History of Iraq (2003–2011) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Between 65,000 BC and 35,000 BC, northern Iraq was home to a
Between 65,000 BC and 35,000 BC, northern Iraq was home to a
 The
The 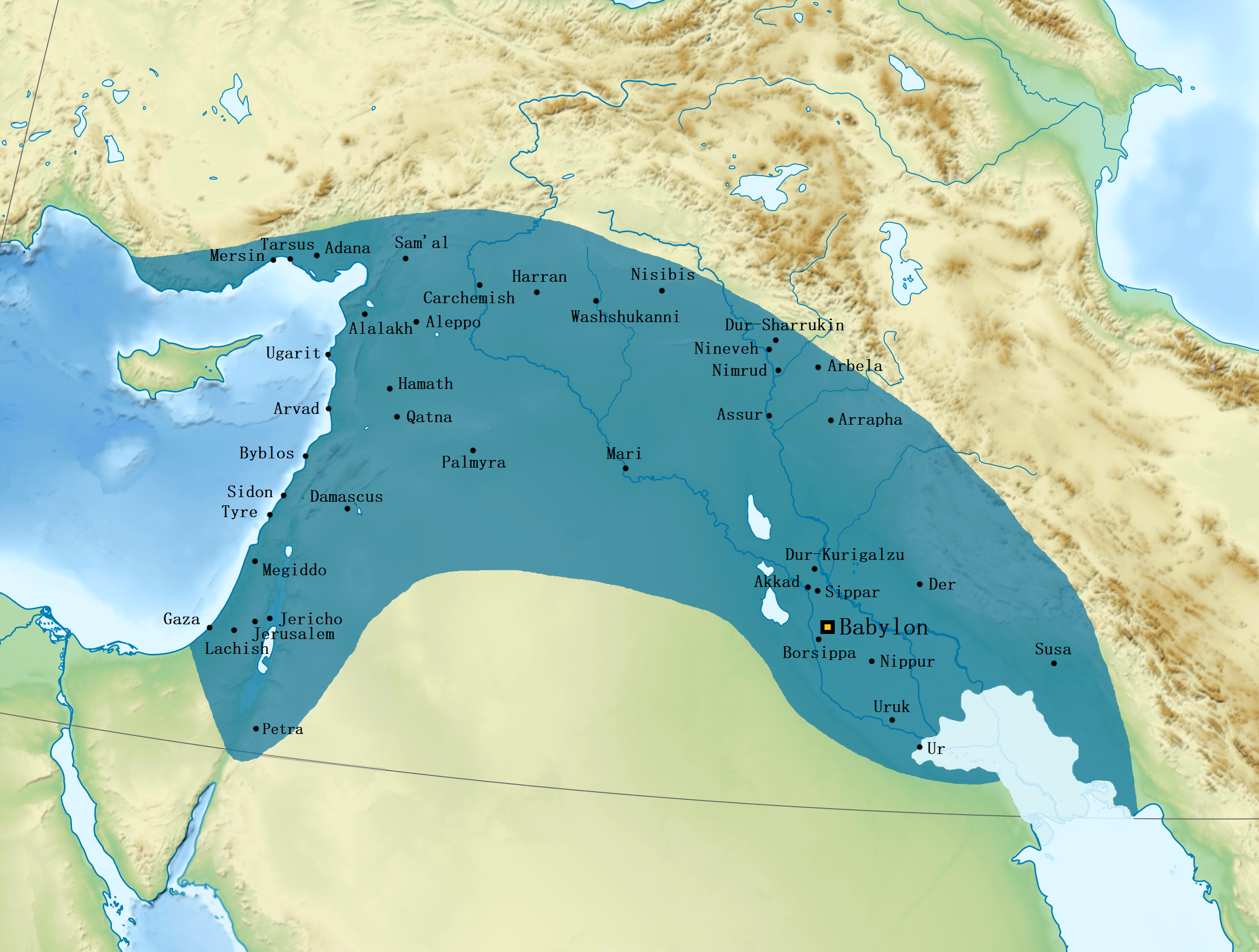 The short-lived
The short-lived  The transfer of empire to
The transfer of empire to
 At the beginning of the 2nd century AD, the Romans, led by emperor
At the beginning of the 2nd century AD, the Romans, led by emperor
 In the 3rd century AD, the Parthians were in turn succeeded by the Sassanid dynasty, which ruled Mesopotamia until the 7th-century Islamic invasion. The Sassanids conquered the independent states of Adiabene,
In the 3rd century AD, the Parthians were in turn succeeded by the Sassanid dynasty, which ruled Mesopotamia until the 7th-century Islamic invasion. The Sassanids conquered the independent states of Adiabene,

 The first organized conflict between invading Arab-Muslim forces and occupying Sassanid domains in Mesopotamia seems to have been in 634, when the Arabs were defeated at the Battle of the Bridge. There was a force of some 5,000
The first organized conflict between invading Arab-Muslim forces and occupying Sassanid domains in Mesopotamia seems to have been in 634, when the Arabs were defeated at the Battle of the Bridge. There was a force of some 5,000
 The city of
The city of
 In the later 11th century, Iraq fell under the rule of the
In the later 11th century, Iraq fell under the rule of the
 During the late 14th and early 15th centuries, the Qara Qoyunlu, or Black Sheep Turkmens, ruled the area now known as Iraq. In 1466, the
During the late 14th and early 15th centuries, the Qara Qoyunlu, or Black Sheep Turkmens, ruled the area now known as Iraq. In 1466, the
 Qāsim was assassinated in February 1963 when the
Qāsim was assassinated in February 1963 when the
 In July 1979, President Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr was forced to resign by
In July 1979, President Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr was forced to resign by  Territorial disputes with
Territorial disputes with
The same month, US President Bill Clinton authorized air strikes on government targets and military facilities. Air strikes against military facilities and alleged WMD sites continued into 2002.
 In 2003, after the American and British invasion, Iraq was occupied by U.S.-led Coalition forces. On 23 May 2003, the UN Security Council unanimously approved a resolution lifting all economic sanctions against Iraq. As the country struggled to rebuild after three wars and a decade of sanctions, it was plagued by violence between a growing Iraqi insurgency and occupation forces. Saddam Hussein, who vanished in April, was captured on 13 December 2003 in
In 2003, after the American and British invasion, Iraq was occupied by U.S.-led Coalition forces. On 23 May 2003, the UN Security Council unanimously approved a resolution lifting all economic sanctions against Iraq. As the country struggled to rebuild after three wars and a decade of sanctions, it was plagued by violence between a growing Iraqi insurgency and occupation forces. Saddam Hussein, who vanished in April, was captured on 13 December 2003 in
Iraq: The Cradle of Civilization
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20180927085237/https://repository.library.georgetown.edu/handle/10822/552703 Historical Context of the Iran – Iraq Warfrom th
Dean Peter Krogh Foreign Affairs Digital Archives
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Iraq
Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
, a country located in West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
, largely coincides with the ancient region of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, often referred to as the cradle of civilization
A cradle of civilization is a location and a culture where civilization was developed independent of other civilizations in other locations. A civilization is any complex society characterized by the development of the state, social strati ...
. The history of Mesopotamia extends back to the Lower Paleolithic period, with significant developments continuing through the establishment of the Caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
in the late 7th century AD, after which the region became known as Iraq. Within its borders lies the ancient land of Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
, which emerged between 6000 and 5000 BC during the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
Ubaid period. Sumer is recognized as the world’s earliest civilization, marking the beginning of urban development, written language, and monumental architecture. Iraq's territory also includes the heartlands of the Akkadian, Neo-Sumerian, Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
n, Neo-Assyrian, and Neo-Babylonian empires, which dominated Mesopotamia and much of the Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was home to many cradles of civilization, spanning Mesopotamia, Egypt, Iran (or Persia), Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, and the Arabian Peninsula. As such, the fields of ancient Near East studies and Nea ...
during the Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
and Iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
Ages.
Iraq was a center of innovation in antiquity, producing early written languages, literary works, and significant advancements in astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
, mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
, law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a science and as the ar ...
, and philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
. This era of indigenous rule ended in 539 BC when the Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to ancient Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC a ...
was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
under Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia ( ; 530 BC), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Hailing from Persis, he brought the Achaemenid dynasty to power by defeating the Media ...
, who declared himself the " King of Babylon." The city of Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
, the ancient seat of Babylonian power, became one of the key capitals of the Achaemenid Empire.
In the following centuries, the regions constituting modern Iraq came under the control of several empires, including the Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, Parthians, and Romans, establishing new centers like Seleucia
Seleucia (; ), also known as or or Seleucia ad Tigrim, was a major Mesopotamian city, located on the west bank of the Tigris River within the present-day Baghdad Governorate in Iraq. It was founded around 305 BC by Seleucus I Nicator as th ...
and Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; , ''Tyspwn'' or ''Tysfwn''; ; , ; Thomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modified July 28, 2014, http://syriaca.org/place/58.) was an ancient city in modern Iraq, on the eastern ba ...
. By the 3rd century AD, the region fell under Persian control through the Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, th ...
, during which time Arab tribes from South Arabia
South Arabia (), or Greater Yemen, is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jazan, ...
migrated into Lower Mesopotamia, leading to the formation of the Sassanid-aligned Lakhmid kingdom. The Arabic name '' al-ʿIrāq'' likely originated during this period. The Sasanian Empire was eventually conquered
Conquest involves the annexation or control of another entity's territory through war or coercion. Historically, conquests occurred frequently in the international system, and there were limited normative or legal prohibitions against conquest ...
by the Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
in the 7th century, bringing Iraq under Islamic rule after the Battle of al-Qadisiyyah in 636. The city of Kufa
Kufa ( ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates, Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000.
Along with Samarra, Karbala, Kadhimiya ...
, founded shortly thereafter, became a central hub for the Rashidun dynasty until their overthrow by the Umayyads in 661.
With the rise of the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes ...
in the mid-8th century, Iraq became the center of Islamic rule, with Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
, founded in 762, serving as the capital. Baghdad flourished during the Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of scientific, economic, and cultural flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 13th century.
This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign o ...
, becoming a global center for culture, science, and intellectualism. However, the city's prosperity declined following the Buwayhid and Seljuq invasions in the 10th century and suffered further with the Mongol invasion of 1258. Iraq later came under the control of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
in the 16th century, remaining under Ottoman rule until the end of World War I, after which Mandatory Iraq was established by the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
. During Ottoman rule of Iraq, the Kingdom of Khaza'il, ruled by the Banu Khuza'ah Royal dynasty was founded, controlling most of the Middle and Lower Euphrates until 1921 when sovereign control was ceded to the Hashemite family. Iraq gained independence in 1932 as the Kingdom of Iraq
The Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq was the Iraqi state located in the Middle East from 1932 to 1958. It was founded on 23 August 1921 as the Kingdom of Iraq, following the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in the Mesopotamian campaign of the First World W ...
, which became a republic in 1958. The modern era has seen Iraq facing challenges, including the rule of Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein (28 April 1937 – 30 December 2006) was an Iraqi politician and revolutionary who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 1979 until Saddam Hussein statue destruction, his overthrow in 2003 during the 2003 invasion of Ira ...
, the 2003 invasion of Iraq, and subsequent efforts to rebuild the country amidst sectarian violence and the rise of the Islamic State
The Islamic State (IS), also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) and Daesh, is a transnational Salafi jihadism, Salafi jihadist organization and unrecognized quasi-state. IS ...
. Despite these difficulties, Iraq plays a vital role in the geopolitics of the Middle East.
Prehistory
 Between 65,000 BC and 35,000 BC, northern Iraq was home to a
Between 65,000 BC and 35,000 BC, northern Iraq was home to a Neanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
culture, archaeological remains of which have been discovered at Shanidar Cave. During 1957–1961, Shanidar Cave was excavated by Ralph Solecki and his team from Columbia University
Columbia University in the City of New York, commonly referred to as Columbia University, is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Churc ...
, uncovering nine skeletons of Neanderthal man of varying ages and states of preservation (labelled Shanidar I–IX). A tenth individual was later discovered by M. Zeder during examination of a faunal assemblage from the site at the Smithsonian Institution. The remains seemed to suggest that Neanderthals had funeral ceremonies, burying their dead with flowers (although the flowers are now thought to be a modern contaminant), and that they took care of injured and elderly individuals.
This region is also the location of a number of pre-Neolithic burials, dating from approximately 11,000 BC.Ralph S. Solecki, Rose L. Solecki, and Anagnostis P. Agelarakis (2004). The Proto-Neolithic Cemetery in Shanidar Cave. Texas A&M University Press. pp. 3–5. . Since approximately 10,000 BC, Iraq, together with a large part of the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent () is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria, together with northern Kuwait, south-eastern Turkey, and western Iran. Some authors also include ...
, was a center of a Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
culture known as Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA), where agriculture and cattle breeding appeared for the first time. In Iraq, this period has been excavated at sites like M'lefaat and Nemrik 9. The following Neolithic period, PPNB, is represented by rectangular houses. At the time of the pre-pottery Neolithic, people used vessels made of stone, gypsum, and burnt lime (Vaisselle blanche). Finds of obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
tools from Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
are evidence of early trade relations. Further important sites of human advancement were Jarmo (circa 7100 BC), a number of sites belonging to the Halaf culture
The Halaf culture is a prehistoric period which lasted between about 6100 BC and 5100 BC. The period is a continuous development out of the earlier Pottery Neolithic and is located primarily in the fertile valley of the Khabur (Euphrates), Khabu ...
, and Tell al-'Ubaid, the type site
In archaeology, a type site (American English) or type-site (British English) is the site used to define a particular archaeological culture or other typological unit, which is often named after it. For example, discoveries at La Tène and H ...
of the Ubaid period (between 6500 BC and 3800 BC).
Ancient Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of theNeolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period in Afro-Eurasia from a lifestyle of hunter-gatherer, hunting and gathering to one of a ...
from around 10,000 BC. It has been identified as having "inspired some of the most important developments in human history including the invention of the wheel, the planting of the first cereal crops, and the development of cursive script, mathematics, astronomy, and agriculture."
The " Cradle of Civilisation" is a common term for the area comprising modern Iraq as it was home to the earliest known civilisation, the Sumerian civilisation, which arose in the fertile Tigris-Euphrates river valley of southern Iraq in the Chalcolithic
The Chalcolithic ( ) (also called the Copper Age and Eneolithic) was an archaeological period characterized by the increasing use of smelted copper. It followed the Neolithic and preceded the Bronze Age. It occurred at different periods in di ...
( Ubaid period). It was there, in the late 4th millennium BC
File:4th millennium BC montage.jpg, 400x400px, From top left clockwise: The Temple of Ġgantija, one of the oldest freestanding structures in the world; Warka Vase; Bronocice pot with one of the earliest known depictions of a wheeled vehicle; Kish ...
, that the world's first known writing system
A writing system comprises a set of symbols, called a ''script'', as well as the rules by which the script represents a particular language. The earliest writing appeared during the late 4th millennium BC. Throughout history, each independen ...
emerged. The Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
ians were also the first known to harness the wheel
A wheel is a rotating component (typically circular in shape) that is intended to turn on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machin ...
and create city-states; their writings record the first known evidence of mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
, astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
, astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions ...
, written law, medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
, and organised religion. The Sumerian language
Sumerian ) was the language of ancient Sumer. It is one of the List of languages by first written account, oldest attested languages, dating back to at least 2900 BC. It is a local language isolate that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia, in the a ...
is a language isolate
A language isolate is a language that has no demonstrable genetic relationship with any other languages. Basque in Europe, Ainu and Burushaski in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, Haida and Zuni in North America, Kanoê in South America, and Tiwi ...
. The major city-states of the early Sumerian period included Eridu, Bad-tibira, Larsa
Larsa (, read ''Larsamki''), also referred to as Larancha/Laranchon (Gk. Λαραγχων) by Berossus, Berossos and connected with the biblical Arioch, Ellasar, was an important city-state of ancient Sumer, the center of the Cult (religious pra ...
, Sippar
Sippar (Sumerian language, Sumerian: , Zimbir) (also Sippir or Sippara) was an ancient Near Eastern Sumerian and later Babylonian city on the east bank of the Euphrates river. Its ''Tell (archaeology), tell'' is located at the site of modern Tell ...
, Shuruppak
Shuruppak ( , SU.KUR.RUki, "the healing place"), modern Tell Fara, was an ancient Sumerian city situated about 55 kilometres (35 mi) south of Nippur and 30 kilometers north of ancient Uruk on the banks of the Euphrates in Iraq's Al-Qādisiy ...
, Uruk
Uruk, the archeological site known today as Warka, was an ancient city in the Near East, located east of the current bed of the Euphrates River, on an ancient, now-dried channel of the river in Muthanna Governorate, Iraq. The site lies 93 kilo ...
, Kish
Kish may refer to:
Businesses and organisations
* KISH, a radio station in Guam
* Kish Air, an Iranian airline
* Korean International School in Hanoi, Vietnam
People
* Kish (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Kish, a former ...
, Ur, Nippur, Lagash
Lagash (; cuneiform: LAGAŠKI; Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Lagaš'') was an ancient city-state located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Al-Shatrah, Iraq. Lagash ( ...
, Girsu, Umma, Hamazi, Adab, Mari, Isin, Kutha, Der, and Akshak. The cities to the north, like Ashur, Arbela (modern Erbil
Erbil (, ; , ), also called Hawler (, ), is the capital and most populated city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. The city is the capital of the Erbil Governorate.
Human settlement at Erbil may be dated back to the 5th millennium BC. At the h ...
), and Arrapha (modern Kirkuk
Kirkuk (; ; ; ) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of the Kirkuk Governorate. The city is home to a diverse population of Kurds, Iraqi Turkmen, Iraqi Turkmens and Arabs. Kirkuk sits on the ruins of the original Kirkuk Cit ...
), were also extant in what was to be called Assyria from the 25th century BC; however, at this stage, they were Sumerian-ruled administrative centers.
Bronze Age
Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
emerged as the civilization of Lower Mesopotamia out of the prehistoric Ubaid period (mid-6th millennium BC) in the Early Bronze Age (Uruk period
The Uruk period (; also known as Protoliterate period) existed from the protohistory, protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, after the Ubaid period and before the Jemdet Nasr period. Named after the S ...
). Classical Sumer ended with the rise of the Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first known empire, succeeding the long-lived city-states of Sumer. Centered on the city of Akkad (city), Akkad ( or ) and its surrounding region, the empire united Akkadian language, Akkadian and Sumerian languag ...
in the 24th century BC. Following the Gutian period, the Ur III kingdom was once again able to unite large parts of southern and central Mesopotamia under a single ruler in the 21st century. It may have eventually disintegrated due to Amorite incursions. The Amorite dynasty of Isin persisted until c. 1600 BC, when southern Mesopotamia was united under Kassite Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
n rule.
During the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
, in the 26th century BC, Eannatum
Eannatum ( ; ) was a Sumerian ''Ensi (Sumerian), Ensi'' (ruler or king) of Lagash. He established one of the first verifiable empires in history, subduing Elam and destroying the city of Susa, and extending his domain over the rest of Sumer and Akk ...
of Lagash
Lagash (; cuneiform: LAGAŠKI; Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Lagaš'') was an ancient city-state located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Al-Shatrah, Iraq. Lagash ( ...
created a short-lived empire
An empire is a political unit made up of several territories, military outpost (military), outposts, and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a hegemony, dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the ...
. Later, Lugal-Zage-Si, the priest-king of Umma, overthrew the primacy of the Lagash dynasty in the area, then conquered Uruk
Uruk, the archeological site known today as Warka, was an ancient city in the Near East, located east of the current bed of the Euphrates River, on an ancient, now-dried channel of the river in Muthanna Governorate, Iraq. The site lies 93 kilo ...
, making it his capital, and claimed an empire extending from the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
to the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
. It was during this period that the Epic of Gilgamesh
The ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' () is an epic poetry, epic from ancient Mesopotamia. The literary history of Gilgamesh begins with five Sumerian language, Sumerian poems about Gilgamesh (formerly read as Sumerian "Bilgames"), king of Uruk, some of ...
originated, which includes the tale of The Great Flood. The origin and location of Akkad remain unclear. Its people spoke Akkadian, an East Semitic language. Between the 29th and 24th centuries BC, a number of kingdoms and city-states within Iraq began to have Akkadian-speaking dynasties, including Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
, Ekallatum, Isin, and Larsa
Larsa (, read ''Larsamki''), also referred to as Larancha/Laranchon (Gk. Λαραγχων) by Berossus, Berossos and connected with the biblical Arioch, Ellasar, was an important city-state of ancient Sumer, the center of the Cult (religious pra ...
. However, the Sumerians remained generally dominant until the rise of the Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first known empire, succeeding the long-lived city-states of Sumer. Centered on the city of Akkad (city), Akkad ( or ) and its surrounding region, the empire united Akkadian language, Akkadian and Sumerian languag ...
(2335–2124 BC), based in the city of Akkad in central Iraq. Sargon of Akkad founded the empire, conquered all the city-states of southern and central Iraq, and subjugated the kings of Assyria, thus uniting the Sumerians and Akkadians in one state. The Akkadian Empire was the first ancient empire
An empire is a political unit made up of several territories, military outpost (military), outposts, and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a hegemony, dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the ...
of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
after the long-lived civilization of Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
.
He then set about expanding his empire, conquering Gutium, Elam
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems fr ...
in modern-day Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, and had victories that did not result in full conquest against the Amorites
The Amorites () were an ancient Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic-speaking Bronze Age people from the Levant. Initially appearing in Sumerian records c. 2500 BC, they expanded and ruled most of the Levant, Mesopotamia and parts of Eg ...
and Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was ...
ites of the Levant. The empire of Akkad likely fell in the 22nd century BC, within 180 years of its founding, ushering in a " Dark Age" with no prominent imperial authority until the Third Dynasty of Ur
The Third Dynasty of Ur or Ur III was a Sumerian dynasty based in the city of Ur in the 22nd and 21st centuries BC ( middle chronology). For a short period they were the preeminent power in Mesopotamia and their realm is sometimes referred to by ...
. The region's political structure may have reverted to the ''status quo ante'' of local governance by city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
s.Zettler (2003), pp. 24–25. "Moreover, the Dynasty of Akkade's fall did not lead to social collapse, but the re-emergence of the normative political organization. The southern cities reasserted their independence, and if we know little about the period between the death of Sharkalisharri and the accession of Urnamma, it may be due more to accidents of discovery than because of widespread 'collapse.' The extensive French excavations at Tello produced relevant remains dating right through the period."
After the collapse of the Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first known empire, succeeding the long-lived city-states of Sumer. Centered on the city of Akkad (city), Akkad ( or ) and its surrounding region, the empire united Akkadian language, Akkadian and Sumerian languag ...
in the late 22nd century BC, the Gutians
The Guti (), also known by the derived exonyms Gutians or Guteans, were a people of the ancient Near East who both appeared and disappeared during the Bronze Age. Their homeland was known as Gutium (Sumerian language, Sumerian: , ''GutūmKI'' o ...
occupied the south for a few decades, while Assyria reasserted its independence in the north. Most of southern Mesopotamia was again united under one ruler during the Ur III period, most notably during the rule of the prolific king Shulgi. His accomplishments include the completion of construction of the Great Ziggurat of Ur, begun by his father Ur-Nammu
Ur-Nammu (or Ur-Namma, Ur-Engur, Ur-Gur, Sumerian language, Sumerian: ; died 2094 BC) founded the Sumerian Third Dynasty of Ur, in southern Mesopotamia, following several centuries of Akkadian Empire, Akkadian and Gutian period, Gutian rule. Thou ...
. In 1792 BC, an Amorite ruler named Hammurabi came to power and immediately set about building Babylon into a major city, declaring himself its king. Hammurabi conquered southern and central Iraq, as well as Elam to the east and Mari to the west, then engaged in a protracted war with the Assyrian king Ishme-Dagan for domination of the region, creating the short-lived Babylonian Empire. He eventually prevailed over the successor of Ishme-Dagan and subjected Assyria and its Anatolian colonies. By the middle of the eighteenth century BC, the Sumerians had lost their cultural identity and ceased to exist as a distinct people.
It is from the period of Hammurabi that southern Iraq came to be known as Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
, while the north had already coalesced into Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
hundreds of years before. However, his empire was short-lived, and rapidly collapsed after his death, with both Assyria and southern Iraq, in the form of the Sealand Dynasty, falling back into native Akkadian hands. After this, another foreign people, the language-isolate-speaking Kassites, seized control of Babylonia. Iraq was from this point divided into three polities: Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
in the north, Kassite Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
in the south-central region, and the Sealand Dynasty in the far south. The Sealand Dynasty was finally conquered by Kassite Babylonia circa 1380 BC. The origin of the Kassites is uncertain.
The Middle Assyrian Empire
The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I 1363 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. ...
(1365–1020 BC) saw Assyria rise to be the most powerful nation in the known world. Beginning with the campaigns of Ashur-uballit I, Assyria destroyed the rival Hurrian
The Hurrians (; ; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri) were a people who inhabited the Ancient Near East during the Bronze Age. They spoke the Hurro-Urartian language, Hurrian language, and lived throughout northern Syria (region) ...
-Mitanni
Mitanni (–1260 BC), earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, ; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat in Assyrian records, or in Ancient Egypt, Egyptian texts, was a Hurrian language, Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria (region), Syria an ...
Empire, annexed huge swathes of the Hittite Empire
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
for itself, annexed northern Babylonia from the Kassites, forced the Egyptian Empire from the region, and defeated the Elamites, Phrygians, Canaanites, Phoenicians
Phoenicians were an ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syrian coast. They developed a maritime civi ...
, Cilicians, Gutians
The Guti (), also known by the derived exonyms Gutians or Guteans, were a people of the ancient Near East who both appeared and disappeared during the Bronze Age. Their homeland was known as Gutium (Sumerian language, Sumerian: , ''GutūmKI'' o ...
, Dilmunites, and Arameans
The Arameans, or Aramaeans (; ; , ), were a tribal Semitic people in the ancient Near East, first documented in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. Their homeland, often referred to as the land of Aram, originally covered c ...
. At its height, the Middle Assyrian Empire
The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I 1363 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. ...
stretched from The Caucasus to Dilmun (modern Bahrain
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is an island country in West Asia. Situated on the Persian Gulf, it comprises a small archipelago of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island, which mak ...
), and from the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
coasts of Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
to the Zagros Mountains of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
. In 1235 BC, Tukulti-Ninurta I of Assyria took the throne of Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
.
During the Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BC), Babylonia was in a state of chaos, dominated for long periods by Assyria and Elam
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems fr ...
. The Kassites were driven from power by Assyria and Elam, allowing native south Mesopotamian kings to rule Babylonia for the first time, although often subject to Assyrian or Elamite rulers. However, these Akkadian kings were unable to prevent new waves of West Semitic migrants from entering southern Iraq, and during the 11th century BC, Arameans
The Arameans, or Aramaeans (; ; , ), were a tribal Semitic people in the ancient Near East, first documented in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. Their homeland, often referred to as the land of Aram, originally covered c ...
and Suteans entered Babylonia from The Levant, followed in the late 10th to early 9th century BC by the Chaldea
Chaldea () refers to a region probably located in the marshy land of southern Mesopotamia. It is mentioned, with varying meaning, in Neo-Assyrian cuneiform, the Hebrew Bible, and in classical Greek texts. The Hebrew Bible uses the term (''Ka� ...
ns. However, the Chaldeans were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
.
Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
was an Akkadian (East Semitic) kingdom in Upper Mesopotamia, that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur ( Akkadian ').
Of the early history of the kingdom of Assyria, little is positively known. In the Assyrian King List
The king of Assyria (Akkadian language, Akkadian: , later ) was the ruler of the ancient Mesopotamian kingdom of Assyria, which was founded in the late 21st century BC and fell in the late 7th century BC. For much of its early history, Assyria was ...
, the earliest king recorded was Tudiya. He was a contemporary of Ibrium of Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was ...
, who appears to have lived in the late 25th or early 24th century BC, according to the king list. The foundation of the first true urbanised Assyrian monarchy was traditionally ascribed to Ushpia, a contemporary of Ishbi-Erra of Isin and Naplanum of Larsa
Larsa (, read ''Larsamki''), also referred to as Larancha/Laranchon (Gk. Λαραγχων) by Berossus, Berossos and connected with the biblical Arioch, Ellasar, was an important city-state of ancient Sumer, the center of the Cult (religious pra ...
. c. 2030 BC.
Assyria had a period of empire from the 19th to 18th centuries BC. From the 14th to 11th centuries BC, Assyria once more became a major power with the rise of the Middle Assyrian Empire
The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I 1363 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. ...
.
Iron Age
 The
The Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew to dominate the ancient Near East and parts of South Caucasus, Nort ...
(911–609 BC) was the dominant political force in the Ancient Near East during the Iron Age, eclipsing Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, Urartu
Urartu was an Iron Age kingdom centered around the Armenian highlands between Lake Van, Lake Urmia, and Lake Sevan. The territory of the ancient kingdom of Urartu extended over the modern frontiers of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Armenia.Kleiss, Wo ...
, and Elam
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems fr ...
. Because of its geopolitical dominance and ideology based on world domination
World domination (also called global domination, world conquest, global conquest, or cosmocracy) is a hypothetical power structure, either achieved or aspired to, in which a single political authority holds power over all or virtually all the i ...
, the Neo-Assyrian Empire is regarded by many researchers as the first world empire. At its height, the empire ruled over all of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
, and Egypt, as well as portions of Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
, and modern-day Iran and Armenia. Under rulers such as Adad-Nirari II
Adad-nīrārī II (also spelled Adad-nērārī, which means "Adad (the storm god) is my help") reigned from 911 BCE to 891 BCE. He was the first King of Assyria in the Neo-Assyrian empire. He instigated the first renewed period of major expansion ...
, Ashurnasirpal, Shalmaneser III
Shalmaneser III (''Šulmānu-ašarēdu'', "the god Shulmanu is pre-eminent") was king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 859 BC to 824 BC.
His long reign was a constant series of campaigns against the eastern tribes, the Babylonians, the nations o ...
, Semiramis, Tiglath-pileser III, Sargon II, Sennacherib
Sennacherib ( or , meaning "Sin (mythology), Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 705BC until his assassination in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynasty, Sennacherib is one of the most famous A ...
, Esarhaddon, and Ashurbanipal, Iraq became the center of an empire stretching from Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, Parthia
Parthia ( ''Parθava''; ''Parθaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemeni ...
, and Elam
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems fr ...
in the east to Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
and Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
in the west, and from The Caucasus in the north to Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract ...
, and Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
in the south.
It was during this period that an Akkadian-influenced form of Eastern Aramaic was adopted by the Assyrians as their lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
, and Mesopotamian Aramaic began to supplant Akkadian as the spoken language of the general populace of both Assyria and Babylonia. The descendant dialects of this tongue survive among the Mandaeans
Mandaeans (Mandaic language, Mandaic: ࡌࡀࡍࡃࡀࡉࡉࡀ) ( ), also known as Mandaean Sabians ( ) or simply as Sabians ( ), are an ethnoreligious group who are followers of Mandaeism. They believe that John the Baptist was the final and ...
of southern Iraq and Assyrians of northern Iraq. The Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
and the Chaldea
Chaldea () refers to a region probably located in the marshy land of southern Mesopotamia. It is mentioned, with varying meaning, in Neo-Assyrian cuneiform, the Hebrew Bible, and in classical Greek texts. The Hebrew Bible uses the term (''Ka� ...
ns are first mentioned in written history (circa 850 BC) in the annals of Shalmaneser III
Shalmaneser III (''Šulmānu-ašarēdu'', "the god Shulmanu is pre-eminent") was king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 859 BC to 824 BC.
His long reign was a constant series of campaigns against the eastern tribes, the Babylonians, the nations o ...
. The Neo-Assyrian Empire left a legacy of great cultural significance. The political structures established by the Neo-Assyrian Empire became the model for the later empires that succeeded it, and the ideology of universal rule promulgated by the Neo-Assyrian kings inspired similar ideas of rights to world domination
World domination (also called global domination, world conquest, global conquest, or cosmocracy) is a hypothetical power structure, either achieved or aspired to, in which a single political authority holds power over all or virtually all the i ...
in later empires. The Neo-Assyrian Empire became an important part of later folklore and literary traditions in northern Mesopotamia. Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
, and thus in turn also Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
and Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
, was profoundly affected by the period of Neo-Assyrian rule; numerous Biblical stories appear to draw on earlier Assyrian mythology and history, and the Assyrian impact on early Jewish theology was immense. Although the Neo-Assyrian Empire is prominently remembered today for the supposed excessive brutality of the Neo-Assyrian army, the Assyrians were not excessively brutal compared to other civilizations.
In the late 7th century BC, the Assyrian Empire tore itself apart with a series of brutal civil wars, weakening itself to such a degree that a coalition of its former subjects, including the Babylonians, Chaldea
Chaldea () refers to a region probably located in the marshy land of southern Mesopotamia. It is mentioned, with varying meaning, in Neo-Assyrian cuneiform, the Hebrew Bible, and in classical Greek texts. The Hebrew Bible uses the term (''Ka� ...
ns, Medes
The Medes were an Iron Age Iranian peoples, Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media (region), Media between western Iran, western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, they occupied the m ...
, Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
, Parthians, Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian noma ...
, and Cimmerians
The Cimmerians were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into W ...
, were able to attack Assyria, finally bringing its empire down by 605 BC.
 The short-lived
The short-lived Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to ancient Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC a ...
(626–539 BC) succeeded that of Assyria. It failed to attain the size, power, or longevity of its predecessor; however, it came to dominate The Levant, Canaan
CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
, Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
, Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
, and Judah, and even defeated Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
. Initially, Babylon was ruled by the Chaldea
Chaldea () refers to a region probably located in the marshy land of southern Mesopotamia. It is mentioned, with varying meaning, in Neo-Assyrian cuneiform, the Hebrew Bible, and in classical Greek texts. The Hebrew Bible uses the term (''Ka� ...
ns, who had migrated to the region in the late 10th or early 9th century BC. Its greatest king, Nebuchadnezzar II
Nebuchadnezzar II, also Nebuchadrezzar II, meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir", was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from the death of his father Nabopolassar in 605 BC to his own death in 562 BC. Often titled Nebuchadnezzar ...
, rivaled Hammurabi as the greatest king of Babylon. However, by 556 BC, the Chaldeans had been deposed by the Assyrian-born Nabonidus
Nabonidus (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-naʾid'', meaning "May Nabu be exalted" or "Nabu is praised") was the last king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from 556 BC to the fall of Babylon to the Achaemenian Empire under Cyrus the Great in 53 ...
and his son and regent Belshazzar.
 The transfer of empire to
The transfer of empire to Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
marked the first time the city, and southern Mesopotamia in general, had risen to dominate the Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was home to many cradles of civilization, spanning Mesopotamia, Egypt, Iran (or Persia), Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, and the Arabian Peninsula. As such, the fields of ancient Near East studies and Nea ...
since the collapse of Hammurabi's Old Babylonian Empire
The Old Babylonian Empire, or First Babylonian Empire, is dated to , and comes after the end of Sumerian power with the destruction of the Third Dynasty of Ur, and the subsequent Isin-Larsa period. The chronology of the first dynasty of Babylon ...
. The period of Neo-Babylonian rule saw unprecedented economic and population growth and a renaissance of culture and artwork. Nebuchadnezzar II
Nebuchadnezzar II, also Nebuchadrezzar II, meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir", was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from the death of his father Nabopolassar in 605 BC to his own death in 562 BC. Often titled Nebuchadnezzar ...
succeeded Nabopolassar in 605 BC. The empire Nebuchadnezzar inherited was among the most powerful in the world. He quickly reinforced his father's alliance with the Medes by marrying Cyaxares's daughter or granddaughter, Amytis. Some sources suggest that the famous Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, were built by Nebuchadnezzar for his wife (though the existence of these gardens is debated). Nebuchadnezzar's 43-year reign brought a golden age for Babylon, which became the most powerful kingdom in the Middle East.
The Neo-Babylonian period ended with the reign of Nabonidus
Nabonidus (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-naʾid'', meaning "May Nabu be exalted" or "Nabu is praised") was the last king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from 556 BC to the fall of Babylon to the Achaemenian Empire under Cyrus the Great in 53 ...
in 539 BC. To the east, the Persians had been growing in strength, and eventually Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia ( ; 530 BC), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Hailing from Persis, he brought the Achaemenid dynasty to power by defeating the Media ...
established his dominion over Babylon. The Chaldeans disappeared around this time, though both Assyria and Babylonia endured and thrived under Achaemenid rule (see Achaemenid Assyria). The Persian rulers retained Assyrian Imperial Aramaic as the language of empire, together with the Assyrian imperial infrastructure and an Assyrian style of art and architecture.
Classical Antiquity
Achaemenid and Seleucid rule
Mesopotamia was conquered by the Achaemenid Persians underCyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia ( ; 530 BC), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Hailing from Persis, he brought the Achaemenid dynasty to power by defeating the Media ...
in 539 BC, and remained under Persian rule for two centuries.
The Persian Empire fell to Alexander of Macedon in 331 BC and came under Greek rule as part of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
. Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
declined after the founding of Seleucia on the Tigris
Seleucia (; ), also known as or or Seleucia ad Tigrim, was a major Mesopotamian city, located on the west bank of the Tigris River within the present-day Baghdad Governorate in Iraq. It was founded around 305 BC by Seleucus I Nicator as the f ...
, the new Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
capital. The Seleucid Empire at the height of its power stretched from the Aegean in the west to India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
in the east. It was a major center of Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
culture that maintained the preeminence of Greek customs where a Greek political elite dominated, mostly in the urban areas. The Greek population of the cities who formed the dominant elite were reinforced by immigration from Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
. Much of the eastern part of the empire was conquered by the Parthians under Mithridates I of Parthia in the mid-2nd century BC.
Parthian and Roman rule
Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
, invaded Parthia and conquered Mesopotamia, making it an imperial province. It was returned to the Parthians shortly after by Trajan's successor, Hadrian
Hadrian ( ; ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic peoples, Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, Aelia '' ...
.
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
reached Mesopotamia in the 1st century AD, and Roman Syria in particular became the center of Eastern Rite Christianity and the Syriac literary tradition. Mandeism is also believed to have either originated there around this time or entered as Mandaeans sought refuge from Palestine.
Sumerian-Akkadian religious tradition disappeared during this period, as did the last remnants of cuneiform
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform script ...
literacy, although temples were still being dedicated to the Assyrian national god Ashur in his home city as late as the 4th century.George Roux – Ancient Iraq
Sassanid Empire
Osroene
Osroene or Osrhoene (; ) was an ancient kingdom and region in Upper Mesopotamia. The ''Kingdom of Osroene'', also known as the "Kingdom of Edessa" ( / "Kingdom of Urhay"), according to the name of its capital city (now Urfa, Şanlıurfa, Turkey), ...
, Hatra, and finally Assur during the 3rd century. In the mid-6th century, the Persian Empire under the Sassanid dynasty was divided by Khosrow I into four quarters, of which the western one, called ''Khvārvarān'', included most of modern Iraq, and was subdivided into the provinces of ''Mishān'', Asuristān (Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
), Adiabene, and Lower Media. The term Iraq is widely used in the medieval Arabic sources for the area in the center and south of the modern republic as a geographic rather than a political term, implying no greater precision of boundaries than the term "Mesopotamia" or, indeed, many of the names of modern states before the 20th century.
There was a substantial influx of Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
in the Sassanid period. Upper Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia constitutes the Upland and lowland, uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the regio ...
came to be known as ''Al-Jazirah'' in Arabic (meaning "The Island" in reference to the "island" between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers), and Lower Mesopotamia came to be known as '' ʿIrāq-i ʿArab'', meaning "the escarpment of the Arabs" (viz. to the south and east of "the island").
Until 602, the desert frontier of the Persian Empire had been guarded by the Arab Lakhmid kings of Al-Hirah
Al-Hira ( Middle Persian: ''Hērt'' ) was an ancient Lakhmid Arabic city in Mesopotamia located south of what is now Kufa in south-central Iraq.
The Sasanian Empire, Sasanian government established the Lakhmid state (Al-Hirah) on the edge of the ...
. In that year, Shahanshah
Shāh (; ) is a royal title meaning "king" in the Persian language.Yarshater, Ehsa, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII, no. 1 (1989) Though chiefly associated with the List of monarchs of Iran, monarchs of Iran, it was also used to refer to the ...
Khosrow II Aparviz (Persian خسرو پرويز) abolished the Lakhmid kingdom and laid the frontier open to nomad incursions. Farther north, the western quarter was bounded by the Byzantine Empire. The frontier more or less followed the modern Syria-Iraq border and continued northward, passing between Nisibis
Nusaybin () is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Mardin Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,079 km2, and its population is 115,586 (2022). The city is populated by Kurds of different tribal affiliation.
Nusaybin is separated ...
(modern Nusaybin) as the Sassanian frontier fortress and Dara and Amida (modern Diyarbakır
Diyarbakır is the largest Kurdish-majority city in Turkey. It is the administrative center of Diyarbakır Province.
Situated around a high plateau by the banks of the Tigris river on which stands the historic Diyarbakır Fortress, it is ...
) held by the Byzantines.
Middle Ages
Islamic conquest
 The first organized conflict between invading Arab-Muslim forces and occupying Sassanid domains in Mesopotamia seems to have been in 634, when the Arabs were defeated at the Battle of the Bridge. There was a force of some 5,000
The first organized conflict between invading Arab-Muslim forces and occupying Sassanid domains in Mesopotamia seems to have been in 634, when the Arabs were defeated at the Battle of the Bridge. There was a force of some 5,000 Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
under Abū `Ubayd ath-Thaqafī, which was routed by the Persians. This was followed by Khalid ibn al-Walid's successful campaign, which saw all of Iraq come under Arab rule within a year, with the exception of the Sassanid Empire's capital, Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; , ''Tyspwn'' or ''Tysfwn''; ; , ; Thomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modified July 28, 2014, http://syriaca.org/place/58.) was an ancient city in modern Iraq, on the eastern ba ...
. Around 636, a larger Arab Muslim force under Sa`d ibn Abī Waqqās defeated the main Persian army at the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah and moved on to capture Ctesiphon. By the end of 638, the Muslims had conquered all of the Western Sassanid provinces (including modern Iraq), and the last Sassanid Emperor, Yazdegerd III, had fled to central and then northern Persia, where he was killed in 651.
The Islamic expansions constituted the largest of the Semitic expansions in history. These new arrivals established two new garrison cities, at Kufa
Kufa ( ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates, Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000.
Along with Samarra, Karbala, Kadhimiya ...
, near ancient Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
, and at Basra
Basra () is a port city in Iraq, southern Iraq. It is the capital of the eponymous Basra Governorate, as well as the List of largest cities of Iraq, third largest city in Iraq overall, behind Baghdad and Mosul. Located near the Iran–Iraq bor ...
in the south and established Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
in these cities, while the north remained largely Assyrian and Christian in character.
Abbasid Caliphate
 The city of
The city of Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
, established in the 8th century as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, quickly became the leading cultural and intellectual hub of the Muslim world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
during the Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of scientific, economic, and cultural flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 13th century.
This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign o ...
. At its peak, Baghdad was the largest and most multicultural city of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, with a population exceeding a million. However, its prominence was dramatically curtailed in the 13th century when the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
sacked the city and destroyed its famed library during the Siege of Baghdad (1258).
In the 9th century, the Abbasid Caliphate entered a period of decline. During the late 9th to early 11th centuries, a period known as the " Iranian Intermezzo", parts of (the modern territory of) Iraq were governed by a number of minor Iranian emirates, including the Tahirids, Saffarids, Samanids, Buyids and Sallarids. Tughril, the founder of the Seljuk Empire
The Seljuk Empire, or the Great Seljuk Empire, was a High Middle Ages, high medieval, culturally Turco-Persian tradition, Turco-Persian, Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim empire, established and ruled by the Qiniq (tribe), Qïnïq branch of Oghuz Turks. ...
, captured Baghdad in 1055. In spite of having lost all governance, the Abbasid caliphs nevertheless maintained a highly ritualized court in Baghdad and remained influential in religious matters, maintaining the orthodoxy of their Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
sect in opposition to the Ismaili and Shia sects of Islam.
Mongol invasion
 In the later 11th century, Iraq fell under the rule of the
In the later 11th century, Iraq fell under the rule of the Khwarazmian dynasty
The Anushtegin dynasty or Anushteginids (English: , ), also known as the Khwarazmian dynasty () was a Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic peoples, Turkic ''mamluk'' origin from the Begdili, Bekdili clan of the Oghuz Turks. The Anushteg ...
. Both Turkic secular rule and Abbasid caliphate came to an end with the Mongol invasions of the 13th century.
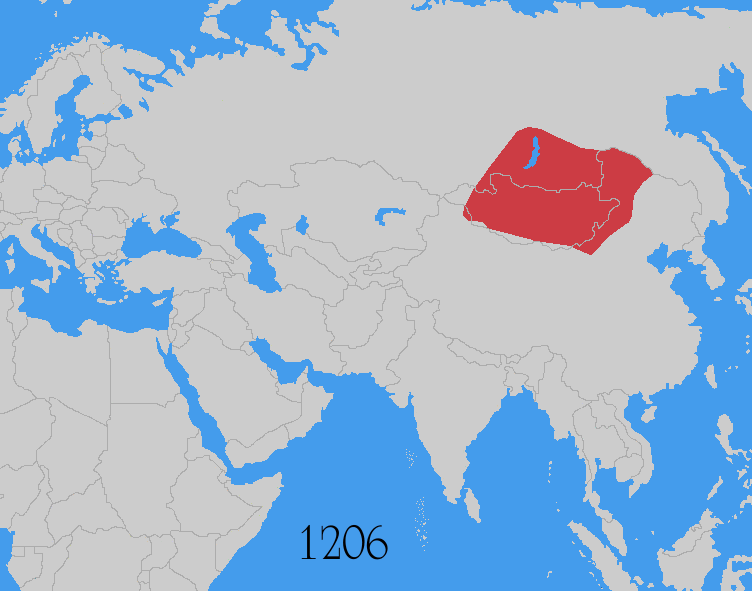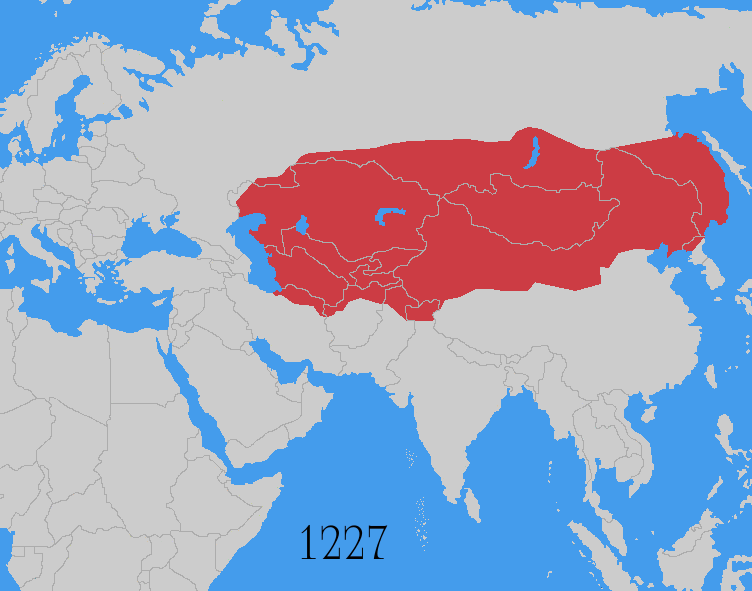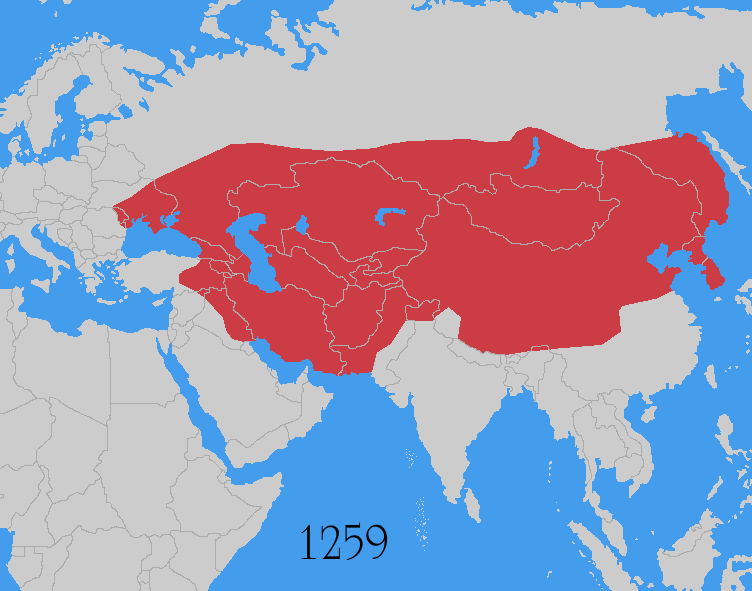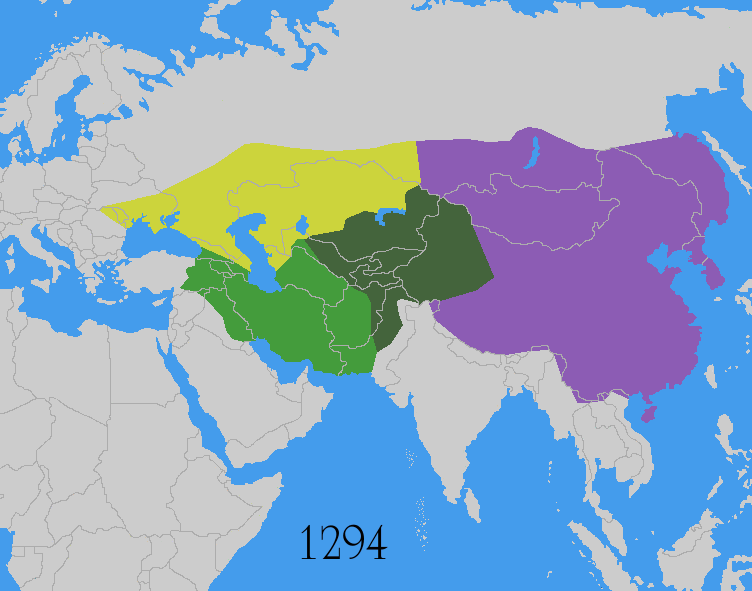
The Mongols under Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
had conquered Khwarezmia by 1221, but Iraq proper gained a respite due to the death of Genghis Khan in 1227 and the subsequent power struggles.
Möngke Khan from 1251 began a renewed expansion of the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
, and when caliph al-Mustasim refused to submit to the Mongols, Baghdad was besieged and captured by Hulagu Khan in 1258. Estimates of the number of dead range from 200,000 to a million. With the destruction of the Abbasid Caliphate, Hulagu had an open route to Syria and moved against the other Muslim powers in the region.Morgan. ''The Mongols''. pp. 132–135.
The Mongols destroyed the Abbasid Caliphate and Baghdad's House of Wisdom
The House of Wisdom ( ), also known as the Grand Library of Baghdad, was believed to be a major Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid-era public academy and intellectual center in Baghdad. In popular reference, it acted as one of the world's largest publ ...
. The city has never regained its previous pre-eminence as a major centre of culture and influence. Some historians believe that the Mongol invasion destroyed much of the irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
infrastructure that had sustained Mesopotamia for millennia. Other historians point to soil salination as the culprit in the decline in agriculture.
Turko-Mongol rule
Iraq now became a province on the southwestern fringes of theIlkhanate
The Ilkhanate or Il-khanate was a Mongol khanate founded in the southwestern territories of the Mongol Empire. It was ruled by the Il-Khans or Ilkhanids (), and known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (). The Ilkhanid realm was officially known ...
and Baghdad would never regain its former importance.
The Jalayirids were a Mongol Jalayir dynasty which ruled over Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
and western Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
after the breakup of the Ilkhanate in the 1330s. The Jalayirid sultanate lasted about fifty years, until disrupted by Tamerlane
Timur, also known as Tamerlane (1320s17/18 February 1405), was a Turco-Mongol tradition, Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timuri ...
's conquests and the revolts of the "Black Sheep Turks" or Qara Qoyunlu Turkmen.
The mid-14th-century Black Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. ...
ravaged much of the Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
. The best estimate for the Middle East is a death rate of roughly one-third.
In 1401, a warlord of Mongol descent, Tamerlane (Timur Lenk), invaded Iraq. After the capture of Baghdad, most of its citizens were massacred. Timur also conducted massacres of the indigenous Assyrian Christian population, and it was during this time that the ancient Assyrian city of Assur was finally abandoned. After Tamerlane's death in 1405, there was a brief attempt to re-establish the sultanate in southern Iraq and Khuzistan. The Jalayirids were finally eliminated by Kara Koyunlu in 1432.
Ottoman and Mamluk rule
 During the late 14th and early 15th centuries, the Qara Qoyunlu, or Black Sheep Turkmens, ruled the area now known as Iraq. In 1466, the
During the late 14th and early 15th centuries, the Qara Qoyunlu, or Black Sheep Turkmens, ruled the area now known as Iraq. In 1466, the Aq Qoyunlu
The Aq Qoyunlu or the White Sheep Turkomans (, ; ) was a culturally Persianate society, Persianate,Kaushik Roy, ''Military Transition in Early Modern Asia, 1400–1750'', (Bloomsbury, 2014), 38; "Post-Mongol Persia and Iraq were ruled by two trib ...
, or White Sheep, defeated the Qara Qoyunlu and took control. From 1508, as with all territories of the former White Sheep Turkmen, Iraq fell into the hands of the Iranian Safavids. With the Treaty of Zuhab in 1639, most of the territory of present-day Iraq came under the control of the Ottoman Empire as the eyalet of Baghdad as a result of wars
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of State (polity), states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or betwe ...
with the neighboring rival, Safavid Iran
The Guarded Domains of Iran, commonly called Safavid Iran, Safavid Persia or the Safavid Empire, was one of the largest and longest-lasting Iranian empires. It was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often considered the begi ...
. Throughout most of the period of Ottoman rule (1533–1918), the territory of present-day Iraq was a battle zone between rival regional empires and tribal alliances. Iraq was divided into three vilayets:
* Mosul Province
* Baghdad Province
*Basra Province
Basra Governorate ( ), also called Basra Province, is a governorate in southern Iraq in the region of Arabian Peninsula, bordering Kuwait to the south and Iran to the east. The capital is the city of Basra, located in the Basrah district. Other ...
In the 16th century, the Portuguese commanded by António Tenreiro crossed from Aleppo to Basra
Basra () is a port city in Iraq, southern Iraq. It is the capital of the eponymous Basra Governorate, as well as the List of largest cities of Iraq, third largest city in Iraq overall, behind Baghdad and Mosul. Located near the Iran–Iraq bor ...
in 1523, attempting to make alliances with local lords in the name of the Portuguese king. In 1550, the local kingdom of Basra and tribal rulers relied on the Portuguese against the Ottomans, leading to threats of invasion and conquest by the Portuguese. From 1595, the Portuguese acted as military protectors of Basra, and in 1624, they helped the Ottoman pasha of Basra repel a Persian invasion. The Portuguese were granted a share of customs revenue and exemption from tolls. From approximately 1625 to 1668, Basra and the Delta marshes were in the hands of local chiefs independent of the Ottoman administration in Baghdad. In the 17th century, frequent conflicts with the Safavids sapped the strength of the Ottoman Empire and weakened its control over its provinces. The nomadic population swelled with the influx of bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu ( ; , singular ) are pastorally nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia (Iraq). The Bedouin originated in the Sy ...
s from Najd
Najd is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes most of the central region of Saudi Arabia. It is roughly bounded by the Hejaz region to the west, the Nafud desert in Al-Jawf Province, al-Jawf to the north, ...
, leading to raids on settled areas that became difficult to curb.
During the years 1747–1831, Iraq was ruled by a Mamluk dynasty of Georgian origin, who succeeded in obtaining autonomy from the Ottoman Empire. They suppressed tribal revolts, curbed the power of the Janissaries
A janissary (, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman sultan's household troops. They were the first modern standing army, and perhaps the first infantry force in the world to be equipped with firearms, adopted du ...
, restored order, and introduced a program of modernization in the economy and military. In 1802, Wahhabis from Najd attacked Karbala in Iraq, killing up to 5,000 people and plundering the Imam Husayn Shrine. In 1831, the Ottomans managed to overthrow the Mamluk regime and imposed their direct control over Iraq. The population of Iraq, estimated at 30 million in 800 AD, was only 5 million at the start of the 20th century.
Kingdom of Khaza'il
The Kingdom of Khaza'il (Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
: مملكة الخزاعل, romanized
In linguistics, romanization is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and transcription, ...
: Mamlakat al-Khaza'il), also known as the Emirate of Khaza'il (Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
: إمارة الخزاعل, romanized
In linguistics, romanization is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and transcription, ...
: Imārat al-Khaza'il) to the Arabs and officially as the Kingdom of the Middle and Lower Euphrates (Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
: مملكة الفرات الأوسط والأسفل, romanized
In linguistics, romanization is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and transcription, ...
: Mamlakat al-Furāt al-Awsaṭ wa-al-Asfal) by Britain, was an autonomous kingdom in present-day Iraq that resisted Ottoman colonial rule from the early 16th century to the early 20th century. Ruled by the Khaza'il Royal family, also known as the Banu Khuza'ah Sheikh
Sheikh ( , , , , ''shuyūkh'' ) is an honorific title in the Arabic language, literally meaning "elder (administrative title), elder". It commonly designates a tribal chief or a Muslim ulama, scholar. Though this title generally refers to me ...
ly dynasty, the Kingdom exercised military, economic, and political sovereignty, particularly in the Middle and Lower Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
region.
At the height of their power in the 17th, 18th and 19th century, the Khaza'il ruled from the northern city of Anah to Basra
Basra () is a port city in Iraq, southern Iraq. It is the capital of the eponymous Basra Governorate, as well as the List of largest cities of Iraq, third largest city in Iraq overall, behind Baghdad and Mosul. Located near the Iran–Iraq bor ...
, including the southern outskirts of Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
and all cities along both sides of the Euphrates River, controlling all cultivatable land and tribal forces in their territory. The Emir
Emir (; ' (), also Romanization of Arabic, transliterated as amir, is a word of Arabic language, Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocratic, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person po ...
s of Khaza'il were known for their fierce armed resistance to Ottoman imperial authority lasting several centuries, vast land ownership, and their immense wealth established through the creation of Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
taxation mechanisms and agricultural monopoly. They are also known for establishing the dominance of Shiism in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
and ending 383 years of Ottoman Empire rule in Iraq.
20th century
British mandate of Mesopotamia
Ottoman rule over Iraq lasted untilWorld War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, when the Ottomans sided with Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
. In the Mesopotamian campaign against the Central Powers, British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
forces invaded the country and suffered a defeat at the hands of the Turkish army during the Siege of Kut (1915–16). However, the British ultimately won the Mesopotamian Campaign with the capture of Baghdad in March 1917. During the war, the British employed the help of several Assyrian, Armenian, and Arab tribes against the Ottomans, who in turn employed the Kurds as allies. Following the defeat of the Ottoman Empire and its subsequent division, the British Mandate of Mesopotamia was established by the League of Nations mandate.
In line with their " Sharifian Solution" policy, the British established a monarchy on 23 August 1921, with Faisal I of Iraq
Faisal I bin Hussein bin Ali Al-Hashemi (, ''Fayṣal al-Awwal bin Ḥusayn bin ʻAlī al-Hāshimī''; 20 May 1885 – 8 September 1933) was King of Iraq from 23 August 1921 until his death in 1933. A member of the Hashemites, Hashemite family, ...
as king, who was previously King of Syria but was forced out by the French. The official English name of the country simultaneously changed from ''Mesopotamia'' to the endonymic ''Iraq''. Likewise, British authorities selected Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
Arab elites from the region for appointments to government and ministry offices. The royal family were Hashemites, who were also rulers of the neighboring Emirate of Transjordan, which later became the Kingdom of Jordan.
During the rise of the Zionist movement and Arab nationalism, Faisal envisioned a federation consisting of the modern states of Iraq, Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
, Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, and Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
, including both modern Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
and Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
. He also signed the Faisal–Weizmann agreement.
Faced with spiraling costs and influenced by the public protestations of the war hero T. E. Lawrence, Britain replaced Arnold Wilson in October 1920 with a new Civil Commissioner, Sir Percy Cox. Cox managed to quell a rebellion and was also responsible for implementing the policy of close cooperation with Iraq's Sunni minority. Slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
was abolished in Iraq in the 1920s. Britain granted independence to the Kingdom of Iraq
The Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq was the Iraqi state located in the Middle East from 1932 to 1958. It was founded on 23 August 1921 as the Kingdom of Iraq, following the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in the Mesopotamian campaign of the First World W ...
in 1932, on the urging of King Faisal, though the British retained military base
A military base is a facility directly owned and operated by or for the military or one of its branches that shelters military equipment and personnel, and facilitates training and operations. A military base always provides accommodations for ...
s and local militia in the form of Assyrian Levies. King Ghazi ruled as a figurehead after King Faisal's death in 1933. His rule, which lasted until his death in 1939, was undermined by numerous attempted military coups until his death in 1939. His underage son, Faisal II succeeded him, with 'Abd al-Ilah as Regent
In a monarchy, a regent () is a person appointed to govern a state because the actual monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge their powers and duties, or the throne is vacant and a new monarch has not yet been dete ...
.
Independent Kingdom of Iraq
In 1934 Iraq became an oil exporter with the completion of the Kirkuk-Haifa oil pipeline which transported oil from the Kirkuk Field, discovered in 1927, to the Mediterranean coast for shipment to Europe. The first commercial oil production on a small scale for domestic consumption had begun in 1927 from the Naft Khana field on the border with Iran. Establishment of Arab Sunni domination in Iraq was followed by Assyrian, Yazidi andShi'a
Shia Islam is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political successor ( caliph) and as the spiritual leader of the Muslim community ( imam). However, his right is understoo ...
unrests, which were all brutally suppressed. In 1936, the first military coup took place in the Kingdom of Iraq, as Bakr Sidqi succeeded in replacing the acting Prime Minister with his associate. Multiple coups followed in a period of political instability, peaking in 1941.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Iraqi regime of Regent 'Abd al-Ilah was overthrown in 1941 by the Golden Square officers, headed by Rashid Ali. The short lived pro-Nazi government of Iraq was defeated in May 1941 by the allied forces (with local Assyrian and Kurdish help) in the Anglo-Iraqi War. Iraq was later used as a base for allied attacks on Vichy-French held Mandate of Syria and support for the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran.
In 1945, Iraq joined the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
and became a founding member of the Arab League
The Arab League (, ' ), officially the League of Arab States (, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world. The Arab League was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945, initially with seven members: Kingdom of Egypt, Egypt, Kingdom of Iraq, ...
.
In 1948, massive violent protests known as the Al-Wathbah uprising broke out across Baghdad with partial communist support, having demands against the government's treaty with Britain. Protests continued into spring and were interrupted in May when martial law was enforced as Iraq entered the failed 1948 Arab–Israeli War along with other Arab League members.
In February 1958, King Hussein of Jordan
Hussein bin Talal (14 November 1935 – 7 February 1999) was King of Jordan from 1952 until Death and state funeral of King Hussein, his death in 1999. As a member of the Hashemites, Hashemite dynasty, the royal family of Jordan since 1921, Hu ...
and `Abd al-Ilāh proposed a union of Hāshimite monarchies to counter the recently formed Egyptian-Syrian union. The prime minister Nuri as-Said wanted Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait ...
to be part of the proposed Arab-Hāshimite Union. Shaykh `Abd-Allāh as-Salīm, the ruler of Kuwait, was invited to Baghdad to discuss Kuwait's future. This policy brought the government of Iraq into direct conflict with Britain, which did not want to grant independence to Kuwait. At that point, the monarchy found itself completely isolated. Nuri as-Said was able to contain the rising discontent only by resorting to even greater political oppression.
Republic of Iraq
In 1958, inspired byGamal Abdel Nasser
Gamal Abdel Nasser Hussein (15 January 1918 – 28 September 1970) was an Egyptian military officer and revolutionary who served as the second president of Egypt from 1954 until his death in 1970. Nasser led the Egyptian revolution of 1952 a ...
of Egypt, officers from the Nineteenth Brigade, 3rd Division, known as "The Four Colonels," under the leadership of Brigadier Abd al-Karīm Qāsim (known as ''"az-Za`īm"'', 'the leader') and Colonel Abdul Salam Arif overthrew the Hashemite monarchy on 14 July 1958. The new government proclaimed Iraq to be a republic
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a State (polity), state in which Power (social and political), political power rests with the public (people), typically through their Representat ...
and rejected the idea of a union with Jordan. Iraq's activity in the Baghdad Pact ceased.
This revolution was strongly anti-imperial and anti-monarchical in nature and had strong socialist elements. Numerous people were killed in the coup, including King Faisal II, Prince Abd al-Ilah, and Nuri al-Sa'id, as well as members of the royal family, which came to be known as the "Royal family massacre". After burial, their bodies were dragged through the streets of Baghdad by their opponents and mutilated. The short-lived federation between Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
and Iraq was abolished by King Hussein following the coup in 1958.
Abd al-Karim Qasim promoted a civic nationalism in Iraq, which asserted the belief that Iraqis
Iraqis ( ; ) are the citizens and nationals of the Republic of Iraq. The majority of Iraqis are Arabs, with Kurds accounting for the largest ethnic minority, followed by Turkmen. Other ethnic groups from the country include Yazidis, As ...
are a nation
A nation is a type of social organization where a collective Identity (social science), identity, a national identity, has emerged from a combination of shared features across a given population, such as language, history, ethnicity, culture, t ...
and emphasized the cultural unity of Iraqis
Iraqis ( ; ) are the citizens and nationals of the Republic of Iraq. The majority of Iraqis are Arabs, with Kurds accounting for the largest ethnic minority, followed by Turkmen. Other ethnic groups from the country include Yazidis, As ...
of different ethnoreligious groups such as Mesopotamian Arabs, Kurds
Kurds (), or the Kurdish people, are an Iranian peoples, Iranic ethnic group from West Asia. They are indigenous to Kurdistan, which is a geographic region spanning southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Iraq, and northeastern Syri ...
, Turkmens, Assyrians, Yazidis
Yazidis, also spelled Yezidis (; ), are a Kurdish languages, Kurdish-speaking Endogamy, endogamous religious group indigenous to Kurdistan, a geographical region in Western Asia that includes parts of Iraq, Syria, Turkey, and Iran. The major ...
, Mandeans, Yarsans, and others. His vision of nationalism involved the recognition of an Iraqi identity stemming from ancient Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, including its civilization
A civilization (also spelled civilisation in British English) is any complex society characterized by the development of state (polity), the state, social stratification, urban area, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyon ...
s of Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
, Akkad, Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
, and Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
.Reich, Bernard. ''Political leaders of the contemporary Middle East and North Africa: A Bibliographical Dictionary''. Westport, Connecticut, USA: Greenwood Press, Ltd, 1990. Pp. 245.
Qasim controlled Iraq through military rule and began forcibly redistributing surplus land owned by some citizens in 1958. The Iraqi state emblem under Qasim was largely based on the Mesopotamian symbol of Shamash
Shamash (Akkadian language, Akkadian: ''šamaš''), also known as Utu (Sumerian language, Sumerian: dutu "Sun") was the List of Mesopotamian deities, ancient Mesopotamian Solar deity, sun god. He was believed to see everything that happened in t ...
, avoiding pan-Arab symbolism by incorporating elements of Socialist heraldry. Under Qasim, freedom of religion was granted to religious minorities, and early restrictions on Jews were removed, leading to their reintegration into society.
Qasim's political ideologies were based on Iraqi nationalism instead of Arab nationalism, and he refused to join Gamal Abdel Nasser
Gamal Abdel Nasser Hussein (15 January 1918 – 28 September 1970) was an Egyptian military officer and revolutionary who served as the second president of Egypt from 1954 until his death in 1970. Nasser led the Egyptian revolution of 1952 a ...
's political union between Egypt and Syria, known as the United Arab Republic
The United Arab Republic (UAR; ) was a sovereign state in the Middle East from 1958 to 1971. It was initially a short-lived political union between Republic of Egypt (1953–1958), Egypt (including Occupation of the Gaza Strip by the United Ara ...
. In 1959, Colonel Abd al-Wahab al-Shawaf led an uprising in Mosul against Qasim with the aim of joining the United Arab Republic, but was defeated by the government.
Iraq withdrew from the Baghdad Pact in 1959, leading to strained relations with the West and developing a close alliance with the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
.Tripp, Charles. ''A History of Iraq'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2002, p.165 Qasim began claiming Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait ...
as part of Iraq when it was officially declared an independent country in 1961. During Ottoman rule, Kuwait was part of Basra Province
Basra Governorate ( ), also called Basra Province, is a governorate in southern Iraq in the region of Arabian Peninsula, bordering Kuwait to the south and Iran to the east. The capital is the city of Basra, located in the Basrah district. Other ...
and was separated by the British to establish the Kuwait protectorate. In response, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
sent its armed forces to the Iraq–Kuwait border, and Qasim was forced to back down.
In 1961, Kurdish nationalist movements, led by Mustafa Barzani's Kurdistan Democratic Party
The Kurdistan Democratic Party (), usually abbreviated as KDP or PDK, is the ruling Political party, party in Iraqi Kurdistan and the senior partner in the Kurdistan Regional Government. It was founded in 1946 in Mahabad in Iranian Kurdistan. ...
, launched an armed rebellion against the Iraqi government, seeking Kurdish autonomy. The government faced challenges in quelling the Kurdish uprising, leading to intermittent conflict between Kurdish forces and the Iraqi military. The armed rebellion escalated into war, which officially lasted for nine years until 1970, during which numerous coups occurred.
Ba'athist Iraq
 Qāsim was assassinated in February 1963 when the
Qāsim was assassinated in February 1963 when the Ba'ath Party
The Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party ( ' ), also known simply as Bath Party (), was a political party founded in Syria by Michel Aflaq, Salah al-Din al-Bitar, and associates of Zaki al-Arsuzi. The party espoused Ba'athism, which is an ideology ...
took power under the leadership of General Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr (prime minister) and Colonel Abdul Salam Arif (president). In June 1963, Syria, which by then had also fallen under Ba'athist rule, took part in the Iraqi military campaign
A military campaign is large-scale long-duration significant military strategy plan incorporating a series of interrelated military operations or battles forming a distinct part of a larger conflict often called a war. The term derives from th ...
against the Kurds by providing aircraft, armoured vehicles, and a force of 6,000 soldiers. Several months later, Abd as-Salam Muhammad Arif led a successful coup against the Ba'ath government. Arif declared a ceasefire in February 1964, which provoked a split among Kurdish urban radicals on one hand and Peshmerga (Freedom fighters) forces led by Barzani on the other.
On 13 April 1966, President Abdul Salam Arif died in a helicopter crash and was succeeded by his brother, General Abdul Rahman Arif. Following this unexpected death, the Iraqi government launched a last-ditch effort to defeat the Kurds. This campaign failed in May 1966, when Barzani forces thoroughly defeated the Iraqi Army at the Battle of Mount Handrin, near Rawanduz. Following the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states, primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan from 5 to 10June ...
of 1967, the Ba'ath Party felt strong enough to retake power in 1968. Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr became president and chairman of the Revolutionary Command Council (RCC). The Ba'ath government started a campaign to end the Kurdish insurrection, which stalled in 1969 due to internal power struggles and tensions with Iran. The war ended with more than 100,000 casualties and little achievement for both sides.
In March 1970, a peace plan was announced that provided for broader Kurdish autonomy and gave Kurds representation in government bodies, to be implemented in four years. Despite this, the Iraqi government embarked on an Arabization program in the oil-rich regions of Kirkuk and Khanaqin. By 1974, tensions escalated again, leading to the Second Kurdish Iraqi War, which lasted until 1975. The 1975 peace treaty between Iraq and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
resolved the Shatt al-Arab dispute, leading to Iran withdrawing support for the Kurdish rebels and their subsequent defeat by the Iraqi government.
Under Saddam Hussein
 In July 1979, President Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr was forced to resign by
In July 1979, President Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr was forced to resign by Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein (28 April 1937 – 30 December 2006) was an Iraqi politician and revolutionary who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 1979 until Saddam Hussein statue destruction, his overthrow in 2003 during the 2003 invasion of Ira ...
, who assumed the offices of both President and Chairman of the Revolutionary Command Council. Saddam then purged his opponents including those from within the Baath party.
;Iraq's Territorial Claims to Neighboring Countries
Iraq's territorial claims to neighboring countries were largely due to the plans and promises of the Entente countries in 1919–1920, when the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
was divided, to create a more extensive Arab state in Iraq and Jazeera, which would also include significant territories of eastern Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, southeastern Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, all of Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait ...
and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
’s border areas, which are shown on this English map of 1920.
 Territorial disputes with
Territorial disputes with Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
led to an inconclusive and costly eight-year war, the ''Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War, also known as the First Gulf War, was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. Active hostilities began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for nearly eight years, unti ...
'' (1980–1988, termed '' Qādisiyyat-Saddām'' – 'Saddam's Qādisiyyah'), which devastated the economy. Iraq falsely declared victory in 1988 but actually only achieved a weary return to the '' status quo ante bellum'', meaning both sides retained their original borders.
The war began when Iraq invaded Iran, launching a simultaneous invasion by air and land into Iranian territory on 22 September 1980, following a long history of border disputes, and fears of Shia insurgency among Iraq's long-suppressed Shia majority influenced by the Iranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution (, ), also known as the 1979 Revolution, or the Islamic Revolution of 1979 (, ) was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynasty in 1979. The revolution led to the replacement of the Impe ...
. Iraq was also aiming to replace Iran as the dominant Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
. The United States supported Saddam Hussein in the war against Iran. Although Iraq hoped to take advantage of the revolutionary chaos in Iran and attacked without formal warning, they made only limited progress into Iran and within several months were repelled by the Iranians who regained virtually all lost territory by June 1982. For the next six years, Iran was on the offensive. Despite calls for a ceasefire by the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
, hostilities continued until 20 August 1988. The war finally ended with a United Nations-brokered ceasefire in the form of United Nations Security Council Resolution 598, which was accepted by both sides. It took several weeks for the Iranian armed forces to evacuate Iraqi territory to honor pre-war international borders between the two nations (see 1975 Algiers Agreement). The last prisoners of war were exchanged in 2003.
The war came at a great cost in lives and economic damage—half a million Iraqi and Iranian soldiers, as well as civilians, are believed to have died in the war with many more injured—but it brought neither reparations nor change in borders. The conflict is often compared to World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, in that the tactics used closely mirrored those of that conflict, including large scale trench warfare
Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising Trench#Military engineering, military trenches, in which combatants are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from a ...
, manned machine-gun posts, bayonet charges, use of barbed wire across trenches, human wave attacks across no-man's land, and extensive use of chemical weapons such as mustard gas by the Iraqi government against Iranian troops
A troop is a military sub-subunit, originally a small formation of cavalry, subordinate to a Squadron (cavalry), squadron. In many armies a troop is the equivalent element to the infantry section (military unit), section or platoon. Exception ...
and civilians as well as Iraqi Kurd
Kurds (), or the Kurdish people, are an Iranian peoples, Iranic ethnic group from West Asia. They are indigenous to Kurdistan, which is a geographic region spanning southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Iraq, and northeastern Syri ...
s. At the time, the UN Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
issued statements that "chemical weapons had been used in the war." However, in these UN statements, it was never made clear that it was only Iraq that was using chemical weapons, so it has been said that "the international community remained silent as Iraq used weapons of mass destruction against Iranian as well as Iraqi Kurds" and it is believed.
A long-standing territorial dispute was the ostensible reason for Iraq's invasion of Kuwait
The Iraqi invasion of Kuwait, codenamed Project 17, began on 2 August 1990 and marked the beginning of the Gulf War. After defeating the Kuwait, State of Kuwait on 4 August 1990, Ba'athist Iraq, Iraq went on to militarily occupy the country fo ...
in 1990. In November 1990, the UN Security Council adopted Resolution 678, permitting member states to use all necessary means, authorizing military action against the Iraqi forces occupying Kuwait and demanded a complete withdrawal by 15 January 1991. When Saddam Hussein failed to comply with this demand, the Gulf War
, combatant2 =
, commander1 =
, commander2 =
, strength1 = Over 950,000 soldiers3,113 tanks1,800 aircraft2,200 artillery systems
, page = https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/GAOREPORTS-PEMD-96- ...
(Operation " Desert Storm") ensued on 17 January 1991. Estimates range from 1,500 to as many as 30,000 Iraqi soldiers killed, as well as less than a thousand civilians.
In March 1991 revolts in the Shia-dominated southern Iraq started involving demoralized Iraqi Army
The Iraqi Ground Forces (Arabic: القوات البرية العراقية), also referred to as the Iraqi Army (Arabic: الجيش العراقي), is the ground force component of the Iraqi Armed Forces. It was formerly known as the Royal Iraq ...
troops and the anti-government Shia parties. Another wave of insurgency broke out shortly afterwards in the Kurdish populated northern Iraq (see 1991 Iraqi uprisings). Although they presented a serious threat to the Iraqi Ba'ath Party
The Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party ( ' ), also known simply as Bath Party (), was a political party founded in Syria by Michel Aflaq, Salah al-Din al-Bitar, and associates of Zaki al-Arsuzi. The party espoused Ba'athism, which is an ideology ...
regime, Saddam Hussein managed to suppress the rebellions with massive and indiscriminate force and maintained power. They were ruthlessly crushed by the loyalist forces spearheaded by the Iraqi Republican Guard and the population was successfully terrorized. During the few weeks of unrest tens of thousands of people were killed. Many more died during the following months, while nearly two million Iraqis fled for their lives. In the aftermath, the government intensified the forced relocating of Marsh Arabs and the draining of the Iraqi marshlands, while the Coalition established the Iraqi no-fly zones.
On 6 August 1990, after the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait, the U.N. Security Council adopted Resolution 661 which imposed economic sanctions
Economic sanctions or embargoes are Commerce, commercial and Finance, financial penalties applied by states or institutions against states, groups, or individuals. Economic sanctions are a form of Coercion (international relations), coercion tha ...
on Iraq, providing for a full trade embargo, excluding medical supplies, food and other items of humanitarian necessity, these to be determined by the Security Council sanctions committee. After the end of the Gulf War and after the Iraqi withdrawal from Kuwait, the sanctions were linked to removal of weapons of mass destruction
A weapon of mass destruction (WMD) is a Biological agent, biological, chemical weapon, chemical, Radiological weapon, radiological, nuclear weapon, nuclear, or any other weapon that can kill or significantly harm many people or cause great dam ...
by Resolution 687. To varying degrees, the effects of government policy, the aftermath of Gulf War and the sanctions regime have been blamed for these conditions.
The effects of the sanctions on the civilian population of Iraq have been disputed.Iraq surveys show 'humanitarian emergency'UNICEF
UNICEF ( ), originally the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, officially United Nations Children's Fund since 1953, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Development a ...
Newsline 12 August 1999 Whereas it was widely believed that the sanctions caused a major rise in child mortality, recent research has shown that commonly cited data were fabricated by the Iraqi government and that "there was no major rise in child mortality in Iraq after 1990 and during the period of the sanctions." An oil for food program was established in 1996 to ease the effects of sanctions.
Iraqi cooperation with UN weapons inspection teams was questioned on several occasions during the 1990s. UNSCOM chief weapons inspector Richard Butler withdrew his team from Iraq in November 1998 because of Iraq's lack of cooperation. The team returned in December. Butler prepared a report for the UN Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
afterwards in which he expressed dissatisfaction with the level of compliancThe same month, US President Bill Clinton authorized air strikes on government targets and military facilities. Air strikes against military facilities and alleged WMD sites continued into 2002.
U.S. invasion and the aftermath (2003–present)
2003 U.S. invasion
After the September 11 attacks, terrorist attacks on New York and Washington in the United States in 2001 were linked to the group formed by the multi-millionaire SaudiOsama bin Laden
Osama bin Laden (10 March 19572 May 2011) was a militant leader who was the founder and first general emir of al-Qaeda. Ideologically a pan-Islamist, Bin Laden participated in the Afghan ''mujahideen'' against the Soviet Union, and support ...
, American foreign policy began to call for the removal of the Ba'ath government in Iraq. Neoconservative think-tanks in Washington had for years been urging regime change in Baghdad. On 14 August 1998, President Clinton signed Public Law 105–235, which declared that ‘‘the Government of Iraq is in material and unacceptable breach of its international obligations.’’ It urged the President ‘‘to take appropriate action, in accordance with the Constitution and relevant laws of the United States, to bring Iraq into compliance with its international obligations.’’ Several months later, Congress enacted the Iraq Liberation Act of 1998 on 31 October 1998. This law stated that it "should be the policy of the United States to support efforts to remove the regime headed by Saddam Hussein from power in Iraq and to promote the emergence of a democratic government to replace that regime." It was passed 360 - 38 by the United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is a chamber of the Bicameralism, bicameral United States Congress; it is the lower house, with the U.S. Senate being the upper house. Together, the House and Senate have the authority under Artic ...
and 99–0 by the United States Senate
The United States Senate is a chamber of the Bicameralism, bicameral United States Congress; it is the upper house, with the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives being the lower house. Together, the Senate and ...
in 1998.
The US urged the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
to take military action against Iraq. American president George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician and businessman who was the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Bush family and the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he i ...
stated that Saddām had repeatedly violated 16 UN Security Council resolutions. The Iraqi government rejected Bush's assertions. A team of U.N. inspectors, led by Swedish diplomat Hans Blix
Hans Martin Blix (; born 28 June 1928) is a Swedish diplomat and politician for the Liberal People's Party. He was Swedish Minister for Foreign Affairs (1978–1979) and later became the head of the International Atomic Energy Agency. Blix wa ...
was admitted, into the country; their final report stated that Iraqis capability in producing "weapons of mass destruction" was not significantly different from 1992 when the country dismantled the bulk of their remaining arsenals under terms of the ceasefire agreement with U.N. forces, but did not completely rule out the possibility that Saddam still had weapons of mass destruction. The United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
charged that Iraq was hiding WMD and opposed the team's requests for more time to further investigate the matter. Resolution 1441 was passed unanimously by the UN Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
on 8 November 2002, offering Iraq "a final opportunity to comply with its disarmament obligations" that had been set out in several previous UN resolutions, threatening "serious consequences" if the obligations were not fulfilled. The UN Security Council did not issue a resolution authorizing the use of force against Iraq.
In March 2003, the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, with military aid from other nations, invaded Iraq.
Over the following years in the U.S. occupation of Iraq, Iraq disintegrated into a civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
from 2006 to 2008, and the situation deteriorated in 2011 which later escalated into a renewed war following ISIL gains in the country in 2014. By 2015, Iraq was effectively divided, the central and southern part being controlled by the government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), execu ...
, the northwest by the Kurdistan Regional Government
The Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG) is the official executive body of the semi-autonomous Kurdistan Region in northern Iraq.
The cabinet is selected by the majority party or list who also select the prime minister of the Iraqi Kurdish poli ...
and the western part by the Islamic State
The Islamic State (IS), also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) and Daesh, is a transnational Salafi jihadism, Salafi jihadist organization and unrecognized quasi-state. IS ...
. IS was expelled from Iraq in 2017, but a low-intensity ISIL insurgency continues mostly in the rural parts of northern western parts of the country, due to Iraq's long border with Syria.
Occupation (2003–11)
 In 2003, after the American and British invasion, Iraq was occupied by U.S.-led Coalition forces. On 23 May 2003, the UN Security Council unanimously approved a resolution lifting all economic sanctions against Iraq. As the country struggled to rebuild after three wars and a decade of sanctions, it was plagued by violence between a growing Iraqi insurgency and occupation forces. Saddam Hussein, who vanished in April, was captured on 13 December 2003 in
In 2003, after the American and British invasion, Iraq was occupied by U.S.-led Coalition forces. On 23 May 2003, the UN Security Council unanimously approved a resolution lifting all economic sanctions against Iraq. As the country struggled to rebuild after three wars and a decade of sanctions, it was plagued by violence between a growing Iraqi insurgency and occupation forces. Saddam Hussein, who vanished in April, was captured on 13 December 2003 in ad-Dawr
Ad-Dawr () is a small agricultural town in Saladin Governorate, Iraq, near Tikrit. It includes a great number of people from four tribes, al-Shuwaykhat, al-Mawashet, al-Bu Haydar and al-Bu Mdallal. Al-Mawashet tribe is famous for supporting Saddam ...
, Saladin Governorate. Jay Garner was appointed Interim Civil Administrator with three deputies, including Tim Cross. Garner was replaced in May 2003 by Paul Bremer, who was himself replaced by John Negroponte on 19 April 2004. Negroponte was the last US interim administrator and left Iraq in 2005. A parliamentary election was held in January 2005, followed by the drafting and ratification of a constitution and a further parliamentary election in December 2005.
Terrorism emerged as a threat to Iraq's people not long after the invasion of 2003. Al Qaeda now had a presence in the country, in the form of several terrorist groups formerly led by Abu Musab Al Zarqawi. Al Zarqawi was a Jordanian militant Islamist who ran a militant training camp in Afghanistan. He became known after going to Iraq and being responsible for a series of bombings, beheadings and attacks during the Iraq war. Al Zarqawi was killed on 7 June 2006. Many foreign fighters and former Ba'ath Party officials also joined the insurgency, which was mainly aimed at attacking American forces and Iraqis who worked with them. The most dangerous insurgent area was the Sunni Triangle, a mostly Sunni-Muslim area just north of Baghdad.
Reported acts of violence conducted by an uneasy tapestry of insurgents steadily increased by the end of 2006. Sunni jihadist forces including Al Qaeda in Iraq continued to target Shia civilians, notably in the 23 February 2006 attack on the Al Askari Mosque in Samarra, one of Shi'ite Islam's holiest sites leading to a civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
between Sunni and Shia militants in Iraq. Analysis of the attack suggested that the Mujahideen Shura Council and Al-Qaeda in Iraq were responsible, and that the motivation was to provoke further violence by outraging the Shia population. In mid-October 2006, a statement was released stating that the Mujahideen Shura Council had been disbanded and was replaced by the " Islamic State of Iraq". It was formed to resist efforts by the U.S. and Iraqi authorities to win over Sunni supporters of the insurgency. Shia militias, some of whom were associated with elements in the Iraq government, reacted with reprisal acts against the Sunni minority. A cycle of violence thus ensued whereby Sunni insurgent attacks were followed reprisals by Shiite militias, often in the form of Shi'ite death squads that sought out and killed Sunnis. Following a surge in U.S. troops in 2007 and 2008, violence in Iraq began to decrease. The U.S. ended their main military presence in 2011, however, resulting in renewed escalation into war.
Insurgency and war (2011–2017)
The departure of US troops from Iraq in 2011 triggered a renewed insurgency and by a spillover of the Syrian civil war into Iraq. By 2013, the insurgency escalated into a state renewed war, the centralgovernment of Iraq
The government of Iraq is defined under the current Constitution of Iraq, Constitution, approved in 2005, as a Democracy in Iraq, democratic, Parliamentary system, parliamentary republic with Islam as the official state religion. The government i ...
being opposed by various factions, primarily radical Sunni forces.
The Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
The Islamic State (IS), also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) and Daesh, is a transnational Salafi jihadist organization and unrecognized quasi-state. IS occupied signi ...
invaded Iraq in 2013–14 and seized the majority of Al Anbar Governorate, including the cities of Fallujah, Al Qaim, Abu Ghraib and (in May 2015) Ramadi, leaving them in control of 90% of Anbar. Tikrit, Mosul
Mosul ( ; , , ; ; ; ) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. It is the second largest city in Iraq overall after the capital Baghdad. Situated on the banks of Tigris, the city encloses the ruins of the ...
and most of the Nineveh province, along with parts of Salahuddin, Kirkuk and Diyala provinces, were seized by insurgent forces in the June 2014 offensive. ISIL also captured Sinjar and a number of other towns in the August 2014 offensive, but were halted by the Sinjar offensive launched in December 2014 by Kurdish Peshmerga and YPG forces. The war ended with a government victory in December 2017.
On 30 April 2016, thousands of protesters entered the Green Zone
The Green Zone () is the most common name for the International Zone of Baghdad. It is a area in the Karkh, Karkh district of central Baghdad, Iraq. It is the chief government precinct and the seat of the Iraqi government.
History
Pre-200 ...
in Baghdad and occupied the Iraqi parliament building. This happened after the Iraqi parliament did not approve new government ministers. The protesters included supporters of Shia cleric Muqtada Al Sadr. Although Iraqi security forces were present, they did not attempt to stop the protesters from entering the parliament building.
Continued ISIL insurgency and protests (2017–present)
Tensions between the federal Iraqi government andKurdistan Region
Kurdistan Region (KRI) is a semi-autonomous Federal regions of Iraq, federal region of the Iraq, Republic of Iraq. It comprises four Kurds, Kurdish-majority governorates of Arabs, Arab-majority Iraq: Erbil Governorate, Sulaymaniyah Governorate ...
arising from the Kurdistan Region independence referendum of 25 September 2017 escalated into armed conflict in October 2017. As a result of the conflict, Kurdistan Region lost a fifth of the land mass it had administered prior to the conflict and was forced to cancel the results of the referendum.
By 2018, violence in Iraq was at its lowest level in ten years.
Protests over deteriorating economic conditions and state corruption started in July 2018 in Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
and other major Iraqi cities, mainly in the central and southern provinces. The latest nationwide protests, erupting in October 2019, had a death toll of at least 93 people, including police.
In November 2021, Iraqi Prime Minister Mustafa al-Kadhimi survived a failed assassination attempt.
Cleric Muqtada al-Sadr's Sadrist Movement was the biggest winner in the 2021 parliamentary elections. Governmental stalemate lead to the 2022 Iraqi political crisis.
In October 2022, Abdul Latif Rashid was elected as the new President of Iraq
The President of the Republic of Iraq is the head of state of Iraq. Since the mid-2000s, the presidency is primarily a symbolic office, as the position does not possess significant power within the country according to the Constitution of Iraq, ...
after winning the parliamentary election against incumbent Barham Salih, who was running for a second term. The presidency is largely ceremonial and is traditionally held by a Kurd. On 27 October 2022, Mohammed Shia al-Sudani, close ally of former Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki, took the office to succeed Mustafa al-Kadhimi as new Prime Minister of Iraq.
See also
*Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes ...
* Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first known empire, succeeding the long-lived city-states of Sumer. Centered on the city of Akkad (city), Akkad ( or ) and its surrounding region, the empire united Akkadian language, Akkadian and Sumerian languag ...
* Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
* Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
* History of Asia
The history of Asia can be seen as the collective history of several distinct peripheral coastal regions such as East Asia, South Asia, History of Southeast Asia, Southeast Asia and the Middle East linked by the interior mass of the Eurasian ste ...
* History of Baghdad
* History of the Middle East
* List of kings of Iraq
* List of presidents of Iraq
* List of prime ministers of Iraq
* Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
* Politics of Iraq
* Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
* Timeline of Baghdad
* Timeline of Basra
References
Sources
* * *Further reading
* Broich, John. ''Blood, Oil and the Axis: The Allied Resistance Against a Fascist State in Iraq and the Levant, 1941'' (Abrams, 2019). * de Gaury, Gerald. ''Three Kings in Baghdad: The Tragedy of Iraq's Monarchy'', (IB Taurus, 2008). * Elliot, Matthew. ''Independent Iraq: British Influence from 1941 to 1958'' (IB Tauris, 1996). * Fattah, Hala Mundhir, and Frank Caso. ''A brief history of Iraq'' (Infobase Publishing, 2009). * Franzén, Johan. "Development vs. Reform: Attempts at Modernisation during the Twilight of British Influence in Iraq, 1946–1958," ''Journal of Imperial and Commonwealth History'' 37#1 (2009), pp. 77–98 * Kriwaczek, Paul. ''Babylon: Mesopotamia and the Birth of Civilization''. Atlantic Books (2010). * Murray, Williamson, and Kevin M. Woods. ''The Iran-Iraq War: A military and strategic history'' (Cambridge UP, 2014). * Roux, Georges. ''Ancient Iraq''. Penguin Books (1992). * Silverfarb, Daniel. ''Britain's informal empire in the Middle East: a case study of Iraq, 1929-1941'' ( Oxford University Press, 1986). * Silverfarb, Daniel. ''The twilight of British ascendancy in the Middle East: a case study of Iraq, 1941-1950'' (1994) * Silverfarb, Daniel. "The revision of Iraq's oil concession, 1949–52." ''Middle Eastern Studies'' 32.1 (1996): 69-95. * Simons, Geoff. ''Iraq: From Sumer to Saddam'' (Springer, 2016). * Tarbush, Mohammad A. ''The role of the military in politics: A case study of Iraq to 1941'' (Routledge, 2015). *Historiography
*External links
Iraq: The Cradle of Civilization
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20180927085237/https://repository.library.georgetown.edu/handle/10822/552703 Historical Context of the Iran – Iraq Warfrom th
Dean Peter Krogh Foreign Affairs Digital Archives
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Iraq
Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...