|
Stochastic Discount Factor
The concept of the stochastic discount factor (SDF) is used in financial economics and mathematical finance. The name derives from the price of an asset being computable by "discounting" the future cash flow \tilde_i by the stochastic factor \tilde, and then taking the expectation. This definition is of fundamental importance in asset pricing. If there are ''n'' assets with initial prices p_1, \ldots, p_n at the beginning of a period and payoffs \tilde_1, \ldots, \tilde_n at the end of the period (all ''x''s are random (stochastic) variables), then SDF is any random variable \tilde satisfying :E(\tilde\tilde_i) = p_i, \text i=1,\ldots,n. The stochastic discount factor is sometimes referred to as the pricing kernel as, if the expectation E(\tilde\,\tilde_i) is written as an integral, then \tilde can be interpreted as the kernel function in an integral transform. Other names sometimes used for the SDF are the "marginal rate of substitution" (the ratio of utility of states, when ut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Economics
Financial economics is the branch of economics characterized by a "concentration on monetary activities", in which "money of one type or another is likely to appear on ''both sides'' of a trade".William F. Sharpe"Financial Economics", in Its concern is thus the interrelation of financial variables, such as share prices, interest rates and exchange rates, as opposed to those concerning the real economy. It has two main areas of focus:Merton H. Miller, (1999). The History of Finance: An Eyewitness Account, ''Journal of Portfolio Management''. Summer 1999. asset pricing and corporate finance; the first being the perspective of providers of Financial capital, capital, i.e. investors, and the second of users of capital. It thus provides the theoretical underpinning for much of finance. The subject is concerned with "the allocation and deployment of economic resources, both spatially and across time, in an uncertain environment".See Fama and Miller (1972), ''The Theory of Finance'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of One Price
In economics, the law of one price (LOOP) states that in the absence of trade frictions (such as transport costs and tariffs), and under conditions of free competition and price flexibility (where no individual sellers or buyers have power to manipulate prices and prices can freely adjust), identical goods sold at different locations should be sold for the same price when prices are expressed in a common currency. This law is derived from the assumption of the inevitable elimination of all arbitrage. See . Overview The intuition behind the law of one price is based on the assumption that differences between prices are eliminated by market participants taking advantage of arbitrage opportunities. There are three pre-requisites underlying the law: *Absence of trade frictions *Free competition *Price flexibility. Examples In regular trade Assume different prices for a single identical good in two locations, no transport costs, and no economic barriers between the two locations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Calculus
Stochastic calculus is a branch of mathematics that operates on stochastic processes. It allows a consistent theory of integration to be defined for integrals of stochastic processes with respect to stochastic processes. This field was created and started by the Japanese people, Japanese mathematician Kiyosi Itô during World War II. The best-known stochastic process to which stochastic calculus is applied is the Wiener process (named in honor of Norbert Wiener), which is used for modeling Brownian motion as described by Louis Bachelier in 1900 and by Albert Einstein in 1905 and other physical diffusion processes in space of particles subject to random forces. Since the 1970s, the Wiener process has been widely applied in financial mathematics and economics to model the evolution in time of stock prices and bond interest rates. The main flavours of stochastic calculus are the Itô calculus and its variational relative the Malliavin calculus. For technical reasons the Itô integ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hansen–Jagannathan Bound
Hansen–Jagannathan bound is a theorem in financial economics that says that the ratio of the standard deviation of a stochastic discount factor to its mean exceeds the Sharpe ratio attained by any portfolio. This result applies, among others, the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality The Cauchy–Schwarz inequality (also called Cauchy–Bunyakovsky–Schwarz inequality) is an upper bound on the absolute value of the inner product between two vectors in an inner product space in terms of the product of the vector norms. It is .... The Hansen-Jagannathan (H-J) bound is a type of mean-variance frontier. The main contribution is that it allows us to say something about moments of the stochastic discount factor, which is unobservable, in terms of moments of returns, which can be (in principle) observed. Specifically, given the observed Sharpe ratio (say, around 0.4), the bound tells us that the SDF must be at least just as volatile. References * * External links Hansen and Jagannathan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
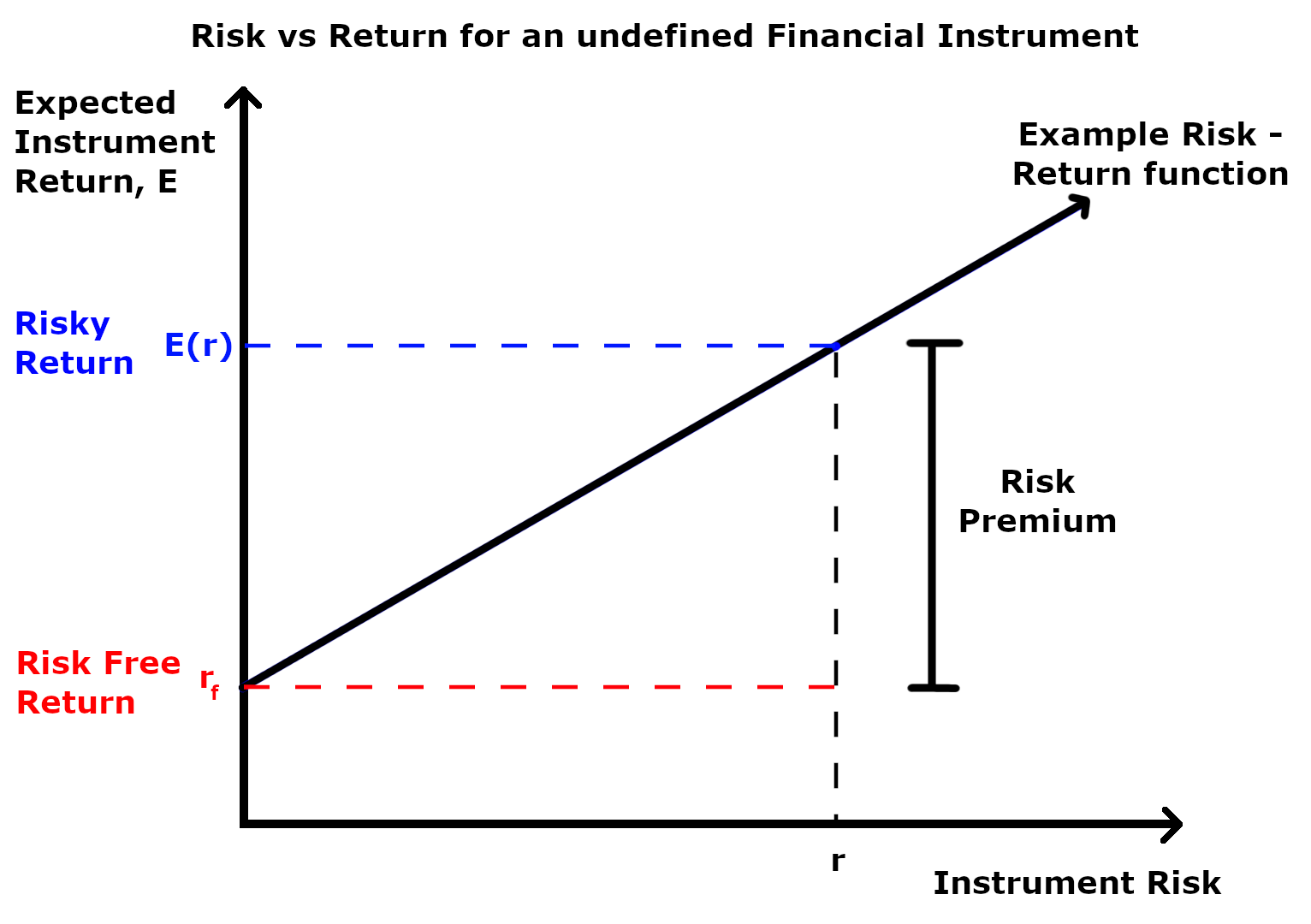
Risk Premium
A risk premium is a measure of excess return that is required by an individual to compensate being subjected to an increased level of risk. It is used widely in finance and economics, the general definition being the expected risky Rate of return, return less the Risk-free interest rate, risk-free return, as demonstrated by the formula below. Risk \ premium = E(r) - r_f Where E(r) is the risky expected rate of return and r_f is the risk-free return. The inputs for each of these variables and the ultimate interpretation of the risk premium value differs depending on the application as explained in the following sections. Regardless of the application, the market premium can be volatile as both comprising variables can be impacted independent of each other by both cyclical and abrupt changes. This means that the market premium is dynamic in nature and ever-changing. Additionally, a general observation regardless of application is that the risk premium is larger during economic do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of the joint variability of two random variables. The sign of the covariance, therefore, shows the tendency in the linear relationship between the variables. If greater values of one variable mainly correspond with greater values of the other variable, and the same holds for lesser values (that is, the variables tend to show similar behavior), the covariance is positive. In the opposite case, when greater values of one variable mainly correspond to lesser values of the other (that is, the variables tend to show opposite behavior), the covariance is negative. The magnitude of the covariance is the geometric mean of the variances that are in common for the two random variables. The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient, correlation coefficient normalizes the covariance by dividing by the geometric mean of the total variances for the two random variables. A distinction must be made between (1) the covariance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portfolio (finance)
In finance, a portfolio is a collection of investments. Definition The term "portfolio" refers to any combination of financial assets such as stocks, bonds and cash. Portfolios may be held by individual investors or managed by financial professionals, hedge funds, banks and other financial institutions. It is a generally accepted principle that a portfolio is designed according to the investor's risk tolerance, time frame and investment objectives. The monetary value of each asset may influence the risk/reward ratio of the portfolio. When determining asset allocation, the aim is to maximise the expected return and minimise the risk. This is an example of a multi-objective optimization problem: many efficient solutions are available and the preferred solution must be selected by considering a tradeoff between risk and return. In particular, a portfolio A is dominated by another portfolio A' if A' has a greater expected gain and a lesser risk than A. If no portfolio dominates A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamental Theorem Of Asset Pricing
The fundamental theorems of asset pricing (also: of arbitrage, of finance), in both financial economics and mathematical finance, provide necessary and sufficient conditions for a market to be arbitrage-free, and for a market to be complete. An arbitrage opportunity is a way of making money with no initial investment without any possibility of loss. Though arbitrage opportunities do exist briefly in real life, it has been said that any sensible market model must avoid this type of profit.Pascucci, Andrea (2011) ''PDE and Martingale Methods in Option Pricing''. Berlin: Springer-Verlag The first theorem is important in that it ensures a fundamental property of market models. Completeness is a common property of market models (for instance the Black–Scholes model). A complete market is one in which every contingent claim can be replicated. Though this property is common in models, it is not always considered desirable or realistic. Discrete markets In a discrete (i.e. finite sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Price
In financial economics, a state-price security, also called an Arrow–Debreu security (from its origins in the Arrow–Debreu model), a pure security, or a primitive security is a contract that agrees to pay one unit of a numeraire (a currency or a commodity) if a particular state occurs at a particular time in the future and pays zero numeraire in all the other states. The price of this security is the state price of this particular state of the world. The state price vector space, vector is the vector of state prices for all states. See . An Arrow security is an instrument with a fixed payout of one unit in a specified state and no payout in other states. It is a type of hypothetical asset used in the Arrow market structure model. In contrast to the Arrow-Debreu model, Arrow-Debreu market structure model, an Arrow market is a market in which the individual agents engage in trading assets at every time period t. In an Arrow-Debreu model, trading occurs only once at the begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Finance
Mathematical finance, also known as quantitative finance and financial mathematics, is a field of applied mathematics, concerned with mathematical modeling in the financial field. In general, there exist two separate branches of finance that require advanced quantitative techniques: derivatives pricing on the one hand, and risk and portfolio management on the other. Mathematical finance overlaps heavily with the fields of computational finance and financial engineering. The latter focuses on applications and modeling, often with the help of stochastic asset models, while the former focuses, in addition to analysis, on building tools of implementation for the models. Also related is quantitative investing, which relies on statistical and numerical models (and lately machine learning) as opposed to traditional fundamental analysis when managing portfolios. French mathematician Louis Bachelier's doctoral thesis, defended in 1900, is considered the first scholarly work on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Prices
In financial economics, a state-price security, also called an Arrow–Debreu security (from its origins in the Arrow–Debreu model), a pure security, or a primitive security is a contract that agrees to pay one unit of a numeraire (a currency or a commodity) if a particular state occurs at a particular time in the future and pays zero numeraire in all the other states. The price of this security is the state price of this particular state of the world. The state price vector is the vector of state prices for all states. See . An Arrow security is an instrument with a fixed payout of one unit in a specified state and no payout in other states. It is a type of hypothetical asset used in the Arrow market structure model. In contrast to the Arrow-Debreu market structure model, an Arrow market is a market in which the individual agents engage in trading assets at every time period t. In an Arrow-Debreu model, trading occurs only once at the beginning of time. An Arrow Security ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility
In economics, utility is a measure of a certain person's satisfaction from a certain state of the world. Over time, the term has been used with at least two meanings. * In a normative context, utility refers to a goal or objective that we wish to maximize, i.e., an objective function. This kind of utility bears a closer resemblance to the original utilitarian concept, developed by moral philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill. * In a descriptive context, the term refers to an ''apparent'' objective function; such a function is revealed by a person's behavior, and specifically by their preferences over lotteries, which can be any quantified choice. The relationship between these two kinds of utility functions has been a source of controversy among both economists and ethicists, with most maintaining that the two are distinct but generally related. Utility function Consider a set of alternatives among which a person has a preference ordering. A utility fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |