|
Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian language, Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway in the Arctic Ocean. Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of , making it the largest island in Norway and the List of islands by area, 36th largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), previously known as Spitsbergen or Spitzbergen, is a Norway, Norwegian archipelago that lies at the convergence of the Arctic Ocean with the Atlantic Ocean. North of continental Europe, mainland Europe, it lies about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74th parallel north, 74° to 81st parallel north, 81° north latitude, and from 10th meridian east, 10° to 35th meridian east, 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen (37,673 km2), followed in size by Nordaustlandet (14,443 km2), (5,073 km2), and Barentsøya (1,288 km2). Bear Island (Norway), Bjørnøya or Bear Island (178 km2) is the most southerly island in the territory, situated some 147 km south of Spitsbergen. Other small islands in the group include Hopen (Svalbard), Hopen to the southeast of Edgeøya, Kongsøya and Svenskøya in the east, and Kvitøya to the northeast. The largest settlement is Longyearbyen, situated in Isfjor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard Treaty
The Svalbard Treaty (originally the Spitsbergen Treaty) recognises the sovereignty of Norway over the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, at the time called Spitsbergen. The exercise of sovereignty is, however, subject to certain stipulations, and not all Norwegian law applies. The treaty restricts military uses of the archipelago, but it is not demilitarized. The signatories were given equal rights to engage in commercial activities (mainly coal mining) on the islands. , Norway and Russia make use of this right. Uniquely, the archipelago is an entirely visa-free zone under the terms of the Svalbard Treaty. The treaty was signed on 9 February 1920 and submitted for registration in the ''League of Nations Treaty Series'' on 21 October 1920. There were 14 original High Contracting Parties: Denmark, France, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, the United Kingdom (including Australia, Canada, New Zealand, South Africa, and India), and the United States. Of the original signat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
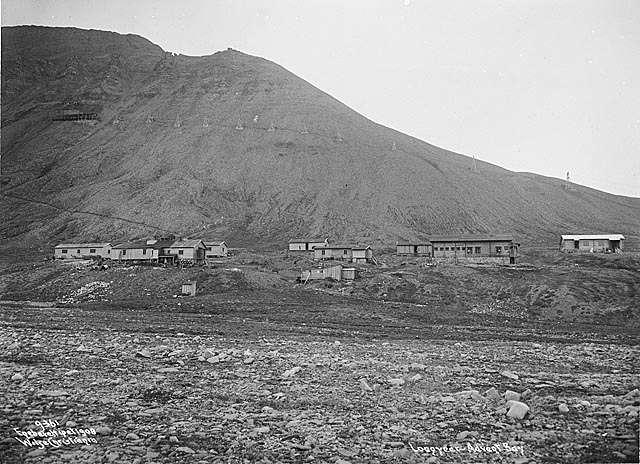
Longyearbyen
Longyearbyen (, , "Longyear Town") is the world's northernmost settlements, northernmost settlement with a population greater than 1,000, and the capital and the largest inhabited area of Svalbard. It stretches along the foot of the left bank (geography), bank of the Longyear Valley and on the shore of Adventfjorden, the short estuary leading into Isfjorden (Svalbard), Isfjorden on the west coast of Spitsbergen, the island's broadest inlet. As of 2002, Longyearbyen Community Council became an official municipalities of Norway, Norwegian municipality. It is the seat of the Governor of Svalbard. As of 2024, the town's mayor is Leif Terje Aunevik. Known as Longyear City until 1926, the town was established by and named after American John Munro Longyear, whose Arctic Coal Company started coal-mining there in 1906. Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani (SNSK) took over the mining operations in 1916, and still conducts mining. The German ''Kriegsmarine'' almost completely Operation Zit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani
Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani (SNSK), or simply Store Norske, is a Norwegian coal mining company based on the Svalbard archipelago. It was formed in 1916, after a Norwegian purchase of the American Arctic Coal Company (ACC). The company has 360 employees and operated two coal mines. The larger one was located in the Sveagruva settlement, about 60 km south of Longyearbyen. The Svea Nord longwall mine has an annual output of 2 million tonnes of bituminous coal. A third of it is sold for metallurgical purposes. The managing director of Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani was Per Andersson. The Sveagruva mine closed in 2017. The Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani has a shipping port at Cape Amsterdam, 15 km from Sveagruva. In 2021, the Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani was ranked no. 81 in the Arctic Environmental Responsibility Index (AERI) that covers 120 oil, gas, and mining companies involved in resource extraction north of the Arctic Circle The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barentsburg
Barentsburg () is the second-largest settlement in Svalbard, Norway, with about 455 inhabitants (). A coal mining town, the settlement was almost entirely made up of Russian and Ukrainian nationals. History Rijpsburg, a now abandoned Dutch settlement on Spitsbergen on Cape Boheman (Bohemanflya), at the north site of Nordfjorden in the Isfjord, stood roughly diagonally opposite Longyearbyen. The Rotterdam-based Van der Eb and Dresselhuys Scheepvaartmaatschappij (navigation company) built it in 1920, using prefabricated huts, for the mining of coal. Twelve Dutch staff and 52 German miners started mining coal here that year. The Dutch Spitsbergen Company, founded in 1920, bought a mine in Green Harbour from the Russians and mined coal from 1921 to 1926. The company renamed its settlement Barentsburg after the Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz. In 1932 the company sold the mine, including its settlement Barentsburg, to the Soviet trust Arktikugol. 2006 fire On October 17, 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ny-Ålesund
Ny-Ålesund ("New Ålesund") is a small town in Oscar II Land in the west of the island of Spitsbergen in Svalbard. It is situated on the Brøgger peninsula (Brøggerhalvøya) and on the shore of the bay of Kongsfjorden. The company town is owned and operated by Kings Bay (company), Kings Bay, which provides facilities for permanent research activities by 19 institutions from 11 countries. The town is ultimately owned by the Ministry of Climate and Environment (Norway), Ministry of Climate and Environment and is not incorporated (i.e. is not recognised as a town by the Norwegian government). Ny-Ålesund has an all-year permanent population of 30 to 35, with the summer population reaching 114. Its facilities include Ny-Ålesund Airport, Hamnerabben, Svalbard Rocket Range, a port and Ny-Ålesund Town and Mine Museum, as well as a number of buildings dedicated to research and environmental monitoring activities. It is the Northernmost settlements, northernmost functional civilian settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland Sea
The Greenland Sea ( Danish: ''Grønlandshavet'') is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as part of the Arctic Ocean, sometimes as part of the Atlantic Ocean. However, definitions of the Arctic Ocean and its seas tend to be imprecise or arbitrary. In general usage the term "Arctic Ocean" would exclude the Greenland Sea. In oceanographic studies the Greenland Sea is considered part of the Nordic Seas, along with the Norwegian Sea. The Nordic Seas are the main connection between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans and, as such, could be of great significance in a possible shutdown of thermohaline circulation. In oceanography the Arctic Ocean and Nordic Seas are often referred to collectively as the "Arctic Mediterranean Sea", a marginal sea of the Atlantic. The sea has Arctic climate with regular northe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard Global Seed Vault
The Svalbard Global Seed Vault () is a secure backup facility for the world's crop diversity on the Norwegian island of Spitsbergen in the remote Arctic Svalbard archipelago. The Seed Vault provides long-term storage for duplicates of seeds from around the world, conserved in gene banks. This provides security of the world's food supply against the loss of seeds in genebanks due to mismanagement, accident, equipment failures, funding cuts, war, sabotage, disease, and natural disasters. The Seed Vault is managed under terms spelled out in a tripartite agreement among the Norwegian government, the Crop Trust, and the Nordic Genetic Resource Center (NordGen). The Norwegian government entirely funded the Seed Vault's approximately ( in 2008) construction cost. Norway and the Crop Trust pay for operational costs. Storing seeds in the vault is free to depositors. As of June 2025, the Seed Vault conserves 1,355,591 accessions, representing more than 13,000 years of History of agricu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Sea
The Norwegian Sea (; ; ) is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to the northeast. In the southwest, it is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a submarine ridge running between Iceland and the Faroe Islands. To the north, the Jan Mayen Ridge separates it from the Greenland Sea. Unlike many other seas, most of the bottom of the Norwegian Sea is not part of a continental shelf and therefore lies at a great depth of about two kilometres on average. Rich deposits of oil and natural gas are found under the sea bottom and are being explored commercially, in the areas with sea depths of up to about one kilometre. The coastal zones are rich in fish that visit the Norwegian Sea from the North Atlantic or Barents Sea (cod) for spawning. The warm North Atlantic Current ensures relatively stable and high water temperatures, so that unlike the Arctic seas, the No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newtontoppen
Newtontoppen (Newton Peak) is the largest and highest mountain in Svalbard, at . Its peak is the highest point on Svalbard. It is located at the north east corner on the island of Spitsbergen in the Chydeniusfjella range. The nearest settlement is the formerly Soviet coal mining settlement Pyramiden. The mountain is mostly made of Silurian granite. The mountain was first ascended by on 4 August 1900. Etymology The mountain was named after Isaac Newton in 1898. The surrounding mountains were named after other famous astronomers and mathematicians the same year. See also * List of European ultra-prominent peaks This is a list of all the mountains in Europe with ultra-prominent peaks with topographic prominence greater than . European peaks by prominence The column "Col" in the chart below denotes the highest elevation to which one must descend from a p ... References Mountains of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-mountain-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arktikugol
Arktikugol () is a Russian coal mining unitary enterprise which operates on the island of Spitsbergen in Svalbard, Norway. Owned by the government of Russia, Arktikugol currently performs limited mining in Barentsburg. It has carried out mining operations in the towns of Pyramiden and Grumant, which it still owns, and once operated a port at Colesbukta. The company is headquartered in Moscow and is the official agency through which Russia, and previously the Soviet Union, exercised its Svalbard policy. The company was established on 7 October 1931 to take over all Soviet mining interests on Svalbard. At the time Grumant and Pyramiden were bought, although only Grumant was in operation. It also bought Barentsburg from Dutch interests. The company retained operation there and in Grumant until 1941, when all employees were evacuated to the mainland as part of Operation Gauntlet. Mining resumed in 1947 and commenced in Pyramiden in 1955. Declining coal deposits resulted in Grumant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sveagruva
Sveagruva (), or simply Svea, was a mining settlement in the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard, lying at the head of Van Mijenfjord. When occupied by the workers, it was the third largest settlement in the archipelago (after Longyearbyen and Barentsburg) but there were no permanent inhabitants. Around 300 workers living in Longyearbyen commuted to Sveagruva for work on a daily or weekly basis. The mine was operated by Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani. There is no road to Longyearbyen or any other settlements, so travel is done by air from Svea Airport and coal transport by ship from a port southwest. Sveagruva closed in 2020 and currently has no permanent inhabitants. As of 2023, Sveagruva has been re-wilded to a pristine state. Almost every structure from its mining past has been removed in the largest operation of its kind. History The town was established in 1917 by Swedes. It was thereafter destroyed in 1944, but quickly re-established after World War II Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |