|
Legio XIX
Legio XIX ("Nineteenth Legion") was a legion of the Imperial Roman army. It was destroyed in 9 AD in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. The emblem of the XIXth legion is unknown but was probably the Capricorn like other legions levied by Augustus. History It was founded in 41 or 40 BC by Augustus. Their first assignment was in Sicily where Sextus Pompey, son of Pompey, was leading a revolt. This revolt put Rome's grain supply in peril and it needed a harsh response. In 30 BC, veterans of the XIX legion were settled near Pisa, and after that, the rest of the legion was allocated in the Rhine frontier with base camp at Cologne. The XIX legion participated in the German campaigns of Drusus (13–9 BC) and Tiberius (8–5 BC). By the year 5 BC Germania was a Roman province and Publius Quinctilius Varus was assigned as governor. The legion could have been stationed in Dangstetten. It is possible the reason the legion was stationed here was to police the nearby Roman Road. In Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Aquila
An ''aquila'' (; ) was a prominent symbol used in ancient Rome, especially as the standard of a Roman legion. A legionary known as an ''aquilifer'', the "eagle-bearer", carried this standard. Each legion carried one eagle. It represents the Eagle of Jove ( Aëtos), being Jove the "Father of the Roman state". The eagle had quasi-religious importance to the Roman soldier, far beyond being merely a symbol of his legion. To lose a standard was seen as extremely grave, shameful and dishonorable, and the Roman military went to great lengths both to protect a standard and to recover one if it were to be lost. For example, after the annihilation of three legions in the Teutoburg Forest, the Romans spent decades retaliating for the defeat while also attempting to recover the three lost eagles. No legionary eagle standards are known to have survived. However, other Roman eagles, either symbolizing imperial rule or used as funerary emblems, have been discovered. History The ''s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
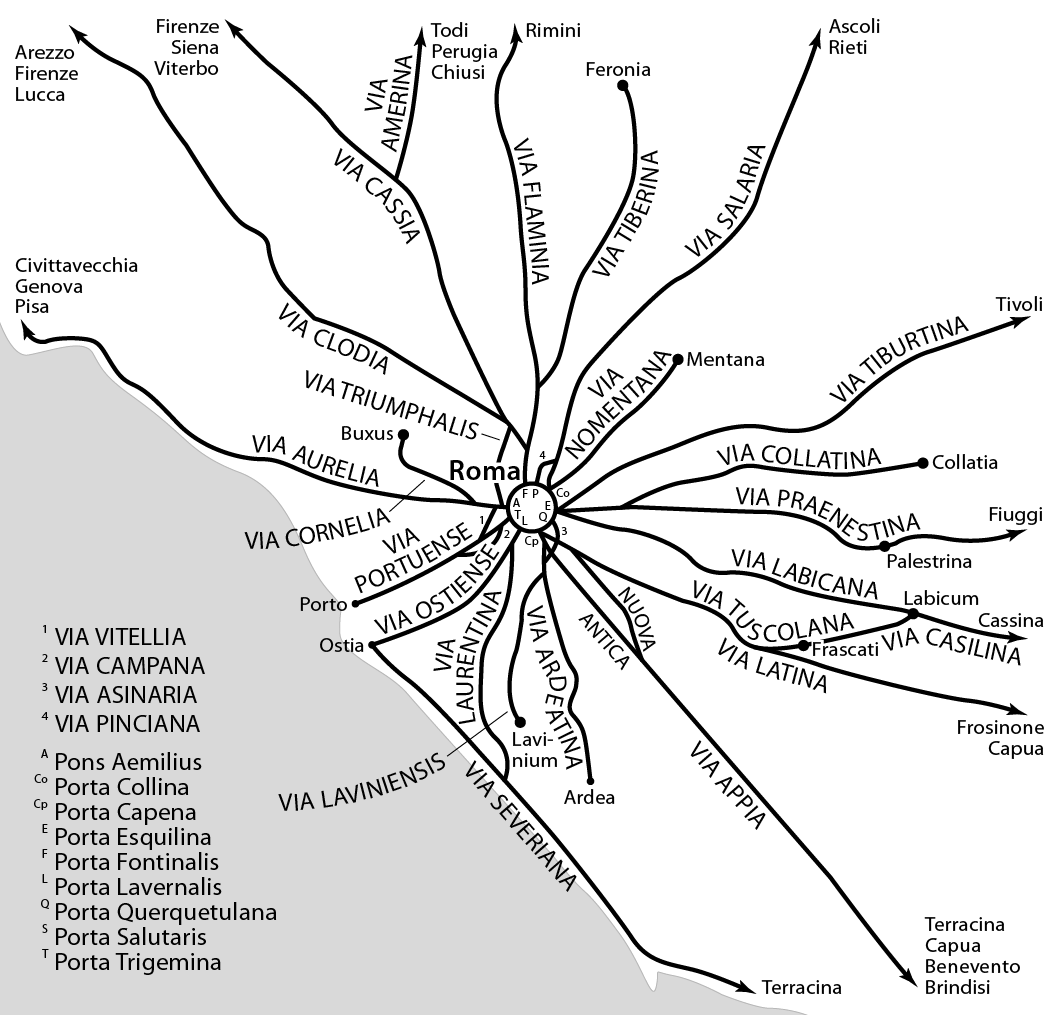
Roman Roads
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of Military history of ancient Rome, armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and Roman commerce, trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, Bridle path, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
40s BC Establishments
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is a square number, the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. Evolution of the Hindu-Arabic digit Brahmic numerals represented 1, 2, and 3 with as many lines. 4 was simplified by joining its four lines into a cross that looks like the modern plus sign. The Shunga would add a horizontal line on top of the digit, and the Kshatrapa and Pallava evolved the digit to a point where the speed of writing was a secondary concern. The Arabs' 4 still had the early concept of the cross, but for the sake of efficiency, was made in one stroke by connecting the "western" end to the "northern" end; the "eastern" end was finished off with a curve. The Europeans dropped the finishing curve and gradually made the digit less cursive, ending up with a digit very close to the original Brahmin cross. While the shape of the character fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Legions
The Roman legion (, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of Roman citizens serving as legionaries. During the Roman Republic the manipular legion comprised 4,200 infantry and 300 cavalry. After the Marian reforms in 107 BC, the legions were formed of 5,200 men and were restructured around 10 cohorts, the first cohort being double strength. This structure persisted throughout the Principate and Roman Empire, middle Empire, before further changes in the fourth century resulted in new formations of around 1,000 men. Size The size of a typical legion varied throughout the history of ancient Rome, with complements ranging from 4,200 legionaries and 300 ''equites'' (drawn from the wealthier classes – in early Rome all troops provided their own equipment) in the Republic, to 5,500 in the Imperial period, when most legions were led by a Roman Imperial Legate. A legion had 4,800 Legionary, legionaries (in 10 Cohort (military unit), cohorts of 6 centuries o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Roman Legions
This is a list of Roman legions, including key facts about each legion, primarily focusing on the Principate (early Empire, 27 BC – 284 AD) legions, for which there exists substantial literary, epigraphic and archaeological evidence. When Augustus became sole ruler in 31 BC, he disbanded about half of the over 50 legions then in existence. The remaining 28 legions became the core of the early Imperial army of the Principate (27 BC – AD 284), most lasting over three centuries. Augustus and his immediate successors transformed legions into permanent units, staffed by entirely career soldiers on standard 25-year terms. During the Dominate period (near the end of the Empire, 284–476), legions were also professional, but are little understood due to scarcity of evidence compared to the Principate. What is clear is that late legions were radically different in size, structure, and tactical role from their predecessors, despite several retaining early period names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legionary
The Roman legionary (in Latin ''legionarius''; : ''legionarii'') was a citizen soldier of the Roman army. These soldiers would conquer and defend the territories of ancient Rome during the Republic and Principate eras, alongside auxiliary and cavalry detachments. At its height, Roman Legionnaires were viewed as the foremost fighting force in the Roman world, with commentators such as Vegetius praising their fighting effectiveness centuries after the classical Roman legionary disappeared. Roman legionnaires were recruited from Roman citizens under age 45. They were first predominantly made up of recruits from Roman Italy, but more were recruited from the provinces as time went on. As legionnaires moved into newly conquered provinces, they helped Romanize the native population and helped integrate the disparate regions of the Roman Empire into one polity. They enlisted in a legion for 25 years of service, a change from the early practice of enlisting only for a campaign. Legionna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centurion
In the Roman army during classical antiquity, a centurion (; , . ; , or ), was a commander, nominally of a century (), a military unit originally consisting of 100 legionaries. The size of the century changed over time; from the 1st century BC through most of the imperial era it was reduced to 80 men. A centurion was promoted for being an exemplary soldier and was then expected to become a strict commander of his subordinates, to lead his troops by example, and coordinate his century's actions. They were also responsible for handling logistics and supplies, as well as any discipline that was required. In a Roman legion, centuries were grouped into cohorts and commanded by a senior centurion. The prestigious first cohort (a formation of five double-strength centuries of 160 men each) was led by the '' primus pilus,'' who commanded the ''primi ordines'' who were the centurions of the first cohort. A centurion's symbol of office was the vine staff, with which they disciplined e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribunus Angusticlavius
A ''tribunus angusticlavius'' ("narrow-striped military tribune, tribune"; : ''tribuni angusticlavii'') was a senior military officer in the Roman legions during the late Roman Republic and the Principate. The ''tribunus angusticlavius'' was a junior military tribune who was at least 20 years old, chosen from among the Equites, Equestrian order, as opposed to the ''tribunus laticlavius'', who was chosen from the Roman Senate, Senatorial class. There were five to each Roman legion, legion, identified by a narrow purple stripe (''Angusticlavia, angustus clavus'' or ''angusticlavus'') on their tunics. Despite their youth, the tribunes had previous experience, usually as a ''praefectus'' leading a quingenary Auxilia, auxiliary Cohort (military unit), cohort. Their duties varied, mostly staff work, but also lead two cohorts. The next step of promotion was often as ''praefectus'' of a 500-strong cavalry ''Auxilia#Alae, ala''. There were 141 of these at a time. References {{Reflist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bructeri
The Bructeri were a Germanic people, who lived in present-day North Rhine-Westphalia, just outside what was then the Roman Empire. The Romans originally reported them living east of the lower Rhine river, in a large area centred around present day Münster stretching from both sides of the upper River Ems in the north, to both sides of the River Lippe in the south. At its greatest extent, their territory apparently stretched between the vicinities of the Rhine in the west and the Teutoburg Forest and Weser river in the east. During the aggressive Roman campaigns of Augustus and his dynasty east of the Rhine into , the Bructeri were among the most dangerous enemies of Rome along with the Cherusci and Chatti. Compared to many neighbouring tribes they had a relatively large population and homeland, and could put significant armies into the field. Unlike many other tribes in their region they also continued to be an important power even during the centuries after the Romans consoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was a Roman people, Roman general and politician most famously known for his campaigns against Arminius in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the Patrician (ancient Rome), patrician ''gens Claudia''. The Victory title, agnomen ''Germanicus'' was added to his full name in 9 BC when it was posthumously awarded to his father in honor of his victories in Germania. In AD 4 he was adopted by his paternal uncle Tiberius, himself the stepson and heir of Germanicus' great-uncle Augustus; ten years later, Tiberius succeeded Augustus as Roman emperor. As a result of his adoption, Germanicus became an official member of the ''gens Julia'', another prominent family, to which he was related on his mother's side. His connection to the ''Julii Caesares'' was further consolidated through a marriage between him and Agrippina the Elder, a granddaughter of Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osnabrück
Osnabrück (; ; archaic English: ''Osnaburg'') is a city in Lower Saxony in western Germany. It is situated on the river Hase in a valley penned between the Wiehen Hills and the northern tip of the Teutoburg Forest. With a population of 168,145 Osnabrück is the fourth largest city in Lower Saxony. More recently Osnabrück has become well known for its industry. Numerous companies in the automobile, paper, steel and grocery sectors are located in the city and its surrounding area. In spite of the massive destruction inflicted on the city during World War II, the Altstadt (old town) was eventually reconstructed extensively with designs loyal to the original medieval architecture there. Osnabrück was also the home of the largest British garrison outside the United Kingdom. Osnabrück's modern, urban image is enhanced by the presence of more than 22,000 students studying at the University and the University of Applied Sciences. Although part of the state of Lower Saxony, his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio XVIII
Legio XVIII ("Eighteenth Legion", spelled XVIII or XIIX) was a Roman legion, legion of the Imperial Roman army. It was founded ca. 41 BC by the future emperor Augustus. The legion was, along with Legio XVII and Legio XIX, destroyed in the Battle of Teutoburg Forest (September, 9 AD). The legion's symbol and ''cognomen'' are unknown. This legion was probably created to deal with Sextus Pompeius, the last opponent of the Second Triumvirate, garrisoned in Sicily and threatening Grain supply to the city of Rome, Rome's grain supply. It was probably one of the eight legions Augustus promised Mark Antony for his campaign against the Parthians, but never delivered. Following the defeat of Antony and Cleopatra VII of Egypt, Cleopatra in the battle of Actium (31 BC), the legion was stationed in Gaul. In the end of the 1st century BC, the XVIIIth was sent to the Germania Roman provinces, provinces in the Rhine to take part in the enormous army led by Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and later T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |