Aïr Mountains on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Aïr Mountains or Aïr Massif ( Tamajăq: ''Ayǝr''; Hausa: Eastern ''Azbin'', Western ''Abzin'') is a triangular
 The
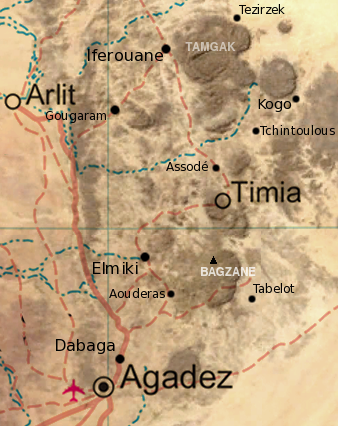
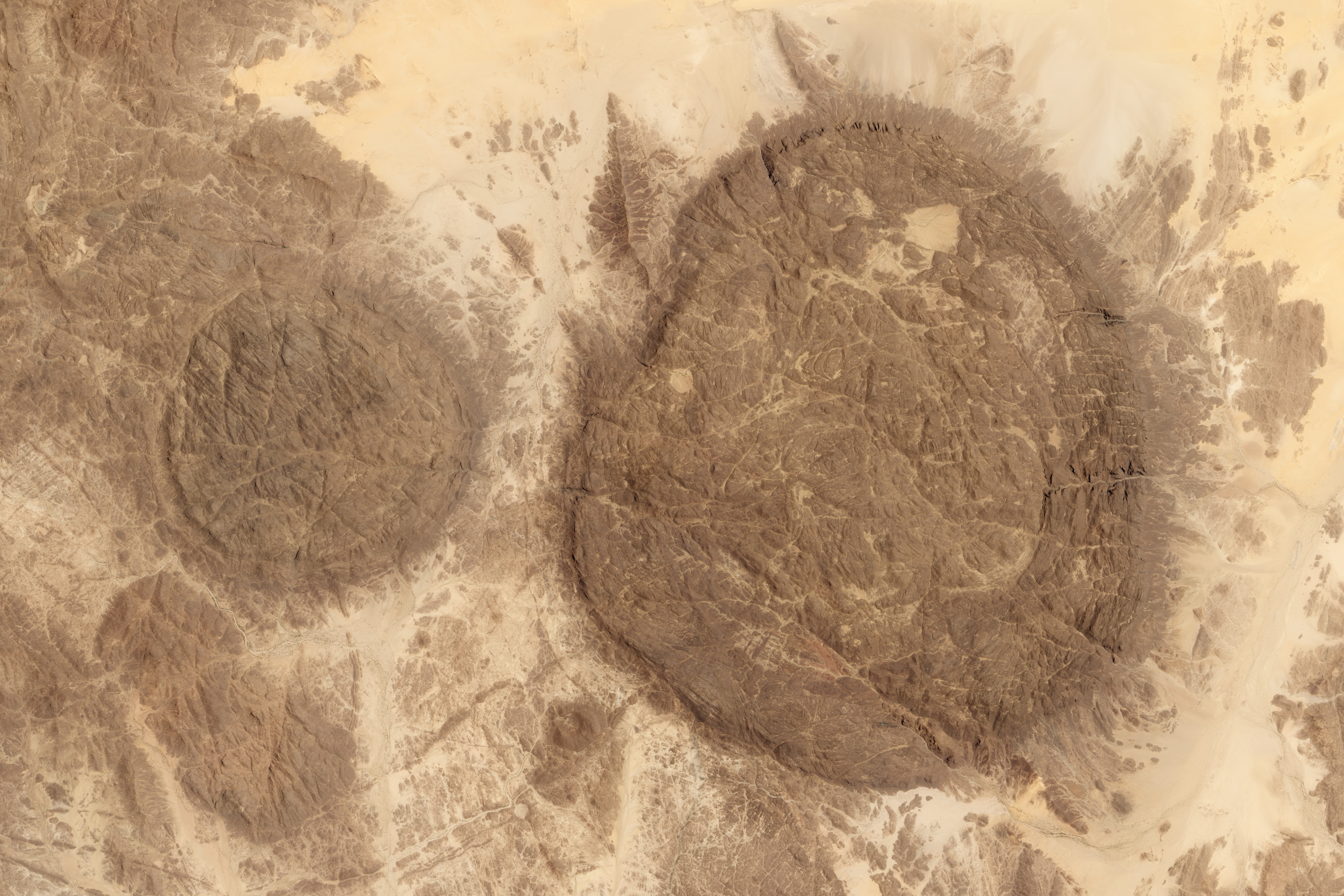
The  The Aïr mountains themselves consist of nine almost circular massifs rising from a rocky plateau, bordered by the sand dunes and plain of the Ténéré Desert to the east. The massif is a
The Aïr mountains themselves consist of nine almost circular massifs rising from a rocky plateau, bordered by the sand dunes and plain of the Ténéré Desert to the east. The massif is a 

 Because of its altitude (on average between 500 and 900 m) and despite its low rainfall (50 to 160 mm/year on the lower plateau), the Aïr forms a green region in comparison with the surrounding deserts, especially after the August–September seasonal rains. The climate is classified as
Because of its altitude (on average between 500 and 900 m) and despite its low rainfall (50 to 160 mm/year on the lower plateau), the Aïr forms a green region in comparison with the surrounding deserts, especially after the August–September seasonal rains. The climate is classified as
 The Aïr is known for its
The Aïr is known for its

Uranium Geology: NIGER, WEST AFRICA
NWT Uranium Corp. ''Includes technical summation of the geology of the Air Massif and surrounding region. {{DEFAULTSORT:Air Mountains Mountain ranges of Niger Tuareg Agadez Region World Heritage Sites in Niger Biosphere reserves of Niger Sahara World Heritage Sites in Danger Ring dikes
massif
A massif () is a principal mountain mass, such as a compact portion of a mountain range, containing one or more summits (e.g. France's Massif Central). In mountaineering literature, ''massif'' is frequently used to denote the main mass of an ...
, located in northern Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
, within the Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
. Part of the West Saharan montane xeric woodlands ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) is an ecological and geographic area that exists on multiple different levels, defined by type, quality, and quantity of environmental resources. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and c ...
, they rise to more than and extend over . Lying in the midst of desert north of the 17th parallel, the Aïr plateau, with an average altitude between , forms an island of Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
climate which supports a wide variety of life, many pastoral and farming communities, and dramatic geological and archaeological sites. There are notable archaeological excavations in the region that illustrate the prehistoric past of this region. The endangered African wild dog
The African wild dog (''Lycaon pictus''), also called painted dog and Cape hunting dog, is a wild canine native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is the largest wild canine in Africa, and the only extant member of the genus '' Lycaon'', which is disti ...
(''Lycaon pictus'') once existed in this region, but may now be extirpated
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinctions.
Local extinctions mark a chan ...
due to human population pressures in this region.
Geology
 The
The Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of t ...
to Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three g ...
Aïr Mountains consist of peralkaline granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
intrusions which appear dark in colour (unusual since most granitic masses are light-toned in the field). In the Sahara Desert such mountains often stand out in stark relief as topographic heights amidst lowlands covered by sand. The terrain consists of high plateau, mountain ranges, and broad, sandy valleys and seasonal wadis which once contained rivers. Areas of these deep, often intersecting, valleys also contain waterborne clay and silt deposits. Underground watercourses in some of these valleys continue to provide year-round oasis and seasonal vegetation.
 The Aïr mountains themselves consist of nine almost circular massifs rising from a rocky plateau, bordered by the sand dunes and plain of the Ténéré Desert to the east. The massif is a
The Aïr mountains themselves consist of nine almost circular massifs rising from a rocky plateau, bordered by the sand dunes and plain of the Ténéré Desert to the east. The massif is a plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; : plateaus or plateaux), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. ...
consisting of a sub-Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
age erosion surface
In geology and geomorphology, an erosion surface is a surface of rock (geology), rock or regolith that was formed by erosion and not by construction (e.g. lava flows, sediment deposition) nor fault (geology), fault displacement. Erosional surfaces ...
on Precambrian metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, caus ...
s, punctuated by a series of flat-topped, granite intrusion peaks, which include Mont Idoukal-n-Taghès
Mont Idoukal-n-Taghès (also Mont Bagzane, Mont Bagzan) is the highest mountain in Niger. Mont Idoukal-n-Taghès is located in the south central Aïr Mountains, and is at the northern end of the Bagzane plateau. The village and pilgrimage site o ...
(Niger's highest point at 2022 m), Mont Tamgak
Mont may refer to:
Places
* Mont., an abbreviation for Montana, a U.S. state
* Mont, Belgium (disambiguation), several places in Belgium
* Mont, Hautes-Pyrénées, a commune in France
* Mont, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, a commune in France
* Mont, Sa� ...
(1988 m), Mont Greboun
Mont may refer to:
Places
* Mont., an abbreviation for Montana, a U.S. state
* Mont, Belgium (disambiguation), several places in Belgium
* Mont, Hautes-Pyrénées, a commune in France
* Mont, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, a commune in France
* Mont, Sa� ...
(1944 m), Adrar Bous, Fadei, Chirriet, Taghmert, Agueraguer, Takaloukouzet, and Goundai.
The massif contains volcanic
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ...
features including the extinct caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. An eruption that ejects large volumes of magma over a short period of time can cause significant detriment to the str ...
of Arakao, Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three g ...
lava flows of hawaiite
Hawaiite is an olivine basalt with a composition between alkali basalt and mugearite. It was first used as a name for some lavas found on the island of Hawaii.
It occurs during the later stages of volcanic activity on oceanic islands such as Ha ...
to trachyte
Trachyte () is an extrusive igneous rock composed mostly of alkali feldspar. It is usually light-colored and aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained), with minor amounts of mafic minerals, and is formed by the rapid cooling of lava (or shallow intrus ...
composition, volcanic cone
Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic landforms. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and s ...
s, tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock co ...
rings and one of the largest ring dike systems in the world. At Izouzaoenehe, lie the marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
Blue Mountains, and the lower Zagado valley is surrounded by white marble hills. Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
and coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
units in the Iullemmeden Basin
The Iullemmeden Basin (Berber language: Iwellemmedden) is a major sub-Saharan inland basin in West Africa, extending about north to south and east to west. It covers western Niger and parts of Algeria, Mali and Nigeria. It is named after the Iul ...
just to the west of the massif contain uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
mineralisation sourced from the granites of the massif.


Climate
Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
, like that of the regions well to its south. While the mountains are largely bare of vegetation, the dry wadi
Wadi ( ; ) is a river valley or a wet (ephemerality, ephemeral) Stream bed, riverbed that contains water only when heavy rain occurs. Wadis are located on gently sloping, nearly flat parts of deserts; commonly they begin on the distal portion ...
river valleys (known by the Hausa term "''Kori''") channel and hold rainwater in guelta
A guelta (Arabic: قلتة, also transliterated ''qalta'' or ''galta'') is a pocket of water that forms within rock formations in the Sahara, Sahara Desert and Arabian Desert. The term is of Arabic origin and specifically refers to oases that eme ...
s (stone pools, such as that near the town of Timia), creating oases which provide forage for animals, and in some areas, farming. The high Bagzane plateau of the central Aïr in particular provides adequate rainfall for intensive agriculture. Other, vast, areas of the region are entirely devoid of plant life and with their volcanic protrusions and rock fields present an otherworldly appearance.
Vegetation
More than 430 vascular species have been recorded so far in the Aïr mountains. The location of the Aïr as a southern extension of the Hoggar mountain range makes it a connection between the Saharan Flora and the Sahelian Flora. However, the presence of mountains up to 2000 m a.s.l. generates locally favourable conditions for several species of the Sudanian zone and the Mediterranean zone. During the 20th century a series of scientific missions in the Aïr has permitted to identify the majority of plant species developing in the Aïr. ''Vachellia tortilis
''Vachellia tortilis'', widely known as ''Acacia tortilis'' but now attributed to the genus ''Vachellia'' of the Mimosa Family ( Mimosaceae), is the umbrella thorn acacia, also known as umbrella thorn and Israeli babool, a medium to large canop ...
'', subsp. ''raddiana'' (''afagag'') and '' Balanites aegyptiaca'' (''aborak'') are among the most frequent tree species in the intermountain zone. In the vicinity of temporary rivers named ''koris'', species like ''Vachellia nilotica
''Vachellia nilotica'', more commonly known as ''Acacia nilotica'', and by the vernacular names of gum arabic tree, babul, thorn mimosa, Egyptian acacia or thorny acacia, is a flowering plant, flowering tree in the family Fabaceae. It is native t ...
'', '' Faidherbia albida'' and the palm '' Hyphaene thebaica'' coexist with date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as the date palm, is a flowering-plant species in the palm family Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet #Fruits, fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across North Africa, northern A ...
cultivars (''Phoenix dactylifera''). Severe droughts and high aridity have made the intermountain zone of the Aïr a particularly harsh place for plants to develop. The additional presence of domestic herbivores has led to a severe deficit in tree regeneration, which has been cited as a major ecological concern. Tree regeneration has been observed enhanced as soon as tree seedlings are protected by large tussocks of the frequent grass ''Panicum turgidum
''Panicum turgidum'' is an old world clumping desert bunchgrass of the genus '' Panicum''. It is a plant of arid regions across Africa and Asia, and has been introduced to other parts of the world.
Description
''Panicum turgidum'' is a perenni ...
''. This positive interaction between plants represents a promising restoration tool to be used by local inhabitants.
In comparison, mountainous areas are even less documented. Tropical tree species less resistant to drought have been described in the highlands, among which the Fabaceae '' Senegalia laeta'' and '' Vachellia seyal''. Quezel has observed the remnant presence of a rare endemic taxon related to the olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'' ("European olive"), is a species of Subtropics, subtropical evergreen tree in the Family (biology), family Oleaceae. Originating in Anatolia, Asia Minor, it is abundant throughout the Mediterranean ...
in the northern sector of the Aïr range. Recently, this taxon, ''Olea europaea'' subsp. ''laperrinei'', has been found in other mountains of the Aïr: these very isolated, small populations represent the southern limit of the species distribution.
A study led on the slopes of the highest summit in the Aïr, Mont Idoukal-n-Taghès
Mont Idoukal-n-Taghès (also Mont Bagzane, Mont Bagzan) is the highest mountain in Niger. Mont Idoukal-n-Taghès is located in the south central Aïr Mountains, and is at the northern end of the Bagzane plateau. The village and pilgrimage site o ...
(2022 m a.s.l.), identified plant species that had never been inventoried in Niger before. Among them, '' Pachycymbium decaisneanum'', '' Cleome aculeata'', '' Echinops mildbraedii'' and '' Indigofera nummularia'' are tropical species with relatively low resistance to water stress, whereas '' Silene lynesii'', '' Tephrosia elegans'', and '' Echinops mildbraedii'' have a Saharan-Mediterranean distribution. Three ferns were found for the first time in the Aïr recently, ''Cheilanthes coriacea
''Cheilanthes'', commonly known as lip ferns, is a genus of about 180 species of rock-dwelling ferns with a cosmopolitan distribution in warm, dry, rocky regions, often growing in small crevices high up on cliffs. Most are small, sturdy and ever ...
'', '' Actiniopteris radiata'', and '' Ophioglossum polyphyllum'', suggesting that ferns may be more prone to develop in arid environments than commonly proposed. All these data evidence a marked mountain climatic specificity in the Aïr, with a positive impact on species richness and species diversity. Because of their strong geographic isolation within a Saharan matrix, these species have a high conservation value.
Population
The town ofAgadez
Agadez ( Air Tamajeq: ⴰⴶⴰⴷⴰⵣ, ''Agadaz''), formerly spelled Agadès, is the fifth largest city in Niger, with a population of 110,497 based on the 2012 census. The capital of the eponymous Agadez Region, the city lies in the Sahara ...
in the heart of the Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym, depending on variety: ''Imuhaɣ'', ''Imušaɣ'', ''Imašeɣăn'' or ''Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group, traditionally nomadic pastoralists, who principally inhabit th ...
country is the capital of Aïr. Much of the Tuareg population of Aïr until recently led a nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic life, relying essentially on camel and goats from which they take milk, meat and skins used in the production of local handicrafts. Most sedentary populations were either dependents of higher caste Tuareg pastoralists or the Ikelan (''Bouzou'' in Hausa / ''Bella'' in Songhai), Tuareg slaves. These peoples were settled in northern oases, to tend the date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as the date palm, is a flowering-plant species in the palm family Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet #Fruits, fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across North Africa, northern A ...
plantations held by the noble clans.
Agriculture products from oases such as Timia, Aouderas
Aouderas (alt: ''Adharous'', ''Auderas'') is an oasis village in the Aïr Mountains of northeastern Niger, about north-northeast of the regional capital of Agadez. It is also the name of the valley in which the town is located.
Geography
Aoude ...
and Tabelot are traditionally exchanged against clothes, or salt, brought by camel caravans ( Azalai) from the remote Tenere oases of Bilma and Fachi to the east.
History
 The Aïr is known for its
The Aïr is known for its rock art
In archaeology, rock arts are human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type al ...
, dating from 6000 BCE to around 1000CE. During the African humid period, the region was a pastoral
The pastoral genre of literature, art, or music depicts an idealised form of the shepherd's lifestyle – herding livestock around open areas of land according to the seasons and the changing availability of water and pasture. The target au ...
area, as is illustrated by images of cattle and large mammals. During the 3rd millennium BC, however, a process of desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.
The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This i ...
began and the Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym, depending on variety: ''Imuhaɣ'', ''Imušaɣ'', ''Imašeɣăn'' or ''Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group, traditionally nomadic pastoralists, who principally inhabit th ...
from further north migrated into the region. Later art indicated war, depicting horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
s and chariot
A chariot is a type of vehicle similar to a cart, driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid Propulsion, motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk O ...
s. In particular, the five-meter-high carvings of the " Dabous Giraffes" discovered in 1999 is internationally famous. Cave art in the region is predominantly stone carving
Stone carving is an activity where pieces of rough natural stone are shaped by the controlled removal of stone. Owing to the permanence of the material, stone work has survived which was created during our prehistory or past time.
Work carried ...
, initially with sharp rock, and from around 1200 BC perhaps with metal.
When the Tuareg tribes were pushed south by Arab invaders in the eighth and ninth centuries, there were Gobirwa Hausa in the southern Aïr. Successive Tuareg ''Kel''s have controlled the area since at least the twelfth century. Agadez, as well as In-Gall to the east, were the farthest outposts of the Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire was a state located in the western part of the Sahel during the 15th and 16th centuries. At its peak, it was one of the largest African empires in history. The state is known by its historiographical name, derived from its lar ...
in the early 15th century. In the sixteenth century, the area fell under the newly created Tuareg Sultanate of Agadez
The Sultanate of Agadez (also known as Tenere Sultanate of Aïr, Sultanate of Aïr, or Asben") was a Berber kingdom centered first in the city of Agadez (initially, in the village of Tadaliza) in the Aïr Mountains, located at the southern edge o ...
, and remained so until the arrival of the French at the end of the 19th.
The emergence of the French weakened the Tuareg Kels and provoked both infighting and resistance to colonialism. From the 1880s, Toubu raids increased, and when the Tuareg Ag Mohammed Wau Teguidda Kaocen rose against the French in 1917, many towns were destroyed on his way to the siege of Agadez. When the French retook Agadez, a brutal punitive expedition
A punitive expedition is a military journey undertaken to punish a political entity or any group of people outside the borders of the punishing state or union. It is usually undertaken in response to perceived disobedient or morally wrong beha ...
through the Aïr left many formerly populous places abandoned, razed by Kaosen and the French successively.
While the Kel Owey continued to dominate the settled oasis towns and pastoral herding, the sedentary farmers (Tuareg, Hausa, or Songhai) expanded farming and sedentary livestock cultivation in the mid-20th century.
The famines of the 1970s and 1980s brought an end to this expansion, and as Agadez
Agadez ( Air Tamajeq: ⴰⴶⴰⴷⴰⵣ, ''Agadaz''), formerly spelled Agadès, is the fifth largest city in Niger, with a population of 110,497 based on the 2012 census. The capital of the eponymous Agadez Region, the city lies in the Sahara ...
and Arlit
Arlit is an industrial town and capital of the Arlit Department of the Agadez Region of northern-central Niger, built between the Sahara Desert and the eastern edge of the Aïr Mountains. It is 200 kilometers south by road from the bord ...
grew, the towns of the Aïr have shrunk. The first Tuareg rebellion of 1990-95 saw brutal government reprisals which depopulated many villages in the Aïr. Peace from the mid-1990s, as well as the uranium mines of Arlit
Arlit is an industrial town and capital of the Arlit Department of the Agadez Region of northern-central Niger, built between the Sahara Desert and the eastern edge of the Aïr Mountains. It is 200 kilometers south by road from the bord ...
brought unprecedented growth to the region, with many small towns gaining valuable tourism revenue. In 2004, a locust invasion ravaged many gardens, bringing scarcity and contributing to the Second Tuareg Rebellion of 2007–2009. Unrest continues in the region, effectively ending the nascent tourist industry.Geels (2006)
View


See also
* Aïr and Ténéré National Nature Reserve *Ténéré
The Ténéré (Tuareg languages, Tuareg: Tenere, literally: "desert") is a desert region in south central Sahara. It comprises a vast plain of sand stretching from northeastern Niger to western Chad, occupying an area of over . The Ténéré's b ...
* World Heritage Sites in Danger
References
Further reading
* * *External links
Uranium Geology: NIGER, WEST AFRICA
NWT Uranium Corp. ''Includes technical summation of the geology of the Air Massif and surrounding region. {{DEFAULTSORT:Air Mountains Mountain ranges of Niger Tuareg Agadez Region World Heritage Sites in Niger Biosphere reserves of Niger Sahara World Heritage Sites in Danger Ring dikes