D layer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The ionosphere () is the
The ionosphere () is the
 At night the F layer is the only layer of significant ionization present, while the ionization in the E and D layers is extremely low. During the day, the D and E layers become much more heavily ionized, as does the F layer, which develops an additional, weaker region of ionization known as the F layer. The F layer persists by day and night and is the main region responsible for the refraction and reflection of radio waves.
At night the F layer is the only layer of significant ionization present, while the ionization in the E and D layers is extremely low. During the day, the D and E layers become much more heavily ionized, as does the F layer, which develops an additional, weaker region of ionization known as the F layer. The F layer persists by day and night and is the main region responsible for the refraction and reflection of radio waves.
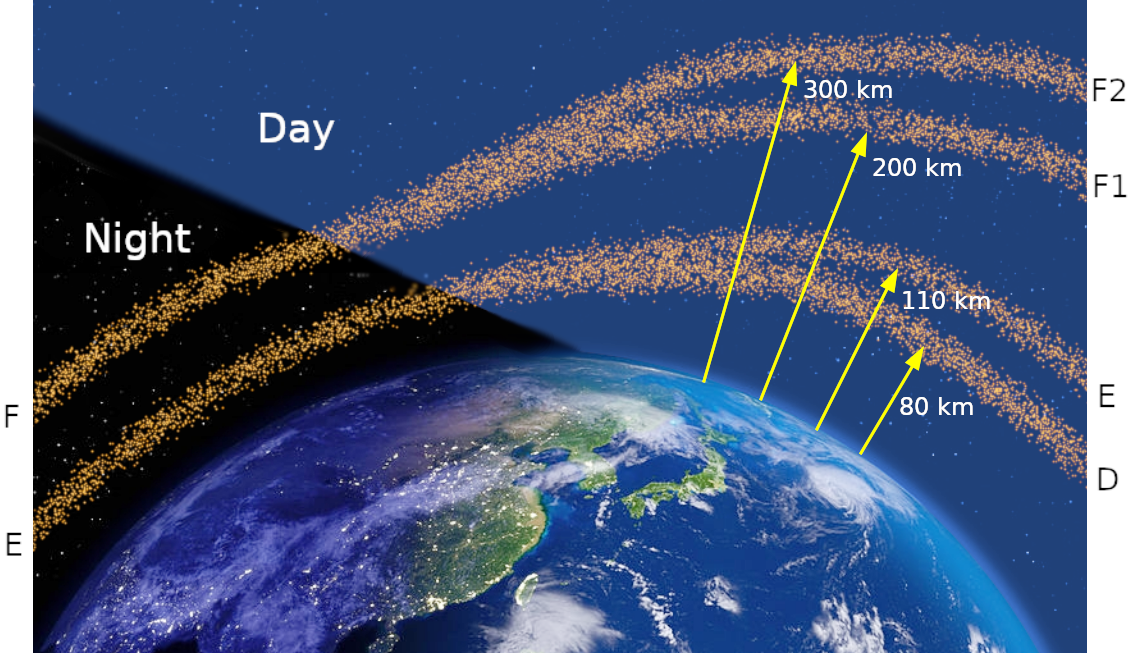

 The F layer or region, also known as the Appleton–Barnett layer, extends from about to more than above the surface of Earth. It is the layer with the highest electron density, which implies signals penetrating this layer will escape into space. Electron production is dominated by extreme ultraviolet (UV, 10–100 nm) radiation ionizing atomic oxygen. The F layer consists of one layer (F) at night, but during the day, a secondary peak (labelled F) often forms in the electron density profile. Because the F layer remains by day and night, it is responsible for most
The F layer or region, also known as the Appleton–Barnett layer, extends from about to more than above the surface of Earth. It is the layer with the highest electron density, which implies signals penetrating this layer will escape into space. Electron production is dominated by extreme ultraviolet (UV, 10–100 nm) radiation ionizing atomic oxygen. The F layer consists of one layer (F) at night, but during the day, a secondary peak (labelled F) often forms in the electron density profile. Because the F layer remains by day and night, it is responsible for most
 Ionograms allow deducing, via computation, the true shape of the different layers. Nonhomogeneous structure of the
Ionograms allow deducing, via computation, the true shape of the different layers. Nonhomogeneous structure of the

NASA/JPL: Titan's upper atmosphere
Accessed 2010-08-25 Ionospheres have also been observed at Io, Europa, Ganymede, Triton, and
SWPC's Radio User's Page
'.
Amsat-Italia project on Ionospheric propagation (ESA SWENET website)
Layman Level Explanations Of "Seemingly" Mysterious 160 Meter (MF/HF) Propagation Occurrences
USGS Geomagnetism ProgramEncyclopædia Britannica, Ionosphere and magnetosphereCurrent Space Weather ConditionsSuper Dual Auroral Radar NetworkEuropean Incoherent Scatter radar system
{{Authority control Terrestrial plasmas Radio frequency propagation
 The ionosphere () is the
The ionosphere () is the ionized
Ionization or ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule i ...
part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of a location's vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) in reference to a vertical datum based on a historic mean sea level. In geodesy, it is formalized as orthometric height. The zero level ...
, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere
The exosphere is a thin, atmosphere-like volume surrounding a planet or natural satellite where molecules are gravitationally bound to that body, but where the density is so low that the molecules are essentially collision-less. In the case of ...
. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrared (typically p ...
. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity
Atmospheric electricity describes the electrical charges in the Earth's atmosphere (or that of another planet). The movement of charge between the Earth's surface, the atmosphere, and the ionosphere is known as the global atmospheric electrica ...
and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves as they travel, or are wave propagation, propagated, from one point to another in vacuum, or into various parts of the atmosphere.
As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio w ...
to distant places on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
. Travel through this layer also impacts GPS signals, resulting in effects such as deflection in their path and delay in the arrival of the signal.
History of discovery
As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicistCarl Friedrich Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observatory and ...
postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquess of Marconi ( ; ; 25 April 1874 – 20 July 1937) was an Italian electrical engineer, inventor, and politician known for his creation of a practical radio wave-based Wireless telegraphy, wireless tel ...
received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
) using a kite-supported antenna for reception. The transmitting station in Poldhu, Cornwall, used a spark-gap transmitter
A spark-gap transmitter is an obsolete type of transmitter, radio transmitter which generates radio waves by means of an electric spark."Radio Transmitters, Early" in Spark-gap transmitters were the first type of radio transmitter, and were the m ...
to produce a signal with a frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
of approximately 500 kHz and a power of 100 times more than any radio signal previously produced. The message received was three dits, the Morse code
Morse code is a telecommunications method which Character encoding, encodes Written language, text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code i ...
for the letter S. To reach Newfoundland the signal would have to bounce off the ionosphere twice. Dr. Jack Belrose has contested this, however, based on theoretical and experimental work. However, Marconi did achieve transatlantic wireless communications in Glace Bay, Nova Scotia, one year later.
In 1902, Oliver Heaviside
Oliver Heaviside ( ; 18 May 1850 – 3 February 1925) was an English mathematician and physicist who invented a new technique for solving differential equations (equivalent to the Laplace transform), independently developed vector calculus, an ...
proposed the existence of the Kennelly–Heaviside layer
The Heaviside layer, sometimes called the Kennelly–Heaviside layer, named after Arthur E. Kennelly and Oliver Heaviside, is a layer of ionised gas occurring roughly between above the ground — one of several layers in the Earth's ion ...
of the ionosphere which bears his name. Heaviside's proposal included means by which radio signals are transmitted around the Earth's curvature. Also in 1902, Arthur Edwin Kennelly discovered some of the ionosphere's radio-electrical properties.
In 1912, the U.S. Congress imposed the Radio Act of 1912 on amateur radio operators, limiting their operations to frequencies above 1.5 MHz (wavelength 200 meters or smaller). The government thought those frequencies were useless. This led to the discovery of HF radio propagation via the ionosphere in 1923.
In 1925, observations during a solar eclipse in New York by Dr. Alfred N. Goldsmith and his team demonstrated the influence of sunlight on radio wave propagation, revealing that short waves became weak or inaudible while long waves steadied during the eclipse, thus contributing to the understanding of the ionosphere's role in radio transmission.
In 1926, Scottish physicist Robert Watson-Watt introduced the term ''ionosphere'' in a letter published only in 1969 in ''Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
'':
In the early 1930s, test transmissions of Radio Luxembourg inadvertently provided evidence of the first radio modification of the ionosphere; HAARP ran a series of experiments in 2017 using the eponymous Luxembourg Effect.
Edward V. Appleton was awarded a Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were first awarded in 1901, marking the fifth anniversary of Alfred N ...
in 1947 for his confirmation in 1927 of the existence of the ionosphere. Lloyd Berkner first measured the height and density of the ionosphere. This permitted the first complete theory of short-wave radio propagation. Maurice V. Wilkes and J. A. Ratcliffe researched the topic of radio propagation of very long radio waves in the ionosphere. Vitaly Ginzburg has developed a theory of electromagnetic wave propagation in plasmas such as the ionosphere.
In 1962, the Canadian
Canadians () are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''C ...
satellite Alouette 1 was launched to study the ionosphere. Following its success were Alouette 2 in 1965 and the two ISIS
Isis was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingdom () as one of the main characters of the Osiris myth, in which she resurrects her sla ...
satellites in 1969 and 1971, further AEROS-A and -B in 1972 and 1975, all for measuring the ionosphere.
On July 26, 1963, the first operational geosynchronous satellite Syncom 2 was launched. On board radio beacons on this satellite (and its successors) enabled – for the first time – the measurement of total electron content (TEC) variation along a radio beam from geostationary orbit to an earth receiver. (The rotation of the plane of polarization directly measures TEC along the path.) Australian geophysicist Elizabeth Essex-Cohen from 1969 onwards was using this technique to monitor the atmosphere above Australia and Antarctica.
