Caspian sea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland
p. 28
, Lonely Planet Publications, Some Turkic ethnic groups refer to it with the Caspi(an) descriptor; in
body of water
A body of water or waterbody (often spelled water body) is any significant accumulation of water on the surface of Earth or another planet. The term most often refers to oceans, seas, and lakes, but it includes smaller pools of water such ...
, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into la ...
, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
, west of the broad steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslan ...
of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, wh ...
, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau of Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes A ...
. It covers a surface area of (excluding the highly saline lagoon of Garabogazköl to its east) and a volume of . It has a salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
of approximately 1.2% (12 g/L), about a third of the salinity of average seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has appr ...
. It is bounded by Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
to the northeast, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
to the northwest, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
to the southwest, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
to the south, and Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the s ...
to the southeast.
The sea stretches nearly from north to south, with an average width of . Its gross coverage is and the surface is about below sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise ...
. Its main freshwater inflow, Europe's longest river, the Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchm ...
, enters at the shallow north end. Two deep basins form its central and southern zones. These lead to horizontal differences in temperature, salinity, and ecology. The seabed
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
in the south reaches below sea level, which is the second-lowest natural non-oceanic depression on Earth after Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, I ...
(). Written accounts from the ancient inhabitants of its coast perceived the Caspian Sea as an ocean, probably because of its salinity and large size.
The Caspian Sea is home to a wide range of species and is known for its caviar and oil industries. Pollution from the oil industry and dams on rivers draining into it have harmed its ecology.
Etymology
The lake's name stems from Caspi, an ancient people who lived to the southwest of the sea inTranscaucasia
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
. Strabo (died circa AD 24) wrote that "to the country of the Albanians (Caucasus Albania
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus: mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', among t ...
not to be confused with the country of Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the ...
) belongs also the territory called Caspiane, which was named after the Caspian tribe, as was also the sea; but the tribe has now disappeared". Moreover, the Caspian Gates, part of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
's Tehran province, may evince such a people migrated to the south. The Iranian city of Qazvin shares the root of its name with this common name for the sea. The traditional and medieval Arabic name for the sea was Bahr(sea) Xazar but in recent centuries common and standard name in Arabic language is Baḥr Qazvin Arabized from Caspian. In modern russian: Каспи́йское мо́ре, ''Kaspiyskoye more''.''Iran'' (5th ed., 2008), by Andrew Burke and Mark Elliottp. 28
, Lonely Planet Publications, Some Turkic ethnic groups refer to it with the Caspi(an) descriptor; in
Kazakh
Kazakh, Qazaq or Kazakhstani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Kazakhstan
*Kazakhs, an ethnic group
*Kazakh language
*The Kazakh Khanate
* Kazakh cuisine
* Qazakh Rayon, Azerbaijan
*Qazax, Azerbaijan
*Kazakh Uyezd, administrative dis ...
it is called , ''Kaspiy teñizi'', ky, Каспий деңизи, Kaspiy deñizi, uz, Kaspiy dengizi. Others refer to it as the ''Khazar sea'': tk, Hazar deňizi; az, Xəzər dənizi, tr, Hazar denizi. In all these the first word refers to the historical Khazars who had a large empire based to the north of the Caspian Sea between the 7th and 10th centuries.
In Iran, the lake is referred to as the ''Mazandaran Sea'' ( fa, دریای مازندران), after the historic Mazandaran Province at its southern shores.
Old Russian sources use the ''Khvalyn'' or ''Khvalis'' Sea () after the name of Khwarezmia.
Among Greeks and Persians in classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations ...
it was the Hyrcania
Hyrcania () ( el, ''Hyrkania'', Old Persian: 𐎺𐎼𐎣𐎠𐎴 ''Varkâna'',Lendering (1996) Middle Persian: 𐭢𐭥𐭫𐭢𐭠𐭭 ''Gurgān'', Akkadian: ''Urqananu'') is a historical region composed of the land south-east of the Caspian ...
n ocean.
Renaissance European maps labelled it as the ''Abbacuch Sea'' (Oronce Fine's 1531 world map), ''Mar de Bachu
Maralbexi County (Maralbeshi, Maralbishi, transliterated from ; ), Bachu County (), and ) the former long Chinese name as well, is located in the southwest of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China and is under ...
'' (Ortellius' 1570 map), or ''Mar de Sala'' (Mercator's 1569 map).
It was also sometimes called the Kumyk Sea and Tarki Sea (derived from the name of the Kumyks
, image = Abdul-Wahab son of Mustafa — a prominent Kumyk architect of the 19th century.
, population = near 600,000
, region1 =
, pop1 = 503,060
, ref1 =
, region2 =
, pop2 ...
and their historical capital Tarki).
Basin countries
Border countries
*Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
*Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
*Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
*Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
*Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the s ...
Non-border countries
*Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ...
(entirety)
*Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
(its east part)
*Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
(extreme north-eastern parts)
*Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
(extreme western parts)
Physical characteristics
Formation
The Caspian Sea, like theBlack Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
, is a remnant of the ancient Paratethys Sea. Its seafloor is, therefore, a standard oceanic basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
and not a continental granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies und ...
body. It became landlocked in the Late Miocene, about 5.5 million years ago, due to tectonic uplift and a fall in sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise ...
. The Caspian Sea was a comparatively small endorheic lake during the Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58 During warm and dry climatic periods, the landlocked sea almost dried up, depositing evaporitic sediments like
 The Caspian Sea is the largest inland body of water in the world by area and accounts for 40 to 44% of the total lacustrine waters of the world, and covers an area larger than
The Caspian Sea is the largest inland body of water in the world by area and accounts for 40 to 44% of the total lacustrine waters of the world, and covers an area larger than
 The Caspian has characteristics common to both seas and lakes. It is often listed as the world's largest lake, although it is not
The Caspian has characteristics common to both seas and lakes. It is often listed as the world's largest lake, although it is not
 The rising level of the Caspian Sea between 1994 and 1996 reduced the number of habitats for rare species of aquatic vegetation. This has been attributed to a general lack of seeding material in newly formed coastal
The rising level of the Caspian Sea between 1994 and 1996 reduced the number of habitats for rare species of aquatic vegetation. This has been attributed to a general lack of seeding material in newly formed coastal
 The Caspian turtle (''Mauremys caspica''), although found in neighboring areas, is a wholly freshwater species. The zebra mussel is native to the Caspian and
The Caspian turtle (''Mauremys caspica''), although found in neighboring areas, is a wholly freshwater species. The zebra mussel is native to the Caspian and  Reptiles native to the region include the spur-thighed tortoise (''Testudo graeca buxtoni'') and Horsfield's tortoise.
*The Asiatic cheetah used to occur in the Trans-Caucasus and
Reptiles native to the region include the spur-thighed tortoise (''Testudo graeca buxtoni'') and Horsfield's tortoise.
*The Asiatic cheetah used to occur in the Trans-Caucasus and
Lion and Gazelle: The Mammals and Birds of Iran
. Images Publishing, Avon. *The Asiatic lion used to occur in the Trans-Caucasus, Iran, and possibly the southern part of Turkestan. *The Caspian tiger used to occur in northern Iran, the Caucasus and

". SOCAR By the 16th century, Europeans were aware of the rich oil and gas deposits locally. English traders Thomas Bannister and Jeffrey Duckett described the area around Baku as "a strange thing to behold, for there issueth out of the ground a marvelous quantity of oil, which serveth all the country to burn in their houses. This oil is black and is called nefte. There is also by the town of Baku, another kind of oil which is white and very precious .e., petroleum">petroleum.html" ;"title=".e., petroleum">.e., petroleum""Back to the Future: Britain, Baku Oil and the Cycle of History
". SOCAR Today, oil and gas platforms abound along the edges of the sea.

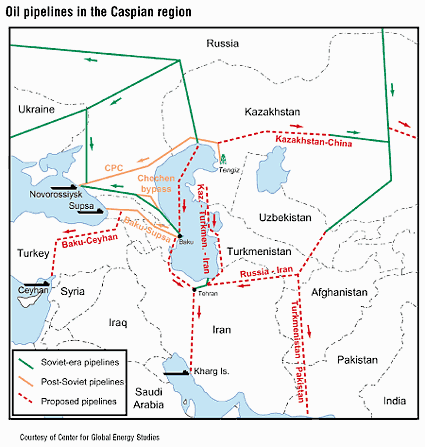 Countries in the Caspian region, particularly
Countries in the Caspian region, particularly
 The Caspian Sea region presently is a significant, but not major, supplier of crude oil to world markets, based upon estimates by BP Amoco and the U.S. Energy Information Administration,
The Caspian Sea region presently is a significant, but not major, supplier of crude oil to world markets, based upon estimates by BP Amoco and the U.S. Energy Information Administration,  The world's first offshore wells and machine-drilled wells were made in Bibi-Heybat Bay, near Baku, Azerbaijan. In 1873, exploration and development of oil began in some of the largest fields known to exist in the world at that time on the Absheron Peninsula near the villages of Balakhanli, Sabunchi, Ramana, and Bibi Heybat. Total recoverable reserves were more than 500 million tons. By 1900, Baku had more than 3,000 oil wells, 2,000 of which were producing at industrial levels. By the end of the 19th century, Baku became known as the "black gold capital", and many skilled workers and specialists flocked to the city.
By the beginning of the 20th century, Baku was the center of the international oil industry. In 1920, when the
The world's first offshore wells and machine-drilled wells were made in Bibi-Heybat Bay, near Baku, Azerbaijan. In 1873, exploration and development of oil began in some of the largest fields known to exist in the world at that time on the Absheron Peninsula near the villages of Balakhanli, Sabunchi, Ramana, and Bibi Heybat. Total recoverable reserves were more than 500 million tons. By 1900, Baku had more than 3,000 oil wells, 2,000 of which were producing at industrial levels. By the end of the 19th century, Baku became known as the "black gold capital", and many skilled workers and specialists flocked to the city.
By the beginning of the 20th century, Baku was the center of the international oil industry. In 1920, when the
Russia Tries to Scuttle Proposed Trans-Caspian Pipeline
", Eurasianet (2006-03-27) However, analysts note that the pipelines would bypass Russia completely, thereby denying the country valuable transit fees, as well as destroying its current


"Caspian Canal Could Boost Kazakh Trade"
''
Names of the Caspian Sea
Caspian Sea Region
{{Authority control Ancient lakes Azerbaijan–Iran border Azerbaijan–Russia border Bodies of water of Iran Border tripoints Endorheic lakes of Europe Endorheic lakes of Asia Eutrophication Geography of Central Asia Geography of Eastern Europe Geography of Southern Russia Geography of Western Asia International disputes International lakes of Asia International lakes of Europe Iran–Soviet Union border Iran–Turkmenistan border Kazakhstan–Russia border Kazakhstan–Turkmenistan border Lakes of Astrakhan Oblast Lakes of Azerbaijan Lakes of Dagestan Lakes of Iran Lakes of Kalmykia Lakes of Kazakhstan Lakes of Turkmenistan Landforms of Central Asia Landforms of Western Asia Lowest points Saline lakes of Asia Saline lakes of Europe Seas of Iran
halite
Halite (), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, ...
that were covered by wind-blown deposits and were sealed off as an evaporite
An evaporite () is a water- soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as oce ...
sink when cool, wet climates refilled the basin. (Comparable evaporite beds underlie the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
.) Due to the current inflow of fresh water in the north, the Caspian Sea water is almost fresh in its northern portions, getting more brackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuari ...
toward the south. It is most saline on the Iranian shore, where the catchment basin contributes little flow. Currently, the mean salinity of the Caspian is one third that of Earth's oceans. The Garabogazköl embayment
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a ...
, which dried up when water flow from the main body of the Caspian was blocked in the 1980s but has since been restored, routinely exceeds oceanic salinity by a factor of 10.
Geography
 The Caspian Sea is the largest inland body of water in the world by area and accounts for 40 to 44% of the total lacustrine waters of the world, and covers an area larger than
The Caspian Sea is the largest inland body of water in the world by area and accounts for 40 to 44% of the total lacustrine waters of the world, and covers an area larger than Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
. The coastlines of the Caspian are shared by Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, Iran, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
, Russia, and Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the s ...
. The Caspian is divided into three distinct physical regions: the Northern, Middle, and Southern Caspian. The Northern–Middle boundary is the Mangyshlak Threshold, which runs through Chechen Island and Cape Tiub-Karagan. The Middle–Southern boundary is the Apsheron Threshold The Apsheron Sill, Absheron Sill, Apsheron Ridge or Apsheron Threshold is a major northwest–southeast trending bathymetric high that runs for about 250 km across the whole of the Caspian Sea from Baku in Azerbaijan to the Cheleken Peninsula in Tu ...
, a sill
Sill may refer to:
* Sill (dock), a weir at the low water mark retaining water within a dock
* Sill (geology), a subhorizontal sheet intrusion of molten or solidified magma
* Sill (geostatistics)
* Sill (river), a river in Austria
* Sill plate, a ...
of tectonic origin between the Eurasian continent and an oceanic remnant, that runs through Zhiloi Island and Cape Kuuli. The Garabogazköl Bay is the saline eastern inlet of the Caspian, which is part of Turkmenistan and at times has been a lake in its own right due to the isthmus that cuts it off from the Caspian.
Differences between the three regions are dramatic. The Northern Caspian only includes the Caspian shelf, and is very shallow; it accounts for less than 1% of the total water volume with an average depth of only . The sea noticeably drops off towards the Middle Caspian, where the average depth is . The Southern Caspian is the deepest, with oceanic depths of over , greatly exceeding the depth of other regional seas, such as the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
. The Middle and Southern Caspian account for 33% and 66% of the total water volume, respectively. The northern portion of the Caspian Sea typically freezes in the winter, and in the coldest winters ice forms in the south as well.
Over 130 rivers provide inflow to the Caspian, the Volga River
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchm ...
being the largest. A second affluent, the Ural River, flows in from the north, and the Kura River from the west. In the past, the Amu Darya
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
(Oxus) of Central Asia in the east often changed course to empty into the Caspian through a now-desiccated riverbed called the Uzboy River, as did the Syr Darya farther north. The Caspian has several small islands, primarily located in the north with a collective land area of roughly . Adjacent to the North Caspian is the Caspian Depression, a low-lying region below sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise ...
