Haraldr Sigurðarson on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Harald Sigurdsson (; – 25 September 1066), also known as Harald III of Norway and given the epithet ''Hardrada'' in the
vol. 3
p. x. While
The Early Kings of Norway, the Issue of Agnatic Succession, and the Settlement of Iceland
, ''Viator'', 47 (2016), 171–188 (pp. 1–18 in open-access text, at p. 7); . However, in a number of independent sources associated with the
 Harald was born in Ringerike, Norway,Hjardar & Vike (2011) p. 284 in 1015 (or possibly 1016) to Åsta Gudbrandsdatter and her second husband
Harald was born in Ringerike, Norway,Hjardar & Vike (2011) p. 284 in 1015 (or possibly 1016) to Åsta Gudbrandsdatter and her second husband
 After a few years in Kievan Rus', Harald and his force of around 500 men moved on south to
After a few years in Kievan Rus', Harald and his force of around 500 men moved on south to
saga
Sagas are prose stories and histories, composed in Iceland and to a lesser extent elsewhere in Scandinavia.
The most famous saga-genre is the (sagas concerning Icelanders), which feature Viking voyages, migration to Iceland, and feuds between ...
s, was King of Norway
The Norwegian monarch is the head of state of Norway, which is a constitutional and hereditary monarchy with a parliamentary system. The Norwegian monarchy can trace its line back to the reign of Harald Fairhair and the previous petty king ...
from 1046 to 1066. He unsuccessfully claimed the Danish throne
The monarchy of Denmark is a constitutional institution and a historic office of the Kingdom of Denmark. The Kingdom includes Denmark proper and the autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland. The Kingdom of Denmark was alrea ...
until 1064 and the English throne
The Throne of England is the throne of the Monarch of England. "Throne of England" also refers metonymically to the office of monarch, and monarchy itself.Gordon, Delahay. (1760) ''A General History of the Lives, Trials, and Executions of All t ...
in 1066. Before becoming king, Harald spent 15 years in exile as a mercenary and military commander in Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,.
* was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical At ...
and chief of the Varangian Guard
The Varangian Guard () was an elite unit of the Byzantine army from the tenth to the fourteenth century who served as personal bodyguards to the Byzantine emperors. The Varangian Guard was known for being primarily composed of recruits from Nort ...
in the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
. In his chronicle
A chronicle (, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and local events ...
, Adam of Bremen
Adam of Bremen (; ; before 1050 – 12 October 1081/1085) was a German medieval chronicler. He lived and worked in the second half of the eleventh century. Adam is most famous for his chronicle '' Gesta Hammaburgensis ecclesiae pontificum'' ('' ...
called him the "''Thunderbolt of the North''".
In 1030, the fifteen-year-old Harald fought in the Battle of Stiklestad
The Battle of Stiklestad (; ) in 1030 is one of the most famous battles in the history of Norway. In this battle, King Olaf II of Norway () was killed. During the pontificate of Pope Alexander III, the Roman Catholic Church declared Olaf a saint ...
along-side his half-brother Olaf Haraldsson. Olaf sought to reclaim the Norwegian throne, which he had lost to Danish king Cnut
Cnut ( ; ; – 12 November 1035), also known as Canute and with the epithet the Great, was King of England from 1016, King of Denmark from 1018, and King of Norway from 1028 until his death in 1035. The three kingdoms united under Cnut's rul ...
two years previously. Olaf and Harald were defeated by forces loyal to Cnut, and Harald was forced into exile to Kievan Rus'. Thereafter, he was in the army of Grand Prince Yaroslav the Wise
Yaroslav I Vladimirovich ( 978 – 20 February 1054), better known as Yaroslav the Wise, was Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019 until his death in 1054. He was also earlier Prince of Novgorod from 1010 to 1034 and Prince of Rostov from 987 to 1010, ...
, becoming captain, until he moved on to Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
with his companions around 1034. In Constantinople, he rose quickly to become the commander of the Byzantine Varangian Guard, seeing action on the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
, in Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, Sicily, possibly in the Holy Land
The term "Holy Land" is used to collectively denote areas of the Southern Levant that hold great significance in the Abrahamic religions, primarily because of their association with people and events featured in the Bible. It is traditionall ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
and in Constantinople itself, where he became involved in the imperial dynastic disputes. Harald amassed wealth whilst in the Byzantine Empire, which he shipped to Yaroslav in Kievan Rus' for safekeeping. In 1042, he left the Byzantine Empire, returning to Kievan Rus' to prepare to reclaim the Norwegian throne. In his absence the Norwegian throne had been restored from the Danes to Olaf's illegitimate son Magnus the Good
Magnus Olafsson (; Norwegian and Danish: ''Magnus Olavsson''; – 25 October 1047), better known as Magnus the Good (; Norwegian and Danish: ''Magnus den gode''), was King of Norway from 1035 and King of Denmark from 1042 until his death in ...
.
In 1046, Harald joined forces with Magnus's rival in Denmark, the pretender
A pretender is someone who claims to be the rightful ruler of a country although not recognized as such by the current government. The term may often be used to either refer to a descendant of a deposed monarchy or a claim that is not legitimat ...
Sweyn II of Denmark
Sweyn II ( – 28 April 1076), also known as Sweyn Estridsson (, ) and Sweyn Ulfsson, was King of Denmark from 1047 until his death in 1076. He was the son of Ulf Thorgilsson and Estrid Svendsdatter, and the grandson of Sweyn Forkbeard through ...
, raiding the Danish coast. Magnus, unwilling to fight his uncle, agreed to share the kingship with Harald, since Harald in turn would share his wealth with him. The co-rule ended abruptly the next year as Magnus died: Harald became the sole ruler of Norway. Domestically, Harald crushed opposition, and outlined the unification of Norway. Harald's reign was one of relative peace and stability, and he instituted a coin economy and foreign trade. Seeking to restore Cnut's "North Sea Empire
The North Sea Empire, also known as the Anglo-Scandinavian Empire, was the personal union of the kingdoms of England, Denmark and Norway for most of the period between 1013 and 1042 towards the end of the Viking Age. This ephemeral Norse-ruled ...
", Harald claimed the Danish throne, and spent nearly every year until 1064 raiding the Danish coast and fighting his former ally, Sweyn. Although the campaigns were successful, he was never able to conquer Denmark.
Not long after Harald had renounced his claim to Denmark, the former Earl of Northumbria
Earl of Northumbria or Ealdorman of Northumbria was a title in the late Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon, Scandinavian people, Anglo-Scandinavian and early Anglo-Norman England, Anglo-Norman period in England. The ealdordom was a successor of the ...
, Tostig Godwinson
Tostig Godwinson ( 102925 September 1066) was an Anglo-Saxon Earl of Northumbria and brother of King Harold Godwinson. After being exiled by his brother, Tostig supported the Norwegian king Harald Hardrada's invasion of England, and was killed ...
, brother of English king Harold Godwinson
Harold Godwinson ( – 14 October 1066), also called Harold II, was the last crowned Anglo-Saxon King of England. Harold reigned from 6 January 1066 until his death at the Battle of Hastings on 14 October 1066, the decisive battle of the Norman ...
, pledged his allegiance to Harald, inviting him to claim the English throne. Harald assented, invading northern England with 10,000 troops and 300 longships in September 1066, defeating the English regional forces of Northumbria and Mercia in the Battle of Fulford near York
York is a cathedral city in North Yorkshire, England, with Roman Britain, Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Foss, Foss. It has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a Yor ...
on 20 September. Harald was defeated and killed in a surprise attack by Harold Godwinson's forces in the Battle of Stamford Bridge
The Battle of Stamford Bridge () took place at the village of Stamford Bridge, East Riding of Yorkshire, in England, on 25 September 1066, between an English army under Harold Godwinson, King Harold Godwinson and an invading Norwegian force l ...
on 25 September, which wiped out his army. Historians often consider Harald's death the end of the Viking Age
The Viking Age (about ) was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonising, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. The Viking Age applies not only to their ...
.
Epithets
Harald's most famous epithet is Old Norse ''harðráði'', which has been translated variously as 'hard in counsel', 'tyrannical', 'tyrant', 'hard-ruler', 'ruthless', 'savage in counsel', 'tough', and 'severe'.Snorri Sturluson, ''Heimskringla'', trans. by Alison Finlay and Anthony Faulkes, 3 vols (London: Viking Society for Northern Research, 2011–15) (2nd ed. 2016)vol. 3
p. x. While
Judith Jesch
Judith Jesch (born 1954) is a British scholar of Old Norse language and literature, runology, and the Viking Age. She is Professor of Viking Age Studies at the University of Nottingham. Jesch is chair of the international Runic Advisory Group an ...
has argued for 'severe' as the best translation,Judith Jesch, 'Norse Historical Traditions and Historia Gruffud vab Kenan: Magnus Berfoettr and Haraldr Harfagri', in ''Gruffudd ap Cynan: A Collaborative Biography'', edited by K.L. Maund (Cambridge, 1996), pp. 117–147 (p. 139 n. 62). Alison Finlay and Anthony Faulkes prefer 'resolute'. ''Harðráði'' has traditionally been Anglicised as 'Hardrada', though Judith Jesch
Judith Jesch (born 1954) is a British scholar of Old Norse language and literature, runology, and the Viking Age. She is Professor of Viking Age Studies at the University of Nottingham. Jesch is chair of the international Runic Advisory Group an ...
characterises this form as 'a bastard Anglicisation of the original epithet in an oblique case
In grammar, an oblique ( abbreviated ; from ) or objective case ( abbr. ) is a nominal case other than the nominative case and, sometimes, the vocative.
A noun or pronoun in the oblique case can generally appear in any role except as subject, ...
'. This epithet predominates in the later Icelandic saga-tradition.Sverrir Jakobsson,The Early Kings of Norway, the Issue of Agnatic Succession, and the Settlement of Iceland
, ''Viator'', 47 (2016), 171–188 (pp. 1–18 in open-access text, at p. 7); . However, in a number of independent sources associated with the
British Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebr ...
, mostly earlier than the Icelandic sagas, Harald is given epithets deriving from Old Norse ''hárfagri'' (literally 'hair-beautiful'). These sources include:
* Manuscript D of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons.
The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the ninth century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of ...
'' ('Harold Harfagera', under the year 1066) and the related histories by Orderic Vitalis
Orderic Vitalis (; 16 February 1075 – ) was an English chronicler and Benedictine monk who wrote one of the great contemporary chronicles of 11th- and 12th-century Normandy and Anglo-Norman England.Hollister ''Henry I'' p. 6 Working out of ...
('Harafagh', re events in 1066), John of Worcester
John of Worcester (died c. 1140) was an English monk and chronicler who worked at Worcester Priory. He is now usually held to be the author of the .
Works
John of Worcester's principal work was the (Latin for "Chronicle from Chronicles") or ...
('Harvagra', s.aa. 1066 and 1098), and William of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury (; ) was the foremost English historian of the 12th century. He has been ranked among the most talented English historians since Bede. Modern historian C. Warren Hollister described him as "a gifted historical scholar and a ...
(''Gesta regum Anglorum
The (Latin for "Deeds of the Kings of the English"), originally titled ("On the Deeds of the Kings of the English") and also anglicized as or , is an early-12th-century history of the kings of England
This list of kings and reigning q ...
'', 'Harvagre', regarding 1066).
* Marianus Scotus of Mainz ('Arbach', d. 1082/1083).
* The ''Life'' of Gruffydd ap Cynan ('Haralld Harfagyr', later twelfth century).
In Icelandic sagas the name ''Harald Fairhair'' is more famously associated with an earlier Norwegian king, and twentieth-century historians assumed that the name was attached to Harald Hardrada in error by Insular historians. However, recognising the independence of some of the Insular sources, historians have since favoured the idea that Harald Hardrada was widely known as Harald Fairhair, and indeed now doubt that the earlier Harald Fairhair existed in any form resembling the later saga-accounts.
Sverrir Jakobsson has suggested that 'fairhair' 'might be the name by which King Harald wished himself to be known. It must have been his opponents who gave him the epithet "severe" (ON. ''harðráði''), by which he is generally known in thirteenth-century Old Norse kings' sagas'.
Early life
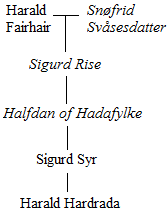
 Harald was born in Ringerike, Norway,Hjardar & Vike (2011) p. 284 in 1015 (or possibly 1016) to Åsta Gudbrandsdatter and her second husband
Harald was born in Ringerike, Norway,Hjardar & Vike (2011) p. 284 in 1015 (or possibly 1016) to Åsta Gudbrandsdatter and her second husband Sigurd Syr
Sigurd Syr (Old Norse: ''Sigurðr Sýr'') (died c. 1018) was a Norwegian petty king of Ringerike, a region in Buskerud. He was notable in Norwegian history largely through his association with Kings Harald Hardrada and Olaf II of Norway. By his ...
. Sigurd was a petty king of Ringerike, and among the strongest and wealthiest chieftains in the Uplands. Through his mother Åsta, Harald was the youngest of three half-brothers to King Olaf Haraldsson (later Saint Olaf). In his youth, Harald displayed traits of a typical rebel with big ambitions, and admired Olaf as his role model. He thus differed from his two older brothers, who were more similar to their father, down-to-earth and mostly concerned with maintaining the farm.
The Icelandic sagas, in particular Snorri Sturluson
Snorri Sturluson ( ; ; 1179 – 22 September 1241) was an Icelandic historian, poet, and politician. He was elected twice as lawspeaker of the Icelandic parliament, the Althing. He is commonly thought to have authored or compiled portions of th ...
in ''Heimskringla
() is the best known of the Old Norse kings' sagas. It was written in Old Norse in Iceland. While authorship of ''Heimskringla'' is nowhere attributed, some scholars assume it is written by the Icelandic poet and historian Snorri Sturluson (117 ...
'', claim that Sigurd, like Olaf's father, was a great-grandson of King Harald Fairhair
Harald Fairhair (; – ) was a Norwegian king. According to traditions current in Norway and Iceland in the eleventh and twelfth centuries, he reigned from 872 to 930 and was the first Monarchy of Norway, King of Norway. Supposedly, two ...
in the male line. Most modern scholars believe that the ancestors attributed to Harald Hardrada's father, along with other parts of the Fairhair genealogy, are inventions reflecting the political and social expectations of the time of the authors (around two centuries after Harald Hardrada's lifetime) rather than historical reality. Harald Hardrada's alleged descent from Harald Fairhair is not mentioned and played no part during Harald Hardrada's own time, which seems odd considering that it would have provided significant legitimacy in connection with his claim to the Norwegian throne.
Following a revolt in 1028, Harald's brother Olaf was forced into exile until he returned to Norway in early 1030. On hearing news of Olaf's planned return, Harald gathered 600 men from the Uplands to meet Olaf and his men upon their arrival in the east of Norway. After a friendly welcome, Olaf went on to gather an army and eventually fight in the Battle of Stiklestad
The Battle of Stiklestad (; ) in 1030 is one of the most famous battles in the history of Norway. In this battle, King Olaf II of Norway () was killed. During the pontificate of Pope Alexander III, the Roman Catholic Church declared Olaf a saint ...
on 29 July 1030, in which Harald took part on his brother's side. The battle was part of an attempt to restore Olaf to the Norwegian throne, which had been captured by the Danish king Cnut the Great
Cnut ( ; ; – 12 November 1035), also known as Canute and with the epithet the Great, was King of England from 1016, King of Denmark from 1018, and King of Norway from 1028 until his death in 1035. The three kingdoms united under Cnut's rul ...
(Canute). The battle resulted in defeat for the brothers at the hands of those Norwegians who were loyal to Cnut, and Olaf was killed while Harald was badly wounded. Harald was nonetheless remarked to have shown considerable military talent during the battle.
Exile in the East
To Kievan Rus'
After the defeat at the Battle of Stiklestad, Harald managed to escape with the aid ofRögnvald Brusason
Rognvald Brusason (died 1046), son of Brusi Sigurdsson, was Earl of Orkney jointly with Thorfinn Sigurdsson from about 1037 onwards. He could possibly be the grandfather of Magnus Barelegs through an unnamed daughter. His life is recorded in th ...
(later Earl of Orkney
Earl of Orkney, historically Jarl of Orkney, is a title of nobility encompassing the archipelagoes of Orkney and Shetland, which comprise the Northern Isles of Scotland. Originally Scandinavian Scotland, founded by Norse invaders, the status ...
) to a remote farm in Eastern Norway
Eastern Norway (, ) is the geographical region of the south-eastern part of Norway. It consists of the counties Oslo, Akershus, Vestfold, Østfold, Buskerud, Telemark, and Innlandet.
Eastern Norway is by far the most populous region of Norw ...
. He stayed there for some time to heal his wounds, and thereafter (possibly up to a month later) journeyed north over the mountains to Sweden. A year after the Battle of Stiklestad, Harald arrived in Kievan Rus' (referred to in the sagas as ''Garðaríki
(anglicized Gardariki or Gardarike) or was the Old Norse term used in the Middle Ages for the lands of Rus'_people, Rus'. According to ''Göngu-Hrólfs saga'', the name (also used as a name for Novgorod Land, Novgorodian Rus') was synonymous ...
'' or ''Svíþjóð hin mikla''). He likely spent at least part of his time in the town of Staraya Ladoga
Staraya Ladoga ( rus, Ста́рая Ла́дога, p=ˈstarəjə ˈladəɡə, r=Stáraya Ládoga, t=Old Ladoga), known as Ladoga until 1704, is a rural locality (a '' selo'') in Volkhovsky District of Leningrad Oblast, Russia, located on the ...
(''Aldeigjuborg''), arriving there in the first half of 1031. Harald and his men were welcomed by Grand Prince Yaroslav the Wise
Yaroslav I Vladimirovich ( 978 – 20 February 1054), better known as Yaroslav the Wise, was Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019 until his death in 1054. He was also earlier Prince of Novgorod from 1010 to 1034 and Prince of Rostov from 987 to 1010, ...
, whose wife Ingegerd was a distant relative of Harald. Badly in need of military leaders, Yaroslav recognised a military potential in Harald and made him a captain of his forces. Harald's brother Olaf Haraldsson had previously been in exile to Yaroslav following the revolt in 1028, and ''Morkinskinna
''Morkinskinna'' is an Old Norse kings' saga, relating the history of Norwegian kings from approximately 1025 to 1157. The saga was written in Iceland around 1220, and has been preserved in a manuscript from around 1275.
The name ''Morkinskinn ...
'' says that Yaroslav embraced Harald first and foremost because he was the brother of Olaf. Harald took part in Yaroslav's campaign against the Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
in 1031, and possibly also fought against other 1030s Kievan enemies and rivals such as the Chud
Chud or Chude (, , ) is a term historically applied in the early East Slavic annals to several Baltic Finnic peoples in the area of what is now Estonia, Karelia and Northwestern Russia. It has also been used to refer to other Finno-Ugric peo ...
es in Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
, and the Byzantines, as well as the Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
and other steppe nomad people.
In Byzantine service
 After a few years in Kievan Rus', Harald and his force of around 500 men moved on south to
After a few years in Kievan Rus', Harald and his force of around 500 men moved on south to Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
('' Miklagard''), the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
(also known todaybut not to contemporariesas the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
), probably in 1033 or 1034, where they joined the Varangian Guard
The Varangian Guard () was an elite unit of the Byzantine army from the tenth to the fourteenth century who served as personal bodyguards to the Byzantine emperors. The Varangian Guard was known for being primarily composed of recruits from Nort ...
. Although the ''Flateyjarbók
''Flateyjarbók'' (; "Book of Flatey, Breiðafjörður, Flatey") is an important medieval Iceland, Icelandic manuscript. It is also known as GkS 1005 fol. and by the Latin name ''Codex Flateyensis''. It was commissioned by Jón Hákonarson and p ...
'' maintains that Harald at first sought to keep his royal identity a secret, most sources agree that Harald and his men's reputation was well known in the east at the time. While the Varangian Guard was primarily meant to function as the emperor's bodyguard, Harald was found fighting on "nearly every frontier" of the empire. He first saw action in campaigns against Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
pirates in the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
, and then in inland towns in Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
/ Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
that had supported the pirates. By this time, he had, according to Snorri Sturluson
Snorri Sturluson ( ; ; 1179 – 22 September 1241) was an Icelandic historian, poet, and politician. He was elected twice as lawspeaker of the Icelandic parliament, the Althing. He is commonly thought to have authored or compiled portions of th ...
(a 12th-century Icelandic historian, poet, and politician), become the "leader over all the Varangians". By 1035, the Byzantines had pushed the Arabs out of Asia Minor to the east and southeast, and Harald took part in campaigns that went as far east as the Tigris River
The Tigris ( ; see below) is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, before merging ...
and Euphrates River
The Euphrates ( ; see below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through S ...
in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, where according to his skald
A skald, or skáld (Old Norse: ; , meaning "poet"), is one of the often named poets who composed skaldic poetry, one of the two kinds of Old Norse poetry in alliterative verse, the other being Eddic poetry. Skaldic poems were traditionally compo ...
(poet) Þjóðólfr Arnórsson
Þjóðólfr Arnórsson (Old Norse: ; Modern Icelandic: ; Modern Norwegian: ) was an 11th-century Icelandic people, Icelandic skáld, who spent his career as a court poet to the Monarchy of Norway, Norwegian kings Magnus the Good and Harald Hardr ...
(recounted in the sagas) he participated in the capture of eighty Arab strongholds, a number which historians Sigfus Blöndal and Benedikt Benedikz see no particular reason to question. Although not holding independent command of an army as the sagas imply, it is not unlikely that King Harald and the Varangians at times could have been sent off to capture a castle or town. During the first four years of the reign of Byzantine Emperor
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised s ...
Michael IV the Paphlagonian
Michael IV the Paphlagonian (; c. 1010 – 10 December 1041) was Byzantine Emperor from 11 April 1034 to his death on 10 December 1041.
The son of a peasant, Michael worked as a money changer until he was found a job at court by his brother ...
, Harald probably also fought in campaigns against the Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
.
Thereafter, Harald is reported in the sagas to have gone to Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
and fought in battles in the area. Although the sagas place this after his expedition to Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, historian Kelly DeVries has questioned that chronology.DeVries (1999) p. 30 Whether his trip was of a military or peaceful nature would depend on whether it took place before or after the 1036 peace treaty between Michael IV and the Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate (; ), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimid dynasty, Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa ...
Caliph Ma'ad al-Mustansir Billah (in reality the Caliph's mother, originally a Byzantine Christian, since the Caliph was a minor), although it is considered unlikely to have been made before. Modern historians have speculated that Harald may have been in a party sent to escort pilgrims to Jerusalem (possibly including members of the Imperial family) following the peace agreement, as it was also agreed that the Byzantines were allowed to repair the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, also known as the Church of the Resurrection, is a fourth-century church in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem, Old City of Jerusalem. The church is the seat of the Greek Orthodox Patriarchat ...
. Furthermore, this may in turn have presented Harald with opportunities to fight against bandits who preyed on Christian pilgrims.
In 1038, Harald joined the Byzantines in their expedition to Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
,DeVries (1999) p. 31Tjønn (2010) p. 47 in George Maniakes
George Maniakes (; ; died 1043) was a prominent general of the Byzantine Empire during the 11th century. He was the catepan of Italy in 1042. He is known as Gyrgir in Scandinavian sagas. He is popularly said to have been extremely tall and well ...
's (the sagas' "Gyrge") attempt to reconquer the island from the Muslim Saracen
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens
''Saracen'' ( ) was a term used both in Greek and Latin writings between the 5th and 15th centuries to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Rom ...
s, who had established the Emirate of Sicily
The island of SicilyIn Arabic, the island was known as (). was under Islam, Islamic rule from the late ninth to the late eleventh centuries. It became a prosperous and influential commercial power in the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, with ...
on the island. During the campaign, Harald fought alongside Norman mercenaries such as William Iron Arm
{{Infobox noble
, name = William Iron Arm
, title =
, image = {{CSS image crop, Image = Statue cathédrale Coutances Guillaume Bras-de-fer.JPG, bSize = 607, cWidth = 235, cHeight = 247, oTop = 175, oLeft = 178, Location = center
, caption = S ...
. According to Snorri Sturluson, Harald captured four towns on Sicily. In 1041, when the Byzantine expedition to Sicily was over, a Lombard-Norman revolt erupted in southern Italy, and Harald led the Varangian Guard in multiple battles. Harald fought with the Catepan of Italy
The Catepanate of Italy (, ''Katepaníkion Italías'') was a province ('' theme'') of the Byzantine Empire, that existed from c. 965 until 1071. It was headed by a governor (''katepano'') with both civil and military powers. At its greatest exten ...
, Michael Dokeianos
Michael Dokeianos (), erroneously called Doukeianos by some modern writers, was a Byzantine nobleman and military leader, who married into the Komnenos family. He was active in Sicily under George Maniakes before going to Southern Italy as Catep ...
with initial success, but the Normans, led by their former ally William Iron Arm, defeated the Byzantines in the Battle of Olivento in March, and in the Battle of Montemaggiore in May. After the defeat, Harald and the Varangian Guard were called back to Constantinople, following Maniakes's imprisonment by the emperor and the onset of other more pressing issues. Harald and the Varangians were thereafter sent to fight in the southeastern European frontier in Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, where they arrived in late 1041. There, he fought in the army of Emperor Michael IV in the Battle of Ostrovo of the 1041 campaign against the Bulgarian uprising led by Peter Delyan, which later gained Harald the nickname the "Bulgar-burner" (''Bolgara brennir'') by his skald.
Harald was not affected by Maniakes's conflict with Emperor Michael IV, and received honours and respect upon his return to Constantinople. In a Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
book written in the 1070s, the ''Strategikon of Kekaumenos
The ''Strategikon of Kekaumenos'' (, ) is a late 11th century Byzantine manual offering advice on warfare and the handling of public and domestic affairs.
The book was composed between 1075 and 1078 by a Byzantine general of partly Armenian des ...
'', Araltes (i.e. Harald) is said to have won the favour of the emperor. The book says that the Byzantine emperor first appointed him '' manglabites'' (possibly identified with the title ''protospatharios
''Prōtospatharios'' () was one of the highest Byzantine aristocracy and bureaucracy, court dignities of the middle Byzantine Empire, Byzantine period (8th to 12th centuries), awarded to senior generals and provincial governors, as well as to forei ...
''), a soldier of the imperial guard, after the Sicilian campaign. Following the campaign against the Bulgarians, in which Harald again served with distinction, he received the rank while at Mosynopolis
Mosynopolis (), of which only ruins now remain in Greek Thrace, was a city in the Roman province of Rhodope, which was known until the 9th century as Maximianopolis (Μαξιμιανούπολις) or, to distinguish it from other cities of the ...
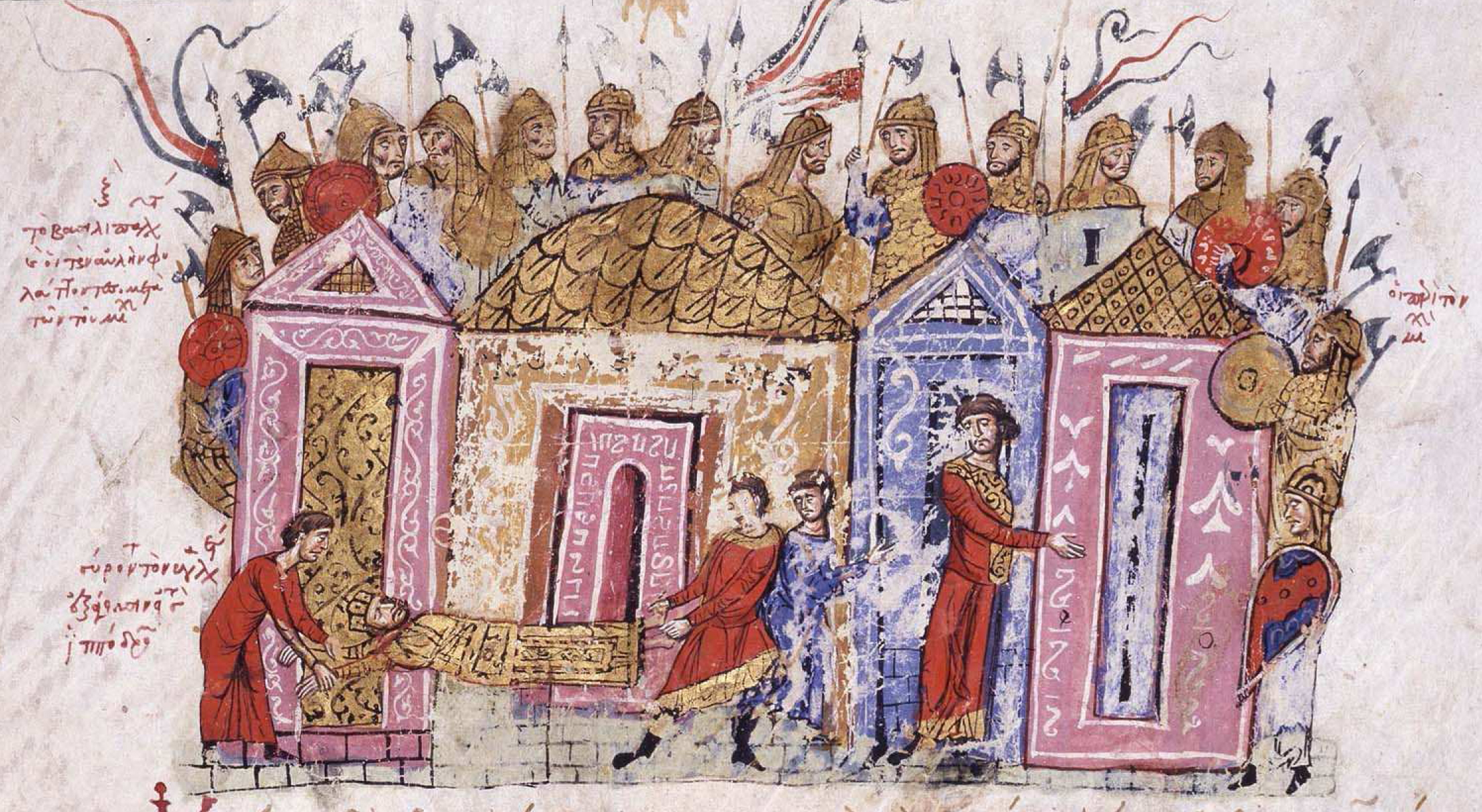
of '' spatharokandidatos'', identified by DeVries as a promotion to the possibly third highest Byzantine rank, but by Mikhail Bibikov as a lesser rank than ''protospatharios'' that was ordinarily awarded to foreign allies to the emperor. The ''Strategikon'' indicates that the ranks awarded to Harald were rather low, since Harald reportedly was "not angry for just having been appointed to ''manglabites'' or ''spatharokandidatos''". According to his skald Þjóðólfr Arnórsson, Harald had participated in eighteen greater battles during his Byzantine service. Harald's favour at the imperial court quickly declined after the death of Michael IV in December 1041, which was followed by conflicts between the new emperor Michael V Michael V may refer to:
* Michael V Kalaphates (1015–1042), Byzantine Emperor
*Coptic Pope Michael V of Alexandria (fl. 1145–1146)
* Michael V. (born 1969), Filipino actor and comedian
{{hndis, Michael 05