Hokianga on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
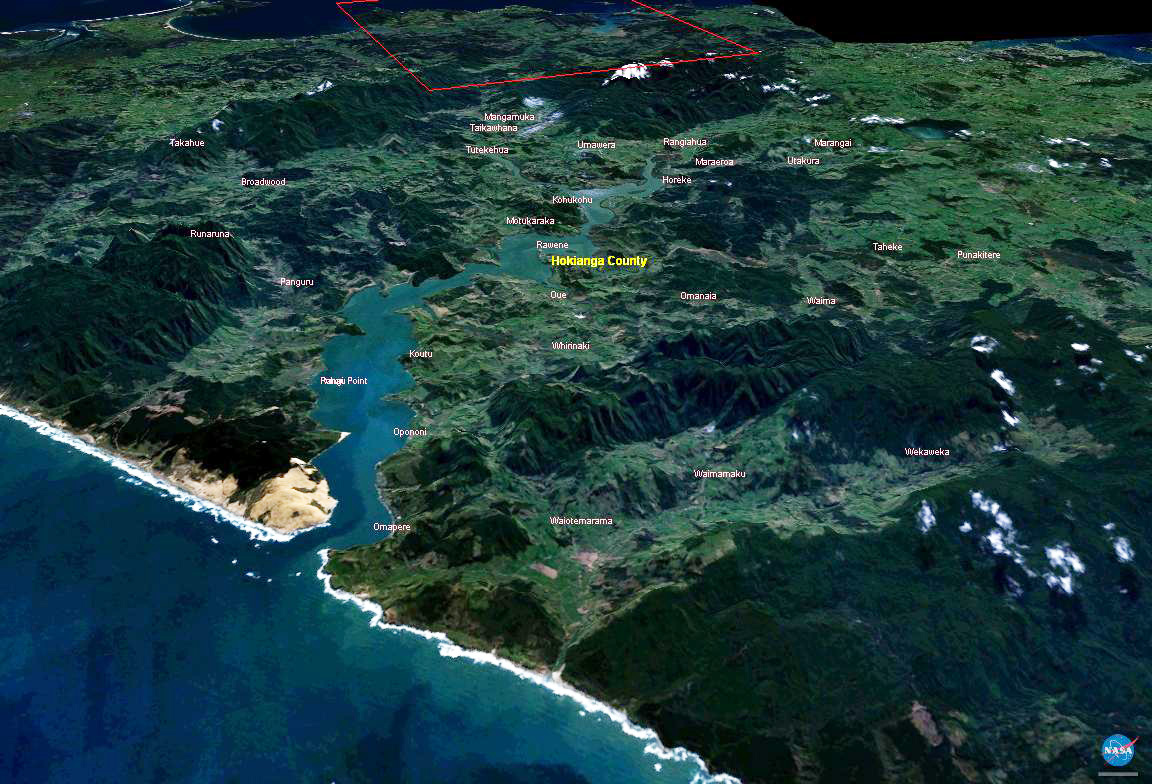 The Hokianga is an area surrounding the Hokianga Harbour, also known as the Hokianga River, a long
The Hokianga is an area surrounding the Hokianga Harbour, also known as the Hokianga River, a long
 In the 14th century, the great chief Puhi landed just south of the
In the 14th century, the great chief Puhi landed just south of the  In the course of expansion, Ngāpuhi created and maintained over centuries a complex network of walking tracks, many of which evolved into today's roads.
In the course of expansion, Ngāpuhi created and maintained over centuries a complex network of walking tracks, many of which evolved into today's roads.
 While the fate of the country was being signed into history, the axemen of Hokianga scarcely missed a beat. At any one time, as many as 20 ships could be loading Hokianga timber. Whole hillsides, suddenly bared of vegetation, began to slip into the harbour, choking its tributaries with mud.
The relationship between Māori and
While the fate of the country was being signed into history, the axemen of Hokianga scarcely missed a beat. At any one time, as many as 20 ships could be loading Hokianga timber. Whole hillsides, suddenly bared of vegetation, began to slip into the harbour, choking its tributaries with mud.