. The Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
n steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslan ...
s stretch across the northeast coast, while the Caucasus mountains
The Caucasus Mountains,
: pronounced
* hy, Կովկասյան լեռներ,
: pronounced
* az, Qafqaz dağları, pronounced
* rus, Кавка́зские го́ры, Kavkázskiye góry, kɐfˈkasːkʲɪje ˈɡorɨ
* tr, Kafkas Dağla ...
hug the western shore. The biomes
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
to both the north and east are characterized by cold, continental deserts. Conversely, the climate to the southwest and south are generally warm with uneven elevation due to a mix of highlands and mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
s; the drastic changes in climate alongside the Caspian have led to a great deal of biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic ('' genetic variability''), species ('' species diversity''), and ecosystem ('' ecosystem diversity' ...
in the region.
The Caspian Sea has numerous islands near the coasts, but none in the deeper parts of the sea. Ogurja Ada is the largest island. The island is long, with gazelle
A gazelle is one of many antelope species in the genus ''Gazella'' . This article also deals with the seven species included in two further genera, ''Eudorcas'' and '' Nanger'', which were formerly considered subgenera of ''Gazella''. A third ...
s roaming freely on it. In the North Caspian, the majority of the islands are small and uninhabited, like the Tyuleniy Archipelago
The Tyuleniy Archipelago ( kk, Түлен аралдары ''Tülen araldary'', russian: Тюленьи острова), is an island group in the north-eastern Caspian Sea off the Mangyshlak Bay west of the Mangyshlak Peninsula and about northw ...
, an Important Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations.
IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife Int ...
(IBA).
Climate
The climate of the Caspian Sea is variable, with thecold desert climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk''), is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in deser ...
(BWk), cold semi-arid climate (BSk), and humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
(Dsa, Dfa) being present in the northern portions of the Caspian Sea, while the Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
(Csa) and humid subtropical climate (Cfa) are present in the southern portions of the Caspian Sea.
Hydrology
 The Caspian has characteristics common to both seas and lakes. It is often listed as the world's largest lake, although it is not
The Caspian has characteristics common to both seas and lakes. It is often listed as the world's largest lake, although it is not freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does in ...
: the 1.2% salinity classes it with brackish water
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuari ...
bodies.
It contains about 3.5 times as much water, by volume, as all five of North America's Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five la ...
combined. The Volga River
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchm ...
(about 80% of the inflow) and the Ural River discharge into the Caspian Sea, but it has no natural outflow other than by evaporation. Thus the Caspian ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
is a closed basin, with its own sea level history that is independent of the eustatic level of the world's oceans.
The sea level of the Caspian has fallen and risen, often rapidly, many times over the centuries. Some Russian historians claim that a medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
rising of the Caspian, perhaps caused by the Amu Darya
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
changing its inflow to the Caspian from the 13th century to the 16th century, caused the coastal towns of Khazaria, such as Atil, to flood. In 2004, the water level was below sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise ...
.
Over the centuries, Caspian Sea levels have changed in synchrony with the estimated discharge of the Volga, which in turn depends on rainfall levels in its vast catchment basin. Precipitation is related to variations in the amount of North Atlantic depressions that reach the interior, and they in turn are affected by cycles of the North Atlantic oscillation. Thus levels in the Caspian Sea relate to atmospheric conditions in the North Atlantic, thousands of kilometres to the northwest.
The last short-term sea-level cycle started with a sea-level fall of from 1929 to 1977, followed by a rise of from 1977 until 1995. Since then smaller oscillations have taken place.
A study by the Azerbaijan Academy of Sciences estimated that the level of the sea was dropping by more than six centimetres per year due to increased evaporation due to rising temperatures caused by climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
.
Environmental degradation
TheVolga River
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchm ...
, the longest river in Europe, drains 20% of the European land area and is the source of 80% of the Caspian's inflow. Heavy development in its lower reaches has caused numerous unregulated releases of chemical and biological pollutants. The UN Environment Programme warns that the Caspian "suffers from an enormous burden of pollution from oil extraction and refining, offshore oil fields, radioactive wastes from nuclear power plants and huge volumes of untreated sewage and industrial waste introduced mainly by the Volga River".
The magnitude of fossil fuel extraction and transport activity in the Caspian also poses a risk to the environment. The island of Vulf off Baku, for example, has suffered ecological damage as a result of the petrochemical industry; this has significantly decreased the number of species of marine birds in the area. Existing and planned oil and gas pipelines under the sea further increase the potential threat to the environment.
The high concentration of mud volcanoes under the Caspian Sea were thought to be the cause of a fire that broke out 75 kilometers from Baku on July 5, 2021. The State oil company of Azerbaijan SOCAR said preliminary information indicated it was a mud volcano which spewed both mud and flammable gas.
It is calculated that during the 21st century, the water level of the Caspian Sea will decrease by 9–18 m (30–60 ft) due to the acceleration of evaporation due to global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes ...
and the process of desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused b ...
.
On October 23, 2021, Kazakhstan President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev
Kassym-Jomart Kemeluly Tokayev ( kk, Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев, Qasym-Jomart Kemelūly Toqaev ; born 17 May 1953) is a Kazakh politician and diplomat who is currently serving as the President of Kazakhstan since 12 Ju ...
signed the Protocol for the Protection of the Caspian Sea against Pollution from Land-based Sources in order to ensure better protection for the biodiversity of the Caspian Sea.
Flora and fauna
Flora
 The rising level of the Caspian Sea between 1994 and 1996 reduced the number of habitats for rare species of aquatic vegetation. This has been attributed to a general lack of seeding material in newly formed coastal
The rising level of the Caspian Sea between 1994 and 1996 reduced the number of habitats for rare species of aquatic vegetation. This has been attributed to a general lack of seeding material in newly formed coastal lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into '' coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons' ...
s and water bodies.
Many rare and endemic plant species of Russia are associated with the tidal areas of the Volga delta and riparian forests of the Samur River delta. The shoreline is also a unique refuge for plants adapted to the loose sands of the Central Asian Deserts. The principal limiting factors to successful establishment of plant species are hydrological imbalances within the surrounding deltas, water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, so that it negatively affects its uses. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. Wate ...
, and various land reclamation activities. The water level change within the Caspian Sea is an indirect reason for which plants may not get established.
These affect aquatic plants of the Volga Delta, such as ''Aldrovanda vesiculosa
''Aldrovanda vesiculosa'', commonly known as the waterwheel plant, is the sole extant species in the flowering plant genus ''Aldrovanda'' of the family Droseraceae. The plant captures small aquatic invertebrates using traps similar to those of ...
'' and the native '' Nelumbo caspica''. About 11 plant species are found in the Samur River delta, including the unique liana
A liana is a long- stemmed, woody vine that is rooted in the soil at ground level and uses trees, as well as other means of vertical support, to climb up to the canopy in search of direct sunlight. The word ''liana'' does not refer to a ...
forests that date back to the Tertiary period.
Since 2019 UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
has admitted the lush Hyrcanian forests of Mazandaran, Iran as World Heritage Site under category (ix).
Fauna
 The Caspian turtle (''Mauremys caspica''), although found in neighboring areas, is a wholly freshwater species. The zebra mussel is native to the Caspian and
The Caspian turtle (''Mauremys caspica''), although found in neighboring areas, is a wholly freshwater species. The zebra mussel is native to the Caspian and Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
basins, but has become an invasive species
An invasive species otherwise known as an alien is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Although most introduced species are neutral or beneficial with respect to other species, invasive species adv ...
elsewhere, when introduced. The area has given its name to several species, including the Caspian gull and the Caspian tern. The Caspian seal (''Pusa caspica'') is the only aquatic mammal endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found els ...
to the Caspian Sea, being one of very few seal species that live in inland waters, but it is different from those inhabiting freshwaters due to the hydrological environment of the sea. A century ago the Caspian was home to more than one million seals. Today, fewer than 10% remain.
Archeological studies of Gobustan Rock Art
Gobustan Rock Art represents flora and fauna, hunting, lifestyles, and culture of pre-historic and medieval periods of time. The carvings on the rocks illustrates primitive men, ritual dances, men with lances in their hands, animals, bull fights, ...
have identified what may be dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (t ...
s and porpoise
Porpoises are a group of fully aquatic marine mammals, all of which are classified under the family Phocoenidae, parvorder Odontoceti (toothed whales). Although similar in appearance to dolphins, they are more closely related to narwhals ...
s, likely present in the Caspian Sea at least until the Quaternary or much more recent periods such as the last glacial period or antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
. Although the rock art on Kichikdash Mountain is assumed to be of a dolphin it might instead represent the famous beluga sturgeon due to its size (430 cm in length), but fossil records suggest certain ancestors of modern dolphins and whales, such as '' Macrokentriodon morani'' (bottlenose dolphin
Bottlenose dolphins are aquatic mammals in the genus ''Tursiops.'' They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus definitively contains two species: the co ...
s) and '' Balaenoptera sibbaldina'' (blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known to have ever existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can b ...
s) were presumably larger than their present descendants. From the same artworks, auks, like Brunnich's Guillemot
The thick-billed murre or Brünnich's guillemot (''Uria lomvia'') is a bird in the auk family (Alcidae). This bird is named after the Danish zoologist Morten Thrane Brünnich. The very deeply black North Pacific subspecies ''Uria lomvia arra'' ...
could also have been in the sea as well, and these petroglyphs suggest marine inflow between the current Caspian Sea and the Arctic Ocean or North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
, or the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
. This is supported by the existences of current endemic, oceanic species such as lagoon cockles which was genetically identified to originate in Caspian/Black Seas regions.
The sea's basin (including associated waters such as rivers) has 160 native species and subspecies of fish in more than 60 genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial ...
.Naseka, A.M. and Bogutskaya, N.G. (2009). "Fishes of the Caspian Sea: zoogeography and updated check-list". ''Zoosystematica Rossica'' 18(2): 295–317. About 62% of the species and subspecies are endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found els ...
, as are 4–6 genera (depending on taxonomic treatment). The lake proper has 115 natives, including 73 endemics (63.5%). Among the more than 50 genera in the lake proper, 3–4 are endemic: '' Anatirostrum'', '' Caspiomyzon'', '' Chasar'' (often included in '' Ponticola'') and ''Hyrcanogobius
''Hyrcanogobius bergi'', the Volga dwarf goby, is a species of goby endemic to the Caspian Sea where it occurs in fresh, brackish and marine waters along the coast. Unusually for gobies, this species is almost a pelagic fish. This species grow ...
''. By far the most numerous families in the lake proper are gobies (35 species and subspecies), cyprinid
Cyprinidae is a family of freshwater fish commonly called the carp or minnow family. It includes the carps, the true minnows, and relatives like the barbs and barbels. Cyprinidae is the largest and most diverse fish family and the largest ve ...
s (32) and clupeids (22). Two particularly rich genera are ''Alosa
''Alosa'' is a genus of fish, the river herrings, in the family (biology), family Clupeidae. Along with other genera in the subfamily Alosinae, they are generally known as shads. tp://ftp.fao.org/docrep/fao/009/ac482e/ac482e27.pdf Subfamily A ...
'' with 18 endemic species/subspecies and ''Benthophilus'' with 16 endemic species. Other examples of endemics are four species of ''Clupeonella'', ''Gobio volgensis'', two ''Rutilus'', three ''Sabanejewia'', ''Stenodus leucichthys'', two ''Salmo'', two ''Mesogobius'' and three ''Neogobius''. Most non-endemic natives are either shared with the Black Sea basin or widespread Palearctic
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.
The realm consists of several bioregions: the Euro-Si ...
species such as crucian carp, Prussian carp, common carp
The Eurasian carp or European carp (''Cyprinus carpio''), widely known as the common carp, is a widespread freshwater fish of eutrophic waters in lakes and large rivers in Europe and Asia.Fishbase''Cyprinus carpio'' Linnaeus, 1758/ref>Arkive The ...
, common bream
The common bream, freshwater bream, bream, bronze bream, carp bream or sweaty bream (''Abramis brama''), is a European species of freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae. It is now considered to be the only species in the genus ''Abramis''. ...
, common bleak, asp
Asp may refer to:
Places
* Asp, part of Densbüren, Aargau, Switzerland
* Aspe (''Asp'' in Valencian), Alicante, Spain
* Asp Lake, a lake in Minnesota
Animals
* Asp (fish)
* Asp (snake), in antiquity, one of several venomous snakes
** ''Cera ...
, white bream
''Blicca bjoerkna'', alternatively called the white bream or the silver bream, is a European species of freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae.
Distribution
''Blicca bjoerkna'' is distributed across most of Europe and in adjacent Western As ...
, sunbleak
''Leucaspius delineatus'', known as the sunbleak, belica or moderlieschen is a species of freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae. It is currently the only species included in genus ''Leucaspius'', whereas formerly others were included, which no ...
, common dace, common roach, common rudd, European chub
''Squalius cephalus'' is a European species of freshwater fish in the carp family Cyprinidae. It frequents both slow and moderate rivers, as well as canals and still waters of various kinds. This species is referred to as the common chub, Europe ...
, sichel Sichel is a surname of German origin. Individuals with the name "Sichel" include:
* Alice Model, philanthropist born Alice Sichel
* Edith Helen Sichel, author
* Ernest Leopold Sichel, artist
* Frédéric Jules Sichel, established the first ophthal ...
, tench
The tench or doctor fish (''Tinca tinca'') is a fresh- and brackish-water fish of the order Cypriniformes found throughout Eurasia from Western Europe including the British Isles east into Asia as far as the Ob and Yenisei Rivers. It is als ...
, European weatherfish
The weatherfish (''Misgurnus fossilis'') is a species of true loach that has a wide range in Europe and some parts of Asia. It is an omnivorous scavenger bottom feeder, using its sensitive barbels to find edible items. The diet mostly consists o ...
, wels catfish, northern pike
The northern pike (''Esox lucius'') is a species of carnivorous fish of the genus ''Esox'' (the pikes). They are typical of brackish water, brackish and fresh waters of the Northern Hemisphere (''i.e.'' holarctic in distribution). They are kno ...
, burbot
The burbot (''Lota lota'') is the only gadiformes, gadiform (cod-like) freshwater fish. It is also known as bubbot, mariah, loche, cusk, freshwater cod, freshwater ling, freshwater cusk, the lawyer, coney-fish, lingcod, and eelpout. The species ...
, European perch and zander. Almost 30 non-indigenous, introduced fish species have been reported from the Caspian Sea, but only a few have become established.