Geophysics
The ionosphere is a shell ofelectron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s and electrically charged atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s and molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s that surrounds the Earth, stretching from a height of about to more than . It exists primarily due to ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
radiation from the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
.
The lowest part of the Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weathe ...
, the troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
, extends from the surface to about . Above that is the stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second-lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is composed of stratified temperature zones, with the warmer layers of air located higher ...
, followed by the mesosphere. In the stratosphere incoming solar radiation creates the ozone layer
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the a ...
. At heights of above , in the thermosphere, the atmosphere is so thin that free electrons can exist for short periods of time before they are captured by a nearby positive ion. The number of these free electrons is sufficient to affect radio propagation
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves as they travel, or are wave propagation, propagated, from one point to another in vacuum, or into various parts of the atmosphere.
As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio w ...
. This portion of the atmosphere is partially ''ionized'' and contains a plasma which is referred to as the ionosphere.
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
(UV), X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
and shorter wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
s of solar radiation
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrared (typically p ...
are ''ionizing,'' since photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s at these frequencies contain sufficient energy to dislodge an electron from a neutral gas atom or molecule upon absorption. In this process the light electron obtains a high velocity so that the temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
of the created electronic gas is much higher (of the order of thousand K) than the one of ions and neutrals. The reverse process to ionization
Ionization or ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive Electric charge, charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged at ...
is recombination, in which a free electron is "captured" by a positive ion. Recombination occurs spontaneously, and causes the emission of a photon carrying away the energy produced upon recombination. As gas density increases at lower altitudes, the recombination process prevails, since the gas molecules and ions are closer together. The balance between these two processes determines the quantity of ionization present.
Ionization depends primarily on the Sun and its Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) and X-ray irradiance which varies strongly with solar activity
Solar phenomena are natural phenomena which occur within the Stellar atmosphere, atmosphere of the Sun. They take many forms, including solar wind, Solar radio emission, radio wave flux, solar flares, coronal mass ejections, Stellar corona#Coron ...
. The more magnetically active the Sun is, the more sunspot
Sunspots are temporary spots on the Sun's surface that are darker than the surrounding area. They are one of the most recognizable Solar phenomena and despite the fact that they are mostly visible in the solar photosphere they usually aff ...
active regions there are on the Sun at any one time. Sunspot active regions are the source of increased coronal heating and accompanying increases in EUV and X-ray irradiance, particularly during episodic magnetic eruptions that include solar flares
A solar flare is a relatively intense, localized emission of electromagnetic radiation in the Stellar atmosphere, Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar partic ...
that increase ionization on the sunlit side of the Earth and solar energetic particle events that can increase ionization in the polar regions. Thus the degree of ionization in the ionosphere follows both a diurnal (time of day) cycle and the 11-year solar cycle
The Solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of Modern Maximum, variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun ...
. There is also a seasonal dependence in ionization degree since the local winter hemisphere
Hemisphere may refer to:
In geometry
* Hemisphere (geometry), a half of a sphere
As half of Earth or any spherical astronomical object
* A hemisphere of Earth
** Northern Hemisphere
** Southern Hemisphere
** Eastern Hemisphere
** Western Hemi ...
is tipped away from the Sun, thus there is less received solar radiation. Radiation received also varies with geographical location (polar, auroral
An aurora ( aurorae or auroras),
also commonly known as the northern lights (aurora borealis) or southern lights (aurora australis), is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly observed in polar regions of Earth, high-latitude ...
zones, mid-latitudes, and equatorial regions). There are also mechanisms that disturb the ionosphere and decrease the ionization.
Sydney Chapman proposed that the region below the ionosphere be called ''neutrosphere''
(the ''neutral atmosphere'').
Layers of ionization

D layer
The D layer is the innermost layer, above the surface of the Earth. Ionization here is due to Lyman series-alpha hydrogen radiation at awavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of 121.6 nanometre
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the Molecule">molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm), or nanometer (American spelling), is a unit of length ...
(nm) ionizing nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes den ...
(NO). In addition, solar flares
A solar flare is a relatively intense, localized emission of electromagnetic radiation in the Stellar atmosphere, Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar partic ...
can generate hard X-rays (wavelength ) that ionize N and O. Recombination rates are high in the D layer, so there are many more neutral air molecules than ions.
Medium frequency (MF) and lower high frequency (HF) radio wave
Radio waves (formerly called Hertzian waves) are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies below 300 gigahertz (GHz) and wavelengths g ...
s are significantly attenuated within the D layer, as the passing radio waves cause electrons to move, which then collide with the neutral molecules, giving up their energy. Lower frequencies experience greater absorption because they move the electrons farther, leading to greater chance of collisions. This is the main reason for absorption of HF radio waves, particularly at 10 MHz and below, with progressively less absorption at higher frequencies. This effect peaks around noon and is reduced at night due to a decrease in the D layer's thickness; only a small part remains due to cosmic rays
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar ...
. A common example of the D layer in action is the disappearance of distant AM broadcast band stations in the daytime.
During solar proton events, ionization can reach unusually high levels in the D-region over high and polar latitudes. Such very rare events are known as Polar Cap Absorption (PCA) events, because the increased ionization significantly enhances the absorption of radio signals passing through the region. In fact, absorption levels can increase by many tens of dB during intense events, which is enough to absorb most (if not all) transpolar HF radio signal transmissions. Such events typically last less than 24 to 48 hours.
E layer
The E layer is the middle layer, above the surface of the Earth. Ionization is due to soft X-ray (1–10 nm) and far ultraviolet (UV) solar radiation ionization of molecularoxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
(O). Normally, at oblique incidence, this layer can only reflect radio waves having frequencies lower than about 10 MHz and may contribute a bit to absorption on frequencies above. However, during intense sporadic E events, the E layer can reflect frequencies up to 50 MHz and higher. The vertical structure of the E layer is primarily determined by the competing effects of ionization and recombination. At night the E layer weakens because the primary source of ionization is no longer present. After sunset an increase in the height of the E layer maximum increases the range to which radio waves can travel by reflection from the layer.
This region is also known as the Kennelly–Heaviside layer
The Heaviside layer, sometimes called the Kennelly–Heaviside layer, named after Arthur E. Kennelly and Oliver Heaviside, is a layer of ionised gas occurring roughly between above the ground — one of several layers in the Earth's ion ...
or simply the Heaviside layer. Its existence was predicted in 1902 independently and almost simultaneously by the American electrical engineer Arthur Edwin Kennelly (1861–1939) and the British physicist Oliver Heaviside
Oliver Heaviside ( ; 18 May 1850 – 3 February 1925) was an English mathematician and physicist who invented a new technique for solving differential equations (equivalent to the Laplace transform), independently developed vector calculus, an ...
(1850–1925). In 1924 its existence was detected by Edward V. Appleton and Miles Barnett.
E layer
The E layer ( sporadic E-layer) is characterized by small, thin clouds of intense ionization, which can support reflection of radio waves, frequently up to 50 MHz and rarely up to 450 MHz. Sporadic-E events may last for just a few minutes to many hours. Sporadic E propagation makes VHF-operating byradio amateurs
An amateur radio operator is someone who uses equipment at an amateur radio station to engage in two-way personal communications with other amateur operators on radio frequencies assigned to the amateur radio service. Amateur radio operators ...
very exciting when long-distance propagation paths that are generally unreachable "open up" to two-way communication. There are multiple causes of sporadic-E that are still being pursued by researchers. This propagation occurs every day during June and July in northern hemisphere mid-latitudes when high signal levels are often reached. The skip distances are generally around . Distances for one hop propagation can be anywhere from . Multi-hop propagation over is also common, sometimes to distances of or more.
F layer
skywave
In radio communication, skywave or skip refers to the propagation of radio waves reflected or refracted back toward Earth from the ionosphere, an electrically charged layer of the upper atmosphere. Since it is not limited by the curvatur ...
propagation of radio
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connec ...
waves and long distance high frequency
High frequency (HF) is the ITU designation for the band of radio waves with frequency between 3 and 30 megahertz (MHz). It is also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as its wavelengths range from one to ten decameters (ten to one ...
(HF, or shortwave
Shortwave radio is radio transmission using radio frequencies in the shortwave bands (SW). There is no official definition of the band range, but it always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz (app ...
) radio communications.
Above the F layer, the number of oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
ions decreases and lighter ions such as hydrogen and helium become dominant. This region above the F layer peak and below the plasmasphere is called the topside ionosphere.
From 1972 to 1975 NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
launched the AEROS and AEROS B satellites to study the F region. p. 12 AEROS
Ionospheric model
An ionospheric model is a mathematical description of the ionosphere as a function of location, altitude, day of year, phase of the sunspot cycle and geomagnetic activity. Geophysically, the state of the ionospheric plasma may be described by four parameters: ''electron density, electron and iontemperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
'' and, since several species of ions are present, ''ionic composition''. Radio propagation
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves as they travel, or are wave propagation, propagated, from one point to another in vacuum, or into various parts of the atmosphere.
As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio w ...
depends uniquely on electron density.
Models are usually expressed as computer programs. The model may be based on basic physics of the interactions of the ions and electrons with the neutral atmosphere and sunlight, or it may be a statistical description based on a large number of observations or a combination of physics and observations. One of the most widely used models is the International Reference Ionosphere (IRI), which is based on data and specifies the four parameters just mentioned. The IRI is an international project sponsored by the Committee on Space Research (COSPAR) and the International Union of Radio Science
The International Union of Radio Science (abbreviated ''URSI'', after its French name, ) is one of 26 international scientific unions affiliated to the International Council for Science (ICSU).
History and objectives
URSI was officially cr ...
(URSI). The major data sources are the worldwide network of ionosonde
An ionosonde, or chirpsounder, is a special radar for the examination of the ionosphere. The basic ionosonde technology was invented in 1925 by Gregory Breit and Merle A. Tuve and further developed in the late 1920s by a number of prominent phys ...
s, the powerful incoherent scatter radars (Jicamarca, Arecibo
Arecibo (; ) is a Arecibo barrio-pueblo, city and Municipalities of Puerto Rico, municipality on the northern coast of Puerto Rico, on the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, located north of Utuado, Puerto Rico, Utuado and Ciales, Puerto Rico, Ciale ...
, Millstone Hill, Malvern, St Santin), the ISIS and Alouette topside sounders, and in situ instruments on several satellites and rockets. IRI is updated yearly. IRI is more accurate in describing the variation of the electron density from bottom of the ionosphere to the altitude of maximum density than in describing the total electron content (TEC). Since 1999 this model is "International Standard" for the terrestrial ionosphere (standard TS16457).
Persistent anomalies to the idealized model
 Ionograms allow deducing, via computation, the true shape of the different layers. Nonhomogeneous structure of the
Ionograms allow deducing, via computation, the true shape of the different layers. Nonhomogeneous structure of the electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
/ ion- plasma produces rough echo traces, seen predominantly at night and at higher latitudes, and during disturbed conditions.
Winter anomaly
At mid-latitudes, the F2 layer daytime ion production is higher in the summer, as expected, since the Sun shines more directly on the Earth. However, there are seasonal changes in the molecular-to-atomic ratio of the neutral atmosphere that cause the summer ion loss rate to be even higher. The result is that the increase in the summertime loss overwhelms the increase in summertime production, and total F2 ionization is actually lower in the local summer months. This effect is known as the winter anomaly. The anomaly is always present in the northern hemisphere, but is usually absent in the southern hemisphere during periods of low solar activity.Equatorial anomaly
Within approximately ± 20 degrees of the ''magnetic equator'', is the ''equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
ial anomaly.'' It is the occurrence of a trough in the ionization in the F2 layer at the equator and crests at about 17 degrees in magnetic latitude. The Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from structure of Earth, Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from ...
lines are horizontal at the magnetic equator. Solar heating and tidal oscillations in the lower ionosphere move plasma up and across the magnetic field lines. This sets up a sheet of electric current in the E region which, with the horizontal magnetic field, forces ionization up into the F layer, concentrating at ± 20 degrees from the magnetic equator. This phenomenon is known as the ''equatorial fountain''.
Equatorial electrojet
The worldwide solar-driven wind results in the so-called Sq (solar quiet) current system in the E region of the Earth's ionosphere ( ionospheric dynamo region) ( altitude). Resulting from this current is an electrostatic field directed west–east (dawn–dusk) in the equatorial day side of the ionosphere. At the magnetic dip equator, where the geomagnetic field is horizontal, this electric field results in an enhanced eastward current flow within ± 3 degrees of the magnetic equator, known as the equatorial electrojet.Ephemeral ionospheric perturbations
X-rays: sudden ionospheric disturbances (SID)
When the Sun is active, strongsolar flare
A solar flare is a relatively intense, localized emission of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and ot ...
s can occur that hit the sunlit side of Earth with hard X-rays. The X-rays penetrate to the D-region, releasing electrons that rapidly increase absorption, causing a high frequency (3–30 MHz) radio blackout that can persist for many hours after strong flares. During this time very low frequency (3–30 kHz) signals will be reflected by the D layer instead of the E layer, where the increased atmospheric density will usually increase the absorption of the wave and thus dampen it. As soon as the X-rays end, the sudden ionospheric disturbance (SID) or radio black-out steadily declines as the electrons in the D-region recombine rapidly and propagation gradually returns to pre-flare conditions over minutes to hours depending on the solar flare strength and frequency.
Protons: polar cap absorption (PCA)
Associated with solar flares is a release of high-energy protons. These particles can hit the Earth within 15 minutes to 2 hours of the solar flare. The protons spiral around and down the magnetic field lines of the Earth and penetrate into the atmosphere near the magnetic poles increasing the ionization of the D and E layers. PCA's typically last anywhere from about an hour to several days, with an average of around 24 to 36 hours.Coronal mass ejection
A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant ejection of plasma mass from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accepted theoretical understandin ...
s can also release energetic protons that enhance D-region absorption in the polar regions.
Storms
Geomagnetic storms and ionospheric storms are temporary and intense disturbances of the Earth'smagnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
and ionosphere.
During a geomagnetic storm the F₂ layer will become unstable, fragment, and may even disappear completely. In the Northern and Southern polar regions of the Earth aurora
An aurora ( aurorae or auroras),
also commonly known as the northern lights (aurora borealis) or southern lights (aurora australis), is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly observed in high-latitude regions (around the Arc ...
e will be observable in the night sky.
Lightning
Lightning can cause ionospheric perturbations in the D-region in one of two ways. The first is through VLF (very low frequency) radio waves launched into themagnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
. These so-called "whistler" mode waves can interact with radiation belt particles and cause them to precipitate onto the ionosphere, adding ionization to the D-region. These disturbances are called "lightning-induced electron precipitation Electron precipitation (also called energetic electron precipitation or EEP) is an atmospheric phenomenon that occurs when previously trapped electrons enter the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere, thus creating communications interferences and ...
" (LEP) events.
Additional ionization can also occur from direct heating/ionization as a result of huge motions of charge in lightning strikes. These events are called early/fast.
In 1925, C. T. R. Wilson proposed a mechanism by which electrical discharge from lightning storms could propagate upwards from clouds to the ionosphere. Around the same time, Robert Watson-Watt, working at the Radio Research Station in Slough, UK, suggested that the ionospheric sporadic E layer (Es) appeared to be enhanced as a result of lightning but that more work was needed. In 2005, C. Davis and C. Johnson, working at the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory in Oxfordshire, UK, demonstrated that the Es layer was indeed enhanced as a result of lightning activity. Their subsequent research has focused on the mechanism by which this process can occur.
Applications
Radio communication
Due to the ability of ionized atmospheric gases to refract high frequency (HF, orshortwave
Shortwave radio is radio transmission using radio frequencies in the shortwave bands (SW). There is no official definition of the band range, but it always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz (app ...
) radio waves, the ionosphere can reflect radio waves directed into the sky back toward the Earth. Radio waves directed at an angle into the sky can return to Earth beyond the horizon. This technique, called "skip" or "skywave
In radio communication, skywave or skip refers to the propagation of radio waves reflected or refracted back toward Earth from the ionosphere, an electrically charged layer of the upper atmosphere. Since it is not limited by the curvatur ...
" propagation, has been used since the 1920s to communicate at international or intercontinental distances. The returning radio waves can reflect off the Earth's surface into the sky again, allowing greater ranges to be achieved with multiple hops. This communication method is variable and unreliable, with reception over a given path depending on time of day or night, the seasons, weather, and the 11-year sunspot cycle. During the first half of the 20th century it was widely used for transoceanic telephone and telegraph service, and business and diplomatic communication. Due to its relative unreliability, shortwave radio communication has been mostly abandoned by the telecommunications industry, though it remains important for high-latitude communication where the availability of satellite-based radio communication may be insufficient. Shortwave broadcasting is useful in crossing international boundaries and covering large areas at low cost. Automated services still use shortwave radio
Shortwave radio is radio transmission using radio frequencies in the shortwave bands (SW). There is no official definition of the band range, but it always includes all of the High frequency, high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30& ...
frequencies, as do radio amateur hobbyists for private recreational contacts and to assist with emergency communications during natural disasters. Armed forces use shortwave so as to be independent of vulnerable infrastructure, including satellites, and the low latency of shortwave communications make it attractive to stock traders, where milliseconds count.
Mechanism of refraction
When a radio wave reaches the ionosphere, theelectric field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) descri ...
in the wave forces the electrons in the ionosphere into oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
at the same frequency as the radio wave. Some of the radio-frequency energy is given up to this resonant oscillation. The oscillating electrons will then either be lost to recombination or will re-radiate the original wave energy. Total refraction can occur when the collision frequency of the ionosphere is less than the radio frequency, and if the electron density in the ionosphere is great enough.
A qualitative understanding of how an electromagnetic wave propagates through the ionosphere can be obtained by recalling geometric optics
Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician ...
. Since the ionosphere is a plasma, it can be shown that the refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refrac ...
is less than unity. Hence, the electromagnetic "ray" is bent away from the normal rather than toward the normal as would be indicated when the refractive index is greater than unity. It can also be shown that the refractive index of a plasma, and hence the ionosphere, is frequency-dependent, see Dispersion (optics)
Dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency. Sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used to refer to optics specifically, as opposed to wave propagation in general. A medium having this common ...
.
The critical frequency is the limiting frequency at or below which a radio wave is reflected by an ionospheric layer at vertical incidence. If the transmitted frequency is higher than the plasma frequency of the ionosphere, then the electrons cannot respond fast enough, and they are not able to re-radiate the signal. It is calculated as shown below:
:
where N = electron density per m3 and fcritical is in Hz.
The Maximum Usable Frequency (MUF) is defined as the upper frequency limit that can be used for transmission between two points at a specified time.
:
where = angle of arrival, the angle of the wave relative to the horizon
The horizon is the apparent curve that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This curve divides all viewing directions based on whethe ...
, and sin is the sine
In mathematics, sine and cosine are trigonometric functions of an angle. The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right triangle: for the specified angle, its sine is the ratio of the length of the side opposite th ...
function.
The cutoff frequency
In physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced ( attenuated or reflected) rather than ...
is the frequency below which a radio wave fails to penetrate a layer of the ionosphere at the incidence angle required for transmission between two specified points by refraction from the layer.
GPS/GNSS ionospheric correction
There are a number of models used to understand the effects of the ionosphere on global navigation satellite systems. The Klobuchar model is currently used to compensate for ionospheric effects in GPS. This model was developed at the US Air Force Geophysical Research Laboratory circa 1974 by John (Jack) Klobuchar. TheGalileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
navigation system uses the NeQuick model. GALILEO broadcasts 3 coefficients to compute the effective ionization level, which is then used by the NeQuick model to compute a range delay along the line-of-sight.
Other applications
The open systemelectrodynamic tether
Electrodynamic tethers (EDTs) are long conducting wires, such as one deployed from a tether satellite, which can operate on electromagnetism, electromagnetic principles as electrical generator, generators, by converting their kinetic energy to ele ...
, which uses the ionosphere, is being researched. The space tether uses plasma contactors and the ionosphere as parts of a circuit to extract energy from the Earth's magnetic field by electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force, electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field.
Michael Faraday is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1 ...
.
Measurements

Overview
Scientists explore the structure of the ionosphere by a wide variety of methods. They include: * passive observations of optical and radio emissions generated in the ionosphere * bouncing radio waves of different frequencies from it * incoherent scatter radars such as the EISCAT, Sondre Stromfjord, Millstone Hill,Arecibo
Arecibo (; ) is a Arecibo barrio-pueblo, city and Municipalities of Puerto Rico, municipality on the northern coast of Puerto Rico, on the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, located north of Utuado, Puerto Rico, Utuado and Ciales, Puerto Rico, Ciale ...
, Advanced Modular Incoherent Scatter Radar (AMISR) and Jicamarca radars
* coherent scatter radars such as the Super Dual Auroral Radar Network (SuperDARN) radars
* special receivers to detect how the reflected waves have changed from the transmitted waves.
A variety of experiments, such as HAARP ( High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program), involve high power radio transmitters to modify the properties of the ionosphere. These investigations focus on studying the properties and behavior of ionospheric plasma, with particular emphasis on being able to understand and use it to enhance communications and surveillance systems for both civilian and military purposes. HAARP was started in 1993 as a proposed twenty-year experiment, and is currently active near Gakona, Alaska.
The SuperDARN radar project researches the high- and mid-latitudes using coherent backscatter of radio waves in the 8 to 20 MHz range. Coherent backscatter is similar to Bragg scattering in crystals and involves the constructive interference of scattering from ionospheric density irregularities. The project involves more than 11 countries and multiple radars in both hemispheres.
Scientists are also examining the ionosphere by the changes to radio waves, from satellites and stars, passing through it. The Arecibo Telescope located in Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
, was originally intended to study Earth's ionosphere.
Ionograms
Ionograms show the virtual heights and critical frequencies of the ionospheric layers and which are measured by anionosonde
An ionosonde, or chirpsounder, is a special radar for the examination of the ionosphere. The basic ionosonde technology was invented in 1925 by Gregory Breit and Merle A. Tuve and further developed in the late 1920s by a number of prominent phys ...
. An ionosonde sweeps a range of frequencies, usually from 0.1 to 30 MHz, transmitting at vertical incidence to the ionosphere. As the frequency increases, each wave is refracted less by the ionization in the layer, and so each penetrates further before it is reflected. Eventually, a frequency is reached that enables the wave to penetrate the layer without being reflected. For ordinary mode waves, this occurs when the transmitted frequency just exceeds the peak plasma, or critical, frequency of the layer. Tracings of the reflected high frequency radio pulses are known as ionograms. Reduction rules are given in: "URSI Handbook of Ionogram Interpretation and Reduction", edited by William Roy Piggott and Karl Rawer, Elsevier Amsterdam, 1961 (translations into Chinese, French, Japanese and Russian are available).
Incoherent scatter radars
Incoherent scatter radars operate above the critical frequencies. Therefore, the technique allows probing the ionosphere, unlike ionosondes, also above the electron density peaks. The thermal fluctuations of the electron density scattering the transmitted signals lack coherence, which gave the technique its name. Their power spectrum contains information not only on the density, but also on the ion and electron temperatures, ion masses and drift velocities. Incoherent scatter radars can also measure neutral atmosphere movements, such as atmospheric tides, after making assumptions about ion-neutralcollision frequency
Collision frequency describes the rate of collisions between two atomic or molecular species in a given volume, per unit time. In an ideal gas, assuming that the species behave like hard spheres, the collision frequency between entities of speci ...
across the ionospheric dynamo region.
GNSS radio occultation
Radio occultation is aremote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an physical object, object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring inform ...
technique where a GNSS signal tangentially scrapes the Earth, passing through the atmosphere, and is received by a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite. As the signal passes through the atmosphere, it is refracted, curved and delayed. An LEO satellite samples the total electron content and bending angle of many such signal paths as it watches the GNSS satellite rise or set behind the Earth. Using an Inverse Abel's transform, a radial profile of refractivity at that tangent point on earth can be reconstructed.
