History Of Sugar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of sugar has five main phases:
# The extraction of sugar cane juice from the
The history of sugar has five main phases:
# The extraction of sugar cane juice from the
 There are records of knowledge of sugar among the ancient Greeks and Romans, but only as an imported medicine, and not as a food. For example, the Greek physician
There are records of knowledge of sugar among the ancient Greeks and Romans, but only as an imported medicine, and not as a food. For example, the Greek physician
''Extracts from the Account Rolls of the Abbey of Durham''
In the Durham Abbey account books the word for sugar is spelled Zuker (year 1299), succre (1309), sucore (1311), Zucar (1316), suker (1323), Zuccoris (1326), Succoris (1329), sugre (1363), suggir (1440). Clive Ponting traces the spread of the cultivation of sugarcane from its introduction into
 The Portuguese took sugar to
The Portuguese took sugar to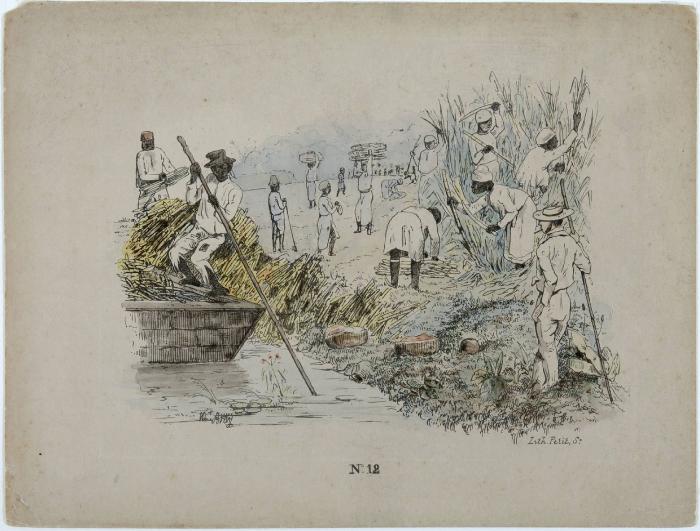  As Europeans established sugar plantations on the larger Caribbean islands, prices fell in Europe. By the 18th century all levels of society had become common consumers of the former luxury product. At first most sugar in Britain went into tea, but later
As Europeans established sugar plantations on the larger Caribbean islands, prices fell in Europe. By the 18th century all levels of society had become common consumers of the former luxury product. At first most sugar in Britain went into tea, but later  Beginning in the mid-1740s, the French colony of Saint-Domingue emerged as the world’s largest producer of sugar. However, following the abolition of slavery and the colony’s independence in 1804, sugar production declined sharply. In the following decades, Cuba surpassed Saint-Domingue and became the leading global producer of sugar.
Long established in
Beginning in the mid-1740s, the French colony of Saint-Domingue emerged as the world’s largest producer of sugar. However, following the abolition of slavery and the colony’s independence in 1804, sugar production declined sharply. In the following decades, Cuba surpassed Saint-Domingue and became the leading global producer of sugar.
Long established in
 Sugar was a luxury in Europe until the early 19th century, when it became more widely available, due to the rise of
Sugar was a luxury in Europe until the early 19th century, when it became more widely available, due to the rise of
 In the United States and Japan,
In the United States and Japan,
Sugar: The Most Evil Molecule
fromhttps://doi.org/10.61511/jcbau.v2i1.2024.913 .
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sugar
History of food and drink
 The history of sugar has five main phases:
# The extraction of sugar cane juice from the
The history of sugar has five main phases:
# The extraction of sugar cane juice from the sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
plant, and the subsequent domestication of the plant in tropical India and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
sometime around 4,000 BC.
# The invention of manufacture of cane sugar granules from sugarcane juice in India a little over two thousand years ago, followed by improvements in refining the crystal granules in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
in the early centuries AD.
# The spread of cultivation and manufacture of cane sugar to the medieval Islamic world together with some improvements in production methods.
# The spread of cultivation and manufacture of cane sugar to the West Indies and tropical parts of the Americas beginning in the 16th century, followed by more intensive improvements in production in the 17th through 19th centuries in that part of the world.
# The development of beet sugar
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
, high-fructose corn syrup
High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), also known as glucose–fructose, isoglucose, and glucose–fructose syrup, is a sweetener made from corn starch. As in the production of conventional corn syrup, the starch is broken down into glucose by enzy ...
and other sweeteners in the 19th and 20th centuries.
Sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecul ...
was first produced from sugarcane plants in India sometime after the first century AD. The derivation of the word "sugar" is thought to be from Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
(''śarkarā''), meaning "ground or candied sugar," originally "grit, gravel". Sanskrit literature from ancient India
Anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. The earliest known human remains in South Asia date to 30,000 years ago. Sedentism, Sedentariness began in South Asia around 7000 BCE; ...
, written between 1500 and 500 BC provides the first documentation of the cultivation of sugar cane and of the manufacture of sugar in the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
.
Known worldwide by the end of the medieval period
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
, sugar was very expensive and was considered a " fine spice", but from about the year 1500, technological improvements and New World sources began turning it into a much cheaper bulk commodity.
The spread of sugarcane cultivation
There are two centers of domestication for sugarcane: one for ''Saccharum officinarum
''Saccharum officinarum'' is a large, strong-growing species of grass in the sugarcane genus. Its stout stalks are rich in sucrose, a disaccharide sugar which accumulates in the stalk internodes. It originated in New Guinea, and is now cultivate ...
'' by Papuans Papuans may refer to:
* Indonesian Papuans – the Native Indonesians of Papua-origin
* Papua New Guineans – the nationals of Papua New Guinea
* Indigenous people of New Guinea
The indigenous peoples of Western New Guinea in Indonesia and Pap ...
in New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
and another for '' Saccharum sinense'' by Austronesians
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesi ...
in Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
and southern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
. Papuans and Austronesians originally primarily used sugarcane as food for domesticated pigs. The spread of both ''S. officinarum'' and ''S. sinense'' is closely linked to the migrations of the Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melan ...
. '' Saccharum barberi'' was only cultivated in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
after the introduction of ''S. officinarum''.
''Saccharum officinarum'' was first domesticated in New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
and the islands east of the Wallace Line
The Wallace Line or Wallace's Line is a faunal boundary line drawn in 1859 by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace and named by the English biologist Thomas Henry Huxley.
It separates the biogeographic realms of Asia and 'Wallacea', a ...
by Papuans Papuans may refer to:
* Indonesian Papuans – the Native Indonesians of Papua-origin
* Papua New Guineans – the nationals of Papua New Guinea
* Indigenous people of New Guinea
The indigenous peoples of Western New Guinea in Indonesia and Pap ...
, where it is the modern center of diversity. Beginning at around 6,000 BP they were selectively bred
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant ma ...
from the native '' Saccharum robustum''. From New Guinea it spread westwards to Island Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the Southeast Asian countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor.
The terms Island Southeast Asia and Insular Southeast Asia are sometimes given the same meaning as Mari ...
after contact with Austronesians, where it hybridized with '' Saccharum spontaneum''.The second domestication center is mainland southern China and Taiwan where ''S. sinense'' was a primary cultigen
A cultigen (), or cultivated plant, is a plant that has been deliberately altered or selected by humans, by means of genetic modification, graft-chimaeras, plant breeding, or wild or cultivated plant selection. These plants have commercial val ...
of the Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melan ...
. Words for sugarcane exist in the Proto-Austronesian
Proto-Austronesian (commonly abbreviated as PAN or PAn) is a proto-language. It is the reconstructed ancestor of the Austronesian languages, one of the world's major language families. Proto-Austronesian is assumed to have begun to diversify in ...
languages in Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, reconstructed as ''*təbuS'' or ''**CebuS'', which became ''*tebuh'' in Proto-Malayo-Polynesian
Proto-Malayo-Polynesian (PMP) is the reconstructed ancestor of the Malayo-Polynesian languages, which is by far the largest branch (by current speakers) of the Austronesian language family. Proto-Malayo-Polynesian is ancestral to all Austronesia ...
. It was one of the original major crops of the Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melan ...
from at least 5,500 BP. Introduction of the sweeter ''S. officinarum'' may have gradually replaced it throughout its cultivated range in Island Southeast Asia.
From Island Southeast Asia, ''S. officinarum'' was spread eastward into Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in ...
and Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of approximately 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Poly ...
by Austronesian voyagers as a canoe plant
One of the major human migration events was the maritime settlement of the islands of the Indo-Pacific by the Austronesian peoples, believed to have started from at least 5,500 to 4,000 BP (3500 to 2000 BCE). These migrations were accompani ...
by around 3,500 BP. It was also spread westward and northward by around 3,000 BP to China and India by Austronesian traders, where it further hybridized with '' Saccharum sinense'' and '' Saccharum barberi''. From there it spread further into western Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
and the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
.
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, where the process of refining cane juice into granulated crystals was developed, was often visited by imperial convoys (such as those from China) to learn about cultivation and sugar refining. By the sixth century AD, sugar cultivation and processing had reached Persia. In the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
, sugarcane was possibly brought through the Arab medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
expansion. "Wherever they went, the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
Arabs brought with them sugar, the product and the technology of its production."
Spanish and Portuguese exploration and conquest in the fifteenth century carried sugar south-west of Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, compri ...
. Henry the Navigator
Princy Henry of Portugal, Duke of Viseu ( Portuguese: ''Infante Dom Henrique''; 4 March 1394 – 13 November 1460), better known as Prince Henry the Navigator (), was a Portuguese prince and a central figure in the early days of the Portuguese ...
introduced cane to Madeira
Madeira ( ; ), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (), is an autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous region of Portugal. It is an archipelago situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, in the region of Macaronesia, just under north of ...
in 1425, while the Spanish, having eventually subdued the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
, introduced sugar cane to them. In 1493, on his second voyage, Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the At ...
carried sugarcane seedlings to the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
, in particular Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ) is an island between Geography of Cuba, Cuba and Geography of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and the second-largest by List of C ...
.
Early use of sugarcane in India
Sugarcane originated in tropical Indian subcontinent andSoutheast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
. Different species likely originated in different locations with ''S. barberi'' originating in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and ''S. edule'' and ''S. officinarum'' coming from New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
. Originally, people chewed sugarcane raw to extract its sweetness. India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
ns discovered how to crystallize sugar during the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an Indian empire during the classical period of the Indian subcontinent which existed from the mid 3rd century to mid 6th century CE. At its zenith, the dynasty ruled over an empire that spanned much of the northern Indian ...
, although literary evidence from Indian treatises such as Arthashastra
''Kautilya's Arthashastra'' (, ; ) is an Ancient Indian Sanskrit treatise on statecraft, politics, economic policy and military strategy. The text is likely the work of several authors over centuries, starting as a compilation of ''Arthashas ...
in the 2nd century AD indicates that refined sugar was already being produced in India.
Indian sailors, consumers of clarified butter and sugar, carried sugar by various trade routes
A trade route is a Logistics, logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over land or water. Allowing Good (economics and accounting ...
. Travelling Buddhist monks brought sugar crystallization methods to China. During the reign of Harsha
Harshavardhana (Sanskrit: हर्षवर्धन; 4 June 590 – 647) was an emperor of Kannauj from April 606 until his death in 647. He was the king of Thanesar who had defeated the Alchon Huns, and the younger brother of Rajyava ...
(r. 606–647) in North India
North India is a geographical region, loosely defined as a cultural region comprising the northern part of India (or historically, the Indian subcontinent) wherein Indo-Aryans (speaking Indo-Aryan languages) form the prominent majority populati ...
, Indian envoys in Tang China
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
taught sugarcane cultivation methods after Emperor Taizong of Tang
Emperor Taizong of Tang (28January 59810July 649), previously Prince of Qin, personal name Li Shimin, was the second emperor of the Tang dynasty of China, ruling from 626 to 649. He is traditionally regarded as a co-founder of the dynasty fo ...
(r. 626–649) made his interest in sugar known, and China soon established its first sugarcane cultivation in the seventh century. Chinese documents confirm at least two missions to India, initiated in 647 AD, for obtaining technology for sugar-refining. In India, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, sugar became a staple of cooking and dessert
Dessert is a course (food), course that concludes a meal; the course consists of sweet foods, such as cake, biscuit, ice cream, and possibly a beverage, such as dessert wine or liqueur. Some cultures sweeten foods that are more commonly umami, ...
s.
Early refining methods involved grinding or pounding the cane in order to extract the juice, and then boiling down the juice or drying it in the sun to yield sugary solids that looked like gravel
Gravel () is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally on Earth as a result of sedimentation, sedimentary and erosion, erosive geological processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone.
Gr ...
. The Sanskrit word for "sugar" (''sharkara'') also means "gravel" or "sand". In Persian: shakar ( Traditional Persian: شکر ) (the root of the world word sugar from Persian shakar, which is from Sanskrit śarkarā) means sweetening seeds in Persian. Similarly, the Chinese use the term "gravel sugar" (Traditional Chinese
A tradition is a system of beliefs or behaviors (folk custom) passed down within a group of people or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examp ...
: 砂糖) for what is known in the west as "table sugar".
In 1792, sugar prices soared in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
. On 15 March 1792, his Majesty's Ministers to the British parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, and may also legislate for the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of ...
presented a report related to the production of refined sugar in British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
. Lieutenant J. Paterson, of the Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William in Bengal until 1937, later the Bengal Province, was the largest of all three presidencies of British India during Company rule in India, Company rule and later a Provinces o ...
, reported that refined sugar could be produced in India with many superior advantages, and a lot more cheaply than in the West Indies.
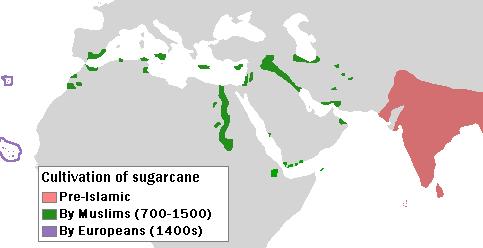
Cane sugar in the medieval era in the Muslim World and Europe
Dioscorides
Pedanius Dioscorides (, ; 40–90 AD), "the father of pharmacognosy", was a Greek physician, pharmacologist, botanist, and author of (in the original , , both meaning "On Materia medica, Medical Material") , a 5-volume Greek encyclopedic phar ...
in the 1st century (AD) wrote: "There is a kind of coalesced honey called ''sakcharon'' .e. sugarfound in reeds in India and Eudaimon Arabia .e. Yemensimilar in consistency to salt and brittle enough to be broken between the teeth like salt. It is good dissolved in water for the intestines and stomach, and an betaken as a drink to help elievea painful bladder and kidneys." Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
, a 1st-century (AD) Roman, also described sugar as medicinal: "Sugar is made in Arabia as well, but Indian sugar is better. It is a kind of honey found in cane, white as gum, and it crunches between the teeth. It comes in lumps the size of a hazelnut. Sugar is used only for medical purposes." Patrick Faas (2003). ''Around the Roman Table: Food and Feasting in Ancient Rome''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 149./ref> Sweets held a significant cultural and religious role in Islamic societies. According to Islamic tradition, the enjoyment of sweets was viewed as a sign of faith, as referenced in the Qur'an. Sugar was considered a valuable ingredient and was sometimes used as a substitute for honey in dishes such as quince paste (''membrillo'').
During the medieval era, Arab entrepreneurs adopted sugar production techniques from India and expanded the industry. Medieval Arabs in some cases set up large plantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tob ...
s equipped with on-site sugar mills or refineries. The cane sugar plant, which is native to a tropical climate, requires both a lot of water and a lot of heat to thrive. The cultivation of the plant spread throughout the medieval Arab world using artificial irrigation. The Islamic agricultural revolution played a major role in the westward spread of crops originally domesticated in India, including sugarcane. Sugarcane was first grown extensively in medieval Southern Europe during the period of Arab rule in Sicily beginning around the 9th century. In addition to Sicily, Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most o ...
(in what is currently Spain and Portugal) was an important center of sugar production, beginning by the tenth century.
From the Arab world, sugar was exported throughout Europe. The volume of imports increased in the later medieval centuries as indicated by the increasing references to sugar consumption in late medieval Western writings. But cane sugar remained an expensive import. Its price per pound in 14th and 15th century England was about equally as high as imported spices from tropical Asia such as mace (nutmeg), ginger, cloves, and pepper, which had to be transported across the Indian Ocean in that era.One source for the price of cane sugar in late medieval England is the annual account books of a large abbey at Durham, which recorded the purchases of many different goods for use in the abbey, including sugar and various spices, giving the quantity bought and the price paid, with records existing for many years in the 14th and 15th centuries. Selections from these account books are online in two volumes at Archive.org''Extracts from the Account Rolls of the Abbey of Durham''
In the Durham Abbey account books the word for sugar is spelled Zuker (year 1299), succre (1309), sucore (1311), Zucar (1316), suker (1323), Zuccoris (1326), Succoris (1329), sugre (1363), suggir (1440). Clive Ponting traces the spread of the cultivation of sugarcane from its introduction into
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, then the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
and the islands of the eastern Mediterranean, especially Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, by the 10th century. He also notes that it spread along the coast of East Africa to reach Zanzibar
Zanzibar is a Tanzanian archipelago off the coast of East Africa. It is located in the Indian Ocean, and consists of many small Island, islands and two large ones: Unguja (the main island, referred to informally as Zanzibar) and Pemba Island. ...
.
Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding ...
brought sugar home with them to Europe after their campaigns in the Holy Land
The term "Holy Land" is used to collectively denote areas of the Southern Levant that hold great significance in the Abrahamic religions, primarily because of their association with people and events featured in the Bible. It is traditionall ...
, where they encountered caravans carrying what they called "sweet salt". Early in the 12th century, Venice acquired some villages near Tyre and set up estates to produce sugar for export to Europe, where it supplemented honey as the only other available sweetener.
Crusade chronicler William of Tyre
William of Tyre (; 29 September 1186) was a Middle Ages, medieval prelate and chronicler. As Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Tyre, archbishop of Tyre, he is sometimes known as William II to distinguish him from his predecessor, William I of Tyr ...
, writing in the late 12th century, described sugar as "a most precious product, very necessary for the use and health of mankind". The first record of sugar in English is in the late 13th century.
Ponting recounts the reliance on slavery of the early European sugar entrepreneurs:
The crucial problem with sugar production was that it was highly labour-intensive in both growing and processing. Because of the huge weight and bulk of the raw cane it was very costly to transport, especially by land, and therefore each estate had to have its own factory. There the cane had to be crushed to extract the juices, which were boiled to concentrate them, in a series of backbreaking and intensive operations lasting many hours. However, once it had been processed and concentrated, the sugar had a very high value for its bulk and could be traded over long distances by ship at a considerable profit. The uropean sugarindustry only began on a major scale after the loss of the Levant to a resurgent Islam and the shift of production to Cyprus under a mixture of Crusader aristocrats and Venetian merchants. The local population on Cyprus spent most of their time growing their own food and few would work on the sugar estates. The owners therefore brought in slaves from the Black Sea area (and a few from Africa) to do most of the work. The level of demand and production was low and therefore so was the trade in slaves — no more than about a thousand people a year. It was not much larger when sugar production began in Sicily. In the Atlantic ocean Canaries,During the 1390s, a better press was developed, which doubled the amount of juice that was obtained from the sugarcane and helped to cause the economic expansion of sugar plantations toMadeira Madeira ( ; ), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (), is an autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous region of Portugal. It is an archipelago situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, in the region of Macaronesia, just under north of ..., and the Cape Verde Islands], once the initial exploitation of the timber and raw materials was over, it rapidly became clear that sugar production would be the most profitable way of getting money from the new territories. The problem was the heavy labour involved because the Europeans refused to work except as supervisors. The solution was to bring in slaves from Africa. The crucial developments in this trade began in the 1440's...
Andalusia
Andalusia ( , ; , ) is the southernmost autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Peninsular Spain, located in the south of the Iberian Peninsula, in southwestern Europe. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomou ...
and to the Algarve
The Algarve (, , ) is the southernmost NUTS statistical regions of Portugal, NUTS II region of continental Portugal. It has an area of with 467,495 permanent inhabitants and incorporates 16 municipalities (concelho, ''concelhos'' or ''município ...
. It started in Madeira
Madeira ( ; ), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (), is an autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous region of Portugal. It is an archipelago situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, in the region of Macaronesia, just under north of ...
in 1455, using advisers from Sicily and (largely) Genoese capital for the mills. The accessibility of Madeira attracted Genoese and Flemish traders keen to bypass Venetian monopolies. "By 1480 Antwerp had some seventy ships engaged in the Madeira sugar trade, with the refining and distribution concentrated in Antwerp. The 1480's saw sugar production extended to the Canary Islands. By the 1490's Madeira had overtaken Cyprus as a producer of sugar."
African slaves also worked in the sugar plantations of the Kingdom of Castile around Valencia.
Sugar cultivation in the New World
 The Portuguese took sugar to
The Portuguese took sugar to Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. By 1540, there were 800 cane sugar mills in Santa Catarina Island and there were another 2,000 on the north coast of Brazil, Demarara, and Surinam. The first sugar harvest happened in Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ) is an island between Geography of Cuba, Cuba and Geography of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and the second-largest by List of C ...
in 1501; and many sugar mills had been constructed in Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
and Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. At , it is the third-largest island—after Cuba and Hispaniola—of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, west of Hispaniola (the is ...
by the 1520s.
The approximately 3,000 small sugar mills that were built before 1550 in the New World created an unprecedented demand for cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
gear
A gear or gearwheel is a rotating machine part typically used to transmit rotational motion and/or torque by means of a series of teeth that engage with compatible teeth of another gear or other part. The teeth can be integral saliences or ...
s, levers, axles and other implements. Specialist trades in mold-making and iron casting developed in Europe due to the expansion of sugar production. Sugar mill construction sparked development of the technological skills needed for a nascent Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
in the early 17th century.
After 1625, sugarcane was introduced to the Caribbean islands from South America by the Dutch. Cultivation expanded across the region, including areas such as Barbados
Barbados, officially the Republic of Barbados, is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies and the easternmost island of the Caribbean region. It lies on the boundary of the South American ...
and the Virgin Islands
The Virgin Islands () are an archipelago between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and northeastern Caribbean Sea, geographically forming part of the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean, Caribbean islands or West Indie ...
.
Around the same time, its East India Company landed in Taiwan and started to produce and export sugarcane up until their expulsion in 1662. (See also: Netherlands–Taiwan relations)
Contemporaries often compared the worth of sugar with valuable commodities including musk
Musk is a class of aromatic substances commonly used as base notes in perfumery. They include glandular secretions from animals such as the musk deer, numerous plants emitting similar fragrances, and artificial substances with similar odors. ' ...
, pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle (mollusc), mantle) of a living Exoskeleton, shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pear ...
s, and spice
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of pl ...
s. Sugar prices declined slowly as its production became multi-sourced throughout the European colonies. Once an indulgence only of the rich, the consumption of sugar also became increasingly common among the poor as well. Sugar production increased in the mainland North American colonies, in Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
, and in Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. The labour force at first included European indentured servant
Indentured servitude is a form of Work (human activity), labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract called an "indenture", may be entered voluntarily for a prepaid lump sum, as paymen ...
s and local Native American, and African enslaved people. However, European diseases such as smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
and African ones such as malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
and yellow fever soon reduced the numbers of local Native Americans. Europeans were also very susceptible to malaria and yellow fever, and the supply of indentured servants was limited. African enslaved people became the primary labor force on sugar plantations, due to their relative resistance to diseases such as malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
and yellow fever, and the establishment of transatlantic slave trading systems along the African coast.
In the process of whitening sugar, the charred bones of dead enslaved people often supplemented the traditionally used animal bones.
During the 18th century, sugar became enormously popular. Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
, for example, consumed five times as much sugar in 1770 as in 1710.
By 1750, sugar surpassed grain as "the most valuable commodity in European trade — it made up a fifth of all European imports and in the last decades of the century four-fifths of the sugar came from the British and French colonies in the West Indies." From the 1740s until the 1820s, sugar was Britain's most valuable import.
The sugar market went through a series of booms. The heightened demand and production of sugar came about to a large extent due to a great change in the eating habits of many Europeans. For example, they began consuming jams, candy
Candy, alternatively called sweets or lollies, is a Confectionery, confection that features sugar as a principal ingredient. The category, also called ''sugar confectionery'', encompasses any sweet confection, including chocolate, chewing gum ...
, tea, coffee, cocoa, processed foods, and other sweet victuals in much greater amounts. In Britain, tea sweetened with sugar became a daily staple not only among the wealthy but also among the working class. Short tea breaks during the workday allowed laborers to quickly replenish energy, with sugary tea serving as an affordable and accessible source of calories, particularly for those engaged in physically demanding jobs.
Reacting to this increasing trend, the Caribbean islands took advantage of the situation and set about producing still more sugar. In fact, they produced up to ninety percent of the sugar that the western Europeans consumed. Some islands proved more successful than others when it came to producing the product. In Barbados and the British Leeward Islands
The Leeward Islands () are a group of islands situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the western Atlantic Ocean. Starting with the Virgin Islands east of Puerto Rico, they extend southeast to Guadeloupe and its dependencies. In Engl ...
, sugar provided 93% and 97% respectively of exports.
Planters later began developing ways to boost production even more. For example, they began using more farming methods when growing their crops. They also developed more advanced mills and began using better types of sugarcane. In the eighteenth century "the French colonies were the most successful, especially Saint-Domingue, where better irrigation, water-power and machinery, together with concentration on newer types of sugar, increased profits."
Despite these and other improvements, the price of sugar reached soaring heights, especially during events such as the revolt against the Dutch and the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
. Sugar remained in high demand, and the islands' planters knew exactly how to take advantage of the situation.
 As Europeans established sugar plantations on the larger Caribbean islands, prices fell in Europe. By the 18th century all levels of society had become common consumers of the former luxury product. At first most sugar in Britain went into tea, but later
As Europeans established sugar plantations on the larger Caribbean islands, prices fell in Europe. By the 18th century all levels of society had become common consumers of the former luxury product. At first most sugar in Britain went into tea, but later confectionery
Confectionery is the Art (skill), art of making confections, or sweet foods. Confections are items that are rich in sugar and carbohydrates, although exact definitions are difficult. In general, however, confections are divided into two bro ...
and chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cocoa beans that can be a liquid, solid, or paste, either by itself or to flavoring, flavor other foods.
Cocoa beans are the processed seeds of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao''); unprocesse ...
s became extremely popular. Many Britons (especially children) also ate jams. Suppliers commonly sold sugar in the form of a sugarloaf
A sugarloaf was the usual form in which refined sugar was produced and sold until the late 19th century, when granulated and cube sugars were introduced. A tall cone with a rounded top was the end product of a process in which dark molasses, ...
and consumers required sugar nips
Sugar nips are a large pair of pincers with sharp blades, designed to cut sugar from a block. Before the introduction of granulated and cube
A cube or regular hexahedron is a three-dimensional space, three-dimensional solid object in geometr ...
, a pliers-like tool, to break off pieces.
Sugarcane quickly exhausts the soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
in which it grows, and planters pressed larger islands with fresher soil into production in the nineteenth century as demand for sugar in Europe continued to increase: "average consumption in Britain rose from four pounds per head in 1700 to eighteen pounds in 1800, thirty-six pounds by 1850 and over one hundred pounds by the twentieth century."
In the 19th century Cuba rose to become the richest land in the Caribbean (with sugar as its dominant crop) because it formed the only major island landmass
A landmass, or land mass, is a large region or area of land that is in one piece and not noticeably broken up by oceans. The term is often used to refer to lands surrounded by an ocean or sea, such as a continent or a large island. In the fiel ...
free of mountainous terrain. Instead, nearly three-quarters of its land formed a rolling plain — ideal for planting crops. Cuba also prospered above other islands because Cubans used better methods when harvesting the sugar crops: they adopted modern milling methods such as watermill
A watermill or water mill is a mill that uses hydropower. It is a structure that uses a water wheel or water turbine to drive a mechanical process such as mill (grinding), milling (grinding), rolling, or hammering. Such processes are needed in ...
s, enclosed furnaces, steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
s, and vacuum pans. All these technologies increased productivity. Cuba also retained slavery longer than most of the rest of the Caribbean islands.
 Beginning in the mid-1740s, the French colony of Saint-Domingue emerged as the world’s largest producer of sugar. However, following the abolition of slavery and the colony’s independence in 1804, sugar production declined sharply. In the following decades, Cuba surpassed Saint-Domingue and became the leading global producer of sugar.
Long established in
Beginning in the mid-1740s, the French colony of Saint-Domingue emerged as the world’s largest producer of sugar. However, following the abolition of slavery and the colony’s independence in 1804, sugar production declined sharply. In the following decades, Cuba surpassed Saint-Domingue and became the leading global producer of sugar.
Long established in Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
, sugar production spread to other parts of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
, as well as to newer European colonies in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
and in the Pacific, where it became especially important in Fiji
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about ...
. Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
, Natal and Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
in Australia started growing sugar. The older and newer sugar production areas now tended to use indentured labour rather than enslaved people, with workers "shipped across the world ... nd... held in conditions of near slavery for up to ten years... In the second half of the nineteenth century over 450,000 indentured labourers went from India to the British West Indies, others went to Natal, Mauritius and Fiji (where they became a majority of the population). In Queensland workers from the Pacific islands were moved in. On Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, they came from China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
and Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. The Dutch transferred large numbers of people from Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
to Surinam."
It is said that the sugar plantations would not have thrived without the aid of the African enslaved people. In Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
, the planting of sugar started very early on, and entrepreneurs imported many African enslaved people to cultivate the fields. The industrialization of the Colombian industry started in 1901 with the establishment of Manuelita, the first steam-powered sugar mill in South America, by Latvian Jewish immigrant James Martin Eder.
The rise of beet sugar
 Sugar was a luxury in Europe until the early 19th century, when it became more widely available, due to the rise of
Sugar was a luxury in Europe until the early 19th century, when it became more widely available, due to the rise of beet sugar
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
in Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
, and later in France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
under Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
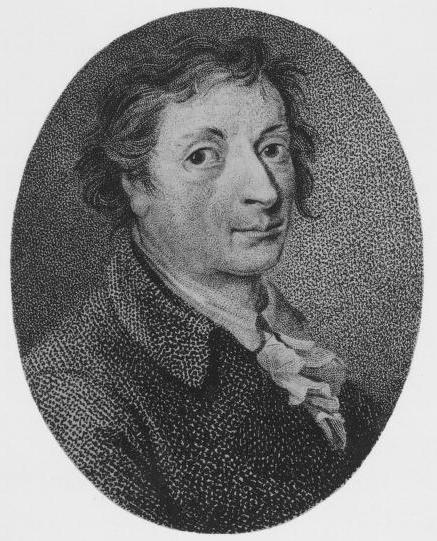
. Beet sugar was a German invention, since, in 1747, Andreas Sigismund Marggraf
Andreas Sigismund Marggraf (; 3 March 1709 – 7 August 1782) was a German chemist from Berlin, then capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg, and a pioneer of analytical chemistry. He isolated zinc in 1746 by heating calamine and carbon. Though ...
announced the discovery of sugar in beets and devised a method using alcohol to extract it. Marggraf's student, Franz Karl Achard
Franz Karl Achard (28 April 1753 – 20 April 1821) was a German (Prussian) chemist, geoscientist, physicist, and biologist. His principal discovery was the production of sugar from sugar beets.
Life and work
Achard was born in Berlin, the so ...
, devised an economical industrial method to extract the sugar in its pure form in the late 18th century. Achard first produced beet sugar in 1783 in Kaulsdorf. In 1801, under the patronage of King Frederick William III of Prussia
Frederick William III (; 3 August 1770 – 7 June 1840) was King of Prussia from 16 November 1797 until his death in 1840. He was concurrently Elector of Brandenburg in the Holy Roman Empire until 6 August 1806, when the empire was dissolved ...
(reigned 1797–1840), the world's first beet sugar production facility was established in Cunern, Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
(then part of Prussia). While never profitable, this plant operated from 1801 until its destruction during the Napoleonic War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
s (ca. 1802–1815).
The works of Marggraf and Achard were the starting point for the sugar industry in Europe, and for the modern sugar industry in general, since sugar was no longer a luxury product and a product almost only produced in warmer climates.
In France, Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
cut off from Caribbean imports by a British blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force.
A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are ...
, and at any rate not wanting to fund British merchants, banned imports of sugar in 1813 and ordered the planting of 32,000 hectares with beetroot. A beet sugar industry emerged, especially after Jean-Baptiste Quéruel industrialized the operation of Benjamin Delessert.
The United Kingdom Beetroot Sugar Association was established in 1832 but efforts to establish sugar beet in the UK were not very successful. Sugar beets provided approximately 2/3 of world sugar production in 1899. 46% of British sugar came from Germany and Austria. Sugar prices in Britain collapsed towards the end of the 19th century. The British Sugar Beet Society was set up in 1915 and by 1930 there were 17 factories in England and one in Scotland, supported under the provisions of the British Sugar (Subsidy) Act 1925. By 1935 homegrown sugar was 27.6% of British consumption. By 1929 109,201 people were employed in the British sugar beet industry, with about 25,000 more casual labourers.
Mechanization
Beginning in the late 18th century, the production of sugar became increasingly mechanized. Thesteam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
first powered a sugar mill in Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. At , it is the third-largest island—after Cuba and Hispaniola—of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, west of Hispaniola (the is ...
in 1768, and soon after, steam replaced direct firing as the source of process heat.
In 1813 the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
chemist Edward Charles Howard
Edward Charles Howard FRS (28 May 1774 – 28 September 1816) the youngest brother of Bernard Howard, 12th Duke of Norfolk, was a British chemist who has been described as "the first chemical engineer of any eminence."
Career
In January 1799 ...
invented a method of refining sugar that involved boiling the cane juice not in an open kettle, but in a closed vessel heated by steam and held under partial vacuum. At reduced pressure, water boils at a lower temperature, and this development both saved fuel and reduced the amount of sugar lost through caramelization
Caramelization (or caramelisation) is a process of browning of sugar used extensively in cooking for the resulting butter-like flavor and brown color. The brown colors are produced by three groups of polymers: (C24H36O18), (C36H50O25), and ...
. Further gains in fuel-efficiency came from the multiple-effect evaporator
In chemical engineering, a multiple-effect evaporator is an apparatus for efficiently using the heat from steam to evaporate water. Water is boiled in a sequence of vessels, each held at a lower pressure than the last. Because the boiling ...
, designed by the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
engineer Norbert Rillieux
Norbert Rillieux (March 17, 1806 – October 8, 1894) was a Louisiana Creole inventor who was widely considered one of the earliest chemical engineers and noted for his pioneering invention of the multiple-effect evaporator. This invention w ...
(perhaps as early as the 1820s, although the first working model dates from 1845). This system consisted of a series of vacuum pans, each held at a lower pressure than the previous one. The vapors from each pan served to heat the next, with minimal heat wasted. Modern industries use multiple-effect evaporators for evaporating water.
The process of separating sugar from molasses
Molasses () is a viscous byproduct, principally obtained from the refining of sugarcane or sugar beet juice into sugar. Molasses varies in the amount of sugar, the method of extraction, and the age of the plant. Sugarcane molasses is usuall ...
also received mechanical attention: David Weston first applied the centrifuge
A centrifuge is a device that uses centrifugal force to subject a specimen to a specified constant force - for example, to separate various components of a fluid. This is achieved by spinning the fluid at high speed within a container, thereby ...
to this task in Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
in 1852.
Other sweeteners
high-fructose corn syrup
High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), also known as glucose–fructose, isoglucose, and glucose–fructose syrup, is a sweetener made from corn starch. As in the production of conventional corn syrup, the starch is broken down into glucose by enzy ...
has replaced sugar in some uses, particularly in soft drinks and processed foods.
The process by which high-fructose corn syrup is produced was first developed by Richard O. Marshall and Earl R. Kooi in 1957. The industrial production process was refined by Dr. Y. Takasaki at Agency of Industrial Science and Technology of Ministry of International Trade and Industry of Japan in 1965–1970. High-fructose corn syrup was rapidly introduced to many processed foods and soft drink
A soft drink (see #Terminology, § Terminology for other names) is a class of non-alcoholic drink, usually (but not necessarily) Carbonated water, carbonated, and typically including added Sweetness, sweetener. Flavors used to be Natural flav ...
s in the United States from around 1975 to 1985.
A system of sugar tariffs and sugar quotas imposed in 1977 in the United States significantly increased the cost of imported sugar and U.S. producers sought cheaper sources. High-fructose corn syrup, derived from corn, is more economical because the domestic U.S. price of sugar is twice the global price
and the price of corn
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago ...
is kept low through government subsidies paid to growers. High-fructose corn syrup became an attractive substitute, and is preferred over cane sugar among the vast majority of American food and beverage manufacturers. Soft drink makers such as Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola, or Coke, is a cola soft drink manufactured by the Coca-Cola Company. In 2013, Coke products were sold in over 200 countries and territories worldwide, with consumers drinking more than 1.8 billion company beverage servings ...
and Pepsi
Pepsi is a Carbonated water, carbonated soft drink with a cola flavor, manufactured by PepsiCo which serves as its flagship product. In 2023, Pepsi was the second most valuable soft drink brand worldwide behind Coca-Cola; the two share a long ...
use sugar in other nations, but switched to high-fructose corn syrup in the United States in 1984.
The average American consumed approximately of high-fructose corn syrup in 2008, versus of sucrose.
In recent years it has been hypothesized that the increase of high-fructose corn syrup usage in processed foods may be linked to various health conditions, including metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndro ...
, hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
, dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia is a metabolic disorder characterized by abnormally high or low amounts of any or all lipids (e.g. fats, triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids) or lipoproteins in the blood. Dyslipidemia is a risk factor for the development of ...
, hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological response in which cells in insulin-sensitive tissues in the body fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin or downregulate insulin receptors in response to hyperinsulinemia.
Insulin is a horm ...
, and obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
. However, there is to date little evidence that high-fructose corn syrup is any unhealthier, calorie for calorie, than sucrose or other simple sugars. The fructose content and fructose:glucose ratio of high-fructose corn syrup do not differ markedly from clarified apple juice. Some researchers hypothesize that fructose may trigger the process by which fats are formed, to a greater extent than other simple sugars.. However, most commonly used blends of high-fructose corn syrup contain a nearly one-to-one ratio of fructose and glucose, just like common sucrose, and should therefore be metabolically identical after the first steps of sucrose metabolism, in which the sucrose is split into fructose and glucose components. At the very least, the increasing prevalence of high-fructose corn syrup has certainly led to an increase in added sugar calories in food, which may reasonably increase the incidence of these and other diseases..
See also
* Sugar Cane and Rum Museum * '' Castillo Serrallés'' * '' Hacienda Mercedita'' * Food history *Sugar industry
The sugar industry subsumes the production, Sugar refinery, processing and marketing of sugars (mostly sucrose and fructose). Globally, about 80% of sugar is extracted from sugar cane, grown predominantly in the tropics, and 20% from sugar beet, ...
* Sugar Museum (Berlin)
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Sugar: The Most Evil Molecule
from
Science History Institute
The Science History Institute is an institution that preserves and promotes understanding of the history of science. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it includes a library, museum, archive, research center and conference center.
It was ...
*
* Widiantara, et al. “Heritage and identity: The vernacular transformation of De Tjolomadoe.” ''Journal of City: Branding and Authenticity'', vol. 2, no. 1, 31 July 2024,