase from east to west and north to south). This numbering system usually holds true even if the local direction of the route does not match the compass directions. Numbers divisible
In mathematics, a divisor of an integer n, also called a factor of n, is an integer m that may be multiplied by some integer to produce n. In this case, one also says that n is a '' multiple'' of m. An integer n is divisible or evenly divisibl ...
by five are intended to be major arteries among the primary routes, carrying traffic long distances. Primary north–south Interstates increase in number from I-5 between Canada and Mexico along the West Coast to I‑95 between Canada and Miami, Florida
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
along the East Coast. Major west–east arterial Interstates increase in number from I-10 between Santa Monica, California
Santa Monica (; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Santa Mónica'') is a city in Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles County, situated along Santa Monica Bay on California's South Coast (California), South Coast. Santa Monica's 2020 United Sta ...
, and Jacksonville, Florida
Jacksonville ( ) is the most populous city proper in the U.S. state of Florida, located on the Atlantic coast of North Florida, northeastern Florida. It is the county seat of Duval County, Florida, Duval County, with which the City of Jacksonv ...
, to I-90 between Seattle, Washington
Seattle ( ) is the List of municipalities in Washington, most populous city in the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington and in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. With a population of 780,995 in 2024, it is the List of Unit ...
, and Boston, Massachusetts
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, with two exceptions. There are no I-50 and I-60, as routes with those numbers would likely pass through states that currently have US Highways with the same numbers, which is generally disallowed under highway administration guidelines.
Several two-digit numbers are shared between unconnected road segments at opposite ends of the country for various reasons. Some such highways are incomplete Interstates (such as I-69
Interstate 69 (I-69) is an Interstate Highway in the United States currently consisting of eight unconnected segments. The longest segment runs from Evansville, Indiana, northeast to the Canada–United States border, Canadian border in Po ...
and I-74
Interstate 74 (I-74) is an Interstate Highway in the Midwestern and Southeastern United States. Its western end is at an interchange with I-80 in Davenport, Iowa; the eastern end of its Midwest segment is at an interchange with I-75 ...
) and some just happen to share route designations (such as I-76, I-84, I‑86, I-87, and I-88). Some of these were due to a change in the numbering system as a result of a new policy adopted in 1973. Previously, letter-suffixed numbers were used for long spurs off primary routes; for example, western I‑84 was I‑80N, as it went north from I‑80. The new policy stated, "No new divided numbers (such as I-35W and I-35E, etc.) shall be adopted." The new policy also recommended that existing divided numbers be eliminated as quickly as possible; however, an I-35W and I-35E still exist in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex
The Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, officially designated Dallas–Fort Worth–Arlington by the U.S. Office of Management and Budget, is the most populous metropolitan statistical area in the U.S. state of Texas and the Southern United States, ...
in Texas, and an I-35W and I-35E that run through Minneapolis
Minneapolis is a city in Hennepin County, Minnesota, United States, and its county seat. With a population of 429,954 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the state's List of cities in Minnesota, most populous city. Locat ...
and Saint Paul, Minnesota, still exist. Additionally, due to Congressional requirements, three sections of I-69 in southern Texas will be divided into I-69W, I-69E, and I-69C (for Central).
AASHTO policy allows dual numbering to provide continuity between major control points. This is referred to as a concurrency or overlap. For example, I‑75 and I‑85 share the same roadway in Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Georgia (U.S. state), most populous city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It is the county seat, seat of Fulton County, Georg ...
; this section, called the Downtown Connector, is labeled both I‑75 and I‑85. Concurrencies between Interstate and US Highway numbers are also allowed in accordance with AASHTO policy, as long as the length of the concurrency is reasonable. In rare instances, two highway designations sharing the same roadway are signed as traveling in opposite directions; one such wrong-way concurrency Wrong way may refer to:
* a traffic sign to warn of wrong-way driving
* nickname of Douglas Corrigan (1907–1995), an American aviator who flew east from New York to Ireland instead of west to California in 1938
* nickname of Roy Riegels (1908–1 ...
is found between Wytheville and Fort Chiswell, Virginia, where I‑81 north and I‑77 south are equivalent (with that section of road traveling almost due east), as are I‑81 south and I‑77 north.
Auxiliary (three-digit) Interstates
urban area
An urban area is a human settlement with a high population density and an infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas originate through urbanization, and researchers categorize them as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs. In urbani ...
s. These types of Interstate Highways are given three-digit route numbers, which consist of a single digit prefixed to the two-digit number of its parent Interstate Highway. Spur routes deviate from their parent and do not return; these are given an odd first digit. Circumferential and radial loop routes return to the parent, and are given an even first digit. Unlike primary Interstates, three-digit Interstates are signed as either east–west or north–south, depending on the general orientation of the route, without regard to the route number. For instance, I-190 in Massachusetts is labeled north–south, while I-195 in New Jersey is labeled east–west. Some looped Interstate routes use inner–outer directions instead of compass directions, when the use of compass directions would create ambiguity. Due to the large number of these routes, auxiliary route numbers may be repeated in different states along the mainline. Some auxiliary highways do not follow these guidelines, however.
Alaska, Hawaii, and Puerto Rico
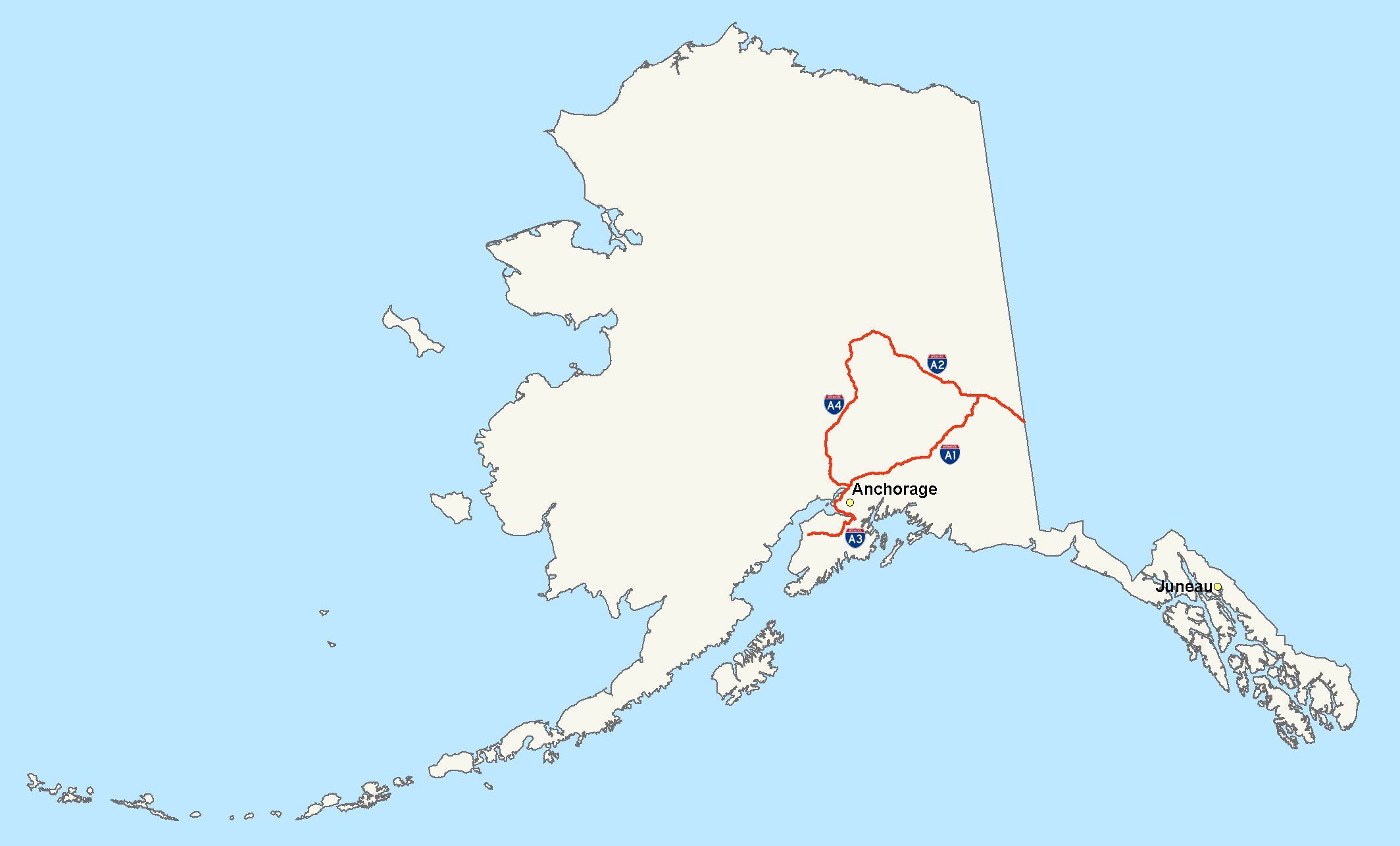
 The Interstate Highway System also extends to
The Interstate Highway System also extends to Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
, Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, and Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
, even though they have no direct land connections to any other states or territories. However, their residents still pay federal fuel and tire taxes.
The Interstates in Hawaii, all located on the most populous island of Oahu
Oahu (, , sometimes written Oahu) is the third-largest and most populated island of the Hawaiian Islands and of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oahu's southeast coast. The island of Oahu and the uninhabited Northwe ...
, carry the prefix H. There are three one-digit routes in the state ( H-1, H-2, and H-3) and one auxiliary route ( H-201). These Interstates connect several military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
and naval bases together, as well as the important communities spread across Oahu, and especially within the urban core of Honolulu
Honolulu ( ; ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, located in the Pacific Ocean. It is the county seat of the Consolidated city-county, consolidated City and County of Honol ...
.
Both Alaska and Puerto Rico also have public highways that receive 90 percent of their funding from the Interstate Highway program. The Interstates of Alaska and Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
are numbered sequentially in order of funding without regard to the rules on odd and even numbers. They also carry the prefixes A and PR, respectively. However, these highways are signed according to their local designations, not their Interstate Highway numbers. Furthermore, these routes were neither planned according to nor constructed to the official Interstate Highway standards
Standards for Interstate Highways in the United States are defined by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) in the publication ''A Policy on Design Standards: Interstate System''. For a certain highway t ...
.
Mile markers and exit numbers
On one- or two-digit Interstates, the mile marker numbering almost always begins at the southern or western state line. If an Interstate originates within a state, the numbering begins from the location where the road begins in the south or west. As with all guidelines for Interstate routes, however, numerous exceptions exist. Three-digit Interstates with an even first number that form a complete circumferential (circle) bypass around a city feature mile markers that are numbered in a clockwise direction, beginning just west of an Interstate that bisects the circumferential route near a south polar location. In other words, mile marker 1 on I-465, a route around Indianapolis, is just west of its junction with I-65 on the south side of Indianapolis (on the south leg of I-465), and mile marker 53 is just east of this same junction. An exception is I-495 in theWashington metropolitan area
The Washington metropolitan area, also referred to as the National Capital Region, Greater Washington, or locally as the DMV (short for Washington, D.C., District of Columbia, Maryland, and Virginia), is the metropolitan area comprising Washing ...
, with mileposts increasing counterclockwise because part of that road is also part of I-95.
Most Interstate Highways use distance-based exit numbers so that the exit number is the same as the nearest mile marker. If multiple exits occur within the same mile, letter suffixes may be appended to the numbers in alphabetical order starting with A. A small number of Interstate Highways (mostly in the Northeastern United States) use sequential-based exit numbering schemes (where each exit is numbered in order starting with 1, without regard for the mile markers on the road). One Interstate Highway, I-19 in Arizona, is signed with kilometer-based exit numbers. In the state of New York, most Interstate Highways use sequential exit numbering, with some exceptions.
Business routes
AASHTO defines a category of special routes separate from primary and auxiliary Interstate designations. These routes do not have to comply to Interstate construction or limited-access standards but are routes that may be identified and approved by the association. The same route marking policy applies to both US Numbered Highways and Interstate Highways; however,business route
A business route (or business loop, business spur, or city route) in the United States is a short special route that branches off a parent numbered highway at its beginning, continues through the central business district of a nearby city or to ...
designations are sometimes used for Interstate Highways. Known as Business Loops and Business Spurs, these routes principally travel through the corporate limits of a city, passing through the central business district when the regular route is directed around the city. They also use a green shield instead of the red and blue shield. An example would be Business Loop Interstate 75 at Pontiac, Michigan
Pontiac ( ') is a city in and the county seat of Oakland County, Michigan, Oakland County in the U.S. state of Michigan. Located roughly northwest of downtown Detroit, Pontiac is part of the Metro Detroit, Detroit metropolitan area, and is vari ...
, which follows surface roads into and through downtown. Sections of BL I-75's routing had been part of US 10 and M-24, predecessors of I-75
Interstate 75 (I-75) is a major north–south Interstate Highway System, Interstate Highway in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes and Southeastern United States, Southeastern regions of the United States. As with most Interstates that end ...
in the area.
Financing
Taxes and user fees
About 70 percent of the construction and maintenance costs of Interstate Highways in the United States have been paid through user fees, primarily the fuel taxes collected by the federal, state, and local governments. To a much lesser extent they have been paid for by tolls collected ontoll highway
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road for which a fee (or ''Toll (fee), toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically implemented to help recoup the costs of road construction and ...
s and bridges. The federal gasoline tax was first imposed in 1932 at one cent per gallon; during the Eisenhower administration, the Highway Trust Fund, established by the Highway Revenue Act in 1956, prescribed a three-cent-per-gallon fuel tax, soon increased to 4.5 cents per gallon. Since 1993 the tax has remained at 18.4 cents per gallon. Other excise taxes related to highway travel also accumulated in the Highway Trust Fund. Initially, that fund was sufficient for the federal portion of building the Interstate system, built in the early years with "10 cent dollars", from the perspective of the states, as the federal government paid 90% of the costs while the state paid 10%. The system grew more rapidly than the rate of the taxes on fuel and other aspects of driving (e. g., excise tax on tires).
The rest of the costs of these highways are borne by general fund receipts, bond issues, designated property taxes, and other taxes. The federal contribution is funded primarily through fuel taxes and through transfers from the Treasury's general fund. Local government contributions are overwhelmingly from sources besides user fees. As decades passed in the 20th century and into the 21st century, the portion of the user fees spent on highways themselves covers about 57 percent of their costs, with about one-sixth of the user fees being sent to other programs, including the mass transit systems in large cities. Some large sections of Interstate Highways that were planned or constructed before 1956 are still operated as toll roads, for example the Massachusetts Turnpike (I-90), the New York State Thruway (I-87 and I-90), and Kansas Turnpike (I-35, I-335, I-470, I-70). Others have had their construction bonds paid off and they have become toll-free, such as the Connecticut Turnpike (I‑95, I-395), the Richmond-Petersburg Turnpike in Virginia (also I‑95), and the Kentucky Turnpike (I‑65).
As American suburbs have expanded, the costs incurred in maintaining freeway infrastructure have also grown, leaving little in the way of funds for new Interstate construction. This has led to the proliferation of toll roads (turnpikes) as the new method of building limited-access highways in suburban areas. Some Interstates are privately maintained (for example, the VMS company maintains I‑35 in Texas) to meet rising costs of maintenance and allow state departments of transportation to focus on serving the fastest-growing regions in their states.
Parts of the Interstate System might have to be tolled in the future to meet maintenance and expansion demands, as has been done with adding toll HOV/ HOT lanes in cities such as Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Georgia (U.S. state), most populous city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It is the county seat, seat of Fulton County, Georg ...
, Dallas
Dallas () is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the List of Texas metropolitan areas, most populous metropolitan area in Texas and the Metropolitan statistical area, fourth-most ...
, and Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
. Although part of the tolling is an effect of the SAFETEA‑LU act, which has put an emphasis on toll roads as a means to reduce congestion, present federal law does not allow for a state to change a freeway section to a tolled section for all traffic.
Tolls
About of toll roads are included in the Interstate Highway System. While federal legislation initially banned the collection of tolls on Interstates, many of the toll roads on the system were either completed or under construction when the Interstate Highway System was established. Since these highways provided logical connections to other parts of the system, they were designated as Interstate highways.Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
also decided that it was too costly to either build toll-free Interstates parallel to these toll roads, or directly repay all the bondholders who financed these facilities and remove the tolls. Thus, these toll roads were grandfathered into the Interstate Highway System.
Toll roads designated as Interstates (such as the Massachusetts Turnpike) were typically allowed to continue collecting tolls, but are generally ineligible to receive federal funds for maintenance and improvements. Some toll roads that did receive federal funds to finance emergency repairs (notably the Connecticut Turnpike (I-95) following the Mianus River Bridge collapse) were required to remove tolls as soon as the highway's construction bonds were paid off. In addition, these toll facilities were grandfathered from Interstate Highway standards
Standards for Interstate Highways in the United States are defined by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) in the publication ''A Policy on Design Standards: Interstate System''. For a certain highway t ...
. A notable example is the western approach to the Benjamin Franklin Bridge in Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, where I-676 has a surface street section through a historic area.
Policies on toll facilities and Interstate Highways have since changed. The Federal Highway Administration
The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) is a division of the United States Department of Transportation that specializes in highway transportation. The agency's major activities are grouped into two programs, the Federal-aid Highway Program a ...
has allowed some states to collect tolls on existing Interstate Highways, while a recent extension of I-376 included a section of Pennsylvania Route 60 that was tolled by the Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission
The Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission (PTC) is an agency created in 1937 to construct, finance, operate, and maintain the Pennsylvania Turnpike (both the mainline and the Northeast Extension). The commission consists of five members. Four memb ...
before receiving Interstate designation. Also, newer toll facilities (like the tolled section of I-376, which was built in the early 1990s) must conform to Interstate standards. A new addition of the '' Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices'' in 2009 requires a black-on-yellow "Toll" sign to be placed above the Interstate trailblazer on Interstate Highways that collect tolls.
Legislation passed in 2005 known as SAFETEA-LU encouraged states to construct new Interstate Highways through "innovative financing" methods. SAFETEA-LU facilitated states to pursue innovative financing by easing the restrictions on building interstates as toll roads, either through state agencies or through public–private partnership
A public–private partnership (PPP, 3P, or P3) is a long-term arrangement between a government and private sectors, private sector institutions.Hodge, G. A and Greve, C. (2007), Public–Private Partnerships: An International Performance Revie ...
s. However, SAFETEA-LU left in place a prohibition of installing tolls on existing toll-free Interstates, and states wishing to toll such routes to finance upgrades and repairs must first seek approval from Congress. Many states have started using High-occupancy toll lane and other partial tolling methods, whereby certain lanes of highly congested freeways are tolled, while others are left free, allowing people to pay a fee to travel in less congested lanes. Examples of recent projects to add HOT lanes to existing freeways include the Virginia HOT lanes on the Virginia portions of the Capital Beltway and other related interstate highways (I-95, I-495, I-395) and the addition of express toll lanes to Interstate 77 in North Carolina in the Charlotte metropolitan area.
Chargeable and non-chargeable Interstate routes
Interstate Highways financed with federal funds are known as "chargeable" Interstate routes, and are considered part of the network of highways. Federal laws also allow "non-chargeable" Interstate routes, highways funded similarly to state and US Highways to be signed as Interstates, if they both meet the Interstate Highway standards and are logical additions or connections to the system. These additions fall under two categories: routes that already meet Interstate standards, and routes not yet upgraded to Interstate standards. Only routes that meet Interstate standards may be signed as Interstates once their proposed number is approved.Signage
Interstate shield
 Interstate Highways are signed by a number placed on a red, white, and blue sign. The shield design itself is a registered trademark of the
Interstate Highways are signed by a number placed on a red, white, and blue sign. The shield design itself is a registered trademark of the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials
The American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) is a standards setting body which publishes specifications, test protocols, and guidelines that are used in highway
A highway is any public or private road ...
. The colors red, white, and blue were chosen because they are the colors of the American flag. In the original design, the name of the state was displayed above the highway number, but in many states, this area is now left blank, allowing for the printing of larger and more-legible digits. Signs with the shield alone are placed periodically throughout each Interstate as reassurance markers. These signs usually measure high, and are wide for two-digit Interstates or for three-digit Interstates.
Interstate business loops and spurs use a special shield in which the red and blue are replaced with green, the word "BUSINESS" appears instead of "INTERSTATE", and the word "SPUR" or "LOOP" usually appears above the number. The green shield is employed to mark the main route through a city's central business district, which intersects the associated Interstate at one (spur) or both (loop) ends of the business route. The route usually traverses the main thoroughfare(s) of the city's downtown area or other major business district. A city may have more than one Interstate-derived business route, depending on the number of Interstates passing through a city and the number of significant business districts therein.
Over time, the design of the Interstate shield has changed. In 1957 the Interstate shield designed by Texas Highway Department employee Richard Oliver was introduced, the winner of a contest that included 100 entries; at the time, the shield color was a dark navy blue and only wide. The '' Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices'' (MUTCD) standards revised the shield in the 1961, 1971, and 1978 editions.
Exit numbering
The majority of Interstates have exit numbers. Like other highways, Interstates feature guide signs that list control cities to help direct drivers through interchanges and exits toward their desired destination. Alltraffic sign
Traffic signs or road signs are signs erected at the side of or above roads to give instructions or provide information to road users. The earliest signs were simple wooden or stone milestones. Later, signs with directional arms were introduc ...
s and lane markings on the Interstates are supposed to be designed in compliance with the Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD). There are, however, many local and regional variations in signage.