Six sturgeon species, the Russian, bastard, Persian, sterlet, starry and beluga, are native to the Caspian Sea. The last of these is arguably the largest freshwater fish in the world. The sturgeon yield roe (eggs) that are processed into caviar. Overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in the ...
has depleted a number of the historic fisheries. In recent years, overfishing has threatened the sturgeon population to the point that environmentalists
An environmentalist is a person who is concerned with and/or advocates for the protection of the environment. An environmentalist can be considered a supporter of the goals of the environmental movement, "a political and ethical movement that se ...
advocate banning sturgeon fishing completely until the population recovers. The high price of sturgeon caviar—more than 1,500 Azerbaijani manats (US$880 ) per kilo—allows fishermen to afford bribes to ensure the authorities look the other way, making regulations in many locations ineffective. Caviar harvesting further endangers the fish stocks, since it targets reproductive females.
 Reptiles native to the region include the spur-thighed tortoise (''Testudo graeca buxtoni'') and Horsfield's tortoise.
*The Asiatic cheetah used to occur in the Trans-Caucasus and
Reptiles native to the region include the spur-thighed tortoise (''Testudo graeca buxtoni'') and Horsfield's tortoise.
*The Asiatic cheetah used to occur in the Trans-Caucasus and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
, but is today restricted to Iran.Humphreys, P., Kahrom, E. (1999)Lion and Gazelle: The Mammals and Birds of Iran
. Images Publishing, Avon. *The Asiatic lion used to occur in the Trans-Caucasus, Iran, and possibly the southern part of Turkestan. *The Caspian tiger used to occur in northern Iran, the Caucasus and
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
.
*The endangered Persian leopard is found in Iran, the Caucasus and Central Asia.
History
Geology
The main geologic history locally had two stages. The first is theMiocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" ...
, determined by tectonic events that correlate with the closing of the Tethys Sea. The second is the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the '' Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed ...
noted for its glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate bet ...
cycles and the full run of the present Volga. During the first stage, the Tethys Sea had evolved into the Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th ...
Lake, that was created from the modern Black Sea and south Caspian, when the collision of the Arabian peninsula with Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes A ...
pushed up the Kopet Dag
The Köpet Dag, Kopet Dagh, or Koppeh Dagh ( tk, Köpetdag; fa, کپهداغ), also known as the Turkmen-Khorasan Mountain Range, is a mountain range on the border between Turkmenistan and Iran that extends about along the border southeast o ...
and Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains,
: pronounced
* hy, Կովկասյան լեռներ,
: pronounced
* az, Qafqaz dağları, pronounced
* rus, Кавка́зские го́ры, Kavkázskiye góry, kɐfˈkasːkʲɪje ˈɡorɨ
* tr, Kafkas Dağla ...
, lasting south and west limits to the basin. This orogeneic movement was continuous, while the Caspian was regularly disconnected from the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
. In the late Pontian, a mountain arch rose across the south basin and divided it into the Khachmaz and Lankaran Lakes (or early Balaxani). The period of restriction to the south basin was reversed during the Akchagylian – the lake became more than three times its size today and took again the first of a series of contacts with the Black Sea and with Lake Aral. A recession of Lake Akchagyl completed stage one.

Early settlement nearby
The earliest hominid remains found around the Caspian Sea are fromDmanisi
Dmanisi ( ka, დმანისი, tr, , az, Başkeçid) is a town and archaeological site in the Kvemo Kartli region of Georgia approximately 93 km southwest of the nation’s capital Tbilisi in the river valley of Mashavera. The homini ...
dating back to around 1.8 Ma and yielded a number of skeletal remains of Homo erectus or Homo ergaster. More later evidence for human occupation of the region came from a number of caves in Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
and Azerbaijan such as Kudaro and Azykh Caves. There is evidence for Lower Palaeolithic human occupation south of the Caspian from western Alburz. These are Ganj Par and Darband Cave sites.
Neanderthal remains also have been discovered at a cave in Georgia. Discoveries in the Hotu cave and the adjacent Kamarband cave, near the town of Behshahr, Mazandaran south of the Caspian in Iran, suggest human habitation of the area as early as 11,000 years ago. Ancient Greeks focused on the civilization on the south shore – they call it the (H)yr(c/k)anian Sea ( grc, Υρκανία θάλαττα, with sources noting the latter word was evolving then to today's ''Thelessa'': late grc, θάλασσα).
Chinese maximal limit
Later, in theTang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdo ...
(618-907), the sea was the western limit of the Chinese Empire.
Fossil fuel
The area is rich in fossil fuels. Oil wells were being dug in the region as early as the 10th century to reach oil "for use in everyday life, both for medicinal purposes and for heating and lighting in homes"."The Development of the Oil and Gas Industry in Azerbaijan". SOCAR By the 16th century, Europeans were aware of the rich oil and gas deposits locally. English traders Thomas Bannister and Jeffrey Duckett described the area around Baku as "a strange thing to behold, for there issueth out of the ground a marvelous quantity of oil, which serveth all the country to burn in their houses. This oil is black and is called nefte. There is also by the town of Baku, another kind of oil which is white and very precious .e., petroleum">petroleum.html" ;"title=".e., petroleum">.e., petroleum""Back to the Future: Britain, Baku Oil and the Cycle of History
". SOCAR Today, oil and gas platforms abound along the edges of the sea.
Geography, geology and navigation studies
During the rule of Peter I the Great, Fedor Ivanovich Soimonov, Fedor I. Soimonov was a pioneering explorer of the sea. He was a hydrographer who charted and greatly expanded knowledge of the sea. He drew a set of four maps and wrote ''Pilot of the Caspian Sea'', the first lengthy report and modern maps. These were published in 1720 by theRussian Academy of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across t ...
.
Cities

Ancient
*Hyrcania
Hyrcania () ( el, ''Hyrkania'', Old Persian: 𐎺𐎼𐎣𐎠𐎴 ''Varkâna'',Lendering (1996) Middle Persian: 𐭢𐭥𐭫𐭢𐭠𐭭 ''Gurgān'', Akkadian: ''Urqananu'') is a historical region composed of the land south-east of the Caspian ...
, ancient state in the north of Iran
* Sari, Mazandaran Province of Iran
* Anzali, Gilan Province of Iran
* Astara, Gilan Province of Iran
* Astarabad, Golestan Province of Iran
* Tamisheh, Golestan Province of Iran
*Atil, Khazaria
Atil (also Itil) , was the capital of the Khazar Khaganate from the middle of the 8th century until the end of the 10th century.
Known to have been situated on the Silk Road in the vicinity of the Caspian Sea, its precise location has long been ...
* Khazaran
* Baku, Azerbaijan
* Derbent, Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; rus, Дагеста́н, , dəɡʲɪˈstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: Респу́блика Дагеста́н, Respúblika Dagestán, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North ...
, Russia
* Xacitarxan, modern-day Astrakhan
Astrakhan ( rus, Астрахань, p=ˈastrəxənʲ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in Southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of ...
Modern
*Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
:
** Ali Abad
** Astane-ye Ashrafiye
** Astara
** Babolsar
** Bandar-e Anzali
** Bandar-e-Gaz
** Bandar Torkaman
** Behshahr
** Chalus
** Fenderesk
** Gomishan
** Gonbad-e Kavus
** Gorgan
**Juybar
Juybar ( fa, جويبار, also Romanized as Jūybār; also known as Bāghlū) is a city and capital of Juybar County, Mazandaran Province, Iran. In the 2006 census, its population was 27,117, with 7,052 families. This city is known as the wr ...
** Kordkuy
** Lahijan
** Langarud
** Mahmudabad
** Neka
** Nowshahr
** Nur
** Ramsar
** Rasht
** Rudbar
** Rudsar
** Sari
**Sorkhrud
Sorkhrud ( fa, سرخرود, also Romanized as Sorkhrūd, Sorkh Rūd, and Surkhrūd; also known as Sokhrun and Sorkhrūd-e Gharbī) is a city and capital of Sorkhrud District, in Mahmudabad County, Mazandaran Province, Iran
Iran, ...
** Tonekabon
*Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
:
** Astara
** Baku
** Gobustan
** Khudat
** Khachmaz
** Lankaran
** Masallı
** Nabran
** Neftchala
**Shabran
Shabran District ( az, Şabran rayonu) is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the north-east of the country and belongs to the Guba-Khachmaz Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Khachmaz, Quba, Khizi and Si ...
** Siyazan
** Oil Rocks
** Sumqayit
*Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
:
** Atyrau
**Aktau
Aktau ( kk, Aqtau, Ақтау , russian: Актау) is a city in Kazakhstan, located on the eastern shore of the Caspian Sea. Its current name means "white mountain" in Kazakh, which may be due to its cliffs that overlook the Caspian. From 1964 to ...
*Russia:
**Astrakhan
Astrakhan ( rus, Астрахань, p=ˈastrəxənʲ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in Southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of ...
**Dagestanskiye Ogni
Dagestanskiye Ogni (russian: Дагестанские Огни ; tab, Дагъустнан ЦIаяр; az, Дағыстан Ишыглары, ''Dağıstan İşıqları''; lez, Дагъустандин ЦӀаяр) is a town in the Republic of Da ...
** Derbent
**Izberbash
Izberbash (russian: Изберба́ш; Dargwa: Избир; kum, Йизбирба́ш, ''Yizbirbaş'') is a town in the Republic of Dagestan, Russia, located on the coast of the Caspian Sea southeast of Makhachkala, the capital of the republic. ...
** Kaspiysk
**Makhachkala
Makhachkala ( rus, Махачкала, , məxətɕkɐˈla, links=yes),; av, Махӏачхъала, Maħaçqala; ce, ХӀинжа-ГӀала, Hinƶa-Ġala; az, Маһачгала, Mahaçqala; nog, Махачкала; lbe, Махачкъала; ...
*Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the s ...
:
** Türkmenbaşy (formerly Krasnovodsk)
** Hazar (formerly Çeleken)
** Esenguly
** Garabogaz (formerly Bekdaş)
Economy
 Countries in the Caspian region, particularly
Countries in the Caspian region, particularly Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
and Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the s ...
, have high-value natural-resource-based economies, where the oil and gas compose more than 10 percent of their GDP and 40 percent of their exports. All the Caspian region economies are highly dependent on this type of mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ...
wealth. The world energy markets were influenced by Azerbaijan and Kazakhstan, as they became strategically crucial in this sphere, thus attracting the largest share of FDI (foreign direct investment).
All of the countries are rich in solar energy and harnessing potential, with the highest rainfall much less than the mountains of central Europe in the mountains of the west, which are also rich in hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined a ...
sources.
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
has high fossil fuel energy potential. It has reserves of 137.5 billion barrels
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, u ...
of crude oil, the fourth largest in the world, producing around four million barrels a day. Iran has an estimated 988.4 trillion cubic feet of natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon ...
, around 16 percent of world reserves, thus key to current paradigms in global energy security.
Russia's economy ranks as the twelfth largest by nominal GDP and sixth largest by purchasing power parity
Purchasing power parity (PPP) is the measurement of prices in different countries that uses the prices of specific goods to compare the absolute purchasing power of the countries' currencies. PPP is effectively the ratio of the price of a baske ...
in 2015. Russia's extensive mineral and energy resources are the largest such reserves in the world, making it the second leading producer of oil and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon ...
globally.
Caspian littoral
The littoral zone or nearshore is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely inundated), to coastal areas ...
states join efforts to develop infrastructure, tourism and trade in the region. The first Caspian Economic Forum was convened on August 12, 2019, in Turkmenistan and brought together representatives of Kazakhstan, Russia, Azerbaijan, Iran and that state. It hosted several meetings of their ministers of economy and transport.
The Caspian countries develop robust cooperation in the tech and digital field as part of the Caspian Digital Hub. The project helps expand data transmission capabilities in Kazakhstan as well as data transit capabilities between Asia and Europe. The project generated interest from investors from all over the world, including the UK.
Oil and gas
U.S. Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United States. ...
. The region output about 1.4–1.5 million barrels
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, u ...
per day plus natural gas liquids in 2001, 1.9% of total world output. More than a dozen countries output more than this top figure. Caspian region production has been higher, but waned during and after the collapse of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
. Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
accounts for 55% and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
for about 20% of the states' oil output. The world's first offshore wells and machine-drilled wells were made in Bibi-Heybat Bay, near Baku, Azerbaijan. In 1873, exploration and development of oil began in some of the largest fields known to exist in the world at that time on the Absheron Peninsula near the villages of Balakhanli, Sabunchi, Ramana, and Bibi Heybat. Total recoverable reserves were more than 500 million tons. By 1900, Baku had more than 3,000 oil wells, 2,000 of which were producing at industrial levels. By the end of the 19th century, Baku became known as the "black gold capital", and many skilled workers and specialists flocked to the city.
By the beginning of the 20th century, Baku was the center of the international oil industry. In 1920, when the
The world's first offshore wells and machine-drilled wells were made in Bibi-Heybat Bay, near Baku, Azerbaijan. In 1873, exploration and development of oil began in some of the largest fields known to exist in the world at that time on the Absheron Peninsula near the villages of Balakhanli, Sabunchi, Ramana, and Bibi Heybat. Total recoverable reserves were more than 500 million tons. By 1900, Baku had more than 3,000 oil wells, 2,000 of which were producing at industrial levels. By the end of the 19th century, Baku became known as the "black gold capital", and many skilled workers and specialists flocked to the city.
By the beginning of the 20th century, Baku was the center of the international oil industry. In 1920, when the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
captured Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, all private property, including oil wells and factories, was confiscated. Rapidly the republic's oil industry came under the control of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
. By 1941, Azerbaijan was producing a record 23.5 million tons of oil per year – its Baku region output was nearly 72 percent of the Soviet Union's oil.
In 1994, the " Contract of the Century" was signed, heralding extra-regional development of the Baku oil fields. The large Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline conveys Azeri oil to the Turkish Mediterranean port of Ceyhan and opened in 2006.
The oil field in the Russian section of the body of water was discovered in 2005. It is reportedly the largest found in 25 years. It was announced in October 2016 that Lukoil
The PJSC Lukoil Oil Company ( stylized as LUKOIL or ЛУКОЙЛ in Cyrillic script) is a Russian multinational energy corporation headquartered in Moscow, specializing in the business of extraction, production, transport, and sale of petrol ...
would start production from it.
Transport
Baku has the main moorings of all large vessels, such as oil tankers, inAzerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
. It is the largest port of the Caspian Sea. The port (and tankers) have access to the oceans along the Caspian Sea–Volga– Don Canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface fl ...
, and the Don– Sea of Azov. A northern alternate is the Volga–Baltic (a sea which has a connection to the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
of the Atlantic, as the White Sea
The White Sea (russian: Белое море, ''Béloye móre''; Karelian and fi, Vienanmeri, lit. Dvina Sea; yrk, Сэрако ямʼ, ''Serako yam'') is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is s ...
does via the White Sea-Baltic canal. Baku Sea Trade Port and Caspian Shipping Company CJSC, have a big role in the sea transportation of Azerbaijan. The Caspian Sea Shipping Company CJSC has two fleets plus shipyards. Its transport fleet has 51 vessels: 20 tankers, 13 ferries, 15 universal dry cargo vessels, 2 Ro-Ro vessels, as well as 1 technical vessel and 1 floating workshop. Its specialized fleet has 210 vessels: 20 cranes, 25 towing and supplying vehicles, 26 passenger, two pipe-laying, six fire-fighting, seven engineering-geological, two diving and 88 auxiliary vessels.
The Caspian Sea Shipping Company of Azerbaijan, which acts as a liaison in the Transport Corridor Europe-Caucasus-Asia (TRACECA), simultaneously with the transportation of cargo and passengers in the Trans-Caspian direction, also performs work to fully ensure the processes of oil and gas production at sea. In the 19th century, the sharp increase in oil production in Baku gave a huge impetus to the development of shipping in the Caspian Sea, and as a result, there was a need to create fundamentally new floating facilities for the transportation of oil and oil products.
Political issues
Many of the islands along the Azerbaijani coast retain great geopolitical and economic importance for demarcation-line oil fields relying on their national status. Bulla Island, Pirallahı Island, and Nargin, which is still used as a former Soviet base and is the largest island in the Baku bay, hold oil reserves. The collapse of the Soviet Union allowed the market opening of the region. This led to intense investment and development by international oil companies. In 1998,Dick Cheney
Richard Bruce Cheney ( ; born January 30, 1941) is an American politician and businessman who served as the 46th vice president of the United States from 2001 to 2009 under President George W. Bush. He is currently the oldest living former ...
commented that "I can't think of a time when we've had a region emerge as suddenly to become as strategically significant as the Caspian."
A key problem to further local development is arriving at precise, agreed demarcation lines among the five littoral
The littoral zone or nearshore is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely inundated), to coastal areas ...
states. The current disputes along Azerbaijan's maritime borders with Turkmenistan and Iran could impinge future development.
Much controversy currently exists over the proposed Trans-Caspian oil and gas pipelines. These projects would allow Western markets easier access to Kazakh oil and, potentially, Uzbek and Turkmen gas as well. Russia officially opposes the project on environmental grounds.Sergei Blagov,Russia Tries to Scuttle Proposed Trans-Caspian Pipeline
", Eurasianet (2006-03-27) However, analysts note that the pipelines would bypass Russia completely, thereby denying the country valuable transit fees, as well as destroying its current
monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situation where a speci ...
on westward-bound hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
exports from the region. Recently, both Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan have expressed their support for the Trans-Caspian Pipeline.
U.S. diplomatic cables disclosed by WikiLeaks
WikiLeaks () is an international non-profit organisation that published news leaks and classified media provided by anonymous sources. Julian Assange, an Australian Internet activist, is generally described as its founder and director and ...
revealed that BP covered up a gas leak and blowout
Blowout or Blow out may refer to:
Film and television
*''Blow Out'', a 1981 film by Brian De Palma
* ''The Blow Out'', a 1936 short film
* ''Blow Out'' (TV series), a TV series on Bravo
* "Blow Out" (''Prison Break''), an episode of ''Prison ...
incident in September 2008 at an operating gas field in the Azeri-Chirag-Guneshi area of the Azerbaijan Caspian Sea.
Territorial status


Coastline
Five states are located along about of Caspian coastline. The length of the coastline of these countries: # Kazakhstan - # Turkmenistan - # Azerbaijan - # Russia - # Iran -Negotiations
In 2000, negotiations as to thedemarcation
Demarcation is the act of creating a boundary around a place or thing.
Demarcation may also refer to:
*Demarcation line, a temporary border between the countries
*Demarcation problem, the question of which practices of doing science permit the re ...
of the sea had been going on for nearly a decade among all the states bordering it. Whether it was by law a sea, a lake, or an agreed hybrid, the decision would set the demarcation rules and was heavily debated. Access to mineral resources ( oil and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon ...
), access for fishing, and access to international waters
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed region ...
(through Russia's Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchm ...
river and the canals connecting it to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
and Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and fr ...
) all rest on the negotiations' outcome. Access to the Volga is key for market efficiency and economic diversity of the landlocked
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest ...
states of Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, and Turkmenistan. This concerns Russia as more traffic seeks to use — and at some points congest — its inland waterway
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary ...
s. If the body of water is, by law, a sea, many precedents and international treaties oblige free access to foreign vessels. If it is a lake there are no such obligations.
Resolving and improving some environmental issues properly rests on the status and border
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political bo ...
s issue.
All five Caspian littoral states maintain naval forces on the sea.
According to a treaty signed between Iran and the Soviet Union, the sea is technically a lake and was divided into two sectors (Iranian and Soviet), but the resources (then mainly fish) were commonly shared. The line between the two sectors was considered an international border in a common lake, like Lake Albert. The Soviet sector was sub-divided into the four littoral republics' administrative sectors.
Russia, Kazakhstan, and Azerbaijan have bilateral agreements with each other based on median lines. Because of their use by the three nations, median lines seem to be the most likely method of delineating territory in future agreements. However, Iran insists on a single, multilateral agreement between the five nations (aiming for a one-fifth share). Azerbaijan is at odds with Iran over some of the sea's oil fields. Occasionally, Iranian patrol boats have fired at vessels sent by Azerbaijan for exploration into the disputed region. There are similar tensions between Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan (the latter claims that the former has pumped more oil than agreed from a field, recognized by both parties as shared).
The Caspian littoral states' meeting in 2007 signed an accord that only allows littoral-state flag-bearing ships to enter the sea.
Negotiations among the five states ebbed and flowed, from about 1990 to 2018. Progress was notable in the fourth Caspian Summit held in Astrakhan
Astrakhan ( rus, Астрахань, p=ˈastrəxənʲ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in Southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of ...
in 2014.
Caspian Summit
The Caspian Summit is a head of state-level meeting of the five littoral states. The fifth Caspian Summit took place on August 12, 2018, in the Kazakh port city ofAktau
Aktau ( kk, Aqtau, Ақтау , russian: Актау) is a city in Kazakhstan, located on the eastern shore of the Caspian Sea. Its current name means "white mountain" in Kazakh, which may be due to its cliffs that overlook the Caspian. From 1964 to ...
. The five leaders signed the ‘Convention on the Legal Status of the Caspian Sea’.
Representatives of the Caspian littoral states held a meeting in the capital of Kazakhstan on September 28, 2018, as a follow-up to the Aktau Summit. The conference was hosted by the Kazakh Ministry of Investment and Development. The participants in the meeting agreed to host an investment forum for the Caspian region every two years.
Convention on the legal status of the Caspian Sea
The five littoral states build consensus on legally binding governance of the Caspian Sea through Special Working Groups of a Convention on the Legal Status of the Caspian Sea. In advance of a Caspian Summit, the 51st Special Working Group took place inAstana
Astana, previously known as Akmolinsk, Tselinograd, Akmola, and most recently Nur-Sultan, is the capital city of Kazakhstan.
The city lies on the banks of the Ishim River in the north-central part of Kazakhstan, within the Akmola Region, tho ...
in May 2018 and found consensus on multiple agreements: Agreements on cooperation in the field of transport; trade and economic cooperation; prevention of incidents on the sea; combating terrorism; fighting against organized crime; and border security cooperation.
The convention grants jurisdiction over of territorial waters to each neighboring country, plus an additional of exclusive fishing rights on the surface, while the rest is international waters
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed region ...
. The seabed, on the other hand, remains undefined, subject to bilateral agreements between countries. Thus, the Caspian Sea is legally neither fully a sea nor a lake.
While the convention addresses caviar production, oil and gas extraction, and military uses, it does not touch on environmental issues.
Crossborder inflow
UNECE
The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (ECE or UNECE) is one of the five regional commissions under the jurisdiction of the United Nations Economic and Social Council. It was established in order to promote economic cooperation and i ...
recognizes several rivers that cross international borders which flow into the Caspian Sea.
These are:
Transportation
Although the Caspian Sea is endorheic, its main tributary, theVolga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchm ...
, is connected by important shipping canals with the Don River (and thus the Black Sea) and with the Baltic Sea, with branch canals to Northern Dvina and to the White Sea.
Another Caspian tributary, the Kuma River, is connected by an irrigation canal with the Don basin as well.
Scheduled ferry services (including train ferries) across the sea chiefly are between:
* Türkmenbaşy in Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the s ...
, (formerly Krasnovodsk) and Baku.
*Aktau
Aktau ( kk, Aqtau, Ақтау , russian: Актау) is a city in Kazakhstan, located on the eastern shore of the Caspian Sea. Its current name means "white mountain" in Kazakh, which may be due to its cliffs that overlook the Caspian. From 1964 to ...
, Kazakhstan and Baku.
*Cities in Iran and Russia (chiefly for cargo.)
Canals
As anendorheic basin
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into la ...
, the Caspian Sea basin has no natural connection with the ocean. Since the medieval period, traders reached the Caspian via a number of portages that connected the Volga and its tributaries with the Don River (which flows into the Sea of Azov) and various rivers that flow into the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and fr ...
. Primitive canals connecting the Volga Basin with the Baltic were constructed as early as the early 18th century. Since then, a number of canal projects have been completed.
The two modern canal systems that connect the Volga Basin, and hence the Caspian Sea, with the ocean are the Volga–Baltic Waterway
The Volga–Baltic Waterway (Volgobalt, Волгобалт), formerly known as the Mariinsk Canal System (Russian: Мариинская водная система), is a series of canals and rivers in Russia which link the Volga with the Ba ...
and the Volga–Don Canal.
The proposed Pechora–Kama Canal was a project that was widely discussed between the 1930s and 1980s. Shipping was a secondary consideration. Its main goal was to redirect some of the water of the Pechora River (which flows into the Arctic Ocean) via the Kama River
The Kama (russian: Ка́ма, ; tt-Cyrl, Чулман, ''Çulman''; udm, Кам) is a long«Река � ...
into the Volga. The goals were both irrigation and the stabilization of the water level in the Caspian, which was thought to be falling dangerously fast at the time. During 1971, some peaceful nuclear construction experiments were carried out in the region by the U.S.S.R.
In June 2007, in order to boost his oil-rich country's access to markets, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
's President Nursultan Nazarbayev
Nursultan Abishuly Nazarbayev ( kk, Нұрсұлтан Әбішұлы Назарбаев, Nūrsūltan Äbişūlı Nazarbaev, ; born 6 July 1940) is a Kazakhs, Kazakh politician and military officer who served as the first President of Kazakhstan ...
proposed a link between the Caspian Sea and the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
. It is hoped that the " Eurasia Canal" ( Manych Ship Canal) would transform landlocked Kazakhstan and other Central Asian countries into maritime states, enabling them to significantly increase trade volume. Although the canal would traverse Russian territory, it would benefit Kazakhstan through its Caspian Sea ports. The most likely route for the canal, the officials at the Committee on Water Resources at Kazakhstan's Agriculture Ministry say, would follow the Kuma–Manych Depression, where currently a chain of rivers and lakes is already connected by an irrigation canal (the Kuma–Manych Canal). Upgrading the Volga–Don Canal would be another option.''
Business Week
''Bloomberg Businessweek'', previously known as ''BusinessWeek'', is an American weekly business magazine published fifty times a year. Since 2009, the magazine is owned by New York City-based Bloomberg L.P. The magazine debuted in New York City ...
'' (2007-07-09)See also
* Caspians *Caspian languages
The Caspian languages are a branch of Northwestern Iranian languages spoken in northern Iran and south-eastern Azerbaijan, south of the Caspian Sea. They are unique in that they share certain typological features with South Caucasian language ...
* Baku oil fields
The petroleum industry in Azerbaijan produces about of oil per day and 29 billion cubic meters of gas per year as of 2013. Azerbaijan is one of the birthplaces of the oil industry.
The State Oil Company of Azerbaijan Republic (known as SOCAR) ...
* Epoch of Extreme Inundations
* Eurasia Canal
* Framework Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Caspian Sea
* Iranrud
* Shah Deniz gas field
* South Caucasus Pipeline
* Southern Gas Corridor
* Tengiz Field
* Trans-Caspian Gas Pipeline
* Trans-Caspian Oil Transport System
The Trans-Caspian Oil Transport System is a proposed project to transport oil through the Caspian Sea from Kazakhstani Caspian oilfields to Baku in Azerbaijan for the further transportation to the Mediterranean or Black Sea coast. The main options ...
* Volga–Don Canal
* Wildlife of Azerbaijan
* Wildlife of Iran The wildlife of Iran include the fauna and flora of Iran.
One of the most famous wildlife of Iran is the critically endangered Asiatic cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus venaticus''), which today survives only in Iran.
History
The wildlife of Iran first ...
* Wildlife of Kazakhstan
* Wildlife of Turkmenistan
The wildlife of Turkmenistan is the flora and fauna of Turkmenistan, and the natural habitats in which they live. Turkmenistan is a country in Central Asia to the east of the Caspian Sea. Two thirds of the country is hot dry plains and desert, and ...
* Wildlife of Russia
The wildlife of Russia inhabits terrain that extends across 12 time zones and from the tundra region in the far north to the Caucasus Mountains and prairies in the south, including temperate forests which cover 70% of the country's territory. Russi ...
References
External links
*Names of the Caspian Sea
Caspian Sea Region
{{Authority control Ancient lakes Azerbaijan–Iran border Azerbaijan–Russia border Bodies of water of Iran Border tripoints Endorheic lakes of Europe Endorheic lakes of Asia Eutrophication Geography of Central Asia Geography of Eastern Europe Geography of Southern Russia Geography of Western Asia International disputes International lakes of Asia International lakes of Europe Iran–Soviet Union border Iran–Turkmenistan border Kazakhstan–Russia border Kazakhstan–Turkmenistan border Lakes of Astrakhan Oblast Lakes of Azerbaijan Lakes of Dagestan Lakes of Iran Lakes of Kalmykia Lakes of Kazakhstan Lakes of Turkmenistan Landforms of Central Asia Landforms of Western Asia Lowest points Saline lakes of Asia Saline lakes of Europe Seas of Iran