Canton Zürich on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The canton of Zurich is an administrative unit ( canton) of Switzerland, situated in the northeastern part of the country. With a population of (as of ), it is the most populous canton of Switzerland.
 The prehistoric pile dwellings around Lake Zurich, which are located around
The prehistoric pile dwellings around Lake Zurich, which are located around 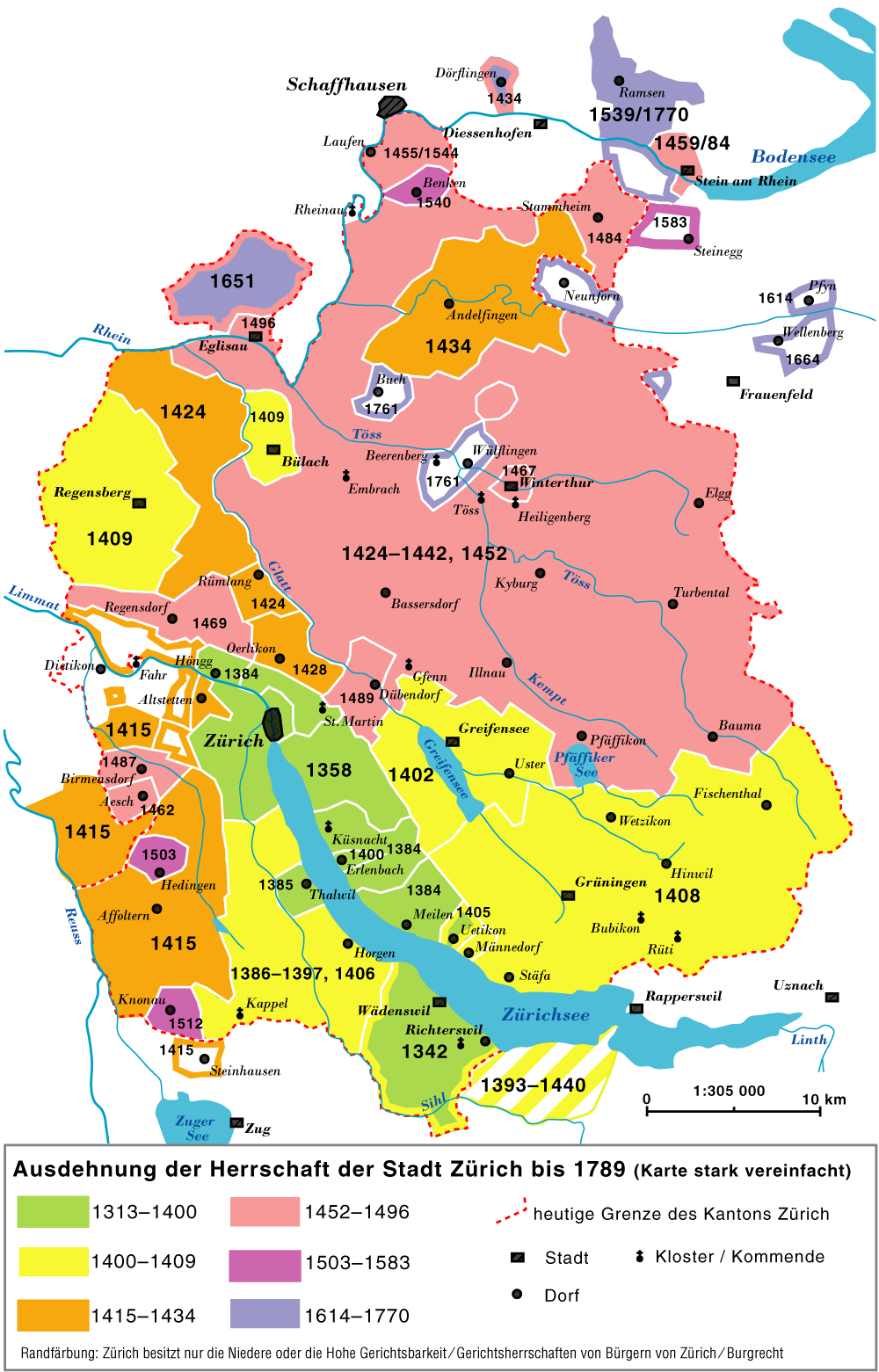 Zurihgauuia (Zürichgau) was a subdivision of Turgowe (Thurgau) in the Duchy of Alamannia, consisting roughly of the territory between
Zurihgauuia (Zürichgau) was a subdivision of Turgowe (Thurgau) in the Duchy of Alamannia, consisting roughly of the territory between
accessed 27 October 2016
accessed 5 January 2012 Most of the population () speaks
single
and never married in the canton. There were 566,636 married individuals, 66,012 widows or widowers and 84,164 individuals who are divorced.STAT-TAB Datenwürfel für Thema 40.3 – 2000
accessed 2 February 2011 , there were 567,573 private households in the canton, and an average of 2.1 persons per household. There were 223,869 households that consist of only one person and 27,935 households with five or more people. , the construction rate of new housing units was 5.3 new units per 1000 residents. the average price to rent an average apartment in the city of Zurich was 1288.84
2003 data accessed 26 May 2010 The vacancy rate for the canton, , was 0.63%.
Swiss Federal Tax Office
2015 numbers accessed 19 April 2017
 Railways in standard gauge run through all major valleys in the canton. The centre for transport is Zurich, where a great number of local railways connect to national and international rail links. The railway station of the city of Zurich,
Railways in standard gauge run through all major valleys in the canton. The centre for transport is Zurich, where a great number of local railways connect to national and international rail links. The railway station of the city of Zurich,
Official StatisticsZürich Tourism
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Zurich Cantons of Switzerland Cantons of the Helvetic Republic 14th-century establishments in the Old Swiss Confederacy 1350s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1351 establishments in Europe
Zurich
Zurich (; ) is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich. , the municipality had 448,664 inhabitants. The ...
is the ''de facto'' capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
of the canton, but is not specifically mentioned in the constitution. The official language
An official language is defined by the Cambridge English Dictionary as, "the language or one of the languages that is accepted by a country's government, is taught in schools, used in the courts of law, etc." Depending on the decree, establishmen ...
is German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
. The local Swiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , ,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no #Conventions, defined orthography for any of them, many different spellings can be found. and others; ) is any of the Alemannic German, Alemannic ...
dialect, called ''Züritüütsch
Zurich German (natively ; ) is the High Alemannic dialect spoken in the Canton of Zurich, Switzerland. Its area covers most of the canton, with the exception of the parts north of the Thur and the Rhine, which belong to the areal of the north ...
'', is commonly spoken.
The canton has the highest Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, Education Index, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income i ...
score (0.994) out of 1,790 subnational regions as of 2022. It is also a global financial center
A financial centre (financial center in American English) or financial hub is a location with a significant concentration of commerce in financial services.
The commercial activity that takes place in a financial centre may include banking, ...
and has the fourth-highest GRP in Switzerland behind Basel-Stadt
Canton of Basel-Stadt or Basel-City ( ; ; ; ) is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of three municipalities with Basel as the capital. It is traditionally considered a " half-canton", the other half being B ...
, Zug
Zug (Standard German: , Alemannic German: ; ; ; ; )Named in the 16th century. is the largest List of cities in Switzerland, town and capital of the Swiss canton of Zug. Zug is renowned as a hub for some of the wealthiest individuals in the wor ...
and Geneva
Geneva ( , ; ) ; ; . is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland and the most populous in French-speaking Romandy. Situated in the southwest of the country, where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the ca ...
by GDP per capita.
History
Early history
 The prehistoric pile dwellings around Lake Zurich, which are located around
The prehistoric pile dwellings around Lake Zurich, which are located around Lake Zurich
Lake Zurich (, ; ) is a lake in Switzerland, extending southeast of the city of Zurich. Depending on the context, Lake Zurich or can be used to describe the lake as a whole, or just that part of the lake downstream of the Hurden peninsula and ...
in the cantons
A canton is a type of administrative division of a country. In general, cantons are relatively small in terms of area and population when compared with other administrative divisions such as counties, departments, or provinces. Internationally, th ...
of Schwyz
Schwyz (; ; ) is a town and the capital of the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland.
The Federal Charter of 1291 or ''Bundesbrief'', the charter that eventually led to the foundation of Switzerland, can be seen at the ''Bundesbriefmuseum''.
The of ...
, St. Gallen and Zurich, make up a considerable portion of the 56 sites in Switzerland that are included in the UNESCO World Heritage Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps. Nine of these UNESCO World Heritage sites are located on the shore of Lake Zurich: Freienbach–Hurden Rosshorn, Freienbach–Hurden Seefeld, Rapperswil-Jona/Hombrechtikon–Feldbach, Rapperswil-Jona–Technikum, Erlenbach–Winkel, Meilen–Rorenhaab
Meilen–Rorenhaab is one of the 111 serial sites of the UNESCO World Heritage Site ''Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps'', of which 56 are located in Switzerland.
Geography
The site is located on Lake Zurich {''Zürichsee'') lakeshore ...
, Wädenswil–Vorder Au, Zürich–Enge Alpenquai and Kleiner Hafner. Because the lake has grown in size over time, the original piles are now around to under the water level of . Within an area of about around Lake Zurich, there also the settlements Greifensee–Storen/Wildsberg at the Greifensee and Wetzikon–Robenhausen at the Pfäffikersee. As well as being part of the 56 Swiss sites of the UNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
, each of these 11 prehistoric pile dwellings is also listed as a ''Class object'' in the Swiss inventory of cultural property of national and regional significance #REDIRECT Swiss Inventory of Cultural Property of National and Regional Significance {{R from other capitalisation ...
.
 Zurihgauuia (Zürichgau) was a subdivision of Turgowe (Thurgau) in the Duchy of Alamannia, consisting roughly of the territory between
Zurihgauuia (Zürichgau) was a subdivision of Turgowe (Thurgau) in the Duchy of Alamannia, consisting roughly of the territory between Reuss Reuss may refer to:
*Reuss (surname)
* Reuss (river) in Switzerland
* Imperial County of Reuss or Reuß, several former states or countries in present-day Germany, and the People's State of Reuss
* Principality of Reuss-Greiz and Principality of R ...
and Töss. From the 740s, substantial portions of Zürichgau were owned by the Abbey of St. Gall. In , an administrative re-organisation under counts Ruthard and Warin exempted the castle town of Zurich from comital rule. A county of Zürichgau was established under Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious (; ; ; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and Holy Roman Emperor, co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aquitaine from 781. As the only ...
, for a count Ruadker, in 820. Zürichgau (''Zurichgeuue'') remained a nominally separate territory in the later 9th century but was often ruled by the same count as Thurgau. In 915, Zürichgau together with Thurgau fell to the Bucharding dukes of Swabia
The Dukes of Swabia were the rulers of the Duchy of Swabia during the Middle Ages. Swabia was one of the five stem duchy, stem duchies of the medieval German kingdom, and its dukes were thus among the most powerful magnates of Germany. The most no ...
. In the late 10th century, the county of Zurich was ruled by the Nellenburger, and during 1077–1172 by the Lenzburger.
By the 13th century, Zürichgau was divided between the Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
and the Kyburger, who held the territory west and east of Lake Zurich, respectively.
City state
The territory of the canton of Zurich corresponds to the lands acquired by the city of Zurich after it became ''reichsfrei
In the Holy Roman Empire, imperial immediacy ( or ) was the status of an individual or a territory which was defined as 'immediate' () to Emperor and Empire () and not to any other intermediate authorities, while one that did not possess that stat ...
'' in 1218. Zurich pursued a policy of aggressive territorial expansion especially during the century following the revolution of the guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular territory. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradespeople belonging to a professional association. They so ...
s in 1336. Zurich joined the Swiss Confederacy
The Old Swiss Confederacy, also known as Switzerland or the Swiss Confederacy, was a loose confederation of independent small states (, German or ), initially within the Holy Roman Empire. It is the precursor of the modern state of Switzerlan ...
in 1351.
Zurich claimed and lost the Toggenburg in the Old Zürich War of the 1440s. The northern parts up to the river Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
came to the canton after the city of Zurich purchased Winterthur
Winterthur (; ) is a city in the canton of Zurich in northern Switzerland. With over 120,000 residents, it is the country's List of cities in Switzerland, sixth-largest city by population, as well as its ninth-largest agglomeration with about 14 ...
from the Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
in 1468.
In 1651, Zurich purchased Rafz
Rafz is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Bülach (district), Bülach in the northwest of the canton of Zürich in Switzerland.
Rafz was first mentioned in 1413 as ''Rafsa''.
Geography
Rafz has an area of . Of th ...
erfeld from the counts of Sulz. At this point, almost all of the territory of the modern canton (as well as some territories beyond its modern borders) was owned by Zurich; exceptions include Wülflingen (acquired 1760), Buch
Buch (the German word for book or a modification of the German word '' Buche'' for beech) may refer to:
People
* Buch (surname), a list of people with the surname Buch - mostly, in India or abroad as of Indian origin.
Geography
Germany
* Buch ...
(acquired 1761), Dietikon
Dietikon is the fifth biggest city of the canton of Zürich in Switzerland, after Zürich, Winterthur, Uster and Dübendorf. It is the capital of the same-named district of Dietikon and part of the Zürich metropolitan area.
Geography
The ...
, which was a condominium
A condominium (or condo for short) is an ownership regime in which a building (or group of buildings) is divided into multiple units that are either each separately owned, or owned in common with exclusive rights of occupation by individual own ...
, and Rheinau (owned by Rheinau Abbey).
In the 18th century, the "inner bailiwicks" (''Innere Vogteien'') were under direct administration of city officials, while the "outer bailiwicks" (''Äussere Vogteien'') were ruled by the reeves
Reeves may refer to:
People
* Reeves (surname)
* B. Reeves Eason (1886–1956), American director, actor and screenwriter
* Reeves Nelson (born 1991), American basketball player
Places
;Ireland
* Reeves, County Kildare, townland in County Kild ...
of Kyburg, Grüningen, Greifensee, Eglisau, Regensberg, Andelfingen, Wädenswil, and Knonau. The city of Winterthur
Winterthur (; ) is a city in the canton of Zurich in northern Switzerland. With over 120,000 residents, it is the country's List of cities in Switzerland, sixth-largest city by population, as well as its ninth-largest agglomeration with about 14 ...
was nominally subject to Zurich but retained far-reaching autonomy.
''Zürichgau'', the name of the medieval ''pagus'', was in use for the territories of the city of Zurich during the 15th and 16th century; the term ''canton'' (''Kanton'') gradually entered use in the 16th century, but ''Zürichgau'' remained widely used well into the 19th century (becoming obsolescent after the formation of the modern canton in 1831).
Under the short-lived Helvetic Republic (1798–1803), the canton of Zurich became a purely administrative division. In 1803, some former possessions of Zurich to the west gained independence as part of the Canton of Aargau
Aargau ( ; ), more formally the Canton of Aargau (; ; ; ), is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capital is Aarau.
Aargau is one of the most northerly cantons of Switzerland, by th ...
. In 1804 the Kantonspolizei Zürich
The Kantonspolizei Zürich () is the police department of the canton of Zürich in Switzerland. The Kantonspolizei Zürich exists within the cantonal legal structure to enforce criminal, security, and traffic law on behalf of the government of th ...
was established as ''Landjägerkorps'' (rural police).
Modern canton
A cantonal constitution was drawn up in 1814 and replaced in 1831 by aradical-liberal
Radicalism (from French ) was a political movement representing the leftward flank of liberalism between the late 18th and early 20th century. Certain aspects of the movement were precursors to a wide variety of modern-day movements, ranging f ...
constitution. The Züriputsch
The Züriputsch of 6 September 1839 was a putsch of the rural conservative population against the liberal rule of the city of Zurich on the eve of the formation of the Swiss federal state. The reason for the putsch was the appointment of the ...
, an armed uprising of the conservative rural population against the radical-liberal order, led to the dissolution of the cantonal government, and a provisional conservative government was installed by colonel Paul Carl Eduard Ziegler.
Under the threat of intervention of the other radical-liberal cantons of the Confederacy, the provisional government declared that the 1831 constitution would remain in effect. In a tumultuous session on 9 September 1839, the cantonal parliament declared its dissolution
In the so-called ''Septemberregime'', the newly elected cantonal government replaced all cantonal officials with conservatives, but it was again ousted by a radical-liberal election victory in 1844.
Alfred Escher was a member of the new cantonal parliament of 1844; he was elected to the cantonal government in 1848 and later in the same year into the first National Council under the new federal constitution.
The radical-liberal era of 1844–1868 was dominated by the so-called ''System Escher'', a network of liberal politicians and industrialists built by Alfred Escher. Escher governed the canton almost in monarchical fashion, and was popularly dubbed ''Alfred I.'' or ''Tsar of All Zurich''. Escher controlled all cantonal institutions, at first with very little political opposition, expunging all trace of the conservative takeover of 1839. Under Escher, the city of Zurich rose to the status of economic and financial center it still retains.
Opposition against the dominance of ''Sytstem Escher'' increased after 1863. The cantonal government was accused to continue the system of aristocratic rule liberalism had claimed to abolish. The oppositional ''Democratic Movement'' was centered in Winterthur
Winterthur (; ) is a city in the canton of Zurich in northern Switzerland. With over 120,000 residents, it is the country's List of cities in Switzerland, sixth-largest city by population, as well as its ninth-largest agglomeration with about 14 ...
, led by mayor Johann Jakob Sulzer and publicist Salomon Bleuler. They succeeded in imposing the introduction of the direct democratic
Direct democracy or pure democracy is a form of democracy in which the electorate directly decides on policy initiatives, without elected representatives as proxies, as opposed to the representative democracy model which occurs in the major ...
instrument of the popular initiative
A popular initiative (also citizens' initiative) is a form of direct democracy by which a petition meeting certain hurdles can force a legal procedure on a proposition.
In direct initiative, the proposition is put directly to a plebiscite o ...
in 1865, which precipitated a revision of the cantonal constitution.
In April 1869, a new cantonal constitution was adopted by popular vote, introducing additional direct democratic elements and the popular election of both the cantonal government and the cantonal representatives in the federal Council of States.
The new constitution also abolished the death penalty
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in s ...
(the last execution by hanging in Zurich took place in 1810, the last public execution by guillotine in 1865), guaranteed freedom of religion
Freedom of religion or religious liberty, also known as freedom of religion or belief (FoRB), is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice ...
and freedom of association
Freedom of association encompasses both an individual's right to join or leave groups voluntarily, the right of the group to take collective action to pursue the interests of its members, and the right of an association to accept or decline membe ...
and introduced progressive tax
A progressive tax is a tax in which the tax rate increases as the taxable amount increases. The term ''progressive'' refers to the way the tax rate progresses from low to high, with the result that a taxpayer's average tax rate is less than the ...
es.
In 1877, the Cantonal Laboratory Zurich was founded in order to regulate the quality of food and drinking water. The first cantonal chemist was Haruthiun Abeljanz, who was instrumental in setting up the new laboratory, moving it from an unpromising start in converted storage rooms to Lintheschergasse 10, which was located just behind the Pestalozziwiese, a memorial to Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi
Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi (; ; ; 12 January 1746 – 17 February 1827) was a Swiss pedagogue and educational reformer who exemplified Romanticism in his approach.
He founded several educational institutions both in German- and French-speaking ...
.
The Cantonal Bank was established in 1870 to regulate cantonal loans at fixed interest rates to farms and businesses.
A law of proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to any electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions (Political party, political parties) amon ...
was passed in 1916, favouring the rise of the Social Democrats
Social democracy is a social, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achieving social equality. In modern practice, s ...
.
A proposal for the introduction of female suffrage was rejected in 1920; female suffrage was introduced on the municipal level in 1969 and on the cantonal level in 1970, shortly before its imposition by federal law, passed in 1971.
Economic growth continued in the 20th century. A first airport was built at Dübendorf
Dübendorf is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Uster (district), Uster in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Zürich (canton), Zürich in Switzerland.
It is a suburb of Zürich in Switzerland with a population o ...
in 1910, replaced by the international airport
An international airport is an airport with customs and border control facilities enabling passengers to travel between countries. International airports are usually larger than domestic airports, and feature longer runways and have faciliti ...
at Kloten in 1948. Rapid urbanisation
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It can also ...
expanded throughout the canton and beyond in the final decades of the 20th century, further accelerated by the S-Bahn
The S-Bahn ( , ), , is a hybrid urban rail, urban–suburban rail system serving a metropolitan region predominantly in German language, German-speaking countries. Some of the larger S-Bahn systems provide service similar to rapid transit syst ...
from 1990, with only a few municipalities in Weinland, Knonaueramt and Oberland remaining out of easy commuting distance to the city.
The current constitution replaced the one of 1869 in January 2006.
The Antiquarische Gesellschaft in Zürich is an organization devoted to preserving the canton's history, the Staatsarchiv Zürich houses the state archives.
Geography
The canton of Zurich is situated in the eastern part of the Swiss plateau. It is entirely within the drainage basin of theHigh Rhine
High Rhine (, ; kilometres 0 to 167 of the Rhine) is the section of the Rhine between Lake Constance () and the city of Basel, flowing in a general east-to-west direction and forming mostly the Germany–Switzerland border. It is the first of fo ...
.
It is characterized by Glacial landform and traversed by a series of rivers generally flowing south-east to north-west, listed west to east: Reuss Reuss may refer to:
*Reuss (surname)
* Reuss (river) in Switzerland
* Imperial County of Reuss or Reuß, several former states or countries in present-day Germany, and the People's State of Reuss
* Principality of Reuss-Greiz and Principality of R ...
, Reppisch
The Reppisch is a river in Switzerland. It rises in the Türlersee and joins the Limmat as its tributary, near the town of Dietikon. The Reppisch flows in the Säuliamt (Affoltern district), canton of Zürich, an area featuring still partially u ...
, Sihl
The Sihl is a Switzerland, Swiss river that rises near the Druesberg mountain in the canton of Schwyz, and eventually flows into the Limmat in the centre of the Zürich, city of Zürich, after crossing the Zürich–Winterthur railway at . It has ...
, Linth
The Linth (pronounced "lint") is a Switzerland, Swiss river that rises near the Linthal, Glarus, village of Linthal in the mountains of the cantons of Switzerland, canton of canton of Glarus, Glarus, and eventually flows into the Obersee (Züri ...
-Limmat
The Limmat is a river in Switzerland. The river commences at the outfall of Lake Zurich, in the southern part of the city of Zurich. From Zurich it flows in a northwesterly direction, continuing a further 35 km until it reaches the river A ...
(forming Lake Zurich
Lake Zurich (, ; ) is a lake in Switzerland, extending southeast of the city of Zurich. Depending on the context, Lake Zurich or can be used to describe the lake as a whole, or just that part of the lake downstream of the Hurden peninsula and ...
), Glatt, Töss and Thur. The main lakes are the Lake Zurich
Lake Zurich (, ; ) is a lake in Switzerland, extending southeast of the city of Zurich. Depending on the context, Lake Zurich or can be used to describe the lake as a whole, or just that part of the lake downstream of the Hurden peninsula and ...
(Linth-Limmat, 88 km2), Greifensee (Glatt, 8.4 km2) and Pfäffikersee (Glatt, 3.3 km2). Minor lakes include Türlersee (Limmat), Katzensee (Glatt), Hüttnersee (Sihl), Lützelsee (Limmat).
Its neighbouring cantons are Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; ; ; ; ), historically known in English as Shaffhouse, is a list of towns in Switzerland, town with historic roots, a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of Schaffh ...
to the north, Aargau
Aargau ( ; ), more formally the Canton of Aargau (; ; ; ), is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capital is Aarau.
Aargau is one of the most nort ...
to the west, the cantons of Zug
Zug (Standard German: , Alemannic German: ; ; ; ; )Named in the 16th century. is the largest List of cities in Switzerland, town and capital of the Swiss canton of Zug. Zug is renowned as a hub for some of the wealthiest individuals in the wor ...
and Schwyz
Schwyz (; ; ) is a town and the capital of the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland.
The Federal Charter of 1291 or ''Bundesbrief'', the charter that eventually led to the foundation of Switzerland, can be seen at the ''Bundesbriefmuseum''.
The of ...
to the south and the cantons of Thurgau
Thurgau (; ; ; ), anglicized as Thurgovia, and formally as the Canton of Thurgau, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of five districts. Its capital is Frauenfeld.
Thurgau is part of Eastern Switzerland. I ...
and St. Gallen to the east.
It also has an international border with the German district of Waldshut and though only for ) the district of Konstanz
Konstanz ( , , , ), traditionally known as Constance in English, is a college town, university city with approximately 83,000 inhabitants located at the western end of Lake Constance in the Baden-Württemberg state of south Germany. The city ho ...
in Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million i ...
owing to its short border with Stemmer, an outlying hamlet belonging to the municipality which forms the small German enclave
An enclave is a territory that is entirely surrounded by the territory of only one other state or entity. An enclave can be an independent territory or part of a larger one. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is so ...
of Büsingen am Hochrhein
Büsingen am Hochrhein (, ; Alemannic: ', ), often known simply as Büsingen, is a German municipality () in the south of Baden-Württemberg with a population of about 1,548 inhabitants. It is an exclave of Germany and Baden-Württemberg, and ...
.
The canton can be roughly divided into the city and lake, the Unterland in the northwest, the Oberland in the southeast, the Weinland and Winterthur
Winterthur (; ) is a city in the canton of Zurich in northern Switzerland. With over 120,000 residents, it is the country's List of cities in Switzerland, sixth-largest city by population, as well as its ninth-largest agglomeration with about 14 ...
in the northeast, and the Knonaueramt southwest of the Albis. The Zurich Metropolitan Area extends beyond the cantonal borders.
The canton has an area, , of . Of this area, 43.4% is used for agricultural purposes, while 30.7% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 20.1% is settled (buildings or roads) and 5.8% is unproductive land.
Most of the canton consists of shallow river valleys which drain towards the High Rhine
High Rhine (, ; kilometres 0 to 167 of the Rhine) is the section of the Rhine between Lake Constance () and the city of Basel, flowing in a general east-to-west direction and forming mostly the Germany–Switzerland border. It is the first of fo ...
to the north. Rafz
Rafz is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Bülach (district), Bülach in the northwest of the canton of Zürich in Switzerland.
Rafz was first mentioned in 1413 as ''Rafsa''.
Geography
Rafz has an area of . Of th ...
erfeld is a territory north of the Rhine acquired by the canton in 1651. In the northwest and southeast of the canton the territory rises towards the Jura and Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
, respectively. The valley of the Linth
The Linth (pronounced "lint") is a Switzerland, Swiss river that rises near the Linthal, Glarus, village of Linthal in the mountains of the cantons of Switzerland, canton of canton of Glarus, Glarus, and eventually flows into the Obersee (Züri ...
leads into the Lake Zurich and continues as the Limmat
The Limmat is a river in Switzerland. The river commences at the outfall of Lake Zurich, in the southern part of the city of Zurich. From Zurich it flows in a northwesterly direction, continuing a further 35 km until it reaches the river A ...
. This valley is the most significant valley of the canton of Zurich. The valley of the Glatt originates in the Greifensee and is separated from the Limmat by ridges. The valley of the Töss is gorge-like. It is located in the east of the canton and is separated from the Toggenburg area in the canton of St. Gallen by a mountainous area.
The ''Hörnli'' (1133 m) is the highest elevation of this mountain ridge. The valley of the river Sihl
The Sihl is a Switzerland, Swiss river that rises near the Druesberg mountain in the canton of Schwyz, and eventually flows into the Limmat in the centre of the Zürich, city of Zürich, after crossing the Zürich–Winterthur railway at . It has ...
is located in the west of the canton. In converges with the Limmat
The Limmat is a river in Switzerland. The river commences at the outfall of Lake Zurich, in the southern part of the city of Zurich. From Zurich it flows in a northwesterly direction, continuing a further 35 km until it reaches the river A ...
in the city of Zurich. The Sihl is separated from the lake of Zurich by the '' Albis Range''. The ''Albishorn'' () is the highest elevation of this range.
The Schnebelhorn is a mountain located near Fischenthal in the Töss Valley, between the cantons of Zurich (west) and St. Gallen (east). It is the highest summit () of the canton of Zurich. The ''Uetliberg
__NOTOC__
The Uetliberg (also known as Üetliberg) is a mountain in the Swiss plateau, part of the Albis chain, rising to . The mountain offers a panoramic view of the entire city of Zürich (to the northeast of its summit), Zürichberg and ...
'' is part of the Albis Range. This mountain is popular with the population of the city of Zurich for recreation.
The vast majority of the canton lies to the south of the Rhine, the exceptions being Rafzerfeld as mentioned and a tiny portion of the village of Laufen-Uhwiesen called Nohl.
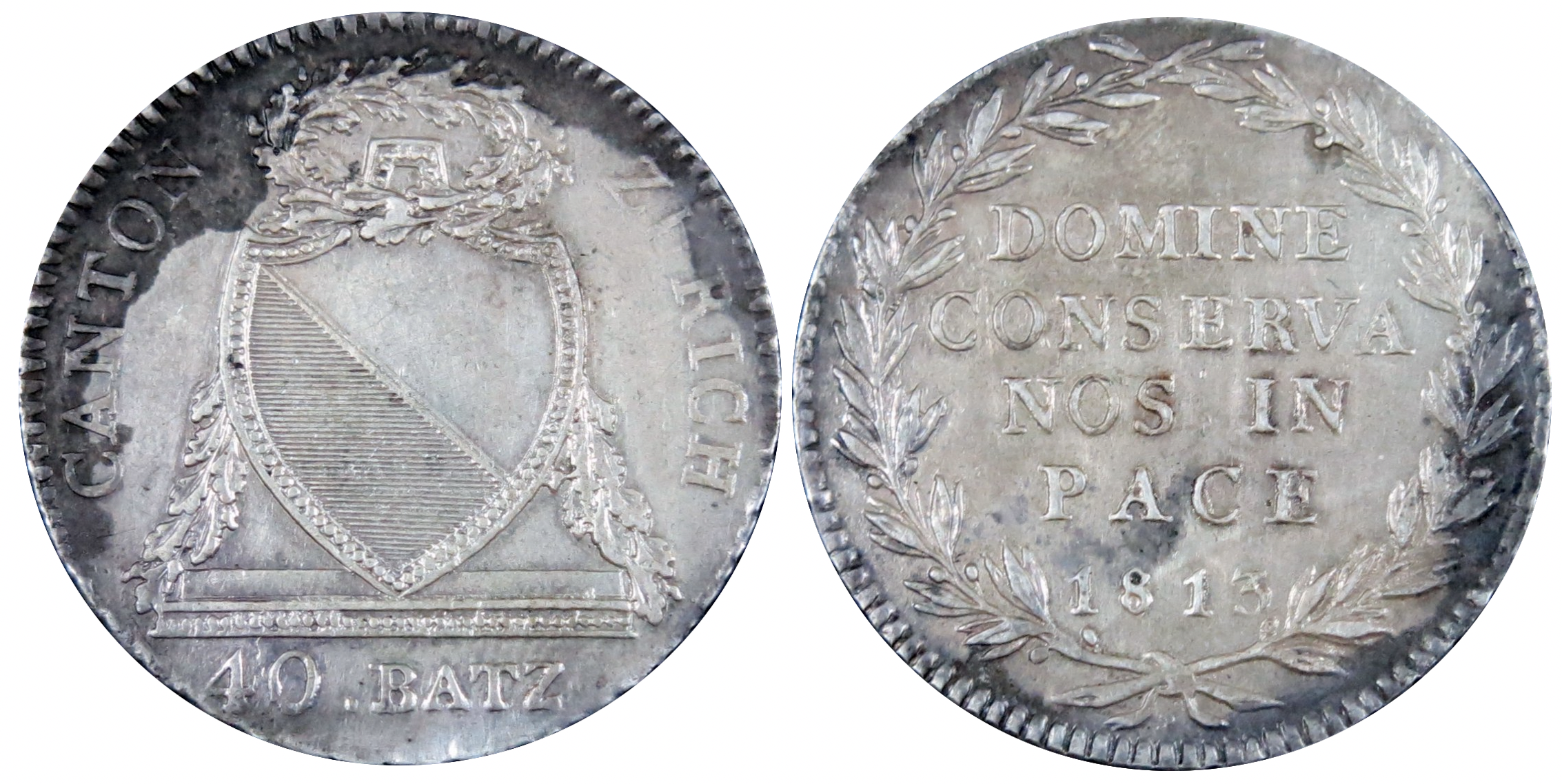
Coat of arms
Theblazon
In heraldry and heraldic vexillology, a blazon is a formal description of a coat of arms, flag or similar emblem, from which the reader can reconstruct an accurate image. The verb ''to blazon'' means to create such a description. The visual d ...
of the coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon f ...
is ''Per bend azure and argent.''
Government
Legislative power
The Cantonal Council (''Kantonsrat'') has 180 members elected every four years.Executive power
The canton is governed by a seven-member council (''Regierungsrat''). On 24 March 2019, the following were elected for four years: *Jacqueline Fehr
Jacqueline Fehr (born 1 June 1963) is a Swiss politician of the Social Democratic Party of Switzerland. She represents the Canton of Zürich in the Swiss National Council.
Professional career
Born in Wallisellen, Jacqueline Fehr grew up in ...
( SP)
* Mario Fehr (Independent)
* Martin Neukom ( Greens)
* Natalie Rickli ( SVP)
* Silvia Steiner ( CVP)
* Ernst Stocker ( SVP)
* Carmen Walker Späh ( FDP)
Political subdivisions
Districts
The canton is divided into 12 districts (German: ''Bezirke''): *Zurich
Zurich (; ) is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich. , the municipality had 448,664 inhabitants. The ...
comprises the city of Zurich
Zurich (; ) is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich. , the municipality had 448,664 inhabitants. The ...
* Affoltern with capital Affoltern am Albis
* Andelfingen with capital Andelfingen
* Bülach with capital Bülach
* Dielsdorf with capital Dielsdorf
*Dietikon
Dietikon is the fifth biggest city of the canton of Zürich in Switzerland, after Zürich, Winterthur, Uster and Dübendorf. It is the capital of the same-named district of Dietikon and part of the Zürich metropolitan area.
Geography
The ...
with capital Dietikon
Dietikon is the fifth biggest city of the canton of Zürich in Switzerland, after Zürich, Winterthur, Uster and Dübendorf. It is the capital of the same-named district of Dietikon and part of the Zürich metropolitan area.
Geography
The ...
* Hinwil with capital Hinwil
* Horgen with capital Horgen
*Meilen
Meilen is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Meilen (district), Meilen in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Zürich (canton), Zürich in Switzerland.
History
Archaeological finds in Meilen date back more than ...
with capital Meilen
Meilen is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Meilen (district), Meilen in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Zürich (canton), Zürich in Switzerland.
History
Archaeological finds in Meilen date back more than ...
* Pfäffikon with capital Pfäffikon
* Uster with capital Uster
*Winterthur
Winterthur (; ) is a city in the canton of Zurich in northern Switzerland. With over 120,000 residents, it is the country's List of cities in Switzerland, sixth-largest city by population, as well as its ninth-largest agglomeration with about 14 ...
with capital Winterthur
Winterthur (; ) is a city in the canton of Zurich in northern Switzerland. With over 120,000 residents, it is the country's List of cities in Switzerland, sixth-largest city by population, as well as its ninth-largest agglomeration with about 14 ...
Municipalities
There are, , 169 municipalities in the canton (''Politische Gemeinden'').Swiss Federal Statistical Office – Regional portraitsaccessed 27 October 2016
Merger of municipalities
There were no changes between 1934 and 2013, but the following occurred after 2013. * 2014: '' Bertschikon bei Attikon'' and ''Wiesendangen
Wiesendangen is a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Winterthur (district), Winterthur in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Zurich (canton), Zürich in Switzerland. On 1 January 2014 the former municipality of Bert ...
'' → Wiesendangen
Wiesendangen is a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Winterthur (district), Winterthur in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Zurich (canton), Zürich in Switzerland. On 1 January 2014 the former municipality of Bert ...
Bertschikon and Wiesendangen
Wiesendangen is a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Winterthur (district), Winterthur in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Zurich (canton), Zürich in Switzerland. On 1 January 2014 the former municipality of Bert ...
merged to ''Wiesendangen'' on 1 January 2014.
* 2015: '' Bauma'' and '' Sternenberg'' → Bauma Bauma and Sternenberg merged to ''Bauma'' on 1 January 2015.
* 2016: '' Kyburg'' → Illnau-Effretikon.
Politics
In the 2011 federal election the most popular party was the SVP which received 29.8% of the vote. The next three most popular parties were the SP (19.3%), the FDP (11.6%) and the glp (11.5%). The SVP received about the same percentage of the vote as they did in the 2007 Federal election (33.9% in 2007 vs 29.8% in 2011). The SPS retained about the same popularity (19.8% in 2007), as well as the FDP (13.2% in 2007), while the glp was the big winner of the election (7.0% in 2007).Federal election results
: FDP before 2009, FDP.The Liberals after 2009 : "*" indicates that the party was not on the ballot in this canton. : Part of a coalition with the POCH : Part of a coalition with the parties listed under Other : Party fragmented, part remained in a coalition with the FGA and the remainder joining the Green PartyDemographics
Zurich has a population () of . , 23.7% of the population are resident foreign nationals. Over the last 10 years (2000–2010) the population has changed at a rate of 12.7%. Migration accounted for 10.3%, while births and deaths accounted for 2.6%.Swiss Federal Statistical Officeaccessed 5 January 2012 Most of the population () speaks
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
(1,040,168 or 83.4%) as their first language, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
is the second most common (49,750 or 4.0%) and Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian ( / ), also known as Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS), is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually i ...
is the third (21,334 or 1.7%). There are 17,685 people who speak French and 2,606 people who speak Romansh.
Of the population in the canton, 314,394 or about 25.2% were born in Zurich and lived there in 2000. There were 291,631 or 23.4% who were born in the same canton, while 284,461 or 22.8% were born somewhere else in Switzerland, and 310,532 or 24.9% were born outside of Switzerland.
, children and teenagers (0–17 years old) make up 20.5% of the population, while adults (18–64 years old) make up 64.4% and seniors (over 64 years old) make up 15%. , there were 531,094 people who wersingle
and never married in the canton. There were 566,636 married individuals, 66,012 widows or widowers and 84,164 individuals who are divorced.STAT-TAB Datenwürfel für Thema 40.3 – 2000
accessed 2 February 2011 , there were 567,573 private households in the canton, and an average of 2.1 persons per household. There were 223,869 households that consist of only one person and 27,935 households with five or more people. , the construction rate of new housing units was 5.3 new units per 1000 residents. the average price to rent an average apartment in the city of Zurich was 1288.84
Swiss franc
The Swiss franc, or simply the franc, is the currency and legal tender of Switzerland and Liechtenstein. It is also legal tender in the Italian exclave of Campione d'Italia which is surrounded by Swiss territory. The Swiss National Bank (SNB) iss ...
s (CHF) per month (US$1030, £580, €820 approx. exchange rate from 2003). The average rate for a one-room apartment was 733.01 CHF (US$590, £330, €470), a two-room apartment was about 1009.94 CHF (US$810, £450, €650), a three-room apartment was about 1192.66 CHF (US$950, £540, €760) and a six or more room apartment cost an average of 2550.35 CHF (US$2040, £1150, €1630). The average apartment price in the city of Zurich was 115.5% of the national average of 1116 CHF.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Rental prices2003 data accessed 26 May 2010 The vacancy rate for the canton, , was 0.63%.
Religion
In 1519,Huldrych Zwingli
Huldrych or Ulrich Zwingli (1 January 1484 – 11 October 1531) was a Swiss Christian theologian, musician, and leader of the Reformation in Switzerland. Born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swis ...
became the pastor of the Grossmünster
The Grossmünster (; "great minster") is a Romanesque-style Protestant church in Zürich, Switzerland. It is one of the four major churches in the city (the others being the Fraumünster, Predigerkirche, and St. Peterskirche). Its congregation ...
in Zurich, and soon thereafter Zurich became a reformed
Reform is beneficial change.
Reform, reformed or reforming may also refer to:
Media
* ''Reform'' (album), a 2011 album by Jane Zhang
* Reform (band), a Swedish jazz fusion group
* ''Reform'' (magazine), a Christian magazine
Places
* Reform, Al ...
or Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
canton. Even though Zwingli died in battle in 1531, the canton remained a stronghold of the Swiss Reformed Church
The Protestant Church in Switzerland (PCS), formerly named Federation of Swiss Protestant Churches until 31 December 2019, is a federation of 25 member churches – 24 cantonal churches and the Evangelical-Methodist Church of Switzerland. The P ...
over the following centuries. While a plurality of the population is Protestant (43%), 31% of the population was Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
in 2004, a legacy of considerable immigration from Southern Europe.
From the , 497,986 or 39.9% belonged to the Swiss Reformed Church
The Protestant Church in Switzerland (PCS), formerly named Federation of Swiss Protestant Churches until 31 December 2019, is a federation of 25 member churches – 24 cantonal churches and the Evangelical-Methodist Church of Switzerland. The P ...
, while 380,440 or 30.5% were Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
. Of the rest of the population, there were 29,592 members of an Orthodox church (or about 2.37% of the population), there were 1,435 individuals (or about 0.11% of the population) who belonged to the Christian Catholic Church, and there were 70,897 individuals (or about 5.68% of the population) who belonged to another Christian church. There were 6,461 individuals (or about 0.52% of the population) who were Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
, and 66,520 (or about 5.33% of the population) who were Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
ic. There were 5,878 individuals who were Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, 6,024 individuals who were Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
and 1,456 individuals who belonged to another church. 165,324 (or about 13.25% of the population) belonged to no church, are agnostic
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, the divine, or the supernatural is either unknowable in principle or unknown in fact. (page 56 in 1967 edition) It can also mean an apathy towards such religious belief and refer to ...
or atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
, and 50,090 individuals (or about 4.01% of the population) did not answer the question.
Economy
Most of the land is cultivated, but the canton of Zurich is not considered as an agricultural area. The lands to the north and east are more agricultural, but in every part of the canton manufacturing predominates. The canton of Zurich is noted for machinery. Silk and cotton weaving were important in the past, but have now ceased to be of importance. There is a large paper industry. Small and middle sized companies are important contributors to the economy of the canton of Zurich. The city of Zurich is a major banking centre, and insurance is also of importance. In 2014, about 1.2% of the workers in Zurich work in theprimary sector
The primary sector of the economy includes any industry involved in the extraction and production of raw materials, such as farming, logging, fishing, forestry and mining.
The primary sector tends to make up a larger portion of the economy in d ...
(the total for all of Switzerland is 3.3%). In 2014 the secondary sector employed 145,744 or about 14.7% of the total, which is much lower than 21.8% for the entire country. Of those in the secondary sector, over a quarter of the workers worked in construction trades and 9.5% worked in general construction. Additionally, almost 9% of the workers manufactured electronics. The tertiary sector
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector (raw materials) and the ...
employed 836,410 or about 84.1% of the total, which is much higher than 74.9% nationwide. This number has increased by about 180,000 since 2010 while the population in the canton has only increased by 73,000 over the same time period. Of those in the tertiary sector, the fourth largest sub-sector (in 2008) was financial services with 6.2% of the tertiary total.
, Zurich had an unemployment rate of 3.9%. , there were 12,507 people employed in the primary economic sector and about 4,227 businesses involved in this sector. 143,231 people were employed in the secondary sector and there were 11,383 businesses in this sector. 655,848 people were employed in the tertiary sector
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector (raw materials) and the ...
, with 58,796 businesses in this sector.
the total number of full-time equivalent
Full-time equivalent (FTE), or whole time equivalent (WTE), is a unit of measurement that indicates the workload of an employed person (or student) in a way that makes workloads or class loads comparable across various contexts. FTE is often use ...
jobs was 678,306. The number of jobs in the primary sector was 8,120, of which 7,771 were in agriculture, 320 were in forestry or lumber production and 29 were in fishing or fisheries. The number of jobs in the secondary sector was 133,723 of which 81,212 or (60.7%) were in manufacturing, 774 or (0.6%) were in mining and 47,014 (35.2%) were in construction.
The number of jobs in the tertiary sector was 536,463. In the tertiary sector; 105,226 or 19.6% were in the sale or repair of motor vehicles, 38,005 or 7.1% were in the movement and storage of goods, 33,417 or 6.2% were in a hotel or restaurant, 35,571 or 6.6% were in the information industry, 81,163 or 15.1% were the insurance or financial industry, 65,139 or 12.1% were technical professionals or scientists, 36,792 or 6.9% were in education and 63,800 or 11.9% were in health care.
Of the working population, 37.4% used public transportation to get to work, and 41.8% used a private car.
The cantonal, local and church tax rates in the canton is generally slightly lower than the average rate for the entire country.2015 numbers accessed 19 April 2017
Transport
 Railways in standard gauge run through all major valleys in the canton. The centre for transport is Zurich, where a great number of local railways connect to national and international rail links. The railway station of the city of Zurich,
Railways in standard gauge run through all major valleys in the canton. The centre for transport is Zurich, where a great number of local railways connect to national and international rail links. The railway station of the city of Zurich, Zürich Hauptbahnhof
Zürich Hauptbahnhof, often shortened to Zürich HB or just HB, and known in English as Zurich Main Station, is the largest railway station in Switzerland and one of the busiest in Europe. It is a major railway hub, with services to and from a ...
, is one of the busiest in Europe, counting the number of arriving and departing trains. Zurich is well connected to other European cities using rail links. The major trains ICE
Ice is water that is frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 ° C, 32 ° F, or 273.15 K. It occurs naturally on Earth, on other planets, in Oort cloud objects, and as interstellar ice. As a naturally oc ...
, TGV
The TGV (; , , 'high-speed train') is France's intercity high-speed rail service. With commercial operating speeds of up to on the newer lines, the TGV was conceived at the same period as other technological projects such as the Ariane 1 rocke ...
and Cisalpino connect to Zurich.
The first Swiss railway ran in the Limmat valley
The Limmat Valley (German: ''Limmattal'') is a river valley and a region in the Canton (Switzerland), cantons of Canton of Zürich, Zürich and Canton of Aargau, Aargau in Switzerland.
Geography
The Limmat () is a long river located in ...
in 1847, connecting Zurich to Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in southern Germany. In earlier times it was considered to be on both sides of the Upper Rhine, but since the Napoleonic Wars, it has been considered only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Ba ...
.
The major airport of Switzerland Zurich Airport
Zurich Airport is the largest international airport of Switzerland and the airline hub, principal hub of Swiss International Air Lines. It serves Zurich, the largest city in Switzerland, and, with its surface transport links, much of the rest o ...
is located in Kloten, a mere from the city centre of Zurich. It is home to Swiss International Air Lines.
The A1, A3 and A4 motorways run through the canton. Other motorways and expressways which also run through the canton include the A7, the A51, the A52 and the A53. Major hubs are Zurich and Winterthur.
Education
In Zurich about 493,209 or (39.5%) of the population have completed non-mandatory upper secondary education, and 212,154 or (17.0%) have completed additional higher education (eitheruniversity
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
or a ). Of the 212,154 who completed tertiary schooling, 55.8% were Swiss men, 25.5% were Swiss women, 11.6% were non-Swiss men and 7.1% were non-Swiss women.
Notes
References
External links
*Official Statistics
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Zurich Cantons of Switzerland Cantons of the Helvetic Republic 14th-century establishments in the Old Swiss Confederacy 1350s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1351 establishments in Europe