Major GNSS radio occultation missions include the GRACE
Grace may refer to:
Places United States
* Grace, Idaho, a city
* Grace (CTA station), Chicago Transit Authority's Howard Line, Illinois
* Little Goose Creek (Kentucky), location of Grace post office
* Grace, Carroll County, Missouri, an uni ...
, CHAMP, and COSMIC.
Indices of the ionosphere
In empirical models of the ionosphere such as Nequick, the following indices are used as indirect indicators of the state of the ionosphere.Solar intensity
F10.7 and R12 are two indices commonly used in ionospheric modelling. Both are valuable for their long historical records covering multiple solar cycles. F10.7 is a measurement of the intensity of solar radio emissions at a frequency of 2800 MHz made using a groundradio telescope
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna (radio), antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the r ...
. R12 is a 12 months average of daily sunspot numbers. The two indices have been shown to be correlated with each other.
However, both indices are only indirect indicators of solar ultraviolet and X-ray emissions, which are primarily responsible for causing ionization in the Earth's upper atmosphere. We now have data from the GOES
The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES), operated by the United States' National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)'s National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service division, supports weather fo ...
spacecraft that measures the background X-ray flux from the Sun, a parameter more closely related to the ionization levels in the ionosphere.
Geomagnetic disturbances
* The '' A''- and '' K''-indices are a measurement of the behavior of the horizontal component of the geomagnetic field. The ''K''-index uses a semi-logarithmic scale from 0 to 9 to measure the strength of the horizontal component of the geomagnetic field. The Boulder ''K''-index is measured at the Boulder Geomagnetic Observatory. * The geomagnetic activity levels of the Earth are measured by the fluctuation of the Earth's magnetic field in SI units called teslas (or in non-SIgauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, Geodesy, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observat ...
, especially in older literature). The Earth's magnetic field is measured around the planet by many observatories. The data retrieved is processed and turned into measurement indices. Daily measurements for the entire planet are made available through an estimate of the ''A''p-index, called the ''planetary A-index'' (PAI).
Ionospheres of other planets and natural satellites
Objects in the Solar System that have appreciable atmospheres (i.e., all of the major planets and many of the largernatural satellite
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are colloquially referred to as moons, a deriv ...
s) generally produce ionospheres. Planets known to have ionospheres include Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
, Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
, Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
, Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
, Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile ( ...
, and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the List of Solar System objects by size, fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 t ...
.
The atmosphere of Titan includes an ionosphere that ranges from about in altitude and contains carbon compounds.Accessed 2010-08-25 Ionospheres have also been observed at Io, Europa, Ganymede, Triton, and
Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Su ...
.
See also
* Aeronomy * Geospace * Space physics *Geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and Physical property, properties of Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. Geophysicists conduct i ...
** International Reference Ionosphere
** Ionospheric dynamo region
** Magnetospheric electric convection field
** Protonosphere
** Schumann resonances
** Van Allen radiation belt
The Van Allen radiation belt is a zone of energetic charged particles, most of which originate from the solar wind, that are captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetosphere. Earth has two such belts, and sometimes others ma ...
* Radio
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connec ...
** Earth–ionosphere waveguide
** Fading
In wireless communications, fading is the variation of signal attenuation over variables like time, geographical position, and radio frequency. Fading is often modeled as a random process. In wireless systems, fading may either be due to mul ...
** Ionospheric absorption
** Ionospheric scintillation
** Line-of-sight propagation
Line-of-sight propagation is a characteristic of electromagnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation which means waves can only travel in a direct visual path from the source to the receiver without obstacles. Electromagnetic transmission in ...
** Sferics
A radio atmospheric signal or sferic (sometimes also spelled "spheric") is a broadband Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic impulse that occurs as a result of natural atmospheric lightning discharges. Sferics may propagate from their lightn ...
* Related
** Canadian Geospace Monitoring
** High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program
** Ionospheric heater
** S4 Index
** Soft gamma repeater
** Upper-atmospheric lightning
** Sura Ionospheric Heating Facility
** TIMED (Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics)
Notes
References
* * * * * * * J. Lilensten, P.-L. Blelly: ''Du Soleil à la Terre, Aéronomie et météorologie de l'espace'', Collection Grenoble Sciences, Université Joseph Fourier Grenoble I, 2000. . * P.-L. Blelly, D. Alcaydé: ''Ionosphere'', in: Y. Kamide, A. Chian, ''Handbook of the Solar-Terrestrial Environment'', Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 189–220, 2007. * *External links
* Gehred, Paul, and Norm Cohen,SWPC's Radio User's Page
'.
Amsat-Italia project on Ionospheric propagation (ESA SWENET website)
Layman Level Explanations Of "Seemingly" Mysterious 160 Meter (MF/HF) Propagation Occurrences
USGS Geomagnetism Program
{{Authority control Terrestrial plasmas Radio frequency propagation