Spitsbergen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the
 The Dutch navigator
The Dutch navigator
 Early
Early
 From 1617 onwards, a Danish-chartered company began sending whaling fleets to Spitsbergen. This successful expansion by Denmark into the North Atlantic has recently been cited by historians as the first step of the Danish–Norwegian state into overseas colonialism. It eventually built a small overseas empire of East Indian trade posts, North Atlantic possessions (such as Greenland and Iceland), and a small Atlantic trade route between possessions on the Guinea Coast (in modern Ghana) and what are now the
From 1617 onwards, a Danish-chartered company began sending whaling fleets to Spitsbergen. This successful expansion by Denmark into the North Atlantic has recently been cited by historians as the first step of the Danish–Norwegian state into overseas colonialism. It eventually built a small overseas empire of East Indian trade posts, North Atlantic possessions (such as Greenland and Iceland), and a small Atlantic trade route between possessions on the Guinea Coast (in modern Ghana) and what are now the
 In 2009, Spitsbergen had a population of 2,753, of whom 423 were Russian or Ukrainian, 10 were Polish and 322 were non-Norwegians living in Norwegian settlements. The largest non-Norwegian groups in
In 2009, Spitsbergen had a population of 2,753, of whom 423 were Russian or Ukrainian, 10 were Polish and 322 were non-Norwegians living in Norwegian settlements. The largest non-Norwegian groups in
 The three main industries on Spitsbergen are coal mining, tourism and research. In 2007, there were 484 people working in the mining sector, 211 people working in the tourism sector and 111 people working in the education sector. The same year, mining produced a revenue of NOK 2,008 million, tourism NOK 317 million and research NOK 142 million. In 2006, the average income for economically active people was NOK 494,700—23% higher than on the mainland. Almost all housing is owned by the various employers and institutions and rented to their employees; there are only a few privately owned houses, most of which are recreational cabins. Because of this, it is almost impossible to live on Spitsbergen without working for an established institution.
Since the resettlement of Spitsbergen in the early 20th century, coal mining has been the dominant commercial activity. Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani, a subsidiary of the
The three main industries on Spitsbergen are coal mining, tourism and research. In 2007, there were 484 people working in the mining sector, 211 people working in the tourism sector and 111 people working in the education sector. The same year, mining produced a revenue of NOK 2,008 million, tourism NOK 317 million and research NOK 142 million. In 2006, the average income for economically active people was NOK 494,700—23% higher than on the mainland. Almost all housing is owned by the various employers and institutions and rented to their employees; there are only a few privately owned houses, most of which are recreational cabins. Because of this, it is almost impossible to live on Spitsbergen without working for an established institution.
Since the resettlement of Spitsbergen in the early 20th century, coal mining has been the dominant commercial activity. Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani, a subsidiary of the  Spitsbergen was historically a base for both
Spitsbergen was historically a base for both
 Within Longyearbyen, Barentsburg and Ny-Ålesund, there are road systems, but they do not connect with each other.
Within Longyearbyen, Barentsburg and Ny-Ålesund, there are road systems, but they do not connect with each other.
 Two partial skeletons of '' Pliosaurus funkei'' from the
Two partial skeletons of '' Pliosaurus funkei'' from the
Governor of Svalbard
Svalbard Tourism
{{Authority control Islands of Svalbard 1590s in the Dutch Empire Maritime history of the Dutch Republic
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), previously known as Spitsbergen or Spitzbergen, is a Norway, Norwegian archipelago that lies at the convergence of the Arctic Ocean with the Atlantic Ocean. North of continental Europe, mainland Europe, it lies about midway be ...
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
in northern Norway in the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
.
Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea
The Norwegian Sea (; ; ) is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to the northeast. In the southwest, it is separate ...
and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of , making it the largest island in Norway and the 36th largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen
Longyearbyen (, , "Longyear Town") is the world's northernmost settlements, northernmost settlement with a population greater than 1,000, and the capital and the largest inhabited area of Svalbard. It stretches along the foot of the left bank ( ...
. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund
Ny-Ålesund ("New Ålesund") is a small town in Oscar II Land in the west of the island of Spitsbergen in Svalbard. It is situated on the Brøgger peninsula (Brøggerhalvøya) and on the shore of the bay of Kongsfjorden. The company town is owned ...
, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area.
The island was first used as a whaling
Whaling is the hunting of whales for their products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that was important in the Industrial Revolution. Whaling was practiced as an organized industry as early as 875 AD. By the 16t ...
base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty
The Svalbard Treaty (originally the Spitsbergen Treaty) recognises the sovereignty of Norway over the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, at the time called Spitsbergen. The exercise of sovereignty is, however, subject to certain stipulations, and no ...
of 1920 recognized Norwegian sovereignty
Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within a state as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate au ...
and established Svalbard as a free economic zone
A free-trade zone (FTZ) is a class of special economic zone. It is a geographic area where goods may be imported, stored, handled, manufactured, or reconfigured and re- exported under specific customs regulation and generally not subjec ...
and a demilitarized zone
A demilitarized zone (DMZ or DZ) is an area in which treaties or agreements between states, military powers or contending groups forbid military installations, activities, or personnel. A DZ often lies along an established frontier or boundary ...