For many years, California was the only state that did not use an exit numbering system. It was granted an exemption in the 1950s due to having an already largely completed and signed highway system; placing exit number signage across the state was deemed too expensive. To control costs, California began to incorporate exit numbers on its freeways in 2002—Interstate, US, and state routes alike. Caltrans
The California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) is an Executive (government), executive department of the U.S. state of California. The department is part of the Government of California#State agencies, cabinet-level California State Tran ...
commonly installs exit number signage only when a freeway or interchange is built, reconstructed, retrofitted, or repaired, and it is usually tacked onto the top-right corner of an already existing sign. Newer signs along the freeways follow this practice as well. Most exits along California's Interstates now have exit number signage, particularly in rural areas. California, however, still does not use mileposts, although a few exist for experiments or for special purposes.
In 2010–2011, the Illinois State Toll Highway Authority posted all new mile markers to be uniform with the rest of the state on I‑90 (Jane Addams Memorial/Northwest Tollway) and the I‑94 section of the Tri‑State Tollway, which previously had matched the I‑294 section starting in the south at I‑80/I‑94/IL Route 394. This also applied to the tolled portion of the Ronald Reagan Tollway (I-88). The tollway also added exit number tabs to the exits.
Exit numbers correspond to Interstate mileage markers in most states. On I‑19 in Arizona
Arizona is a U.S. state, state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States, sharing the Four Corners region of the western United States with Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah. It also borders Nevada to the nort ...
, however, length is measured in kilometers instead of miles because, at the time of construction, a push for the United States to change to a metric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that standardization, standardizes a set of base units and a nomenclature for describing relatively large and small quantities via decimal-based multiplicative unit prefixes. Though the rules gover ...
of measurement had gained enough traction that it was mistakenly assumed that all highway measurements would eventually be changed to metric (and some distance signs retain metric distances); proximity to metric-using Mexico may also have been a factor, as I‑19 indirectly connects I‑10 to the Mexican Federal Highway system via surface streets in Nogales. Mileage count increases from west to east on most even-numbered Interstates; on odd-numbered Interstates mileage count increases from south to north.
Some highways, including the New York State Thruway, use sequential exit-numbering schemes. Exits on the New York State Thruway count up from Yonkers
Yonkers () is the List of municipalities in New York, third-most populous city in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York and the most-populous City (New York), city in Westchester County, New York, Westchester County. A centrally locate ...
traveling north, and then west from Albany. I‑87 in New York State is numbered in three sections. The first section makes up the Major Deegan Expressway in the Bronx
The Bronx ( ) is the northernmost of the five Boroughs of New York City, boroughs of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. It shares a land border with Westchester County, New York, West ...
, with interchanges numbered sequentially from 1 to 14. The second section of I‑87 is a part of the New York State Thruway that starts in Yonkers (exit 1) and continues north to Albany (exit 24); at Albany, the Thruway turns west and becomes I‑90 for exits 25 to 61. From Albany north to the Canadian border, the exits on I‑87 are numbered sequentially from 1 to 44 along the Adirondack Northway. This often leads to confusion as there is more than one exit on I‑87 with the same number. For example, exit 4 on Thruway section of I‑87 connects with the Cross County Parkway in Yonkers, but exit 4 on the Northway is the exit for the Albany airport. These two exits share a number but are located apart.
Many northeastern states label exit numbers sequentially, regardless of how many miles have passed between exits. States in which Interstate exits are still numbered sequentially are Connecticut, Delaware, New Hampshire, New York, and Vermont; as such, three of the main Interstate Highways that remain completely within these states ( 87, 88, 89) have interchanges numbered sequentially along their entire routes. Maine, Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, Virginia, Georgia, and Florida followed this system for a number of years, but have since converted to mileage-based exit numbers. Georgia renumbered in 2000, while Maine did so in 2004. Massachusetts converted its exit numbers in 2021, and most recently Rhode Island in 2022. The Pennsylvania Turnpike uses both mile marker numbers and sequential numbers. Mile marker numbers are used for signage, while sequential numbers are used for numbering interchanges internally. The New Jersey Turnpike, including the portions that are signed as I‑95 and I‑78, also has sequential numbering, but other Interstates within New Jersey use mile markers.
Sign locations
There are four common signage methods on Interstates: * Locating a sign on the ground to the side of the highway, mostly the right, and is used to denote exits, as well asrest area
A rest area is a public facility located next to a large thoroughfare such as a motorway, Limited-access road, expressway, or highway, at which drivers and passengers can rest, eat, or refuel without exiting onto secondary roads. Other names ...
s, motorist services such as gas and lodging, recreational sites, and freeway names
* Attaching the sign to an overpass
* Mounting on full gantries that bridge the entire width of the highway and often show two or more signs
* Mounting on half-gantries that are located on one side of the highway, like a ground-mounted sign
Statistics
Volume
* Heaviest traveled: 379,000 vehicles per day: I-405 in Los Angeles, California (2011 estimate).Elevation
* Highest: : I-70 in the Eisenhower Tunnel at the Continental Divide in theColorado
Colorado is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States. It is one of the Mountain states, sharing the Four Corners region with Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah. It is also bordered by Wyoming to the north, Nebraska to the northeast, Kansas ...
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
.
* Lowest (land): : I-8 at the New River near Seeley, California.
* Lowest (underwater): : I-95 in the Fort McHenry Tunnel under the Baltimore Inner Harbor.
Length
* Longest (east–west): : I-90 fromBoston, Massachusetts
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, to Seattle, Washington
Seattle ( ) is the List of municipalities in Washington, most populous city in the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington and in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. With a population of 780,995 in 2024, it is the List of Unit ...
.
* Longest (north–south): : I-95 from the Canadian border near Houlton, Maine, to Miami, Florida
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
.
* Shortest (two-digit): : I-69W in Laredo, Texas.
* Shortest (auxiliary): : I-878 in Queens
Queens is the largest by area of the Boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. Located near the western end of Long Island, it is bordered by the ...
, New York, New York.
* Longest segment between state lines: : I-10 in Texas from the New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
state line near El Paso to the Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
state line near Orange, Texas.
* Shortest segment between state lines: : I-95/ I-495 (Capital Beltway) on the Woodrow Wilson Bridge across the Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
where they briefly cross the southernmost tip of the District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
between its borders with Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
.
* Longest concurrency: : I-80 and I-90; Gary, Indiana
Gary ( ) is a city in Lake County, Indiana, United States. The population was 69,093 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, making it Indiana's List of municipalities in Indiana, eleventh-most populous city. The city has been historical ...
, to Elyria, Ohio.
States
* Most states served by an Interstate: 15 states plus the District of Columbia: I-95 throughFlorida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, DC, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, New York, Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
, Rhode Island
Rhode Island ( ) is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Connecticut to its west; Massachusetts to its north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to its south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Is ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
, New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
, and Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
.
* Most Interstates in a state: 32 routes: New York, totaling
* Most primary Interstates in a state: 13 routes: Illinois
* Most Interstate mileage in a state: : Texas, in 17 different routes.
* Fewest Interstates in a state: 3 routes: Delaware, New Mexico, North Dakota, and Rhode Island. Puerto Rico also has 3 routes.
* Fewest primary Interstates in a state: 1 route: Delaware, Maine, and Rhode Island (I-95 in each case).
* Least Interstate mileage in a state: : Delaware, in 3 different routes.
Impact and reception
Following the passage of the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1956, passenger rail declined sharply as did freight rail for a short time, but the trucking industry expanded dramatically and the cost of shipping and travel fell sharply.Suburbanization
Suburbanization (American English), also spelled suburbanisation (British English), is a population shift from historic core cities or rural areas into suburbs. Most suburbs are built in a formation of (sub)urban sprawl. As a consequence ...
became possible, with the rapid growth of larger, sprawling, and more car-dependent housing than was available in central cities, enabling racial segregation
Racial segregation is the separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Segregation can involve the spatial separation of the races, and mandatory use of different institutions, ...
by white flight
The white flight, also known as white exodus, is the sudden or gradual large-scale migration of white people from areas becoming more racially or ethnoculturally diverse. Starting in the 1950s and 1960s, the terms became popular in the Racism ...
. A sense of isolationism developed in suburbs, with suburbanites wanting to keep urban areas disconnected from the suburbs. Tourism dramatically expanded, creating a demand for more service stations, motels, restaurants and visitor attractions. The Interstate System was the basis for urban expansion in the Sun Belt, and many urban areas in the region are thus very car-dependent. The highways may have contributed to increased economic productivity in, and thereby increased migration to, the Sun Belt. In rural areas, towns and small cities off the grid lost out as shoppers followed the interstate and new factories were located near them.
The system had a profound effect on interstate shipping. The Interstate Highway System was being constructed at the same time as the intermodal shipping container made its debut. These containers could be placed on trailers behind trucks and shipped across the country with ease. A new road network and shipping containers that could be easily moved from ship to train to truck, meant that overseas manufacturers and domestic startups could get their products to market quicker than ever, allowing for accelerated economic growth. Forty years after its construction, the Interstate Highway system returned on investment, making $6 for every $1 spent on the project. According to research by the FHWA, "from 1950 to 1989, approximately one-quarter of the nation's productivity increase is attributable to increased investment in the highway system."
The system had a particularly strong effect in Southern states, where major highways were inadequate. The new system facilitated the relocation of heavy manufacturing to the South and spurred the development of Southern-based corporations like Walmart
Walmart Inc. (; formerly Wal-Mart Stores, Inc.) is an American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets (also called supercenters), discount department stores, and grocery stores in the United States and 23 other ...
(in Arkansas) and FedEx
FedEx Corporation, originally known as Federal Express Corporation, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate holding company specializing in Package delivery, transportation, e-commerce, and ...
(in Tennessee).
The Interstate Highway System also dramatically affected American culture, contributing to cars becoming more central to the American identity. Before, driving was considered an excursion that required some amount of skill and could have some chance of unpredictability. With the standardization of signs, road widths and rules, certain unpredictabilities lessened. Justin Fox wrote, "By making road more reliable and by making Americans more reliant on them, they took away most of the adventure and romance associated with driving."
The Interstate Highway System has been criticized for contributing to the decline of some cities that were divided by Interstates, and for displacing minority neighborhoods in urban centers. Between 1957 and 1977, the Interstate System alone displaced over 475,000 households and one million people across the country. Highways have also been criticized for increasing racial segregation by creating physical barriers between neighborhoods, and for overall reductions in available housing and population in neighborhoods affected by highway construction. Other critics have blamed the Interstate Highway System for the decline of public transportation in the United States
The United States is served by a wide array of public transportation, including various forms of bus, Rail transport, rail, ferry, and sometimes, airline services. Most public transit systems are in urban areas with enough density and public d ...
since the 1950s, which minorities and low-income residents are three to six times more likely to use. Previous highways, such as US 66, were also bypassed by the new Interstate system, turning countless rural communities along the way into ghost towns. The Interstate System has also contributed to continued resistance against new public transportation.
The Interstate Highway System had a negative impact on minority groups, especially in urban areas. Even though the government used eminent domain
Eminent domain, also known as land acquisition, compulsory purchase, resumption, resumption/compulsory acquisition, or expropriation, is the compulsory acquisition of private property for public use. It does not include the power to take and t ...
to obtain land for the Interstates, it was still economical to build where land was cheapest. This cheap land was often located in predominately minority areas. Not only were minority neighborhoods destroyed, but in some cities the Interstates were used to divide white and minority neighborhoods. These practices were common in cities both in the North and South, including Nashville
Nashville, often known as Music City, is the capital and List of municipalities in Tennessee, most populous city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the county seat, seat of Davidson County, Tennessee, Davidson County in Middle Tennessee, locat ...
, Miami
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
, Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
, Detroit
Detroit ( , ) is the List of municipalities in Michigan, most populous city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is situated on the bank of the Detroit River across from Windsor, Ontario. It had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 United State ...
, and many other cities. The division and destruction of neighborhoods led to the limitation of employment and other opportunities, which deteriorated the economic fabric of neighborhoods. Neighborhoods bordering Interstates have a much higher level of particulate air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
and are more likely to be chosen for polluting industrial facilities.
See also
*Highway systems by country
This article describes the highway systems available in selected countries.
Africa
Algeria
About of highways in Algeria are in service and another are under construction.
Botswana
Botswana has a network of roads, of varied quality ...
* List of controlled-access highway systems
* Non-motorized access on freeways
Notes
References
Further reading
* * * * * * *External links
*Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways
Federal Highway Administration (FHWA)
Route Log and Finder List
FHWA
State-by-state maps of the National Highway System
of the FHWA include Interstate highways
Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center
FHWA
Interstate Highway System
Dwight D. Eisenhower Presidential Library and Museum
''NOW'' on PBS {{Authority control 1956 establishments in the United States Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower Transport systems Types of roads