Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
. It is the largest country by area in
Mainland Southeast Asia
Mainland Southeast Asia (historically known as Indochina and the Indochinese Peninsula) is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to th ...
and has a population of about 55 million. It is bordered by
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and
Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
to its northwest,
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
to its northeast,
Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
and
Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
to its east and southeast, and the
Andaman Sea
The Andaman Sea (historically also known as the Burma Sea) is a marginal sea of the northeastern Indian Ocean bounded by the coastlines of Myanmar and Thailand along the Gulf of Martaban and the west side of the Malay Peninsula, and separated f ...
and the
Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is
Naypyidaw, and its largest city is
Yangon
Yangon, formerly romanized as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar. Yangon was the List of capitals of Myanmar, capital of Myanmar until 2005 and served as such until 2006, when the State Peace and Dev ...
(formerly Rangoon).
Early civilisations in the area included the
Tibeto-Burman-speaking
Pyu city-states
The Pyu city-states ( ) were a group of city-states that existed from about the 2nd century BCE to the mid-11th century in present-day Upper Myanmar. The city-states were founded as part of the southward migration by the Tibeto-Burman languages, ...
in
Upper Myanmar and the
Mon kingdoms in
Lower Myanmar. In the 9th century, the
Bamar people entered the upper
Irrawaddy valley, and following the establishment of the
Pagan Kingdom in the 1050s, the
Burmese language
Burmese (; ) is a Tibeto-Burman languages, Tibeto-Burman language spoken in Myanmar, where it is the official language, lingua franca, and the native language of the Bamar people, Bamar, the country's largest ethnic group. Burmese dialects are a ...
and
culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
and
Theravada Buddhism slowly became dominant in the country. The
Pagan Kingdom fell to
Mongol invasions, and several warring states emerged. In the 16th century, reunified by the
Taungoo dynasty, the country became the largest empire in the
history of Southeast Asia for a short period. The early 19th-century
Konbaung dynasty ruled over an area that included modern Myanmar and briefly controlled
Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, nor ...
, the
Lushai Hills, and
Manipur
Manipur () is a state in northeastern India with Imphal as its capital. It borders the Indian states of Assam to the west, Mizoram to the south, and Nagaland to the north and shares the international border with Myanmar, specifically t ...
as well. The British
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
seized control of the administration of Myanmar after three
Anglo-Burmese Wars
The Anglo-Burmese people, also known as the Anglo-Burmans, are a community of Eurasians of Burmese and European descent; they emerged as a distinct community through mixed relationships (sometimes permanent, sometimes temporary) between the B ...
in the 19th century, and the country became a
British colony. After a brief
Japanese occupation, Myanmar was reconquered by the Allies. On 4 January 1948, Myanmar declared
independence
Independence is a condition of a nation, country, or state, in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the status of ...
under the terms of the
Burma Independence Act 1947.
Myanmar's post-independence history has been checkered by continuing unrest and conflict to this day. The
coup d'état in 1962 resulted in a
military dictatorship
A military dictatorship, or a military regime, is a type of dictatorship in which Power (social and political), power is held by one or more military officers. Military dictatorships are led by either a single military dictator, known as a Polit ...
under the
Burma Socialist Programme Party
The Burma Socialist Programme Party (BSPP) was the ruling party of Burma (now Myanmar) from 1962 to 1988 and the country's sole legal party from 1964 to 1988. Party chairman Ne Win overthrew the country's democratically elected government i ...
. On 8 August 1988, the
8888 Uprising then resulted in a nominal transition to a
multi-party system
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system where more than two meaningfully-distinct political parties regularly run for office and win elections. Multi-party systems tend to be more common in countries using proportional ...
two years later, but the country's
post-uprising military council refused to cede power, and has continued to rule the country through to the present. The country remains riven by ethnic strife among its
myriad ethnic groups and has one of the world's
longest-running ongoing civil wars. The
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
and several other organisations have reported consistent and systemic
human rights
Human rights are universally recognized Morality, moral principles or Social norm, norms that establish standards of human behavior and are often protected by both Municipal law, national and international laws. These rights are considered ...
violations in the country.
In 2011, the
military junta
A military junta () is a system of government led by a committee of military leaders. The term ''Junta (governing body), junta'' means "meeting" or "committee" and originated in the Junta (Peninsular War), national and local junta organized by t ...
was officially dissolved following a
2010 general election, and a nominally
civilian government was installed.
Aung San Suu Kyi
Aung San Suu Kyi (born 19 June 1945) is a Burmese politician, diplomat, author, and political activist. She was awarded the 1991 Nobel Peace Prize. She served as State Counsellor of Myanmar and Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Myanmar), Ministe ...
and
political prisoners were released and the
2015 Myanmar general election was held, leading to improved
foreign relations and eased
economic sanctions
Economic sanctions or embargoes are Commerce, commercial and Finance, financial penalties applied by states or institutions against states, groups, or individuals. Economic sanctions are a form of Coercion (international relations), coercion tha ...
,
although the country's treatment of its
ethnic minorities, particularly in connection with the
Rohingya conflict, continued to be a source of international tension and consternation.
Following the
2020 Myanmar general election, in which
Aung San Suu Kyi's party won a clear majority in both houses, the
Burmese military (Tatmadaw) again seized power
in a coup d'état.
The coup, which was widely condemned by the
international community
The international community is a term used in geopolitics and international relations to refer to a broad group of people and governments of the world.
Usage
Aside from its use as a general descriptor, the term is typically used to imply the ...
, led to
continuous ongoing widespread protests in Myanmar and has been marked by violent
political repression by the military, as well as a larger outbreak of the
civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
. The military also arrested Aung San Suu Kyi in order to remove her from public life, and charged her with crimes ranging from
corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense that is undertaken by a person or an organization that is entrusted in a position of authority to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's gain. Corruption may involve activities ...
to violation of
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
protocols; all of the charges against her are "politically motivated" according to independent observers.
Myanmar is a member of the
East Asia Summit
The East Asia Summit (EAS) is a regional forum held annually by leaders of, initially, 16 countries in the East Asian, Southeast Asian, South Asian and Oceanian regions, based on the Association of Southeast Asian Nations#ASEAN Plus Three and A ...
,
Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 121 countries that Non-belligerent, are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. It was founded with the view to advancing interests of developing countries in the context of Cold W ...
,
ASEAN
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations,
commonly abbreviated as ASEAN, is a regional grouping of 10 states in Southeast Asia "that aims to promote economic and security cooperation among its ten members." Together, its member states r ...
, and
BIMSTEC, but it is not a member of the
Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, often referred to as the British Commonwealth or simply the Commonwealth, is an International organization, international association of member states of the Commonwealth of Nations, 56 member states, the vast majo ...
despite once being part of the
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
. Myanmar is a Dialogue Partner of the
Shanghai Cooperation Organization. The country is very rich in
natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest, and cultural value. ...
s, such as
jade
Jade is an umbrella term for two different types of decorative rocks used for jewelry or Ornament (art), ornaments. Jade is often referred to by either of two different silicate mineral names: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in t ...
,
gems,
oil,
natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
,
teak and other
mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
s, as well as endowed with
renewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
, having the highest
solar power
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to c ...
potential compared to other countries of the Great
Mekong Subregion. However, Myanmar has long suffered from
instability, factional violence,
corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense that is undertaken by a person or an organization that is entrusted in a position of authority to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's gain. Corruption may involve activities ...
, poor infrastructure, as well as a long history of
colonial exploitation with little regard to
human development. In 2013, its GDP (nominal) stood at US$56.7 billion and its GDP (
PPP) at US$221.5 billion.
The
income gap in Myanmar is among the widest in the world, as a large proportion of the
economy
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
is controlled by
cronies of the
military junta
A military junta () is a system of government led by a committee of military leaders. The term ''Junta (governing body), junta'' means "meeting" or "committee" and originated in the Junta (Peninsular War), national and local junta organized by t ...
.
Myanmar is one of the
least developed countries
The least developed countries (LDCs) are developing countries listed by the United Nations that exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed b ...
.
Since 2021, more than 600,000 people have been displaced across Myanmar due to the
civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
post-coup, with more than three million people in dire need of humanitarian assistance. According to the
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees
The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a United Nations agency mandated to aid and protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people, and to assist in their voluntary repatriation, l ...
(UNHCR), there are over 1.3 million people counted as refugees and asylum seekers, and 3.5 million people displaced internally as of December 2024.
Etymology
The name of the country has been a matter of dispute and disagreement, particularly in the early 21st century, focusing mainly on the political legitimacy of those using ''Myanmar'' versus ''Burma''. Both names derive from the earlier
Burmese ''Mranma'' or ''Mramma'', an
ethnonym
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and used ...
for the majority
Burman ethnic group, of uncertain etymology.
The terms are also popularly thought to derive from
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
''Brahma Desha'', 'land of
Brahma
Brahma (, ) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the triple deity, trinity of Para Brahman, supreme divinity that includes Vishnu and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity, Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp. 212– ...
'.
In 1989, the
military government officially changed the English translations of many names dating back to
Burma's colonial period or earlier, including that of the country itself: ''Burma'' became ''Myanmar''. The renaming remains a contested issue.
Many political and ethnic opposition groups and countries continue to use ''Burma'' because they do not recognise the legitimacy or authority of the military government.
The country's official full name is "Republic of the Union of Myanmar" (, ', ). Countries that do not officially recognise that name use the long form "Union of Burma" instead.
In English, the country is popularly known as either ''Burma'' or ''Myanmar''. In Burmese, the pronunciation depends on the
register used and is either ' () or ' ().
Official
United States foreign policy retains ''Burma'' as the country's name although the
State Department's website lists the country as ''Burma (Myanmar)''.
The
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
uses ''Myanmar'', as does the
ASEAN
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations,
commonly abbreviated as ASEAN, is a regional grouping of 10 states in Southeast Asia "that aims to promote economic and security cooperation among its ten members." Together, its member states r ...
and as do
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
,
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
,
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
,
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
,
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
,
Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
,
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
,
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
,
Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
,
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
and
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
. Most English-speaking international news media refer to the country by the name ''Myanmar'', including the
BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
,
CNN,
Al Jazeera,
Reuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide writing in 16 languages. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world.
The agency ...
, and the
Australian Broadcasting Corporation
The Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) is Australia’s principal public service broadcaster. It is funded primarily by grants from the federal government and is administered by a government-appointed board of directors. The ABC is ...
(
ABC)/
Radio Australia.
Myanmar is known by a name deriving from ''Burma'' in
Spanish,
Italian,
Romanian, and
Greek. French-language media consistently use ''Birmanie''.
There are at least nine different pronunciations of the English name ''Myanmar'', and no single one is standard. Pronunciations with two syllables are found most often in major British and American dictionaries.
[examples of two-syllable pronunciations: , , , or ] Dictionaries—such as
Collins—and other sources also report pronunciations with three syllables.
[examples of three-syllable pronunciations: , , , , or ]
History
Prehistory

Archaeological evidence shows that ''
Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' ( ) is an extinction, extinct species of Homo, archaic human from the Pleistocene, spanning nearly 2 million years. It is the first human species to evolve a humanlike body plan and human gait, gait, to early expansions of h ...
'' lived in the region now known as Myanmar as early as 750,000 years ago, with no more ''erectus'' finds after 75,000 years ago.
The first evidence of ''
Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
'' is dated to about 25,000 BP with discoveries of stone tools in central Myanmar. Evidence of
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
age domestication of plants and animals and the use of polished stone tools dating to sometime between 10,000 and 6,000 BCE has been discovered in the form of
cave painting
In archaeology, cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric art, prehistoric origin. These paintings were often c ...
s in
Padah-Lin Caves.
The
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
arrived when people in the region were turning copper into bronze, growing rice and domesticating poultry and pigs; they were among the first people in the world to do so. Human remains and artefacts from this era were discovered in
Monywa District in the
Sagaing Region. The
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
began around 500 BCE with the emergence of iron-working settlements in an area south of present-day
Mandalay. Evidence also shows the presence of rice-growing settlements of large villages and small towns that traded with their surroundings as far as China between 500 BCE and 200 CE. Iron Age Burmese cultures also had influences from outside sources such as
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and
Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, as seen in their funerary practices concerning child burials. This indicates some form of communication between groups in Myanmar and other places, possibly through trade.
Early city-states
Around the second century BCE the first-known
city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
s emerged in central Myanmar. The city-states were founded as part of the southward migration by the Tibeto-Burman-speaking Pyu people, the earliest inhabitants of Myanmar of whom records are extant, from present-day
Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces ...
.
The Pyu culture was heavily influenced by trade with India, importing Buddhism as well as other cultural, architectural and political concepts, which would have an enduring influence on later Burmese culture and political organisation.
By the 9th century, several city-states had sprouted across the land: the Pyu in the central dry zone, Mon along the southern coastline and Arakanese along the western littoral. The balance was upset when the Pyu came under repeated attacks from
Nanzhao between the 750s and the 830s. In the mid-to-late 9th century the
Bamar people founded a small settlement at
Bagan
Bagan ( ; ; formerly Pagan) is an ancient city and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the Mandalay Region of Myanmar. From the 9th to 13th centuries, the city was the capital of the Pagan Kingdom, the first kingdom that unified the regions that w ...
. It was one of several competing city-states until the late 10th century, when it grew in authority and grandeur.
Pagan Kingdom
Pagan gradually grew to absorb its surrounding states until the 1050s–1060s when
Anawrahta founded the Pagan Kingdom, the first ever unification of the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. In the 12th and 13th centuries, the Pagan Empire and the
Khmer Empire were two main powers in mainland Southeast Asia. The
Burmese language
Burmese (; ) is a Tibeto-Burman languages, Tibeto-Burman language spoken in Myanmar, where it is the official language, lingua franca, and the native language of the Bamar people, Bamar, the country's largest ethnic group. Burmese dialects are a ...
and culture gradually became dominant in the upper Irrawaddy valley, eclipsing the
Pyu,
Mon and
Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...
norms by the late 12th century.
Theravada
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
slowly began to spread to the village level, although
Tantric,
Mahayana
Mahāyāna ( ; , , ; ) is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, Buddhist texts#Mahāyāna texts, texts, Buddhist philosophy, philosophies, and practices developed in ancient India ( onwards). It is considered one of the three main ex ...
,
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
, and
folk religion remained heavily entrenched. Pagan's rulers and wealthy built over 10,000
Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
temples in the Pagan capital zone alone. Repeated Mongol invasions in the late 13th century toppled the four-century-old kingdom in 1287.

Pagan's collapse was followed by 250 years of political fragmentation that lasted well into the 16th century. Like the Burmans four centuries earlier,
Shan migrants who arrived with the Mongol invasions stayed behind. Several competing
Shan States
The Shan States were a collection of minor Shan people, Shan kingdoms called ''mueang, möng'' whose rulers bore the title ''saopha'' (''sawbwa''). In British rule in Burma, British Burma, they were analogous to the princely states of Britis ...
came to dominate the entire northwestern to eastern arc surrounding the Irrawaddy valley. The valley too was beset with petty states until the late 14th century when two sizeable powers,
Ava Kingdom and
Hanthawaddy Kingdom, emerged. In the west, a politically fragmented Arakan was under competing influences of its stronger neighbours until the
Kingdom of Mrauk U
The Kingdom of Mrauk-U (Arakanese language, Arakanese: မြောက်ဦး ဘုရင့်နိုင်ငံတော်) was a kingdom that existed on the Arakan coastal plain from 1429 to 1785. Based in the capital Mrauk-U, near t ...
unified the Arakan coastline for the first time in 1437. The kingdom was a protectorate of the
Bengal Sultanate
The Bengal Sultanate (Middle Bengali: , Classical Persian: ) was a Post-classical history, late medieval sultanate based in the Bengal region in the eastern South Asia between the 14th and 16th century. It was the dominant power of the Ganges- ...
at different time periods.
[Maung Maung Tin, Vol. 2, p. 25]
In the 14th and 15th centuries, Ava fought
wars of unification but could never quite reassemble the lost empire. Having held off Ava, the
Mon-speaking Hanthawaddy entered its golden age, and Arakan went on to become a power in its own right for the next 350 years. In contrast, constant warfare left Ava greatly weakened, and it slowly disintegrated from 1481 onward. In 1527, the Confederation of Shan States conquered Ava and ruled Upper Myanmar until 1555.
Like the Pagan Empire, Ava,
Hanthawaddy and the Shan states were all
multi-ethnic polities. Despite the wars, cultural synchronisation continued. This period is considered a golden age for
Burmese culture
The culture of Myanmar (Burma) ( ) has been heavily influenced by Buddhism. Owing to its history, Burmese culture has significant influence over neighboring countries such as Laos, Siam, Assam in India, and Xishuangbanna regions in China. It h ...
.
Burmese literature "grew more confident, popular, and stylistically diverse", and the second generation of Burmese law codes as well as the earliest
pan-Burma chronicles emerged. Hanthawaddy monarchs introduced religious reforms that later spread to the rest of the country.
Taungoo and Konbaung

Political unification returned in the mid-16th century, through the efforts of
Taungoo, a former vassal state of Ava. Taungoo's young, ambitious King
Tabinshwehti defeated the more powerful Hanthawaddy in the
Toungoo–Hanthawaddy War. His successor
Bayinnaung went on to conquer a vast swath of mainland Southeast Asia including the Shan states,
Lan Na, Manipur,
Mong Mao, the
Ayutthaya Kingdom,
Lan Xang and southern Arakan. However, the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia unravelled soon after Bayinnaung's death in 1581, completely collapsing by 1599. Ayutthaya seized Tenasserim and Lan Na, and Portuguese mercenaries established
Portuguese rule at
Thanlyin (Syriam).
The dynasty regrouped and defeated the Portuguese in 1613 and Siam in 1614. It restored a smaller, more manageable kingdom, encompassing
Lower Myanmar,
Upper Myanmar,
Shan states
The Shan States were a collection of minor Shan people, Shan kingdoms called ''mueang, möng'' whose rulers bore the title ''saopha'' (''sawbwa''). In British rule in Burma, British Burma, they were analogous to the princely states of Britis ...
,
Lan Na and upper
Tenasserim. The restored Toungoo kings created a legal and political framework whose basic features continued well into the 19th century. The crown completely replaced the hereditary chieftainships with appointed governorships in the entire Irrawaddy valley and greatly reduced the hereditary rights of Shan chiefs. Its trade and secular administrative reforms built a prosperous economy for more than 80 years. From the 1720s onward, the kingdom was beset with repeated
Meithei raids into Upper Myanmar and a nagging rebellion in Lan Na. In 1740, the Mon of Lower Myanmar founded the
Restored Hanthawaddy Kingdom. Hanthawaddy forces sacked Ava in 1752, ending the 266-year-old Toungoo Dynasty.

After the fall of Ava, the
Konbaung–Hanthawaddy War involved one resistance group under
Alaungpaya
Alaungpaya (, ; also spelled Alaunghpaya or Alaung-Phra; 11 May 1760) was the founder and first emperor of the Konbaung dynasty of Burma. By the time of his death from illness during his Burmese–Siamese War (1759–60), campaign in Siam, this ...
defeating the Restored Hanthawaddy, and by 1759 he had reunited all of Myanmar and Manipur and driven out the French and the British, who had provided arms to Hanthawaddy. By 1770, Alaungpaya's heirs had subdued much of Laos and fought and won the
Burmese–Siamese War against
Ayutthaya and the
Sino-Burmese War against
Qing China
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty ...
.
With Burma preoccupied by the Chinese threat, Ayutthaya recovered its territories by 1770 and went on to capture Lan Na by 1776. Burma and Siam went to war until 1855, but all resulted in a stalemate, exchanging
Tenasserim (to Burma) and Lan Na (to Ayutthaya). Faced with a powerful China and a resurgent Ayutthaya in the east, King
Bodawpaya turned west, acquiring Arakan (1785), Manipur (1814) and Assam (1817). It was the second-largest empire in Burmese history but also one with a long ill-defined border with
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
.
In 1826, Burma lost Arakan,
Manipur
Manipur () is a state in northeastern India with Imphal as its capital. It borders the Indian states of Assam to the west, Mizoram to the south, and Nagaland to the north and shares the international border with Myanmar, specifically t ...
, Assam and Tenasserim to the British in the
First Anglo-Burmese War. In 1852, the British easily seized Lower Burma in the
Second Anglo-Burmese War. King
Mindon Min tried to modernise the kingdom and in 1875 narrowly avoided annexation by ceding the
Karenni States. The British, alarmed by the consolidation of
French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China), officially known as the Indochinese Union and after 1941 as the Indochinese Federation, was a group of French dependent territories in Southeast Asia from 1887 to 1954. It was initial ...
, annexed the remainder of the country in the
Third Anglo-Burmese War in 1885.
Konbaung kings extended Restored Toungoo's administrative reforms and achieved unprecedented levels of internal control and external expansion. For the first time in history, the Burmese language and culture came to predominate the entire Irrawaddy valley. The evolution and growth of Burmese literature and theatre continued, aided by an extremely high adult male literacy rate for the era (half of all males and 5% of females). Nonetheless, the extent and pace of reforms were uneven and ultimately proved insufficient to stem the advance of British colonialism.
British Burma (1885–1948)

In the 19th century, Burmese rulers sought to maintain their traditional influence in the western areas of Assam, Manipur and Arakan. Pressing them, however, was the
British East India Company, which was expanding its interests eastwards over the same territory. Over the next 60 years, diplomacy, raids, treaties and compromises, known collectively as the
Anglo-Burmese Wars
The Anglo-Burmese people, also known as the Anglo-Burmans, are a community of Eurasians of Burmese and European descent; they emerged as a distinct community through mixed relationships (sometimes permanent, sometimes temporary) between the B ...
, continued until Britain proclaimed control over most of Burma. With the fall of Mandalay, all of Burma came under British rule, being
annexed on 1 January 1886.
Throughout the colonial era, many Indians arrived as soldiers, civil servants, construction workers and traders and, along with the
Anglo-Burmese community, dominated commercial and civil life in Burma.
Rangoon became the capital of British Burma and an important port between
Calcutta
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta (List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern ba ...
and
Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
. Burmese resentment was strong, and was vented in violent riots that periodically paralysed Rangoon until the 1930s. Some of the discontent was caused by a disrespect for Burmese culture and traditions.
Buddhist monks became the vanguards of the independence movement.
U Wisara, an activist monk, died in prison after a 166-day hunger strike.
On 1 April 1937, Burma became a separately administered colony of Britain, and
Ba Maw became the first Prime Minister and Premier of Burma. Ba Maw was an outspoken advocate for Burmese self-rule, and he opposed the participation of Britain, and by extension Burma, in
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. He resigned from the Legislative Assembly and was arrested for sedition. In 1940, before
Japan formally entered the war,
Aung San formed the
Burma Independence Army in Japan.
As a major battleground, Burma was devastated during World War II by the
Japanese invasion. Within months after they entered the war, Japanese troops had advanced on Rangoon, and the British administration had collapsed. A
Burmese Executive Administration headed by Ba Maw was established by the Japanese in August 1942.
Wingate's British
Chindits were formed into
long-range penetration groups trained to operate deep behind Japanese lines. A similar American unit,
Merrill's Marauders, followed the Chindits into the Burmese jungle in 1943.
Beginning in late 1944, allied troops launched a
series of offensives that led to the
end of Japanese rule in July 1945. The battles were intense with much of Burma laid waste by the fighting. Overall, the Japanese lost some 150,000 men in Burma with 1,700 prisoners taken. Although many Burmese fought initially for the Japanese as part of the Burma Independence Army, many Burmese, mostly from the ethnic minorities, served in the British Burma Army. The
Burma National Army and the Arakan National Army fought with the Japanese from 1942 to 1944 but switched allegiance to the Allied side in 1945. Overall, 170,000 to 250,000 Burmese civilians died during World War II.
Following World War II,
Aung San negotiated the
Panglong Agreement with ethnic leaders that guaranteed the independence of Myanmar as a unified state.
Aung Zan Wai, Pe Khin,
Bo Hmu Aung, Sir Maung Gyi, Sein Mya Maung,
Myoma U Than Kywe were among the negotiators of the historic
Panglong Conference negotiated with Bamar leader General Aung San and other ethnic leaders in 1947. In 1947, Aung San became Deputy Chairman of the Executive Council of Myanmar, a transitional government. But in July 1947, political rivals
assassinated Aung San and several cabinet members.
Independence (1948–1962)
On 4 January 1948, the nation became an independent republic, under the terms of the
Burma Independence Act 1947. The new country was named the ''Union of Burma'', with
Sao Shwe Thaik as its first president and
U Nu
Nu (; ; 25 May 1907 – 14 February 1995), commonly known as Burmese names#Honorifics, U Nu and also by the honorific name Thakin Nu, was a prominent Burmese people, Burmese statesman and the first Prime Minister of Union of Burma. He was ...
as its first prime minister. Unlike most other former British colonies and overseas territories, Burma did not become a member of the
Commonwealth. A
bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature that is divided into two separate Deliberative assembly, assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate ...
parliament was formed, consisting of a
Chamber of Deputies
The chamber of deputies is the lower house in many bicameral legislatures and the sole house in some unicameral legislatures.
Description
Historically, French Chamber of Deputies was the lower house of the French Parliament during the Bourb ...
and a
Chamber of Nationalities, and
multi-party elections were held in
1951–1952,
1956
Events
January
* January 1 – The Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, Anglo-Egyptian Condominium ends in Sudan after 57 years.
* January 8 – Operation Auca: Five U.S. evangelical Christian Missionary, missionaries, Nate Saint, Roger Youderian, E ...
and
1960.
The geographical area Burma encompasses today can be traced to the
Panglong Agreement, which combined Burma Proper, which consisted of Lower Burma and Upper Burma, and the Frontier Areas, which had been administered separately by the British.
In 1961,
U Thant, the Union of Burma's Permanent Representative to the United Nations and former secretary to the prime minister, was elected
Secretary-General of the United Nations
The secretary-general of the United Nations (UNSG or UNSECGEN) is the chief administrative officer of the United Nations and head of the United Nations Secretariat, one of the United Nations System#Six principal organs, six principal organs of ...
, a position he held for ten years.
When the non-Burman ethnic groups pushed for autonomy or federalism, alongside having a weak civilian government at the centre, the military leadership staged a coup d'état in 1962. Though incorporated in the 1947 Constitution, successive military governments construed the use of the term '
federalism
Federalism is a mode of government that combines a general level of government (a central or federal government) with a regional level of sub-unit governments (e.g., provinces, State (sub-national), states, Canton (administrative division), ca ...
' as being anti-national, anti-unity and pro-disintegration.
Military rule (1962–2011)
On 2 March 1962, the military led by General
Ne Win
Ne Win (; ; 24 May 1911 – 5 December 2002), born Shu Maung (; ), was a Burmese army general, politician and Prime Minister of Burma from 1958 to 1960 and 1962 to 1974, and also President of Burma from 1962 to 1981. Ne Win was Burma's mili ...
took control of Burma through a coup d'état, and the government had been under direct or indirect control by the military since then. Between 1962 and 1974, Myanmar was ruled by a
revolutionary council headed by the general. Almost all aspects of society (business, media, production) were
nationalised
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English)
is the process of transforming privately owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization contrasts with ...
or brought under government control under the
Burmese Way to Socialism,
[ Myint-U] which combined Soviet-style nationalisation and
central planning.
A
new constitution of the
Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma was adopted in 1974. Until 1988, the country was ruled as a
one-party system, with the general and other military officers resigning and ruling through the
Burma Socialist Programme Party
The Burma Socialist Programme Party (BSPP) was the ruling party of Burma (now Myanmar) from 1962 to 1988 and the country's sole legal party from 1964 to 1988. Party chairman Ne Win overthrew the country's democratically elected government i ...
(BSPP).
During this period, Myanmar became one of the world's most impoverished countries.
There were sporadic protests against military rule during the Ne Win years, and these were almost always violently suppressed. On 7 July 1962, the government broke up
demonstrations at Rangoon University, killing 15 students.
In 1974, the military violently suppressed
anti-government protests at the funeral of U Thant. Student protests in 1975, 1976, and 1977 were quickly suppressed by overwhelming force.
In 1988, unrest over economic mismanagement and political oppression by the government led to widespread pro-democracy demonstrations throughout the country known as the
8888 Uprising. Security forces killed thousands of demonstrators, and General
Saw Maung staged a coup d'état and formed the
State Law and Order Restoration Council (SLORC). In 1989, SLORC declared martial law after widespread protests. The military government finalised plans for People's Assembly elections on 31 May 1989. SLORC changed the country's official English name from the "Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma" to the "Union of Myanmar" on 18 June 1989 by enacting the adaptation of the expression law.
In May 1990, the government held free multiparty elections for the first time in almost 30 years, and the
National League for Democracy (NLD), the party of Aung San Suu Kyi, won
[Erlanger, Steven]
"Burmese Vote Rejects Army Rule With Big Victory for Opposition,"
, 29 May 1990, ''The New York Times'', retrieved 1 March 2021 earning 392 out of a total 492 seats (i.e., 80% of the seats). However, the military junta refused to cede power and continued to rule the nation, first as SLORC and, from 1997, as the State Peace and Development Council (SPDC) until its dissolution in March 2011. General
Than Shwe took over the Chairmanship – effectively the position of Myanmar's top ruler – from General Saw Maung in 1992 and held it until 2011.
On 23 June 1997, Myanmar was admitted into the Association of Southeast Asian Nations. On 27 March 2006, the military junta, which had moved the national capital from Yangon to a site near
Pyinmana in November 2005, officially named the new capital
Naypyidaw, meaning "city of the kings".

In August 2007, an increase in the price of fuel led to the
Saffron Revolution led by Buddhist monks that were dealt with harshly by the government.
The government cracked down on them on 26 September 2007, with reports of barricades at the
Shwedagon Pagoda and monks killed. There were also rumours of disagreement within the Burmese armed forces, but none was confirmed. The military crackdown against unarmed
protesters was widely condemned as part of the
international reactions to the Saffron Revolution and led to an increase in economic sanctions against the
Burmese Government.
In May 2008,
Cyclone Nargis caused extensive damage in the densely populated rice-farming delta of the
Irrawaddy Division. It was the worst natural disaster in Burmese history with reports of an estimated 200,000 people dead or missing, damages totalled to 10 billion US dollars, and as many as 1 million were left homeless. In the critical days following this disaster, Myanmar's
isolationist government was accused of hindering United Nations recovery efforts.
Humanitarian aid
Humanitarian aid is material and Humanitarian Logistics, logistic assistance, usually in the short-term, to people in need. Among the people in need are the homelessness, homeless, refugees, and victims of natural disasters, wars, and famines. Th ...
was requested, but concerns about foreign military or intelligence presence in the country delayed the entry of United States military planes delivering medicine, food, and other supplies.
In early August 2009,
a conflict broke out in Shan State in northern Myanmar. For several weeks, junta troops fought against ethnic minorities including the
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese, alternatively the Han people, are an East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Greater China. With a global population of over 1.4 billion, the Han Chinese are the list of contemporary ethnic groups, world's la ...
,
Wa, and
Kachin.
During 8–12 August, the first days of the conflict, as many as 10,000 Burmese civilians fled to Yunnan in neighbouring China.
Civil wars
Civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
s have been a constant feature of Myanmar's socio-political landscape since the attainment of independence in 1948. These wars are predominantly struggles for ethnic and sub-national autonomy, with the areas surrounding the ethnically Bamar central districts of the country serving as the primary geographical setting of conflict. Foreign journalists and visitors require a special travel permit to visit the areas in which Myanmar's civil wars continue.
In October 2012, the ongoing conflicts in Myanmar included the
Kachin conflict, between the Pro-Christian
Kachin Independence Army and the government;
a civil war between the
Rohingya Muslims,
and the government and non-government groups in
Rakhine State
Rakhine State ( ; , ; ), formerly known as Arakan State, is a Administrative divisions of Myanmar, state in Myanmar (Burma). Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State to the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady Re ...
; and a conflict between the
Shan,
, and
Karen minority groups, and the government in the eastern half of the country. In addition,
al-Qaeda
, image = Flag of Jihad.svg
, caption = Jihadist flag, Flag used by various al-Qaeda factions
, founder = Osama bin Laden{{Assassinated, Killing of Osama bin Laden
, leaders = {{Plainlist,
* Osama bin Lad ...
signalled an intention to become involved in Myanmar.
Armed conflict between
ethnic Chinese rebels and the
Myanmar Armed Forces resulted in the
Kokang offensive in February 2015. The conflict had forced 40,000 to 50,000 civilians to flee their homes and seek shelter on the Chinese side of the border. During the incident, the government of China was accused of giving military assistance to the
ethnic Chinese rebels. Clashes between Burmese troops and local insurgent groups have continued, fuelling tensions between China and Myanmar.
Period of liberalisation, 2011–2021
The military-backed Government had promulgated a
"Roadmap to Discipline-flourishing Democracy" in 1993, but the process appeared to stall several times, until 2008 when the Government published a new draft national constitution, and organised a (flawed) national referendum which adopted it. The new constitution provided for election of a national assembly with powers to appoint a president, while practically ensuring army control at all levels.

A
general election in 2010 – the first for twenty years – was boycotted by the
NLD. The military-backed
Union Solidarity and Development Party declared victory, stating that it had been favoured by 80 per cent of the votes; fraud, however, was alleged.
A nominally civilian government was then formed, with retired general
Thein Sein as president.
A series of liberalising political and economic actions – or reforms – then took place. By the end of 2011 these included the release of pro-democracy leader Aung San Suu Kyi from house arrest, the establishment of the
National Human Rights Commission, the granting of general amnesties for more than 200 political prisoners, new labour laws that permitted labour unions and strikes, a relaxation of press censorship, and the regulation of currency practices. In response,
United States Secretary of State
The United States secretary of state (SecState) is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State.
The secretary of state serves as the principal advisor to the ...
Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, lawyer and diplomat. She was the 67th United States secretary of state in the administration of Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, a U.S. senator represent ...
visited Myanmar in December 2011 – the first visit by a US Secretary of State in more than fifty years – meeting both President Thein Sein and opposition leader Aung San Suu Kyi.
Aung San Suu Kyi
Aung San Suu Kyi (born 19 June 1945) is a Burmese politician, diplomat, author, and political activist. She was awarded the 1991 Nobel Peace Prize. She served as State Counsellor of Myanmar and Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Myanmar), Ministe ...
's
NLD party participated in the 2012 by-elections, facilitated by the government's abolition of the laws that previously barred it. In the April 2012
by-elections
A by-election, also known as a special election in the United States and the Philippines, or a bypoll in India, is an election used to fill an office that has become vacant between general elections.
A vacancy may arise as a result of an incumben ...
, the NLD won 43 of the 45 available seats. The 2012 by-elections were also the first time that international representatives were allowed to monitor the voting process in Myanmar.
Myanmar's improved international reputation was indicated by
ASEAN
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations,
commonly abbreviated as ASEAN, is a regional grouping of 10 states in Southeast Asia "that aims to promote economic and security cooperation among its ten members." Together, its member states r ...
's approval of Myanmar's bid for the position of ASEAN chair in 2014.
2015 general elections
General elections
were held on 8 November 2015. These were the first openly contested elections held in Myanmar since the 1990 general election (which was annulled
["Myanmar's 2015 landmark elections explained,"](_blank)
3 December 2015, BBC News, retrieved 1 March 2021). The results gave the NLD an
absolute majority of seats in both chambers of the
national parliament, enough to ensure that its candidate would become president, while NLD leader
Aung San Suu Kyi
Aung San Suu Kyi (born 19 June 1945) is a Burmese politician, diplomat, author, and political activist. She was awarded the 1991 Nobel Peace Prize. She served as State Counsellor of Myanmar and Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Myanmar), Ministe ...
is constitutionally barred from the presidency.
The new parliament convened on 1 February 2016, and on 15 March 2016,
Htin Kyaw was elected as the first non-military president since the military coup of 1962. On 6 April 2016,
Aung San Suu Kyi
Aung San Suu Kyi (born 19 June 1945) is a Burmese politician, diplomat, author, and political activist. She was awarded the 1991 Nobel Peace Prize. She served as State Counsellor of Myanmar and Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Myanmar), Ministe ...
assumed the newly created role of
state counsellor, a role akin to a
prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
.
Coup d'état and civil war
In Myanmar's 2020 parliamentary election, the ostensibly ruling
National League for Democracy (NLD), the party of State Counsellor
Aung San Suu Kyi
Aung San Suu Kyi (born 19 June 1945) is a Burmese politician, diplomat, author, and political activist. She was awarded the 1991 Nobel Peace Prize. She served as State Counsellor of Myanmar and Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Myanmar), Ministe ...
, competed with various other smaller parties – particularly the military-affiliated
Union Solidarity and Development Party (USDP).
["Myanmar Election Delivers Another Decisive Win for Aung San Suu Kyi,"](_blank)
11 November 2020, ''The New York Times'', retrieved 18 December 2020 Suu Kyi's NLD won the
2020 Myanmar general election on 8 November in a landslide.
["Myanmar: Aung San Suu Kyi's party wins majority in election,"](_blank)
11 November 2020, BBC News, retrieved 18 December 2020["Myanmar election commission rejects military's fraud claims,"](_blank)
29 January 2021, Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American not-for-profit organization, not-for-profit news agency headquartered in New York City.
Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association, and produces news reports that are dist ...
, retrieved 28 February 2021 The USDP, regarded as a proxy for the military, suffered a "humiliating" defeat
["Explainer: Crisis in Myanmar after army alleges election fraud,"](_blank)
31 January 2021, updated 1 February 2021, Reuters News Service, retrieved 28 February 2021["Military-Backed USDP Leaders Defeated by NLD in Myanmar Election,"](_blank)
12 November 2020, '' The Irrawaddy'', retrieved 28 February 2021 – even worse than in 2015
– capturing only 33 of the 476 elected seats.
As the election results began emerging, the USDP rejected them, urging a new election with the military as observers.
More than 90 other smaller parties contested the vote, including more than 15 who complained of irregularities. However, election observers declared there were no major irregularities.
["Myanmar Election Body Rejects Military Allegations of Electoral Fraud,"](_blank)
28 January 2021, '' The Irrawaddy'', retrieved 6 February 2021 However, despite the election commission validating the NLD's overwhelming victory,
the USDP and Myanmar's military persistently alleged fraud.
["Myanmar Military Condemns Speaker's Refusal to Probe Election Fraud Claims,"](_blank)
15 January 2021, '' The Irrawaddy'', retrieved 7 February 2021["Myanmar Military Refuses to Rule Out Coup as It Presses Claim of Fraud in Nov Election,"](_blank)
26 January 2021, '' The Irrawaddy'', retrieved 7 February 2021["Military Thrests: Coup Fears Overshadow Myanmar Parliament Opening,"](_blank)
'' Channel NewsAsia'',["Myanmar Military Chief Warns Constitution Should Be Revoked If Laws Not Followed,"](_blank)
28 January 2021, '' The Irrawaddy'', retrieved 7 February 2021["UN, embassies fret over Myanmar coup talk,"](_blank)
28 January 2021, '' Bangkok Post'', retrieved 30 January 2021
In January 2021, just before the new parliament was to be sworn in, the NLD announced that Suu Kyi would retain her State Counsellor role in the upcoming government.
["Myanmar's Daw Aung San Suu Kyi to Keep State Counselor Position NLD Says,"](_blank)
25 January 2021, '' The Irrawaddy'', retrieved 6 February 2021

In the early morning of 1 February 2021, the day parliament was set to convene, the
Tatmadaw, Myanmar's military, detained Suu Kyi and other members of the ruling party.
["Myanmar coup: Week(s) of Feb.1 to Feb. 21, EU action in focus as foreign ministers set to meet; Candlelight vigil held in Yangon; Facebook removes military's 'True News' page,"](_blank)
(reverse chronology) 1 February through 21 February 2021, '' Nikkei Asia'', retrieved 1 March 2021 The military handed power to military chief
Min Aung Hlaing and declared a state of emergency for one year
and began closing the borders, restricting travel and electronic communications nationwide.
The military announced it would replace the existing election commission with a new one, and a military media outlet indicated new elections would be held in about one year – though the military avoided making an official commitment to that.
The military expelled NLD party Members of Parliament from the capital city,
Naypyidaw.
By 15 March 2021 the military leadership continued to extend martial law into more parts of Yangon, while security forces killed 38 people in a single day of violence.
By the second day of the coup, thousands of protesters were marching in the streets of Yangon, and other protests erupted nationwide, largely halting commerce and transportation. Despite the military's arrests and killings of protesters, the first weeks of the coup found growing public participation, including groups of civil servants, teachers, students, workers, monks and religious leaders – even normally disaffected ethnic minorities.
["Myanmar coup: Teachers join growing protests against military,"](_blank)
5 February 2021, BBC News, retrieved 28 February 2021
12 November 2020, '' The Irrawaddy'', retrieved 28 February 2021
The coup was immediately condemned by the
United Nations Secretary General, and leaders of democratic nations. The U.S. threatened sanctions on the military and its leaders, including a "freeze" of US$1 billion of their assets in the U.S.
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
,
Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
,
Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
,
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
,
Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
,
Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, the
Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
and
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
refrained from criticizing the military coup. A
United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
resolution called for the release of Aung San Suu Kyi and the other detained leaders
– a position shared by the
United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights.
International development and aid partners – business, non-governmental, and governmental – hinted at suspension of partnerships with Myanmar. Banks were closed and
social media
Social media are interactive technologies that facilitate the Content creation, creation, information exchange, sharing and news aggregator, aggregation of Content (media), content (such as ideas, interests, and other forms of expression) amongs ...
communications platforms, including
Facebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
and
Twitter
Twitter, officially known as X since 2023, is an American microblogging and social networking service. It is one of the world's largest social media platforms and one of the most-visited websites. Users can share short text messages, image ...
, removed Tatmadaw postings. Protesters appeared at Myanmar embassies in foreign countries.
The National Unity Government then declared the formation of an armed wing on 5 May 2021, a date that is often cited as the start of a
full-scale civil war. This armed wing was named the
People's Defence Force (PDF) to protect its supporters from military junta attacks and as a first step towards a Federal Union Army. The civil war is ongoing as of 2025.

Geography
Myanmar has a total area of . It lies between latitudes
9° and
29°N, and longitudes
92° and
102°E. Myanmar is bordered in the northwest by the
Chittagong Division of
Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
and the
Mizoram, Manipur,
Nagaland
Nagaland () is a States and union territories of India, state in the northeast India, north-eastern region of India. It is bordered by the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Assam to the west, Manipur to the south, and the Naga Sel ...
and
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeast India. It was formed from the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and India declared it as a state on 20 February 1987. Itanagar is its capital and la ...
states of India. Its north and northeast border is with the
Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR), often shortened to Tibet in English or Xizang in Pinyin, Hanyu Pinyin, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China. It was established in 1965 to replace the ...
and
Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces ...
for a Sino-Myanmar border total of . It is bounded by
Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
and
Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
to the southeast. Myanmar has of contiguous coastline along the
Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
and
Andaman Sea
The Andaman Sea (historically also known as the Burma Sea) is a marginal sea of the northeastern Indian Ocean bounded by the coastlines of Myanmar and Thailand along the Gulf of Martaban and the west side of the Malay Peninsula, and separated f ...
to the southwest and the south, which forms one quarter of its total perimeter.
In the north, the
Hengduan Mountains
The Hengduan Mountains () are a group of mountain ranges in southwest China, southwest China that connect the southeast portions of the Tibetan Plateau with the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau. The Hengduan Mountains are primarily large north-south ...
form the border with China.
Hkakabo Razi
Hkakabo Razi (, ; ) is believed to be Myanmar's highest mountain. The -tall mountain is the highest mountain in Southeast Asia as well. It is located in the northern Myanmar state of Kachin State, Kachin in an outlying subrange of the Greater Him ...
, located in
Kachin State
Kachin State (; Jingpho language, Kachin: ) is the northernmost administrative divisions of Myanmar, state of Myanmar. It is bordered by China to the north and east (Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet and Yunnan, respectively), Shan State to the sou ...
, at an elevation of , is the highest point in Myanmar. Many mountain ranges, such as the
Rakhine Yoma, the
Bago Yoma, the
Shan Hills and the
Tenasserim Hills exist within Myanmar, all of which run north-to-south from the
Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
.
The mountain chains divide Myanmar's three river systems, which are the
Irrawaddy,
Salween (Thanlwin), and the
Sittaung rivers.
The Irrawaddy River, Myanmar's longest river at nearly , flows into the
Gulf of Martaban. Fertile plains exist in the valleys between the
mountain chains.
The majority of Myanmar's population lives in the
Irrawaddy valley, which is situated between the
Rakhine Yoma and the
Shan Plateau.
Myanmar is one of the most seismically prone countries in the world.
The
Sagaing Fault between the
Indian Plate and the
Eurasian Plate runs north-south through the center of the country.
There have been many small and some big
earthquakes with a 7-8 magnitude.
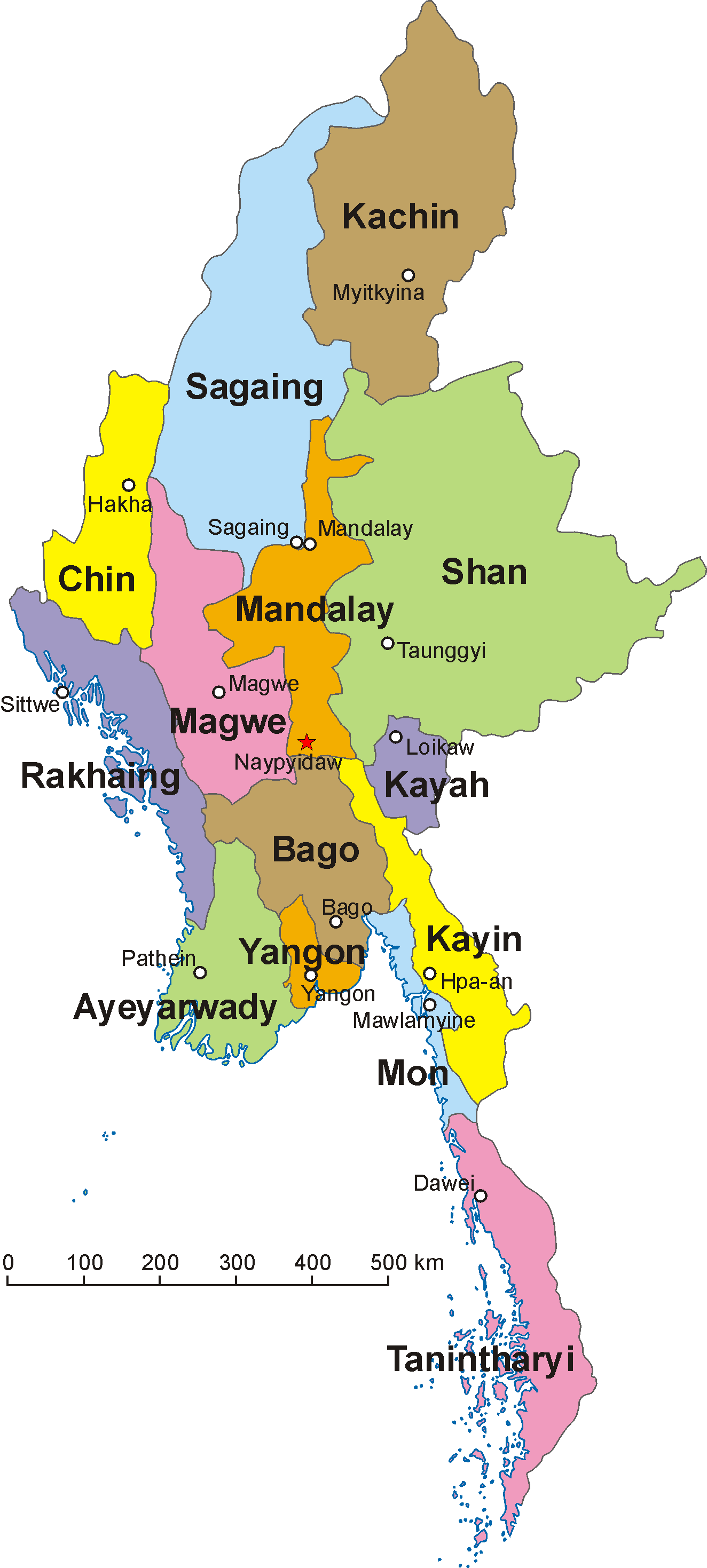
Administrative divisions
Myanmar is divided into seven states () and seven regions (), formerly called divisions. Regions are predominantly Bamar (that is, mainly inhabited by Myanmar's dominant ethnic group). States, in essence, are regions that are home to particular ethnic minorities. The administrative divisions are further subdivided into
districts, which are further subdivided into townships,
wards, and villages. Since 30 April 2022, districts inside regions and states have been expanded to total count of 121.
Below are the number of districts, townships, cities/towns, wards, village groups and villages in each division and state of Myanmar as of 30 April 2022:
Climate

Much of the country lies between the
Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, also known as the Northern Tropic, is the Earth's northernmost circle of latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun ...
and the
Equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
. It lies in the
monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
region of Asia, with its coastal regions receiving over of rain annually. Annual
rainfall in the
delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier ...
region is approximately , while average annual rainfall in the dry zone in central Myanmar is less than . The northern regions of Myanmar are the coolest, with average temperatures of . Coastal and delta regions have an average maximum temperature of .
Previously and currently analysed data, as well as future projections on changes caused by
climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
predict serious consequences to development for all economic, productive, social, and environmental sectors in Myanmar.
In order to combat the hardships ahead and do its part to help
combat climate change Myanmar has displayed interest in expanding its use of renewable energy and lowering its level of carbon emissions. Groups involved in helping Myanmar with the transition and move forward include the
UN Environment Programme, Myanmar Climate Change Alliance, and the
Ministry of Natural Resources and Environmental Conservation which directed in producing the final draft of the Myanmar national climate change policy that was presented to various sectors of the Myanmar government for review.
In April 2015, it was announced that the
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
and Myanmar would enter a full partnership framework aimed to better access to electricity and other basic services for about six million people and expected to benefit three million pregnant woman and children through improved health services.
Acquired funding and proper planning has allowed Myanmar to better prepare for the impacts of climate change by enacting programs which teach its people new farming methods, rebuild its infrastructure with materials resilient to natural disasters, and transition various sectors towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Biodiversity

Myanmar is a
biodiverse country with more than 16,000
plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
, 314
mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
, 1131
bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
, 293
reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
, and 139
amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
species, and 64 terrestrial
ecosystems
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
including tropical and subtropical vegetation, seasonally inundated wetlands, shoreline and tidal systems, and alpine ecosystems. Myanmar houses some of the largest intact natural ecosystems in
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, but the remaining ecosystems are under threat from land use intensification and over-exploitation. According to the
IUCN Red List of Ecosystems categories and criteria more than a third of Myanmar's land area has been converted to
anthropogenic ecosystems over the last 2–3 centuries, and nearly half of its ecosystems are threatened. Despite large gaps in information for some ecosystems, there is a large potential to develop a comprehensive
protected area network that protects its terrestrial biodiversity.
Myanmar continues to perform badly in the global
Environmental Performance Index (EPI) with an overall ranking of 153 out of 180 countries in 2016, among the worst in the
South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
n region. The environmental areas where Myanmar performs worst (i.e. highest ranking) are
air quality
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
(174), health impacts of environmental issues (143) and biodiversity and habitat (142). Myanmar performs best (i.e. lowest ranking) in environmental impacts of fisheries (21) but with declining Fish stocks, fish stocks. Despite several issues, Myanmar also ranks 64 and scores very good (i.e. a high percentage of 93.73%) in environmental effects of the agricultural industry because of an excellent management of the nitrogen cycle. Myanmar is one of the most highly vulnerable countries to climate change; this poses a number of social, political, economic and foreign policy challenges to the country.
Myanmar's slow economic growth has contributed to the preservation of much of its environment and ecosystems. Forests, including dense tropical growth and valuable teak in lower Myanmar, cover over 49% of the country, including areas of acacia, bamboo, Hopea odorata, ironwood and ''Magnolia champaca''. Coconut and betel palm and rubber have been introduced. In the highlands of the north, oak, pine and various rhododendrons cover much of the land.
Heavy logging since the new 1995 forestry law went into effect has seriously reduced forest area and wildlife habitat. The lands along the coast support all varieties of tropical fruits and once had large areas of Myanmar Coast mangroves, mangroves although much of the protective mangroves have disappeared. In much of central Myanmar (the dry zone), vegetation is sparse and stunted.
Typical jungle animals, particularly tigers, occur sparsely in Myanmar. In upper Myanmar, there are rhinoceros, wild water buffalo, clouded leopard, wild boars, deer, antelope, and elephants, which are also tamed or bred in captivity for use as work animals, particularly in the lumber industry. Smaller mammals are also numerous, ranging from gibbons and monkeys to flying foxes. The abundance of
bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s is notable with over 800 species, including Rose-ringed parakeet, parrots, myna, peafowl, red junglefowl, weaverbirds, crows, herons, and Eastern barn owl, barn owl. Among reptile species there are crocodiles, geckos, cobras, Burmese pythons, and turtles. Hundreds of species of freshwater fish are wide-ranging, plentiful and are very important food sources.
Government and politics
Myanmar operates ''de jure'' as a unitary state, unitary assembly-independent republic under its 2008 Constitution of Myanmar, 2008 constitution. But in February 2021, the civilian government led by
Aung San Suu Kyi
Aung San Suu Kyi (born 19 June 1945) is a Burmese politician, diplomat, author, and political activist. She was awarded the 1991 Nobel Peace Prize. She served as State Counsellor of Myanmar and Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Myanmar), Ministe ...
, was deposed by the
Tatmadaw. In February 2021, Myanmar military declared a one-year state emergency and First Vice President Myint Swe became the President of Myanmar, Acting President of Myanmar and handed the power to the Commander-in-Chief of Defence Services
Min Aung Hlaing and he assumed the role Chairman of the State Administration Council, then Prime Minister of Myanmar, Prime Minister. The President of Myanmar acts as the de jure head of state and the Chairman of the State Administration Council acts as the de facto head of government.

The constitution of Myanmar, its third since independence, was drafted by its military rulers and published in September 2008. The country is governed as a parliamentary system with a bicameral legislature (with an executive President of Myanmar, president accountable to the legislature), with 25% of the legislators appointed by the military and the rest elected in general elections.
The legislature, called the Assembly of the Union, is bicameral and made up of two houses: The 224-seat upper House of Nationalities and the 440-seat lower House of Representatives (Myanmar), House of Representatives. The upper house consists 168 members who are directly elected and 56 who are appointed by the Burmese Armed Forces. The lower house consists of 330 members who are directly elected and 110 who are appointed by the armed forces.
Political culture
The major political parties are the
National League for Democracy and the
Union Solidarity and Development Party.
Myanmar's army-drafted constitution was approved in a 2008 Burmese constitutional referendum, referendum in May 2008. The results, 92.4% of the 22 million voters with an official turnout of 99%, are considered suspect by many international observers and by the National League of Democracy with reports of widespread Electoral fraud, fraud, ballot stuffing, and voter intimidation.
The 2010 Myanmar general election, elections of 2010 resulted in a victory for the military-backed Union Solidarity and Development Party. Various foreign observers questioned the fairness of the elections.
One criticism of the election was that only government-sanctioned political parties were allowed to contest in it and the popular
National League for Democracy was declared illegal.
However, immediately following the elections, the government ended the house arrest of the democracy advocate and leader of the National League for Democracy,
Aung San Suu Kyi
Aung San Suu Kyi (born 19 June 1945) is a Burmese politician, diplomat, author, and political activist. She was awarded the 1991 Nobel Peace Prize. She served as State Counsellor of Myanmar and Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Myanmar), Ministe ...
, and her ability to move freely around the country is considered an important test of the military's movement toward more openness.
Foreign relations
Though the country's foreign relations, particularly with Western nations, have historically been strained, the situation has markedly improved since the reforms following the 2010 elections. After years of diplomatic isolation and economic and military sanctions, the United States relaxed curbs on foreign aid to Myanmar in November 2011
and announced the resumption of diplomatic relations on 13 January 2012 The European Union has placed sanctions on Myanmar, including an arms embargo, cessation of trade preferences, and suspension of all aid with the exception of humanitarian aid.
Sanctions imposed by the United States and European countries against the former military government, coupled with boycotts and other direct pressure on corporations by supporters of the democracy movement, have resulted in the withdrawal from the country of most U.S. and many European companies. Despite Western isolation, Asian corporations have generally remained willing to continue investing in the country and to initiate new investments, particularly in natural resource extraction. The country has close relations with neighbouring India and China with several Indian and Chinese companies operating in the country. Under India's Look East policy (India), Look East policy, fields of co-operation between India and Myanmar include remote sensing, oil and gas exploration, information technology, hydropower and construction of ports and buildings. Myanmar also has close political relations with Vietnam and Japan.
In May 2013, Thein Sein became the first Myanmar president to visit the White House in 47 years. President Barack Obama praised the former general for political and economic reforms and the cessation of tensions between Myanmar and the United States. Political activists objected to the visit because of concerns over human rights abuses in Myanmar, but Obama assured Thein Sein that Myanmar will receive U.S. support. The two governments agreed to sign a bilateral trade and investment framework agreement on 21 May 2013.
In June 2013, Myanmar held its first ever summit, the World Economic Forum on East Asia 2013. A regional spinoff of the annual World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland, the summit was held on 5–7 June and attended by 1,200 participants, including 10 heads of state, 12 ministers and 40 senior directors from around the world.
On 19 January 2025, Reuters reported that
ASEAN
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations,
commonly abbreviated as ASEAN, is a regional grouping of 10 states in Southeast Asia "that aims to promote economic and security cooperation among its ten members." Together, its member states r ...
had told Myanmar's military government to prioritise ceasefire, "urging the junta to start dialogue and end hostilities immediately" and "to allow unhindered humanitarian access", citing Malaysia's foreign minister Mohamad Hasan (politician), Mohamad Hasan. The ASEAN chair's statement denounced "the continued acts of violence against civilians and public facilities and urged all parties involved" to "immediately halt indiscriminate violence, exercise utmost restraint, ensure the protection and safety of all civilians and civilian infrastructures, and create a conducive environment for the delivery of humanitarian assistance and inclusive national dialogue".
Military
Since the late 1950s, Myanmar's military has had major roles in Myanmar's politics.

Myanmar has received extensive military aid from China in the past.
Myanmar has been a member of ASEAN since 1997. Though it gave up its turn to hold the ASEAN chair and host the ASEAN Summit in 2006, it chaired the forum and hosted the summit in 2014.
In November 2008, Myanmar's political situation with neighbouring Bangladesh became tense as they began searching for natural gas in a disputed block of the Bay of Bengal.
Controversy surrounding the Rohingya population also remains an issue between Bangladesh and Myanmar.
Myanmar's armed forces are known as the
Tatmadaw, which numbers 488,000. The Tatmadaw comprises the Myanmar Army, Army, the Myanmar Navy, Navy, and the Myanmar Air Force, Air Force. The country List of countries by number of military and paramilitary personnel, ranked twelfth in the world for its number of active troops in service.
The military is very influential in Myanmar, with all top cabinet and ministry posts usually held by military officials. Official figures for military spending are not available. Estimates vary widely because of uncertain exchange rates, but Myanmar's military forces' expenses are high. Myanmar imports most of its weapons from Russia, Ukraine, China and India.
Myanmar is building a research nuclear reactor near Pyin Oo Lwin with help from Russia. It is one of the signatories of the nuclear non-proliferation pact since 1992 and a member of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) since 1957. The military junta had informed the IAEA in September 2000 of its intention to construct the reactor. In 2010 as part of the United States diplomatic cables leak, leaked diplomatic cables, Myanmar was suspected of using North Korean construction teams to build a fortified surface-to-air missile facility. As of 2019, the United States Bureau of Arms Control, Verification, and Compliance, Bureau of Arms Control assessed that Myanmar is not in violation of its obligations under the Non-Proliferation Treaty but that the Myanmar government had a history of non-transparency on its nuclear programs and aims.
Until 2005, the United Nations General Assembly annually adopted a detailed resolution about the situation in Myanmar by consensus.
But in 2006 a divided United Nations General Assembly voted through a resolution that strongly called upon the government of Myanmar to end its systematic violations of human rights. In January 2007, Russia and China vetoed a draft resolution before the
United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
calling on the government of Myanmar to respect human rights and begin a democratic transition. South Africa also voted against the resolution.
Human rights and internal conflicts
There is consensus that the former military regime in Myanmar (1962–2010) was one of the world's most repressive and abusive regimes. In November 2012, Samantha Power, Barack Obama's Special Assistant to the President on Human Rights, wrote on the White House blog that "Serious human rights abuses against civilians in several regions continue, including against women and children."
Members of the United Nations and major international human rights organisations have issued repeated and consistent reports of widespread and systematic human rights violations in Myanmar. The United Nations General Assembly has repeatedly called on the Burmese military junta to respect human rights and in November 2009 the General Assembly adopted a resolution "strongly condemning the ongoing systematic violations of human rights and fundamental freedoms" and calling on the Burmese military regime "to take urgent measures to put an end to violations of international human rights and humanitarian law."
International human rights organisations including Human Rights Watch and Amnesty International have repeatedly documented and condemned widespread human rights violations in Myanmar. The ''Freedom in the World 2011'' report by Freedom House notes, "The military junta has ... suppressed nearly all basic rights; and committed human rights abuses with impunity." In July 2013, the Assistance Association for Political Prisoners indicated that there were approximately 100 political prisoners being held in Burmese prisons.
Evidence gathered by a British researcher was published in 2005 regarding the extermination or "Burmisation" of certain ethnic minorities, such as the
Karen, Karenni people, Karenni and
Shan.

Based on the evidence gathered by Amnesty photographs and video of the ongoing armed conflict between the Myanmar military and the Arakan Army (AA), attacks escalated on civilians in Rakhine State. Ming Yu Hah, Amnesty International's Deputy Regional Director for Campaigns said, the UN Security Council must urgently refer the situation in Myanmar to the International Criminal Court. The military is notorious for rampant use of sexual violence.
In November 2024, the International Criminal Court, ICC prosecutor Karim Ahmad Khan, Karim A.A. Khan KC filed an arrest warrant application of Senior General, Acting President and Commander-in-Chief of the Myanmar Defence Services
Min Aung Hlaing for "criminal responsibility for the crimes against humanity of deportation and persecution of the Rohingya, committed in Myanmar, and in part in Bangladesh".
Genocide allegations, Organ trading and human trafficking
Child soldiers have been a major issue in Myanmar, with reports of children being sold into the military for as little as $40. The Burmese Army and rebel groups have used child soldiers, though some efforts have been made to release them. The UN and other organizations have pressured the government to reform, but progress has been slow.
The military takeover in 2021 worsened poverty in country pushing people to extreme measures like illegal organ trade. Many Myanmar citizens sell their organs online for money, sometimes earning the equivalent of a two-year salary, as financial desperation forces families into a cycle of selling body parts.
The Myanmar government has been alleged to have committed genocide against the Rohingya. The Rohingya people face severe persecution, denied citizenship and basic rights since 1982. Many have been expelled, making them one of the world's most persecuted minorities.
Government reforms
According to the Crisis Group, since Myanmar transitioned to a new government in August 2011, the country's human rights record has been improving. Previously giving Myanmar its lowest rating of 7, the 2012 ''Freedom in the World'' report also notes improvement, giving Myanmar a 6 for improvements in civil liberties and political rights, the release of political prisoners, and a loosening of restrictions. In 2013, Myanmar improved yet again, receiving a score of 5 in civil liberties and 6 in political freedoms.
The government has assembled a
National Human Rights Commission that consists of 15 members from various backgrounds. Several activists in exile, including Thee Lay Thee Anyeint members, have returned to Myanmar after President Thein Sein's invitation to expatriates to return home to work for national development. In an address to the United Nations Security Council on 22 September 2011, Myanmar's Foreign Minister Wunna Maung Lwin confirmed the government's intention to release prisoners in the near future.
The government has also relaxed reporting laws, but these remain highly restrictive. In September 2011, several banned websites, including YouTube, Democratic Voice of Burma and Voice of America, were unblocked. A 2011 report by the Hauser Center for Nonprofit Organizations found that, while contact with the Myanmar government was constrained by donor restrictions, international humanitarian non-governmental organisations (NGOs) see opportunities for effective advocacy with government officials, especially at the local level. At the same time, international NGOs are mindful of the ethical quandary of how to work with the government without bolstering or appeasing it.
Following Thein Sein's first ever visit to the UK and a meeting with Prime Minister David Cameron, the Myanmar president declared that all of his nation's political prisoners will be released by the end of 2013, in addition to a statement of support for the well-being of the Rohingya Muslim community. In a speech at Chatham House, he revealed that "We [Myanmar government] are reviewing all cases. I guarantee to you that by the end of this year, there will be no prisoners of conscience in Myanmar."
Homosexual acts are LGBT rights in Myanmar, illegal in Myanmar and can be punishable by life imprisonment.
In 2016, Myanmar leader
Aung San Suu Kyi
Aung San Suu Kyi (born 19 June 1945) is a Burmese politician, diplomat, author, and political activist. She was awarded the 1991 Nobel Peace Prize. She served as State Counsellor of Myanmar and Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Myanmar), Ministe ...
was accused of failing to protect Myanmar's Islam in Myanmar, Muslim minority. Since August 2017 Doctors Without Borders have treated 113 Rohingya refugee females for sexual assault with all but one describing military assailants.
Economy
Myanmar's economy is one of the fastest growing economies in the world with a nominal GDP of US$76.09 billion in 2019 and an estimated purchasing power adjusted GDP of US$327.629 billion in 2017 according to the World Bank. Foreigners are able to legally lease but not own property.
In December 2014, Myanmar set up its first stock exchange, the Yangon Stock Exchange.
The informal economy's share in Myanmar is one of the biggest in the world and is closely linked to corruption, smuggling and illegal trade activities. In addition, decades of civil war and unrest have contributed to Myanmar's current levels of poverty and lack of economic progress. Myanmar lacks adequate infrastructure. Goods travel primarily across the Thai border (where most illegal drugs are exported) and along the Irrawaddy River.
Notably, opium production in Myanmar is the world's second-largest source of opium after Opium production in Afghanistan, Afghanistan, producing some 25% of the world's opium, forming part of the Golden Triangle. While opium poppy cultivation in Myanmar had declined year-on-year since 2015, cultivation area increased by 33% totalling 40,100 hectares alongside an 88% increase in yield potential to 790 tonnes in 2022 according to latest data from the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) Myanmar Opium Survey 2022. With that said, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) has also warned that opium production in Myanmar may rise again if the economic crunch brought on by COVID-19 and the country's 1 February military coup persists, with significant public health and security consequences for much of Asia. At the same time, the Golden Triangle, and specifically Shan State in Myanmar, is believed to be the largest methamphetamine-producing area in the world. The growing signs of an intensification of methamphetamine manufacturing activity within and around the Golden Triangle, and a corresponding decrease in the number of production facilities dismantled in other parts of the region, suggests that methamphetamine manufacture in East and Southeast Asia is now consolidated into the lower Mekong region. Countries in East and Southeast Asia have collectively witnessed sustained increases in seizures of methamphetamine over the last decade, totalling over 171 tons and a record of over 1 billion methamphetamine tablets in 2021 according to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, more than any other part of the world. In April and May 2020, Myanmar authorities reported Asia's largest ever drug operation in Shan State, totalling what was believed to be 193 million methamphetamine tablets, hundreds of kilogrammes of crystal methamphetamine as well as some heroin, and over 162,000 litres and 35.5 tons of drug precursors as well as sophisticated production equipment and several staging and storage facilities.
Both China and India have attempted to strengthen ties with the government for economic benefit in the early 2010s. Many Western nations, including the United States and Canada, and the European Union, historically imposed investment and trade sanctions on Myanmar. The United States and European Union eased most of their sanctions in 2012. From May 2012 to February 2013, the United States began to lift its economic sanctions on Myanmar "in response to the historic reforms that have been taking place in that country." Foreign investment comes primarily from China, Singapore, the Philippines, South Korea, India, and Thailand. The military has stakes in some major industrial corporations of the country (from oil production and consumer goods to transportation and tourism).
Economic history

Under the British Empire, British administration, the people of Burma were at the bottom of the social hierarchy, with Europeans at the top, Indians, Chinese, and Christianized minorities in the middle, and Buddhist Burmese at the bottom.
Forcefully integrated into the world economy, Burma's economy grew by involving itself with extractive industries and cash crop agriculture. However, much of the wealth was concentrated in the hands of Europeans. The country became the world's largest exporter of rice, mainly to European markets, while other colonies like India suffered mass starvation. Being a follower of free market principles, the British opened up the country to large-scale immigration with Rangoon exceeding New York City as the greatest immigration port in the world in the 1920s. Historian Thant Myint-U states, "This was out of a total population of only 13 million; it was equivalent to the United Kingdom today taking 2 million people a year." By then, in most of Burma's largest cities,
Rangoon, Akyab, Pathein, Bassein and Moulmein, the Indian immigrants formed a majority of the population. The Burmese under British rule felt helpless, and reacted with a "racism that combined feelings of superiority and fear".
Crude oil production, an indigenous industry of Yenangyaung, was taken over by the British and put under Burmah Oil monopoly. British Burma began exporting crude oil in 1853. European firms produced 75% of the world's teak.
The wealth was, however, mainly concentrated in the hands of Europeans. In the 1930s, agricultural production fell dramatically as international rice prices declined and did not recover for several decades. During the Japanese invasion of Burma in World War II, the British followed a scorched earth policy. They destroyed major government buildings, oil wells and mines that developed for tungsten (Mawchi), tin, lead and silver to keep them from the Japanese. Myanmar was bombed extensively by the Allies.
After independence, the country was in ruins with its major infrastructure completely destroyed. With the loss of India, Burma lost relevance and obtained independence from the British. After a parliamentary government was formed in 1948, Prime Minister
U Nu
Nu (; ; 25 May 1907 – 14 February 1995), commonly known as Burmese names#Honorifics, U Nu and also by the honorific name Thakin Nu, was a prominent Burmese people, Burmese statesman and the first Prime Minister of Union of Burma. He was ...
embarked upon a policy of nationalisation and the state was declared the owner of all of the land in Burma. The government tried to implement an eight-year plan partly financed by injecting money into the economy, but this caused inflation to rise. The 1962 Burmese coup d'état, 1962 coup d'état was followed by an economic scheme called the
Burmese Way to Socialism, a plan to nationalise all industries, with the exception of agriculture. While the economy continued to grow at a slower rate, the country eschewed a Western-oriented development model, and by the 1980s, was left behind capitalist powerhouses like
Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
which were integrated with Western economies.
Myanmar asked for admittance to a least developed country status in 1987 to receive debt relief.
Agriculture

The major agricultural product is Rice production in Myanmar, rice, which covers about 60% of the country's total cultivated land area. Rice accounts for 97% of total food grain production by weight. Through collaboration with the International Rice Research Institute, 52 modern rice varieties were released in the country between 1966 and 1997, helping increase national rice production to 14 million tons in 1987 and to 19 million tons in 1996. By 1988, modern varieties were planted on half of the country's ricelands, including 98 percent of the irrigated areas. In 2008 rice production was estimated at 50 million tons.
Extractive industries
Myanmar produces precious stones such as rubies, sapphires, pearls, and
jade
Jade is an umbrella term for two different types of decorative rocks used for jewelry or Ornament (art), ornaments. Jade is often referred to by either of two different silicate mineral names: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in t ...
. Rubies are the biggest earner; 90% of the world's rubies come from the country, whose red stones are prized for their purity and hue. Thailand buys the majority of the country's gems. Myanmar's "Valley of Rubies", the mountainous Mogok Township, Mogok area, north of
Mandalay, is noted for its rare pigeon's blood rubies and blue sapphires.
Many U.S. and European Union, European jewellery companies, including Bulgari, Tiffany and Cartier, refuse to import these stones based on reports of deplorable working conditions in the mines. Human Rights Watch has encouraged a complete ban on the purchase of Burmese gems based on these reports and because nearly all profits go to the ruling junta, as the majority of mining activity in the country is government-run. The government of Myanmar controls the gem trade by direct ownership or by joint ventures with private owners of mines.
Rare-earth elements are also a significant export, as Myanmar supplies around 10% of the world's rare earths. Conflict in Kachin State has threatened the operations of its mines as of February 2021.
Other industries include agricultural goods, textiles, wood products, construction materials, gems, metals, oil and natural gas. Myanmar Engineering Society has identified at least 39 locations capable of geothermal power production and some of these hydrothermal reservoirs lie quite close to Yangon which is a significant underutilised resource for electrical production.
Tourism
The government receives a significant percentage of the income of private-sector tourism services. The most popular available tourist destinations in Myanmar include big cities such as
Yangon
Yangon, formerly romanized as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar. Yangon was the List of capitals of Myanmar, capital of Myanmar until 2005 and served as such until 2006, when the State Peace and Dev ...
and
Mandalay; religious sites in Mon State, Pindaya, Bago, Burma, Bago and Hpa-An; nature trails in Inle Lake, Kengtung, Putao District, Putao, Pyin Oo Lwin; ancient cities such as
Bagan
Bagan ( ; ; formerly Pagan) is an ancient city and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the Mandalay Region of Myanmar. From the 9th to 13th centuries, the city was the capital of the Pagan Kingdom, the first kingdom that unified the regions that w ...
and Mrauk-U; as well as beaches in Nabule, Ngapali Beach, Ngapali, Ngwe Saung Beach, Ngwe-Saung, and Mergui. Nevertheless, much of the country is off-limits to tourists, and interactions between foreigners and the people of Myanmar, particularly in the border regions, are subject to police scrutiny. They are not to discuss politics with foreigners, under penalty of imprisonment and, in 2001, the Myanmar Tourism Promotion Board issued an order for local officials to protect tourists and limit "unnecessary contact" between foreigners and ordinary Burmese people.
The most common way for travellers to enter the country is by air.
According to the website ''Lonely Planet'', getting into Myanmar is problematic: "No bus or train service connects Myanmar with another country, nor can you travel by car or motorcycle across the border – you must walk across." They further state that "It is not possible for foreigners to go to/from Myanmar by sea or river."
There are a few border crossings that allow the passage of private vehicles, such as the border between Ruili (China) to Mu-se, the border between Htee Kee (Myanmar) and Phu Nam Ron (Thailand)—the most direct border between Dawei and Kanchanaburi, and the border between Myawaddy and Mae Sot, Thailand. At least one tourist company has successfully run commercial overland routes through these borders since 2013.
Flights are available from most countries, though direct flights are limited to mainly Thai and other
ASEAN
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations,
commonly abbreviated as ASEAN, is a regional grouping of 10 states in Southeast Asia "that aims to promote economic and security cooperation among its ten members." Together, its member states r ...
airlines. According to ''Weekly Eleven, Eleven'' magazine, "In the past, there were only 15 international airlines and increasing numbers of airlines have begun launching direct flights from Japan, Qatar, Taiwan, South Korea, Germany and Singapore."
Demographics

The provisional results of the 2014 Myanmar Census showed that the total population was 51,419,420. This figure includes an estimated 1,206,353 persons in parts of northern
Rakhine State
Rakhine State ( ; , ; ), formerly known as Arakan State, is a Administrative divisions of Myanmar, state in Myanmar (Burma). Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State to the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady Re ...
,
Kachin State
Kachin State (; Jingpho language, Kachin: ) is the northernmost administrative divisions of Myanmar, state of Myanmar. It is bordered by China to the north and east (Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet and Yunnan, respectively), Shan State to the sou ...
and Kayin State who were not counted.
People who were out of the country at the time of the census are not included in these figures. There are over 600,000 registered migrant workers from Myanmar in
Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, and millions more work illegally. Burmese citizens account for 80% of all migrant workers in Thailand. At the beginning of the 20th century, Burma's Census in Myanmar, population was approximately 10 million. The national population density is , among the lowest in Southeast Asia.
Myanmar's fertility rate in 2011 was 2.23, slightly above the Sub-replacement fertility, replacement level
and low compared to Southeast Asian countries of similar economic standing.
There has been a significant decline in fertility in the 2000s, from a rate of 4.7 children per woman in 1983, down to 2.4 in 2001, despite the absence of any national population policy.
The fertility rate is much lower in urban areas.
The relatively rapid decline in fertility is attributed to several factors, including extreme delays in marriage (almost unparalleled among developing countries in the region), the prevalence of illegal abortions, and the high proportion of single, unmarried women of reproductive age, with 25.9% of women aged 30–34 and 33.1% of men and women aged 25–34 being single.
[WorldMarriage Patterns 2000]
. United Nations
These patterns stem from economic dynamics, including high income inequality, which results in residents of reproductive age opting for delay of marriage and family-building in favour of attempting to find employment and establish some form of wealth;
the average age of marriage in Myanmar is 27.5 for men, 26.4 for women.
Largest cities
Ethnic groups

Myanmar is ethnically diverse. The government recognises List of ethnic groups in Myanmar, 135 distinct ethnic groups. There are at least 108 different ethnolinguistic groups in Myanmar, consisting mainly of distinct
Tibeto-Burman peoples, but with sizeable populations of Tai–Kadai-speaking peoples, Tai–Kadai, Hmong–Mien, and Austroasiatic (Mon–Khmer) peoples.
Ethnic identity in modern-day Myanmar has been significantly shaped by British colonial rule, Christian missionaries, and Decolonization, decolonisation in the post-independence era. To this day, the
Burmese language
Burmese (; ) is a Tibeto-Burman languages, Tibeto-Burman language spoken in Myanmar, where it is the official language, lingua franca, and the native language of the Bamar people, Bamar, the country's largest ethnic group. Burmese dialects are a ...
does not have precise terminology that distinguishes the European concepts of Ethnicity, race Ethnicity, and ethnicity; the term ''lu-myo'' (, ) can reference race, ethnicity, and religion. For instance, many Bamar people, Bamar self-identify as members of the 'Buddhist ''lu-myo or the 'Burmese people, Myanmar ''lu-myo'',' which has posed a significant challenge for census-takers.
The Bamar form an estimated 68% of the population.
10% of the population are
Shan.
The Kayin make up 7% of the population.
The Rakhine people constitute 4% of the population. Burmese Chinese, Overseas Chinese form approximately 3% of the population.
Myanmar's ethnic Minority group, minority groups prefer the term "ethnic nationality" over "ethnic minority" as the term "minority" furthers their sense of insecurity in the face of what is often described as "Burmanisation"—the proliferation and domination of the dominant Bamar people, Bamar culture over minority cultures.
Mon, who form 2% of the population, are ethno-linguistically related to the Khmer people, Khmer.
Burmese Indians, Overseas Indians are 2%.
The remainder are Kachin people, Kachin, Chin people, Chin,
Rohingya, Anglo-Indians, Burmese Gurkha, Gurkha, People of Nepal, Nepali and other ethnic minorities. Included in this group are the
Anglo-Burmese. Once forming a large and influential community, the Anglo-Burmese left the country in steady streams from 1958 onwards, principally to Australia and the United Kingdom. It is estimated that 52,000 Anglo-Burmese remain in Myanmar. , 110,000 Burmese refugees were living in refugee camps in Thailand.
Refugee camps exist along Indian, Bangladeshi and Thai borders while several thousand are in Malaysia. Conservative estimates state that there are over 295,800 minority refugees from Myanmar, with the majority being
Rohingya,
Karen, and Karenni people, Karenni are principally located along the Thai-Myanmar border. There are nine permanent refugee camps along the Thai-Myanmar border, most of which were established in the mid-1980s. The refugee camps are under the care of the Thai-Burma Border Consortium (TBBC). Since 2006, over 55,000 Burmese refugees have been resettled in the United States.
The persecution of Burmese Indians, Burmese Chinese and other ethnic groups after the military coup headed by General
Ne Win
Ne Win (; ; 24 May 1911 – 5 December 2002), born Shu Maung (; ), was a Burmese army general, politician and Prime Minister of Burma from 1958 to 1960 and 1962 to 1974, and also President of Burma from 1962 to 1981. Ne Win was Burma's mili ...
in 1962 led to the expulsion or emigration of 300,000 people. They migrated to escape Racial Discrimination against Burmese Indians, racial discrimination and the wholesale nationalisation of private enterprise that took place in 1964. The Anglo-Burmese at this time either fled the country or changed their names and blended in with the broader Burmese society.
Many
Rohingya Muslims have fled Myanmar. Many refugees headed to neighbouring Bangladesh, including 200,000 in 1978 as a result of the King Dragon operation in Arakan. 250,000 more left in 1991. Since August 2017, an estimated 23,000-43,700 Rohingya have been killed in the ongoing Rohingya genocide, and another 730,000 have fled to Bangladesh.
Languages
Myanmar is home to four major language families: Sino-Tibetan, Tai–Kadai, Austroasiatic, and Indo-European.
Sino-Tibetan languages are most widely spoken. They include
Burmese,
Karen,
Kachin, Chin people, Chin, and Chinese (mainly Hokkien). The primary Tai–Kadai language is Shan language, Shan.
Mon, Palaung language, Palaung, and Va people, Wa are the major Austroasiatic languages spoken in Myanmar. The two major Indo-European languages are
Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...
, the liturgical language of Theravada Buddhism, and English.
More than a hundred languages are spoken in total. Since many of them are known only within small tribes around the country, they may have been lost (many if not all) after a few generations.
Burmese, the mother tongue of the Bamar and official language of Myanmar, is related to Tibetic languages, Tibetan and Chinese.
It is written in a Burmese alphabet, script consisting of circular and semi-circular letters, which were adapted from the Mon language, Mon script, which in turn was developed from a southern Indian script in the 5th century. The earliest known inscriptions in the Burmese script date from the 11th century. It is also used to write
Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...
, the sacred language of Theravada Buddhism, as well as several ethnic minority languages, including Shan, several Karen dialects, and Kayah (Karenni), with the addition of specialised characters and diacritics for each language.
Religion
Many religions are practised in Myanmar. Religious edifices and orders have been in existence for many years. The Christian and Muslim populations do, however, face religious persecution and it is hard, if not impossible, for non-Buddhists to join the army or get government jobs, the main route to success in the country. Such persecution and targeting of civilians is particularly notable in eastern Myanmar, where over 3,000 villages have been destroyed in the past ten years. More than 200,000 Muslims have fled to Bangladesh by 2007 to escape persecution.

A large majority of the population practices Buddhism; estimates range from 80%
[Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project: Burma](_blank)
. Pew Research Center. 2010. to 89%.
According to the 2014 Myanmar Census, 87.9% of the population identifies as Buddhists.
Theravāda Buddhism is the most widespread.
There are some 500,000 Buddhist monks and 75,000 nuns in this country of 54 million. Other religions are practised largely without obstruction, with the notable exception of some religious minorities such as the Rohingya people, who have continued to have their citizenship status denied and treated as illegal immigrants instead,
and Christians in Chin State.
According to 2014 census, 6.2% of the population identifies as Christian; 4.3% as Muslim; 0.8% as followers of tribal religions; 0.5% as Hinduism, Hindus; 0.2% as followers of other religions; and 0.1% follow no religion.
According to the 2010 estimates of the Pew Research Center, 7% of the population is Christian; 4% is Muslim; 1% follows traditional animistic beliefs; and 2% follow other religions, including Mahayana Buddhism,
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
, and East Asian religions.
Jehovah's Witnesses have been present since 1914 and have about 80 congregations around the country and a branch office in Yangon publishing in 16 languages. A tiny Jewish community in Yangon had a synagogue but no resident rabbi.
Although Hinduism is practised by 0.5% of the population, it was a major religion in Myanmar's past. Burmese folk religion is practised by many Bamars alongside Buddhism.
Health
The general state of health care in Myanmar is poor. The government spends anywhere from 0.5% to 3% of the country's GDP on health care, consistently ranking among the lowest in the world. Although health care is nominally free, in reality, patients have to pay for medicine and treatment, even in public clinics and hospitals. Public hospitals lack many of the basic facilities and equipment. The 2010 maternal mortality rate per 100,000 births for Myanmar is 240. This is compared with 219.3 in 2008 and 662 in 1990. The under 5 mortality rate, per 1,000 births is 73 and the neonatal mortality as a percentage of under 5's mortality is 47. According to Doctors without Borders, 25,000 Burmese AIDS patients died in 2007, deaths that could largely have been prevented by antiretroviral therapy drugs and proper treatment.
[A preventable fate: The failure of ART scale-up in Myanmar](_blank)
Médecins Sans Frontières. November 2008
HIV/AIDS, recognised as a disease of concern by the Ministry of Health (Myanmar), Myanmar Ministry of Health, is most prevalent among sex workers and intravenous drug users. In 2005, the estimated adult HIV/AIDS in Myanmar, HIV prevalence rate in Myanmar was 1.3% (200,000–570,000 people), according to UNAIDS, and early indicators of any progress against the HIV epidemic are inconsistent.
However, the National AIDS Programme Myanmar found that 32% of sex workers and 43% of intravenous drug users in Myanmar have HIV.
Education
According to the UNESCO Institute of Statistics, Myanmar's official literacy rate as of 2000 was 90%. Historically, Myanmar has had high literacy rates. The educational system of Myanmar is operated by the government agency, the Ministry of Education (Myanmar), Ministry of Education. The education system is based on the United Kingdom's system after nearly a century of British and Christian presences in Myanmar. Nearly all schools are government-operated, but there has been an increase in privately funded English language schools in the early 21st century. Schooling is compulsory until the end of elementary school, approximately 9 years old, while the compulsory schooling age is 15 or 16 at international level.
There are 101 universities, 12 institutes, 9 degree colleges and 24 colleges in Myanmar, a total of 146 higher education institutions. There are 10 technical training schools, 23 nursing training schools, 1 sport academy and 20 midwifery schools. There are four international schools acknowledged by WASC and College Board—The International School Yangon, Myanmar International School, Yangon International School, and International School of Myanmar in Yangon. Myanmar was ranked 125th in the Global Innovation Index in 2024.
Crime
Myanmar had a murder rate of 15.2 per 100,000 population with a total of 8,044 murders in 2012.
Factors influencing Myanmar's high murder rate include communal violence and armed conflict. Myanmar is one of the world's most corrupt nations. The 2012 Transparency International Corruption Perceptions Index ranked the country at number 171, out of 176 countries in total. Myanmar is the world's second largest producer of opium after Opium production in Afghanistan, Afghanistan, producing some 25% of the world's opium, and forms part of the Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), Golden Triangle. The opium industry was a monopoly during colonial times and has since been illegally operated by corrupt officials in the Burmese military and rebel fighters, primarily as the basis for heroin manufacture. Myanmar is the largest producer of methamphetamines in the world, with the majority of ''Ya ba'' found in Thailand produced in Myanmar, particularly in the Golden Triangle and northeastern Shan State, which borders Thailand, Laos and China. Burmese-produced ''ya ba'' is typically trafficked to Thailand via Laos, before being transported through the northeastern Thai region of Isan.
Culture

A diverse range of indigenous cultures exist in Myanmar, with majority culture primarily Buddhist and Bamar. Bamar culture has been influenced by the cultures of neighbouring countries, manifested in its language, cuisine, music, dance and theatre. The arts, particularly literature, have historically been influenced by the local form of Theravada Buddhism. Considered the national epic of Myanmar, the ''Yama Zatdaw'', an adaptation of India's ''Ramayana'', has been influenced greatly by Thai, Mon, and Indian versions of the play. Buddhism is practised along with nat (spirit), nat worship, which involves elaborate rituals to propitiate one from a pantheon of 37 nats.

In a traditional village, the monastery is the centre of cultural life. Monks are venerated and supported by the lay people. A novitiation ceremony called shinbyu is the most important coming of age events for a boy, during which he enters the monastery for a short time.
All male children in Buddhist families are encouraged to be a novice (beginner for Buddhism) before the age of twenty and to be a monk after the age of twenty. Girls have ear-piercing ceremonies () at the same time.
Burmese culture is most evident in villages where local festivals are held throughout the year, the most important being the pagoda festival.
Many villages have a guardian nat, and superstition and taboos are commonplace.

British colonial rule introduced Western elements of culture to Myanmar. Myanmar's education system is modelled after that of the United Kingdom. Colonial architectural influences are most evident in major cities such as Yangon. Many ethnic minorities, particularly the Karen in the southeast and the Kachin and Chin who populate the north and northeast, practice Christianity. According to ''The World Factbook'', the Burman population is 68% and the ethnic groups constitute 32%. In contrast, the exiled leaders and organisations claim the country is 40% ethnic.
Cuisine
Burmese cuisine is characterised by extensive use of fish products such as fish sauce, ngapi (fermented seafood) and dried prawn. Mohinga is the traditional breakfast dish and is Myanmar's national dish. Seafood is a common ingredient in coastal cities, while meat and poultry are more commonly used in landlocked cities like Mandalay. Freshwater fish and shrimp have been incorporated into inland cooking as a primary source of protein and are used in a variety of ways, fresh, salted whole or filleted, salted and dried, made into a salty paste, or fermented sour and pressed. Burmese cuisine also includes a variety of salads (''a thoke''), centred on one major ingredient, ranging from starches like rice, wheat and rice noodles, glass noodles and vermicelli, to potato, ginger, tomato, kaffir lime, long bean, and lahpet (pickled tea leaves).
Sport
The Lethwei, Bando, Banshay, and Pongyi thaing martial arts and chinlone are traditional sports in Myanmar. Football is played all over the country, even in villages, and its Myanmar national football team, national team is ruled by the Myanmar Football Federation. The 2013 Southeast Asian Games took place in Naypyidaw, Yangon, Mandalay and Ngwesaung Beach in December representing the third occasion that the event has been staged in Myanmar. Myanmar previously hosted the games in 1961 Southeast Asian Peninsular Games, 1961 and 1969 Southeast Asian Peninsular Games, 1969.
Art
Burmese traditional art concepts are popular and respected by the Burmese people and people from abroad. Burmese contemporary art has developed quite rapidly on its own terms. Artists born after the 1980s have had greater chances of art practice outside the country.
One of the first to study western art was Ba Nyan. Together with Ngwe Gaing and a handful of other artists, they were the pioneers of western painting style. Later on most young children learned the concepts from them. Some well known contemporary artists are Lun Gywe, Aung Kyaw Htet, MPP Yei Myint, Myint Swe, Min Wai Aung, Aung Myint, Kin Maung Yin, Po Po and Zaw Zaw Aung.
Media and communications
Because of Myanmar's political climate, there are not many media companies in relation to the country's population. Some are privately owned. All programming must meet with the approval of the censorship board. The Burmese government announced on 20 August 2012 that it would stop censoring media before publication. Following the announcement, newspapers and other outlets no longer required approved by state censors; however, journalists in the country can still face consequences for what they write and say. In April 2013, international media reports were published to relay the enactment of the media liberalisation reforms that we announced in August 2012. For the first time in numerous decades, the publication of privately owned newspapers commenced in the country.
Internet

Internet use is estimated to be relatively low compared to other countries.
Myanmar's internet used to be subject to censorship, and authorities viewed e-mails and posts on Internet blogs until 2012 when the government removed media censorship. During the strict censorship days, activity at internet cafes was regulated, and one blogger named Zarganar was sentenced to prison for publishing a video of destruction caused by
Cyclone Nargis in 2008; Zarganar was released in October 2011.
In regards to communications infrastructure, Myanmar is the last ranked Asian country in the World Economic Forum's Networked Readiness Index (NRI) – an indicator for determining the development level of a country's information and communication technologies. With 139 countries reported on, Myanmar ranked number 133 overall in the 2016 NRI ranking.
Film
Myanmar's first film was a documentary of the funeral of Tun Shein—a leading politician of the 1910s, who campaigned for Burmese independence in London. The first Burmese silent film ''Myitta Ne Thuya'' (''Love and Liquor'') in 1920 which proved a major success, despite its poor quality. During the 1920s and 1930s, many Burmese-owned film companies made and produced several films. The first Burmese sound film was produced in 1932 in Bombay, India with the title Ngwe Pay Lo Ma Ya (Money Can't Buy It). After World War II, Burmese cinema continued to address political themes. Many of the films produced in the early Cold War era had a strong propaganda element.
In the era that followed the political events of 1988, the film industry has been increasingly controlled by the government. Film stars who had been involved in the political activities were banned from appearing in films. The government issues strict rules on censorship and largely determines who produces films, as well as who gets academy awards.
Over the years, the movie industry has also shifted to producing many lower-budget direct-to-video films. Most of the movies produced nowadays are Comedy film, comedies. In 2008, only 12 films worthy of being considered for an Academy Award were made, although at least 800 VCDs were produced. Myanmar is the primary subject of a 2007 graphic novel titled ''Chroniques Birmanes'' by Quebec City, Québécois author and animator, Guy Delisle. The graphic novel was translated into English under the title ''Burma Chronicles'' in 2008. In 2009, a documentary about Burmese videojournalists called ''Burma VJ'' was released. This film was nominated for Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature, Best Documentary Feature at the 82nd Academy Awards, 2010 Academy Awards. ''The Lady (2011 film), The Lady'' had its world premiere on 12 September 2011 at the 36th Toronto International Film Festival.
See also
* Outline of Myanmar
* Censorship in Myanmar
* Culture of Myanmar
Notes
Pronunciations of ''Myanmar''
References
Bibliography
* Cameron, Ewan. "The State of Myanmar", ''History Today'', May 2020, vol. 70, issue 4, pp. 90–93.
*
* Combs, Daniel. ''Until the World Shatters: Truth, Lies, and the Looting of Myanmar'' (2021).
*
*
*
*
"Burma's Western Border as Reported by the Diplomatic Correspondence(1947–1975)"by Aye Chan
External links
Government
Republic of the Union of Myanmar – President's Office
Myanmar National Portal from the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)
General information
General information about Myanmar
Burma Myanmar search Engine
Burma. ''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Burmafrom ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''
Burma profile from BBC News
Myanmar at ''Encyclopædia Britannica''
*
*
Interactive timeline of turning points in Burmese history
Key Development Forecasts for Myanmar from International Futures
Online Burma/Myanmar Library: Classified and annotated links to more than 17,000 full-text documents on Burma/Myanmar
Historical Photographs of Burma Southeast Asia Digital Library
{{Coord, 22, N, 96, E, type:country_region:MM, display=title, name=Myanmar (Burma)
Myanmar,
Former socialist republics
Least developed countries
Member states of ASEAN
Member states of the United Nations
Military dictatorships
Southeast Asian countries
States and territories established in 1948
1948 establishments in Burma
Countries in Asia
Buddhist states
 Pagan's collapse was followed by 250 years of political fragmentation that lasted well into the 16th century. Like the Burmans four centuries earlier, Shan migrants who arrived with the Mongol invasions stayed behind. Several competing
Pagan's collapse was followed by 250 years of political fragmentation that lasted well into the 16th century. Like the Burmans four centuries earlier, Shan migrants who arrived with the Mongol invasions stayed behind. Several competing  Political unification returned in the mid-16th century, through the efforts of Taungoo, a former vassal state of Ava. Taungoo's young, ambitious King Tabinshwehti defeated the more powerful Hanthawaddy in the Toungoo–Hanthawaddy War. His successor Bayinnaung went on to conquer a vast swath of mainland Southeast Asia including the Shan states, Lan Na, Manipur, Mong Mao, the Ayutthaya Kingdom, Lan Xang and southern Arakan. However, the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia unravelled soon after Bayinnaung's death in 1581, completely collapsing by 1599. Ayutthaya seized Tenasserim and Lan Na, and Portuguese mercenaries established Portuguese rule at Thanlyin (Syriam).
The dynasty regrouped and defeated the Portuguese in 1613 and Siam in 1614. It restored a smaller, more manageable kingdom, encompassing Lower Myanmar, Upper Myanmar,
Political unification returned in the mid-16th century, through the efforts of Taungoo, a former vassal state of Ava. Taungoo's young, ambitious King Tabinshwehti defeated the more powerful Hanthawaddy in the Toungoo–Hanthawaddy War. His successor Bayinnaung went on to conquer a vast swath of mainland Southeast Asia including the Shan states, Lan Na, Manipur, Mong Mao, the Ayutthaya Kingdom, Lan Xang and southern Arakan. However, the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia unravelled soon after Bayinnaung's death in 1581, completely collapsing by 1599. Ayutthaya seized Tenasserim and Lan Na, and Portuguese mercenaries established Portuguese rule at Thanlyin (Syriam).
The dynasty regrouped and defeated the Portuguese in 1613 and Siam in 1614. It restored a smaller, more manageable kingdom, encompassing Lower Myanmar, Upper Myanmar,  After the fall of Ava, the Konbaung–Hanthawaddy War involved one resistance group under
After the fall of Ava, the Konbaung–Hanthawaddy War involved one resistance group under  In the 19th century, Burmese rulers sought to maintain their traditional influence in the western areas of Assam, Manipur and Arakan. Pressing them, however, was the British East India Company, which was expanding its interests eastwards over the same territory. Over the next 60 years, diplomacy, raids, treaties and compromises, known collectively as the
In the 19th century, Burmese rulers sought to maintain their traditional influence in the western areas of Assam, Manipur and Arakan. Pressing them, however, was the British East India Company, which was expanding its interests eastwards over the same territory. Over the next 60 years, diplomacy, raids, treaties and compromises, known collectively as the  In August 2007, an increase in the price of fuel led to the Saffron Revolution led by Buddhist monks that were dealt with harshly by the government.
In August 2007, an increase in the price of fuel led to the Saffron Revolution led by Buddhist monks that were dealt with harshly by the government. A general election in 2010 – the first for twenty years – was boycotted by the NLD. The military-backed Union Solidarity and Development Party declared victory, stating that it had been favoured by 80 per cent of the votes; fraud, however, was alleged. A nominally civilian government was then formed, with retired general Thein Sein as president.
A series of liberalising political and economic actions – or reforms – then took place. By the end of 2011 these included the release of pro-democracy leader Aung San Suu Kyi from house arrest, the establishment of the National Human Rights Commission, the granting of general amnesties for more than 200 political prisoners, new labour laws that permitted labour unions and strikes, a relaxation of press censorship, and the regulation of currency practices. In response,
A general election in 2010 – the first for twenty years – was boycotted by the NLD. The military-backed Union Solidarity and Development Party declared victory, stating that it had been favoured by 80 per cent of the votes; fraud, however, was alleged. A nominally civilian government was then formed, with retired general Thein Sein as president.
A series of liberalising political and economic actions – or reforms – then took place. By the end of 2011 these included the release of pro-democracy leader Aung San Suu Kyi from house arrest, the establishment of the National Human Rights Commission, the granting of general amnesties for more than 200 political prisoners, new labour laws that permitted labour unions and strikes, a relaxation of press censorship, and the regulation of currency practices. In response, 
 In the early morning of 1 February 2021, the day parliament was set to convene, the Tatmadaw, Myanmar's military, detained Suu Kyi and other members of the ruling party."Myanmar coup: Week(s) of Feb.1 to Feb. 21, EU action in focus as foreign ministers set to meet; Candlelight vigil held in Yangon; Facebook removes military's 'True News' page,"
In the early morning of 1 February 2021, the day parliament was set to convene, the Tatmadaw, Myanmar's military, detained Suu Kyi and other members of the ruling party."Myanmar coup: Week(s) of Feb.1 to Feb. 21, EU action in focus as foreign ministers set to meet; Candlelight vigil held in Yangon; Facebook removes military's 'True News' page," Myanmar is a biodiverse country with more than 16,000
Myanmar is a biodiverse country with more than 16,000  The constitution of Myanmar, its third since independence, was drafted by its military rulers and published in September 2008. The country is governed as a parliamentary system with a bicameral legislature (with an executive President of Myanmar, president accountable to the legislature), with 25% of the legislators appointed by the military and the rest elected in general elections.
The legislature, called the Assembly of the Union, is bicameral and made up of two houses: The 224-seat upper House of Nationalities and the 440-seat lower House of Representatives (Myanmar), House of Representatives. The upper house consists 168 members who are directly elected and 56 who are appointed by the Burmese Armed Forces. The lower house consists of 330 members who are directly elected and 110 who are appointed by the armed forces.
The constitution of Myanmar, its third since independence, was drafted by its military rulers and published in September 2008. The country is governed as a parliamentary system with a bicameral legislature (with an executive President of Myanmar, president accountable to the legislature), with 25% of the legislators appointed by the military and the rest elected in general elections.
The legislature, called the Assembly of the Union, is bicameral and made up of two houses: The 224-seat upper House of Nationalities and the 440-seat lower House of Representatives (Myanmar), House of Representatives. The upper house consists 168 members who are directly elected and 56 who are appointed by the Burmese Armed Forces. The lower house consists of 330 members who are directly elected and 110 who are appointed by the armed forces.
 Myanmar has received extensive military aid from China in the past.
Myanmar has been a member of ASEAN since 1997. Though it gave up its turn to hold the ASEAN chair and host the ASEAN Summit in 2006, it chaired the forum and hosted the summit in 2014. In November 2008, Myanmar's political situation with neighbouring Bangladesh became tense as they began searching for natural gas in a disputed block of the Bay of Bengal. Controversy surrounding the Rohingya population also remains an issue between Bangladesh and Myanmar.
Myanmar's armed forces are known as the Tatmadaw, which numbers 488,000. The Tatmadaw comprises the Myanmar Army, Army, the Myanmar Navy, Navy, and the Myanmar Air Force, Air Force. The country List of countries by number of military and paramilitary personnel, ranked twelfth in the world for its number of active troops in service. The military is very influential in Myanmar, with all top cabinet and ministry posts usually held by military officials. Official figures for military spending are not available. Estimates vary widely because of uncertain exchange rates, but Myanmar's military forces' expenses are high. Myanmar imports most of its weapons from Russia, Ukraine, China and India.
Myanmar is building a research nuclear reactor near Pyin Oo Lwin with help from Russia. It is one of the signatories of the nuclear non-proliferation pact since 1992 and a member of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) since 1957. The military junta had informed the IAEA in September 2000 of its intention to construct the reactor. In 2010 as part of the United States diplomatic cables leak, leaked diplomatic cables, Myanmar was suspected of using North Korean construction teams to build a fortified surface-to-air missile facility. As of 2019, the United States Bureau of Arms Control, Verification, and Compliance, Bureau of Arms Control assessed that Myanmar is not in violation of its obligations under the Non-Proliferation Treaty but that the Myanmar government had a history of non-transparency on its nuclear programs and aims.
Until 2005, the United Nations General Assembly annually adopted a detailed resolution about the situation in Myanmar by consensus. But in 2006 a divided United Nations General Assembly voted through a resolution that strongly called upon the government of Myanmar to end its systematic violations of human rights. In January 2007, Russia and China vetoed a draft resolution before the
Myanmar has received extensive military aid from China in the past.
Myanmar has been a member of ASEAN since 1997. Though it gave up its turn to hold the ASEAN chair and host the ASEAN Summit in 2006, it chaired the forum and hosted the summit in 2014. In November 2008, Myanmar's political situation with neighbouring Bangladesh became tense as they began searching for natural gas in a disputed block of the Bay of Bengal. Controversy surrounding the Rohingya population also remains an issue between Bangladesh and Myanmar.
Myanmar's armed forces are known as the Tatmadaw, which numbers 488,000. The Tatmadaw comprises the Myanmar Army, Army, the Myanmar Navy, Navy, and the Myanmar Air Force, Air Force. The country List of countries by number of military and paramilitary personnel, ranked twelfth in the world for its number of active troops in service. The military is very influential in Myanmar, with all top cabinet and ministry posts usually held by military officials. Official figures for military spending are not available. Estimates vary widely because of uncertain exchange rates, but Myanmar's military forces' expenses are high. Myanmar imports most of its weapons from Russia, Ukraine, China and India.
Myanmar is building a research nuclear reactor near Pyin Oo Lwin with help from Russia. It is one of the signatories of the nuclear non-proliferation pact since 1992 and a member of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) since 1957. The military junta had informed the IAEA in September 2000 of its intention to construct the reactor. In 2010 as part of the United States diplomatic cables leak, leaked diplomatic cables, Myanmar was suspected of using North Korean construction teams to build a fortified surface-to-air missile facility. As of 2019, the United States Bureau of Arms Control, Verification, and Compliance, Bureau of Arms Control assessed that Myanmar is not in violation of its obligations under the Non-Proliferation Treaty but that the Myanmar government had a history of non-transparency on its nuclear programs and aims.
Until 2005, the United Nations General Assembly annually adopted a detailed resolution about the situation in Myanmar by consensus. But in 2006 a divided United Nations General Assembly voted through a resolution that strongly called upon the government of Myanmar to end its systematic violations of human rights. In January 2007, Russia and China vetoed a draft resolution before the  Based on the evidence gathered by Amnesty photographs and video of the ongoing armed conflict between the Myanmar military and the Arakan Army (AA), attacks escalated on civilians in Rakhine State. Ming Yu Hah, Amnesty International's Deputy Regional Director for Campaigns said, the UN Security Council must urgently refer the situation in Myanmar to the International Criminal Court. The military is notorious for rampant use of sexual violence.
In November 2024, the International Criminal Court, ICC prosecutor Karim Ahmad Khan, Karim A.A. Khan KC filed an arrest warrant application of Senior General, Acting President and Commander-in-Chief of the Myanmar Defence Services Min Aung Hlaing for "criminal responsibility for the crimes against humanity of deportation and persecution of the Rohingya, committed in Myanmar, and in part in Bangladesh".
Based on the evidence gathered by Amnesty photographs and video of the ongoing armed conflict between the Myanmar military and the Arakan Army (AA), attacks escalated on civilians in Rakhine State. Ming Yu Hah, Amnesty International's Deputy Regional Director for Campaigns said, the UN Security Council must urgently refer the situation in Myanmar to the International Criminal Court. The military is notorious for rampant use of sexual violence.
In November 2024, the International Criminal Court, ICC prosecutor Karim Ahmad Khan, Karim A.A. Khan KC filed an arrest warrant application of Senior General, Acting President and Commander-in-Chief of the Myanmar Defence Services Min Aung Hlaing for "criminal responsibility for the crimes against humanity of deportation and persecution of the Rohingya, committed in Myanmar, and in part in Bangladesh".
 Under the British Empire, British administration, the people of Burma were at the bottom of the social hierarchy, with Europeans at the top, Indians, Chinese, and Christianized minorities in the middle, and Buddhist Burmese at the bottom. Forcefully integrated into the world economy, Burma's economy grew by involving itself with extractive industries and cash crop agriculture. However, much of the wealth was concentrated in the hands of Europeans. The country became the world's largest exporter of rice, mainly to European markets, while other colonies like India suffered mass starvation. Being a follower of free market principles, the British opened up the country to large-scale immigration with Rangoon exceeding New York City as the greatest immigration port in the world in the 1920s. Historian Thant Myint-U states, "This was out of a total population of only 13 million; it was equivalent to the United Kingdom today taking 2 million people a year." By then, in most of Burma's largest cities, Rangoon, Akyab, Pathein, Bassein and Moulmein, the Indian immigrants formed a majority of the population. The Burmese under British rule felt helpless, and reacted with a "racism that combined feelings of superiority and fear".
Crude oil production, an indigenous industry of Yenangyaung, was taken over by the British and put under Burmah Oil monopoly. British Burma began exporting crude oil in 1853. European firms produced 75% of the world's teak. The wealth was, however, mainly concentrated in the hands of Europeans. In the 1930s, agricultural production fell dramatically as international rice prices declined and did not recover for several decades. During the Japanese invasion of Burma in World War II, the British followed a scorched earth policy. They destroyed major government buildings, oil wells and mines that developed for tungsten (Mawchi), tin, lead and silver to keep them from the Japanese. Myanmar was bombed extensively by the Allies.
After independence, the country was in ruins with its major infrastructure completely destroyed. With the loss of India, Burma lost relevance and obtained independence from the British. After a parliamentary government was formed in 1948, Prime Minister
Under the British Empire, British administration, the people of Burma were at the bottom of the social hierarchy, with Europeans at the top, Indians, Chinese, and Christianized minorities in the middle, and Buddhist Burmese at the bottom. Forcefully integrated into the world economy, Burma's economy grew by involving itself with extractive industries and cash crop agriculture. However, much of the wealth was concentrated in the hands of Europeans. The country became the world's largest exporter of rice, mainly to European markets, while other colonies like India suffered mass starvation. Being a follower of free market principles, the British opened up the country to large-scale immigration with Rangoon exceeding New York City as the greatest immigration port in the world in the 1920s. Historian Thant Myint-U states, "This was out of a total population of only 13 million; it was equivalent to the United Kingdom today taking 2 million people a year." By then, in most of Burma's largest cities, Rangoon, Akyab, Pathein, Bassein and Moulmein, the Indian immigrants formed a majority of the population. The Burmese under British rule felt helpless, and reacted with a "racism that combined feelings of superiority and fear".
Crude oil production, an indigenous industry of Yenangyaung, was taken over by the British and put under Burmah Oil monopoly. British Burma began exporting crude oil in 1853. European firms produced 75% of the world's teak. The wealth was, however, mainly concentrated in the hands of Europeans. In the 1930s, agricultural production fell dramatically as international rice prices declined and did not recover for several decades. During the Japanese invasion of Burma in World War II, the British followed a scorched earth policy. They destroyed major government buildings, oil wells and mines that developed for tungsten (Mawchi), tin, lead and silver to keep them from the Japanese. Myanmar was bombed extensively by the Allies.
After independence, the country was in ruins with its major infrastructure completely destroyed. With the loss of India, Burma lost relevance and obtained independence from the British. After a parliamentary government was formed in 1948, Prime Minister  The major agricultural product is Rice production in Myanmar, rice, which covers about 60% of the country's total cultivated land area. Rice accounts for 97% of total food grain production by weight. Through collaboration with the International Rice Research Institute, 52 modern rice varieties were released in the country between 1966 and 1997, helping increase national rice production to 14 million tons in 1987 and to 19 million tons in 1996. By 1988, modern varieties were planted on half of the country's ricelands, including 98 percent of the irrigated areas. In 2008 rice production was estimated at 50 million tons.
The major agricultural product is Rice production in Myanmar, rice, which covers about 60% of the country's total cultivated land area. Rice accounts for 97% of total food grain production by weight. Through collaboration with the International Rice Research Institute, 52 modern rice varieties were released in the country between 1966 and 1997, helping increase national rice production to 14 million tons in 1987 and to 19 million tons in 1996. By 1988, modern varieties were planted on half of the country's ricelands, including 98 percent of the irrigated areas. In 2008 rice production was estimated at 50 million tons.
 The provisional results of the 2014 Myanmar Census showed that the total population was 51,419,420. This figure includes an estimated 1,206,353 persons in parts of northern
The provisional results of the 2014 Myanmar Census showed that the total population was 51,419,420. This figure includes an estimated 1,206,353 persons in parts of northern  A large majority of the population practices Buddhism; estimates range from 80%Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project: Burma
A large majority of the population practices Buddhism; estimates range from 80%Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project: Burma A diverse range of indigenous cultures exist in Myanmar, with majority culture primarily Buddhist and Bamar. Bamar culture has been influenced by the cultures of neighbouring countries, manifested in its language, cuisine, music, dance and theatre. The arts, particularly literature, have historically been influenced by the local form of Theravada Buddhism. Considered the national epic of Myanmar, the ''Yama Zatdaw'', an adaptation of India's ''Ramayana'', has been influenced greatly by Thai, Mon, and Indian versions of the play. Buddhism is practised along with nat (spirit), nat worship, which involves elaborate rituals to propitiate one from a pantheon of 37 nats.
A diverse range of indigenous cultures exist in Myanmar, with majority culture primarily Buddhist and Bamar. Bamar culture has been influenced by the cultures of neighbouring countries, manifested in its language, cuisine, music, dance and theatre. The arts, particularly literature, have historically been influenced by the local form of Theravada Buddhism. Considered the national epic of Myanmar, the ''Yama Zatdaw'', an adaptation of India's ''Ramayana'', has been influenced greatly by Thai, Mon, and Indian versions of the play. Buddhism is practised along with nat (spirit), nat worship, which involves elaborate rituals to propitiate one from a pantheon of 37 nats.
 British colonial rule introduced Western elements of culture to Myanmar. Myanmar's education system is modelled after that of the United Kingdom. Colonial architectural influences are most evident in major cities such as Yangon. Many ethnic minorities, particularly the Karen in the southeast and the Kachin and Chin who populate the north and northeast, practice Christianity. According to ''The World Factbook'', the Burman population is 68% and the ethnic groups constitute 32%. In contrast, the exiled leaders and organisations claim the country is 40% ethnic.
British colonial rule introduced Western elements of culture to Myanmar. Myanmar's education system is modelled after that of the United Kingdom. Colonial architectural influences are most evident in major cities such as Yangon. Many ethnic minorities, particularly the Karen in the southeast and the Kachin and Chin who populate the north and northeast, practice Christianity. According to ''The World Factbook'', the Burman population is 68% and the ethnic groups constitute 32%. In contrast, the exiled leaders and organisations claim the country is 40% ethnic.
 Internet use is estimated to be relatively low compared to other countries. Myanmar's internet used to be subject to censorship, and authorities viewed e-mails and posts on Internet blogs until 2012 when the government removed media censorship. During the strict censorship days, activity at internet cafes was regulated, and one blogger named Zarganar was sentenced to prison for publishing a video of destruction caused by Cyclone Nargis in 2008; Zarganar was released in October 2011.
In regards to communications infrastructure, Myanmar is the last ranked Asian country in the World Economic Forum's Networked Readiness Index (NRI) – an indicator for determining the development level of a country's information and communication technologies. With 139 countries reported on, Myanmar ranked number 133 overall in the 2016 NRI ranking.
Internet use is estimated to be relatively low compared to other countries. Myanmar's internet used to be subject to censorship, and authorities viewed e-mails and posts on Internet blogs until 2012 when the government removed media censorship. During the strict censorship days, activity at internet cafes was regulated, and one blogger named Zarganar was sentenced to prison for publishing a video of destruction caused by Cyclone Nargis in 2008; Zarganar was released in October 2011.
In regards to communications infrastructure, Myanmar is the last ranked Asian country in the World Economic Forum's Networked Readiness Index (NRI) – an indicator for determining the development level of a country's information and communication technologies. With 139 countries reported on, Myanmar ranked number 133 overall in the 2016 NRI ranking.