A phytochorion, in
phytogeography
Phytogeography (from Greek φυτόν, ''phytón'' = "plant" and γεωγραφία, ''geographía'' = "geography" meaning also distribution) or botanical geography is the branch of biogeography that is concerned with the geographic distribution ...
, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both regions overlap. The region of overlap is called a
vegetation tension zone.
In traditional schemes, areas in phytogeography are classified hierarchically, according to the presence of
endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
families, genera or species, e.g., in floral (or floristic, phytogeographic) zones and regions,
[ or also in kingdoms, regions and provinces, sometimes including the categories empire and domain. However, some authors prefer not to rank areas, referring to them simply as "areas", "regions" (in a non hierarchical sense) or "phytochoria".
Systems used to classify vegetation can be divided in two major groups: those that use physiognomic-environmental parameters and characteristics and those that are based on floristic (i.e. shared genera and species) relationships. Phytochoria are defined by their plant taxonomic composition, while other schemes of regionalization (e.g., ]vegetation type
Vegetation classification is the process of classifying and mapping the vegetation over an area of the Earth's surface. Vegetation classification is often performed by state based agencies as part of land use, resource and environmental management ...
, physiognomy
Physiognomy () or face reading is the practice of assessing a person's character or personality from their outer appearance—especially the face. The term can also refer to the general appearance of a person, object, or terrain without referenc ...
, plant formations, biome
A biome () is a distinct geographical region with specific climate, vegetation, and animal life. It consists of a biological community that has formed in response to its physical environment and regional climate. In 1935, Tansley added the ...
s) may variably take in account, depending on the author, the apparent characteristics of a community (the dominant life-form), environment characteristics, the fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively ...
associated, anthropic factors or political
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social sta ...
- conservationist issues.
Explanation
Several systems of classifying geographic areas where plants grow have been devised. Most systems are organized hierarchically, with the largest units subdivided into smaller geographic areas, which are made up of smaller floristic communities, and so on. Phytochoria are defined as areas possessing a large number of endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
. Floristic kingdoms are characterized by a high degree of family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
endemism, floristic regions by a high degree of generic endemism, and floristic provinces by a high degree of species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
endemism. Systems of phytochoria have both significant similarities and differences with zoogeographic provinces, which follow the composition of mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
families
Family (from ) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as ...
, and with biogeographical provinces or terrestrial ecoregions
An ecoregion (ecological region) is an ecology, ecological and Geography, geographic area that exists on multiple different levels, defined by type, quality, and quantity of environmental resources. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of la ...
, which take into account both plant and animal species.
The term "phytochorion" (Werger & van Gils, 1976) is especially associated with the classifications according to the methodology of Josias Braun-Blanquet, which is tied to the presence or absence of particular species, mainly in Africa.
Taxonomic databases tend to be organized in ways which approximate floristic provinces, but which are more closely aligned to political boundaries, for example according to the World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions
The World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions (WGSRPD) is a biogeographical system developed by the international Biodiversity Information Standards (TDWG) organization, formerly the International Working Group on Taxonomic D ...
.
Early schemes
In the late 19th century, Adolf Engler
Heinrich Gustav Adolf Engler (25 March 1844 – 10 October 1930) was a German botanist. He is notable for his work on plant taxonomy and phytogeography, such as ''Die natürlichen Pflanzenfamilien'' (''The Natural Plant Families''), edited with K ...
(1844-1930) was the first to make a world map with the limits of distribution of floras, with four major floral regions (realms). His '' Syllabus der Pflanzenfamilien'', from the third edition (1903) onwards, also included a sketch of the division of the earth into floral regions.
Other important early works on floristics includes Augustin de Candolle
Augustin Pyramus (or Pyrame) de Candolle (, , ; 4 February 17789 September 1841) was a Swiss people, Swiss botany, botanist. René Louiche Desfontaines launched de Candolle's botanical career by recommending him at a herbarium. Within a couple ...
(1820), Schouw (1823), Alphonse de Candolle
Alphonse Louis Pierre Pyramus (or Pyrame) de Candolle (27 October 18064 April 1893) was a French-Swiss botanist, the son of the Swiss botanist Augustin Pyramus de Candolle.
Biography
De Candolle, son of Augustin Pyramus de Candolle, first devot ...
(1855), Drude
In German folklore, a drude (, , pl. ''Druden'') is a kind of malevolent nocturnal spirit (an alp, kobold or hag) associated with nightmares, prevalent especially in Southern Germany. Druden were said to participate in the Wild Hunt and we ...
(1890),[Drude, O. (1890). ''Handbuch der Pflanzengeographie''. Stuttgart: Engelhorn]
French translation: ''Manuel de géographie botanique''. Paris: P. Klincksieck, 1897. 552 p.
Ludwig Diels, Diels (1908), and Rikli (1913).
Good (1947) regionalization
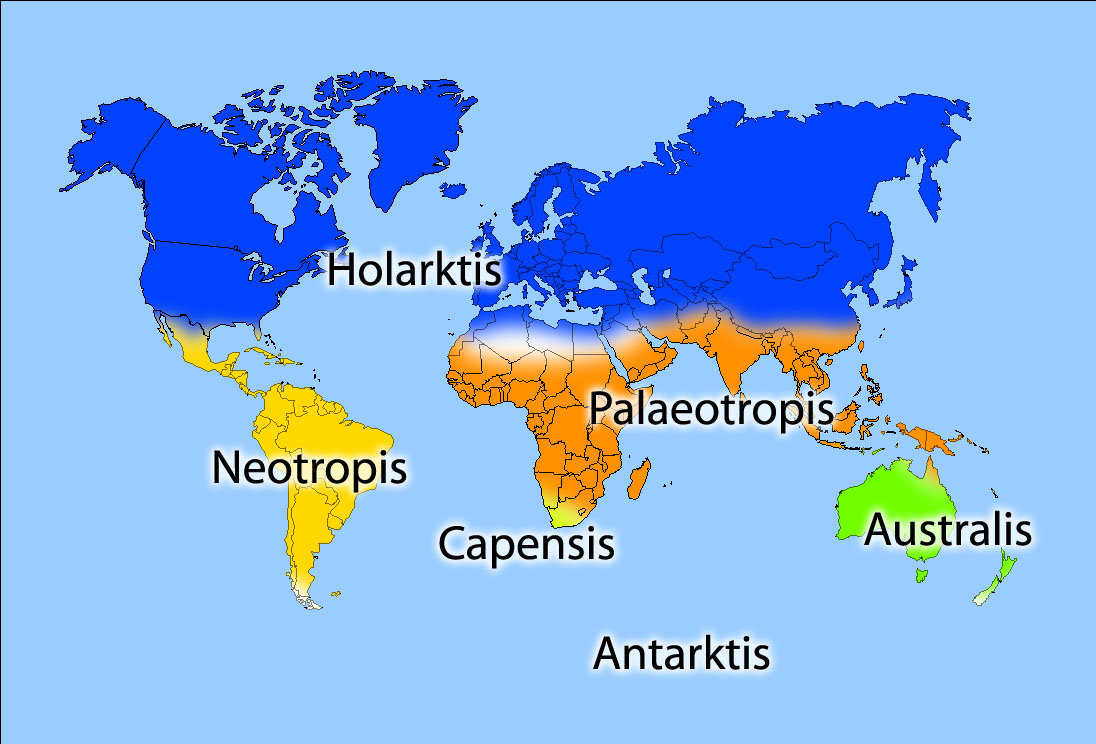 Botanist Ronald Good (1947) identified six floristic kingdoms ( Boreal or Holarctic,
Botanist Ronald Good (1947) identified six floristic kingdoms ( Boreal or Holarctic, Neotropic
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone.
Definition
In biogeogra ...
al, Paleotropical, South African, Australian, and Antarctic
The Antarctic (, ; commonly ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the South Pole, lying within the Antarctic Circle. It is antipodes, diametrically opposite of the Arctic region around the North Pole.
The Antar ...
), the largest natural units he determined for flowering plants. Good's six kingdoms are subdivided into smaller units, called regions and provinces. The Paleotropical kingdom is divided into three subkingdoms, which are each subdivided into floristic regions. Each of the other five kingdoms are subdivided directly into regions. There are a total of 37 floristic regions. Almost all regions are further subdivided into floristic provinces.
Takhtajan (1978, 1986) regionalization
Armen Takhtajan
Armen Leonovich Takhtajan or Takhtajian (; surname also transliterated Takhtadjan, Takhtadzhi︠a︡n or Takhtadzhian, pronounced takh-tuh-JAHN; 10 June 1910 – 13 November 2009), was a Soviet- Armenian botanist, one of the most important fi ...
(1978, 1986), in a widely used scheme that builds on Good's work, identified thirty-five floristic regions, each of which is subdivided into floristic provinces, of which there are 152 in all.
Holarctic kingdom
I.
Circumboreal region
The Circumboreal Region in phytogeography is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in Eurasia and North America, as delineated by such geobotanists as Josias Braun-Blanquet and Armen Takhtajan.
It is the largest floristic region i ...
:1 Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
province
:2 Atlantic Europe
Atlantic Europe encompasses the western portion of Europe which borders the Atlantic Ocean. The term may refer to the idea of Atlantic Europe as a cultural unit and/or as a biogeographical region.
It comprises the British Isles (Great Britain an ...
province
:3 Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
province
:4 Illyria
In classical and late antiquity, Illyria (; , ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; , ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyrians.
The Ancient Gree ...
or Balkan
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
province
:5 Pontus Euxinus
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
province
:6 Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
province
:7 Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
province
:8 Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other ge ...
province
:9 Western Siberia
Western Siberia or West Siberia ( rus, Западная Сибирь, p=ˈzapədnəjə sʲɪˈbʲirʲ; , ) is a region in North Asia. It is part of the wider region of Siberia that is mostly located in the Russia, Russian Federation, with a Sout ...
province
:10 Altai-Sayan province
:11 Central Siberia province
:12 Transbaikalia province
:13 Northeastern Siberia province
:14 Okhotsk-Kamchatka
The Kamchatka Peninsula (, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively.
Immediately offshore along the Pacific ...
province
:15 Canada incl. Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
province
II. Eastern Asiatic region
:16 Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
province
:17 Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in Northeast Asia. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. An islan ...
-Hokkaidō
is the second-largest island of Japan and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by railway via the Seikan Tunnel.
The ...
province
:18 Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
-Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
province
:19 Volcano-Bonin province
:20 Ryūkyū
The , also known as the or the , are a chain of Japanese islands that stretch southwest from Kyushu to Taiwan: the Ryukyu Islands are divided into the Satsunan Islands ( Ōsumi, Tokara and Amami) and Okinawa Prefecture ( Daitō, Miyako, Y ...
or Tokara-Okinawa
most commonly refers to:
* Okinawa Prefecture, Japan's southernmost prefecture
* Okinawa Island, the largest island of Okinawa Prefecture
* Okinawa Islands, an island group including Okinawa itself
* Okinawa (city), the second largest city in th ...
province
:21 Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
province
:22 Northern China
Northern China () and Southern China () are two approximate regions that display certain differences in terms of their geography, demographics, economy, and culture.
Extent
The Qinling, Qinling–Daba Mountains serve as the transition zone ...
province
:23 Central China
Central China () is a List of regions of China, region in China. It mainly includes the provinces of China, provinces of Henan, Hubei and Hunan. Jiangxi is sometimes also regarded to be part of this region. Central China is now officially par ...
province
:24 Southeastern China province
:25 Sikang-Yuennan province
:26 Northern Burma province
:27 Eastern Himalaya
]
The Eastern Himalayas extend from eastern Nepal across Northeast India, Bhutan, the Tibet Autonomous Region to Yunnan in China and northern Myanmar. The climate of this region is influenced by the monsoon of South Asia from June to September. It ...
province
:28 Khasi Hills, Khasi-Manipur
Manipur () is a state in northeastern India with Imphal as its capital. It borders the Indian states of Assam to the west, Mizoram to the south, and Nagaland to the north and shares the international border with Myanmar, specifically t ...
province
III. North American Atlantic region
:29 Appalachian province (forested areas extending east to include the piedmont
Piedmont ( ; ; ) is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the northwest Italy, Northwest of the country. It borders the Liguria region to the south, the Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna regions to the east, and the Aosta Valley region to the ...
and west to the start of the prairies)
:30 Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plain province
:31 North American Prairies province
IV. Rocky Mountain region
:32 Vancouverian province
:33 Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
province
V. Macaronesian region
:34 Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atl ...
province
:35 Madeira
Madeira ( ; ), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (), is an autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous region of Portugal. It is an archipelago situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, in the region of Macaronesia, just under north of ...
province
:36 Canaries province
:37 Cape Verde
Cape Verde or Cabo Verde, officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country and archipelagic state of West Africa in the central Atlantic Ocean, consisting of ten volcanic islands with a combined land area of about . These islands ...
province
VI. Mediterranean region
:38 Southern Morocco province
:39 Southwestern Mediterranean province
:40 South Mediterranean province
:41 Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, compri ...
province
:42 Baleares province
:43 Liguria
Liguria (; ; , ) is a Regions of Italy, region of north-western Italy; its Capital city, capital is Genoa. Its territory is crossed by the Alps and the Apennine Mountains, Apennines Mountain chain, mountain range and is roughly coextensive with ...
- Tyrrhenia province
:44 Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
province
:45 East Mediterranean province
:46 Crimea-Novorossijsk
The Crimean Submediterranean forest complex is an ecoregion on the Black Sea coast of Russia and Ukraine. It is in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome.
Geography
The ecoregion consists of two coastal enclaves on northern coast of the ...
province
VII. Saharo-Arabian region
:47 Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
province
:48 Egypt-Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
province
VIII. Irano-Turanian region
=8A. Western Asiatic subregion
=
:49 Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
province
:50 Central Anatolia province
:51 Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
-Iran province
:52 Hyrcania
Hyrcania (; ''Hyrkanía'', Old Persian: 𐎺𐎼𐎣𐎠𐎴 ''Varkâna'',Lendering (1996) Middle Persian: 𐭢𐭥𐭫𐭢𐭠𐭭 ''Gurgān'', Akkadian: ''Urqananu'') is a historical region composed of the land south-east of the Caspian Sea ...
province
:53 Turania or Aralo-Caspia province
:54 Turkestan province
:55 Northern Baluchistan
Balochistan ( ; , ), also spelled as Baluchistan or Baluchestan, is a historical region in West and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. This arid region of de ...
province
:56 Western Himalaya
The Western Himalayas are the western half of the Himalayas, in Northwestern India, northwestern India and northern Pakistan. Four of the five tributaries of the Indus River in Punjab (Beas River, Beas, Chenab River, Chenab, Jhelum River, Jhelum ...
province
=8B. Central Asiatic subregion
=
:57 Central Tien Shan
The Tian Shan, also known as the Tengri Tagh or Tengir-Too, meaning the "Mountains of God/Heaven", is a large system of mountain ranges in Central Asia. The highest peak is Jengish Chokusu at high and located in Kyrgyzstan. Its lowest point is ...
province
:58 Dzungaria
Dzungaria (; from the Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand'), also known as Northern Xinjiang or Beijiang, is a geographical subregion in Northwest China that corresponds to the northern half of Xinjiang. Bound by the Altai Mountains to the n ...
-Tien Shan province
:59 Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
province
:60 Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
province
IX.
Madrean region
The Madrean region (named after the Sierra Madre Occidental) is a floristic region within the Holarctic kingdom in North America, as delineated by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F. Thorne. It occupies arid or semiarid areas in the southwestern ...
:61 Great Basin
The Great Basin () is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets to the ocean, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja Californi ...
province
:62 Californian province
:63 Sonoran province
:64 Mexican Highlands province
Paleotropical kingdom
X. Guineo-Congolian region
:65 Upper Guinean forests province
:66 Nigeria-Cameroon province
:67 Congo province
XI. Usambara-Zululand region
:68 Zanzibar-Inhambane province
:69 Tongoland-Pondoland province
XII. Sudano-Zambezian region
=12A. Zambezian subregion
=
:70 Zambezi
The Zambezi (also spelled Zambeze and Zambesi) is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers , slightly less than half of t ...
province
=12B. Sahelo–Sudanian subregion
=
:71 Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
province
:72 Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
province
=12C. Eritreo–Arabian subregion
=
:73 Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
-Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
province
:74 South Arabia
South Arabia (), or Greater Yemen, is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jazan, ...
province
:75 Socotra
Socotra, locally known as Saqatri, is a Yemeni island in the Indian Ocean. Situated between the Guardafui Channel and the Arabian Sea, it lies near major shipping routes. Socotra is the largest of the six islands in the Socotra archipelago as ...
province
=12C. Omano-Sindian subregion
=
:76 Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
province
:77 South Iran province
:78 Sindia province
XIII. Karoo-Namib region
:79 Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country on the west coast of Southern Africa. Its borders include the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south; in the no ...
province
:80 Namaland province
:81 Western Cape
The Western Cape ( ; , ) is a provinces of South Africa, province of South Africa, situated on the south-western coast of the country. It is the List of South African provinces by area, fourth largest of the nine provinces with an area of , an ...
province
:82 Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe Khoemana (also known as !Orakobab or Korana) word is a semidesert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its extent is ...
province
XIV. St. Helena and Ascension region
:83 St. Helena
Saint Helena (, ) is one of the three constituent parts of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a remote British overseas territory.
Saint Helena is a volcanic and tropical island, located in the South Atlantic Ocean, some 1,874 km ...
and Ascension province
XV. Madagascan region
:84 Eastern Madagascar province
:85 Western Madagascar province
:86 Southern and Southwestern Madagascar province
:87 Comoro province
:88 Mascarenes province
:89 Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (; Seychellois Creole: ), is an island country and archipelagic state consisting of 155 islands (as per the Constitution) in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, Victoria, ...
province
XVI. Indian region
:90 Ceylon (Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
) province
:91 Malabar province
:92 Deccan
The Deccan is a plateau extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu in the south. It is bound by the mount ...
province
:93 Upper Gangetic Plain province
:94 Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
province
XVII. Indochinese region
:95 South Burma province
:96 Andamans province
:97 South China
South China ( zh, s=, p=Huá'nán, j=jyut6 naam4) is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is ...
province
:98 Thailand province
:99 North Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia (historically known as Indochina and the Indochinese Peninsula) is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to th ...
province
:100 Annam province
:101 South Indochina province
XVIII. Malesian region
=18A. Malesian subregion
=
:102 Malaya province
:103 Borneo
Borneo () is the List of islands by area, third-largest island in the world, with an area of , and population of 23,053,723 (2020 national censuses). Situated at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, it is one of the Greater Sunda ...
province
:104 Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
province
:105 Sumatra
Sumatra () is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the list of islands by area, sixth-largest island in the world at 482,286.55 km2 (182,812 mi. ...
province
:106 Java province
=18B. Papuan subregion
=
:107 Celebes province
:108 Moluccas
The Maluku Islands ( ; , ) or the Moluccas ( ; ) are an archipelago in the eastern part of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located in West Melanesi ...
and West New Guinea province
:109 Papua province
:110 Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago (, ) is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about .
History
The first inhabitants of the archipela ...
province
XIX. Fijian region
:111 New Hebrides
New Hebrides, officially the New Hebrides Condominium () and named after the Hebrides in Scotland, was the colonial name for the island group in the South Pacific Ocean that is now Vanuatu. Native people had inhabited the islands for three th ...
province
:112 Fiji
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about ...
province
XX. Polynesian region
:113 Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of approximately 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Poly ...
province
:114 Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in ...
province
XXI. Hawaiian region
:115 Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
province
XXII. Neocaledonian region
:116 New Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
province
Neotropical kingdom
XXIII. Caribbean region
:117 Central America
Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually ...
province
:118 West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
province
:119 Galápagos Islands
The Galápagos Islands () are an archipelago of volcanic islands in the Eastern Pacific, located around the equator, west of the mainland of South America. They form the Galápagos Province of the Republic of Ecuador, with a population of sli ...
province
XXIV. Region of the Guayana Highlands
:120 The Guianas province
XXV.
Amazon region
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivi ...
:121 Amazonia province
:122 Llanos
The Llanos ( Spanish ''Los Llanos'', "The Plains"; ) is a vast tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela, in northwestern South America. It is an ecoregion of the tropical and subtropical grasslands, ...
province
XXVI. Brazilian region
:123 Caatinga
Caatinga () is a type of semi-arid tropical vegetation, and an ecoregion characterized by this vegetation in interior northeastern Brazil. The name "Caatinga" comes from the Tupi word '' ka'atinga'', meaning "white forest" or "white vegetat ...
province
:124 Central Brazilian Uplands province
:125 Chaco province
:126 Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
province
:127 Paraná province
XXVII. Andean region
:128 Northern Andes province
:129 Central Andes province
South African kingdom
XXVIII. Cape region
:130 Cape province
The Province of the Cape of Good Hope (), commonly referred to as the Cape Province () and colloquially as The Cape (), was a province in the Union of South Africa and subsequently the Republic of South Africa. It encompassed the old Cape Co ...
Australian kingdom
XXIX. Northeast Australian region
:131 North Australia province
:132 Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
province
:133 Southeast Australia province
:134 Tasmania
Tasmania (; palawa kani: ''Lutruwita'') is an island States and territories of Australia, state of Australia. It is located to the south of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland, and is separated from it by the Bass Strait. The sta ...
province
XXX. Southwest Australian region
:135 Southwest Australia
Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna.
The region is also known as the Southwest Au ...
province
XXXI. Central Australian or Eremaean region
:136 Eremaea province
Antarctic kingdom
XXXII. Fernandezian region
:137 Juan Fernández province
XXXIII. Chile-Patagonian region
:138 Northern Chile province
:139 Central Chile province
:140 Pampas
The Pampas (; from Quechua 'plain'), also known as the Pampas Plain, are fertile South American low grasslands that cover more than and include the Argentine provinces of Buenos Aires, La Pampa, Santa Fe, Entre Ríos, and Córdoba; all o ...
province
:141 Patagonia
Patagonia () is a geographical region that includes parts of Argentina and Chile at the southern end of South America. The region includes the southern section of the Andes mountain chain with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers ...
province
:142 Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South America, South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan.
The archipelago consists of the main is ...
province
XXXIV. Region of the South Subantarctic Islands
:143 Tristan
Tristan (Latin/ Brythonic: ''Drustanus''; ; ), also known as Tristran or Tristram and similar names, is the folk hero of the legend of Tristan and Iseult. While escorting the Irish princess Iseult to wed Tristan's uncle, King Mark of ...
- Gough province
:144 Kerguelen province
XXXV. Neozeylandic region
:145 Lord Howe province
:146 Norfolk
Norfolk ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in England, located in East Anglia and officially part of the East of England region. It borders Lincolnshire and The Wash to the north-west, the North Sea to the north and eas ...
province
:147 Kermadec province
:148 Northern New Zealand province
:149 Central New Zealand province
:150 Southern New Zealand province
:151 Chatham province
:152 New Zealand Subantarctic Islands
The New Zealand Subantarctic Islands comprise the five southernmost groups of the New Zealand outlying islands. They are collectively designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Most of the islands lie near the southeast edge of the large ...
province
Regionalization according to Wolfgang Frey and Rainer Lösch (2004, 2010)
;Notes:(with focus on Europe, matching the image on the right)
* The central European region and the central Russian region are sister regions.
* The border between them is similar to the ''Fagus sylvatica
''Fagus sylvatica'', the European beech or common beech, is a large, graceful deciduous tree in the Fagaceae, beech family with smooth silvery-gray bark, large leaf area, and a short trunk with low branches.
Description
''Fagus sylvatica'' i ...
'' limit (January, day-time temperature average: above -2 °C).
* The border between the central Russian region and the boreal region is similar to the ''Quercus
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
'' spp. limit (Day-time temperature average: above 10 °C, 4 months per year).
* The border between the boreal region and the arctic region is similar to the tree line, taiga/arctic tundra limit (July, day-time temperature average: above 10 °C).
* The border of the Atlantic region is the limit of no frost (average), Gulf Stream influence.
* The warm islands in the Atlantic Ocean are in the Macaronesia region: isolated populations in a more humid environment.
* The Mediterranean region is similar to the occurrence of wild '' Olea europea'' and wild '' Cistus salviifolius'' (''Olea europea'' is grown very North in Italy).
* The border between the submediterranean region and the central European region is similar to the alpine arc (upper Rhone, upper Rhine, lower Danube), a weather barrier.
* The Pontic region border is similar to the tree line/ steppe limit (less than 450 mm precipitation per year).
* The Turanian region has a semi-arid climate.
Liu ''et al.'' (2023, 2024) Regionalization
Critiquing previous attempts for their lack of phylogenetic relationships in the construction of their regions, Liu ''et al.'' incorporated distribution data alongside phylogenetic relationships to configure their realms. This led to the classification of eight realms organized into two super-realms and each composed of a number of sub-realms.
* Gondwanan super-realm
:1 African
:2 Indo-Malesian
:3 Australian
:4 Novozealandic
:5 Neotropical
:6 Chile–Patagonian
* Laurasian super-realm
:7 Holarctic
:8 Saharo-Arabian
Differences from Takhtajan's floristic kingdoms mainly focus on emphasizing the uniqueness of certain realms that he had as subdivisions within kingdoms. Two examples are separating some kingdoms into two separate realms, as happened to the Paleotropical and Antarctic kingdoms, reasoning that they have been separated form each other for long enough time to constitute a different phylogenetic trajectory. The merging of the Cape floristic kingdom with the African realm was based by the low endemism of higher taxonomic ranks, which could be found outside the cape region in the rest of Africa. The final major change is the separation of the Saharo-Arabian realm from the Holarctic kingdom, though they admit the northern boundary is not clear, with flora from the Holarctic being found within this area.
After publishing their regions, Dr. Hong Qian criticized Liu ''et al.'' for the inclusion of nonnative distributions in their analyses. In response to this, the group cleaned their data to remove nonnative ranges and reassessed their regions. They suggest that the previous inclusion of exotic species did not significantly affect their mapping and found that the cleaned data revealed the same floristic realms.[Liu, Y., Xu, X., Dimitrov, D., Rahbek, C., & Wang, Z. (2024). Reply to: Reassessing data quality underlying the recently updated floristic map of the world. Nature Communications, 15(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-47544-6 ]
References
Bibliography
* Frodin, D.G. (2001). ''Guide to Standard Floras of the World. An annotated, geographically arranged systematic bibliography of the principal floras, enumerations, checklists and chorological atlases of different areas''. 2nd ed. (1st edn 1984), pp. xxiv, 1100, .Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
{{Biomes
Phytogeography, +
+
+
+
 Botanist Ronald Good (1947) identified six floristic kingdoms ( Boreal or Holarctic,
Botanist Ronald Good (1947) identified six floristic kingdoms ( Boreal or Holarctic,