|
Supernova Nucleosynthesis
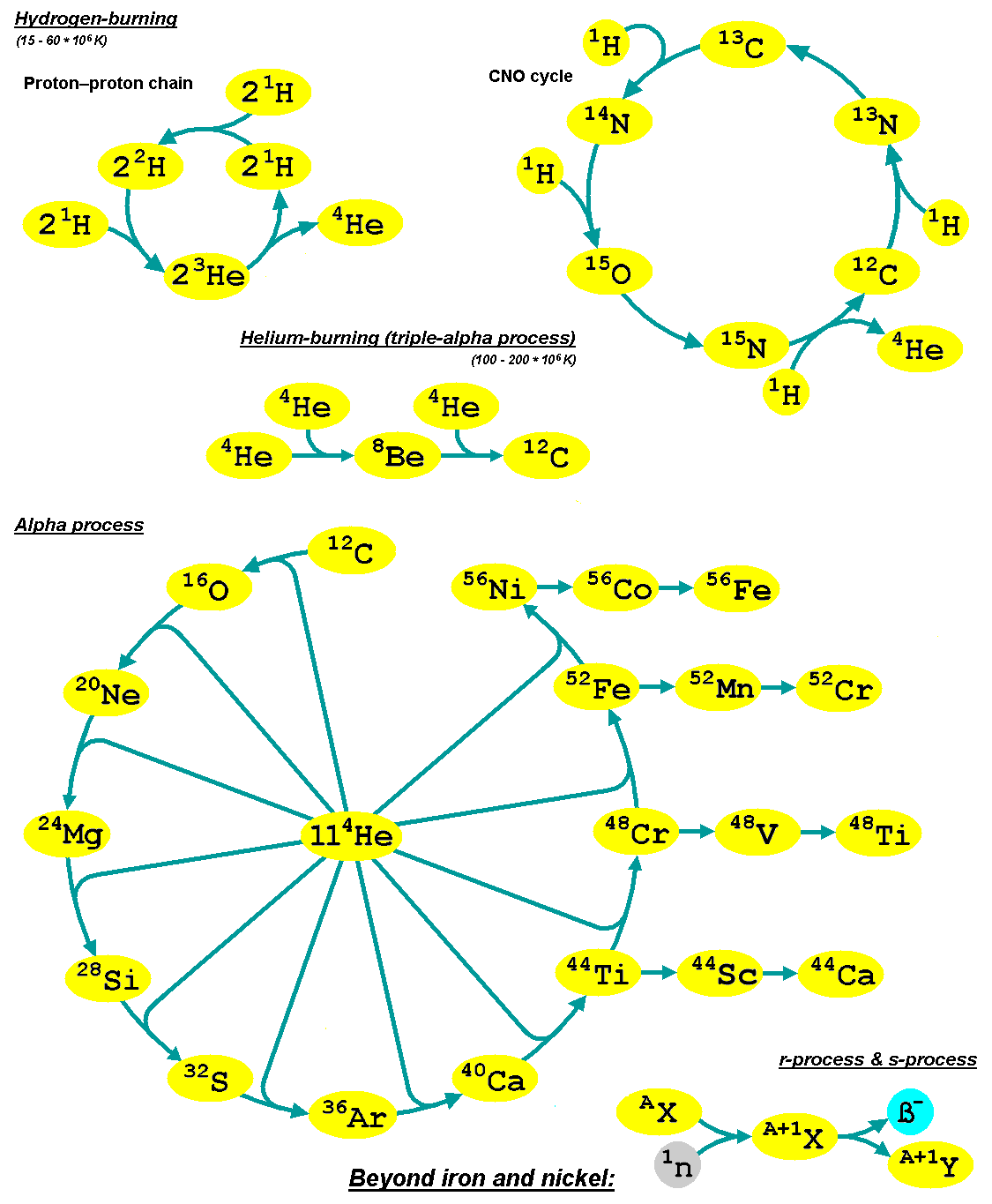
Supernova nucleosynthesis is the nucleosynthesis of chemical elements in supernova explosions. In sufficiently massive stars, the nucleosynthesis by fusion of lighter elements into heavier ones occurs during sequential hydrostatic burning processes called helium burning, carbon burning, oxygen burning, and silicon burning, in which the byproducts of one nuclear fuel become, after compressional heating, the fuel for the subsequent burning stage. In this context, the word "burning" refers to nuclear fusion and not a chemical reaction. During hydrostatic burning these fuels synthesize overwhelmingly the alpha nuclides (), nuclei composed of integer numbers of helium-4 nuclei. Initially, two helium-4 nuclei fuse into a single beryllium-8 nucleus. The addition of another helium 4 nucleus to the beryllium yields carbon-12, followed by oxygen-16, neon-20 and so on, each time adding 2 protons and 2 neutrons to the growing nucleus. A rapid final explosive burning is caused by the sud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nucleosynthesis
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons (protons and neutrons) and nuclei. According to current theories, the first nuclei were formed a few minutes after the Big Bang, through nuclear reactions in a process called Big Bang nucleosynthesis. After about 20 minutes, the universe had expanded and cooled to a point at which these high-energy collisions among nucleons ended, so only the fastest and simplest reactions occurred, leaving our universe containing hydrogen and helium. The rest is traces of other elements such as lithium and the hydrogen isotope deuterium. Nucleosynthesis in stars and their explosions later produced the variety of elements and isotopes that we have today, in a process called cosmic chemical evolution. The amounts of total mass in elements heavier than hydrogen and helium (called 'metals' by astrophysicists) remains small (few percent), so that the universe still has approximately the same composition. Stars ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carbon-burning
The carbon-burning process or carbon fusion is a set of nuclear fusion reactions that take place in the cores of massive stars (at least 4 \beginM_\odot\end at birth) that combines carbon into other elements. It requires high temperatures (> 5×108 K or 50 keV) and densities (> 3×109 kg/m3). These figures for temperature and density are only a guide. More massive stars burn their nuclear fuel more quickly, since they have to offset greater gravitational forces to stay in (approximate) hydrostatic equilibrium. That generally means higher temperatures, although lower densities, than for less massive stars. To get the right figures for a particular mass, and a particular stage of evolution, it is necessary to use a numerical stellar model computed with computer algorithms. Such models are continually being refined based on nuclear physics experiments (which measure nuclear reaction rates) and astronomical observations (which include direct observation of mass loss, detec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fred Hoyle
Sir Fred Hoyle (24 June 1915 – 20 August 2001) was an English astronomer who formulated the theory of stellar nucleosynthesis and was one of the authors of the influential B2FH paper, B2FH paper. He also held controversial stances on other scientific matters—in particular his rejection of the "Big Bang" theory (a term coined by him on BBC Radio) in favor of the "steady-state model", and his promotion of panspermia as the origin of life on Earth. He spent most of his working life at St John's College, Cambridge and served as the founding director of the Institute of Astronomy, Cambridge, Institute of Theoretical Astronomy at Cambridge. Hoyle also wrote science fiction novels, short stories and radio plays, co-created television serials, and co-authored twelve books with his son, Geoffrey Hoyle. Biography Early life Hoyle was born near Bingley in Gilstead, West Riding of Yorkshire, England. His father Ben Hoyle was a violinist and worked in the wool trade in Bradford, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gamma Process (astrophysics)
p-nuclei (''p'' stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury inclusive which cannot be produced in either the s- or the r-process. Definition The classical, ground-breaking works of Burbidge, Burbidge, Fowler and Hoyle (1957) and of A. G. W. Cameron (1957) showed how the majority of naturally occurring nuclides beyond the element iron can be made in two kinds of neutron capture processes, the s- and the r-process. Some proton-rich nuclides found in nature are not reached in these processes and therefore at least one additional process is required to synthesize them. These nuclei are called p-nuclei. Since the definition of the p-nuclei depends on the current knowledge of the s- and r-process (see also nucleosynthesis), the original list of 35 p-nuclei may be modified over the years, as indicated in the Table below. For example, it is recognized today that the abundances of 152Gd and 164Er cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Photodisintegration
Photodisintegration (also called phototransmutation, or a photonuclear reaction) is a nuclear process in which an atomic nucleus absorbs a high-energy gamma ray, enters an excited state, and immediately decays by emitting a subatomic particle. The incoming gamma ray effectively knocks one or more neutrons, protons, or an alpha particle out of the nucleus. The reactions are called (γ,n), (γ,p), and (γ,α), respectively. Photodisintegration is endothermic (energy absorbing) for atomic nuclei lighter than iron and sometimes exothermic (energy releasing) for atomic nuclei heavier than iron. Photodisintegration is responsible for the nucleosynthesis of at least some heavy, proton-rich elements via the p-process in supernovae of type Ib, Ic, or II. This causes the iron to further fuse into the heavier elements. Photodisintegration of deuterium A photon carrying 2.22 MeV or more energy can photodisintegrate an atom of deuterium: : James Chadwick and Maurice Goldhaber used this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
S-process
The slow neutron-capture process, or ''s''-process, is a series of nuclear reactions, reactions in nuclear astrophysics that occur in stars, particularly asymptotic giant branch stars. The ''s''-process is responsible for the creation (nucleosynthesis) of approximately half the Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei Heavy metal (chemical element), heavier than iron. In the ''s''-process, a seed nucleus undergoes neutron capture to form an isotope with one higher atomic mass. If the new isotope is stable nuclide, stable, a series of increases in mass can occur, but if it is unstable nucleus, unstable, then beta decay will occur, producing an element of the next higher atomic number. The process is ''slow'' (hence the name) in the sense that there is sufficient time for this radioactive decay to occur before another neutron is captured. A series of these reactions produces stable isotopes by moving along the valley of stability, valley of beta-decay stable isobars in the table of nuclides. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rp-process
The rp-process (rapid proton capture process) consists of consecutive proton captures onto seed nuclei to produce heavier elements. It is a nucleosynthesis process and, along with the ''s''-process and the ''r''-process, may be responsible for the generation of many of the heavy elements present in the universe. However, it is notably different from the other processes mentioned in that it occurs on the proton-rich side of stability as opposed to on the neutron-rich side of stability. The end point of the rp-process (the highest-mass element it can create) is not yet well established, but recent research has indicated that in neutron stars it cannot progress beyond tellurium. The rp-process is inhibited by alpha decay, which puts an upper limit on the end point at 104Te, the lightest observed alpha-decaying nuclide, and the proton drip line in light antimony isotopes. At this point, further proton captures result in prompt proton emission or alpha emission, and thus the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an electron (the proton-to-electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with a mass of approximately one Dalton (unit), dalton, are jointly referred to as ''nucleons'' (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the Atomic nucleus, nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each chemical element, element is identified by the number of protons in its nucleus, each element has its own atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
R-process
In nuclear astrophysics, the rapid neutron-capture process, also known as the ''r''-process, is a set of nuclear reactions that is responsible for nucleosynthesis, the creation of approximately half of the Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei Heavy metals, heavier than iron, the "heavy elements", with the other half produced by the p-process and s-process, ''s''-process. The ''r''-process usually synthesizes the most neutron-rich stable isotopes of each heavy element. The ''r''-process can typically synthesize the heaviest four isotopes of every heavy element; of these, the heavier two are called ''r-only nuclei'' because they are created exclusively via the ''r''-process. Abundance peaks for the ''r''-process occur near mass numbers (elements Se, Br, and Kr), (elements Te, I, and Xe) and (elements Os, Ir, and Pt). The ''r''-process entails a succession of ''rapid'' neutron captures (hence the name) by one or more heavy Seed nucleus, seed nuclei, typically beginning with nuclei in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nuclear fission in 1938, the first self-sustaining nuclear reactor (Chicago Pile-1, 1942) and the first nuclear weapon (Trinity (nuclear test), Trinity, 1945). Neutrons are found, together with a similar number of protons in the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. Atoms of a chemical element that differ only in neutron number are called isotopes. Free neutrons are produced copiously in nuclear fission and nuclear fusion, fusion. They are a primary contributor to the nucleosynthesis of chemical elements within stars through fission, fusion, and neutron capture processes. Neutron stars, formed from massive collapsing stars, consist of neutrons at the density of atomic nuclei but a total mass more than the Sun. Neutron properties and interactions ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), but different nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have similar chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is derived from the Greek roots isos (wikt:ἴσος, ἴσος "equal") and topos (wikt:τόπος, τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd (doctor), Margaret Todd in a 1913 suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy, who popularized the term. The number of protons within the atomic nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |