|
Chromosome Condensation
Chromosome condensation refers to the process by which dispersed interphase chromatin is transformed into a set of compact, rod-shaped structures during mitosis and meiosis (Figure 1). The term "chromosome condensation" has long been used in biology. However, it is now increasingly recognized that mitotic chromosome condensation proceeds through mechanisms distinct from those governing "condensation" in physical chemistry (e.g., gas-to-liquid phase transitions) or the formation of "biomolecular condensates" in cell biology. Consequently, some researchers have argued that the term "chromosome condensation" may be misleading in this context. For this reason, alternative terms such as "chromosome assembly" or "chromosome formation" are also commonly used. Processes of chromosome condensation From DNA to chromosomes A diploid human cell contains 46 chromosomes: 22 pairs of autosomes (22 × 2) and one pair of sex chromosomes (XX or XY). The total length of DNA within a single nucleus re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Envelope
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material. The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayer membranes: an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. The space between the membranes is called the perinuclear space. It is usually about 10–50 nm wide. The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. The nuclear envelope has many nuclear pores that allow materials to move between the cytosol and the nucleus. Intermediate filament proteins called lamins form a structure called the nuclear lamina on the inner aspect of the inner nuclear membrane and give structural support to the nucleus. Structure The nuclear envelope is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes, an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. These membranes are connected to each other by nuclear pores. Two sets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loop Extrusion
Loop extrusion is a major mechanism of Nuclear organization. It is a dynamic process in which structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) protein complexes progressively grow loops of DNA or chromatin. In this process, SMC complexes, such as condensin or cohesin, bind to DNA/chromatin, use ATP-driven motor activity to reel in DNA, and as a result, extrude the collected DNA as a loop. Background The organization of DNA presents a remarkable biological challenge: human DNA can reach 2 meters and is packed into the nucleus with the diameter of 5-20 μm. At the same time, the critical cell processes involve complex processes on highly compacted DNA, such as transcription, replication, recombination, DNA repair, and cell division. Loop extrusion is a key mechanism that organizes DNA into loops, enabling its efficient compaction and functional organization. For instance, ''in vitro'' experiments show that cohesin can compact DNA by 80%, while condensin achieves a remarkable 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenopus Egg Extract
''Xenopus'' egg extract is a lysate that is prepared by crushing the eggs of the African clawed frog ''Xenopus laevis''. It offers a powerful cell-free (or ''in vitro'') system for studying various cell biological processes, including cell cycle progression, nuclear transport, DNA replication and chromosome segregation. It is also called ''Xenopus'' egg cell-free system or ''Xenopus'' egg cell-free extract. History The first frog egg extract was reported in 1983 by Lohka and Masui. This pioneering work used eggs of the Northern leopard frog ''Rana pipiens'' to prepare an extract. Later, the same procedure was applied to eggs of ''Xenopus laevis'', becoming popular for studying cell cycle progression and cell cycle-dependent cellular events. Extracts derived from eggs of the Japanese common toad '' Bufo japonicus'' or of the Western clawed frog ''Xenopus tropicalis'' have also been reported. Basics of extract preparation The cell cycle of unfertilized eggs of ''X. laevis'' is arres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome Scaffold
In biology, the chromosome scaffold is the backbone that supports the structure of the chromosomes. It is composed of a group of Non-histone protein, non-histone proteins that are essential in the structure and maintenance of eukaryotic chromosomes throughout the cell cycle. These scaffold proteins are responsible for the DNA_condensation, condensation of chromatin during mitosis. Origin In the late 1970s, Ulrich K. Laemmli and colleagues discovered a backbone structure in eukaryotic chromosomes after they depleted the histone proteins. This backbone was localized along the chromosome axis, and was termed the ‘chromosome scaffold’. Proteins of the scaffold In eukaryotic organisms, the DNA of each cell (biology), cell is organized into separated chromosomes, which are composed of chromatin, a mixture of DNA and many different groups of proteins. Among them, the structural proteins (that are not histones) bind the chromatin fiber around themselves forming a long, continuous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FACT (biology)
FACT (facilitates chromatin transcription, sometimes facilitates chromatin transactions) is a heterodimeric protein complex that affects eukaryotic RNA polymerase II (Pol II) transcription elongation both in vitro and in vivo. It was discovered in 1998 as a factor purified from human cells that was essential for productive, in vitro Pol II transcription on a chromatinized DNA template. FACT consists of 140 and 80 kilodalton (kDa) subunits. The 140 kDa subunit is encoded by the human gene SUPT16H, (SPT16 in '' S. cerevisiae'') while the 80 kDa subunit is encoded by the human gene SSRP1 (POB3 in ''S. cerevisiae''). Both of these subunits in yeast affect Pol II transcription elongation, and purified human FACT binds specifically to mononucleosomes and the histone H2A/ H2B dimer, but not to the H3/ H4 tetramer (see: Nucleosome core particle) or Pol II. Co-immunoprecipitation assays with tagged recombinant proteins showed that the Spt16 subunit interacts with H2A/H2B dimers a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleoplasmin
Nucleoplasmin, the first identified molecular chaperone is a thermostable acidic protein with a pentameric structure. The protein was first isolated from Xenopus species Functions The pentameric protein participates in various significant cellular activities like sperm chromatin remodeling, nucleosome assembly, genome stability, ribosome biogenesis, DNA duplication and transcriptional regulation. During the assembly of regular nucleosomal arrays, these nucleoplasmins transfer the DNA to them by binding to the histones. This reaction requires ATP. Human proteins Humans express three members of the nucleoplasmin family: *Nucleophosmin (NPM1 Nucleophosmin (NPM), also known as nucleolar phosphoprotein B23 or numatrin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NPM1'' gene. Gene In humans, the ''NPM1'' gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 5 (5q35). The gene spans 23 kb ...) *Nucleoplasmin 2 (NPM2) *Nucleoplasmin 3 (NPM3) References Further reading * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensin
Condensins are large protein complexes that play a central role in chromosome condensation and segregation during mitosis and meiosis (Figure 1). Their subunits were originally identified as major components of mitotic chromosomes assembled in ''Xenopus'' egg extracts. Subunit composition and phylogeny Eukaryotic types Many eukaryotic cells possess two different types of condensin complexes, known as condensin I and condensin II, each of which is composed of five subunits (Figure 2). Condensins I and II share the same pair of core subunits, SMC2 and SMC4, both belonging to a large family of chromosomal ATPases, known as SMC proteins (SMC stands for Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes). Each of the complexes contains a distinct set of non-SMC regulatory subunits (a kleisin subunit and a pair of HEAT repeat subunits). Both complexes are large, having a total molecular mass of 650-700 kDa. The core subunits condensins (SMC2 and SMC4) are conserved among all eukaryotic spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
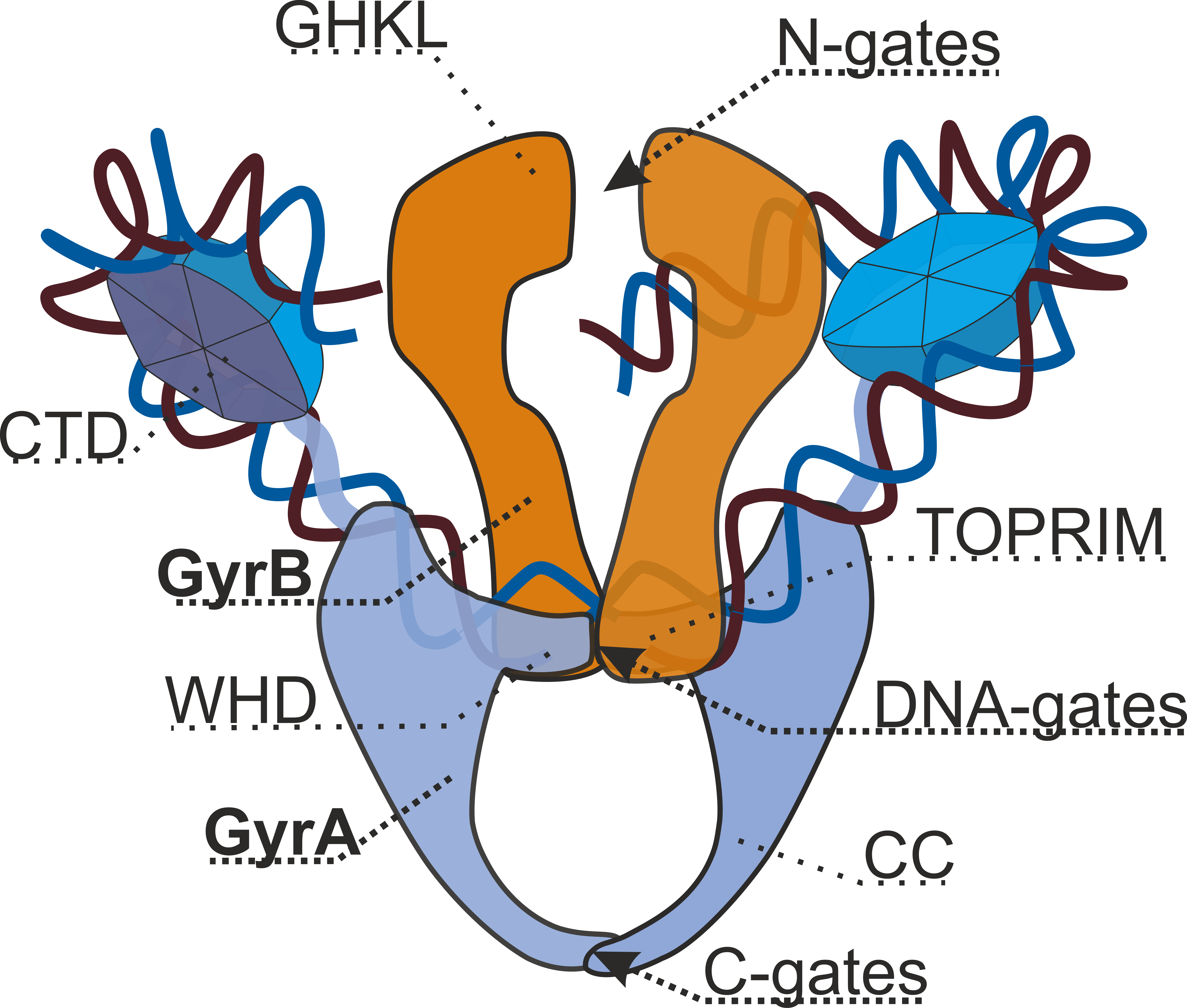
Type II Topoisomerase
Type II topoisomerases are topoisomerases that cut both strands of the DNA helix simultaneously in order to manage DNA tangles and supercoils. They use the hydrolysis of ATP, unlike Type I topoisomerase. In this process, these enzymes change the linking number of circular DNA by ±2. Topoisomerases are ubiquitous enzymes, found in all living organisms. In animals, topoisomerase II is a chemotherapy target. In prokaryotes, gyrase is an antibacterial target. Indeed, these enzymes are of interest for a wide range of effects. Function Type II topoisomerases increase or decrease the linking number of a DNA loop by 2 units, and it promotes chromosome disentanglement. For example, DNA gyrase, a type II topoisomerase observed in '' E. coli'' and most other prokaryotes, introduces negative supercoils and decreases the linking number by 2. Gyrase is also able to remove knots from the bacterial chromosome. Along with gyrase, most prokaryotes also contain a second type IIA topoisomerase, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei and in most Archaeal phyla. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn are wrapped into 30- nanometer fibers that form tightly packed chromatin. Histones prevent DNA from becoming tangled and protect it from DNA damage. In addition, histones play important roles in gene regulation and DNA replication. Without histones, unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long. For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA if completely stretched out; however, when wound about histones, this length is reduced to about 9 micrometers (0.09 mm) of 30 nm diameter chromatin fibers. There are five families of histones, which are designated H1/H5 (linker histones), H2, H3, and H4 (core histones). The nucleosome core is formed of two H2A-H2B dimers and a H3-H4 tetramer. The tight wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sperm Nucleus
A pronucleus (: pronuclei) denotes the nucleus found in either a sperm or egg cell during the process of fertilization. The sperm cell undergoes a transformation into a pronucleus after entering the egg cell but prior to the fusion of the genetic material of both the sperm and egg. In contrast, the egg cell possesses a pronucleus once it becomes haploid, not upon the arrival of the sperm cell. Haploid cells, such as sperm and egg cells in humans, carry half the number of chromosomes present in somatic cells, with 23 chromosomes compared to the 46 found in somatic cells. It is noteworthy that the male and female pronuclei do not physically merge, although their genetic material does. Instead, their membranes dissolve, eliminating any barriers between the male and female chromosomes, facilitating the combination of their chromosomes into a single diploid nucleus in the resulting embryo, which contains a complete set of 46 chromosomes. The presence of two pronuclei serves as the init ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |