Adenosine Triphosphate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a
 ATP is stable in aqueous solutions between pH 6.8 and 7.4 (in the absence of catalysts). At more extreme pH levels, it rapidly
ATP is stable in aqueous solutions between pH 6.8 and 7.4 (in the absence of catalysts). At more extreme pH levels, it rapidly
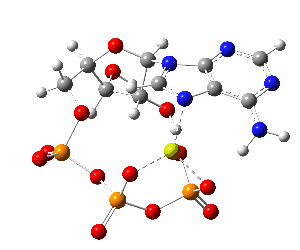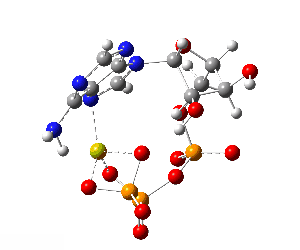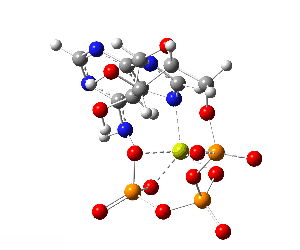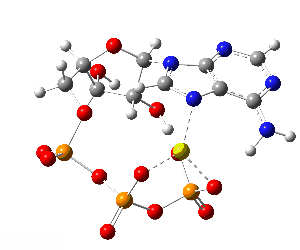
ATP bound to proteins
in the PDB
ScienceAid: Energy ATP and Exercise
PubChem entry for Adenosine Triphosphate
KEGG entry for Adenosine Triphosphate
ATP 3D model
{{DEFAULTSORT:Adenosine phosphate3 Adenosine receptor agonists Cellular respiration Coenzymes Ergogenic aids Exercise physiology Neurotransmitters Nucleotides Phosphate esters Purinergic signalling Purines Substances discovered in the 1920s
nucleoside triphosphate
A nucleoside triphosphate is a nucleoside containing a nitrogenous base bound to a 5-carbon sugar (either ribose or deoxyribose), with three phosphate groups bound to the sugar. They are the molecular precursors of both DNA and RNA, which are chai ...
that provides energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
to drive and support many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of Tension (physics), tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in musc ...
, nerve impulse
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly ri ...
propagation, and chemical synthesis
Chemical synthesis (chemical combination) is the artificial execution of chemical reactions to obtain one or several products. This occurs by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions. In modern laboratory uses ...
. Found in all known forms of life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, met ...
, it is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific envi ...
" for intracellular energy transfer.
When consumed in a metabolic
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the ...
process, ATP converts either to adenosine diphosphate
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP), also known as adenosine pyrophosphate (APP), is an important organic compound in metabolism and is essential to the flow of energy in living cells. ADP consists of three important structural components: a sugar backbon ...
(ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine. It is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. As a substituent it t ...
(AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. It is also a precursor to DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
and RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
, and is used as a coenzyme
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or Metal ions in aqueous solution, metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalysis, catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can ...
. An average adult human processes around 50 kilograms (about 100 moles) daily.
From the perspective of biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ...
, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate
A nucleoside triphosphate is a nucleoside containing a nitrogenous base bound to a 5-carbon sugar (either ribose or deoxyribose), with three phosphate groups bound to the sugar. They are the molecular precursors of both DNA and RNA, which are chai ...
, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
), the sugar ribose
Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C5H10O5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4−H. The naturally occurring form, , is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this comp ...
, and the triphosphate.
Structure
ATP consists of three parts: a sugar, an amine base, and a phosphate group. More specifically, ATP consists of anadenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
attached by the #9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
of a sugar (ribose
Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C5H10O5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4−H. The naturally occurring form, , is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this comp ...
), which in turn is attached at the 5' carbon atom of the sugar to a triphosphate group. In its many reactions related to metabolism, the adenine and sugar groups remain unchanged, but the triphosphate is converted to di- and monophosphate, giving respectively the derivatives ADP and AMP. The three phosphoryl groups are labeled as alpha (α), beta (β), and, for the terminal phosphate, gamma (γ).
In neutral solution, ionized ATP exists mostly as ATP4−, with a small proportion of ATP3−.
Metal cation binding
Polyanionic and featuring a potentially chelating polyphosphate group, ATP binds metal cations with high affinity. Thebinding constant
The binding constant, or affinity constant/association constant, is a special case of the equilibrium constant ''K'', and is the inverse of the dissociation constant. It is associated with the binding and unbinding reaction of receptor (R) and li ...
for is (). The binding of a divalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an atom is a measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules. Valence is generally understood to be the number of chemica ...
cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
, almost always magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
, strongly affects the interaction of ATP with various proteins. Due to the strength of the ATP-Mg2+ interaction, ATP exists in the cell mostly as a complex with Mg2+ bonded to the phosphate oxygen centers.
A second magnesium ion is critical for ATP binding in the kinase domain. The presence of Mg2+ regulates kinase activity. It is interesting from an RNA world perspective that ATP can carry a Mg ion which catalyzes RNA polymerization.
Chemical properties
Salts of ATP can be isolated as colorless solids.hydrolyses
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
to ADP and phosphate. Living cells maintain the ratio of ATP to ADP at a point ten orders of magnitude from equilibrium, with ATP concentrations fivefold higher than the concentration of ADP. In the context of biochemical reactions, the P-O-P bonds are frequently referred to as ''high-energy bonds''.
Reactive aspects
The hydrolysis of ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate: : releases ofenthalpy
Enthalpy () is the sum of a thermodynamic system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function in thermodynamics used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant extern ...
. This may differ under physiological conditions if the reactant and products are not exactly in these ionization states. The values of the free energy released by cleaving either a phosphate (Pi) or a pyrophosphate (PPi) unit from ATP at standard state concentrations of 1 mol/L at pH 7 are:
: Δ''G''°' = −30.5 kJ/mol (−7.3 kcal/mol)
: Δ''G''°' = −45.6 kJ/mol (−10.9 kcal/mol)
These abbreviated equations at a pH near 7 can be written more explicitly (R = adenosyl):
:
:
At cytoplasmic conditions, where the ADP/ATP ratio is 10 orders of magnitude from equilibrium, the Δ''G'' is around −57 kJ/mol.
Along with pH, the free energy change of ATP hydrolysis is also associated with Mg2+ concentration, from ΔG°' = −35.7 kJ/mol at a Mg2+ concentration of zero, to ΔG°' = −31 kJ/mol at g2+= 5 mM. Higher concentrations of Mg2+ decrease free energy released in the reaction due to binding of Mg2+ ions to negatively charged oxygen atoms of ATP at pH 7.

Production from AMP and ADP
Production, aerobic conditions
A typical intracellularconcentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', '' number concentration'', ...
of ATP may be 1–10 μmol per gram of tissue in a variety of eukaryotes. The dephosphorylation of ATP and rephosphorylation of ADP and AMP occur repeatedly in the course of aerobic metabolism.
ATP can be produced by a number of distinct cellular processes; the three main pathways in eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
s are (1) glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form ...
, (2) the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-Co ...
/oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation(UK , US : or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation, is the metabolic pathway in which Cell (biology), cells use enzymes to Redox, oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order ...
, and (3) beta-oxidation
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta oxidation (also β-oxidation) is the Catabolism, catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA. Acetyl ...
. The overall process of oxidizing glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
to carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
, the combination of pathways 1 and 2, known as cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing biological fuels using an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which stores chemical energy in a biologically accessible form. Cell ...
, produces about 30 equivalents of ATP from each molecule of glucose.
ATP production by a non-photosynthetic
Photosynthesis ( ) is a Biological system, system of biological processes by which Photoautotrophism, photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical ener ...
aerobic eukaryote occurs mainly in the mitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is us ...
, which comprise nearly 25% of the volume of a typical cell.
Glycolysis
In glycolysis, glucose and glycerol are metabolized topyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic ...
. Glycolysis generates two equivalents of ATP through substrate phosphorylation catalyzed by two enzymes, phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) and pyruvate kinase. Two equivalents of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a Cofactor (biochemistry), coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cell (biology), cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphat ...
(NADH) are also produced, which can be oxidized via the electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules which transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples th ...
and result in the generation of additional ATP by ATP synthase. The pyruvate generated as an end-product of glycolysis is a substrate for the Krebs Cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-CoA oxidation. The e ...
.
Glycolysis is viewed as consisting of two phases with five steps each. In phase 1, "the preparatory phase", glucose is converted to 2 d-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (g3p). One ATP is invested in Step 1, and another ATP is invested in Step 3. Steps 1 and 3 of glycolysis are referred to as "Priming Steps". In Phase 2, two equivalents of g3p are converted to two pyruvates. In Step 7, two ATP are produced. Also, in Step 10, two further equivalents of ATP are produced. In Steps 7 and 10, ATP is generated from ADP. A net of two ATPs is formed in the glycolysis cycle. The glycolysis pathway is later associated with the Citric Acid Cycle which produces additional equivalents of ATP.
=Regulation
= In glycolysis,hexokinase
A hexokinase is an enzyme that irreversibly phosphorylates hexoses (six-carbon sugars), forming hexose phosphate. In most organisms, glucose is the most important substrate for hexokinases, and glucose-6-phosphate is the most important p ...
is directly inhibited by its product, glucose-6-phosphate, and pyruvate kinase is inhibited by ATP itself. The main control point for the glycolytic pathway is phosphofructokinase (PFK), which is allosterically inhibited by high concentrations of ATP and activated by high concentrations of AMP. The inhibition of PFK by ATP is unusual since ATP is also a substrate in the reaction catalyzed by PFK; the active form of the enzyme is a tetramer
A tetramer () (''tetra-'', "four" + '' -mer'', "parts") is an oligomer formed from four monomers or subunits. The associated property is called ''tetramery''. An example from inorganic chemistry is titanium methoxide with the empirical formula ...
that exists in two conformations, only one of which binds the second substrate fructose-6-phosphate (F6P). The protein has two binding site
In biochemistry and molecular biology, a binding site is a region on a macromolecule such as a protein that binds to another molecule with specificity. The binding partner of the macromolecule is often referred to as a ligand. Ligands may includ ...
s for ATP – the active site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate, the ''binding s ...
is accessible in either protein conformation, but ATP binding to the inhibitor site stabilizes the conformation that binds F6P poorly. A number of other small molecules can compensate for the ATP-induced shift in equilibrium conformation and reactivate PFK, including cyclic AMP, ammonium
Ammonium is a modified form of ammonia that has an extra hydrogen atom. It is a positively charged (cationic) polyatomic ion, molecular ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation, addition of a proton (a hydrogen nucleu ...
ions, inorganic phosphate, and fructose-1,6- and -2,6-biphosphate.
Citric acid cycle
In themitochondrion
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cell (biology), cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine tri ...
, pyruvate is oxidized by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex to the acetyl
In organic chemistry, an acetyl group is a functional group denoted by the chemical formula and the structure . It is sometimes represented by the symbol Ac (not to be confused with the element actinium). In IUPAC nomenclature, an acetyl grou ...
group, which is fully oxidized to carbon dioxide by the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-Co ...
(also known as the Krebs cycle). Every "turn" of the citric acid cycle produces two molecules of carbon dioxide, one equivalent of ATP guanosine triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It is one of the building blocks needed for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. Its structure is similar to that of the guanosine nucleoside, the only di ...
(GTP) through substrate-level phosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation is a metabolism reaction that results in the production of ATP or GTP supported by the energy released from another high-energy bond that leads to phosphorylation of ADP or GDP to ATP or GTP (note that the rea ...
catalyzed by succinyl-CoA synthetase, as succinyl-CoA is converted to succinate, three equivalents of NADH, and one equivalent of FADH2. NADH and FADH2 are recycled (to NAD+ and FAD
A fad, trend, or craze is any form of collective behavior that develops within a culture, a generation, or social group in which a group of people enthusiastically follow an impulse for a short time period.
Fads are objects or behaviors tha ...
, respectively) by oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation(UK , US : or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation, is the metabolic pathway in which Cell (biology), cells use enzymes to Redox, oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order ...
, generating additional ATP. The oxidation of NADH results in the synthesis of 2–3 equivalents of ATP, and the oxidation of one FADH2 yields between 1–2 equivalents of ATP. The majority of cellular ATP is generated by this process. Although the citric acid cycle itself does not involve molecular oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
, it is an obligately aerobic process because O2 is used to recycle the NADH and FADH2. In the absence of oxygen, the citric acid cycle ceases.
The generation of ATP by the mitochondrion from cytosolic NADH relies on the malate-aspartate shuttle (and to a lesser extent, the glycerol-phosphate shuttle) because the inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to NADH and NAD+. Instead of transferring the generated NADH, a malate dehydrogenase enzyme converts oxaloacetate
Oxaloacetic acid (also known as oxalacetic acid or OAA) is a crystalline organic compound with the chemical formula HO2CC(O)CH2CO2H. Oxaloacetic acid, in the form of its conjugate base oxaloacetate, is a metabolic intermediate in many processes ...
to malate
Malic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a dicarboxylic acid that is made by all living organisms, contributes to the sour taste of fruits, and is used as a food additive. Malic acid has two stereoisomeric forms ( ...
, which is translocated to the mitochondrial matrix. Another malate dehydrogenase-catalyzed reaction occurs in the opposite direction, producing oxaloacetate and NADH from the newly transported malate and the mitochondrion's interior store of NAD+. A transaminase converts the oxaloacetate to aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of protein ...
for transport back across the membrane and into the intermembrane space.
In oxidative phosphorylation, the passage of electrons from NADH and FADH2 through the electron transport chain releases the energy to pump proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
s out of the mitochondrial matrix and into the intermembrane space. This pumping generates a proton motive force that is the net effect of a pH gradient and an electric potential
Electric potential (also called the ''electric field potential'', potential drop, the electrostatic potential) is defined as electric potential energy per unit of electric charge. More precisely, electric potential is the amount of work (physic ...
gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Flow of protons down this potential gradient – that is, from the intermembrane space to the matrix – yields ATP by ATP synthase. Three ATP are produced per turn.
Although oxygen consumption appears fundamental for the maintenance of the proton motive force, in the event of oxygen shortage ( hypoxia), intracellular acidosis (mediated by enhanced glycolytic rates and ATP hydrolysis), contributes to mitochondrial membrane potential and directly drives ATP synthesis.
Most of the ATP synthesized in the mitochondria will be used for cellular processes in the cytosol; thus it must be exported from its site of synthesis in the mitochondrial matrix. ATP outward movement is favored by the membrane's electrochemical potential because the cytosol has a relatively positive charge compared to the relatively negative matrix. For every ATP transported out, it costs 1 H+. Producing one ATP costs about 3 H+. Therefore, making and exporting one ATP requires 4H+. The inner membrane contains an antiporter
An antiporter (also called exchanger or counter-transporter) is an integral membrane protein that uses secondary active transport to move two or more molecules in opposite directions across a phospholipid membrane. It is a type of cotransporte ...
, the ADP/ATP translocase, which is an integral membrane protein
An integral, or intrinsic, membrane protein (IMP) is a type of membrane protein that is permanently attached to the biological membrane. All transmembrane proteins can be classified as IMPs, but not all IMPs are transmembrane proteins. IMPs comp ...
used to exchange newly synthesized ATP in the matrix for ADP in the intermembrane space.
=Regulation
= The citric acid cycle is regulated mainly by the availability of key substrates, particularly the ratio of NAD+ to NADH and the concentrations ofcalcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
, inorganic phosphate, ATP, ADP, and AMP. Citrate
Citric acid is an organic compound with the formula . It is a colorless weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relati ...
– the ion that gives its name to the cycle – is a feedback inhibitor of citrate synthase
Citrate synthase ( E.C. 2.3.3.1 (previously 4.1.3.7)) is an enzyme that exists in nearly all living cells. It functions as a pace-making enzyme in the first step of the citric acid cycle (or Krebs cycle). Citrate synthase is located within euka ...
and also inhibits PFK, providing a direct link between the regulation of the citric acid cycle and glycolysis.
Beta oxidation
In the presence of air and various cofactors and enzymes, fatty acids are converted toacetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidation, o ...
. The pathway is called beta-oxidation
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta oxidation (also β-oxidation) is the Catabolism, catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA. Acetyl ...
. Each cycle of beta-oxidation shortens the fatty acid chain by two carbon atoms and produces one equivalent each of acetyl-CoA, NADH, and FADH2. The acetyl-CoA is metabolized by the citric acid cycle to generate ATP, while the NADH and FADH2 are used by oxidative phosphorylation to generate ATP. Dozens of ATP equivalents are generated by the beta-oxidation of a single long acyl chain.
=Regulation
= In oxidative phosphorylation, the key control point is the reaction catalyzed bycytochrome c oxidase
The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase or Complex IV (was , now reclassified as a translocasEC 7.1.1.9 is a large transmembrane protein complex found in bacteria, archaea, and the mitochondria of eukaryotes.
It is the last enzyme in the Cellular respir ...
, which is regulated by the availability of its substrate – the reduced form of cytochrome c. The amount of reduced cytochrome c available is directly related to the amounts of other substrates:
:
which directly implies this equation:
:
Thus, a high ratio of ADHto AD+or a high ratio of DP ito TPimply a high amount of reduced cytochrome c and a high level of cytochrome c oxidase activity. An additional level of regulation is introduced by the transport rates of ATP and NADH between the mitochondrial matrix and the cytoplasm.
Ketosis
Ketone bodies can be used as fuels, yielding 22 ATP and 2 GTP molecules per acetoacetate molecule when oxidized in the mitochondria. Ketone bodies are transported from theliver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
to other tissues, where acetoacetate and ''beta''-hydroxybutyrate can be reconverted to acetyl-CoA to produce reducing equivalents (NADH and FADH2), via the citric acid cycle. Ketone bodies cannot be used as fuel by the liver, because the liver lacks the enzyme β-ketoacyl-CoA transferase, also called thiolase. Acetoacetate in low concentrations is taken up by the liver and undergoes detoxification through the methylglyoxal pathway which ends with lactate. Acetoacetate in high concentrations is absorbed by cells other than those in the liver and enters a different pathway via 1,2-propanediol. Though the pathway follows a different series of steps requiring ATP, 1,2-propanediol can be turned into pyruvate.
Production, anaerobic conditions
Fermentation
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and organic end products. Organic molecules, such as glucose or other sugars, are catabolized and reduce ...
is the metabolism of organic compounds in the absence of air. It involves substrate-level phosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation is a metabolism reaction that results in the production of ATP or GTP supported by the energy released from another high-energy bond that leads to phosphorylation of ADP or GDP to ATP or GTP (note that the rea ...
in the absence of a respiratory electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules which transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples th ...
.
The equation for the reaction of glucose to form lactic acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has the molecular formula C3H6O3. It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as wel ...
is:
:
Anaerobic respiration is respiration in the absence of . Prokaryotes can utilize a variety of electron acceptors. These include nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
, sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
, and carbon dioxide. In anaerobic organisms and prokaryotes, different pathways result in ATP. ATP is produced in the chloroplasts of green plants in a process similar to oxidative phosphorylation, called photophosphorylation.
ATP replenishment by nucleoside diphosphate kinases
ATP can also be synthesized through several so-called "replenishment" reactions catalyzed by the enzyme families of nucleoside diphosphate kinases (NDKs), which use other nucleoside triphosphates as a high-energy phosphate donor, and the ATP:guanido-phosphotransferase family.ATP production during photosynthesis
In plants, ATP is synthesized in the thylakoid membrane of thechloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...
. The process is called photophosphorylation. The "machinery" is similar to that in mitochondria except that light energy is used to pump protons across a membrane to produce a proton-motive force. ATP synthase then ensues exactly as in oxidative phosphorylation. Some of the ATP produced in the chloroplasts is consumed in the Calvin cycle, which produces triose sugars.
ATP recycling
The total quantity of ATP in the human body is about 0.1 mol/L. The majority of ATP is recycled from ADP by the aforementioned processes. Thus, at any given time, the total amount of ATP + ADP remains fairly constant. The energy used by human cells in an adult requires the hydrolysis of 100 to 150 mol/L of ATP daily, which means a human will typically use their body weight worth of ATP over the course of the day. Each equivalent of ATP is recycled 1000–1500 times during a single day (), at approximately 9×1020 molecules/s.Biochemical functions
Cellular energy production
The conversion of ATP to ADP is the principal mechanism for energy supply in biological processes. Energy is produced in cells when the terminal phosphate group in an ATP molecule is removed from the chain to produce adenosine diphosphate (ADP) when water hydrolyzes ATP: ATP + H2O → ADP + HPO4 + H + energy However, removing a phosphate group from ADP to produce adenosine monophosphate (AMP) also produces extra energy.Intracellular signaling
ATP is involved insignal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), rece ...
by serving as substrate for kinases, enzymes that transfer phosphate groups. Kinases are the most common ATP-binding proteins. They share a small number of common folds. Phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
of a protein by a kinase can activate a cascade such as the mitogen-activated protein kinase
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of serine/threonine-specific protein kinases involved in directing cellular responses to a diverse array of stimuli, such as mitogens, osmotic stress, heat shock and proinflamma ...
cascade.
ATP is also a substrate of adenylate cyclase, most commonly in G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related ...
signal transduction pathways and is transformed to second messenger
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form of cell signaling, encompassing both first m ...
, cyclic AMP, which is involved in triggering calcium signals by the release of calcium from intracellular stores. This form of signal transduction is particularly important in brain function, although it is involved in the regulation of a multitude of other cellular processes.
DNA and RNA synthesis
ATP is one of four monomers required in the synthesis ofRNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
. The process is promoted by RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template.
Using the e ...
s. A similar process occurs in the formation of DNA, except that ATP is first converted to the deoxyribonucleotide
A deoxyribonucleotide is a nucleotide that contains deoxyribose. They are the monomeric units of the informational biopolymer, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Each deoxyribonucleotide comprises three parts: a deoxyribose sugar (monosaccharide), a ni ...
dATP. Like many condensation reactions in nature, DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all life, living organisms, acting as the most essential part of heredity, biolog ...
and DNA transcription also consume ATP.
Amino acid activation in protein synthesis
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase enzymes consume ATP in the attachment tRNA to amino acids, forming aminoacyl-tRNA complexes. Aminoacyl transferase binds AMP-amino acid to tRNA. The coupling reaction proceeds in two steps: # aa + ATP ⟶ aa-AMP + PPi # aa-AMP + tRNA ⟶ aa-tRNA + AMP The amino acid is coupled to the penultimate nucleotide at the 3′-end of the tRNA (the A in the sequence CCA) via an ester bond (roll over in illustration).ATP binding cassette transporter
Transporting chemicals out of a cell against a gradient is often associated with ATP hydrolysis. Transport is mediated by ATP binding cassette transporters. The human genome encodes 48 ABC transporters, that are used for exporting drugs, lipids, and other compounds.Extracellular signalling and neurotransmission
Cells secrete ATP to communicate with other cells in a process called purinergic signalling. ATP serves as aneurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
in many parts of the nervous system, modulates ciliary beating, affects vascular oxygen supply etc. ATP is either secreted directly across the cell membrane through channel proteins or is pumped into vesicles which then fuse with the membrane. Cells detect ATP using the purinergic receptor proteins P2X and P2Y. ATP has been shown to be a critically important signalling molecule for microglia
Microglia are a type of glia, glial cell located throughout the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system (CNS). Microglia account for about around 5–10% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as t ...
- neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
interactions in the adult brain, as well as during brain development. Furthermore, tissue-injury induced ATP-signalling is a major factor in rapid microglial phenotype changes.
Muscle contraction
ATP fuelsmuscle contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of Tension (physics), tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in musc ...
s. Muscle contractions are regulated by signaling pathways, although different muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
types being regulated by specific pathways and stimuli based on their particular function. However, in all muscle types, contraction is performed by the proteins actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
and myosin
Myosins () are a Protein family, family of motor proteins (though most often protein complexes) best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are adenosine triphosphate, ATP- ...
.
ATP is initially bound to myosin. When ATPase
ATPases (, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, ATP hydrolase, adenosine triphosphatase) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion or ...
hydrolyzes the bound ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
, myosin is positioned in a way that it can bind to actin. Myosin bound by ADP and Pi forms cross-bridges with actin and the subsequent release of ADP and Pi releases energy as the power stroke. The power stroke causes actin filament to slide past the myosin filament, shortening the muscle and causing a contraction. Another ATP molecule can then bind to myosin, releasing it from actin and allowing this process to repeat.
Protein solubility
ATP has recently been proposed to act as a biological hydrotrope and has been shown to affect proteome-wide solubility.Abiogenic origins
Acetyl phosphate (AcP), a precursor to ATP, can readily be synthesized at modest yields from thioacetate in pH 7 and 20 °C and pH 8 and 50 °C, although acetyl phosphate is less stable in warmer temperatures and alkaline conditions than in cooler and acidic to neutral conditions. It is unable to promote polymerization of ribonucleotides and amino acids and was only capable of phosphorylation of organic compounds. It was shown that it can promote aggregation and stabilization of AMP in the presence of Na+, aggregation of nucleotides could promote polymerization above 75 °C in the absence of Na+. It is possible that polymerization promoted by AcP could occur at mineral surfaces. It was shown that ADP can only be phosphorylated to ATP by AcP and other nucleoside triphosphates were not phosphorylated by AcP. This might explain why all lifeforms use ATP to drive biochemical reactions.ATP analogues
Biochemistry laboratories often use ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in ...
'' studies to explore ATP-dependent molecular processes. ATP analogs are also used in X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring th ...
to determine a protein structure
Protein structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers specifically polypeptides formed from sequences of amino acids, which are the monomers of the polymer. A single amino acid ...
in complex with ATP, often together with other substrates.
Enzyme inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its Enzyme activity, activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which Substrate (biochemistry), substrate molecules are converted ...
s of ATP-dependent enzymes such as kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
s are needed to examine the binding site
In biochemistry and molecular biology, a binding site is a region on a macromolecule such as a protein that binds to another molecule with specificity. The binding partner of the macromolecule is often referred to as a ligand. Ligands may includ ...
s and transition state
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked w ...
s involved in ATP-dependent reactions.
Most useful ATP analogs cannot be hydrolyzed as ATP would be; instead, they trap the enzyme in a structure closely related to the ATP-bound state. Adenosine 5′-(γ-thiotriphosphate) is an extremely common ATP analog in which one of the gamma-phosphate oxygens is replaced by a sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
atom; this anion is hydrolyzed at a dramatically slower rate than ATP itself and functions as an inhibitor of ATP-dependent processes. In crystallographic studies, hydrolysis transition states are modeled by the bound vanadate ion.
Caution is warranted in interpreting the results of experiments using ATP analogs, since some enzymes can hydrolyze them at appreciable rates at high concentration.
Medical use
ATP is used intravenously for some heart-related conditions.History
ATP was discovered in 1929 from muscle tissue by and Jendrassik and, independently, by Cyrus Fiske and Yellapragada Subba Rao ofHarvard Medical School
Harvard Medical School (HMS) is the medical school of Harvard University and is located in the Longwood Medical and Academic Area, Longwood Medical Area in Boston, Massachusetts. Founded in 1782, HMS is the third oldest medical school in the Un ...
, both teams competing against each other to find an assay for phosphorus.
It was proposed to be the intermediary between energy-yielding and energy-requiring reactions in cells by Fritz Albert Lipmann in 1941. He played a major role in establishing that ATP is the energy currency of a cell.
It was first synthesized in the laboratory by Alexander Todd in 1948, and he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outst ...
in 1957 partly for this work.
The 1978 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outst ...
was awarded to Peter Dennis Mitchell for the discovery of the chemiosmotic mechanism of ATP synthesis.
The 1997 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was divided, one half jointly to Paul D. Boyer and John E. Walker "for their elucidation of the enzymatic mechanism underlying the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)" and the other half to Jens C. Skou "for the first discovery of an ion-transporting enzyme, Na+, K+ -ATPase."
See also
* Adenosine-tetraphosphatase * Adenosine methylene triphosphate * ATPases * ATP test *Creatine
Creatine ( or ) is an organic compound with the nominal formula . It exists in various tautomers in solutions (among which are neutral form and various zwitterionic forms). Creatine is found in vertebrates, where it facilitates recycling of ...
* Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger, or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine tri ...
(cAMP)
* Nucleotide exchange factor
* Phosphagen
References
External links
ATP bound to proteins
in the PDB
ScienceAid: Energy ATP and Exercise
PubChem entry for Adenosine Triphosphate
KEGG entry for Adenosine Triphosphate
ATP 3D model
{{DEFAULTSORT:Adenosine phosphate3 Adenosine receptor agonists Cellular respiration Coenzymes Ergogenic aids Exercise physiology Neurotransmitters Nucleotides Phosphate esters Purinergic signalling Purines Substances discovered in the 1920s