|
Tāwhirirangi
In Māori tradition, ''Tāwhirirangi'' was one of the great ocean-going, voyaging canoes that was used in the migrations that settled New Zealand. ''Tāwhirirangi'' was captained by Ngāhue, and originally landed in the Hokianga before heading to the South Island. Ngāhue is said to have then discovered pounamu. Friedrich Ratzel in ''The History of Mankind'',Ratzel, Friedrich. The History of Mankind. (London: MacMillan, 1896). URLhttp://www.inquirewithin.biz/history/american_pacific/oceania/songs.htmaccessed 18 February 2010. when discussing legend preserved in song, reported in 1896 that a chief by the name of Ngahue was driven to flight by a civil war which devastated Hawaiki. After a long journey, he reached New Zealand and returned to Hawaiki with pieces of greenstone and the bones of a giant bird. See also *List of Māori waka This is a list of Māori people, Māori (canoes). The information in this list represents a compilation of different oral traditions from arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
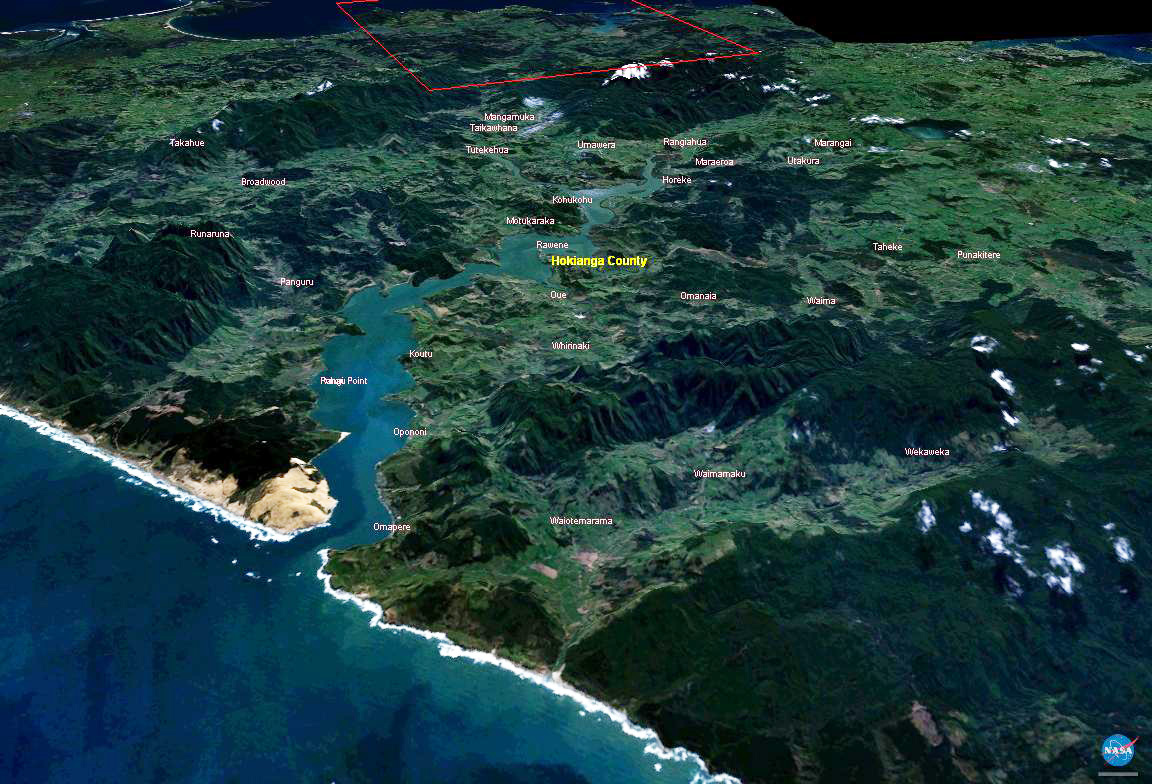
Hokianga
The Hokianga is an area surrounding the Hokianga Harbour, also known as the Hokianga River, a long Estuary, estuarine drowned valley on the west coast in the north of the North Island of New Zealand. The original name, still used by local Māori people, Māori, is ''Te Kohanga o Te Tai Tokerau'' ("the nest of the northern people") or ''Te Puna o Te Ao Marama'' ("the wellspring in the world of light"). The full name of the harbour is Te Hokianga-nui-a-Kupe — "the place of Kupe's great return". Geography The Hokianga is in the Far North (district), New Zealand, Far North District, which is in the Northland Region. The area is northwest of Whangārei City—and west of Kaikohe—by road. The estuary extends inland for from the Tasman Sea. It is navigable for small craft for much of its length, although there is a bar across the mouth. In its upper reaches the Rangiora Narrows separate the mouths of the Waihou and Mangamuka Rivers from the lower parts of the harbour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Mythology
Māori mythology and Māori traditions are two major categories into which the remote oral history of New Zealand's Māori people, Māori may be divided. Māori myths concern tales of supernatural events relating to the origins of what was the observable world for the pre-European Māori, often involving gods and demigods. Māori tradition concerns more folkloric legends often involving historical or semi-historical forebears. Both categories merge in to explain the overall origin of the Māori and their connections to the world which they lived in. The Māori did not have a writing system before European contact, beginning in 1769, therefore they relied on oral retellings and recitations memorised from generation to generation. The three forms of expression prominent in Māori and Polynesian oral literature are genealogical recital, poetry, and narrative prose. Experts in these subjects were broadly known as . The rituals, beliefs, and general worldview of Māori society were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāhue
According to Māori mythology Ngahue (sometimes known as Ngake) was a contemporary of Kupe and one of the first Polynesian explorers to reach New Zealand. He was a native of the Hawaiki and voyaged to New Zealand in “Tāwhirirangi”, his waka (canoe). No time has been fixed for these voyages, but according to legend he discovered pounamu (Greenstone) and Ngahue killed a Moa (large flightless bird - now extinct). Pounamu was sometimes called Te Ika-o-Ngāhue (Ngāhue's fish) and they took several boulders back to Hawaiki. Ngai Tahu tradition Ngati Kahungunu tradition According to a Ngāti Kahungunu tradition, Ngahue was a major chief on Hawaiki at the time when the first Māori travelled to New Zealand. In his old age, he remained in Hawaiki, but his sons and grandsons had gone to the new land. Worried that they might not have enough food, Ngahue ordered a large fish to swim to his children, so that they could eat it. The fish reached the Bay of Plenty, then swam round East ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Māori Waka
This is a list of Māori people, Māori (canoes). The information in this list represents a compilation of different oral traditions from around New Zealand. These accounts give several different uses for the waka: many carried Polynesians, Polynesian migrants and explorers from Hawaiki to New Zealand; others brought supplies or made return journeys to Hawaiki; was said to be lost at sea. List of waka See also *Māori migration canoes *List of Māori iwi *Lists of marae in New Zealand References * {{DEFAULTSORT:List of Maori waka Māori waka, Māori-related lists, Waka Polynesian navigation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Migration Canoes
Māori oral histories recount how their ancestors set out from their homeland in ''waka hourua'', large twin-hulled ocean-going canoes ('' waka''). Some of these traditions name a homeland called Hawaiki. Among these is the story of Kupe, who had eloped with Kūrāmarotini, the wife of Hoturapa, the owner of the great canoe '' Matahourua'', whom Kupe had murdered. To escape punishment for the murder, Kupe and Kura fled in Matahourua and discovered a land he called Aotearoa ('land of the long-white-cloud'). He explored its coast and killed the sea monster Te Wheke-a-Muturangi, finally returning to his home to spread the news of his newly discovered land. Other stories of various Māori tribes report migrations to escape famine, over-population, and warfare. These were made in legendary canoes, the best known of which are '' Aotea'', ''Te Arawa'', '' Kurahaupō'', '' Mātaatua'', '' Tainui'', '' Tākitimu'', and '' Tokomaru''. Various traditions name numerous other cano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area and lies east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The Geography of New Zealand, country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps (), owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. Capital of New Zealand, New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and subsequently developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Island
The South Island ( , 'the waters of Pounamu, Greenstone') is the largest of the three major islands of New Zealand by surface area, the others being the smaller but more populous North Island and Stewart Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, to the south by the Foveaux Strait and Southern Ocean, and to the east by the Pacific Ocean. The South Island covers , making it the List of islands by area, world's 12th-largest island, constituting 56% of New Zealand's land area. At low altitudes, it has an oceanic climate. The most populous cities are Christchurch, Dunedin, Nelson, New Zealand, Nelson and Invercargill. Prior to European settlement, Te Waipounamu was sparsely populated by three major iwi – Kāi Tahu, Kāti Māmoe, and the historical Waitaha (South Island iwi), Waitaha – with major settlements including in Kaiapoi Pā near modern-day Christchurch. During the Musket Wars expanding iwi colonised Te Tau Ihu Māori, Te Tau Ihu, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pounamu
Pounamu is a term for several types of hard and durable stone found in the South Island of New Zealand. They are highly valued in New Zealand, and carvings made from pounamu play an important role in Māori culture. Name The Māori word is derived from ''namu'', an archaic word that describes blue-green (or 'grue') cognate with Tahitian ''ninamu''. , also used in New Zealand English, in itself refers to two main types of green stone valued for carving: nephrite jade, classified by Māori as , , , and other names depending on colour; and translucent bowenite, a type of serpentine, known as . The collective term pounamu is preferred, as the other names in common use are misleading, such as New Zealand jade (not all pounamu is jade) and greenstone (a generic term used for unrelated stone from many countries). Pounamu is only found in New Zealand, whereas much of the carved "greenstone" sold in souvenir shops is jade sourced overseas. The Māori classification of pouna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Ratzel
Friedrich Ratzel (August 30, 1844 – August 9, 1904) was a German geographer and ethnographer, notable for first using the term ''Lebensraum'' ("living space") in the sense that the National Socialists later would. Life Ratzel's father was the head of the household staff of the Grand Duke of Baden. Friedrich attended high school in Karlsruhe for six years before being apprenticed at age 15 to apothecaries. In 1863, he went to Rapperswil on the Lake of Zurich, Switzerland, where he began to study the classics. After a further year as an apothecary at Moers near Krefeld in the Lower Rhine region (1865–1866), he spent a short time at the high school in Karlsruhe and became a student of zoology at the universities of Heidelberg, Jena and Berlin, finishing in 1868. He studied zoology in 1869, publishing ''Sein und Werden der organischen Welt'' on Darwin. After the completion of his schooling Ratzel began a period of travels that saw him transform from zoologist/biologist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaiki
(also rendered as in the Cook Islands, Hawaiki in Māori, in Samoan, in Tahitian, in Hawaiian) is, in Polynesian folklore, the original home of the Polynesians, before dispersal across Polynesia. It also features as the underworld in many Māori stories. Anne Salmond states ''Havaii'' is the old name for Raiatea, the homeland of the Māori. When British explorer James Cook first sighted New Zealand in 1769, he had on board Tupaia, a Raiatean navigator and priest. Cook's arrival seemed to be a confirmation of a prophecy by Toiroa, a priest from Māhia. At Tolaga Bay, Tupaia conversed with the ''tohunga'' associated with the school of learning located there, called Te Rawheoro. The priest asked about the Māori homelands, 'Rangiatea' (Ra'iatea), 'Hawaiki' (Havai'i, the ancient name for Ra'iatea), and 'Tawhiti' (Tahiti). Etymology Linguists have reconstructed the term to Proto- Nuclear Polynesian ''*sawaiki''. The Māori word figures in traditions about the ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Waka
Māori or Maori can refer to: Relating to the Māori people * Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group * Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand * Māori culture * Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Cook Islands * Cook Islands Māori, the language of the Cook Islanders Ships * SS ''Maori'' (1893), a steamship of the Shaw Savill Line, shipwrecked 1909 * , a Royal Navy Tribal-class destroyer, sunk in 1915 * , a Royal Navy Tribal-class destroyer, launched 1936 and sunk 1942 * TEV ''Maori III'', a Union Steam Ship Company inter-island ferry, 1952–74 Sports teams * New Zealand Māori cricket team * New Zealand Māori rugby league team * New Zealand Māori rugby union team Other * ''Maori'', a 1988 novel by Alan Dean Foster * Mayotte Mayotte ( ; , ; , ; , ), officially the Department of Mayotte (), is an Overseas France, overseas Overseas departments and regions of France, department and region and single territorial collecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |