Goslar Kaiserpfalz on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
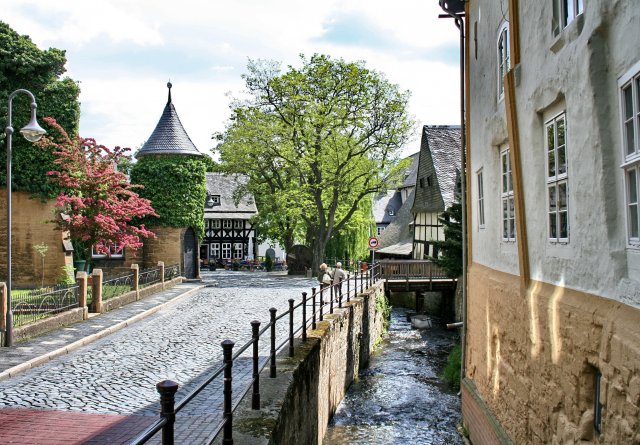
Goslar (; Eastphalian: ''Goslär'') is a historic

 (count: December 31 of each year)
(count: December 31 of each year)


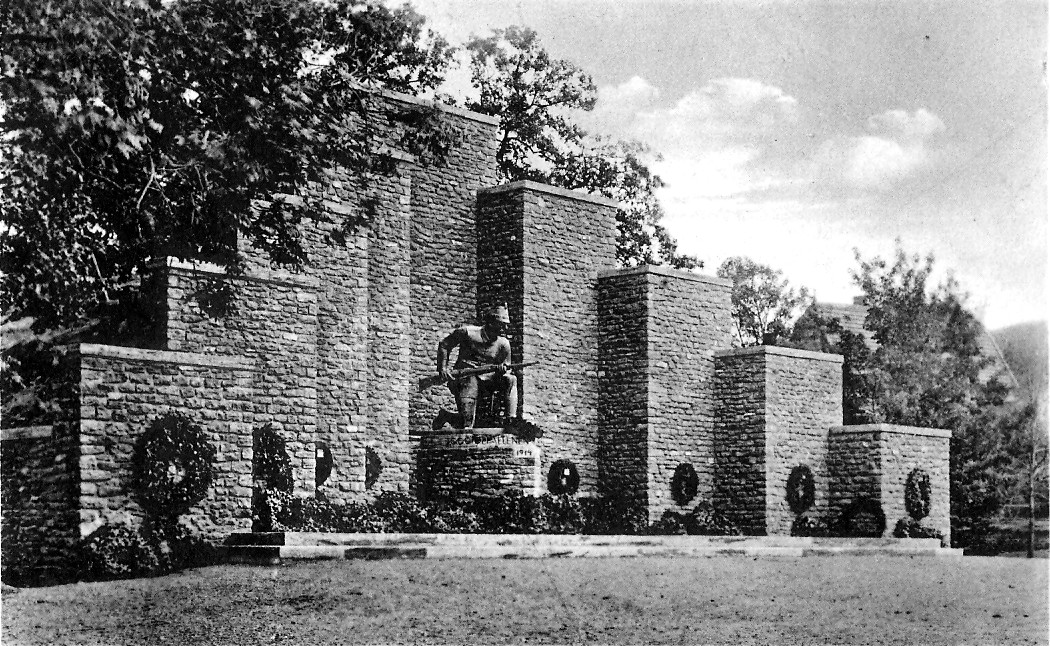

 * Memorial to the fallen riflemen of the 10th Hanover Rifle Battalion in the Franco-Prussian War 1870/1871 (now at the Kahnteich)
* Memorial to the fallen riflemen of the 10th Hanover Rifle Battalion in
* Memorial to the fallen riflemen of the 10th Hanover Rifle Battalion in the Franco-Prussian War 1870/1871 (now at the Kahnteich)
* Memorial to the fallen riflemen of the 10th Hanover Rifle Battalion in
 * Protestant-Lutheran
** Congregation Marktkirche, Market Church (build 1151, North Tower mountable)
** Congregation Neuwerk, Newark Church
** Congregation St Stephani, Saint Stephen
** Congregation Zum Frankenberge, Frankenberg Church
** Congregation Gustav-Adolf-Stabkirche, Gustav Adolf stave church in Hahnenklee
** Congregation Martin-Luther-Kirche, Martin Luther Church
** Congregation St Paulus Kirche, St Paul's Church, in Oker
** Congregation St Georg, St George
** Congregation St Johannes, St John
** Parish Church St Kilian in Hahndorf
** Congregation St Lukas, St Luke
** Parish Church St Matthäus, St Matthew's, in Jerstedt
** Congregation St Peter
* Baptist
** Congregation Christuskirche, Church of Christ
* Roman Catholic
** Congregation St Jakobi, St James the Greater (built in 1073, Goslar's oldest romanesque church still in use)
** Congregation Maria Schnee, St Mary of the Snows, in Hahnenklee
** Congregation St Barbara (part of St James)
** Congregation St Konrad, St Conrad (part of St James) in Oker
** Congregations Ss Benno & George
** Abbey St George
* Islamic Faith
** Mosque of the Turkish-German Society
** Goslar Mosque
* Protestant-Lutheran
** Congregation Marktkirche, Market Church (build 1151, North Tower mountable)
** Congregation Neuwerk, Newark Church
** Congregation St Stephani, Saint Stephen
** Congregation Zum Frankenberge, Frankenberg Church
** Congregation Gustav-Adolf-Stabkirche, Gustav Adolf stave church in Hahnenklee
** Congregation Martin-Luther-Kirche, Martin Luther Church
** Congregation St Paulus Kirche, St Paul's Church, in Oker
** Congregation St Georg, St George
** Congregation St Johannes, St John
** Parish Church St Kilian in Hahndorf
** Congregation St Lukas, St Luke
** Parish Church St Matthäus, St Matthew's, in Jerstedt
** Congregation St Peter
* Baptist
** Congregation Christuskirche, Church of Christ
* Roman Catholic
** Congregation St Jakobi, St James the Greater (built in 1073, Goslar's oldest romanesque church still in use)
** Congregation Maria Schnee, St Mary of the Snows, in Hahnenklee
** Congregation St Barbara (part of St James)
** Congregation St Konrad, St Conrad (part of St James) in Oker
** Congregations Ss Benno & George
** Abbey St George
* Islamic Faith
** Mosque of the Turkish-German Society
** Goslar Mosque
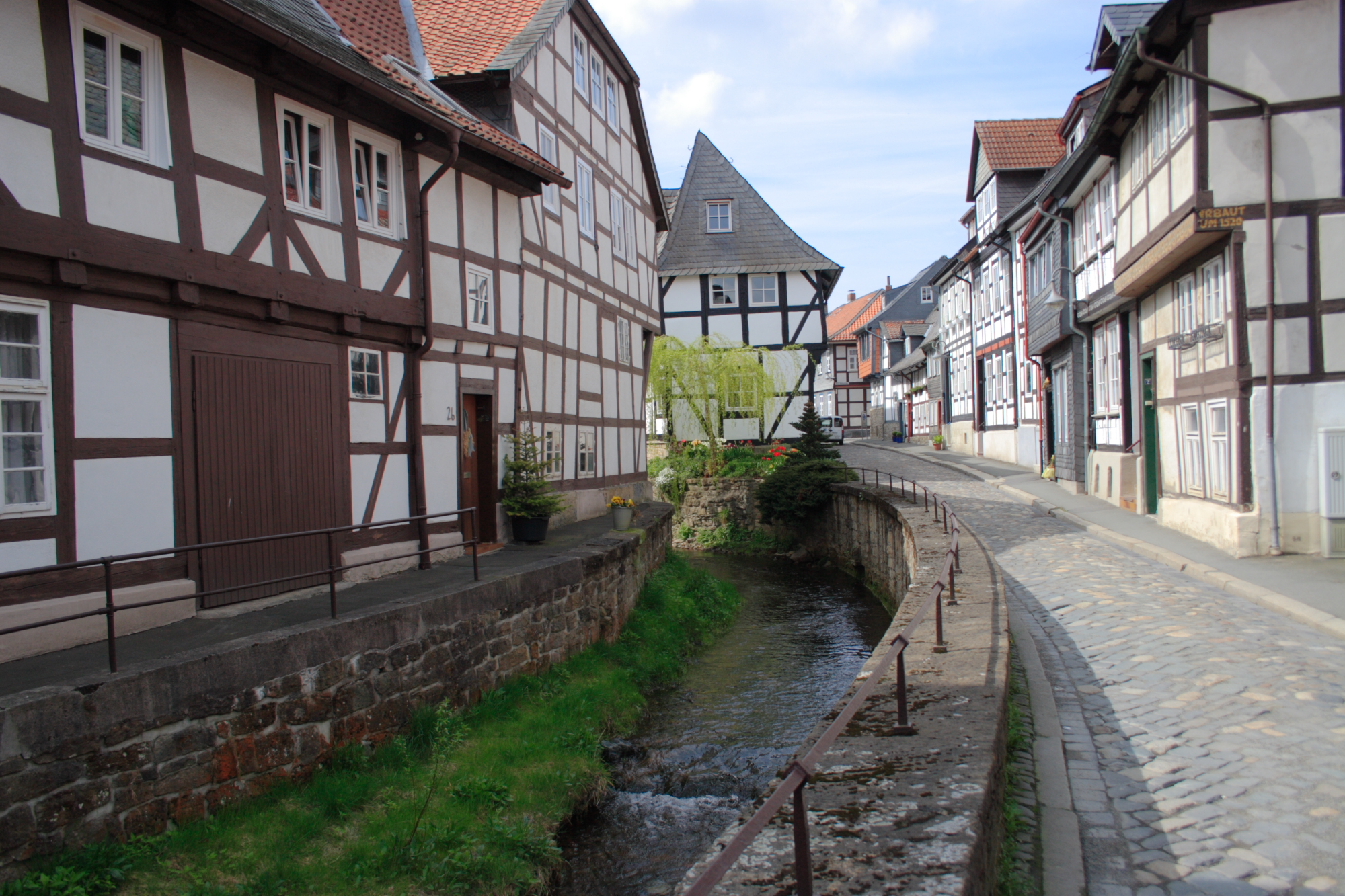
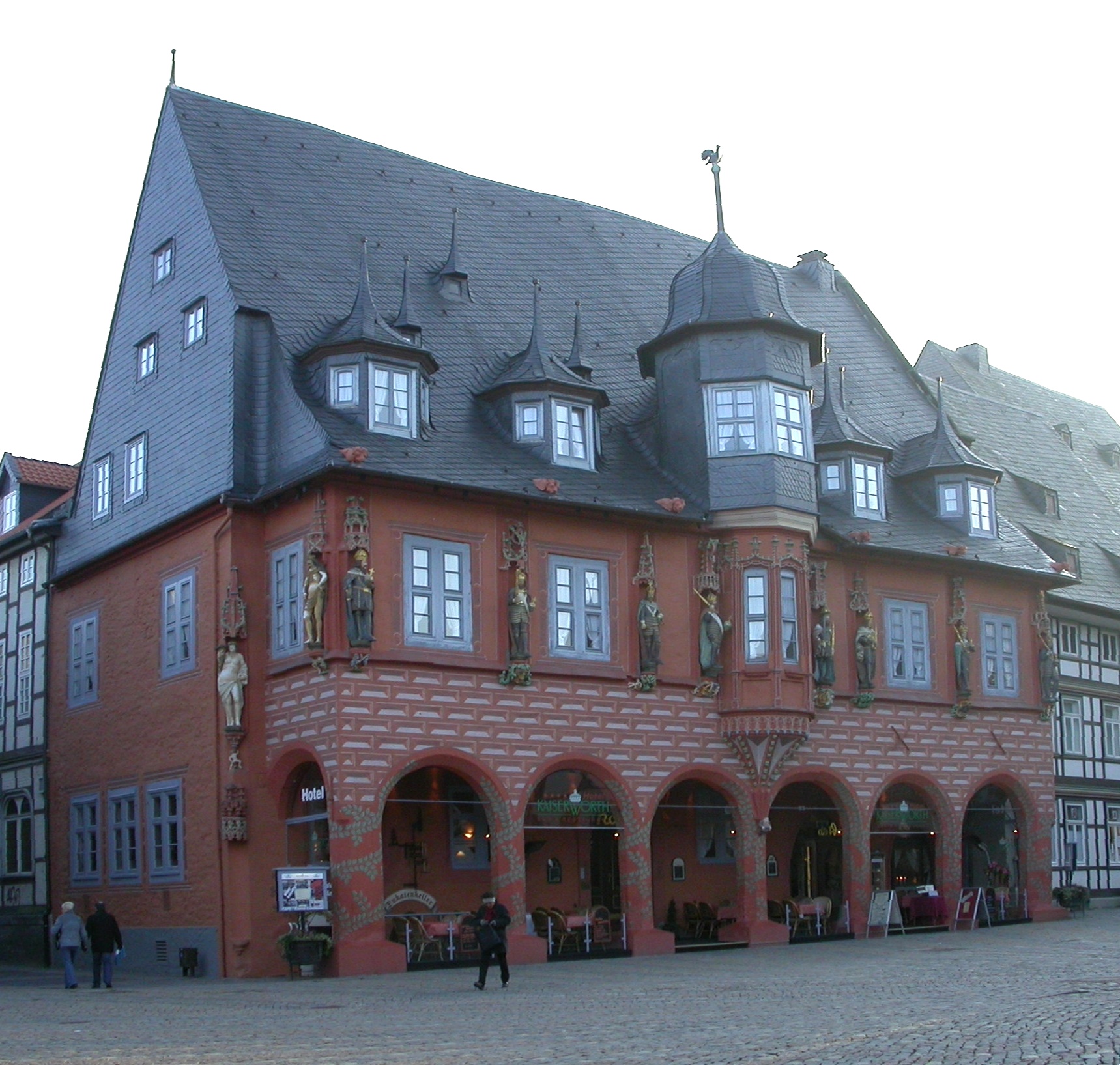

 The town centre of Goslar serves as a regional shopping centre to the Northern Harz region. Here department stores, several supermarkets, elegant boutiques and restaurants can be found. Once weekly, there is also a market, where farmers sell their local produce. There are also several car dealerships in the borough, some of whom specialise in either discount/reimport or custom car sales.
The tourism sector is a booming sector in Goslar. Several hotels and bed and breakfasts are located in or near the town's centre. In addition, the town has become a popular resort for the elderly and there are many care homes in the town.
Goslar has become a popular conference venue. The ''Achtermann Hotel'' and the ''Kaiserpfalz'' are popular conference centres, host to the annual German Road & Transport Tribunal Days: the ''Deutscher Verkehrsgerichtstag''
Largest employers in Goslar are H.C. Starck (chemistry company), the tourism sector, and the civil service. Many residents of Goslar commute to
The town centre of Goslar serves as a regional shopping centre to the Northern Harz region. Here department stores, several supermarkets, elegant boutiques and restaurants can be found. Once weekly, there is also a market, where farmers sell their local produce. There are also several car dealerships in the borough, some of whom specialise in either discount/reimport or custom car sales.
The tourism sector is a booming sector in Goslar. Several hotels and bed and breakfasts are located in or near the town's centre. In addition, the town has become a popular resort for the elderly and there are many care homes in the town.
Goslar has become a popular conference venue. The ''Achtermann Hotel'' and the ''Kaiserpfalz'' are popular conference centres, host to the annual German Road & Transport Tribunal Days: the ''Deutscher Verkehrsgerichtstag''
Largest employers in Goslar are H.C. Starck (chemistry company), the tourism sector, and the civil service. Many residents of Goslar commute to

 * Rudolf Bindig (born 1940), politician (
* Rudolf Bindig (born 1940), politician (
Mines of Rammelsberg, Historic Town of Goslar and Upper Harz Water Management System
UNESCO Official Website
Official website
*
Sound and video of Marktplatz clock
{{Authority control Goslar, World Heritage Sites in Germany Members of the Hanseatic League Landmarks in Germany Free imperial cities Mining communities in Germany
town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an ori ...
in Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
. It is the administrative centre of the district of Goslar and located on the northwestern slopes
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line is a number that describes both the ''direction'' and the ''steepness'' of the line. Slope is often denoted by the letter ''m''; there is no clear answer to the question why the letter ''m'' is use ...
of the Harz
The Harz () is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German ...
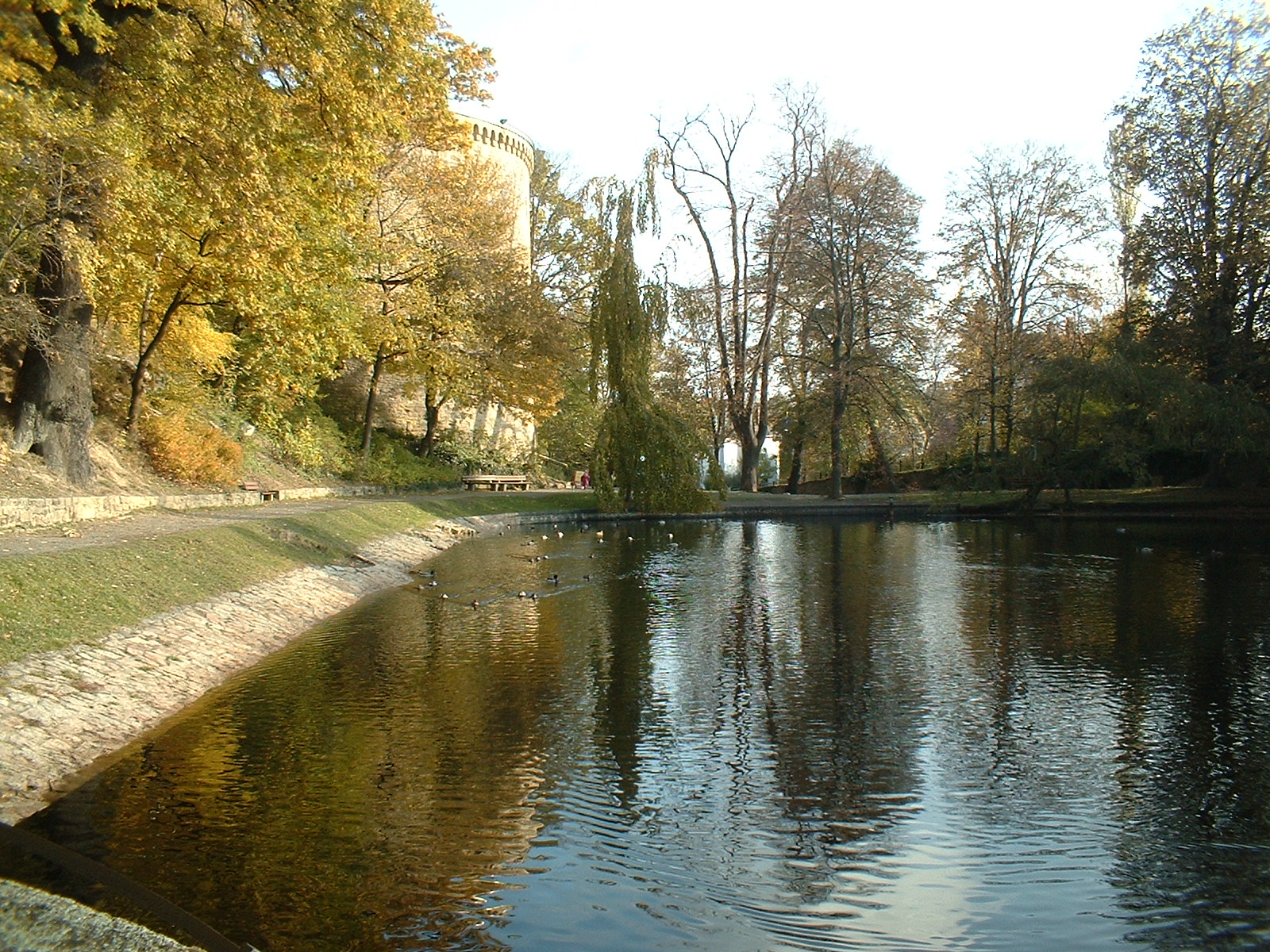
mountain range. The Old Town of Goslar and the Mines of Rammelsberg
The Rammelsberg is a mountain, high, on the northern edge of the Harz range, south of the historic town of Goslar in the North German state of Lower Saxony. The mountain is the location of an important silver, copper, and lead mine, the only mine ...
are UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Sites
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the UNESCO, United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNES ...
for their millenium-long testimony to the history of ore mining and their political importance for the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
and Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
. Each year Goslar awards the Kaiserring to an international artist, called the "Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
" of the art world.
Geography
Goslar is situated in the middle of the upper half of Germany, about south of Brunswick and about southeast of the state capital,Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
. The Schalke
Fußballclub Gelsenkirchen-Schalke 04 e. V., commonly known as FC Schalke 04 (), Schalke 04 (), or abbreviated as S04 (), is a professional German football and multi-sports club originally from the Schalke district of Gelsenkirchen, North Rh ...
mountain is the highest elevation within the municipal boundaries at . The lowest point of is near the Oker
The Oker is a river in Lower Saxony, Germany, that has historically formed an important political boundary. It is a left tributary of the River Aller, in length and runs in a generally northerly direction.
Origin and meaning of the name
The ...
river. Geographically, Goslar forms the boundary between the Hildesheim Börde The Hildesheim Börde (german: Hildesheimer Börde or ''Braunschweig-Hildesheimer Lössbörde'') is a natural region, 272 km2 in area, in the northern part of Hildesheim district, which is known for its especially rich black earth loess soil.
L ...
which is part of the Northern German Plain, and the Harz range, which is the highest, northernmost extension of Germany's Central Uplands
The Central UplandsDickinson (1964), p.18 ff. (german: die MittelgebirgeN.B. In German die ''Mittelgebirge'' (plural) refers to the Central Uplands; das ''Mittelgebirge'' refers to a low mountain range or upland region (''Mittel'' = "medium" and ...
. The Hildesheim Börde is characterised by plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
s with rich clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
soils – used agriculturally for sugar beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and which is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris''). Together wi ...
farming – interlaced with several hill ranges commonly known as the Hildesheim Forest
The Hildesheim Forest (german: Hildesheimer Wald) is a range of hills up to in the district of Hildesheim in the German state of Lower Saxony.
Geography
The Hildesheim Forest is located in the Innerste Uplands, part of the Lower Saxon Hills ...
and Salzgitter Hills
The Salzgitter Hills (german: Salzgitter-Höhenzug, also ''Salzgitterscher Höhenzug'') is an area of upland up to in height, in the Lower Saxon Hills between Salzgitter and Goslar in the districts of Wolfenbüttel and Goslar and in the territory ...
. In the northeast the Harly Forest
The Harly Forest (german: Harly-Wald, also ''Harlywald'' or just ''Harly'') is a hill range up to above NN in the district of Goslar in southeastern Lower Saxony, Germany.
Geography
The low ridge is situated in the northern foothills of the H ...
stretches down to the River Oker, in the east, Goslar borders on the German state of Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it the ...
.
Immediately to the south, the Harz range rise above the historic borough at a height of at Mt. Rammelsberg
The Rammelsberg is a mountain, high, on the northern edge of the Harz range, south of the historic town of Goslar in the North German state of Lower Saxony. The mountain is the location of an important silver, copper, and lead mine, the only min ...
. Extended forests dominate the landscape. The major rivers crossing the municipal boundaries are the Oker with its Gose
Gose () is a warm fermented beer that originated in Goslar, Germany. It is usually brewed with at least 50% of the grain bill being malted wheat. Dominant flavours in gose include a lemon sourness, a herbal characteristic, and a strong salti ...
/Abzucht
The Abzucht, also known in its upper reaches as the Wintertalbach, is a long, orographically left-hand, tributary of the Oker in Lower Saxony, Germany. The stream flows through the town of Goslar.
Geography
The Abzucht rises in the upper W ...
and Radau
Radau is a river of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is right tributary of the Oker. It rises in the Harz range, leaves the mountains at Bad Harzburg, and discharges into the Oker near Vienenburg.
Course
The river rises at around in the Upper Harz re ...
tributaries. The eponymic River Gose originates approximately south-west of Goslar at the Auerhahn Pass () east of the Bocksberg mountain. At the northern foot of the Herzberg () it meets the smaller Abzucht stream, before it flows into the Oker. The Dörpke and Gelmke
The Gelmke is a small stream, roughly long, and right-hand tributary of the Abzucht in Lower Saxony, Germany. The stream flows through part of the town of Goslar.
Geography
The Gelmke rises in the Gelmke Valley (''Gelmketal'') at about . Its ...
streams also flow from the Harz foothills to the south into the Goslar municipal area, where they discharge into the Abzucht.
Neighbouring municipalities
(clockwise from the North):Liebenburg
Liebenburg is a municipality in the district of Goslar, in Lower Saxony, Germany.
Geography
The municipal area is situated north of the Harz mountain range, within the eastern Salzgitter Hills of the Innerste Uplands. It borders on the dist ...
, Schladen-Werla
Schladen-Werla is a municipality in the district of Wolfenbüttel, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It was formed on 1 November 2013, when the municipalities of the former ''Samtgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") Schladen: Gielde, the town of Hornb ...
(Wolfenbüttel
Wolfenbüttel (; nds, Wulfenbüddel) is a town in Lower Saxony, Germany, the administrative capital of Wolfenbüttel District. It is best known as the location of the internationally renowned Herzog August Library and for having the largest c ...
District), Osterwieck
Osterwieck () is a historic town in the Harz district, in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt.
Geography
The municipal area stretches along the river Ilse, north of Wernigerode and the Harz mountain range.
The town Osterwieck consists of the foll ...
(Harz
The Harz () is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German ...
District, Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it the ...
), Bad Harzburg
Bad Harzburg (; Eastphalian: ''Bad Harzborch'') is a spa town in central Germany, in the Goslar district of Lower Saxony. It lies on the northern edge of the Harz mountains and is a recognised saltwater spa and climatic health resort.
Geogra ...
, Clausthal-Zellerfeld
Clausthal-Zellerfeld is a town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is located in the southwestern part of the Harz mountains. Its population is approximately 15,000. The City is the location of the Clausthal University of Technology. The health resort ...
(Oberharz
The Upper Harz (german: Oberharz, ) refers to the northwestern and higher part of the Harz mountain range in Germany. The exact boundaries of this geographical region may be defined differently depending on the context. In its traditional sense, th ...
), and Langelsheim
Langelsheim is a town in the district of Goslar in Lower Saxony, Germany.
Geography
The municipality is situated between the river Innerste and its tributary Grane, on the northern edge of the Harz mountain range and the Harz National Park, loc ...
.
Town districts
The township currently comprises 18 districts (''Stadtteile''):Climate
History

Iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the fo ...
mining was common in the Harz region since Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
times; the earliest known evidences for quarrying and smelting date back to the 3rd century AD. Ancient burial objects made of Harz ore have even been discovered during excavations in England. The settlement on the Gose creek was first mentioned in a 979 deed issued by Emperor Otto II
Otto II (955 – 7 December 983), called the Red (''der Rote''), was Holy Roman Emperor from 973 until his death in 983. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto II was the youngest and sole surviving son of Otto the Great and Adelaide of Italy. ...
; it was located in the Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
homelands of the Ottonian dynasty
The Ottonian dynasty (german: Ottonen) was a Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman Emperors named Otto, especially its first Emperor Otto I. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after the ...
and probably a royal palace
This is a list of royal palaces, sorted by continent.
Africa
* Abdin Palace, Cairo
* Al-Gawhara Palace, Cairo
* Koubbeh Palace, Cairo
* Tahra Palace, Cairo
* Menelik Palace
* Jubilee Palace
* Guenete Leul Palace
* Imperial Palace- Massa ...
() already existed at the site. It became even more important when extensive silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
deposits were discovered at the nearby Rammelsberg
The Rammelsberg is a mountain, high, on the northern edge of the Harz range, south of the historic town of Goslar in the North German state of Lower Saxony. The mountain is the location of an important silver, copper, and lead mine, the only min ...
, today a mining museum.
When Otto's descendant Henry II began to convene Imperial synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word ''wikt:synod, synod'' comes from the meaning "assembly" or "meeting" and is analogous with the Latin ...
s at the Goslar palace from 1009 onwards, Goslar gradually replaced the Royal palace of Werla
The Royal Palace of Werla (German: ''Königspfalz Werla'') is located near Werlaburgdorf (municipality: Schladen-Werla) in Lower Saxony. The grounds of the royal palace cover about 20 hectares rising atop Kreuzberg hill, a 17 m high natural platea ...
as a central place of assembly in the Saxon lands; a development that was again enforced by the Salian
The Salian dynasty or Salic dynasty (german: Salier) was a dynasty in the High Middle Ages. The dynasty provided four kings of Germany (1024–1125), all of whom went on to be crowned Holy Roman emperors (1027–1125).
After the death of the l ...
(" Franconian") emperors. Conrad II
Conrad II ( – 4 June 1039), also known as and , was the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire from 1027 until his death in 1039. The first of a succession of four Salian emperors, who reigned for one century until 1125, Conrad ruled the kingdoms ...
, once elected King of the Romans
King of the Romans ( la, Rex Romanorum; german: König der Römer) was the title used by the king of Germany following his election by the princes from the reign of Henry II (1002–1024) onward.
The title originally referred to any German k ...
, celebrated Christmas 1024 in Goslar and had the foundations laid for the new Imperial Palace () the next year.
Goslar became the favourite residence of Conrad's son Henry III who stayed at the palace about twenty times. Here he received King Peter of Hungary
Peter Orseolo, or Peter the Venetian ( hu, Velencei Péter; 1010 or 1011 – 1046, or late 1050s), was the King of Hungary twice. He first succeeded his uncle, King Stephen I, in 1038. His favoritism towards his foreign courtiers caused an u ...
as well as the emissaries of Prince Yaroslav of Kiev, here he appointed bishops and dukes. His son and successor Henry IV was born here on 11 November 1050. Henry also had Goslar Cathedral
The church known as Goslar Cathedral (german: Goslarer Dom) was a collegiate church dedicated to St. Simon and St. Jude in the town of Goslar, Germany. It was built between 1040 and 1050 as part of the Imperial Palace district. The church building ...
erected and consecrated by Archbishop Herman of Cologne in 1051; shortly before his death in 1056, Emperor Henry III met with Pope Victor II
Pope Victor II (c. 1018 – 28 July 1057), born Gebhard of Dollnstein-Hirschberg, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 13 April 1055 until his death in 1057. Victor II was one of a series of German-born popes w ...
in the church, emphasizing the union of secular and ecclesiastical power. His heart was buried in Goslar, his body in the Salian family vault in Speyer Cathedral
, native_name_lang = German
, image = Speyer_dom_11.jpg
, imagesize = 280px
, imagelink =
, imagealt =
, landscape =
, caption =
, pushpin ma ...
. Of the cathedral only the northern porch survived; the main building was torn down in the early 19th century.
Under Henry IV, Goslar remained a centre of Imperial rule; however, conflicts intensified such as in the violent Precedence Dispute at Pentecost 1063. While Henry aimed to secure the enormous wealth deriving from the Rammlesberg silver mines as a royal demesne
A demesne ( ) or domain was all the land retained and managed by a lord of the manor under the feudal system for his own use, occupation, or support. This distinguished it from land sub-enfeoffed by him to others as sub-tenants. The concept or ...
, the dissatisfaction of local nobles escalated with the Saxon Rebellion
The Saxon Rebellion or Rebellion of the Saxons (german: Sachsenkrieg), also commonly called the Saxon Uprising (not to be confused with the Saxon Wars, also called the Saxon Uprising), refers to the struggle between the Salian dynasty ruling the H ...
in 1073–75. In the subsequent Great Saxon Revolt
The Great Saxon Revolt was a civil war fought between 1077 and 1088, early in the history of the Holy Roman Empire. The revolt was led by a group of opportunistic German princes who elected as their figurehead the duke of Swabia, Rudolf of Rhei ...
, the Goslar citizens sided with anti-king Rudolf of Rheinfelden
Rudolf of Rheinfelden ( – 15 October 1080) was Duke of Swabia from 1057 to 1079. Initially a follower of his brother-in-law, the Salian dynasty, Salian emperor Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Henry IV, his election as German anti-king in 1077 mar ...
, who held a princely assembly here in 1077, and with Hermann of Salm
Herman(n) of Salm ( – 28 September 1088), also known as Herman(n) of Luxembourg, the progenitor of the House of Salm, was Count of Salm and elected German anti-king from 1081 until his death.
Life
Hermann was a son of Count Giselbert of ...
, who was crowned king in Goslar by Archbishop Siegfried of Mainz on 26 December 1081. brought Goslar the status of an Imperial City
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
.
In Spring 1105 Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (c. 1173–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (121 ...
convened the Saxon estates at Goslar, to gain support for the deposition of his father Henry IV. Elected king in the following year, he held six Imperial Diets at the Goslar Palace during his rule. The tradition was adopted by his successor Lothair II
Lothair II (835 – 8 August 869) was the king of Lotharingia from 855 until his death. He was the second son of Emperor Lothair I and Ermengarde of Tours. He was married to Teutberga (died 875), daughter of Boso the Elder.
Reign
For political ...
and even by the Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynasty ...
rulers Conrad III and Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt on ...
. After his election in 1152, King Frederick appointed the Welf Welf is a Germanic first name that may refer to:
*Welf (father of Judith), 9th century Frankish count, father-in-law of Louis the Pious
*Welf I, d. bef. 876, count of Alpgau and Linzgau
*Welf II, Count of Swabia, died 1030, supposed descendant of W ...
duke Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180.
Henry was one of the most powerful German p ...
Imperial ''Vogt
During the Middle Ages, an (sometimes given as modern English: advocate; German: ; French: ) was an office-holder who was legally delegated to perform some of the secular responsibilities of a major feudal lord, or for an institution such as ...
'' (bailiff) of the Goslar mines; nevertheless, the dissatisfied duke besieged the town and at an 1173 meeting in Chiavenna
Chiavenna ( lmo, Ciavèna ; la, Clavenna; rm, Clavenna or ''Claven''; archaic german: Cläven or ''Kleven'') is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Sondrio in the northern Italian region of Lombardy. It is the centre of the Alpine ...
demanded his enfeoffment with the estates in turn for his support on Barbarossa's Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
campaigns. When Henry the Lion was finally declared deposed in 1180, he had the Rammelsberg mines devastated.
Goslar's importance as an Imperial residence began to decline under the rule of Barbarossa's descendants. During the German throne dispute
The German throne dispute or German throne controversy (german: Deutscher Thronstreit) was a political conflict in the Holy Roman Empire from 1198 to 1215. This dispute between the House of Hohenstaufen and House of Welf was over the successor to E ...
the Welf king Otto IV
Otto IV (1175 – 19 May 1218) was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1209 until his death in 1218.
Otto spent most of his early life in England and France. He was a follower of his uncle Richard the Lionheart, who made him Count of Poitou in 1196 ...
laid siege to the town in 1198 but had to yield to the forces of his Hohenstaufen rival Philip of Swabia
Philip of Swabia (February/March 1177 – 21 June 1208) was a member of the House of Hohenstaufen and King of Germany from 1198 until his assassination.
The death of his older brother Emperor Henry VI in 1197 meant that the Hohenstaufen rule (whi ...
. Goslar was again stormed and plundered by Otto's troops in 1206. Frederick II held the last Imperial Diet here; with the Great Interregnum
An interregnum (plural interregna or interregnums) is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order. Archetypally, it was the period of time between the reign of one monarch and the next (coming from Latin '' ...
upon his death in 1250, Goslar's Imperial era ended.
While the Emperors withdraw from Northern Germany, civil liberties in Goslar were strengthened. Market rights
A market town is a settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rural ...
date back to 1025; a municipal council () was first mentioned in 1219. The citizens strived for control of the Rammelsberg silver mines and in 1267 joined the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
. Beside mining in the Upper Harz
Mining in the Upper Harz region of central Germany was a major industry for several centuries, especially for the production of silver, lead, copper, and, latterly, zinc as well. Great wealth was accumulated from the mining of silver from the 16t ...
, commerce and trade in Gose
Gose () is a warm fermented beer that originated in Goslar, Germany. It is usually brewed with at least 50% of the grain bill being malted wheat. Dominant flavours in gose include a lemon sourness, a herbal characteristic, and a strong salti ...
beer, later also slate and vitriol, became important. By 1290 the council had obtained rights, confirming Goslar's status as a free imperial city
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
. In 1340 its citizens were vested with rights by Emperor Louis the Bavarian
Louis IV (german: Ludwig; 1 April 1282 – 11 October 1347), called the Bavarian, of the house of Wittelsbach, was King of the Romans from 1314, King of Italy from 1327, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1328.
Louis' election as king of Germany ...
. The Goslar town law set an example for numerous other municipalities, like the Goslar mining law codified in 1359.
Early modern times saw both a mining boom and rising conflicts with the Welf Dukes of Brunswick-Lüneburg
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ran ...
, mainly with Prince Henry V of Wolfenbüttel who seized the Rammelsberg mines and extended Harz forests in 1527. Though a complaint was successfully lodged with the by the Goslar citizens, a subsequent gruelling feud with the duke lasted for decades. Goslar was temporarily placed under Imperial ban
The imperial ban (german: Reichsacht) was a form of outlawry in the Holy Roman Empire. At different times, it could be declared by the Holy Roman Emperor, by the Imperial Diet, or by courts like the League of the Holy Court (''Vehmgericht'') or th ...
, while the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
was introduced in the city by theologian Nicolaus von Amsdorf
Nicolaus von Amsdorf (German: Nikolaus von Amsdorf, 3 December 1483 – 14 May 1565) was a German Lutheran theologian and an early Protestant reformer. As bishop of Naumburg (1542–1546), he became the first Lutheran bishop in the Holy Roman E ...
who issued a first church constitution in 1531. To assert independence, the citizens in 1536 joined the Schmalkaldic League
The Schmalkaldic League (; ; or ) was a military alliance of Lutheran princes within the Holy Roman Empire during the mid-16th century.
Although created for religious motives soon after the start of the Reformation, its members later came to ...
against the Catholic policies of the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
emperor Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infan ...
. The Schmalkaldic forces indeed occupied the Wolfenbüttel lands of Henry V, however, when they were defeated by Imperial forces at the 1547 Battle of Mühlberg
The Battle of Mühlberg took place near Mühlberg in the Electorate of Saxony in 1547, during the Schmalkaldic War. The Catholic princes of the Holy Roman Empire led by the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V decisively defeated the Lutheran Schmalka ...
, the Welf duke continued his reprisals.
In 1577 the Goslar citizens signed the Lutheran Formula of Concord
Formula of Concord (1577) (German, ''Konkordienformel''; Latin, ''Formula concordiae''; also the "''Bergic Book''" or the "''Bergen Book''") is an authoritative Lutheran statement of faith (called a confession, creed, or "symbol") that, in its t ...
. After years of continued skirmishes, they finally had to grant Duke Henry and his son Julius
The gens Julia (''gēns Iūlia'', ) was one of the most prominent patrician families in ancient Rome. Members of the gens attained the highest dignities of the state in the earliest times of the Republic. The first of the family to obtain the ...
extensive mining rights which ultimately edged out the city council. Nevertheless, several attempts by the Brunswick dukes to incorporate the Imperial city were rejected. Goslar and its economy was hit hard by the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
, mainly by the financial crisis in the 1620s which led to several revolts and pogroms. Facing renewed aggressions by Duke Christian the Younger of Brunswick
Christian the Younger of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (20 September 1599 – 16 June 1626), a member of the House of Welf, titular Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg and administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Halberstadt, was a German Protestant military l ...
, the citizens sought support from the Imperial military leaders Tilly Tilly may refer to:
Places France
* Tilly, Eure, in the Eure ''département''
* Tilly, Indre, in the Indre ''département''
* Tilly, Yvelines, in the Yvelines ''département''
Elsewhere
* Tilly, Belgium, a village in the municipality of Viller ...
and . The city was occupied by the Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
forces of King Gustavus Adolphus
Gustavus Adolphus (9 December Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">N.S_19_December.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Old Style and New Style dates">N.S 19 December">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/now ...
from 1632 to 1635; in 1642 a peace agreement was reached between Emperor Ferdinand III and the Brunswick duke Augustus the Younger. The hopes of the Goslar citizens to regain the Rammelsberg mines were not fulfilled.
Goslar remained loyal to the Imperial authority, solemnly celebrating each accession of a Holy Roman Emperor. While strongly referring to its great medieval traditions, the city continuously decreased in importance and got into rising indebtedness. When stayed at Goslar in 1777, he called it "an Imperial city rotted in and with its privileges".
In the winter of 1798, the coldest of the century, the young English poet William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication ''Lyrical Ballads'' (1798).
Wordsworth's ' ...
stayed in the city. To dispel homesickness he started to write a few verses about his childhood, which would eventually evolve into the masterpiece that was published in 13 volumes after his death as ''The Prelude
''The Prelude or, Growth of a Poet's Mind; An Autobiographical Poem '' is an autobiographical poem in blank verse by the English poet William Wordsworth. Intended as the introduction to the more philosophical poem ''The Recluse,'' which Wordswort ...
''.
First administrative reforms were enacted by councillors of the Siemens family
''Siemens'' is the name of a family of German technology and telecommunications industrialists, founders and to the present day largest shareholders of Siemens AG. The family have a wealth of over €8 billion, making them the 5th richest family in ...
. Nevertheless, the status of Imperial immediacy
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular pri ...
was finally lost, when Goslar was annexed by Prussian
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
forces during the Napoleonic Wars in 1802, confirmed by the German Mediatisation
German mediatisation (; german: deutsche Mediatisierung) was the major territorial restructuring that took place between 1802 and 1814 in Germany and the surrounding region by means of the mass mediatisation and secularisation of a large number ...
the next year. Under Prussian rule, further reforms were pushed ahead by councillor Christian Wilhelm von Dohm
Christian Wilhelm von Dohm (; 11 December 1751 – 29 May 1820) was a German historian and political writer.
Biography
Dohm was born in Lemgo on 11 December 1751. The son of a Lutheran pastor at , he was a radical advocate for Jewish emancipatio ...
. Temporarily part of the Kingdom of Westphalia
The Kingdom of Westphalia was a kingdom in Germany, with a population of 2.6 million, that existed from 1807 to 1813. It included territory in Hesse and other parts of present-day Germany. While formally independent, it was a vassal state of the ...
upon the Prussian defeat at the 1806 Battle of Jena–Auerstedt
The twin battles of Jena and Auerstedt (; older spelling: ''Auerstädt'') were fought on 14 October 1806 on the plateau west of the river Saale in today's Germany, between the forces of Napoleon I of France and Frederick William III of Pruss ...
, Goslar finally was assigned to the newly established Kingdom of Hanover
The Kingdom of Hanover (german: Königreich Hannover) was established in October 1814 by the Congress of Vienna, with the restoration of George III to his Hanoverian territories after the Napoleonic era. It succeeded the former Electorate of Han ...
by resolution of the Vienna Congress
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
. The cathedral was sold and torn down from 1820 to 1822, bitterly mourned by Heinrich Heine
Christian Johann Heinrich Heine (; born Harry Heine; 13 December 1797 – 17 February 1856) was a German poet, writer and literary critic. He is best known outside Germany for his early lyric poetry, which was set to music in the form of '' Lied ...
in his travelogue. Again under Prussian rule after the Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), (; "German war of brothers") and by a variety of other names, was fought in 186 ...
of 1866, Goslar became a popular retirement residence (''Pensionopolis'') and a garrison town of the Prussian Army
The Royal Prussian Army (1701–1919, german: Königlich Preußische Armee) served as the army of the Kingdom of Prussia. It became vital to the development of Brandenburg-Prussia as a European power.
The Prussian Army had its roots in the co ...
. The Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, also , german: Haus Hohenzollern, , ro, Casa de Hohenzollern) is a German royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenb ...
kings and emperors had the Imperial Palace restored, including the mural paintings by Hermann Wislicenus
Hermann Wislicenus (20 September 1825 – 25 April 1899) was a German historical painter. He is chiefly known for his mural paintings in the Imperial Palace of Goslar.
Biography
Born in Eisenach in the Thuringian Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenac ...
.
After the Nazi seizure of power
Adolf Hitler's rise to power began in the newly established Weimar Republic in September 1919 when Hitler joined the '' Deutsche Arbeiterpartei'' (DAP; German Workers' Party). He rose to a place of prominence in the early years of the party. Be ...
in 1933, Reich Minister Richard Walther Darré made Goslar the seat of the agricultural corporation. In 1936, the city obtained the title
A title is one or more words used before or after a person's name, in certain contexts. It may signify either generation, an official position, or a professional or academic qualification. In some languages, titles may be inserted between the f ...
of . In the course of the German re-armament
German rearmament (''Aufrüstung'', ) was a policy and practice of rearmament carried out in Germany during the interwar period (1918–1939), in violation of the Treaty of Versailles which required German disarmament after WWI to prevent Germa ...
, a airbase was built north of the town and several war supplier companies located in the vicinity, including subcamps of the Buchenwald
Buchenwald (; literally 'beech forest') was a Nazi concentration camp established on hill near Weimar, Germany, in July 1937. It was one of the first and the largest of the concentration camps within Germany's 1937 borders. Many actual or su ...
and Neuengamme concentration camp
Neuengamme was a network of Nazi concentration camps in Northern Germany that consisted of the main camp, Neuengamme, and more than 85 satellite camps. Established in 1938 near the village of Neuengamme in the Bergedorf district of Hamburg, th ...
s. Nevertheless, the historic town escaped strategic bombing during World War II
World War II (1939–1945) involved sustained strategic bombing of railways, harbours, cities, workers' and civilian housing, and industrial districts in enemy territory. Strategic bombing as a military strategy is distinct both from close ...
.
Part of the British occupation zone
The British occupation zone in Germany (German: ''Britische Besatzungszone Deutschlands'') was one of the Allied-occupied areas in Germany after World War II. The United Kingdom along with her Commonwealth were one of the three major Allied pow ...
from 1945, Goslar was the site of a displaced persons camp
A refugee camp is a temporary Human settlement, settlement built to receive refugees and people in refugee-like situations. Refugee camps usually accommodate displaced people who have fled their home country, but camps are also made for interna ...
. During the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
era the city near the inner German border
The inner German border (german: Innerdeutsche Grenze or ; initially also ) was the border between the German Democratic Republic (GDR, East Germany) and the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG, West Germany) from 1949 to 1990. Not including the ...
was a major garrison town for the West German
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
army and the border police. After the fall of the Berlin wall
The Berlin Wall (german: Berliner Mauer, ) was a guarded concrete barrier that encircled West Berlin from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and East Germany (GDR). Construction of the Berlin Wall was commenced by the government ...
, the barracks were vacated and a major economic factor was lost. The Rammelberg mines were finally closed in 1988, after a millennial history of mining.
In the summer of 2018, a bottled typewritten message dated March 26, 1930 was discovered in the roof of Goslar Cathedral
The church known as Goslar Cathedral (german: Goslarer Dom) was a collegiate church dedicated to St. Simon and St. Jude in the town of Goslar, Germany. It was built between 1040 and 1050 as part of the Imperial Palace district. The church building ...
, signed by four roofers who bemoaned the economic state of that country. The bottle was discovered by a roofer who was the grandson of one of the signatories, who had been an 18-year-old roofing apprentice in 1930. Goslar's mayor replaced the bottle with a copy of the 1930 message, adding his own confidential message.
Demographics
As of 31 December 2020 there were 50,184 inhabitants in Goslar (including Vienenburg).Politics

Town council
For thelegislature
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its p ...
from 1 November 2016 until 31 October 2021, the seats were allocated as follows:
* SPD
The Social Democratic Party of Germany (german: Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands, ; SPD, ) is a centre-left social democratic political party in Germany. It is one of the major parties of contemporary Germany.
Saskia Esken has been t ...
: 14 seats (37.55%)
* CDU: 10 seats (26.10%)
* AfD: 3 seats (9.28%)
* FDP: 3 seats (6.95%)
* Greens: 3 seats (6.70%)
* Goslarer Linke: 2 seats (5.36%)
* BGL: 2 seats (5.02%)
* AfG AFG may refer to:
* Afghanistan, ISO 3166-1 code
* AFG Arena, St. Gallen, Switzerland
* Afghan Sign Language
Afghan Sign Language is the deaf sign language of Jalalabad in eastern Afghanistan, possibly with some presence in Kabul. It has been ...
: 1 seat (1.69%)
Lord Mayor
Dr Oliver Junk wasMayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well a ...
from September 2011 through October 2021. Since November 2021 Urte Schwerdtner (SPD) is Mayor of Goslar.
Members of Parliament
* ''European'' (Constituency: Southern Lower Saxony), Godelieve Quisthoudt-Rowohl (CDU), Erika Mann (SPD) * ''Bundestag'' (Constituency 52: Goslar, Northeim, Osterode), First: Wilhelm Priesmeier (SPD), List: Hans Georg Faust (CDU) * ''Landtag Lower Saxony'' (Constituency 16: Goslar), First: Petra Emmerich-Kopatsch (SPD), List: Dorothee Prüssner (CDU)Twin towns – sister cities
Goslar is twinned with: *Arcachon
Arcachon ( ; ) is a commune in the southwestern French department of Gironde. It is a popular seaside resort on the Atlantic coast southwest of Bordeaux, in the Landes forest. It has a sandy beach and a mild climate said to be favourable for inv ...
, France (1965)
* Beroun
Beroun (; german: Beraun) is a town in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 20,000 inhabitants. It lies at the confluence of the Berounka and Litavka rivers. Beroun creates a conurbation with Králův Dvůr, former par ...
, Czech Republic (1989)
* Brzeg
Brzeg (; Latin: ''Alta Ripa'', German: ''Brieg'', Silesian German: ''Brigg'', , ) is a town in southwestern Poland with 34,778 inhabitants (December 2021) and the capital of Brzeg County. It is situated in Silesia in the Opole Voivodeship on the ...
, Poland (2000)
* Forres
Forres (; gd, Farrais) is a town and former royal burgh in the north of Scotland on the Moray coast, approximately northeast of Inverness and west of Elgin. Forres has been a winner of the Scotland in Bloom award on several occasions. There ...
, Scotland, UK (1984)
* Ra'anana
Ra'anana ( he, רַעֲנָנָּה, lit. "Fresh") is a city in the southern Sharon Plain of the Central District of Israel. It was founded in 1922 as an American-Jewish settlement, 1 km south of the village of Tabsur, where an important ...
, Israel (2006)
* Windsor and Maidenhead
The Royal Borough of Windsor and Maidenhead is a Royal Borough of Berkshire, in South East England. It is named after both the towns of Maidenhead and Windsor, Berkshire, Windsor, the borough also covers the nearby towns of Ascot, Berkshire, Asc ...
, England, UK (1969)
Culture and sights



 * Memorial to the fallen riflemen of the 10th Hanover Rifle Battalion in the Franco-Prussian War 1870/1871 (now at the Kahnteich)
* Memorial to the fallen riflemen of the 10th Hanover Rifle Battalion in
* Memorial to the fallen riflemen of the 10th Hanover Rifle Battalion in the Franco-Prussian War 1870/1871 (now at the Kahnteich)
* Memorial to the fallen riflemen of the 10th Hanover Rifle Battalion in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
1914-1918
Theatre
The ''Odeon Theatre'' is the town's major theatre venue. It has been recently refurbished. It is host to several productions of visiting theatre companies and music groups. The alternative theatre ''Culture Power Station Harz'' or ''Kulturkraftwerk'' Harz is housed in a disused power station. Being run by volunteers, it produces contemporary theatre, comedy and hosts mostly alternative cultural events. Here the annual Goslar Fringe Culture Days are held from the start to mid June.Museums
* Museum and visitor's mine Rammelsberg, an Anchor Point of ERIH, TheEuropean Route of Industrial Heritage
The European Route of Industrial Heritage (ERIH) is a tourist route of the most important industrial heritage sites in Europe. This is a tourism industry information initiative to present a network of industrial heritage sites across Europe. The a ...
* Museum in the ''Kaiserpfalz
The term ''Kaiserpfalz'' (, "imperial palace") or ''Königspfalz'' (, "royal palace", from Middle High German ''phal ne'' to Old High German ''phalanza'' from Middle Latin ''palatia'' luralto Latin ''palatium'' "palace") refers to a number of ...
'', a 19c reconstruction of the medieval imperial palace
* Monks' House, ''Mönchehaus Museum'' for Contemporary and Modern Arts
* Goslar Museum
* Museum in the Gothic Town Hall
* Zwinger Tower and Dungeon, Museum for Late Mediaeval History
Religion
 * Protestant-Lutheran
** Congregation Marktkirche, Market Church (build 1151, North Tower mountable)
** Congregation Neuwerk, Newark Church
** Congregation St Stephani, Saint Stephen
** Congregation Zum Frankenberge, Frankenberg Church
** Congregation Gustav-Adolf-Stabkirche, Gustav Adolf stave church in Hahnenklee
** Congregation Martin-Luther-Kirche, Martin Luther Church
** Congregation St Paulus Kirche, St Paul's Church, in Oker
** Congregation St Georg, St George
** Congregation St Johannes, St John
** Parish Church St Kilian in Hahndorf
** Congregation St Lukas, St Luke
** Parish Church St Matthäus, St Matthew's, in Jerstedt
** Congregation St Peter
* Baptist
** Congregation Christuskirche, Church of Christ
* Roman Catholic
** Congregation St Jakobi, St James the Greater (built in 1073, Goslar's oldest romanesque church still in use)
** Congregation Maria Schnee, St Mary of the Snows, in Hahnenklee
** Congregation St Barbara (part of St James)
** Congregation St Konrad, St Conrad (part of St James) in Oker
** Congregations Ss Benno & George
** Abbey St George
* Islamic Faith
** Mosque of the Turkish-German Society
** Goslar Mosque
* Protestant-Lutheran
** Congregation Marktkirche, Market Church (build 1151, North Tower mountable)
** Congregation Neuwerk, Newark Church
** Congregation St Stephani, Saint Stephen
** Congregation Zum Frankenberge, Frankenberg Church
** Congregation Gustav-Adolf-Stabkirche, Gustav Adolf stave church in Hahnenklee
** Congregation Martin-Luther-Kirche, Martin Luther Church
** Congregation St Paulus Kirche, St Paul's Church, in Oker
** Congregation St Georg, St George
** Congregation St Johannes, St John
** Parish Church St Kilian in Hahndorf
** Congregation St Lukas, St Luke
** Parish Church St Matthäus, St Matthew's, in Jerstedt
** Congregation St Peter
* Baptist
** Congregation Christuskirche, Church of Christ
* Roman Catholic
** Congregation St Jakobi, St James the Greater (built in 1073, Goslar's oldest romanesque church still in use)
** Congregation Maria Schnee, St Mary of the Snows, in Hahnenklee
** Congregation St Barbara (part of St James)
** Congregation St Konrad, St Conrad (part of St James) in Oker
** Congregations Ss Benno & George
** Abbey St George
* Islamic Faith
** Mosque of the Turkish-German Society
** Goslar Mosque
Sports
Situated at the foot of the Harz hills, Goslar offers a great deal of outdoor pursuit, from swimming to rock climbing; from motor sports and aviation to sailing and cross-country biking. The oldest and most traditional sports club is the ''MTV Goslar'' (founded in 1849). Its main facilities, a football pitch and gymnasium are located at the Golden Meadow (''Goldene Aue'') site. The football department ofGoslarer SC 08
The Goslarer SC 08 is a German association football club from the city of Goslar, Lower Saxony.
The club's most notable achievement was winning the tier-five Niedersachsenliga and earning promotion to the Regionalliga Nord in 2009 and 2012.
A ...
earned the right to play in the fourth division Regionalliga Nord
The Regionalliga Nord ( en, Regional League North) is the fourth tier of the German football league system in the states of Lower Saxony, Schleswig-Holstein, Bremen and Hamburg. It is one of five leagues at this level, together with the Regional ...
in 2009-10 after winning the Oberliga Niedersachsen
The Oberliga Niedersachsen ( en, Upper League Lower Saxony), sometimes referred to as ''Niedersachsenliga'' (Lower Saxony league), is the fifth tier of the German football league system and the highest league in the German state of Lower Saxony (ge ...
championship.
Celebrations and Events
In the year 2006 Goslar hosted the Salier Year to celebrate the foundation of this ancient German Imperial dynasty a millennium ago. Other events include: * Annual award (since 1975) of the "Imperial Ring" to a personality who has made an outstanding contribution to society and the arts. Its laureates includeHenry Moore
Henry Spencer Moore (30 July 1898 – 31 August 1986) was an English artist. He is best known for his semi- abstract monumental bronze sculptures which are located around the world as public works of art. As well as sculpture, Moore produced ...
, Joseph Beuys
Joseph Heinrich Beuys ( , ; 12 May 1921 – 23 January 1986) was a German artist, teacher, performance artist, and art theorist whose work reflected concepts of humanism, sociology, and anthroposophy. He was a founder of a provocative art mov ...
, Christo
Christo Vladimirov Javacheff (1935–2020) and Jeanne-Claude Denat de Guillebon (1935–2009), known as Christo and Jeanne-Claude, were artists noted for their large-scale, site-specific art, site-specific environmental art, environmental art i ...
, Dani Karavan
Daniel "Dani" Karavan ( he, דני קרוון, 7 December 1930 – 29 May 2021) was an Israeli sculptor best known for site specific memorials and monuments which merge into the environment.
Biography
Daniel (Dani) Karavan was born in Tel A ...
etc.
* Goslar International Concerto Days, Mid to End August
* The Goslar Fair, Beginning to Mid July
* Annual Artisans market in the old town, usually beginning of August
* Old Town Festival, mid-September
* Hanseatic Days, Spring (usually during the Easter
Easter,Traditional names for the feast in English are "Easter Day", as in the '' Book of Common Prayer''; "Easter Sunday", used by James Ussher''The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, Volume 4'') and Samuel Pepys''The Diary of Samuel ...
holidays)

Economy and infrastructure

 The town centre of Goslar serves as a regional shopping centre to the Northern Harz region. Here department stores, several supermarkets, elegant boutiques and restaurants can be found. Once weekly, there is also a market, where farmers sell their local produce. There are also several car dealerships in the borough, some of whom specialise in either discount/reimport or custom car sales.
The tourism sector is a booming sector in Goslar. Several hotels and bed and breakfasts are located in or near the town's centre. In addition, the town has become a popular resort for the elderly and there are many care homes in the town.
Goslar has become a popular conference venue. The ''Achtermann Hotel'' and the ''Kaiserpfalz'' are popular conference centres, host to the annual German Road & Transport Tribunal Days: the ''Deutscher Verkehrsgerichtstag''
Largest employers in Goslar are H.C. Starck (chemistry company), the tourism sector, and the civil service. Many residents of Goslar commute to
The town centre of Goslar serves as a regional shopping centre to the Northern Harz region. Here department stores, several supermarkets, elegant boutiques and restaurants can be found. Once weekly, there is also a market, where farmers sell their local produce. There are also several car dealerships in the borough, some of whom specialise in either discount/reimport or custom car sales.
The tourism sector is a booming sector in Goslar. Several hotels and bed and breakfasts are located in or near the town's centre. In addition, the town has become a popular resort for the elderly and there are many care homes in the town.
Goslar has become a popular conference venue. The ''Achtermann Hotel'' and the ''Kaiserpfalz'' are popular conference centres, host to the annual German Road & Transport Tribunal Days: the ''Deutscher Verkehrsgerichtstag''
Largest employers in Goslar are H.C. Starck (chemistry company), the tourism sector, and the civil service. Many residents of Goslar commute to Salzgitter
Salzgitter (; Eastphalian: ''Soltgitter'') is an independent city in southeast Lower Saxony, Germany, located between Hildesheim and Braunschweig. Together with Wolfsburg and Braunschweig, Salzgitter is one of the seven ''Oberzentren'' of Lower ...
, where car production, steel works and white collar jobs are based.
The ''Dr.-Herbert-Nieper-Krankenhaus'' is a privately owned hospital of the ''Asklepios Harzkliniken'' group serving the greater Harz region. A new annex for intensitive medicine is under construction. There are several general practitioners, dentists, and specialist practitioners distributed across the town. There is an emergency service in place.
Transport
Goslar has excellent road links, as well as rail links connecting it to the major European population centres. Goslar also serves as a major transport hub for the Upper Harz mountains (highest peak at 1,141 m (3,744 ft) altitude). With the A 7 and the A 395 there are two mainAutobahn
The (; German plural ) is the federal controlled-access highway system in Germany. The official German term is (abbreviated ''BAB''), which translates as 'federal motorway'. The literal meaning of the word is 'Federal Auto(mobile) Track'. ...
s/Highways within 20 minutes reach of Goslar.
The A 7 connects Hamburg/Hanover in the North to Frankfurt/Munich in the South. The A 395 branches off the main east-west Autobahn A 2 at Brunswick and ends at Vienenburg, some east of Goslar. The A 2 connects Berlin – to the East – to the Ruhr Area and the Netherlands in the West. The Federal highways Bundesstraße 6, B 6 and Bundesstraße 82, B 82 converge at Goslar and are routed via the four-lane by-pass past the town centre. The B 6 is mostly four-laned and approaches Goslar via the scenic Hildesheim–Salzgitter
Salzgitter (; Eastphalian: ''Soltgitter'') is an independent city in southeast Lower Saxony, Germany, located between Hildesheim and Braunschweig. Together with Wolfsburg and Braunschweig, Salzgitter is one of the seven ''Oberzentren'' of Lower ...
route.
Goslar is served by the German Railway network (Deutsche Bahn) lines Hanover–Goslar–Halle (Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it the ...
) as well as Brunswick–Goslar–Kreiensen. The central railway station is located in the vicinity of the town centre. There is a park-and-ride system for commuters to Brunswick and Hanover.
At the railway station there is a central bus station with buses travelling routinely to various destinations in the Harz
The Harz () is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German ...
mountains. The buses are from DB Stadtverkehr.
Media
The regional newspaper is the Goslar Chronicle ''Goslarsche Zeitung,'' which has an estimated daily readership of 90,000. The ''General-Anzeiger'' is a gazette owned by the Heinrich Bauer publishing group with an editorial office in Goslar. Aside from this there are two freely distributed gazettes. ''Radio Okerwelle GoslarRadio'' is the regional private radio station based in Brunswick, which broadcasts contemporary music, information and news in the German language to the Brunswick region.Education
The three tier education system in Goslar district falls under Lower-Saxon legislation. The language of instruction at all schools is German. The nine primary schools are distributed across the entire municipality and the associated hamlets. There are two advanced secondary schools (5-12/13), the Christian-von-Dohm-Gymnasium, and the more traditional Ratsgymnasium, both of which prepare their students for an academic career. Three intermediate level schools (5-10), the Andre-Mouton Realschule, the Realschule Hoher Weg, and the Realschule Goldene Aue prepare their pupils for a professional career. Furthermore, two vocational schools (5-9/10) exist: the Hauptschule Oker, and the Hauptschule Kaiserpfalz. The Sonderschule caters to children with learning difficulties and special needs. The supplementary Public school (government funded), public Waldorf school Harz – Branch Goslar, educates its students along a more spiritual line termed Waldorf Education, anthroposophy, which is based on the teachings of the Austrian pedagogue Rudolf Steiner. At the 10-12 level there are four job-training colleges located at Goslar in crafts, economics, and care for the elderly for students from Goslar district and beyond. There are two public vocational schools offering part-time education within the German dual vocational education, vocational education and training system and full-time education. BBS 1 Goslar -Am Stadtgarten- is focused on education in business administration, economics, health services and information and communications technology (ICT). BBS Goslar-Baßgeige/Seesen is concentrated on education in mechanical, electrical and textile engineering; natural sciences: chemistry, physics, biology; food services, domestic science and industry and administration. The nearest university from Goslar is the old venerable Clausthal University of Technology, Engineering and Mining School atClausthal-Zellerfeld
Clausthal-Zellerfeld is a town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is located in the southwestern part of the Harz mountains. Its population is approximately 15,000. The City is the location of the Clausthal University of Technology. The health resort ...
situated in the Upper Harz mountains some south of Goslar within Goslar district. Some to the south the highly acclaimed University of Göttingen (founded by King George II of Great Britain) is based.
The adult-education program (''Volkshochschule'') of the Goslar district is dedicated to lifelong learning.
Notable people

 * Rudolf Bindig (born 1940), politician (
* Rudolf Bindig (born 1940), politician (SPD
The Social Democratic Party of Germany (german: Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands, ; SPD, ) is a centre-left social democratic political party in Germany. It is one of the major parties of contemporary Germany.
Saskia Esken has been t ...
), Member of Bundestag 1976–2005
* Hans Colbitz (1899–1972), artist, painter, teacher at Albrecht-Duerer-Oberrealschule in Berlin-Neukoelln
* Falko Feldmann (born 1959), German biologist and phytomedicologist
* Sigmar Gabriel (born 1959), politician (SPD), Federal Minister for Foreign Affairs
* Heinz Günther Guderian (1914–2004), officer in the Wehrmacht and later Inspector of armoured mechanized artillery in the German Defence forces Bundeswehr and NATO
* Mathias Hain (born 1972), soccer player
* Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor (1050–1106), King of Kingdom of Germany, Germany and Holy Roman Emperor
* Aaron Hunt (born 1986), footballer
* Ernst Jünger (1895–1998), German soldier (recipient of the Pour le Mérite decoration in World War I) and author, lived in Goslar from December 1933 to 1936. This time represented the beginning of his ''innere Emigration'' (inner emigration), distancing himself from direct political commentary, as he left Berlin following the Gestapo search of his house in April 1933
* Hermann Max (born 1941), church musician and conductor
* Albert Niemann (chemist), Albert Niemann (1834–1861), chemist and pharmacist. Credited with the discovery of cocaine
* Otto Wilhelm August Nieper (1848–1939), Chief Surgeon at the hospital in Goslar, which was renamed the Dr.-Herbert-Nieper-Krankenhaus in his honor.
* Ernst Pistulla (1906–1944), German boxer, competed in the 1928 Summer Olympics
* Wilhelm Ripe (1818–1885), painter and graphic designer
* Maurice, comte de Saxe (1696–1750), Marshal General of France. Adversary of the House of Hanover, Hanoverians
* Ewald Schnug (born 1954), agricultural researcher, professor, Honorary-President of the International Scentific Center for Fertilizers
* Regine Schumann (born 1961), artist, painter and light artist
* Siemens Family. The ancestral home of the Siemens family, who can count toward their more famous offspring, the Prussian-British-Russian industrial pioneers Ernst Werner von Siemens, Werner von Siemens, Carl Wilhelm Siemens, Sir William Siemens and Carl Heinrich von Siemens, Carl von Siemens, is in Goslar
* Rudolf Sprung (1925–2015), politician (Christian Democratic Union of Germany, CDU), Member of Bundestag 1969–1994
* Henning von Tresckow (1901–1944), German military officer and leading anti-Hitler conspirator, was a student at the Goslar Realgymnasium (now Ratsgymnasium Goslar) from 1913 until 1917, when he left to join the army. He boarded in a private home near the school since his own home was far away
* Thomas Wallner (born 1961), consultant (SAP), Ambassador for Martinique
* Phylicia Whitney (Born 1950), journalist and public speaker
* Dieter Zechlin (1926–2012), pianist
References
External links
Mines of Rammelsberg, Historic Town of Goslar and Upper Harz Water Management System
UNESCO Official Website
Official website
*
Sound and video of Marktplatz clock
{{Authority control Goslar, World Heritage Sites in Germany Members of the Hanseatic League Landmarks in Germany Free imperial cities Mining communities in Germany