Arminius on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Arminius (; 18/17 BC–AD 21) was a chieftain of the Germanic
 Born in 18 or 17 BC in
Born in 18 or 17 BC in
 In the autumn of AD 9, the 25-year-old Arminius brought to Varus a false report of rebellion in northern Germany. He persuaded Varus to divert the three legions under his command (composed of the 17th, 18th, and 19th legions, plus three
In the autumn of AD 9, the 25-year-old Arminius brought to Varus a false report of rebellion in northern Germany. He persuaded Varus to divert the three legions under his command (composed of the 17th, 18th, and 19th legions, plus three

 In the accounts of his Roman enemies, Arminius is highly regarded for his military leadership and as a defender of the liberty of his people. Based on these records, the story of Arminius was revived in the 16th century with the recovery of the histories of Tacitus, who wrote in his ''Annales II, 88'':
Arminius was not the only reason for Rome's change of policy towards Germania. Politics also played a factor; emperors found they could rarely trust a large army to a potential rival, though Augustus had enough loyal family members to wage his wars. Also, Augustus, in his 40-year reign, had annexed many territories still at the beginning of the process of Romanization. Tiberius, who succeeded Augustus in AD 14, decided that Germania was a far less developed land, possessing few villages and only a small food surplus, and therefore was not currently important to Rome. Conquering Germania would require a commitment too burdensome for the imperial finances and an excessive expenditure of military force.
Modern scholars have pointed out that the Rhine was a more practical boundary for the Roman Empire than any other river in Germania. Armies on the Rhine could be supplied from the
In the accounts of his Roman enemies, Arminius is highly regarded for his military leadership and as a defender of the liberty of his people. Based on these records, the story of Arminius was revived in the 16th century with the recovery of the histories of Tacitus, who wrote in his ''Annales II, 88'':
Arminius was not the only reason for Rome's change of policy towards Germania. Politics also played a factor; emperors found they could rarely trust a large army to a potential rival, though Augustus had enough loyal family members to wage his wars. Also, Augustus, in his 40-year reign, had annexed many territories still at the beginning of the process of Romanization. Tiberius, who succeeded Augustus in AD 14, decided that Germania was a far less developed land, possessing few villages and only a small food surplus, and therefore was not currently important to Rome. Conquering Germania would require a commitment too burdensome for the imperial finances and an excessive expenditure of military force.
Modern scholars have pointed out that the Rhine was a more practical boundary for the Roman Empire than any other river in Germania. Armies on the Rhine could be supplied from the
p. 329
/ref> During the In 1808, Heinrich von Kleist wrote the play '' Die Hermannsschlacht'', but with Napoleon's victory at Wagram it remained in manuscript, being published in 1821 and not staged until 1860. The play has been revived repeatedly at moments of national crisis and was especially used as
In 1808, Heinrich von Kleist wrote the play '' Die Hermannsschlacht'', but with Napoleon's victory at Wagram it remained in manuscript, being published in 1821 and not staged until 1860. The play has been revived repeatedly at moments of national crisis and was especially used as
''Deutsche Geschichte – Mythos einer Schlacht''
Zeit Online, 4 November 2008 (German) According to journalist David Crossland: "The old nationalism has been replaced by an easy-going
Arminius
at the ''
Arminius
at the '' Ancient History Encyclopedia''
"Arminius / Varus: Die Varusschlacht im Jahre 9 n. Chr."
– LWL-Institut für westfälische Regionalgeschichte (in German)
"Terry Jones' Barbarians: The Savage Goths"
– includes a portion on Arminius
(in German)
"They Need a Hero"
by Clay Risen in '' The National'', 9 October 2009 – article on modern German views of Hermann and the 2,000th anniversary of the battle The Football (Soccer) Team „DSC Arminia Bielefeld“ is named After Arminius {{DEFAULTSORT:Arminius 010s BC births 1st-century monarchs in Europe 021 deaths Ancient Roman soldiers Cherusci chieftains Cherusci warriors Roman campaigns in Germania (12 BC – AD 16)
Cherusci
The Cherusci were a Germanic tribe that inhabited parts of the plains and forests of northwestern Germania in the area of the Weser River and present-day Hanover during the first centuries BC and AD. Roman sources reported they considered thems ...
tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest
The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, also called the Varus Disaster or Varian Disaster () by Ancient Rome, Roman historians, was a major battle fought between an alliance of Germanic peoples and the Roman Empire between September 8 and 11, 9&nbs ...
in AD 9, in which three Roman legion
The Roman legion (, ) was the largest military List of military legions, unit of the Roman army, composed of Roman citizenship, Roman citizens serving as legionary, legionaries. During the Roman Republic the manipular legion comprised 4,200 i ...
s under the command of general and governor Publius Quinctilius Varus
Publius Quinctilius Varus (46 BC or before – September AD 9) was a Roman general and politician. Serving under Augustus, who founded the Roman Empire, he is generally remembered for having lost three Roman legions in the Battle of the Teutob ...
were destroyed. His victory at Teutoburg Forest precipitated the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
's permanent strategic withdrawal and the deprovincialization of Germania Magna
Germania ( ; ), also more specifically called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman provinces of Germania Inferior and Germania Super ...
, and modern historians regard it as one of Imperial Rome's greatest defeats. As it prevented the Romanization
In linguistics, romanization is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Latin script, Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and tra ...
of Germanic peoples east of the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
, it has also been considered one of the most decisive battles in history and a turning point in human history
Human history or world history is the record of humankind from prehistory to the present. Early modern human, Modern humans evolved in Africa around 300,000 years ago and initially lived as hunter-gatherers. They Early expansions of hominin ...
.
Born a prince of the Cherusci tribe, Arminius was part of the Roman-friendly faction of the tribe. He learned Latin and served in the Roman military, which gained him Roman citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome () was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, traditions, and cu ...
, and the rank of ''eques''. After serving with distinction in the Great Illyrian Revolt
The (Latin for ''War of the Batos'') or Great Illyrian Revolt was a military conflict fought in the Roman Empire, Roman province of Illyricum (Roman province), Illyricum in the 1st century AD, in which an alliance of native peoples of the two re ...
, he was sent to Germania to aid the local governor Publius Quinctilius Varus
Publius Quinctilius Varus (46 BC or before – September AD 9) was a Roman general and politician. Serving under Augustus, who founded the Roman Empire, he is generally remembered for having lost three Roman legions in the Battle of the Teutob ...
in completing the Roman conquest of the Germanic tribes. While in this capacity, Arminius secretly plotted a Germanic revolt against Roman rule, which culminated in the ambush and destruction of three Roman legions in the Teutoburg Forest.
In the aftermath of the battle, Arminius fought retaliatory invasions by the Roman general Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was a Roman people, Roman general and politician most famously known for his campaigns against Arminius in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicu ...
in the battles of Pontes Longi, Idistaviso, and the Angrivarian Wall, and defeated a rival, the Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people who lived close to the border of the Roman Empire, north of the River Danube, and are mentioned in Roman records from approximately 60 BC until about 400 AD. They were one of the most important members of th ...
king Maroboduus
Maroboduus (d. AD 37), also known as Marbod, was a king of the Marcomanni, who were a Germanic Suebian people. He spent part of his youth in Rome, and returning, found his people under pressure from invasions by the Roman Empire between the Rhi ...
. Arminius sought to become a king and was assassinated
Assassination is the willful killing, by a sudden, secret, or planned attack, of a personespecially if prominent or important. It may be prompted by political, ideological, religious, financial, or military motives.
Assassinations are orde ...
in 21. He was remembered in Germanic legends for generations afterwards. The Roman historian Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
designated Arminius as the liberator of the Germanic tribes and commended him for having fought the Roman Empire to a standstill at the peak of its power.Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
. The Annals.2.88. "Assuredly he was the deliverer of Germany, one too who had defied Rome, not in her early rise, as other kings and generals, but in the height of her empire's glory, had fought, indeed, indecisive battles, yet in war remained unconquered. He completed thirty-seven years of life, twelve years of power, and he is still a theme of song among barbarous nations, though to Greek historians, who admire only their own achievements, he is unknown, and to Romans not as famous as he should be, while we extol the past and are indifferent to our own times."
During the unification of Germany
The unification of Germany (, ) was a process of building the first nation-state for Germans with federalism, federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without Habsburgs' multi-ethnic Austria or its German-speaking part). I ...
in the 19th century, Arminius was hailed by German nationalists
German nationalism () is an ideological notion that promotes the unity of Germans and of the Germanosphere into one unified nation-state. German nationalism also emphasizes and takes pride in the patriotism and national identity of Germans a ...
as a symbol of German unity and freedom. Following World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, however, Arminius' significance diminished in Germany due to the rise of anti-militarism, pacifism
Pacifism is the opposition to war or violence. The word ''pacifism'' was coined by the French peace campaigner Émile Arnaud and adopted by other peace activists at the tenth Universal Peace Congress in Glasgow in 1901. A related term is ...
, and anti-nationalism; the 2,000th anniversary of his victory at the Teutoburg Forest was only lightly commemorated in Germany.
Name
Theetymology
Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of words—including their constituent units of sound and meaning—across time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. ...
of the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
name
A name is a term used for identification by an external observer. They can identify a class or category of things, or a single thing, either uniquely, or within a given context. The entity identified by a name is called its referent. A person ...
is unknown, and confusion is further created by recent scholars who alternately referred to him as . In his ''History'', Marcus Velleius Paterculus
Marcus Velleius Paterculus (; ) was a Roman historian, soldier and senator. His Roman history, written in a highly rhetorical style, covered the period from the end of the Trojan War to AD 30, but is most useful for the period from the death o ...
calls him "Arminius, the son of Sigimer, a prince of the nation" and states he "attained the dignity of equestrian rank". Due to Roman naming conventions
Over the course of some fourteen centuries, the Ancient Rome, Romans and other peoples of Italy employed a system of nomenclature that differed from that used by other cultures of Europe and the Mediterranean Sea, consisting of a combination of g ...
of the time, it is likely is an adopted name granted to him upon citizenship or in any case not his Germanic name
Germanic given names are traditionally dithematic; that is, they are formed from two elements ( stems), by joining a prefix and a suffix. For example, King Æþelred's name was derived from ', meaning "noble", and ', meaning "counsel". The i ...
. The name instead appears to ultimately be of Etruscan origin, appearing as and on inscriptions found at Volaterrae. According to another theory, that name was given to Arminius for his service in Armenia.
The German translation of as the name
A name is a term used for identification by an external observer. They can identify a class or category of things, or a single thing, either uniquely, or within a given context. The entity identified by a name is called its referent. A person ...
''Hermann'' dates from the 16th century, possibly first by Martin Luther
Martin Luther ( ; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, Theology, theologian, author, hymnwriter, professor, and former Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. Luther was the seminal figure of the Reformation, Pr ...
. In German, Arminius was traditionally distinguished as ("Hermann the Cheruscan") or ("Hermann the Cheruscan Prince"). Hermann etymologically means "Man of War", coming from the Old High German
Old High German (OHG; ) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally identified as the period from around 500/750 to 1050. Rather than representing a single supra-regional form of German, Old High German encompasses the numerous ...
meaning "war" and meaning "man". This has also led to his English nickname "Herman the German".
Early life and Roman military service
 Born in 18 or 17 BC in
Born in 18 or 17 BC in Germania
Germania ( ; ), also more specifically called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman provinces of Germania Inferior and Germania Superio ...
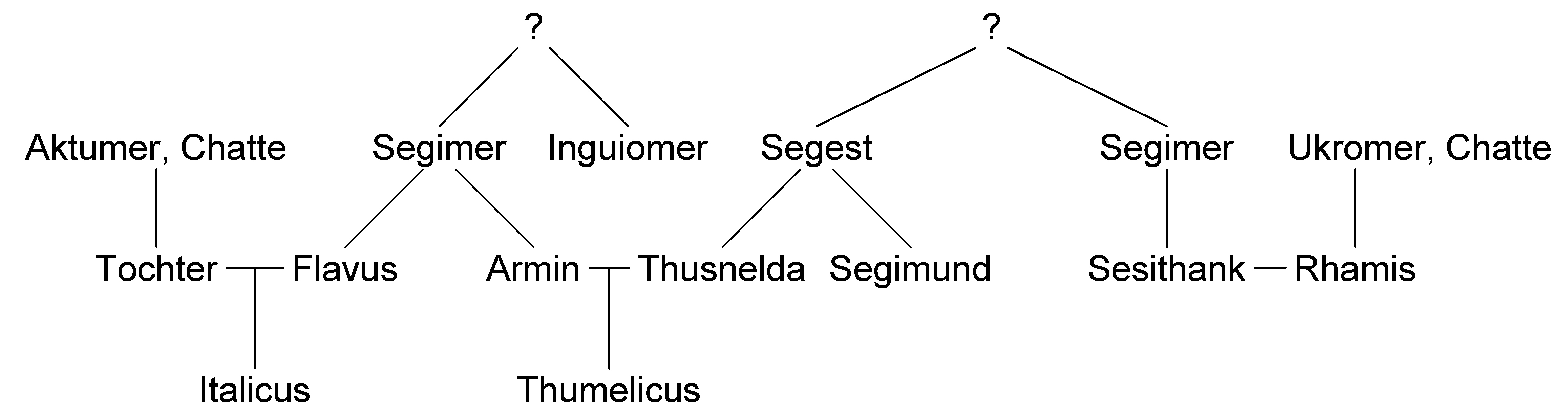
, Arminius was the son of the Cheruscan chief Segimerus (German: ''Segimer''; Proto-Germanic: ''Sigimariz''; Old English: ''Sigemær''), who was allied with Rome.
Arminius learned to speak Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
and joined the Roman military with his younger brother Flavus. He served in the Roman army
The Roman army () served ancient Rome and the Roman people, enduring through the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (509–27 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC–AD 1453), including the Western Roman Empire (collapsed Fall of the W ...
between AD 1 and 6, and received a military education as well as Roman citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome () was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, traditions, and cu ...
and the status of equite before returning to Germania. These experiences gave him knowledge of Roman politics and military tactics, which allowed him to successfully anticipate enemy battle maneuvers during his later campaigns against the Roman army.
Return to Germania
Around the year AD 4, Arminius assumed command of a Cheruscan detachment of Roman auxiliary forces, probably while fighting in the Pannonian wars on theBalkan peninsula
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
. He returned to northern Germania in AD 7 or 8, where the Roman Empire had established secure control of the territories just east of the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
, along the Lippe
Lippe () is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Herford, Minden-Lübbecke, Höxter, Paderborn, Gütersloh, and district-free Bielefeld, which forms the region Ostwestfalen-Lippe. ...
and Main rivers, and was now seeking to extend its hegemony eastward to the Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports o ...
and Elbe
The Elbe ( ; ; or ''Elv''; Upper Sorbian, Upper and , ) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Ge ...
rivers, under Publius Quinctilius Varus
Publius Quinctilius Varus (46 BC or before – September AD 9) was a Roman general and politician. Serving under Augustus, who founded the Roman Empire, he is generally remembered for having lost three Roman legions in the Battle of the Teutob ...
, a high-ranking administrative official appointed by Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
as governor. Arminius began plotting to unite various Germanic tribes in order to thwart Roman efforts to incorporate their lands into the empire. This proved a difficult task, as the tribes were strongly independent and many were traditionally enemies of each other.
Between AD 6 and 9, the Romans were forced to move eight legions, of the eleven present in Germania east of the Rhine, to crush a rebellion in the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, leaving Varus with only three legions to face the Germans. This was still 18,000 troops, or 6,000 men per legion. An additional two legions, under the command of Lucius Nonius Asprenas, were stationed in Moguntiacum. Arminius saw this as the perfect opportunity to defeat Varus.
Anti-Roman uprising
 In the autumn of AD 9, the 25-year-old Arminius brought to Varus a false report of rebellion in northern Germany. He persuaded Varus to divert the three legions under his command (composed of the 17th, 18th, and 19th legions, plus three
In the autumn of AD 9, the 25-year-old Arminius brought to Varus a false report of rebellion in northern Germany. He persuaded Varus to divert the three legions under his command (composed of the 17th, 18th, and 19th legions, plus three cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mob ...
detachments and six cohorts of auxiliaries), which were at the time marching to winter quarters, to suppress the rebellion. Varus and his legions marched right into the trap that Arminius had set for them near Kalkriese. Arminius' tribe, the Cherusci
The Cherusci were a Germanic tribe that inhabited parts of the plains and forests of northwestern Germania in the area of the Weser River and present-day Hanover during the first centuries BC and AD. Roman sources reported they considered thems ...
, and their allies the Marsi
The Marsi were an Italic people of ancient Italy, whose chief centre was Marruvium, on the eastern shore of Lake Fucinus (which was drained in the time of Claudius). The area in which they lived is now called Marsica. They originally spoke a l ...
, Chatti
The Chatti (also Chatthi or Catti) were an ancient Germanic tribe
whose homeland was near the upper Weser (''Visurgis'') river. They lived in central and northern Hesse and southern Lower Saxony, along the upper reaches of that river and in ...
, Bructeri
The Bructeri were a Germanic people, who lived in present-day North Rhine-Westphalia, just outside what was then the Roman Empire. The Romans originally reported them living east of the lower Rhine river, in a large area centred around present day ...
, Chauci, and Sicambri
The Sicambri or Sugambri were a Germanic people who lived in the area between the Rhine, Lippe, and Wupper rivers, in what is now Germany, near the border with the Netherlands. They were first reported by Julius Caesar, who encountered them in 55 ...
(five out of at least fifty Germanic tribes at the time) ambushed and annihilated Varus' entire army, totaling over 20,000 men, as it marched along a narrow road through a dense forest. Recent archaeological finds show the long-debated location of the three-day battle was almost certainly near Kalkriese Hill, about north of present-day Osnabrück
Osnabrück (; ; archaic English: ''Osnaburg'') is a city in Lower Saxony in western Germany. It is situated on the river Hase in a valley penned between the Wiehen Hills and the northern tip of the Teutoburg Forest. With a population of 168 ...
. When defeat was certain, Varus committed suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death.
Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or ac ...
by falling upon his sword. The battle was one of the most devastating defeats Rome suffered in its history. Arminius' success in destroying three entire legions and driving the Romans out of Germany marked a high point of Germanic power for centuries. Roman attempts to reconquer Germania failed, although they did eventually manage to break Arminius' carefully coordinated alliance.
After the battle, the Germans quickly annihilated every trace of Roman presence east of the Rhine. Roman settlements such as the Waldgirmes Forum were abandoned. The vastly outnumbered Roman garrison of Aliso (present-day Haltern am See
Haltern am See (''Haltern at the lake'', before December 2001 only Haltern) is a medium-sized town in the northern part of the Recklinghausen (district), district of Recklinghausen in the Münster (region), ''Regierungsbezirk'' Münster in North Rh ...
), under the command of the prefect Lucius Cedicius, inflicted heavy losses on the Germans before retreating into Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
, resisting long enough for Lucius Nonius Asprenas to organize the Roman defense on the Rhine and Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
to arrive with a new army. This prevented Arminius from crossing the Rhine and invading Gaul.
Marriage
At some point after the battle, Arminius married a Germanic princess named Thusnelda. Her father was the Cheruscan princeSegestes
Segestes was a nobleman of the Germanic tribe of the Cherusci involved in the events surrounding the Roman attempts to conquer northern Germany during the reign of Augustus and then Tiberius.
Arminius, the Cheruscan noble and military leader, ha ...
, who was pro-Roman. But Arminius abducted and then impregnated Thusnelda circa AD 14. This elopement
Elopement is a marriage which is conducted in a sudden and secretive fashion, sometimes involving a hurried flight away from one's place of residence together with one's beloved with the intention of getting married without parental approval. A ...
was likely a result of a dispute between Arminius and Segestes who was against their relationship. In May of 15 the Roman general Germanicus captured Thusnelda. At the point of her capture she was pregnant and living with her father, who had taken her back. Arminius deeply grieved the capture of Thusnelda and did not marry again. Tacitus recorded that Arminius was "driven to frenzy" by the loss of his beloved wife.Tacitus, The Annals 1.59 Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
states in the ''Annals
Annals (, from , "year") are a concise history, historical record in which events are arranged chronology, chronologically, year by year, although the term is also used loosely for any historical record.
Scope
The nature of the distinction betw ...
'':Arminius, with his naturally furious temper, was driven to frenzy by the seizure of his wife and the foredooming to slavery of his wife's unborn child. He flew hither and thither among the Cherusci, demanding "war against Segestes, war against Cæsar." And he refrained not from taunts.Thusnelda gave birth to a son named Thumelicus who grew up in Roman captivity. Tacitus describes him as having an unusual story, which he promises to tell in his later writings, but these writings have never been found.
Roman retribution and death
Between 14 and 16,Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was a Roman people, Roman general and politician most famously known for his campaigns against Arminius in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicu ...
led punitive operations into Germany, fighting Arminius to a draw in the Battle at Pontes Longi and twice defeating him (according to Tacitus): first in the Battle of Idistaviso
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
and later at the Battle of the Angrivarian Wall. In 15, Roman troops managed to recapture one of the three legionary eagles lost in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. In 16, a second eagle was retrieved. Tiberius denied the request of Germanicus to launch an additional campaign for 17, however, having decided the frontier with Germania would stand at the Rhine river. Instead, he offered Germanicus the honor of a triumph for his two victories. The third Roman eagle was recovered in 41 by Publius Gabinius, under the emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Ant ...
. Arminius also faced opposition from his father-in-law and other pro-Roman Germanic leaders. His brother Flavus, who had been raised alongside him in Rome, remained loyal to the Roman Empire and fought under Germanicus against Arminius at the Battle of Idistaviso. With the end of the Roman threat, a war broke out between Arminius and Marbod, king of the Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people who lived close to the border of the Roman Empire, north of the River Danube, and are mentioned in Roman records from approximately 60 BC until about 400 AD. They were one of the most important members of th ...
. It ended with Marbod fleeing to Ravenna
Ravenna ( ; , also ; ) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire during the 5th century until its Fall of Rome, collapse in 476, after which ...
and Roman protection, but Arminius failed to break into the "natural fortification" of Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
, and the war ended in stalemate. In 19, Germanicus died in Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
under circumstances which led many to believe he had been poisoned by his opponents. Arminius died two years later in 21, murdered by opponents within his own tribe who felt that he was becoming too powerful.Tacitus, The Annals 2.88 Tiberius allegedly had refused an earlier offer from a Chatti nobleman to poison Arminius: "It was not by secret treachery but openly and by arms that the people of Rome avenged themselves on their enemies."
Legacy and influence
Arminius' victory against the Roman legions in the Teutoburg Forest had a far-reaching effect on the subsequent history of both the ancientGermanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of ...
and on the Roman Empire. The Romans made no further concerted efforts to conquer and permanently hold Germania beyond the Rhine and the '' Agri Decumates''. Numerous modern historians have regarded Arminius' victory as one of the most decisive battles in history, with some calling it "Rome's greatest defeat".
Roman imperial expansion
 In the accounts of his Roman enemies, Arminius is highly regarded for his military leadership and as a defender of the liberty of his people. Based on these records, the story of Arminius was revived in the 16th century with the recovery of the histories of Tacitus, who wrote in his ''Annales II, 88'':
Arminius was not the only reason for Rome's change of policy towards Germania. Politics also played a factor; emperors found they could rarely trust a large army to a potential rival, though Augustus had enough loyal family members to wage his wars. Also, Augustus, in his 40-year reign, had annexed many territories still at the beginning of the process of Romanization. Tiberius, who succeeded Augustus in AD 14, decided that Germania was a far less developed land, possessing few villages and only a small food surplus, and therefore was not currently important to Rome. Conquering Germania would require a commitment too burdensome for the imperial finances and an excessive expenditure of military force.
Modern scholars have pointed out that the Rhine was a more practical boundary for the Roman Empire than any other river in Germania. Armies on the Rhine could be supplied from the
In the accounts of his Roman enemies, Arminius is highly regarded for his military leadership and as a defender of the liberty of his people. Based on these records, the story of Arminius was revived in the 16th century with the recovery of the histories of Tacitus, who wrote in his ''Annales II, 88'':
Arminius was not the only reason for Rome's change of policy towards Germania. Politics also played a factor; emperors found they could rarely trust a large army to a potential rival, though Augustus had enough loyal family members to wage his wars. Also, Augustus, in his 40-year reign, had annexed many territories still at the beginning of the process of Romanization. Tiberius, who succeeded Augustus in AD 14, decided that Germania was a far less developed land, possessing few villages and only a small food surplus, and therefore was not currently important to Rome. Conquering Germania would require a commitment too burdensome for the imperial finances and an excessive expenditure of military force.
Modern scholars have pointed out that the Rhine was a more practical boundary for the Roman Empire than any other river in Germania. Armies on the Rhine could be supplied from the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
via the Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; Occitan language, Occitan: ''Ròse''; Franco-Provençal, Arpitan: ''Rôno'') is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and Southeastern France before dischargi ...
, Saône
The Saône ( , ; ; ) is a river in eastern France (modern Regions of France, region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté). It is a right tributary of the Rhône, rising at Vioménil in the Vosges (department), Vosges Departments of France, department an ...
, and Mosel, with only a brief area of portage. Armies on the Elbe, however, would have to have been supplied by extensive overland routes or by ships travelling the hazardous Atlantic. Economically, the Rhine already had towns and sizable villages at the time of the Gallic conquest. The Rhine was significantly more accessible from Rome and better equipped to supply sizable garrisons than the regions beyond.
Rome chose no longer to rule directly in Germania east of the Rhine and north of the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
, instead preferring to exert indirect influence through the tactics of using divide and rule
The term divide and conquer in politics refers to an entity gaining and maintaining political power by using divisive measures. This includes the exploitation of existing divisions within a political group by its political opponents, and also ...
and the appointing of client kings, which were cheaper than military campaigns. Italicus, nephew of Arminius, was appointed king of the Cherusci; Vangio and Sido became vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain ...
princes of the powerful Suebi
file:1st century Germani.png, 300px, The approximate positions of some Germanic peoples reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 1st century. Suebian peoples in red, and other Irminones in purple.
The Suebi (also spelled Suavi, Suevi or Suebians ...
, etc. Only when indirect methods proved insufficient to control the Germanic tribes beyond the Rhine, did Roman emperors occasionally lead devastating punitive campaigns deep into Germania. One of them, led by the Roman emperor Maximinus Thrax
Gaius Julius Verus Maximinus "Thrax" () was a Roman emperor from 235 to 238. Born of Thracian origin – given the nickname ''Thrax'' ("the Thracian") – he rose up through the military ranks, ultimately holding high command in the army of th ...
, resulted in a Roman victory in 235 at the Battle at the Harzhorn Hill, located in the modern German state of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a States of Germany, German state (') in Northern Germany, northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' of the Germany, Federal Re ...
, east of the Weser river, between the towns of Kalefeld and Bad Gandersheim.
Germanic sagas
In the early 19th century, attempts were made to show that the story of Arminius and his victory may have lived on in theOld Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
saga
Sagas are prose stories and histories, composed in Iceland and to a lesser extent elsewhere in Scandinavia.
The most famous saga-genre is the (sagas concerning Icelanders), which feature Viking voyages, migration to Iceland, and feuds between ...
s, in the form of the dragon slayer Sigurd
Sigurd ( ) or Siegfried (Middle High German: ''Sîvrit'') is a legendary hero of Germanic heroic legend, who killed a dragon — known in Nordic tradition as Fafnir () — and who was later murdered. In the Nordic countries, he is referred t ...
of the Völsunga saga
The ''Völsunga saga'' (often referred to in English as the ''Volsunga Saga'' or ''Saga of the Völsungs'') is a legendary saga, a late 13th-century prose rendition in Old Norse of the origin and decline of the Völsung clan (including the story ...
and the Nibelungenlied
The (, or ; or ), translated as ''The Song of the Nibelungs'', is an epic poetry, epic poem written around 1200 in Middle High German. Its anonymous poet was likely from the region of Passau. The is based on an oral tradition of Germanic hero ...
. An Icelandic account states that Sigurd "slew the dragon" in the Gnitaheidr—today the suburb Knetterheide of the city of Bad Salzuflen
Bad Salzuflen () is a town and thermal spa resort in the Lippe district of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. At the end of 2013, it had 52,121 inhabitants.
Geography
Bad Salzuflen lies on the eastern edge of the Ravensberg Basin, at the confluenc ...
, located at a strategic site on the Werre
The Werre () is a river in the Detmold region (Regierungsbezirk) of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, left tributary of the Weser. Its source is near Horn-Bad Meinberg. The total length of the Werre is 71.9 km.
The Werre flows generally nor ...
river which could very well have been the point of departure of Varus' legions on their way to their doom in the Teutoburg Forest. One of the foremost Scandinavian scholars of the 19th century, Guðbrandur Vigfússon, identified Sigurd as Arminius. This educated guess was also picked up by Otto Höfler, who was a prominent Nazi
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
academic during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
German nationalism
After Tacitus' ''Annals'' were rediscovered by Renaissance humanists and first published during the Gutenberg Revolution of the 15th century, Arminius became an important symbol of Germannational identity
National identity is a person's identity or sense of belonging to one or more states or one or more nations. It is the sense of "a nation as a cohesive whole, as represented by distinctive traditions, culture, and language".
National identity ...
, as a figure who successfully opposed colonialism
Colonialism is the control of another territory, natural resources and people by a foreign group. Colonizers control the political and tribal power of the colonised territory. While frequently an Imperialism, imperialist project, colonialism c ...
and prevented the Romanization
In linguistics, romanization is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Latin script, Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and tra ...
of his people by outgeneraling and defeating one of the world's first superpowers. Indeed, learning of his victory over the Roman army was especially important to German Renaissance humanists, as the Renaissance only reached the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
much later than southern Europe and German humanists were widely looked down upon by their Italian colleagues. The first literary adaptation of the Arminius story came in 1520 with Ulrich von Hutten's Latin dialogue ''Arminius'', which inserts the Germanic leader into a reimagining of the twelfth chapter of Lucian
Lucian of Samosata (Λουκιανὸς ὁ Σαμοσατεύς, 125 – after 180) was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer who is best known for his characteristic tongue-in-cheek style, with which he frequently ridi ...
's satirical ''Dialogues of the Dead''; a debate between Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
, Hannibal
Hannibal (; ; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Punic people, Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Ancient Carthage, Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
Hannibal's fat ...
, and Scipio Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–) was a Roman general and statesman who was one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Ancient Carthage, Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest milit ...
before the underworld judgment seat of Minos
Main injector neutrino oscillation search (MINOS) was a particle physics experiment designed to study the phenomena of neutrino oscillations, first discovered by a Super-Kamiokande (Super-K) experiment in 1998. Neutrinos produced by the NuMI ...
over who most deserves the position of history's greatest general and military strategist. Arminius argues his own claim and calls upon Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
to bear witness, and ultimately wins the case and the eloquent praise of Minos.
This version influenced later adaptations of the story, and reflected a wide interest in Arminius during the years of the German Reformation; the name ''Arminius'' was interpreted as reflecting the name ''Hermann'' by Martin Luther
Martin Luther ( ; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, Theology, theologian, author, hymnwriter, professor, and former Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. Luther was the seminal figure of the Reformation, Pr ...
, who saw Arminius as a symbol of his religious followers among the German people and their resistance to the Papacy
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
and the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
.
During the military occupation of the German States, first by the French Revolutionary Army
The French Revolutionary Army () was the French land force that fought the French Revolutionary Wars from 1792 to 1802. In the beginning, the French armies were characterised by their revolutionary fervour, their poor equipment and their great nu ...
and then by the French Imperial Army of Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
, ''Hermann der Cheruskerfürst'' once again became a national icon and a martyr within both German Romanticism
German Romanticism () was the dominant intellectual movement of German-speaking countries in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, influencing philosophy, aesthetics, literature, and criticism. Compared to English Romanticism, the German vari ...
and the anti-Colonialist romantic nationalism
Romantic nationalism (also national romanticism, organic nationalism, identity nationalism) is the form of nationalism in which the state claims its political legitimacy as an organic consequence of the unity of those it governs. This includes ...
fueled by the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
, which are still termed in Germany the Wars of Liberation. This may particularly be seen as in Caspar David Friedrich
Caspar David Friedrich (; 5 September 1774 – 7 May 1840) was a German Romanticism, German Romantic Landscape painting, landscape painter, generally considered the most important German artist of his generation, whose often symbolic, and anti ...
's 1812 painting '' The Tombs of the Old Heroes''.Dorothea Klein (ed.), Lutz Käppel (ed.): ''Das diskursive Erbe Europas: Antike und Antikerezeption''. Peter Lang, 2008, p. 329
/ref> During the
unification of Germany
The unification of Germany (, ) was a process of building the first nation-state for Germans with federalism, federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without Habsburgs' multi-ethnic Austria or its German-speaking part). I ...
in the 19th century, Arminius was hailed as a symbol of German unity and liberation.
 In 1808, Heinrich von Kleist wrote the play '' Die Hermannsschlacht'', but with Napoleon's victory at Wagram it remained in manuscript, being published in 1821 and not staged until 1860. The play has been revived repeatedly at moments of national crisis and was especially used as
In 1808, Heinrich von Kleist wrote the play '' Die Hermannsschlacht'', but with Napoleon's victory at Wagram it remained in manuscript, being published in 1821 and not staged until 1860. The play has been revived repeatedly at moments of national crisis and was especially used as propaganda in Nazi Germany
Propaganda was a tool of the Nazi Party in Germany from its earliest days to the end of the regime in May 1945 at the end of World War II. As the party gained power, the scope and efficacy of its propaganda grew and permeated an increasing amou ...
.
In 1838, construction was started on a massive statue of Arminius, known as the '' Hermannsdenkmal'', on a hill near Detmold in the Teutoburg Forest; it was finally completed and dedicated during the early years of the Second German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
in the wake of the German victory over France in the Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. Lasting from 19 July 1870 to 28 Janua ...
of 1870–1871. The monument has been a major tourist attraction ever since, as has the Hermann Heights Monument, a similar statue erected in New Ulm, Minnesota
New Ulm ( ) is a city and the county seat of Brown County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 14,120 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is located on the triangle of land formed by the confluence of the Minnesota River a ...
, in the United States in 1897. The Hermann Heights monument was erected by the Sons of Hermann
The Order of the Sons of Hermann () is a Benefit society, mutual aid society for Germany, German immigrants that was formed in New York City on July 20, 1840,Fritz Schilo"Sons of Hermann" Handbook of Texas Online, Texas State Historical Society, ...
, a fraternal organization formed in New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
by German American
German Americans (, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry.
According to the United States Census Bureau's figures from 2022, German Americans make up roughly 41 million people in the US, which is approximately 12% of the pop ...
s as a means of self protection against anti-German sentiment
Anti-German sentiment (also known as anti-Germanism, Germanophobia or Teutophobia) is fear or dislike of Germany, its Germans, people, and its Culture of Germany, culture. Its opposite is Germanophile, Germanophilia.
Anti-German sentiment main ...
and discrimination in 1840; and that flourished during the 19th century in American cities and rural areas with large populations speaking the German language in the United States
Over 50 million Americans claim German ancestry, which made them the largest single claimed ancestry group in the United States until 2020. Around 1.06 million people in the United States speak the German language at home. It is the second m ...
. Hermann, Missouri
Hermann is a city in and the county seat of Gasconade County, Missouri, Gasconade County, Missouri, United States. It has been the county seat since 1842. It is near the center of the Missouri Rhineland and south of the Missouri River. The popula ...
, a town on the Missouri River
The Missouri River is a river in the Central United States, Central and Mountain states, Mountain West regions of the United States. The nation's longest, it rises in the eastern Centennial Mountains of the Bitterroot Range of the Rocky Moun ...
founded in the 1830s and incorporated in 1845, was also named for Arminius.
Following the defeat of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
in 1945, Arminius became lesser-known among West Germans and the educational system shied away from teaching about his life due to a sense of guilt and shame, rooted in both the Holocaust
The Holocaust (), known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as the (), was the genocide of History of the Jews in Europe, European Jews during World War II. From 1941 to 1945, Nazi Germany and Collaboration with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy ...
and Nazi war crimes, related to any form of German nationalism
German nationalism () is an ideological notion that promotes the unity of Germans and of the Germanosphere into one unified nation-state. German nationalism also emphasizes and takes pride in the patriotism and national identity of Germans as ...
. There was, however, a radically different practice in East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
. Particularly during the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, Arminius and his warriors were anachronistically reinterpreted quite similarly to the slave revolt led by Spartacus
Spartacus (; ) was a Thracians, Thracian gladiator (Thraex) who was one of the Slavery in ancient Rome, escaped slave leaders in the Third Servile War, a major Slave rebellion, slave uprising against the Roman Republic.
Historical accounts o ...
in the Marxist-Leninist official history
An official history is a work of history which is sponsored, authorised or endorsed by its subject. The term is most commonly used for histories which are produced for a government. The term also applies to commissions from non-state bodies includi ...
promoted by the State; as an early socialist revolution and as revolutionary terror
Revolutionary terror, also referred to as revolutionary terrorism or reign of terror, refers to the institutionalized application of force to counter-revolutionaries, particularly during the French Revolution from the years 1793 to 1795 (see t ...
against the "Roman slaveholder society" (''Sklavenhaltergesellschaft''). The legacy of Arminius and his followers was further reinterpreted as symbolic of the allegedly "peace-loving" Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP), formally the Treaty of Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance (TFCMA), was a Collective security#Collective defense, collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Polish People's Republic, Poland, between the Sovi ...
countries, while Imperial Rome was made into a symbol of the capitalist
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
and allegedly Fascist
Fascism ( ) is a far-right, authoritarian, and ultranationalist political ideology and movement. It is characterized by a dictatorial leader, centralized autocracy, militarism, forcible suppression of opposition, belief in a natural soci ...
ic United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and the NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
military alliance
A military alliance is a formal Alliance, agreement between nations that specifies mutual obligations regarding national security. In the event a nation is attacked, members of the alliance are often obligated to come to their defense regardless ...
, which were cast as the new evil empire needing to be resisted.Tillmann Bendikowski''Deutsche Geschichte – Mythos einer Schlacht''
Zeit Online, 4 November 2008 (German) According to journalist David Crossland: "The old nationalism has been replaced by an easy-going
patriotism
Patriotism is the feeling of love, devotion, and a sense of attachment to one's country or state. This attachment can be a combination of different feelings for things such as the language of one's homeland, and its ethnic, cultural, politic ...
that mainly manifests itself at sporting events like the soccer World Cup
A world cup is a global sporting competition in which the participant entities – usually international teams or individuals representing their countries – compete for the title of world champion. The event most associated with the name is ...
." The German Bundesliga football club DSC Arminia Bielefeld is named after Arminius. In the German diaspora, on the other hand, the 2,000-year anniversary of the battle was celebrated in New Ulm, Minnesota
New Ulm ( ) is a city and the county seat of Brown County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 14,120 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is located on the triangle of land formed by the confluence of the Minnesota River a ...
, proudly and without restraint. There were mock battles between Romans and club-wielding barbarians and also a lecture series in an auditorium.
Cultural references
Literature
Fictionalized versions of Arminius or commentary upon his legacy appear in: * ''Arminius
Arminius (; 18/17 BC–AD 21) was a chieftain of the Germanic peoples, Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in AD 9, in which three Roman legions under th ...
'' (1520), by Ulrich von Hutten
* '' Die Hermannschlacht'' (1808) by Heinrich von Kleist
* '' Germany. A Winter's Tale'' (1843) by Heinrich Heine
Christian Johann Heinrich Heine (; ; born Harry Heine; 13 December 1797 – 17 February 1856) was an outstanding poet, writer, and literary criticism, literary critic of 19th-century German Romanticism. He is best known outside Germany for his ...
* '' The Fifteen Decisive Battles of the World'' (1851) by Sir Edward Shepherd Creasy
* '' I, Claudius'' (1934) by Robert Graves
Captain Robert von Ranke Graves (24 July 1895 – 7 December 1985) was an English poet, soldier, historical novelist and critic. His father was Alfred Perceval Graves, a celebrated Irish poet and figure in the Gaelic revival; they were b ...
* '' What If?'' (1999), edited by Robert Cowley
* ''Give Me Back My Legions!'' (2009) by Harry Turtledove
Harry Norman Turtledove (born June 14, 1949) is an American author who is best known for his work in the genres of alternate history, historical fiction, fantasy, science fiction, and mystery fiction. He is a student of history and completed his ...
* ''Eagles At War'' (2015) by Ben Kane
* ''Wolves of Rome'' (2016) by Valerio Massimo Manfredi
Valerio Massimo Manfredi (born 8 March 1943) is an Italian historian, writer, essayist, archaeologist and journalist.
Biography
He was born in Piumazzo di Castelfranco Emilia province of Modena and, after getting a degree in Classical Arts at ...
(first published in Italian as ''Teutoburgo'')
* ''Dead Romans'' (2023) by Fred Kennedy and Nick Markinkovich (published by Image Comics)
Music and opera
* '' Arminio'' is a 1692 opera about Arminius by the Bohemian-Austrian composerHeinrich Ignaz Franz Biber
Heinrich Ignaz Franz von Biber correctly ''Biber von Bibern'' ( bapt. 12 August 1644, Stráž pod Ralskem – 3 May 1704, Salzburg) was a Bohemian-Austrian composer and violinist. Biber worked in Graz and Kroměříž before he illegally left ...
.
* '' Germanico in Germania'', a 1732 opera by Nicola Porpora
Nicola (or Niccolò) Antonio Giacinto Porpora (17 August 16863 March 1768) was an Italian composer and teacher of singing of the Baroque era, whose most famous singing students were the castrati Farinelli and Caffarelli. Other students include ...
* '' Arminio'' is a 1736 opera about Arminius by George Frideric Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel ( ; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque composer well-known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, concerti grossi, and organ concerti.
Born in Halle, Germany, H ...
.
* ''Arminius
Arminius (; 18/17 BC–AD 21) was a chieftain of the Germanic peoples, Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in AD 9, in which three Roman legions under th ...
'' is an 1877 oratorio about Arminius by the German composer Max Bruch
Max Bruch (6 January 1838 – 2 October 1920) was a German Romantic Music, Romantic composer, violinist, teacher, and conductor who wrote more than 200 works, including three violin concertos, the first of which has become a staple of the violin ...
.
Film
* '' Massacre in the Black Forest'', (German: Hermann der Cherusker – Die Schlacht im Teutoburger Wald), a 1967 historical filmTelevision
* ''Barbarians
A barbarian is a person or tribe of people that is perceived to be primitive, savage and warlike. Many cultures have referred to other cultures as barbarians, sometimes out of misunderstanding and sometimes out of prejudice.
A "barbarian" may ...
'' is a 2020 TV show that features a fictionalised version of Arminius (portrayed by Laurence Rupp) as one of the central characters.
See also
*Ariovistus
Ariovistus was a leader of the Suebi and other allied Germanic peoples in the second quarter of the 1st century BC, who name appears prominently in Julius Caesar's '' Commentarii de Bello Gallico''. Before their conflict with the Romans, Ariovis ...
* Bato the Breucian
* Bato the Daesitiate
* Boudica
Boudica or Boudicca (, from Brittonic languages, Brythonic * 'victory, win' + * 'having' suffix, i.e. 'Victorious Woman', known in Latin chronicles as Boadicea or Boudicea, and in Welsh language, Welsh as , ) was a queen of the Iceni, ancient ...
* Divico
* Gaius Julius Civilis
Gaius Julius Civilis (AD 25 – ) was the leader of the Batavian rebellion against the Romans in 69 AD. His Roman naming conventions, nomen shows that he (or one of his male ancestors) was made a Roman citizen (and thus, the tribe a Roman vassal) ...
* Teutobod
* Vercingetorix
Vercingetorix (; ; – 46 BC) was a Gauls, Gallic king and chieftain of the Arverni tribe who united the Gauls in a failed revolt against Roman Republic, Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. After surrendering to C ...
Citations
Sources
* * * * Dörner, Andreas, ''Politischer Mythos und symbolische Politik. Der Hermannmythos: Zur Entstehung des Nationalbewußtseins der Deutschen'' (Reinbek: Rowohlt, 1996). * * * von Essen, Gesa, ''Hermannsschlachten. Germanen- und Römerbilder in der Literatur des 18. und 19. Jahrhunderts'' (Göttingen: Wallstein, 1998). * Kuehnemund, Richard, ''Arminius or the Rise of a National Symbol in Literature: From Hutten to Grabbe'' (New York: AMS Press, 1966). * Münkler Herfried, and Hans Grünberger: "Arminius/ Hermann als nationales Symbol im Diskurs der deutschen Humanisten 1500–1570", In: Herfried Münkler, Hans Grünberger, and Kathrin Mayer, ''Nationenbildung. Die Nationalisierung Europas im Diskurs humanistischer Intellektueller. Italien und Deutschland'' (Berlin: Akademie, 1998), pp. 263–308. * * * Wagner-Egelhaaf, Martina (ed.), ''Hermanns Schlachten. Zur Literaturgeschichte eines nationalen Mythos'' (Bielefeld: Aisthesis, 2008). * * Wolters, Reinhard ''Die Schlacht im Teutoburger Wald: Arminius, Varus und das roemische Germanien'' (München: Verlag C. H. Beck, 2008).External links
Arminius
at the ''
Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, ...
''
Arminius
at the '' Ancient History Encyclopedia''
"Arminius / Varus: Die Varusschlacht im Jahre 9 n. Chr."
– LWL-Institut für westfälische Regionalgeschichte (in German)
"Terry Jones' Barbarians: The Savage Goths"
– includes a portion on Arminius
(in German)
"They Need a Hero"
by Clay Risen in '' The National'', 9 October 2009 – article on modern German views of Hermann and the 2,000th anniversary of the battle The Football (Soccer) Team „DSC Arminia Bielefeld“ is named After Arminius {{DEFAULTSORT:Arminius 010s BC births 1st-century monarchs in Europe 021 deaths Ancient Roman soldiers Cherusci chieftains Cherusci warriors Roman campaigns in Germania (12 BC – AD 16)