.
The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian Arktikugol are the only mining companies at Spitsbergen. Research and tourism have become the important supplementary industries, featuring among others the University Centre in Svalbard
The University Centre in Svalbard (; UNIS) is a Norway, Norwegian state enterprise, state-owned aksjeselskap, limited company that is involved in research and provides some higher education in Arctic studies. The company is wholly owned by the Min ...
and the Svalbard Global Seed Vault
The Svalbard Global Seed Vault () is a secure backup facility for the world's crop diversity on the Norwegian island of Spitsbergen in the remote Arctic Svalbard archipelago. The Seed Vault provides long-term storage for duplicates of seeds fro ...
. No roads connect the settlements; instead snowmobiles, aircraft and boats serve as local transport. Svalbard Airport, Longyearbyen provides the main point of entry and exit.
The island has an Arctic climate, although with significantly higher temperatures than other places at the same latitude. The flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
benefits from the long period of midnight sun
Midnight sun, also known as polar day, is a natural phenomenon that occurs in the summer months in places north of the Arctic Circle or south of the Antarctic Circle, when the Sun remains visible at the local midnight. When midnight sun is see ...
, which compensates for the polar night
Polar night is a phenomenon that occurs in the polar regions of Earth, northernmost and southernmost regions of Earth when the Sun remains below the horizon for more than 24 hours. This only occurs inside the polar circles. The opposite phen ...
. Svalbard is a breeding ground for many seabirds and also supports polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a large bear native to the Arctic and nearby areas. It is closely related to the brown bear, and the two species can Hybrid (biology), interbreed. The polar bear is the largest extant species of bear ...
s, arctic fox
The Arctic fox (''Vulpes lagopus''), also known as the white fox, polar fox, or snow fox, is a small species of fox native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and common throughout the Tundra#Arctic tundra, Arctic tundra biome. I ...
es, reindeer
The reindeer or caribou (''Rangifer tarandus'') is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, subarctic, tundra, taiga, boreal, and mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. It is the only re ...
, and marine mammal
Marine mammals are mammals that rely on marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as cetaceans, pinnipeds, sirenians, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reliance on marine enviro ...
s. Six national parks protect the largely untouched, yet fragile environment. The island has many glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s, mountains, and fjords.
Etymology
 The Dutch navigator
The Dutch navigator Willem Barentsz
Willem Barentsz (; – 20 June 1597), anglicized as William Barents or Barentz, was a Dutch Republic, Dutch navigator, cartographer, and Arctic explorer.
Barentsz went on three expeditions to the far north in search for a Northern Sea Route, N ...
gave Spitsbergen its name when he discovered it in 1596. The name ''Spitsbergen'', meaning "pointed mountains" (from the Dutch ''spits'' - pointed, ''bergen'' - mountains), at first applied both to the main island and to the associated archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
as a whole. In the 17th and 18th centuries, English whalers referred to the islands as "Greenland", a practice still followed in 1780 and criticized by Sigismund Bacstrom at that time. The "Spitzbergen" spelling was used in English during the 19th century, for instance by Beechey, Laing, and the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
.
In 1906 the Arctic explorer Sir Martin Conway regarded the ''Spitzbergen'' spelling as incorrect; he preferred ''Spitsbergen'', as he noted that the name was Dutch, not German. This had little effect on British practice. In 1920 the international treaty
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between sovereign states and/or international organizations that is governed by international law. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention ...
determining the status of the islands was entitled the "Spitsbergen Treaty". The islands were generally referred to in the United States as "Spitsbergen" from that time, although the spelling "Spitzbergen" also commonly occurred through the 20th century.
The Norwegian administrating authorities named the archipelago ''Svalbard'' in 1925, the main island becoming ''Spitsbergen''. By the end of the 20th century, this usage had become common.
History
The first recorded sighting of the island was by Willem Barentsz, a Dutch explorer who came across it while searching for theNorthern Sea Route
The Northern Sea Route (NSR) (, shortened to Севморпуть, ''Sevmorput'') is a shipping route about long. The Northern Sea Route (NSR) is the shortest shipping route between the western part of Eurasia and the Asia-Pacific region.
Ad ...
in June 1596. The first good map, with the east coast roughly indicated, appeared in 1623, printed by Willem Janszoon Blaeu. Around 1660 and 1728, better maps were produced.
The archipelago may have been known to Russian Pomor hunters as early as the 14th or 15th century, although solid evidence preceding the 17th century is lacking. Following the English whalers and others in referring to the archipelago as Greenland, they named it Grumant (Грумант). The name Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), previously known as Spitsbergen or Spitzbergen, is a Norway, Norwegian archipelago that lies at the convergence of the Arctic Ocean with the Atlantic Ocean. North of continental Europe, mainland Europe, it lies about midway be ...
is first mentioned in Icelandic sagas
The sagas of Icelanders (, ), also known as family sagas, are a subgenre, or text group, of Icelandic sagas. They are prose narratives primarily based on historical events that mostly took place in Iceland in the ninth, tenth, and early elev ...
of the 10th and 11th centuries, but this may have been Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norway, Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: la ...
.
Early claims
 Early
Early whaling
Whaling is the hunting of whales for their products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that was important in the Industrial Revolution. Whaling was practiced as an organized industry as early as 875 AD. By the 16t ...
expeditions to Svalbard in general and Spitsbergen in particular tended, because of currents and fauna, to cluster on the western coast of Spitsbergen and the islands off shore. Shortly after whaling began (1611), the Danish–Norwegian crown in 1616 claimed ownership of Jan Mayen and the Spitsbergen islands, as all of Svalbard was then known, but in 1613, the English Muscovy Company
The Muscovy Company (also called the Russia Company or the Muscovy Trading Company; ) was an English trading company chartered in 1555. It was the first major Chartered company, chartered joint-stock company, the precursor of the type of business ...
had done the same.
The primary and most profitable whaling grounds of this joint-stock company came to be centered on Spitsbergen in the early 17th century, and the company's 1613 Royal Charter from the English Crown granted a monopoly on whaling in Spitsbergen, based on the (erroneous) claim that Hugh Willoughby had discovered the land in 1553. Not only had they wrongly assumed a 1553 English voyage had reached the area, but on 27 June 1607, during his first voyage in search of a "northeast passage" on behalf of the company, Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the Northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 16 ...
sighted "Newland" (i.e. Spitsbergen), near the mouth of the great bay Hudson later named the Great Indraught ( Isfjorden). In this way, the English hoped to head off expansion in the region by the Dutch, at the time their major rival.
Initially, the English tried to drive away competitors, but after disputes with the Dutch (1613–24), they, for the most part, only claimed the bays south of Kongsfjorden
Kongsfjorden as seen from Blomstrandhalvøya
Kongsfjorden (Kongs Fjord or Kings Bay) is an inlet on the west coast of Spitsbergen, an island which is part of the Svalbard archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. The inlet is long and ranges in width f ...
.
Danish expansion
 From 1617 onwards, a Danish-chartered company began sending whaling fleets to Spitsbergen. This successful expansion by Denmark into the North Atlantic has recently been cited by historians as the first step of the Danish–Norwegian state into overseas colonialism. It eventually built a small overseas empire of East Indian trade posts, North Atlantic possessions (such as Greenland and Iceland), and a small Atlantic trade route between possessions on the Guinea Coast (in modern Ghana) and what are now the
From 1617 onwards, a Danish-chartered company began sending whaling fleets to Spitsbergen. This successful expansion by Denmark into the North Atlantic has recently been cited by historians as the first step of the Danish–Norwegian state into overseas colonialism. It eventually built a small overseas empire of East Indian trade posts, North Atlantic possessions (such as Greenland and Iceland), and a small Atlantic trade route between possessions on the Guinea Coast (in modern Ghana) and what are now the United States Virgin Islands
The United States Virgin Islands, officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and a territory of the United States. The islands are geographically part of the Virgin Islands archipelago and are located ...
.
The entire Svalbard archipelago, nominally ruled first by Denmark–Norway
Denmark–Norway (Danish language, Danish and Norwegian language, Norwegian: ) is a term for the 16th-to-19th-century multi-national and multi-lingual real unionFeldbæk 1998:11 consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway (includ ...
, and later the Norwegians (as Union between Sweden and Norway
Sweden and Norway or Sweden–Norway (; ), officially the United Kingdoms of Sweden and Norway, and known as the United Kingdoms, was a personal union of the separate kingdoms of Sweden and Norway under a common monarch and common foreign pol ...
from 1814 to 1905, independent Norway from 1905), remained a source of riches for fishery and whaling vessels from many nations. The islands also became the launching point for a number of Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
explorers, including William Edward Parry
Sir William Edward Parry (19 December 1790 – 8 July 1855) was a Royal Navy officer and explorer best known for his 1819–1820 expedition through the Parry Channel, probably the most successful in the long quest for the Northwest Passa ...
, Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld
Nils Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld (; 18 November 183212 August 1901) was a Finland-Swedish aristocrat, geologist, mineralogist and Arctic explorer. He was a member of the noble Nordenskiöld family of scientists and held the title of a friherre (ba ...
, Otto Martin Torell, Alfred Gabriel Nathorst
Alfred Gabriel Nathorst (7 November 1850 – 20 January 1921) was a Swedish Arctic explorer, geologist, and palaeobotanist. He travelled to Spitzbergen, Svalbard and Greenland where he took an interest in the Arctic floras from the Paleozoic ...
, Roald Amundsen
Roald Engelbregt Gravning Amundsen (, ; ; 16 July 1872 – ) was a Norwegians, Norwegian explorer of polar regions. He was a key figure of the period known as the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration.
Born in Borge, Østfold, Norway, Am ...
and Ernest Shackleton
Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton (15 February 1874 – 5 January 1922) was an Anglo-Irish Antarctic explorer who led three British expeditions to the Antarctic. He was one of the principal figures of the period known as the Heroic Age of Antarcti ...
.
Spitsbergen Treaty
Between 1913 and 1920, Spitsbergen was a neutralcondominium
A condominium (or condo for short) is an ownership regime in which a building (or group of buildings) is divided into multiple units that are either each separately owned, or owned in common with exclusive rights of occupation by individual own ...
. The Spitsbergen Treaty of 9 February 1920, recognises the full and absolute sovereignty of Norway over all the arctic archipelago of Svalbard. The exercise of sovereignty is, however, subject to certain stipulations, and not all Norwegian law applies. Originally limited to nine signatory nations, over 40 are now signatories of the treaty. Citizens of any of the signatory countries may settle in the archipelago. Once named Spitsbergen after its largest island, the Svalbard archipelago was made a part of Norway—not a dependency—by the Svalbard Act of 1925. Since this date, it has been a region of Norway, with a Norwegian-appointed governor resident at the administrative centre of Longyearbyen. Limitations on the imposition of certain Norwegian laws are outlined in the Spitsbergen Treaty.
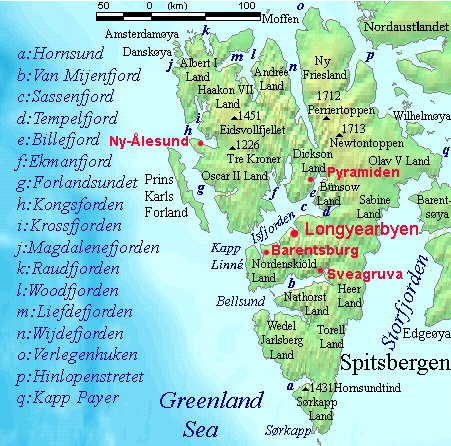
The largest settlement on Spitsbergen is the Norwegian town of Longyearbyen
Longyearbyen (, , "Longyear Town") is the world's northernmost settlements, northernmost settlement with a population greater than 1,000, and the capital and the largest inhabited area of Svalbard. It stretches along the foot of the left bank ( ...
, while the second-largest settlement is the Russian coal-mining settlement of Barentsburg. (This was sold by the Netherlands in 1932 to the Soviet company Arktikugol.) Other settlements on the island include the former Russian mining communities of Grumantbyen and Pyramiden (abandoned in 1961 and 1998, respectively), a Polish research station at Hornsund, and the remote northern settlement of Ny-Ålesund
Ny-Ålesund ("New Ålesund") is a small town in Oscar II Land in the west of the island of Spitsbergen in Svalbard. It is situated on the Brøgger peninsula (Brøggerhalvøya) and on the shore of the bay of Kongsfjorden. The company town is owned ...
.
World War II
Allied soldiers were stationed on the island in 1941 to preventNazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
from occupying the islands. Norway came under German occupation in 1940. Germany took control of the coal fields and the weather station during this time, although most of the inhabitants on the island were Russian and Germany and the Soviet Union had a non-aggression pact
A non-aggression pact or neutrality pact is a treaty between two or more states/countries that includes a promise by the signatories not to engage in military action against each other. Such treaties may be described by other names, such as a t ...
until 22 June 1941. Once the non-aggression pact was ended, the United Kingdom and Canada sent military forces to the island to destroy German installations, both the Soviet coal mines and the German weather station.
In 1943, the German battleship ''Tirpitz Tirpitz may refer to:
People
* Alfred von Tirpitz (1849–1930), German admiral
** Tirpitz Plan, a plan for Germany to achieve world power status through naval power
Ships
* German battleship ''Tirpitz'', a World War II-era Bismarck-class ...
'' and an escort flotilla shelled and destroyed the Allied weather station in Operation Zitronella. On 6 September, a squadron consisting of ''Tirpitz'', the battleship ''Scharnhorst'', and nine destroyers weighed anchor in Altenfjord and Kåfjord and headed for Spitsbergen, to attack the Allied base. At dawn on 8 September 1943, ''Tirpitz'' and ''Scharnhorst'' opened fire against the two 3-inch guns which comprised the defences of Barentsburg, and the destroyers ran inshore with landing parties, destroying a supply dump and wrecking a landing station. By noon, the hostilities had ended, with the landing parties returning to the ships, along with some prisoners. The German ships returned safely to Altenfjord and Kåfjord on 9 September 1943. This was the last operation for the ''Tirpitz''.
Postwar
On 29 August 1996, Vnukovo Airlines Flight 2801 crashed on the island, killing all 141 people on board.Government
TheSvalbard Treaty
The Svalbard Treaty (originally the Spitsbergen Treaty) recognises the sovereignty of Norway over the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, at the time called Spitsbergen. The exercise of sovereignty is, however, subject to certain stipulations, and no ...
of 1920 established full Norwegian sovereignty over Svalbard. All 40 signatory countries of the treaty have the right to conduct commercial activities on the archipelago without discrimination, although all activity is subject to Norwegian legislation. The treaty limits Norway's right to collect taxes to that of financing services on Svalbard. Spitsbergen is a demilitarized zone
A demilitarized zone (DMZ or DZ) is an area in which treaties or agreements between states, military powers or contending groups forbid military installations, activities, or personnel. A DZ often lies along an established frontier or boundary ...
, as the treaty prohibits the establishment of military installations. The treaty requires Norway to protect the natural environment. The island is administered by the Governor of Svalbard, who holds the responsibility as both county governor and chief of police
A chief of police (COP) is the title given to an appointed official or an elected one in the command hierarchy, chain of command of a police department, particularly in North America. A chief of police may also be known as a police chief or somet ...
, as well as authority granted from the executive branch. Although Norway is part of the European Economic Area
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the ''Agreement on the European Economic Area'', an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade Asso ...
(EEA) and the Schengen Agreement
The Schengen Agreement ( , ) is a treaty which led to the creation of Europe's Schengen Area, in which internal border checks have largely been abolished. It was signed on 14 June 1985, near the town of Schengen, Luxembourg, by five of the t ...
, Svalbard is not part of the Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) encompasses European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their common borders. As an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ) policy of the European Union (EU), it ...
nor EEA.
Residents of Spitsbergen do not need visas for Schengen but are prohibited from reaching Svalbard from mainland Norway without them. People without a means of income can be rejected as residents by the governor. Citizens of any treaty signatory country may visit the island without a visa. Russia retains a consulate in Barentsburg.
Population
Longyearbyen
Longyearbyen (, , "Longyear Town") is the world's northernmost settlements, northernmost settlement with a population greater than 1,000, and the capital and the largest inhabited area of Svalbard. It stretches along the foot of the left bank ( ...
in 2005 were from Thailand, Sweden, Denmark, Russia and Germany. Spitsbergen is among the safest places on Earth, with virtually no crime.
Longyearbyen is the largest settlement on the island, the seat of the governor, and the only incorporated town. It features a hospital, primary and secondary school, university, sports centre with a swimming pool, library, cultural centre, cinema, bus transport, hotels, a bank, and several museums. The newspaper '' Svalbardposten'' is published weekly. Only a small fraction of the mining activity remains at Longyearbyen; instead, workers commute to Sveagruva (or Svea) where Store Norske operates a mine. Sveagruva is a dorm town, with workers commuting from Longyearbyen on a weekly basis.
Since 2002, Longyearbyen Community Council has had many of the same responsibilities of a municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
, including utilities, education, cultural facilities, fire department, roads and ports. No care or nursing services are available, nor is welfare payment available. Norwegian residents retain pension and medical rights through their mainland municipalities. The hospital is part of University Hospital of North Norway, while the airport is operated by state-owned Avinor
Avinor AS is a state-owned aksjeselskap, limited company that operates most of the civil airports in Norway. The Norwegian state, via the Norwegian Ministry of Transport and Communications, controls 100 percent of the share capital. Avinor wa ...
. Ny-Ålesund and Barentsburg are company town
A company town is a place where all or most of the stores and housing in the town are owned by the same company that is also the main employer. Company towns are often planned with a suite of amenities such as stores, houses of worship, schoo ...
s with all infrastructure owned by Kings Bay and Arktikugol, respectively. Other public offices with presence on Svalbard are the Norwegian Directorate of Mining, the Norwegian Polar Institute
The Norwegian Polar Institute (NPI; ) is Norway's central governmental institution for scientific research, mapping and environmental monitoring in the Arctic and the Antarctic. The NPI is a directorate under Norway's Ministry of Climate and Envir ...
, the Norwegian Tax Administration and the Church of Norway
The Church of Norway (, , , ) is an Lutheranism, evangelical Lutheran denomination of Protestant Christianity and by far the largest Christian church in Norway. Christianity became the state religion of Norway around 1020, and was established a ...
. Svalbard is subordinate to Nord-Troms District Court and Hålogaland Court of Appeal, both located in Tromsø.
Ny-Ålesund
Ny-Ålesund ("New Ålesund") is a small town in Oscar II Land in the west of the island of Spitsbergen in Svalbard. It is situated on the Brøgger peninsula (Brøggerhalvøya) and on the shore of the bay of Kongsfjorden. The company town is owned ...
is a permanent settlement based entirely on research. Formerly a mining town, it is still a company town
A company town is a place where all or most of the stores and housing in the town are owned by the same company that is also the main employer. Company towns are often planned with a suite of amenities such as stores, houses of worship, schoo ...
operated by the Norwegian state-owned Kings Bay. While there is some tourism at the village, Norwegian authorities limit access to the outpost to minimise impact on the scientific work. Ny-Ålesund has a winter population of 35 and a summer population of 180. Poland operates the Polish Polar Station at Hornsund, with ten permanent residents.
Barentsburg is the only remaining Russian settlement, after Pyramiden was abandoned in 1998. A company town, all facilities are owned by Arktikugol, which operates a coal mine. In addition to the mining facilities, Arktikugol has opened a hotel and souvenir shop, catering to tourists taking day trips or hikes from Longyearbyen. The village has facilities such as a school, library, sports center, community center, swimming pool, farm and greenhouse. Pyramiden has similar facilities; both are built in typical Soviet style and are the site of the world's two most northerly Lenin statues and other socialist realism artwork.
Economy
 The three main industries on Spitsbergen are coal mining, tourism and research. In 2007, there were 484 people working in the mining sector, 211 people working in the tourism sector and 111 people working in the education sector. The same year, mining produced a revenue of NOK 2,008 million, tourism NOK 317 million and research NOK 142 million. In 2006, the average income for economically active people was NOK 494,700—23% higher than on the mainland. Almost all housing is owned by the various employers and institutions and rented to their employees; there are only a few privately owned houses, most of which are recreational cabins. Because of this, it is almost impossible to live on Spitsbergen without working for an established institution.
Since the resettlement of Spitsbergen in the early 20th century, coal mining has been the dominant commercial activity. Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani, a subsidiary of the
The three main industries on Spitsbergen are coal mining, tourism and research. In 2007, there were 484 people working in the mining sector, 211 people working in the tourism sector and 111 people working in the education sector. The same year, mining produced a revenue of NOK 2,008 million, tourism NOK 317 million and research NOK 142 million. In 2006, the average income for economically active people was NOK 494,700—23% higher than on the mainland. Almost all housing is owned by the various employers and institutions and rented to their employees; there are only a few privately owned houses, most of which are recreational cabins. Because of this, it is almost impossible to live on Spitsbergen without working for an established institution.
Since the resettlement of Spitsbergen in the early 20th century, coal mining has been the dominant commercial activity. Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani, a subsidiary of the Norwegian Ministry of Trade and Industry
The Royal Norwegian Ministry of Trade and Industry () was a Norwegian ministry responsible for business, trade and industry.
It was first created in 1916, as the Ministry of Trade (Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Trade, Shipping and Industry). It ...
, operates Svea Nord in Sveagruva and Mine 7 in Longyearbyen. The former produced 3.4 million tonnes in 2008, while the latter sends 35% of its output to Longyearbyen Power Station. Since 2007, there has not been any significant mining by the Russian state-owned Arktikugol in Barentsburg. There has previously been some test drilling for petroleum on land, but this did not give results good enough to justify permanent operation. The Norwegian authorities do not allow offshore petroleum drilling activities for environmental reasons, and the land formerly test-drilled on has been protected as nature reserves or national parks.
Spitsbergen Island coins were issued in 1946, with Russian Cyrillic lettering, in the USSR denomination of 10 and 20 kopecks. Then in 1993, coins were again minted in Russian values of 10, 20, 50 and 100 roubles. Both series have the motto "Arctic coal".
 Spitsbergen was historically a base for both
Spitsbergen was historically a base for both whaling
Whaling is the hunting of whales for their products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that was important in the Industrial Revolution. Whaling was practiced as an organized industry as early as 875 AD. By the 16t ...
and fishing. Norway claimed a exclusive economic zone
An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has exclusive rights regarding the exploration and use of marine natural resource, reso ...
(EEZ) around Svalbard in 1977, Norway retains a restrictive fisheries policy in the zone, and the claims are disputed by Russia. Tourism is focused on the environment and is centered on Longyearbyen. Activities include hiking, kayaking, walks through glacier caves and snow-scooter and dog-sled safaris. Cruise ships generate a significant portion of the traffic, including stops by both offshore vessels and expeditionary cruises starting and ending in Svalbard. Traffic is strongly concentrated between March and August; overnight stays have quintupled from 1991 to 2008, when there were 93,000 guest-nights.
Research on Svalbard centers on Longyearbyen and Ny-Ålesund, the most accessible areas in the high Arctic. Norway grants permission for any nation to conduct research on Svalbard, resulting in the Polish Polar Station, Indian Himadri Station, and the Chinese Arctic Yellow River Station, plus Russian facilities in Barentsburg. The University Centre in Svalbard
The University Centre in Svalbard (; UNIS) is a Norway, Norwegian state enterprise, state-owned aksjeselskap, limited company that is involved in research and provides some higher education in Arctic studies. The company is wholly owned by the Min ...
in Longyearbyen offers undergraduate, graduate and postgraduate courses to 350 students in various arctic sciences, particularly biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
, geology and geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and Physical property, properties of Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. Geophysicists conduct i ...
. Courses are provided to supplement studies at the mainland universities; there are no tuition fees and courses are held in English, with Norwegian and international students equally represented.
The Svalbard Global Seed Vault
The Svalbard Global Seed Vault () is a secure backup facility for the world's crop diversity on the Norwegian island of Spitsbergen in the remote Arctic Svalbard archipelago. The Seed Vault provides long-term storage for duplicates of seeds fro ...
is a " doomsday" seedbank
A seed bank (also seed banks, seeds bank or seed vault) stores seeds to preserve genetic diversity; hence it is a type of gene bank. There are many reasons to store seeds. One is to preserve the genes that plant breeders need to increase yield, ...
to store seeds from as many of the world's crop varieties and their botanical wild relatives as possible. A cooperative enterprise by the government of Norway and the Global Crop Diversity Trust
The Crop Trust, officially known as the Global Crop Diversity Trust, is an international organization, international nonprofit organization with a secretariat in Bonn, Bonn, Germany. Its mission is to conserve and make available the world's crop d ...
, the vault is cut into rock near Longyearbyen, keeping it at a natural and refrigerating the seeds to .
The Svalbard Undersea Cable System is a fibre optic line from Svalbard to Harstad Harstad may refer to:
Places
*Harstad (town)
Harstad (; ) is a List of towns and cities in Norway, city in Harstad Municipality in Troms county, Norway. The city is also the administrative centre of Harstad Municipality. The city has a populati ...
, needed for communicating with polar orbit
A polar orbit is one in which a satellite passes above or nearly above both poles of the body being orbited (usually a planet such as the Earth, but possibly another body such as the Moon or Sun) on each revolution. It has an inclination of abo ...
ing satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
through Svalbard Satellite Station and installations in Ny-Ålesund.
The Arctic World Archive
The Arctic World Archive (AWA) is a facility for data preservation, located in the Svalbard archipelago on the island of Spitsbergen, Norway, not far from the Svalbard Global Seed Vault. It contains data of historical and cultural interest from ...
, a huge digital archiving concern run by Norwegian private company Piql and the state-owned coal-mining company Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani, opened in March 2017. In mid-2020, it acquired its biggest customer in the form of GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug trackin ...
, a subsidiary of Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
.
Transport
 Within Longyearbyen, Barentsburg and Ny-Ålesund, there are road systems, but they do not connect with each other.
Within Longyearbyen, Barentsburg and Ny-Ålesund, there are road systems, but they do not connect with each other. Off-road
Off-roading is the act of driving or riding in a vehicle on unpaved surfaces such as sand, dirt, gravel, riverbeds, mud, snow, rocks, or other natural terrain. Off-roading ranges from casual drives with regular vehicles to competitive events w ...
motorized transport is prohibited on bare ground, but snowmobile
A snowmobile, also known as a snowmachine (chiefly Alaskan), motor sled (chiefly Canadian), motor sledge, skimobile, snow scooter, or simply a sled is a motorized vehicle designed for winter travel and recreation on snow.
Their engines normally ...
s are used extensively during winter—both for commercial and recreational activities. Transport from Longyearbyen to Barentsburg () and Pyramiden () is possible by snowmobile during winter, or by ship all year round. All settlements have ports, and Longyearbyen has a bus system.
Svalbard Airport, Longyear, located from Longyearbyen, is the only airport offering air transport for the island. Scandinavian Airlines
The Scandinavian Airlines System (SAS), commonly known as Scandinavian Airlines, is the national airline of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It is part of SAS Group and is headquartered in Solna, Sweden.
Including its subsidiaries SAS Link and ...
has daily scheduled services to Tromsø
Tromsø is a List of towns and cities in Norway, city in Tromsø Municipality in Troms county, Norway. The city is the administrative centre of the municipality as well as the administrative centre of Troms county. The city is located on the is ...
and Oslo
Oslo ( or ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of 1,064,235 in 2022 ...
; there are also irregular charter services to Russia. Lufttransport provides regular corporate charter services from Longyearbyen to Ny-Ålesund Airport, Hamnerabben and Svea Airport for Kings Bay and Store Norske; these flights are in general not available to the public. There are heliport
A heliport is a small airport which has a helipad, suitable for use by helicopters, powered lift, and various types of vertical lift aircraft.
Designated heliports typically contain one or more touchdown and liftoff areas and may also hav ...
s in Barentsburg and Pyramiden, and helicopters are frequently used by the governor and to a lesser extent the mining company Arktikugol.
Climate
The climate of Svalbard is dominated by its high latitude, with the average summer temperature at to and January averages at to . The North Atlantic Current moderates Spitsbergens's temperatures, particularly during winter, giving it up to higher winter temperature than similar latitudes in Russia and Canada. This keeps the surrounding waters open and navigable most of the year. The interior fjord areas and valleys, sheltered by the mountains, have larger temperature differences than the coast, giving about lower summer temperatures and higher winter temperatures. On the south of Spitsbergen, the temperature is slightly higher than further north and west. During winter, the temperature difference between south and north is typically , while about in summer. Spitsbergen is the meeting place for cold polar air from the north and mild, wet sea air from the south, creating low pressure and changing weather and fast winds, particularly in winter; in January, a strong breeze is registered 17% of the time at Isfjord Radio, but only 1% of the time in July. In summer, particularly away from land, fog is common, with visibility under registered 20% of the time in July. Precipitation is frequent but falls in small quantities, typically less than annually in western Spitsbergen. More rain falls in the uninhabited east side, where there can be more than annually.Nature
Three terrestrial mammalian species inhabit the island: theArctic fox
The Arctic fox (''Vulpes lagopus''), also known as the white fox, polar fox, or snow fox, is a small species of fox native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and common throughout the Tundra#Arctic tundra, Arctic tundra biome. I ...
, the Svalbard reindeer
The reindeer or caribou (''Rangifer tarandus'') is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, subarctic, tundra, taiga, boreal, and mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. It is the only re ...
, and accidentally introduced southern vole, which are only found in Grumant. Attempts to introduce the Arctic hare
The Arctic hare (''Lepus arcticus'') is a species of hare highly adapted to living in the Arctic tundra and other icy biomes. The Arctic hare survives with shortened ears and limbs, a small nose, fat that makes up close to 20% of its body, and a ...
and the muskox have both failed. There are fifteen to twenty types of marine mammal
Marine mammals are mammals that rely on marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as cetaceans, pinnipeds, sirenians, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reliance on marine enviro ...
s, including whales, dolphins, seals, walrus
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large pinniped marine mammal with discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. It is the only extant species in the family Odobeni ...
es and polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a large bear native to the Arctic and nearby areas. It is closely related to the brown bear, and the two species can Hybrid (biology), interbreed. The polar bear is the largest extant species of bear ...
s. Arctic charr inhabit Linne´vatn and other freshwater lakes on the island.
Polar bears are the iconic symbol of Spitsbergen and one of the main tourist attractions. While they are protected, persons going outside settlements are required to carry a rifle to kill polar bears in self-defence
Self-defense (self-defence primarily in Commonwealth English) is a countermeasure that involves defending the health and well-being of oneself from harm. The use of the right of self-defense as a legal justification for the use of force in tim ...
, as a last resort should they attack.Umbriet (2005): 132 Spitsbergen shares a common polar bear population with the rest of Svalbard and Franz Joseph Land. The Svalbard reindeer (''R. tarandus platyrhynchus'') is a distinct sub-species. While it was previously almost extinct, hunting is permitted for both it and the Arctic fox.
About thirty types of bird are found on Spitsbergen, most of which are migratory. The Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; , ; ) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territorial waters.World Wildlife Fund, 2008. It was known earlier among Russi ...
is among the areas in the world with most seabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adaptation, adapted to life within the marine ecosystem, marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent ...
s, with about 20 million counted during late summer. The most common are little auk, northern fulmar, thick-billed murre
The thick-billed murre or Brünnich's guillemot (''Uria lomvia'') is a bird in the auk family (Alcidae). This bird is named after the Danish zoologist Morten Thrane Brünnich. The very deeply black North Pacific subspecies ''Uria lomvia arra'' i ...
and black-legged kittiwake. Sixteen species are on the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an inventory of the global conservation status and extinction risk of biological ...
. Particularly Storfjorden and Nordvest-Spitsbergen are important breeding ground for seabirds. The Arctic tern
The Arctic tern (''Sterna paradisaea'') is a tern in the family Laridae. This bird has a circumpolar breeding distribution covering the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions of Europe (as far south as Brittany), Asia, and North America (as far south ...
has the furthest migration, all the way to Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
. Only two songbirds migrate to Spitsbergen to breed: the snow bunting
The snow bunting (''Plectrophenax nivalis'') is a passerine bird in the family Calcariidae. It is an Arctic specialist, with a circumpolar Arctic breeding range throughout the northern hemisphere. There are small isolated populations on a few ...
and the northern wheatear. Rock ptarmigan
The rock ptarmigan (''Lagopus muta'') is a medium-sized game bird in the grouse family. It is known simply as the ptarmigan in Europe. It is the official bird for the Canadian territory of Nunavut, where it is known as the ''aqiggiq'' (ᐊᕿ� ...
is the only bird to overwinter.
 Two partial skeletons of '' Pliosaurus funkei'' from the
Two partial skeletons of '' Pliosaurus funkei'' from the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
period were discovered in 2008. It is the largest Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
marine reptile
Marine reptiles are reptiles which have become secondarily adapted for an aquatic or semiaquatic life in a marine environment. Only about 100 of the 12,000 extant reptile species and subspecies are classed as marine reptiles, including mari ...
ever found—a pliosaur estimated to be almost long. Svalbard has permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
and tundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic ...
, with both low, middle and high Arctic vegetation. One hundred and sixty-five species of plants have been found on the archipelago. Only those areas which defrost in the summer have vegetation. Vegetation is most abundant in Nordenskiöld Land
Nordenskiöld Land is the land area between Isfjorden and Van Mijenfjorden on Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The area is named after Finnish-Swedish explorer and geologist Nils Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld. The coastal region of Nordenskiöld Land (Norde ...
, around Isfjorden and where effected by guano
Guano (Spanish from ) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats. Guano is a highly effective fertiliser due to the high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium, all key nutrients essential for plant growth. Guano was also, to a le ...
. While there is little precipitation, giving the island a steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
climate, plants still have good access to water because the cold climate reduces evaporation.Torkilsen (1984): 101 The growing season is very short, and may last only a few weeks.
There are six national parks on Spitsbergen: Indre Wijdefjorden, Nordenskiöld Land
Nordenskiöld Land is the land area between Isfjorden and Van Mijenfjorden on Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The area is named after Finnish-Swedish explorer and geologist Nils Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld. The coastal region of Nordenskiöld Land (Norde ...
, Nordre Isfjorden Land, Nordvest-Spitsbergen, Sassen-Bünsow Land and Sør-Spitsbergen. The island also features Festningen Geotope Protected Area; some of the northeastern coast is part of Nordaust-Svalbard Nature Reserve
Nordaust-Svalbard Nature Reserve () is located in the north-eastern part of the Svalbard archipelago in Norway. The nature reserve covers all of Nordaustlandet, Kong Karls Land, Kvitøya, Sjuøyane, Storøya, Lågøya, Wilhelm Island, Wahl ...
. All human traces dating from before 1946 are automatically protected. Svalbard is on Norway's tentative list for nomination as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
.
See also
* Cape Amsterdam * Einar LundborgReferences
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * *External links
Governor of Svalbard
Svalbard Tourism
{{Authority control Islands of Svalbard 1590s in the Dutch Empire Maritime history of the Dutch Republic