Amino acid synthesis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Amino acid biosynthesis is the set of
Amino acid biosynthesis is the set of
 The regulation of proline biosynthesis can depend on the initial controlling step through
The regulation of proline biosynthesis can depend on the initial controlling step through
 Tyrosine and phenylalanine are biosynthesized from prephenate, which is converted to an amino acid-specific intermediate. This process is mediated by a
Tyrosine and phenylalanine are biosynthesized from prephenate, which is converted to an amino acid-specific intermediate. This process is mediated by a
 The associated
The associated
 In general, the histidine biosynthesis is very similar in plants and microorganisms.
HisG → HisE/HisI → HisA → HisH → HisF → HisB → HisC → HisB → HisD (HisE/I and HisB are both bifunctional enzymes)
The enzymes are coded for on the His operon. This operon has a distinct block of the leader sequence, called block 1:
Met-Thr-Arg-Val-Gln-Phe-Lys-His-His-His-His-His-His-His-Pro-Asp
This leader sequence is important for the regulation of histidine in ''E. coli''. The ''His'' operon operates under a system of coordinated regulation where all the gene products will be repressed or depressed equally. The main factor in the repression or derepression of histidine synthesis is the concentration of histidine charged tRNAs. The regulation of histidine is actually quite simple considering the complexity of its biosynthesis pathway and, it closely resembles regulation of
In general, the histidine biosynthesis is very similar in plants and microorganisms.
HisG → HisE/HisI → HisA → HisH → HisF → HisB → HisC → HisB → HisD (HisE/I and HisB are both bifunctional enzymes)
The enzymes are coded for on the His operon. This operon has a distinct block of the leader sequence, called block 1:
Met-Thr-Arg-Val-Gln-Phe-Lys-His-His-His-His-His-His-His-Pro-Asp
This leader sequence is important for the regulation of histidine in ''E. coli''. The ''His'' operon operates under a system of coordinated regulation where all the gene products will be repressed or depressed equally. The main factor in the repression or derepression of histidine synthesis is the concentration of histidine charged tRNAs. The regulation of histidine is actually quite simple considering the complexity of its biosynthesis pathway and, it closely resembles regulation of


NCBI Bookshelf Free Textbook Access
{{Amino acid metabolism enzymes Metabolism
biochemical
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, ...
processes (metabolic pathways
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical ...
) by which the amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids.
α-Ketoglutarates: glutamate, glutamine, proline, arginine
Most amino acids are synthesized from α- ketoacids, and later transaminated from another amino acid, usuallyglutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
. The enzyme involved in this reaction is an aminotransferase.
: α-ketoacid + glutamate ⇄ amino acid + α-ketoglutarate
Glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
itself is formed by amination of α-ketoglutarate:
: α-ketoglutarate + ⇄ glutamate
The α-ketoglutarate family of amino acid synthesis (synthesis of glutamate, glutamine, proline and arginine) begins with α-ketoglutarate, an intermediate in the Citric Acid Cycle. The concentration of α-ketoglutarate is dependent on the activity and metabolism within the cell along with the regulation of enzymatic activity. In ''E. coli'' citrate synthase, the enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
involved in the condensation reaction initiating the Citric Acid Cycle is strongly inhibited by α-ketoglutarate feedback inhibition and can be inhibited by DPNH as well high concentrations of ATP. This is one of the initial regulations of the α-ketoglutarate family of amino acid synthesis.
The regulation of the synthesis of glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
from α-ketoglutarate is subject to regulatory control of the Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-Co ...
as well as mass action dependent on the concentrations of reactants involved due to the reversible nature of the transamination and glutamate dehydrogenase reactions.
The conversion of glutamate to glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral ...
is regulated by glutamine synthetase (GS) and is a key step in nitrogen metabolism. This enzyme is regulated by at least four different mechanisms: 1. Repression and depression due to nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
levels; 2. Activation and inactivation due to enzymatic forms (taut and relaxed); 3. Cumulative feedback inhibition through end product metabolites; and 4. Alterations of the enzyme due to adenylation and deadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In euka ...
. In rich nitrogenous media or growth conditions containing high quantities of ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
there is a low level of GS, whereas in limiting quantities of ammonia the specific activity of the enzyme is 20-fold higher. The confirmation of the enzyme plays a role in regulation depending on if GS is in the taut or relaxed form. The taut form of GS is fully active but, the removal of manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
converts the enzyme to the relaxed state. The specific conformational state occurs based on the binding of specific divalent cations and is also related to adenylation. The feedback inhibition of GS is due to a cumulative feedback due to several metabolites including L-tryptophan, L-histidine, AMP, CTP, glucosamine-6-phosphate and carbamyl phosphate, alanine, and glycine. An excess of any one product does not individually inhibit the enzyme but a combination or accumulation of all the end products have a strong inhibitory effect on the synthesis of glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral ...
. Glutamine synthase activity is also inhibited via adenylation. The adenylation activity is catalyzed by the bifunctional adenylyltransferase/adenylyl removal (AT/AR) enzyme. Glutamine and a regulatory protein called PII act together to stimulate adenylation.
 The regulation of proline biosynthesis can depend on the initial controlling step through
The regulation of proline biosynthesis can depend on the initial controlling step through negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused ...
inhibition. In ''E. coli'', proline allosterically inhibits Glutamate 5-kinase which catalyzes the reaction from L-glutamate to an unstable intermediate L-γ-Glutamyl phosphate.
Arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) a ...
synthesis also utilizes negative feedback as well as repression through a repressor encoded by the gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
''argR''. The gene product of ''argR'', ArgR an aporepressor, and arginine as a corepressor
In genetics and molecular biology, a corepressor is a molecule that represses the expression of genes. In prokaryotes
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a single-celled organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membra ...
affect the operon of arginine biosynthesis. The degree of repression is determined by the concentrations of the repressor protein and corepressor level.
Erythrose 4-phosphate and phosphoenolpyruvate: phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan
Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of ...
, tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is ...
, and tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromat ...
, the aromatic amino acids, arise from chorismate. The first step, condensation of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonic acid 7-phosphate (DAHP) from PEP/E4P, uses three isoenzymes AroF, AroG, and AroH. Each one of these has its synthesis regulated from tyrosine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan, respectively. The rest of the enzymes in the common pathway (conversion of DAHP to chorismate) appear to be synthesized constitutively, except for shikimate kinase, which can be inhibited by shikimate through linear mixed-type inhibition.
 Tyrosine and phenylalanine are biosynthesized from prephenate, which is converted to an amino acid-specific intermediate. This process is mediated by a
Tyrosine and phenylalanine are biosynthesized from prephenate, which is converted to an amino acid-specific intermediate. This process is mediated by a phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of ...
(PheA) or tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is ...
(TyrA) specific chorismate mutase-prephenate dehydrogenase. PheA uses a simple dehydrogenase to convert prephenate to phenylpyruvate, while TyrA uses a NAD-dependent dehydrogenase to make 4-hydroxylphenylpyruvate. Both PheA and TyrA are feedback inhibited by their respective amino acids. Tyrosine can also be inhibited at the transcriptional level by the TyrR repressor. TyrR binds to the TyrR boxes on the operon near the promoter of the gene that it wants to repress.
Tryptophan biosynthesis involves conversion of chorismate to anthranilate using anthranilate synthase. This enzyme requires either glutamine as the amino group donor or ammonia itself. Anthranilate synthase is regulated by the gene products of trpE and trpG. trpE encodes the first subunit, which binds to chorismate and moves the amino group from the donor to chorismate. trpG encodes the second subunit, which facilitates the transfer of the amino group from glutamine. Anthranilate synthase is also regulated by feedback inhibition: tryptophan is a co-repressor to the TrpR repressor.
Oxaloacetate/aspartate: lysine, asparagine, methionine, threonine, and isoleucine
The oxaloacetate/aspartate family of amino acids is composed oflysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
, asparagine
Asparagine (symbol Asn or N) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
, methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans.
As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine play ...
, threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
, and isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
. Aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of protein ...
can be converted into lysine, asparagine, methionine and threonine. Threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
also gives rise to isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
.
 The associated
The associated enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s are subject to regulation via feedback inhibition and/or repression at the genetic level. As is typical in highly branched metabolic pathways, additional regulation at each branch point of the pathway. This type of regulatory scheme allows control over the total flux of the aspartate pathway in addition to the total flux of individual amino acids. The aspartate pathway uses L-aspartic acid as the precursor for the biosynthesis of one-fourth of the building block amino acids.
Aspartate
The biosynthesis of aspartate frequently involves the transamination of oxaloacetate. The enzyme aspartokinase, which catalyzes thephosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
of aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of protein ...
and initiates its conversion into other amino acids, can be broken up into 3 isozymes, AK-I, II and III. AK-I is feed-back inhibited by threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
, while AK-II and III are inhibited by lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
. As a sidenote, AK-III catalyzes the phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
of aspartic acid
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of protei ...
that is the committed step in this biosynthetic pathway. Aspartate kinase becomes downregulated by the presence of threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
or lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
.
Lysine
Lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
is synthesized from aspartate via the diaminopimelate (DAP) pathway. The initial two stages of the DAP pathway are catalyzed by aspartokinase and aspartate semialdehyde dehydrogenase. These enzymes play a key role in the biosynthesis of lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
, threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
, and methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans.
As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine play ...
. There are two bifunctional aspartokinase/homoserine dehydrogenases, ThrA and MetL, in addition to a monofunctional aspartokinase, LysC. Transcription of aspartokinase genes is regulated by concentrations of the subsequently produced amino acids, lysine, threonine, and methionine. The higher these amino acids concentrations, the less the gene is transcribed. ThrA and LysC are also feed-back inhibited by threonine and lysine. Finally, DAP decarboxylase LysA mediates the last step of the lysine synthesis and is common for all studied bacterial species. The formation of aspartate kinase (AK), which catalyzes the phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
of aspartate and initiates its conversion into other amino acids, is also inhibited by both lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
and threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
, which prevents the formation of the amino acids derived from aspartate. Additionally, high lysine concentrations inhibit the activity of dihydrodipicolinate synthase (DHPS). So, in addition to inhibiting the first enzyme of the aspartate families biosynthetic pathway, lysine also inhibits the activity of the first enzyme after the branch point, i.e. the enzyme that is specific for lysine's own synthesis.
Asparagine
The biosynthesis of asparagine originates withaspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of protein ...
using a transaminase
Transaminases or aminotransferases are enzymes that catalyze a transamination reaction between an amino acid and an α-keto acid. They are important in the synthesis of amino acids, which form proteins.
Function and mechanism
An amino acid con ...
enzyme. The enzyme asparagine synthetase produces asparagine, AMP, glutamate, and pyrophosphate
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate () and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (), among others. Often pyrophosphates a ...
from aspartate, glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral ...
, and ATP. In the asparagine synthetase reaction, ATP is used to activate aspartate, forming β-aspartyl-AMP. Glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral ...
donates an ammonium group, which reacts with β-aspartyl-AMP to form asparagine and free AMP.
Two asparagine
Asparagine (symbol Asn or N) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
synthetases are found in bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
. Both are referred to as the AsnC protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
. They are coded for by the genes AsnA and AsnB. AsnC is autogenously regulated, which is where the product of a structural gene regulates the expression of the operon
In genetics, an operon is a functioning unit of DNA containing a cluster of genes under the control of a single promoter. The genes are transcribed together into an mRNA strand and either translated together in the cytoplasm, or undergo splic ...
in which the genes reside. The stimulating effect of AsnC on AsnA transcription is downregulated by asparagine. However, the autoregulation of AsnC is not affected by asparagine.
Methionine
Biosynthesis by the transsulfuration pathway starts with aspartic acid. Relevant enzymes include aspartokinase, aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, homoserine dehydrogenase, homoserine O-transsuccinylase, cystathionine-γ-synthase, Cystathionine-β-lyase (in mammals, this step is performed by homocysteine methyltransferase or betaine—homocysteine S-methyltransferase.)Methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans.
As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine play ...
biosynthesis is subject to tight regulation. The repressor protein MetJ, in cooperation with the corepressor protein S-adenosyl-methionine, mediates the repression of methionine's biosynthesis. The regulator MetR is required for MetE and MetH gene expression and functions as a transactivator of transcription for these gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s. MetR transcriptional activity is regulated by homocystein, which is the metabolic precursor of methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans.
As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine play ...
. It is also known that vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. One of eight B vitamins, it serves as a vital cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA synthesis and both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino a ...
can repress MetE gene expression, which is mediated by the MetH holoenzyme.
Threonine
In plants and microorganisms, threonine is synthesized fromaspartic acid
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of protei ...
via α-aspartyl-semialdehyde and homoserine. Homoserine undergoes ''O''-phosphorylation; this phosphate ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
undergoes hydrolysis concomitant with relocation of the OH group. Enzymes involved in a typical biosynthesis of threonine include aspartokinase, β-aspartate semialdehyde dehydrogenase, homoserine dehydrogenase, homoserine kinase, threonine synthase.
The biosynthesis of threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
is regulated via allosteric regulation of its precursor, homoserine, by structurally altering the enzyme homoserine dehydrogenase. This reaction occurs at a key branch point in the pathway, with the substrate homoserine serving as the precursor for the biosynthesis of lysine, methionine, threonin and isoleucine. High levels of threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
result in low levels of homoserine synthesis. The synthesis of aspartate kinase (AK), which catalyzes the phosphorylation of aspartate and initiates its conversion into other amino acids, is feed-back inhibited by lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
, isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
, and threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
, which prevents the synthesis of the amino acids derived from aspartate. So, in addition to inhibiting the first enzyme of the aspartate families biosynthetic pathway, threonine also inhibits the activity of the first enzyme after the branch point, i.e. the enzyme that is specific for threonine's own synthesis.
Isoleucine
In plants and microorganisms, isoleucine is biosynthesized frompyruvic acid
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the keto acids, alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate acid, conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an metabolic intermediate, intermediate in several m ...
and alpha-ketoglutarate. Enzymes involved in this biosynthesis include acetolactate synthase (also known as acetohydroxy acid synthase), acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase, dihydroxyacid dehydratase, and valine aminotransferase.
In terms of regulation, the enzymes threonine deaminase, dihydroxy acid dehydrase, and transaminase are controlled by end-product regulation. i.e. the presence of isoleucine will downregulate threonine biosynthesis. High concentrations of isoleucine also result in the downregulation of aspartate's conversion into the aspartyl-phosphate intermediate, hence halting further biosynthesis of lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
, methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans.
As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine play ...
, threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
, and isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
.
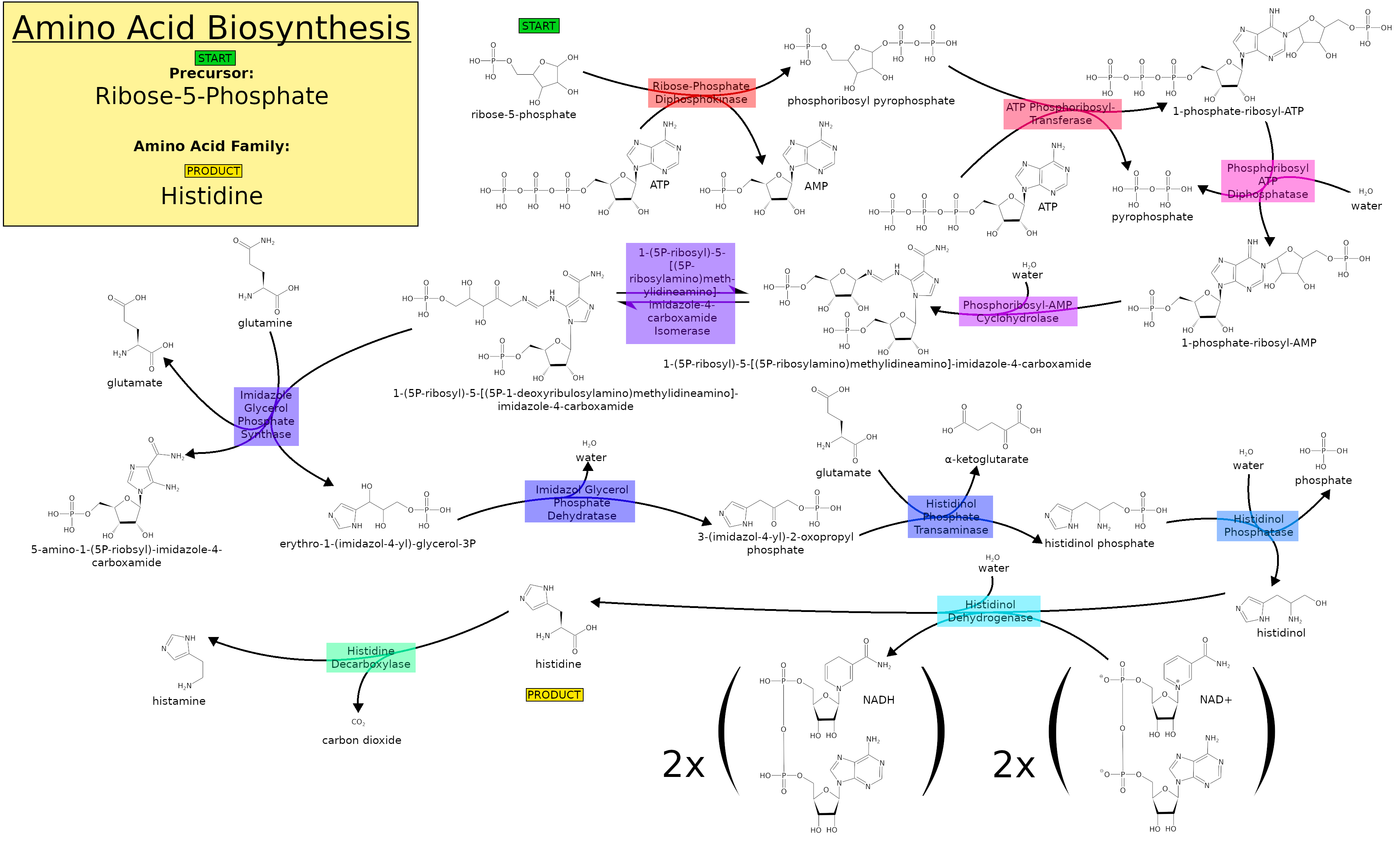
Ribose 5-phosphates: histidine
In ''E. coli'', the biosynthesis begins with phosphorylation of 5-phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphate (PRPP), catalyzed by ATP-phosphoribosyl transferase. Phosphoribosyl-ATP converts to phosphoribosyl-AMP (PRAMP). His4 then catalyzes the formation of phosphoribosylformiminoAICAR-phosphate, which is then converted to phosphoribulosylformimino-AICAR-P by the His6 gene product. His7 splits phosphoribulosylformimino-AICAR-P to form D-erythro-imidazole-glycerol-phosphate. After, His3 forms imidazole acetol-phosphate releasing water. His5 then makes L-histidinol-phosphate, which is then hydrolyzed by His2 making histidinol. His4 catalyzes the oxidation of L-histidinol to form L-histidinal, an amino aldehyde. In the last step, L-histidinal is converted to L-histidine. In general, the histidine biosynthesis is very similar in plants and microorganisms.
HisG → HisE/HisI → HisA → HisH → HisF → HisB → HisC → HisB → HisD (HisE/I and HisB are both bifunctional enzymes)
The enzymes are coded for on the His operon. This operon has a distinct block of the leader sequence, called block 1:
Met-Thr-Arg-Val-Gln-Phe-Lys-His-His-His-His-His-His-His-Pro-Asp
This leader sequence is important for the regulation of histidine in ''E. coli''. The ''His'' operon operates under a system of coordinated regulation where all the gene products will be repressed or depressed equally. The main factor in the repression or derepression of histidine synthesis is the concentration of histidine charged tRNAs. The regulation of histidine is actually quite simple considering the complexity of its biosynthesis pathway and, it closely resembles regulation of
In general, the histidine biosynthesis is very similar in plants and microorganisms.
HisG → HisE/HisI → HisA → HisH → HisF → HisB → HisC → HisB → HisD (HisE/I and HisB are both bifunctional enzymes)
The enzymes are coded for on the His operon. This operon has a distinct block of the leader sequence, called block 1:
Met-Thr-Arg-Val-Gln-Phe-Lys-His-His-His-His-His-His-His-Pro-Asp
This leader sequence is important for the regulation of histidine in ''E. coli''. The ''His'' operon operates under a system of coordinated regulation where all the gene products will be repressed or depressed equally. The main factor in the repression or derepression of histidine synthesis is the concentration of histidine charged tRNAs. The regulation of histidine is actually quite simple considering the complexity of its biosynthesis pathway and, it closely resembles regulation of tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromat ...
. In this system the full leader sequence has 4 blocks of complementary strands that can form hairpin loops structures. Block one, shown above, is the key to regulation. When histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an Amine, α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under Physiological condition, biological conditions), a carboxylic ...
charged tRNA
Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA), formerly referred to as soluble ribonucleic acid (sRNA), is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes). In a cell, it provides the physical link between the gene ...
levels are low in the cell the ribosome will stall at the string of His residues in block 1. This stalling of the ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order s ...
will allow complementary strands 2 and 3 to form a hairpin loop. The loop formed by strands 2 and 3 forms an anti-terminator and translation of the ''his'' genes will continue and histidine will be produced. However, when histidine charged tRNA levels are high the ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order s ...
will not stall at block 1, this will not allow strands 2 and 3 to form a hairpin. Instead strands 3 and 4 will form a hairpin loop further downstream of the ribosome. The hairpin loop formed by strands 3 and 4 is a terminating loop, when the ribosome comes into contact with the loop, it will be “knocked off” the transcript. When the ribosome is removed the ''His'' genes will not be translated and histidine will not be produced by the cell.
3-Phosphoglycerates: serine, glycine, cysteine
The 3-Phosphoglycerate family of amino acids includes serine, glycine, and cysteine.
Serine
Serine
Serine
(symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − ...
is the first amino acid in this family to be produced; it is then modified to produce both glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
and cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as ...
(and many other biologically important molecules). Serine is formed from 3-phosphoglycerate in the following pathway:
3-phosphoglycerate → phosphohydroxyl-pyruvate → phosphoserine → serine
The conversion from 3-phosphoglycerate to phosphohydroxyl-pyruvate is achieved by the enzyme phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase. This enzyme is the key regulatory step in this pathway. Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase is regulated by the concentration of serine in the cell. At high concentrations this enzyme will be inactive and serine will not be produced. At low concentrations of serine the enzyme will be fully active and serine will be produced by the bacterium
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the ...
. Since serine is the first amino acid produced in this family both glycine and cysteine will be regulated by the available concentration of serine in the cell.
Glycine
Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
is biosynthesized from serine, catalyzed by serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT). The enzyme effectively replaces a hydroxymethyl group with a hydrogen atom.
SHMT is coded by the gene ''glyA''. The regulation of ''glyA'' is complex and is known to incorporate serine, glycine, methionine, purines, thymine, and folates, The full mechanism has yet to be elucidated. The methionine gene product MetR and the methionine intermediate homocysteine are known to positively regulate glyA. Homocysteine is a coactivator of ''glyA'' and must act in concert with MetR. On the other hand, PurR, a protein which plays a role in purine synthesis and S-adeno-sylmethionine are known to down regulate ''glyA''. PurR binds directly to the control region of ''glyA'' and effectively turns the gene off so that glycine will not be produced by the bacterium.
Cysteine
The genes required for the synthesis ofcysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as ...
are coded for on the ''cys'' regulon. The integration of sulfur is positively regulated by CysB. Effective inducers of this regulon are N-acetyl-serine (NAS) and very small amounts of reduced sulfur. CysB functions by binding to DNA half sites on the ''cys'' regulon. These half sites differ in quantity and arrangement depending on the promoter of interest. There is however one half site that is conserved. It lies just upstream of the -35 site of the promoter. There are also multiple accessory sites depending on the promoter. In the absence of the inducer, NAS, CysB will bind the DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
and cover many of the accessory half sites. Without the accessory half sites the regulon cannot be transcribed and cysteine will not be produced. It is believed that the presence of NAS causes CysB to undergo a conformational change. This conformational change allows CysB to bind properly to all the half sites and causes the recruitment of the RNA polymerase. The RNA polymerase will then transcribe the ''cys'' regulon and cysteine will be produced.
Further regulation is required for this pathway, however. CysB can down regulate its own transcription by binding to its own DNA sequence and blocking the RNA polymerase. In this case NAS will act to disallow the binding of CysB to its own DNA sequence. OAS is a precursor of NAS, cysteine itself can inhibit CysE which functions to create OAS. Without the necessary OAS, NAS will not be produced and cysteine will not be produced. There are two other negative regulators of cysteine. These are the molecules sulfide
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to large families o ...
and thiosulfate
Thiosulfate ( IUPAC-recommended spelling; sometimes thiosulphate in British English) is an oxyanion of sulfur with the chemical formula . Thiosulfate also refers to the compounds containing this anion, which are the salts of thiosulfuric acid, ...
, they act to bind to CysB and they compete with NAS for the binding of CysB.
Pyruvate: alanine, valine, and leucine
Pyruvate, the result ofglycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form ...
, can feed into both the TCA cycle and fermentation
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and organic end products. Organic molecules, such as glucose or other sugars, are catabolized and reduce ...
processes. Reactions beginning with either one or two molecules of pyruvate lead to the synthesis of alanine, valine, and leucine. Feedback inhibition of final products is the main method of inhibition, and, in ''E. coli'', the ''ilvEDA'' operon also plays a part in this regulation.

Alanine
Alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group sid ...
is produced by the transamination of one molecule of pyruvate using two alternate steps: 1) conversion of glutamate to α-ketoglutarate using a glutamate-alanine transaminase, and 2) conversion of valine to α-ketoisovalerate via Transaminase C.
Not much is known about the regulation of alanine synthesis. The only definite method is the bacterium's ability to repress Transaminase C activity by either valine or leucine (see ''ilvEDA'' operon). Other than that, alanine biosynthesis does not seem to be regulated.
Valine
Valine
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deproton ...
is produced by a four-enzyme pathway. It begins with the condensation of two equivalents of pyruvate catalyzed by acetohydroxy acid synthase yielding α-acetolactate. The second step involves the NADPH+-dependent reduction of α-acetolactate and migration of methyl groups to produce α, β-dihydroxyisovalerate. This is catalyzed by acetohydroxy isomeroreductase. The third step is the dehydration of α, β-dihydroxyisovalerate catalyzed by dihydroxy acid dehydrase. In the fourth and final step, the resulting α-ketoisovalerate undergoes transamination catalyzed either by an alanine-valine transaminase or a glutamate-valine transaminase. Valine biosynthesis is subject to feedback inhibition in the production of acetohydroxy acid synthase.
Leucine
Theleucine
Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an α-amino acid, meaning it contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α-Car ...
synthesis pathway diverges from the valine pathway beginning with α-ketoisovalerate. α-Isopropylmalate synthase catalyzes this condensation with acetyl CoA to produce α-isopropylmalate. An isomerase converts α-isopropylmalate to β-isopropylmalate. The third step is the NAD+-dependent oxidation of β-isopropylmalate catalyzed by a dehydrogenase. The final step is the transamination of the α-ketoisocaproate by the action of a glutamate-leucine transaminase.
Leucine, like valine, regulates the first step of its pathway by inhibiting the action of the α-Isopropylmalate synthase. Because leucine is synthesized by a diversion from the valine synthetic pathway, the feedback inhibition of valine on its pathway also can inhibit the synthesis of leucine.
ilvEDA operon
The genes that encode both the dihydroxy acid dehydrase used in the creation of α-ketoisovalerate and Transaminase E, as well as other enzymes are encoded on the ilvEDA operon. This operon is bound and inactivated byvaline
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deproton ...
, leucine
Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an α-amino acid, meaning it contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α-Car ...
, and isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
. (Isoleucine is not a direct derivative of pyruvate, but is produced by the use of many of the same enzymes used to produce valine and, indirectly, leucine.) When one of these amino acids is limited, the gene furthest from the amino-acid binding site of this operon can be transcribed. When a second of these amino acids is limited, the next-closest gene to the binding site can be transcribed, and so forth.
Commercial syntheses of amino acids
The commercial production of amino acids usually relies on mutant bacteria that overproduce individual amino acids using glucose as a carbon source. Some amino acids are produced by enzymatic conversions of synthetic intermediates.2-Aminothiazoline-4-carboxylic acid
2-Aminothiazoline-4-carboxylic acid (ACTA) is the organosulfur compound and a heterocycle with the formula HO2CCHCH2SCNH2N. This derivative of thiazoline is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of L-cysteine, an amino acid
Amino a ...
is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of L-cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as ...
for example. Aspartic acid
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of protei ...
is produced by the addition of ammonia to fumarate using a lyase.
References
External links
NCBI Bookshelf Free Textbook Access
{{Amino acid metabolism enzymes Metabolism