The relationship between Māori and

Hauora Hokianga
Hokianga's community governed health services
Hokianga Tourism Association
Local Tourism Members and Information
Dictionary of New Zealand Biography essay on Dame Whina Cooper
Rawene Website
Kohukohu Community Website
{{Coord, -35.5258, 173.3786, region:NZ-NTL_type:waterbody_scale:250000, display=title Far North District Ports and harbours of New Zealand Populated places in the Northland Region Geography of the Northland Region
 The Hokianga is an area surrounding the Hokianga Harbour, also known as the Hokianga River, a long
The Hokianga is an area surrounding the Hokianga Harbour, also known as the Hokianga River, a long estuarine
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
drowned valley on the west coast in the north of the North Island
The North Island ( , 'the fish of Māui', historically New Ulster) is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but less populous South Island by Cook Strait. With an area of , it is the List ...
of New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
.
The original name, still used by local Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
, is ''Te Kohanga o Te Tai Tokerau'' ("the nest of the northern people") or ''Te Puna o Te Ao Marama'' ("the wellspring in the world of light"). The full name of the harbour is Te Hokianga-nui-a-Kupe — "the place of Kupe's great return".
Geography
The Hokianga is in theFar North District
The Far North District is the northernmost Territorial authorities of New Zealand, territorial authority district of New Zealand, consisting of the northern part of the Northland Peninsula in the North Island. It stretches from North Cape (New ...
, which is in the Northland Region
Northland (), officially the Northland Region, is the northernmost of New Zealand's 16 regions of New Zealand, local government regions. New Zealanders sometimes refer to it as the Winterless North because of its mild climate all throughout t ...
. The area is northwest of Whangārei
Whangārei () is the northernmost city in New Zealand and the largest settlement of the Northland Region. It is part of the Whangarei District, created in 1989 from the former Whangarei City, Whangarei County and Hikurangi Town councils to admi ...
City—and west of Kaikohe
Kaikohe is the seat of the Far North District of New Zealand, situated on State Highway 12 about from Auckland, and about from Whangārei. It is the largest inland town and highest community above sea level in the Northland Region. With a pop ...
—by road. The estuary extends inland for from the Tasman Sea
The Tasman Sea is a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean, situated between Australia and New Zealand. It measures about across and about from north to south. The sea was named after the Dutch explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman, who in 1642 wa ...
. It is navigable for small craft for much of its length, although there is a bar across the mouth. In its upper reaches the Rangiora Narrows separate the mouths of the Waihou and Mangamuka Rivers from the lower parts of the harbour.
12,000 years ago, the Hokianga was a river valley flanked by steep bush-clad hills. As the last ice age regressed, the dramatic rise in sea level slowly flooded the valley turning it into a tidal saltwater harbour with abundant sheltered deep water anchorages. This was the harbour that the explorer Kupe
Kupe was a legendary Polynesian explorer who, according to Māori oral history, was the first person to discover New Zealand. He is generally held to have been born to a father from Rarotonga and a mother from Raiatea, and probably spoke a ...
left from, and in 1822 it was home to the first European timber entrepreneurs. southern right whale
The southern right whale (''Eubalaena australis'') is a baleen whale, one of three species classified as right whales belonging to the genus ''Eubalaena''. Southern right whales inhabit oceans south of the Equator, between the latitudes of 20� ...
s possibly frequented the bay historically, prior to significant depletion of the species caused by commercial and illegal hunting. Today, large whales are rarely seen in the bay, although the harbour is a well-regarded area in which to watch smaller dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal in the cetacean clade Odontoceti (toothed whale). Dolphins belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontopori ...
s and killer whale
The orca (''Orcinus orca''), or killer whale, is a toothed whale and the largest member of the oceanic dolphin family. The only extant species in the genus '' Orcinus'', it is recognizable by its black-and-white-patterned body. A cosmopolit ...
s.
Numerous small islands dot the Hokianga, notably Ruapapaka Island, Motukaraka Island
Motukaraka Island (Auckland) (Island of Karaka) is a uninhabited island off the coast of Beachlands in Auckland, New Zealand with historical significance and a rich history of Māori occupation.
The island is flat and approximately 15m ab ...
, and To Motu Island, the latter being the site of a former pā
The word pā (; often spelled pa in English) can refer to any Māori people, Māori village or defensive settlement, but often refers to hillforts – fortified settlements with palisades and defensive :wikt:terrace, terraces – and also to fo ...
.
Arms and inlets
As the Hokianga is a drowned valley, it is the mouth of numerous "tributaries", many of which retain the name river while effectively being bays or inlets. Clockwise from the mouth of the Hokianga, these include: *Whakarapa River
The Whakarapa River is a river of the Northland Region of New Zealand's North Island. Despite its name, it is probably better described as a northern silty arm of the Hokianga Harbour, which it meets 15 kilometres northeast of the latter's mouth. ...
*Motuti River
The Motuti River is a short, wide river in the Northland Region of New Zealand's North Island. More a silty arm of the Hokianga Harbour than a true river, it flows south from the settlement of Motuti to the main channel of the Hokianga west of ...
* Whangapapatiki Creek
*Tapuwae River
The Tapuwae River is a river of the Northland Region of New Zealand's North Island. Most of its length is as an arm of the drowned valley of the Hokianga Harbour, which it reaches from the north close to the small settlement of Tapuwae, five ki ...
*Mangamuka River
The Mangamuka River is a river of the far north of the Northland Region of New Zealand's North Island. It flows generally south from the Maungataniwha Range southeast of Kaitaia, and the last few kilometres of its length are a wide, silty arm o ...
*Orira River
The Orira River is a river of the Northland Region of New Zealand's North Island. It flows southwest, and for much of its length it is a northwestern arm of the Hokianga Harbour.
See also
*List of rivers of New Zealand
This is a list of all ...
*Waihou River
The Waihou River is located in the northern North Island of New Zealand. Its former name, Thames River, was bestowed by Captain James Cook in November 1769, when he explored of the river from the mouth. An older Māori name was "Wai Kahou Roung ...
*Wairere River
The Wairere River or Wairere Stream is a river of the Northland Region of New Zealand's North Island. It flows northwest to reach the Waihou River, an arm of the Hokianga Harbour.
See also
*List of rivers of New Zealand
This is a list of all ...
*Waima River
Waima is a suburb of West Auckland, New Zealand. It is under the local governance of the Auckland Council. The majority of the modest population is clustered around the comparatively prominent Waima superette, situated just off the main ar ...
*Omanaia River
The Omanaia River is a river of the Northland Region of New Zealand's North Island. It flows northwest from the Waima Forest, first as a stream and then as a silty arm of the Hokianga Harbour. The township of Rawene stands at the point where th ...
* Whirinaki River
Settlements
The area around the harbour is divided in three by the estuary. To the south are the settlements ofWaimamaku
Waimamaku is a village and rural community, based along the banks of the Waimamaku River south of the Hokianga Harbour on the west coast of New Zealand's North Island. It is located in the Far North District and Northland Region on State Highw ...
, Ōmāpere
Ōmāpere is a settlement on the south shore of Hokianga Harbour in Northland Region, Northland, New Zealand. New Zealand State Highway 12, State Highway 12 runs through Ōmāpere. Opononi is on the shore to the north of Ōmāpere.
The New Zeala ...
, Opononi
Opononi is a settlement on the south shore of Hokianga Harbour in Northland Region, Northland, New Zealand. New Zealand State Highway 12, State Highway 12 runs through Opononi. Ōmāpere is on the shore to the south of Opononi and Pakanae is to ...
, Pakanae, Koutu, Whirinaki, Rawene, Omanaia
Omanaia () is a settlement in the Hokianga area of Northland, New Zealand. It is part of the Hokianga South statistical area, which covers the southern side of Hokianga Harbour between Rawene and Koutu. For demographics of this area, see Rawene ...
, Waima
Waima is a suburb of West Auckland, New Zealand. It is under the local governance of the Auckland Council. The majority of the modest population is clustered around the comparatively prominent Waima superette, situated just off the main art ...
, and Taheke; to the north are Broadwood, Pawarenga, Panguru
Panguru is a community in the northern Hokianga harbour, in Northland, New Zealand. The Whakarapa Stream flows from the Panguru Range in the Warawara Forest to the west, through Panguru and into the Hokianga.
Demographics
The SA1 statistical a ...
, Mitimiti
Mitimiti is a small settlement in Northland Region, Northland, New Zealand. It lies close to the Warawara Forest, between the mouths of the Whangape Harbour and Hokianga Harbour on Northland's west coast, 44 km west of Kohukohu, New Zealan ...
, and Rangi Point; and at the top of the harbour upstream from the narrows are Horeke
Horeke () is a settlement in the upper reaches of the Hokianga Harbour in Northland, New Zealand. Kohukohu is just across the harbour. The Horeke basalts are located near the town, and can be viewed on an easy stroll through the Wairere Boulde ...
, Kohukohu, and Mangamuka.
History
Pre-colonial times
According toTe Tai Tokerau
Te Tai Tokerau () is a New Zealand parliamentary Māori electorate that was created out of the Northern Maori electorate ahead of the first Mixed Member Proportional (MMP) election in 1996. It was held first by Tau Henare representing New Zea ...
tradition, Kupe
Kupe was a legendary Polynesian explorer who, according to Māori oral history, was the first person to discover New Zealand. He is generally held to have been born to a father from Rarotonga and a mother from Raiatea, and probably spoke a ...
and Ngāhue
According to Māori mythology Ngahue (sometimes known as Ngake) was a contemporary of Kupe and one of the first Polynesian explorers to reach New Zealand. He was a native of the Hawaiki and voyaged to New Zealand in “Tāwhirirangi”, his waka ...
, the legendary Polynesian navigators and explorers, settled in Hokianga in approximately 925 AD, after their journey of discovery from Hawaiki
(also rendered as in the Cook Islands, Hawaiki in Māori, in Samoan, in Tahitian, in Hawaiian) is, in Polynesian folklore, the original home of the Polynesians, before dispersal across Polynesia. It also features as the underworld in man ...
aboard their waka (canoe) named '' Matahorua'' and ''Tāwhirirangi
In Māori tradition, ''Tāwhirirangi'' was one of the great ocean-going, voyaging canoes that was used in the migrations that settled New Zealand. ''Tāwhirirangi'' was captained by Ngāhue, and originally landed in the Hokianga before headin ...
''. When Kupe left the area, he declared that this would be the place of his return, leaving several things behind—including the bailer
Bailing is the process of removing water from a vessel.
Hand bailers
A hand bailer is a device used for manually removing water which has entered a vessel. In the simplest case, it is merely a smaller container which can be filled and then emp ...
of his canoe. Later, Kupe's grandson Nukutawhiti returned from Hawaiki to settle in Hokianga.
 In the 14th century, the great chief Puhi landed just south of the
In the 14th century, the great chief Puhi landed just south of the Bay of Islands
The Bay of Islands is an area on the east coast of the Far North District of the North Island of New Zealand. It is one of the most popular fishing, sailing and tourist destinations in the country, and has been renowned internationally for ...
. The tribe of Puhi, Ngāpuhi
Ngāpuhi (also known as Ngāpuhi-Nui-Tonu or Ngā Puhi) is a Māori iwi associated with the Northland regions of New Zealand centred in the Hokianga, the Bay of Islands, and Whangārei.
According to the 2023 New Zealand census, the estimate ...
, slowly extended westwards to reach the west coast and to colonise both sides of Hokianga. Māori regard Hokianga as one of the oldest settlements in Aotearoa
''Aotearoa'' () is the Māori name for New Zealand. The name was originally used by Māori in reference only to the North Island, with the whole country being referred to as ''Aotearoa me Te Waipounamu'' – where ''Te Ika-a-Māui'' means N ...
, and it remains a heartland for the people. Rahiri, the 17th-century founder of the Ngāpuhi iwi
Iwi () are the largest social units in New Zealand Māori society. In Māori, roughly means or , and is often translated as "tribe". The word is both singular and plural in the Māori language, and is typically pluralised as such in English.
...
, was born at Whiria pā
The word pā (; often spelled pa in English) can refer to any Māori people, Māori village or defensive settlement, but often refers to hillforts – fortified settlements with palisades and defensive :wikt:terrace, terraces – and also to fo ...
to the south of the harbour, where a monument stands to his memory.
 In the course of expansion, Ngāpuhi created and maintained over centuries a complex network of walking tracks, many of which evolved into today's roads.
In the course of expansion, Ngāpuhi created and maintained over centuries a complex network of walking tracks, many of which evolved into today's roads.
Pā sites
More than a dozenpā
The word pā (; often spelled pa in English) can refer to any Māori people, Māori village or defensive settlement, but often refers to hillforts – fortified settlements with palisades and defensive :wikt:terrace, terraces – and also to fo ...
sites lie close to the Hokianga, among them notably Motukauri Pã, located on a headland at the end of a tombolo
A tombolo is a sandy or shingle isthmus. It is a deposition landform by which an island becomes attached to the mainland by a narrow piece of land such as a spit or bar. Once attached, the island is then known as a tied island. The word ''t ...
between the Motuti River and Whangapapatiki Creek mouths.
The arrival of the Europeans
Wesleyan
Wesleyan theology, otherwise known as Wesleyan–Arminian theology, or Methodist theology, is a theological tradition in Protestant Christianity based upon the ministry of the 18th-century evangelical reformer brothers John Wesley and Charle ...
(and, later, Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
) missionaries
A missionary is a member of a religious group who is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Miss ...
were guided along the Ngāpuhi walking tracks to make their own discovery of Hokianga and its accessible timber resources. Their reports soon reached merchant captains in the Bay of Islands.
Captain James Herd of the ''Providence'' responded first, and with missionary Thomas Kendall
Thomas Kendall (13 December 1778 – 6 August 1832) was a schoolmaster, an early missionary to Māori people in New Zealand, and a recorder of the Māori language. An evangelical Anglican, he and his family were in the first group of mission ...
as guide and translator, crossed the bar and entered the harbour in 1822. His was the first European ship to do so, and it sailed away with the first shipment of timber from the Hokianga. His success inspired a strong following—the deforestation of Hokianga had begun and would be complete by the turn of the century.
The only disincentive to Hokianga's exploitation was the harbour bar. Among the hundreds of ships that successfully negotiated it, 16 were recorded as being lost. Most came to grief when leaving fully laden, becoming caught in the wind shadow cast by South Head, where deep water lay. A temporary lull or change in wind direction could cause a sailing ship to lose steerage way and be swept onto the rocky shore. In 1828, the missionary schooner
A schooner ( ) is a type of sailing ship, sailing vessel defined by its Rig (sailing), rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more Mast (sailing), masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than t ...
''Herald'', built by Henry Williams Henry Williams may refer to:
Politicians
* Henry Williams (activist) (born 2000), chief of staff of the Mike Gravel 2020 presidential campaign
* Henry Williams (MP for Northamptonshire) (died 1558), member of parliament (MP) for Northamptonshire ...
and sailed by Gilbert Mair, foundered while trying to enter Hokianga Harbour.Crosby, Ron (2004) – ''Gilbert Mair, Te Kooti's Nemesis''. Reed Publ. Auckland. p.27 The last recorded shipwreck was of the schooner ''Isabella de Fraine'', lost with all eight crew in July 1928 after capsizing on the bar.
In 1837, a French adventurer, the self-titled Baron Charles de Thierry
Charles Philippe Hippolyte de Thierry (April 1793 – 8 July 1864) was a nineteenth-century adventurer who attempted to establish his own sovereign state in New Zealand in the years before the Treaty of Waitangi between the British Crown and the M ...
, sailed with 60 settlers into this hive of export activity to claim an immense tract of land that he believed he had purchased 15 years earlier in exchange for 36 axes. He was eventually granted about at Rangiahua where he set up his colony, declaring himself "Sovereign Chief of New Zealand", a title that failed to endear him to Ngāpuhi. His project collapsed, but it highlighted to the Colonial Service the need to protect against rival European powers.
The year after de Thierry arrived, another Frenchman, Bishop Jean Baptiste Pompallier
Jean-Baptiste François Pompallier (11 December 1801 – 21 December 1871) was the first Roman Catholic bishop in New Zealand and, with priests and brothers of the Marist order, he organised the Roman Catholic Church throughout the country ...
, arrived, with the aim of establishing a Catholic mission. He found the southern shores firmly in the hands of Methodist and Anglican missionaries, but the northern side was ripe for conversion. His remains, recently claimed by Ngāpuhi, lie buried where the mission began. Today the harbour, like the Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
itself, stands between Protestant and Catholic.
The lawyer and naturalist Sir Walter Lawry Buller was born in Hokianga in 1838.
Within six days of the Waitangi signing, Governor Hobson, keen to secure full Ngāpuhi support, trekked across to the Māngungu Mission
Māngungu Mission was the second mission station established in New Zealand by the Wesleyan Missionary Society. Located near Horeke, in the Hokianga Harbour, it was founded in 1828 by the missionaries John Hobbs and James Stack after the first ...
near Horeke where 3000 were waiting. The second signing of the Treaty of Waitangi took place on 12 February 1840. With the appropriate signatures (and a few inappropriate entries) Hobson could immediately claim support from the biggest tribe in the country.
 While the fate of the country was being signed into history, the axemen of Hokianga scarcely missed a beat. At any one time, as many as 20 ships could be loading Hokianga timber. Whole hillsides, suddenly bared of vegetation, began to slip into the harbour, choking its tributaries with mud.
The relationship between Māori and
While the fate of the country was being signed into history, the axemen of Hokianga scarcely missed a beat. At any one time, as many as 20 ships could be loading Hokianga timber. Whole hillsides, suddenly bared of vegetation, began to slip into the harbour, choking its tributaries with mud.
The relationship between Māori and Pākehā
''Pākehā'' (or ''Pakeha''; ; ) is a Māori language, Māori-language word used in English, particularly in New Zealand. It generally means a non-Polynesians, Polynesian New Zealanders, New Zealander or more specifically a European New Zeala ...
(European) settlers was frequently tense, never more so than during the Dog Tax War of the 1890s, which was largely centred around Hokianga.
By 1900, the bulk of the forest had sailed over the bar and the little topsoil that remained was turned to dairy farming for butter production. Most of the cream delivered to the Motukaraka Dairy Factory was carried there by a fleet of about fifty locally-built launches that criss-crossed the harbour daily, creating in the process a service for both passengers and freight. For half a century, the communities on both sides of the harbour were linked internally by sea transport, before improved roads in the 1950s finally displaced this energetic flotilla and the harbour once again divided the community.
By 1914, a rustic telephone system linked some of the Hokianga communities with each other and with the outside world. A government-subsidised, weekly coastal shipping service ran between Onehunga
Onehunga is a suburb of Auckland in New Zealand and the location of the Port of Onehunga, the city's small port on the Manukau Harbour. It is south of the city centre, close to the volcanic cone of Maungakiekie / One Tree Hill.
Onehunga is ...
and Hokianga, bringing in freight and taking away butter.
The communities of Horeke and Rawene are the second- and third-oldest European settlements in New Zealand. Rawene is still the most important of the coastal settlements in the Hokianga and is where the base of Hokianga's community owned health services ( Hauora Hokianga) is located, on top of the hill at the Hokianga Hospital.
1918 influenza pandemic
Theinfluenza pandemic
An influenza pandemic is an epidemic of an influenza virus that spreads across a large region (either multiple continents or worldwide) and infects a large proportion of the population. There have been five major influenza pandemics in the l ...
reached Hokianga in September 1918, and remote Waiotemarama was one of the first settlements to succumb. A soup kitchen was organised in each community. On the instructions of Dr George McCall Smith, the Surgeon Superintendent of Rawene Hospital, mounted and armed guards stood at all crossroads to turn back would-be visitors and thus restrict the spread of the disease between settlements. Travellers wishing to enter Hokianga were simply stopped at the boundary. The rule was simple: anyone could leave, but no one could enter.
The local epidemic lasted six weeks and a significant number died. Each community attended to its own, and mass burials were commonplace. Few Maori deaths were recorded – the true impact of the epidemic on Maori is unknown.
Industry
The first major industry of the region was based around thekauri
''Agathis'', commonly known as kauri or dammara, is a genus of evergreen coniferous trees, native to Australasia and Southeast Asia. It is one of three extant genera in the family Araucariaceae, alongside '' Wollemia'' and ''Araucaria'' (being ...
trees, both logging and the gum, the strong thick resin which came from the trees. After the forests started to thin, dairying and cheese production took over as the mainstay of the economy, but they too fell away after the closure of the Motukaraka Dairy Cooperative in 1953. For a while during the 1970s and 1980s, there was little economic base for the area, and it became a haven for alternative lifestyle
An alternative lifestyle or unconventional lifestyle is a lifestyle (sociology), lifestyle perceived to be outside the social norm, norm for a given culture. The term ''alternative lifestyle'' is often used pejoratively. Description of a related ...
rs.
In recent years, however, tourism has been revived in the region. Attractions such as the great kauri trees of the Waipoua Forest
The Waipoua Forest is a forest, on the west coast of the Northland Region of New Zealand's North Island. It preserves some of the best examples of kauri forest remaining in New Zealand. It is notable for having two of the largest living kauri ...
(including the country's largest tree, Tane Mahuta), the historic waterfront villages of Kohukohu and Rawene, cafes, the Horeke basalts
The Horeke basalts is a disused formation that contained Miocene-Pliocene basalt lava flows that covered a large area in central Northland Region of New Zealand, and in places forms a high plateau around Okaihau.
Wairere Boulders is a natur ...
, beaches, historic buildings, nature walks, horse trekking, boat trips, and fishing are bringing more visitors every year. In 2002 the first walking tracks were opened at the Wairere Boulders
Wairere Boulders is a privately-owned nature reserve and tourist attraction at Horeke in the south Hokianga region of Northland Region, Northland, New Zealand. The property contains geologically rare rock formations. Visitors to the property ca ...
allowing a close inspection of the basalt rocks in the Wairere valley. Hokianga offers varied and interesting accommodation for all styles and budgets for travelers who prefer a quieter holiday than the busier east coast offers. A visit to the Hokianga is to see what New Zealand was like in previous decades with unspoiled landscapes.

Notable people
Several iconic and very different figures in New Zealand history have been closely associated with the Hokianga.Frederick Edward Maning
Maning arrived in the Hokianga area at age 22, on 30 June 1833, and lived among theNgāpuhi
Ngāpuhi (also known as Ngāpuhi-Nui-Tonu or Ngā Puhi) is a Māori iwi associated with the Northland regions of New Zealand centred in the Hokianga, the Bay of Islands, and Whangārei.
According to the 2023 New Zealand census, the estimate ...
Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
. Maning was tall, strong, a good fighter, good-humoured, and sensitive to local power relationships and personalities. He became the esteemed possession of the local war chief and a Pākehā Māori (a European turned native). During the signing process of the Treaty of Waitangi
The Treaty of Waitangi (), sometimes referred to as ''Te Tiriti'', is a document of central importance to the history of New Zealand, Constitution of New Zealand, its constitution, and its national mythos. It has played a major role in the tr ...
in 1840, Maning acted as a translator and advised the local Māori not to sign the treaty. He wrote two books, ''Old New Zealand'' and ''A history of the war in the north of New Zealand against the chief Heke'', which are now regarded as classics of New Zealand literature.
Dame Whina Cooper
DameWhina Cooper
Dame Whina Cooper (born Hōhepine Te Wake; 9 December 1895 – 26 March 1994) was a New Zealand ( Māori elder), who worked for many years for the rights of her people, and particularly to improve the lot of Māori women. She is remembered for ...
was born at Te Karaka, Hokianga on 9 December 1895, the daughter of a leader of the Te Rarawa
Te Rarawa is a Māori iwi of Northland, New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New ...
iwi
Iwi () are the largest social units in New Zealand Māori society. In Māori, roughly means or , and is often translated as "tribe". The word is both singular and plural in the Māori language, and is typically pluralised as such in English.
...
.
From an early age she showed an interest in local community affairs and politics, and her flair and abilities led to her becoming the undisputed Māori leader of the northern Hokianga by her mid-30s.
In 1949 she moved to Auckland
Auckland ( ; ) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. It has an urban population of about It is located in the greater Auckland Region, the area governed by Auckland Council, which includes outlying rural areas and ...
, and by 1951 she was elected first president of the new Māori Women's Welfare League. The league's success was largely due to Whina's efforts, and she became well known throughout the country. In 1957 she stepped down as president and the annual conference rewarded her with the title ''Te Whaea o te Motu'' ("Mother of the Nation").
Whina Cooper continued to work for the community throughout the 1960s, but it was her 1975 leadership of a hīkoi
A ''hīkoi'' is a walk or march, and especially a protest march, in New Zealand. The word comes from the Māori language, and often implies a long journey taking many days or weeks. The most famous hīkoi was the 1975 Māori land march, on wh ...
– a symbolic march – to protest against the loss of Māori land for which she is best remembered. The march, from the northern tip of the North Island to Parliament in Wellington
Wellington is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the third-largest city in New Zealand (second largest in the North Island ...
at the other end of the island made her nationally recognised, with her determined figure, no longer strong in body but strong in mana
Mana may refer to:
Religion and mythology
* Mana (Oceanian cultures), the spiritual life force energy or healing power that permeates the universe in Melanesian and Polynesian mythology
* Mana (food), archaic name for manna, an edible substance m ...
and will, walking at the head of the march from Te Hapua to Wellington.
She was made a DBE in 1981 and a member of the Order of New Zealand
The Order of New Zealand is the highest honour in the New Zealand royal honours system, created "to recognise outstanding service to the Crown and people of New Zealand in a civil or military capacity". It was instituted by royal warrant on 6 F ...
in 1991. She had returned to Panguru in the Hokianga in 1983. She died there on 26 March 1994 at the age of 98.
Jean Baptiste Pompallier
BishopJean Baptiste Pompallier
Jean-Baptiste François Pompallier (11 December 1801 – 21 December 1871) was the first Roman Catholic bishop in New Zealand and, with priests and brothers of the Marist order, he organised the Roman Catholic Church throughout the country ...
(1802–1871), was the first Roman Catholic bishop in New Zealand. His first mission station was situated at Pūrākau in the Hokianga from 1839 until 1915. He celebrated the first mass on NZ 'terra firma' at Tōtara Point, Hokianga, in 1838. His remains were reinterred in Motuti, Hokianga, in 2002 after a nationwide hīkoi.
Opo the dolphin
Opononi became famous throughout New Zealand during 1955 and 1956 due to the exploits of abottlenose dolphin
The bottlenose dolphin is a toothed whale in the genus ''Tursiops''. They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus contains three species: the common bot ...
(nicknamed " Opo"). Opo was a wild dolphin who started following fishing boats around Opononi in early 1955 after her mother had been killed, and would swim daily in the bay close to town. She was originally named "Opononi Jack", based on Pelorus Jack
Pelorus Jack (floruit, fl. 1888 – April 1912; pronounced ) was a Risso's dolphin (''Grampus griseus'') that was famous for meeting and escorting ships through a stretch of water in Cook Strait, New Zealand. The animal was reported over ...
, since she was presumed to be male. Unlike the majority of dolphins, she had no qualms about human company, and would perform stunts for locals, play with objects like beach balls and beer bottles, and allow children to swim alongside her and make contact.
The dolphin became a local celebrity but news of her soon spread, and visitors from throughout the country would come to watch her. On 8 March 1956 official protection for Opo, requested by locals, was made law, but on 9 March she was found dead in a rock crevice at Koutu Point. It is suspected that she was killed accidentally by fishermen fishing with gelignite
Gelignite (), also known as blasting gelatin or simply "jelly", is an explosive material consisting of collodion-cotton (a type of nitrocellulose or guncotton) dissolved in either nitroglycerine or nitroglycol and mixed with wood pulp and Potassi ...
. Her death was reported nationwide, and she was buried with full Māori honours in a special plot next to the town hall.
Education
There are composite (years 1–15) schools atOpononi
Opononi is a settlement on the south shore of Hokianga Harbour in Northland Region, Northland, New Zealand. New Zealand State Highway 12, State Highway 12 runs through Opononi. Ōmāpere is on the shore to the south of Opononi and Pakanae is to ...
, Panguru
Panguru is a community in the northern Hokianga harbour, in Northland, New Zealand. The Whakarapa Stream flows from the Panguru Range in the Warawara Forest to the west, through Panguru and into the Hokianga.
Demographics
The SA1 statistical a ...
and Broadwood.
There are also primary schools at Mangamuka, Horeke
Horeke () is a settlement in the upper reaches of the Hokianga Harbour in Northland, New Zealand. Kohukohu is just across the harbour. The Horeke basalts are located near the town, and can be viewed on an easy stroll through the Wairere Boulde ...
, Kohukohu, Matihetihe
Matihetihe is a community in the Hokianga area of Northland Region, Northland, New Zealand. The Warawara Forest lies to the north. The Matihetihe Stream runs into the Tasman Sea to the west. The locality is named for the tihetihe tumbleweed that ...
, Omanaia
Omanaia () is a settlement in the Hokianga area of Northland, New Zealand. It is part of the Hokianga South statistical area, which covers the southern side of Hokianga Harbour between Rawene and Koutu. For demographics of this area, see Rawene ...
, Pawarenga, Rawene, Waimā, Whirinaki, and Umawera.
See also
*Weller brothers
The Weller brothers, Englishmen of Sydney, Australia, and Otago, New Zealand, were the founders of a whaling station on Otago Harbour and New Zealand's most substantial merchant traders in the 1830s.
Immigration
Members of a wealthy land-ownin ...
References
External links
Hauora Hokianga
Hokianga's community governed health services
Hokianga Tourism Association
Local Tourism Members and Information
Dictionary of New Zealand Biography essay on Dame Whina Cooper
Rawene Website
Kohukohu Community Website
{{Coord, -35.5258, 173.3786, region:NZ-NTL_type:waterbody_scale:250000, display=title Far North District Ports and harbours of New Zealand Populated places in the Northland Region Geography of the Northland Region