|
Mesosphere
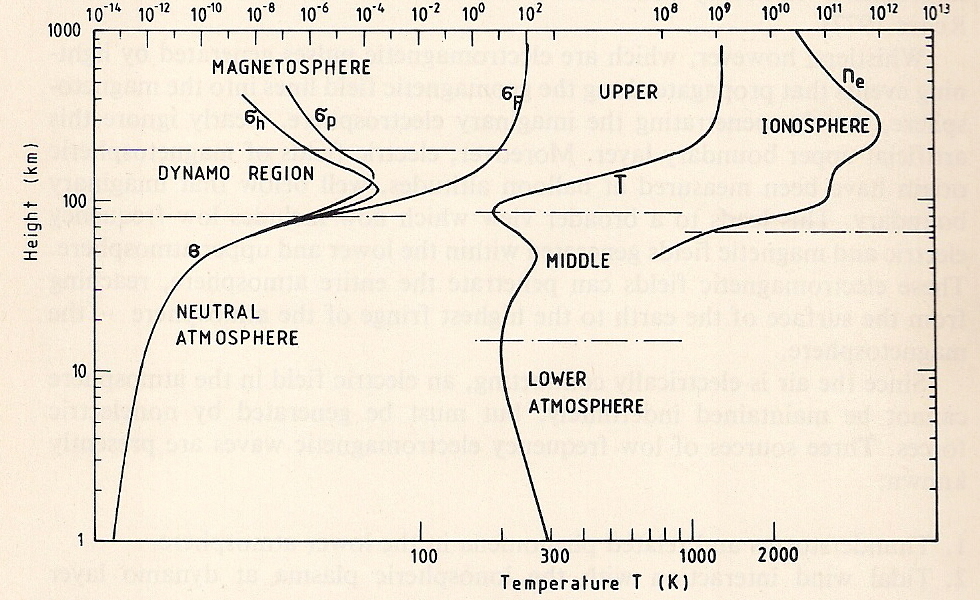
The mesosphere (; ) is the third layer of the atmosphere, directly above the stratosphere and directly below the thermosphere. In the mesosphere, temperature decreases as altitude increases. This characteristic is used to define limits: it begins at the top of the stratosphere (sometimes called the stratopause), and ends at the mesopause, which is the coldest part of Earth's atmosphere, with temperatures below . The exact upper and lower boundaries of the mesosphere vary with latitude and with season (higher in winter and at the tropics, lower in summer and at the poles), but the lower boundary is usually located at altitudes from above sea level, and the upper boundary (the mesopause) is usually from . The stratosphere and mesosphere are sometimes collectively referred to as the "middle atmosphere", which spans altitudes approximately between above Earth's surface. The mesopause, at an altitude of , separates the mesosphere from the thermosphere—the second-outermost la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather features such as clouds and hazes), all retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere serves as a protective buffer between the Earth's surface and outer space, shields the surface from most meteoroids and ultraviolet solar radiation, keeps it warm and reduces diurnal temperature variation (temperature extremes between day and night) through heat retention (greenhouse effect), redistributes heat and moisture among different regions via air currents, and provides the chemical and climate conditions allowing life to exist and evolve on Earth. By mole fraction (i.e., by quantity of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other trace gases (see Composition below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second-lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is composed of stratified temperature zones, with the warmer layers of air located higher (closer to outer space) and the cooler layers lower (closer to the planetary surface of the Earth). The increase of temperature with altitude is a result of the absorption of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation by the ozone layer, where ozone is exothermically photolyzed into oxygen in a cyclical fashion. This temperature inversion is in contrast to the troposphere, where temperature decreases with altitude, and between the troposphere and stratosphere is the tropopause border that demarcates the beginning of the temperature inversion. Near the equator, the lower edge of the stratosphere is as high as , at mid-latitudes around , and at the poles about . Temperatures range from an average of near the tropopause to an average of ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopause
The mesopause is the point of minimum temperature at the boundary between the mesosphere and the thermosphere atmospheric regions. Due to the lack of solar heating and very strong radiative cooling from carbon dioxide, the mesosphere is the coldest region on Earth with temperatures as low as -100 °C (-148 °F or 173 K). The altitude of the mesopause for many years was assumed to be at around 85 km (53 mi), but observations to higher altitudes and modeling studies in the last 10 years have shown that in fact there are two mesopauses - one at about 85 km and a stronger one at about 100 km (62 mi), with a layer of slightly warmer air between them. Another feature is that the summer mesopause is cooler than the winter (sometimes referred to as the ''mesopause anomaly''). It is due to a summer-to-winter circulation giving rise to upwelling at the summer pole and downwelling at the winter pole. Air rising will expand and cool resulting in a cold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone–oxygen Cycle
The ozone–oxygen cycle is the process by which ozone is continually regenerated in Earth's stratosphere, converting ultraviolet radiation (UV) into heat. In 1930 Sydney Chapman resolved the chemistry involved. The process is commonly called the Chapman cycle by atmospheric scientists. Most of the ozone production occurs in the tropical upper stratosphere and mesosphere. The total mass of ozone produced per day over the globe is about 400 million metric tons. The global mass of ozone is relatively constant at about 3 billion metric tons, meaning the Sun produces about 12% of the ozone layer each day. Photochemistry The Chapman cycle describes the main reactions that naturally determine, to first approximation, the concentration of ozone in the stratosphere. It includes four processes - and a fifth, less important one - all involving oxygen atoms and molecules, and UV radiation: Creation An oxygen molecule is split ( photolyzed) by higher frequency UV light (top end of UV-B, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermosphere
The thermosphere is the layer in the Earth's atmosphere directly above the mesosphere and below the exosphere. Within this layer of the atmosphere, ultraviolet radiation causes photoionization/photodissociation of molecules, creating ions; the bulk of the ionosphere thus exists within the thermosphere. Taking its name from the Greek θερμός (pronounced ''thermos'') meaning heat, the thermosphere begins at about 80 km (50 mi) above sea level. At these high altitudes, the residual atmospheric gases sort into strata according to molecular mass (see turbosphere). Thermospheric temperatures increase with altitude due to absorption of highly energetic solar radiation. Temperatures are highly dependent on solar activity, and can rise to or more. Radiation causes the atmospheric particles in this layer to become electrically charged, enabling radio waves to be refracted and thus be received beyond the horizon. In the exosphere, beginning at about 600 km (375 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near Space
