History Of Rail Transport In Great Britain 1830–1922 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of rail transport in Great Britain 1830–1922 covers the period between the opening of the 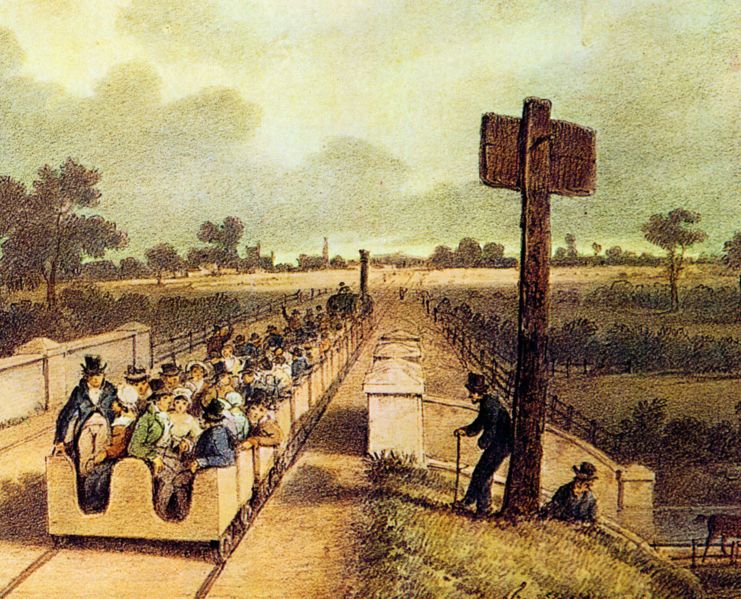
 Although the government was in favour of the development of trunk railways to stimulate economic recovery and to facilitate the movement of troops in times of potential civil unrest, it was legally necessary that each line be authorised by a separate Act of Parliament. While there were entrepreneurs with the vision of an intercity network of lines, such as those through the
Although the government was in favour of the development of trunk railways to stimulate economic recovery and to facilitate the movement of troops in times of potential civil unrest, it was legally necessary that each line be authorised by a separate Act of Parliament. While there were entrepreneurs with the vision of an intercity network of lines, such as those through the
 Through this period the conversion to standard gauge continued, with mixed-gauge track reaching
Through this period the conversion to standard gauge continued, with mixed-gauge track reaching
 By the 1850s, many steam-powered railways had reached the fringes of built-up London (which was much smaller than now), but the new lines were not permitted to demolish enough property to penetrate the City or the West End. Passengers disembarked at
By the 1850s, many steam-powered railways had reached the fringes of built-up London (which was much smaller than now), but the new lines were not permitted to demolish enough property to penetrate the City or the West End. Passengers disembarked at
 ;
;  ;
;  ; North Eastern Railway (NER) : the NER was formed in 1854 as the amalgamation of three railways: the
; North Eastern Railway (NER) : the NER was formed in 1854 as the amalgamation of three railways: the
Liverpool and Manchester Railway
The Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR) was the first inter-city railway in the world. It Opening of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, opened on 15 September 1830 between the Lancashire towns of Liverpool and Manchester in England. It ...
(L&MR), and the Grouping, the amalgamation of almost all of Britain's many railway companies into the Big Four by the Railways Act 1921.

The 1830s
AsManchester
Manchester () is a city and the metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It had an estimated population of in . Greater Manchester is the third-most populous metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.92&nbs ...
had grown on cotton spinning, so Leeds
Leeds is a city in West Yorkshire, England. It is the largest settlement in Yorkshire and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds Metropolitan Borough, which is the second most populous district in the United Kingdom. It is built aro ...
had a growing trade in weaving. The Pennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of highland, uplands mainly located in Northern England. Commonly described as the "Vertebral column, backbone of England" because of its length and position, the ra ...
restricted canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface ...
development, so the railway provided a realistic alternative, especially with the growth in coal usage from the mines in the North East and Yorkshire. A number of lines were approved in the area, such as the Leeds and Selby Railway
The Leeds and Selby Railway was an early British railway company and first mainline railway within Yorkshire. It was opened in 1834.
As built, the line ran west/east between two termini, Marsh Lane station, Leeds and Selby railway station. Th ...
, in 1830, which would link the former to the port of Hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* The hull of an armored fighting vehicle, housing the chassis
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a sea-going craft
* Submarine hull
Ma ...
, via the River Ouse.
While the L&MR had not ousted the Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated ''Lancs'') is a ceremonial county in North West England. It is bordered by Cumbria to the north, North Yorkshire and West Yorkshire to the east, Greater Manchester and Merseyside to the south, and the Irish Sea to ...
canal system from the transport of goods, there was an unexpected enthusiasm for passenger travel. The financial success of these lines was beyond all expectations, and interests in London and Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
soon planned to build lines linking these cities together and with Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population ...
and Manchester via the L&MR. These two lines were the London and Birmingham Railway
The London and Birmingham Railway (L&BR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom, in operation from 1833 to 1846, when it became part of the London and North Western Railway (L&NWR).
The railway line which the company opened in 1838, betw ...
(L&BR), designed by Robert Stephenson, which ran from Euston Square, London, to Curzon Street, Birmingham; and the Grand Junction Railway
The Grand Junction Railway (GJR) was an early railway company in the United Kingdom, which existed between 1833 and 1846. The line built by the company, which opened in 1837, linked the Liverpool and Manchester Railway to Birmingham via Warri ...
, engineered by Joseph Locke
Joseph Locke FRSA (9 August 1805 – 18 September 1860) was an English civil engineer of the nineteenth century, particularly associated with railway projects. Locke ranked alongside Robert Stephenson and Isambard Kingdom Brunel as one of the ...
, which ran from Curzon Street to an end-on junction with the Warrington and Newton Railway, a branch of the L&MR, at Dallam, near Warrington
Warrington () is an industrial town in the Borough of Warrington, borough of the same name in Cheshire, England. The town sits on the banks of the River Mersey and was Historic counties of England, historically part of Lancashire. It is east o ...
in Cheshire. The Grand Junction was designed to link the existing L&MR and the new L&BR; it opened on 4 July 1837, with the L&BR following a few months later.
Although acts of Parliament allowed railway companies compulsory purchase of wayleave
An easement is a nonpossessory right to use or enter onto the real property of another without possessing it. It is "best typified in the right of way which one landowner, A, may enjoy over the land of another, B". An easement is a property rig ...
, some powerful landowners objected to railways being built across their land and raised objections in Parliament to prevent the bill from being passed. Some landowners charged excessive amounts, so these early lines did not always follow the optimal route. In addition, steep gradients were to be avoided as they would require more powerful locomotives, while since speeds were expected to be less than about 30 mph, curves were considered less of a problem. It was the curves on these early lines that, a century later, would lead to British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Comm ...
ways' experimentation with, and later introduction of, tilting trains
A tilting train is a train that has a mechanism enabling increased speed on regular rail tracks. As a train (or other vehicle) rounds a curve at speed, objects inside the train experience centrifugal force. This can cause packages to slide about ...
.
Railway Mania
 Although the government was in favour of the development of trunk railways to stimulate economic recovery and to facilitate the movement of troops in times of potential civil unrest, it was legally necessary that each line be authorised by a separate Act of Parliament. While there were entrepreneurs with the vision of an intercity network of lines, such as those through the
Although the government was in favour of the development of trunk railways to stimulate economic recovery and to facilitate the movement of troops in times of potential civil unrest, it was legally necessary that each line be authorised by a separate Act of Parliament. While there were entrepreneurs with the vision of an intercity network of lines, such as those through the East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Derbyshire, Leicestershire, Lincolnshire (except for North Lincolnshire and North East ...
, it was much easier to find investors to back shorter stretches that were clearly defined in purpose, where rapid returns on investment could be predicted.
The boom years were 1836 and 1845–1847, when Parliament authorized 8,000 miles of lines at a projected cost of £200 million, which was about the same value as the country's annual gross domestic product (GDP) at that time. A new railway needed an Act of Parliament, which typically cost over £200,000 (about $1 million) to obtain, but opposition could effectively prevent its construction. The canal companies, unable or unwilling to upgrade their facilities to compete with railways, used political power to try to stop them. The railways responded by purchasing about a quarter of the canal system, in part to obtain the right of way, and in part to buy off critics. Once an act was obtained, there was little government regulation. The railways largely had exclusive territory, but given the compact size of Britain, this meant that two or more competing lines could connect major cities.
George Hudson
George Hudson (probably 10 March 1800 – 14 December 1871) was an English railway financier and politician who, because he controlled a significant part of the Railway Mania, railway network in the 1840s, became known as "The Railway King"—a ...
(1800–1871) became the most important railway promoter of his time. Called the "railway king" of Britain, Hudson amalgamated numerous short lines and set up a "Clearing House
Clearing house or Clearinghouse may refer to:
Banking and finance
* Clearing house (finance)
* Automated clearing house
* ACH Network, an electronic network for financial transactions in the U.S.
* Bankers' clearing house
* Cheque clearing
* Cl ...
" in 1842 which rationalized the service by providing uniform paperwork and standardized methods for apportioning fares while transferring passengers and freight between lines, and loaning out freight wagons. He could design complex company and line amalgamations, and his activities helped to bring about the beginnings of a more modern railway network. In 1849 he exercised effective control over nearly 30% of the rail track then operating in Britain, most of it owned by four railway groups – the Eastern Counties Railway
The Eastern Counties Railway (ECR) was an English railway company incorporated in 1836 intended to link London with Ipswich via Colchester, and then extend to Norwich and Yarmouth.
Construction began in 1837 on the first at the London end. Co ...
, the Midland, the York, Newcastle and Berwick, and the York and North Midland – before a series of scandalous revelations forced him out of office. The economic, railway, and accounting literatures have treated Hudson as an important figure in railway history, although concentrating largely on the financial reporting malpractices of the Eastern Counties Railway while Hudson was its chairman, which were incorporated into the influential Monteagle Committee Report of 1849. He did away with accountants and manipulated funds – paying large dividends out of capital because profits were low – but no one knew that until his system collapsed.
All the railways were promoted by commercial interests; as those opened by the year 1836 were paying good dividends, financiers wanted to invest in them, and by 1845 over a thousand projected schemes had been put forward. This led to a speculative frenzy, following a common pattern: as the price of railway shares increased, more and more money was poured in by speculators, until the inevitable collapse in price. It reached its zenith in 1846, when no fewer than 272 Acts of Parliament setting up new railway companies were passed. Unlike most stock market bubble
A stock market bubble is a type of economic bubble taking place in stock markets when market participants drive stock prices above their value in relation to some system of stock valuation.
Behavioral finance theory attributes stock market bubb ...
s, there was a net tangible result from all the investment in the form of a vast expansion of the British railway system, though perhaps at an inflated cost. When the government stepped in and announced closure for depositing schemes, the period of "Railway Mania
Railway Mania was a stock market bubble in the rail transportation industry of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in the 1840s. It followed a common pattern: as the price of railway shares increased, speculators invested more mon ...
", as it was called, was brought to an end.
The commercial interests mentioned above were often of a local nature, and there was never a nationwide plan to develop a logical network of railways. Some railways, however, began to grow faster than others, often taking over smaller lines to expand their own. The success of the L&MR led to the idea of linking Liverpool to London, and from that the seeds of the London and North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the LNWR was the largest joint stock company in the world.
Dubbed the "Premier Line", the LNWR's main line connec ...
(L&NWR) – an amalgamation of four hitherto separate enterprises, including the L&MR – were sown.
The legacy of the Railway Mania can still be seen today, with duplication of some routes and cities possessing several stations, sometimes with no direct connection between them, although a significant amount of this duplication was removed by the Beeching Axe
The Beeching cuts, also colloquially referred to as the Beeching Axe, were a major series of route closures and service changes made as part of the restructuring of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain in the 1960s. They are named ...
in the 1960s. The best example of this is London, which has no fewer than twelve main line terminal stations serving its dense and complex suburban network, the result of the many railway companies that were competing during the Mania to run their routes in the capital.
Government involvement
The railway directors often had important political and social connections, and used it to their company's advantage. For example, the directors of the Great Western came from elite backgrounds and typically had political influence when they joined the board. When an issue came up with the government, they knew whom to see in London. Landed aristocrats were especially welcome on the corporate boards. The aristocrats saw railway directorships as a socially acceptable form of contact with the world of commerce and industry. They leveraged the business acumen and connections gained through railways to join corporate boardrooms in other industries. While it had been necessary to obtain an act of Parliament to build a new railway, the government initially took a ''laissez faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( , from , ) is a type of economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies or regulations). As a system of thought, ''laissez-faire'' ...
'' approach to their construction and operation. The government began to take an interest in safety matters, with the 1840 " Act for Regulating Railways", which empowered the Board of Trade
The Board of Trade is a British government body concerned with commerce and industry, currently within the Department for Business and Trade. Its full title is The Lords of the Committee of the Privy Council appointed for the consideration of ...
to appoint railway inspectors. The Railway Inspectorate
Established in 1840, His Majesty's Railway Inspectorate (HMRI) is the organisation responsible for overseeing safety on United Kingdom, Britain's railways and light rail, tramways. It was previously a separate non-departmental public body, but ...
was established in 1840 to enquire after the causes of accidents and recommend ways of avoiding them. The first investigation was conducted by Colonel Frederic Smith into five deaths caused by a large casting falling from a moving train in 1840 ( Howden rail crash). He also conducted an enquiry into the derailment on the GWR when a mixed goods and passenger train derailed on Christmas Eve, 1841. The train hit a landslide at Sonning (Railway accident at Sonning Cutting
The Sonning Cutting railway accident occurred during the early hours of 24 December 1841 in the Sonning Cutting through Sonning Hill, near Reading, Berkshire. A Great Western Railway (GWR) luggage train travelling from London Paddington to Br ...
), killing nine passengers. As early as 1844 a bill had been put before Parliament suggesting the state purchase of the railways; this was not adopted. It did, however, lead to the introduction to minimum standards for the construction of third-class carriages, an issue raised by the Sonning accident, which came to be known as " Parliamentary Carriages".
Public opinion was generally favourable, but there were dissenters, Charles Dickens in ''Dombey and Son'' (1846) discerned enormous interest in London, chiefly positive but with some negative elements:
Some opponents in 1835 saw the passing of a glorious era:
"The Battle of the Gauges"
George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was an English civil engineer and Mechanical engineering, mechanical engineer during the Industrial Revolution. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victoria ...
built the L&MR to the same gauge as the tramroads in use in the North Eastern colliery railways he had grown up working on: a rail gauge
In rail transport, track gauge is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges exist worldwide, gauge dif ...
of , and all railways built by him and his assistants adhered to that gauge. When Bristol businessmen wished to build their railway linking their city with London, they chose Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel ( ; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was an English civil engineer and mechanical engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history", "one of the 19th-century engi ...
as their engineer. Brunel favoured a wider gauge of . He felt that the different railways would not be in close enough proximity to warrant adherence to a uniform British gauge. Thus, the Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, ...
(GWR) (completed in 1841) was constructed to Brunel's 'broad' gauge. However, his assumption proved incorrect, and when railways of a different gauge met, the inconvenience led to an officiating organization looking into the matter. Their conclusion was that Stephenson's "narrow gauge" should be adopted as Britain's standard gauge, and Parliament passed the Regulating the Gauge of Railways Act 1846
The Railway Regulation (Gauge) Act 1846 ( 9 & 10 Vict. c. 57) or the Regulating the Gauge of Railways Act 1846 or the Gauge of Railways Act 1846 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, that was designed to standardise railway track ...
which stipulated the standard gauge of .
The undaunted GWR pressed ahead into the West Midlands, in hard-fought competition with the London and North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the LNWR was the largest joint stock company in the world.
Dubbed the "Premier Line", the LNWR's main line connec ...
. Birmingham was reached in 1852, at Snow Hill and Wolverhampton
Wolverhampton ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands of England. Located around 12 miles (20 km) north of Birmingham, it forms the northwestern part of the West Midlands conurbation, with the towns of ...
at Low Level
High-level and low-level, as technical terms, are used to classify, describe and point to specific goals of a systematic operation; and are applied in a wide range of contexts, such as, for instance, in domains as widely varied as computer scienc ...
(the furthest-north broad-gauge station) in 1854. The Bristol and Gloucester Railway
The Bristol and Gloucester Railway was a railway company opened in 1844 to run services between Bristol and Gloucester. It was built on the , but it was acquired in 1845 by the Midland Railway, which also acquired the Birmingham and Gloucester Ra ...
had been bought by the Midland Railway
The Midland Railway (MR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1844 in rail transport, 1844. The Midland was one of the largest railway companies in Britain in the early 20th century, and the largest employer in Derby, where it had ...
in 1846 and converted to standard gauge in 1854, bringing mixed gauge
Dual gauge railroad track has three or four rails, allowing vehicles of two track gauges to run on it.
Signalling and sidings are more expensive to install on dual gauge tracks than on two single gauge tracks. Dual gauge is used when there i ...
track (with three rails, so that both broad and standard gauge trains could run on it) to Bristol. By the 1860s the gauge war was lost; with the merger of the standard-gauge West Midland Railway
The West Midland Railway was an early British railway company. It was formed on 1 July 1860 by the ( 23 & 24 Vict. c. lxxxi) which merged several older railway companies. It was amalgamated with the Great Western Railway on 1 August 1863. It ...
into the GWR in 1861 mixed gauge came to Paddington
Paddington is an area in the City of Westminster, in central London, England. A medieval parish then a metropolitan borough of the County of London, it was integrated with Westminster and Greater London in 1965. Paddington station, designed b ...
, and by 1869 there was no broad-gauge track north of Oxford.
 Through this period the conversion to standard gauge continued, with mixed-gauge track reaching
Through this period the conversion to standard gauge continued, with mixed-gauge track reaching Exeter
Exeter ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and the county town of Devon in South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter w ...
in 1876. By this time most conversions were bypassing mixed gauge and going directly from broad to standard. The final stretch of broad gauge on the national network was converted to standard in a single weekend in May 1892.
There is one small exception: The Holyhead Breakwater Railway, laid for the construction of the breakwater, was constructed at the broad gauge. Construction finished in 1870, and one locomotive was sold to a local company which had its own sidings leading to the dock. It continued to work this isolated network until 1913 when it wore out and the network was regauged.
London
 By the 1850s, many steam-powered railways had reached the fringes of built-up London (which was much smaller than now), but the new lines were not permitted to demolish enough property to penetrate the City or the West End. Passengers disembarked at
By the 1850s, many steam-powered railways had reached the fringes of built-up London (which was much smaller than now), but the new lines were not permitted to demolish enough property to penetrate the City or the West End. Passengers disembarked at Paddington
Paddington is an area in the City of Westminster, in central London, England. A medieval parish then a metropolitan borough of the County of London, it was integrated with Westminster and Greater London in 1965. Paddington station, designed b ...
, Euston, King's Cross, Fenchurch Street
Fenchurch Street is a street in London, England, linking Aldgate at its eastern end with Lombard Street and Gracechurch Street in the west. It is a well-known thoroughfare in the City of London financial district and is the site of many cor ...
, Charing Cross
Charing Cross ( ) is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Since the early 19th century, Charing Cross has been the notional "centre of London" and became the point from which distances from London are measured. ...
, Waterloo
Waterloo most commonly refers to:
* Battle of Waterloo, 1815 battle where Napoleon's French army was defeated by Anglo-allied and Prussian forces
* Waterloo, Belgium
Waterloo may also refer to:
Other places
Australia
* Waterloo, New South Wale ...
or Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Queen Victoria (1819–1901), Queen of the United Kingdom and Empress of India
* Victoria (state), a state of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, Canada, a provincial capital
* Victoria, Seychelles, the capi ...
and then made their own way via hackney carriage
A hackney or hackney carriage (also called a cab, black cab, hack or taxi) is a carriage or car for hire. A hackney of a more expensive or high class was called a remise. A symbol of London and Britain, the black taxi is a common sight on t ...
or on foot into the centre, thereby increasing congestion in the city. The Metropolitan Railway
The Metropolitan Railway (also known as the Met) was a passenger and goods railway that served London from 1863 to 1933, its main line heading north-west from the capital's financial heart in the City to what were to become the Middlesex su ...
was built under the ground to connect several of these separate railway terminals. It opened in 1863, and was the first line of what was to become the London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or as the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent home counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England.
The Undergro ...
. Marylebone was connected to the Bakerloo line
The Bakerloo line () is a London Underground line that runs between in suburban north-west London and in south London, via the West End. Printed in brown on the Tube map, it serves 25 stations, 15 of which are underground, over . It runs par ...
in 1907, but Fenchurch Street was never connected to the system.
Early successes
The financial success of the early railways was phenomenal, as they had no real competition. The roads were still very slow and in poor condition. Prices of fuel and food fell in cities connected to railways owing to the fall in the cost of transport. The layout of lines with gentle gradients and curves, originating from the need to help the relatively weak engines and brakes, was a boon when speeds increased, avoiding for the most part the need to re-survey the course of a line. Less than 20 years after the Liverpool line opened, it was possible to travel from London to Scotland by train, in a small fraction of the former time by road. Towards the end of the 19th century, competition became fierce between companies on the east and west coast routes to Scotland, leading to the "Race to the North
The Race to the North was the name given by the press to occasions in two summers of the late 19th century when British passenger trains belonging to different companies would literally race each other from London to Edinburgh over the two princ ...
".
By 1923 there were some nine major railways operating in England and five in Scotland. In addition there were smaller companies, such as the Cambrian Railways
The Cambrian Railways owned of Railway track, track over a large area of mid Wales. The system was an amalgamation of a number of railways that were incorporated in 1864, 1865 and 1904. The Cambrian connected with two larger railways with c ...
and the many South Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
lines; the Furness
Furness ( ) is a peninsula and region of Cumbria, England. Together with the Cartmel Peninsula it forms North Lonsdale, Historic counties of England, historically an exclave of Lancashire. On 1 April 2023 it became part of the new unitary author ...
and Hull and Barnsley Railway
The Hull Barnsley & West Riding Junction Railway and Dock Company (HB&WRJR&DCo.) was opened on 20 July 1885. It had a total projected length of but never reached Barnsley, stopping a few miles short at Stairfoot. The name was changed to The ...
s in England; and many much smaller lines. A brief note about each of the larger companies will illustrate how they grew to the importance they had assumed by the time of the huge amalgamations which took place in 1923, in which all but a very few railways were absorbed. Each of the railways described briefly below have their own article.
Major pre-grouping railway companies in Great Britain
English railways
;Great Central Railway
The Great Central Railway in England was formed when the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway changed its name in 1897, anticipating the opening in 1899 of its Great Central Main Line, London Extension. On 1 January 1923, the company ...
(GCR) : the GCR developed from the ''Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway'', which was formed from an amalgamation of various existing and proposed lines in the North and East Midlands. The MS&LR system was based around an east-west Trans-Pennine route, but in 1897 it began a new line via the East Midlands into London to a new terminus at Marylebone
Marylebone (usually , also ) is an area in London, England, and is located in the City of Westminster. It is in Central London and part of the West End. Oxford Street forms its southern boundary.
An ancient parish and latterly a metropo ...
, and was renamed the GCR. It was the last major main line to be built in Britain, and was consequently engineered to a higher standard than earlier lines. After the opening of the ''London Extension'' in 1899, the GCR served an area between the East and West Coast main lines (see below), in competition with several other companies, especially the Midland Railway
The Midland Railway (MR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1844 in rail transport, 1844. The Midland was one of the largest railway companies in Britain in the early 20th century, and the largest employer in Derby, where it had ...
. After nationalisation the GCR network was effectively dismantled, leaving the East Midlands served only by the older Midland main line. Only the Marylebone to Birmingham section survives today.
 ;
; Great Eastern Railway
The Great Eastern Railway (GER) was a pre-grouping British railway company, whose main line linked London Liverpool Street to Norwich and which had other lines through East Anglia. The company was grouped into the London and North Eastern R ...
(GER) : the GER was an amalgamation in 1862 of the Eastern Counties Railway
The Eastern Counties Railway (ECR) was an English railway company incorporated in 1836 intended to link London with Ipswich via Colchester, and then extend to Norwich and Yarmouth.
Construction began in 1837 on the first at the London end. Co ...
with several smaller East Anglian lines; it also absorbed the Northern and Eastern Railway
The Northern & Eastern Railway (N&ER) was an early British railway company, that planned to build a line from London to York. Its ambition was cut successively back, and it was only constructed from Stratford, east of London, to the towns of Bi ...
in 1902. It served the eastern counties of England: Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the East of England and East Anglia. It is bordered by Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfor ...
, Essex
Essex ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the East of England, and one of the home counties. It is bordered by Cambridgeshire and Suffolk to the north, the North Sea to the east, Kent across the Thames Estuary to the ...
, Suffolk
Suffolk ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East of England and East Anglia. It is bordered by Norfolk to the north, the North Sea to the east, Essex to the south, and Cambridgeshire to the west. Ipswich is the largest settlement and the county ...
and Norfolk
Norfolk ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in England, located in East Anglia and officially part of the East of England region. It borders Lincolnshire and The Wash to the north-west, the North Sea to the north and eas ...
, as well an extensive suburban network in East London and Essex. It was one of the few pre-Grouping companies (another being the North Eastern Railway) to have a near monopoly of its territory. Its main London terminus was Liverpool Street.
; Great Northern Railway (GNR) : the GNR began as an amalgamation in 1846 of two rival schemes: the ''London and York Railway'' and the ''Direct Northern Railway'' (both started in 1844). The GNR main line ran northwards from King's Cross to a joint station with the NER at Doncaster
Doncaster ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city in South Yorkshire, England. Named after the River Don, Yorkshire, River Don, it is the administrative centre of the City of Doncaster metropolitan borough, and is the second largest se ...
. Other lines served Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire (), abbreviated ''Lincs'', is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the East Midlands and Yorkshire and the Humber regions of England. It is bordered by the East Riding of Yorkshire across the Humber estuary to th ...
and Derby Friargate. The GNR also had joint ownership of the Cheshire Lines Committee
The Cheshire Lines Committee (CLC) was formed in the 1860s and became the second-largest joint railway in Great Britain. The committee, which was often styled the Cheshire Lines Railway, operated of track in the then counties of Lancashire and ...
, giving access to Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population ...
; other joint workings led to West Yorkshire
West Yorkshire is a Metropolitan counties of England, metropolitan and Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England. It borders North Yorkshire to the north and east, South Yorkshire and De ...
(Leeds
Leeds is a city in West Yorkshire, England. It is the largest settlement in Yorkshire and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds Metropolitan Borough, which is the second most populous district in the United Kingdom. It is built aro ...
and Halifax); and it part-owned, with the Midland Railway, the Midland and Great Northern Joint Railway
The Midland and Great Northern Joint Railway (M&GNJR) was a railway network in England, in the area connecting southern Lincolnshire, the Isle of Ely and north Norfolk. It developed from several local independent concerns and was incorporated i ...
, serving parts of East Anglia. The GNR, with the NER and the NBR, operated the East Coast Main Line
The East Coast Main Line (ECML) is a electrified railway between its northern terminus at and southern terminus at . The key towns and cities of , , , , and are on the line. The line is a key transport artery on the eastern side of Grea ...
between London and Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
.
; Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, ...
(GWR) : the GWR was incorporated in 1835 to construct a railway, operated on the broad gauge of , between Bristol and London. With the addition of several railways – including the ''Bristol and Exeter Railway'' (1876); ''South Wales Railway'' (1863); ''West Midland Railway'' (1863); ''South Devon Railway'' (1878); and the ''Cornwall Railway'' (1889) – the GWR territory took shape. The major routes, apart from the original line, served Weymouth, Plymouth
Plymouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Devon, South West England. It is located on Devon's south coast between the rivers River Plym, Plym and River Tamar, Tamar, about southwest of Exeter and ...
and Penzance
Penzance ( ; ) is a town, civil parish and port in the Penwith district of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is the westernmost major town in Cornwall and is about west-southwest of Plymouth and west-southwest of London. Situated in the ...
to the west; all of South Wales to Fishguard
Fishguard (, meaning "Mouth of the River Gwaun") is a coastal town in Pembrokeshire, Wales, with a population of 3,400 (rounded to the nearest 100) as of the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census. Modern Fishguard consists of two parts, Lowe ...
and Aberystwyth
Aberystwyth (; ) is a University town, university and seaside town and a community (Wales), community in Ceredigion, Wales. It is the largest town in Ceredigion and from Aberaeron, the county's other administrative centre. In 2021, the popula ...
; Birmingham and Chester
Chester is a cathedral city in Cheshire, England, on the River Dee, Wales, River Dee, close to the England–Wales border. With a built-up area population of 92,760 in 2021, it is the most populous settlement in the borough of Cheshire West an ...
to the north-west. A working agreement with the LNWR extended the Chester line to Birkenhead
Birkenhead () is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral, Merseyside, England. The town is on the Wirral Peninsula, along the west bank of the River Mersey, opposite Liverpool. It lies within the Historic counties of England, historic co ...
on Merseyside
Merseyside ( ) is a ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial and metropolitan county in North West England. It borders Lancashire to the north, Greater Manchester to the east, Cheshire to the south, the Wales, Welsh county of Flintshire across ...
. The broad gauge system resulted in what became known as the ''Gauge War'': despite the technical advantages of broad gauge, it caused problems wherever the GWR met other companies' tracks, and eventually (in 1892) the last broad gauge line was abolished. The name "Great Western Railway", alone of all the pre-Grouping companies, was retained until the nationalisation of the railways; and one of the post-British Rail train operating companies
In the railway system of Great Britain, a train operating company (TOC) is a railway undertaking operating passenger trains under the collective National Rail brand. TOCs have existed since the privatisation of the network under the Railways ...
now bears the name in 2005.
; Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway
The Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (L&YR) was a major History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company before the Railways Act 1921, 1923 Grouping. It was Incorporation (business)#Incorporation in the United Kingdom, incorpo ...
(L&YR) : the L&YR was incorporated in 1847; as with all the major railways it was the result of amalgamations, in this instance the Manchester and Leeds Railway
The Manchester and Leeds Railway was a British railway company that built a line from Manchester to Normanton, West Yorkshire, Normanton where it made a junction with the North Midland Railway, over which it relied on running powers to access L ...
which in 1859 joined the East Lancashire Railway
The East Lancashire Railway is a heritage railway line in North West England which runs between Heywood, Greater Manchester and Rawtenstall in Lancashire. There are intermediate stations at Bury Bolton Street, , Summerseat and Ramsbott ...
to form the L&YR. Its lines covered the two counties, and served amongst others Manchester
Manchester () is a city and the metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It had an estimated population of in . Greater Manchester is the third-most populous metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.92&nbs ...
, Leeds
Leeds is a city in West Yorkshire, England. It is the largest settlement in Yorkshire and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds Metropolitan Borough, which is the second most populous district in the United Kingdom. It is built aro ...
, Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population ...
, Preston, Doncaster
Doncaster ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city in South Yorkshire, England. Named after the River Don, Yorkshire, River Don, it is the administrative centre of the City of Doncaster metropolitan borough, and is the second largest se ...
and Goole
Goole is a port town and civil parish on the River Ouse, Yorkshire, River Ouse in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. The town's Historic counties of England, historic county is the West Riding of Yorkshire.
At the 2021 United Kingdom censu ...
. In 1922 the L&YR was combined with the LNWR, the Midland, and others, in the LMSR.
; London and North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the LNWR was the largest joint stock company in the world.
Dubbed the "Premier Line", the LNWR's main line connec ...
(LNWR) : the LNWR was formed in 1846 when four existing lines were amalgamated: the London and Birmingham Railway
The London and Birmingham Railway (L&BR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom, in operation from 1833 to 1846, when it became part of the London and North Western Railway (L&NWR).
The railway line which the company opened in 1838, betw ...
; the Liverpool and Manchester Railway; the Grand Junction Railway
The Grand Junction Railway (GJR) was an early railway company in the United Kingdom, which existed between 1833 and 1846. The line built by the company, which opened in 1837, linked the Liverpool and Manchester Railway to Birmingham via Warri ...
; and the Manchester and Birmingham Railway
The Manchester and Birmingham Railway (M&BR) was built between Manchester and Crewe and opened in stages from 1840. Between Crewe and Birmingham, trains were worked by the Grand Junction Railway. The M&BR was merged into the London and North W ...
, making the LNWR the largest in the country at that time 20 miles (672 km) By 1923 its main line stretched from Euston station
Euston railway station ( ; or London Euston) is a major London station group, central London railway terminus and Euston tube station, connected London Underground station managed by Network Rail in the London Borough of Camden. It is the sout ...
in London to Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from ) is a city in the Cumberland district of Cumbria, England.
Carlisle's early history is marked by the establishment of a settlement called Luguvalium to serve forts along Hadrian's Wall in Roman Britain. Due to its pro ...
, with branches to Oxford
Oxford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and non-metropolitan district in Oxfordshire, England, of which it is the county town.
The city is home to the University of Oxford, the List of oldest universities in continuou ...
and Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 Unit ...
; to Peterborough
Peterborough ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in the City of Peterborough district in the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Cambridgeshire, England. The city is north of London, on the River Nene. A ...
; and from Crewe
Crewe () is a railway town and civil parish in the unitary authority of Cheshire East in Cheshire, England. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the parish had a population of 55,318 and the built-up area had a population of 74,120. ...
to North Wales and West Yorkshire. It had running powers to enable its trains to reach Swansea
Swansea ( ; ) is a coastal City status in the United Kingdom, city and the List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, second-largest city of Wales. It forms a Principal areas of Wales, principal area, officially known as the City and County of ...
and other parts of South Wales; and it also owned a railway in Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
. The LNWR, together with the Caledonian Railway
The Caledonian Railway (CR) was one of the two biggest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping. It was formed in 1845 with the objective of forming a link between English railways and Glasgow. It progressively ex ...
, operated the West Coast Main Line
The West Coast Main Line (WCML) is one of the most important railway corridors in the United Kingdom, connecting the major cities of London and Glasgow with branches to Birmingham, Manchester, Liverpool and Edinburgh. It is one of the busiest ...
between London and Glasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom ...
.
; London and South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exete ...
(LSWR) : Promoted as the ''London and Southampton Railway'', the first section opened in 1838. By 1923 its main line extended from Waterloo
Waterloo most commonly refers to:
* Battle of Waterloo, 1815 battle where Napoleon's French army was defeated by Anglo-allied and Prussian forces
* Waterloo, Belgium
Waterloo may also refer to:
Other places
Australia
* Waterloo, New South Wale ...
in London via Woking
Woking ( ) is a town and borough status in the United Kingdom, borough in north-west Surrey, England, around from central London. It appears in Domesday Book as ''Wochinges'', and its name probably derives from that of a Anglo-Saxon settleme ...
, Basingstoke
Basingstoke ( ) is a town in Hampshire, situated in south-central England across a valley at the source of the River Loddon on the western edge of the North Downs. It is the largest settlement in Hampshire without city status in the United King ...
and Winchester
Winchester (, ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs N ...
to Southampton
Southampton is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Hampshire, England. It is located approximately southwest of London, west of Portsmouth, and southeast of Salisbury. Southampton had a population of 253, ...
, Bournemouth
Bournemouth ( ) is a coastal resort town in the Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole unitary authority area, in the ceremonial county of Dorset, England. At the 2021 census, the built-up area had a population of 196,455, making it the largest ...
, Poole
Poole () is a coastal town and seaport on the south coast of England in the Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole unitary authority area in Dorset, England. The town is east of Dorchester, Dorset, Dorchester and adjoins Bournemouth to the east ...
and Weymouth. It also operated a main line from Waterloo via Guildford
Guildford () is a town in west Surrey, England, around south-west of central London. As of the 2011 census, the town has a population of about 77,000 and is the seat of the wider Borough of Guildford, which had around inhabitants in . The nam ...
to Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Hampshire, England. Most of Portsmouth is located on Portsea Island, off the south coast of England in the Solent, making Portsmouth the only city in En ...
(the "Portsmouth Direct line"), and another via Salisbury
Salisbury ( , ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and civil parish in Wiltshire, England with a population of 41,820, at the confluence of the rivers River Avon, Hampshire, Avon, River Nadder, Nadder and River Bourne, Wi ...
and Exeter
Exeter ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and the county town of Devon in South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter w ...
to Plymouth
Plymouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Devon, South West England. It is located on Devon's south coast between the rivers River Plym, Plym and River Tamar, Tamar, about southwest of Exeter and ...
running parallel to, but south of, the GWR main line. This route, known as "the Withered Arm", extended into Devon and Cornwall serving many of the south and south-west seaside resort
A seaside resort is a city, resort town, town, village, or hotel that serves as a Resort, vacation resort and is located on a coast. Sometimes the concept includes an aspect of an official accreditation based on the satisfaction of certain requi ...
s, served by what was known as the ''Atlantic Coast Express''. The LSWR also had a busy suburban network in south-west London. The Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway
The Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway (S&DJR, also known as the S&D, S&DR or SDJR), was an English railway line Joint railway, jointly owned by the Midland Railway (MR) and the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) that grew to connect Bat ...
was jointly owned with the Midland Railway.
 ;
; London, Brighton and South Coast Railway
The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR (known also as the Brighton line, the Brighton Railway or the Brighton)) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1922. Its territory formed a rough triangle, with London at ...
(LB&SCR) : the LB&SCR began as the ''London and Croydon Railway
The London and Croydon Railway (L&CR) was an early railway in England. It opened in 1839 and in February 1846 merged with other railways to form the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR).
Origins
The Croydon line and other railways
...
'' (opened in 1839) and the ''London and Brighton Railway
The London and Brighton Railway (L&BR) was a railway company in England which was incorporated in 1837 and survived until 1846. Its railway ran from a junction with the London and Croydon Railway (L&CR) at Norwood – which gives it access fr ...
'' (1840). Its network of lines covered a large portion of the South London suburbs and served almost the whole of the county of Sussex
Sussex (Help:IPA/English, /ˈsʌsɪks/; from the Old English ''Sūþseaxe''; lit. 'South Saxons'; 'Sussex') is an area within South East England that was historically a kingdom of Sussex, kingdom and, later, a Historic counties of England, ...
, much of Surrey
Surrey () is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Greater London to the northeast, Kent to the east, East Sussex, East and West Sussex to the south, and Hampshire and Berkshire to the wes ...
and some extensions into Kent
Kent is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Essex across the Thames Estuary to the north, the Strait of Dover to the south-east, East Sussex to the south-west, Surrey to the west, and Gr ...
and Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants.) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Berkshire to the north, Surrey and West Sussex to the east, the Isle of Wight across the Solent to the south, ...
. Many of the south coast resorts owe their existence to the line. Electrification began in 1909 on the overhead system; this was later changed to third rail when the LB&SCR became part of the Southern Railway.
; Midland Railway
The Midland Railway (MR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1844 in rail transport, 1844. The Midland was one of the largest railway companies in Britain in the early 20th century, and the largest employer in Derby, where it had ...
(MidR) : the MidR was formed in 1844 with the amalgamation of three railways: the ''North Midland Railway
The North Midland Railway was a railway line and Great Britain, British railway company, which opened a line from the city of Derby in Derbyshire to the city of Leeds in Yorkshire in 1840.
At Derby, it connected with the Birmingham and Derby J ...
''; the ''Midland Counties Railway
The Midland Counties' Railway (MCR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom which existed between 1839 and 1844, connecting Nottingham, Leicester and Derby with Rugby, Warwickshire, Rugby and thence, via the London and Birmingham Railway, t ...
'', and the ''Birmingham and Derby Junction Railway
The Birmingham and Derby Junction Railway (B&DJR) was a Great Britain, British railway company. From Birmingham it connected at Derby with the North Midland Railway and the Midland Counties Railway at what became known as the Derby Midland Sta ...
''. In its early days it had no London terminus, using termini of other railways (the LNWR and the GNR) until 1862, when its grandiose London terminus at St Pancras was built. By 1923 its main lines ran from St Pancras to Carlisle, via Nottingham
Nottingham ( , East Midlands English, locally ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area in Nottinghamshire, East Midlands, England. It is located south-east of Sheffield and nor ...
and Sheffield
Sheffield is a city in South Yorkshire, England, situated south of Leeds and east of Manchester. The city is the administrative centre of the City of Sheffield. It is historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire and some of its so ...
, and via Derby
Derby ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area on the River Derwent, Derbyshire, River Derwent in Derbyshire, England. Derbyshire is named after Derby, which was its original co ...
(the MidR headquarters) to Manchester
Manchester () is a city and the metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It had an estimated population of in . Greater Manchester is the third-most populous metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.92&nbs ...
. It also had a secondary main line from Derby through Birmingham to Bristol. It part-owned the Midland and Great Northern Joint Railway
The Midland and Great Northern Joint Railway (M&GNJR) was a railway network in England, in the area connecting southern Lincolnshire, the Isle of Ely and north Norfolk. It developed from several local independent concerns and was incorporated i ...
, serving east coast ports and resorts; the Somerset and Dorset Railway
The Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway (S&DJR, also known as the S&D, S&DR or SDJR), was an English railway line Joint railway, jointly owned by the Midland Railway (MR) and the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) that grew to connect Bat ...
(with the L&SWR); and had access using other joint railways to reach Swansea in South Wales, Liverpool, and the port of Stranraer
Stranraer ( , in Scotland also ; ), also known as The Toon or The Cleyhole, is a town in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, on Loch Ryan and the northern side of the isthmus joining the Rhins of Galloway to the mainland. Stranraer is Dumfries ...
in Scotland. The latter route gave it access to its ownership of two of the Irish railways.
 ; North Eastern Railway (NER) : the NER was formed in 1854 as the amalgamation of three railways: the
; North Eastern Railway (NER) : the NER was formed in 1854 as the amalgamation of three railways: the York, Newcastle and Berwick Railway
The York, Newcastle and Berwick Railway (YN&BR) was an English railway company formed in 1847 by the amalgamation of the York and Newcastle Railway as well as the Newcastle and Berwick Railway. Both companies were part of the group of business i ...
; the York and North Midland Railway
The York and North Midland Railway (Y&NMR) was an English railway company that opened in 1839 connecting York with the Leeds and Selby Railway, and in 1840, extended this line to meet the North Midland Railway at Normanton railway station, Norma ...
; and the Leeds Northern Railway
The Leeds Northern Railway (LNR), until 1851 the Leeds and Thirsk Railway, was an English railway company that built and opened a line from Leeds to Stockton via Harrogate and Thirsk. In 1845 the Leeds and Thirsk Railway received permission fo ...
. Since it eventually included the Stockton and Darlington line, it was the successor to the first public steam railway in the world. At the time of the Grouping its main line ran from the joint station at Doncaster, through York
York is a cathedral city in North Yorkshire, England, with Roman Britain, Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Foss, Foss. It has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a Yor ...
and Newcastle-on-Tyne
Newcastle upon Tyne, or simply Newcastle ( , RP: ), is a cathedral city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. It is England's northernmost metropolitan borough, located on the River Tyne's northern bank opposite Gateshead to the ...
to Berwick-on-Tweed
Berwick-upon-Tweed (), sometimes known as Berwick-on-Tweed or simply Berwick, is a town and civil parish in Northumberland, England, south of the Anglo-Scottish border, and the northernmost town in England. The 2011 United Kingdom census recor ...
. It formed part of the East Coast Main Line, and its headquarters were at York. It had a larger tonnage of mineral and coal traffic at the beginning of the 20th century than any other railway in Britain.
; South Eastern and Chatham Railway
The South Eastern and Chatham Railway Companies Joint Management Committee (SE&CRCJMC),Awdry (1990), page 199 known as the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR), was a working union of two neighbouring rival railways, the South Eas ...
(SE&CR) : the SE&CR was a so-called ''working union'' in 1899 of two railways in the south east of England; the '' South Eastern Railway'' (opened in 1842) and the ''London, Chatham and Dover Railway
The London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR or LC&DR) was a railway company in south-eastern England. It was created on 1 August 1859, when the East Kent Railway was given parliamentary approval to change its name. Its lines ran through Lond ...
'' (1859). Like the LB&SCR and the L&SWR, it had a large suburban traffic base and served many of the south east coast seaside resorts. As a result of merging the two networks it had more London termini than any other company: London Bridge and Victoria (both shared with LB&SC), Charing Cross, Blackfriars and Holborn Viaduct. Its main lines ran from these termini via Maidstone
Maidstone is the largest Town status in the United Kingdom, town in Kent, England, of which it is the county town. Maidstone is historically important and lies east-south-east of London. The River Medway runs through the centre of the town, l ...
or Tonbridge
Tonbridge ( ) (historic spelling ''Tunbridge'') is a market town in Kent, England, on the River Medway, north of Royal Tunbridge Wells, south west of Maidstone and south east of London. In the administrative borough of Tonbridge and Mall ...
, and Ashford, to Ramsgate
Ramsgate is a seaside resort, seaside town and civil parish in the district of Thanet District, Thanet in eastern Kent, England. It was one of the great English seaside towns of the 19th century. In 2021 it had a population of 42,027. Ramsgate' ...
, Dover
Dover ( ) is a town and major ferry port in Kent, southeast England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies southeast of Canterbury and east of Maidstone. ...
, Folkestone
Folkestone ( ) is a coastal town on the English Channel, in Kent, south-east England. The town lies on the southern edge of the North Downs at a valley between two cliffs. It was an important harbour, shipping port, and fashionable coastal res ...
and Hastings
Hastings ( ) is a seaside town and Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough in East Sussex on the south coast of England,
east of Lewes and south east of London. The town gives its name to the Battle of Hastings, which took place to th ...
.
Scottish railways
; TheCaledonian Railway
The Caledonian Railway (CR) was one of the two biggest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping. It was formed in 1845 with the objective of forming a link between English railways and Glasgow. It progressively ex ...
: Originally formed to provide the main railway line between Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from ) is a city in the Cumberland district of Cumbria, England.
Carlisle's early history is marked by the establishment of a settlement called Luguvalium to serve forts along Hadrian's Wall in Roman Britain. Due to its pro ...
and Edinburgh and Glasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom ...
. It later merged with the Glasgow, Paisley and Greenock Railway
The Glasgow, Paisley and Greenock Railway (GP&GR) was an early Scotland, Scottish railway, opened in 1841, providing train services between Greenock and Glasgow. At the time the River Clyde was not accessible to sea-going ships, and the intention ...
, which had opened in parts between July 1840 and March 1841. Together with the LNWR it operated the West Coast Main Line
The West Coast Main Line (WCML) is one of the most important railway corridors in the United Kingdom, connecting the major cities of London and Glasgow with branches to Birmingham, Manchester, Liverpool and Edinburgh. It is one of the busiest ...
train services between London and Glasgow, and to Edinburgh, via Carstairs
Carstairs (, Scottish Gaelic: ''Caisteal Tarrais'') is a village in South Lanarkshire, Scotland. Carstairs is located east of the county town of Lanark and the West Coast Main Line runs through the village. The village is served by Carstairs r ...
.
; The Glasgow and South Western Railway
The Glasgow and South Western Railway (G&SWR) was the third biggest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping. It served a triangular area of south-west Scotland between Glasgow, Stranraer and Carlisle, Cumbria, Ca ...
(G&SWR): First section opened 1850. Formed by a merger of the Glasgow, Paisley, Kilmarnock and Ayr Railway
The Glasgow, Paisley, Kilmarnock and Ayr Railway (GPK&AR) was a railway in Scotland that provided train services between Glasgow, Kilmarnock and Ayr. It opened its first line, between Glasgow and Ayr, in stages from 1839 to 1840. The section b ...
, which had opened in parts between August 1839 and August 1840, and the Glasgow, Dumfries and Carlisle Railway
The Glasgow, Dumfries and Carlisle Railway was a railway company in Scotland, which constructed the line from near Cumnock to Gretna Junction, forming the route from Glasgow to Carlisle via Dumfries, in association with other lines. Its promot ...
. Later took over the Ardrossan and Johnstone Railway, which had in part opened in 1831; it then became the Ardrossan Railway
The Ardrossan Railway was a railway company in Scotland, whose line was built in the mid-19th century. It primarily ran services between Kilwinning and Ardrossan, as well as freight services to and from collieries between Kilwinning and Perceton. ...
in July 1840 and was reopened in August 1840 after a change of gauge from Scotch gauge
Scotch most commonly refers to:
* Scotch (adjective), a largely obsolescent adjective meaning "of or from Scotland"
**Scotch, old-fashioned name for the indigenous languages of the Scottish people:
*** Scots language ("Broad Scotch")
*** Scottish ...
to Standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the ...
. The Paisley and Renfrew Railway
The Paisley and Renfrew Railway was an early Scotland, Scottish railway company that constructed and operated a line between Paisley, Renfrewshire, Paisley and the River Clyde at Renfrew, Renfrewshire, Renfrew Wharf, enabling journeys between G ...
, which had opened on 3 April 1835 as Scotch gauge
Scotch most commonly refers to:
* Scotch (adjective), a largely obsolescent adjective meaning "of or from Scotland"
**Scotch, old-fashioned name for the indigenous languages of the Scottish people:
*** Scots language ("Broad Scotch")
*** Scottish ...
railway, was also taken over and converted to Standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the ...
.
; The Great North of Scotland Railway
The Great North of Scotland Railway (GNSR) was one of the two smallest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping, operating in the north-east of the country. Formed in 1845, it carried its first passengers the fro ...
(GNoSR) (1854) : Serving the north east of Scotland from Aberdeen
Aberdeen ( ; ; ) is a port city in North East Scotland, and is the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, third most populous Cities of Scotland, Scottish city. Historically, Aberdeen was within the historic county of Aberdeensh ...
.
; The Highland Railway
The Highland Railway (HR) was one of the two smallest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping, operating north of Perth railway station, Scotland, Perth railway station in Scotland and serving the farthest north o ...
(1865) : Main line northwards from Perth
Perth () is the list of Australian capital cities, capital city of Western Australia. It is the list of cities in Australia by population, fourth-most-populous city in Australia, with a population of over 2.3 million within Greater Perth . The ...
to Inverness with branches to Kyle of Lochalsh
Kyle of Lochalsh ( , "strait of the foaming loch") is a village in the historic county of Ross & Cromarty on the northwest coast of Scotland, located around west-southwest of Inverness. It is located on the Lochalsh peninsula, at the entranc ...
, Wick
Wick most often refers to:
* Capillary action ("wicking")
** Candle wick, the cord used in a candle or oil lamp
** Solder wick, a copper-braided wire used to desolder electronic contacts
Wick or WICK may also refer to:
Places and placenames ...
and Thurso
Thurso (pronounced ; , ) is a town and former burgh on the north coast of the Highland council area of Scotland. Situated in the historical County of Caithness, it is the northernmost town on the island of Great Britain. From a latitudinal s ...
.
; The North British Railway
The North British Railway was one of the two biggest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping. It was established in 1844, with the intention of linking with English railways at Berwick. The line opened in 1846, ...
(NBR) (1846) : Serving the Scottish Lowlands
The Lowlands ( or , ; , ) is a cultural and historical region of Scotland.
The region is characterised by its relatively flat or gently rolling terrain as opposed to the mountainous landscapes of the Scottish Highlands. This area includes ci ...
into Fife
Fife ( , ; ; ) is a council areas of Scotland, council area and lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area in Scotland. A peninsula, it is bordered by the Firth of Tay to the north, the North Sea to the east, the Firth of Forth to the s ...
shire, and the west coast to Mallaig
Mallaig (; ) is a seaport, port in Morar, on the west coast of the Scottish Highlands, Highlands of Scotland. It faces Skye from across the Sound of Sleat. The Mallaig railway station, local railway station is the terminus of the West Highlan ...
. It took over the Edinburgh and Glasgow Railway
The Edinburgh and Glasgow Railway was authorised by act of Parliament on 4 July 1838. It was opened to passenger traffic on 21 February 1842, between its Glasgow Queen Street railway station (sometimes referred to at first as Dundas Street) and ...
, which opened July 1842, and the West Highland Railway
The West Highland Railway was a railway company that constructed a railway line from Craigendoran (on the River Clyde west of Glasgow, Scotland) to Fort William, Highland, Fort William and Mallaig. The line was built through remote and difficul ...
, which opened 1894 and was extended to Mallaig in 1901.
See also
*History of rail transport in Great Britain
The Rail transport in Great Britain, railway system of Great Britain started with the building of local isolated wooden wagonways starting in the 1560s. A patchwork of local rail links operated by small private railway companies developed in t ...
* List of early British railway companies
The following list sets out to show all the railway companies set up by Acts of Parliament in the 19th century before 1860. Most of them became constituent parts of the emerging main-line railway companies, often immediately after being built. So ...
References
General
* * * * * * *English Railways
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Scottish Railways
* * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Rail Transport In Great Britain 1830-19221830
It is known in European history as a rather tumultuous year with the Revolutions of 1830 in France, Belgium, Poland, Switzerland and Italy.
Events January–March
* January 11 – LaGrange College (later the University of North Alabama) ...
Rail 1830