Near space is the upper region of the Earth's atmosphere between airspace and outer space. It is sometimes referred to as the " edge of space". There is no legal definition for this extent, but typically this is the altitude range from . Range The lower limit of this region is set by the flight envelope of normal aircraft. For safety reasons, commercial aircraft are normally limited to altitudes of , and air navigation services only extend to . The upper limit of the near space range is the Kármán line at , where astrodynamics must take over from aerodynamics in order to achieve flight. This range includes the stratosphere, mesosphere and lower thermosphere layers of the Earth's atmosphere. Larger ranges for ''near space'' are used by some authors, such as . These extend from the Armstrong limit to the altitudes where orbital flight in very low Earth orbits becomes practical. Spacecraft have entered into a highly elliptical orbit with a perigee as low as , survivin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kármán Line
The Kármán line (or von Kármán line ) is a conventional definition of the Outer space#Boundary, edge of space; it is widely but not universally accepted. The international record-keeping body Fédération Aéronautique Internationale, FAI (Fédération aéronautique internationale) defines the Kármán line at an altitude of above above mean sea level, mean sea level. While named after Theodore von Kármán, who calculated a theoretical limit of altitude for aeroplane flight at above Earth, the later established Kármán line is more general and has no distinct physical significance, in that there is a rather gradual difference between the characteristics of the atmosphere at the line, and experts disagree on defining a distinct boundary where the atmosphere ends and space begins. It lies well above the altitude reachable by conventional airplanes or high-altitude balloons, and is approximately where satellites, even on very eccentric trajectories, will Orbital decay, dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation which produces ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, solar wind, and cosmic rays and thus protects the organisms from genetic damage. The curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum (geodesy), datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometry, geographical survey, sport, or atmospheric pressure). Although the term ''altitude'' is commonly used to mean the height above sea level of a location, in geography the term elevation is often preferred for this usage. In aviation, altitude is typically measured relative to mean sea level or above ground level to ensure safe navigation and flight operations. In geometry and geographical surveys, altitude helps create accurate topographic maps and understand the terrain's elevation. For high-altitude trekking and sports, knowing and adapting to altitude is vital for performance and safety. Higher altitudes mean reduced oxygen levels, which can lead to altitude sickness if proper acclimatization measures are not taken. Vertical distance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere Layers-en
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation which produces ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, solar wind, and cosmic rays and thus protects the organisms from genetic damage. The current composition o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbopause
The turbopause, also called the homopause, marks the altitude in an atmosphere below which turbulent mixing dominates. Mathematically, it is defined as the point where the coefficient of Eddy diffusion is equal to the coefficient of molecular diffusion. The region below the turbopause is known as the homosphere, where the atmosphere is well mixed for chemical species which have long mean residence times. Highly reactive chemicals tend to have variable concentration throughout the atmosphere, while unreactive species have more homogeneous concentrations. The region above the turbopause is the heterosphere, where molecular diffusion dominates and the chemical composition of the atmosphere varies according to chemical species and their atomic weight. Earth's turbopause lies near the mesopause, at the intersection of the mesosphere and the thermosphere, at an altitude of roughly . Some other turbopauses in the Solar System The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratopause
The stratopause (formerly mesopeak) is the level of the atmosphere which is the boundary between two layers: the stratosphere and the mesosphere. In the stratosphere, the temperature increases with altitude, and the stratopause is the region where a maximum in the temperature occurs. This atmospheric feature is not exclusive to Earth, but also occurs on any other planet or moon with an atmosphere. According to James Kasting, planets whose atmospheres do not absorb shortwave sunlight, such as Venus and Mars, do not have a Stratosphere and thus have no Stratopause. On Earth, the stratopause is above sea level. The atmospheric pressure is around of the pressure at sea level. The temperature in the stratopause is . See also * Jet stream Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow thermal wind, air currents in the Earth's Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere. The main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds, flowing west to east around the gl . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |