|
Zoltán Szabadka
Brotli is a lossless data compression algorithm developed by Jyrki Alakuijala and Zoltán Szabadka. It uses a combination of the general-purpose LZ77 lossless compression algorithm, Huffman coding and 2nd-order context modelling. Brotli is primarily used by web servers and content delivery networks to compress HTTP content, making internet websites load faster. A successor to gzip, it is supported by all major web browsers and has become increasingly popular, as it provides better compression than gzip. History Google employees Jyrki Alakuijala and Zoltán Szabadka initially developed Brotli in 2013 to decrease the size of transmissions of WOFF web font. Alakuijala and Szabadka completed the Brotli specification during 20132016. The specification was accompanied with a reference implementation developed by two additional authors, Evgenii Kliuchnikov and Lode Vandevenne, who had previously developed Google's zopfli implementation of deflate and gzip compatible compression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Engineering Task Force
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet standard, Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster or requirements and all its participants are volunteers. Their work is usually funded by employers or other sponsors. The IETF was initially supported by the federal government of the United States but since 1993 has operated under the auspices of the Internet Society, a non-profit organization with local chapters around the world. Organization There is no membership in the IETF. Anyone can participate by signing up to a working group mailing list, or registering for an IETF meeting. The IETF operates in a bottom-up task creation mode, largely driven by working groups. Each working group normally has appointed two co-chairs (occasionally three); a charter that describes its focus; and what it is expected to produce, and when. It is open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apache License
The Apache License is a permissive free software license written by the Apache Software Foundation (ASF). It allows users to use the software for any purpose, to distribute it, to modify it, and to distribute modified versions of the software under the terms of the license, without concern for royalties. The ASF and its projects release their software products under the Apache License. The license is also used by many non-ASF projects. History Beginning in 1995, the Apache Group (later the Apache Software Foundation) released successive versions of the Apache HTTP Server. Its initial license was essentially the same as the original 4-clause BSD license, with only the names of the organizations changed, and with an additional clause forbidding derivative works from bearing the Apache name. In July 1999, the Berkeley Software Distribution accepted the argument put to it by the Free Software Foundation and retired their ''advertising clause'' (clause 3) to form the new 3-clau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zlib
zlib ( or "zeta-lib", ) is a software library used for data compression as well as a data format. zlib was written by Jean-loup Gailly and Mark Adler and is an abstraction of the DEFLATE compression algorithm used in their gzip file compression program. zlib is also a crucial component of many software platforms, including Linux, macOS, and iOS. It has also been used in gaming consoles such as the PlayStation 4, PlayStation 3, Wii U, Wii, Xbox One and Xbox 360. The first public version of Zlib, 0.9, was released on 1 May 1995 and was originally intended for use with the libpng image library. It is free software, distributed under the zlib License. Capabilities Encapsulation Raw DEFLATE compressed data (RFC 1951) are typically written with a zlib or gzip wrapper encapsulating the data, by adding a header and footer. This provides stream identification and error detection that are not provided by the raw DEFLATE data. The zlib wrapper (RFC 1950) is smaller than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Adler
Mark Adler (born 1959) is an American software engineer. He is best known for his work in the field of data compression as the author of the Adler-32 checksum function, and a co-author, together with Jean-loup Gailly, of the zlib compression library and gzip. He has contributed to Info-ZIP, and has participated in developing the Portable Network Graphics (PNG) image format. Adler was also the Spirit Cruise Mission Manager for the Mars Exploration Rover mission. Early life and education Adler was born in Miami, Florida and raised as the only child of David and Bertha Adler. Adler earned his Bachelor of Science in mathematics and Master of Science in electrical engineering degrees from the University of Florida in 1981 and 1985, respectively. In 1990, Adler earned his Ph.D. in physics from the California Institute of Technology. Career Post-doctoral After his doctorate, Adler worked for Hughes Aircraft in their Space and Communications Group, working on diverse projects includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIT License
The MIT License is a permissive software license originating at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the late 1980s. As a permissive license, it puts very few restrictions on reuse and therefore has high license compatibility. Unlike copyleft software licenses, the MIT License also permits reuse within proprietary software, provided that all copies of the software or its substantial portions include a copy of the terms of the MIT License and also a copyright notice. In 2015, the MIT License was the most popular software license on GitHub, and was still the most popular in 2025. Notable projects that use the MIT License include the X Window System, Ruby on Rails, Node.js, Lua (programming language), Lua, jQuery, .NET, Angular (web framework), Angular, and React (JavaScript library), React. License terms The MIT License has the identifier MIT in the SPDX License List. It is also known as the "#Ambiguity and variants, Expat License". It has the following terms: Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permissive Free Software License
A permissive software license, sometimes also called BSD-like or BSD-style license, is a free-software license which instead of copyleft protections, carries only minimal restrictions on how the software can be used, modified, and redistributed, usually including a warranty disclaimer. Examples include the GNU All-permissive License, MIT License, BSD licenses, Apple Public Source License and Apache license. the most popular free-software license is the permissive MIT license. Comparison table Example The following is the full text of the simple GNU All-permissive License: Definitions The Open Source Initiative defines a permissive software license as a "non-copyleft license that guarantees the freedoms to use, modify and redistribute". GitHub's ''choosealicense'' website describes the permissive MIT license as " ettingpeople do anything they want with your code as long as they provide attribution back to you and don't hold you liable." California Western School o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
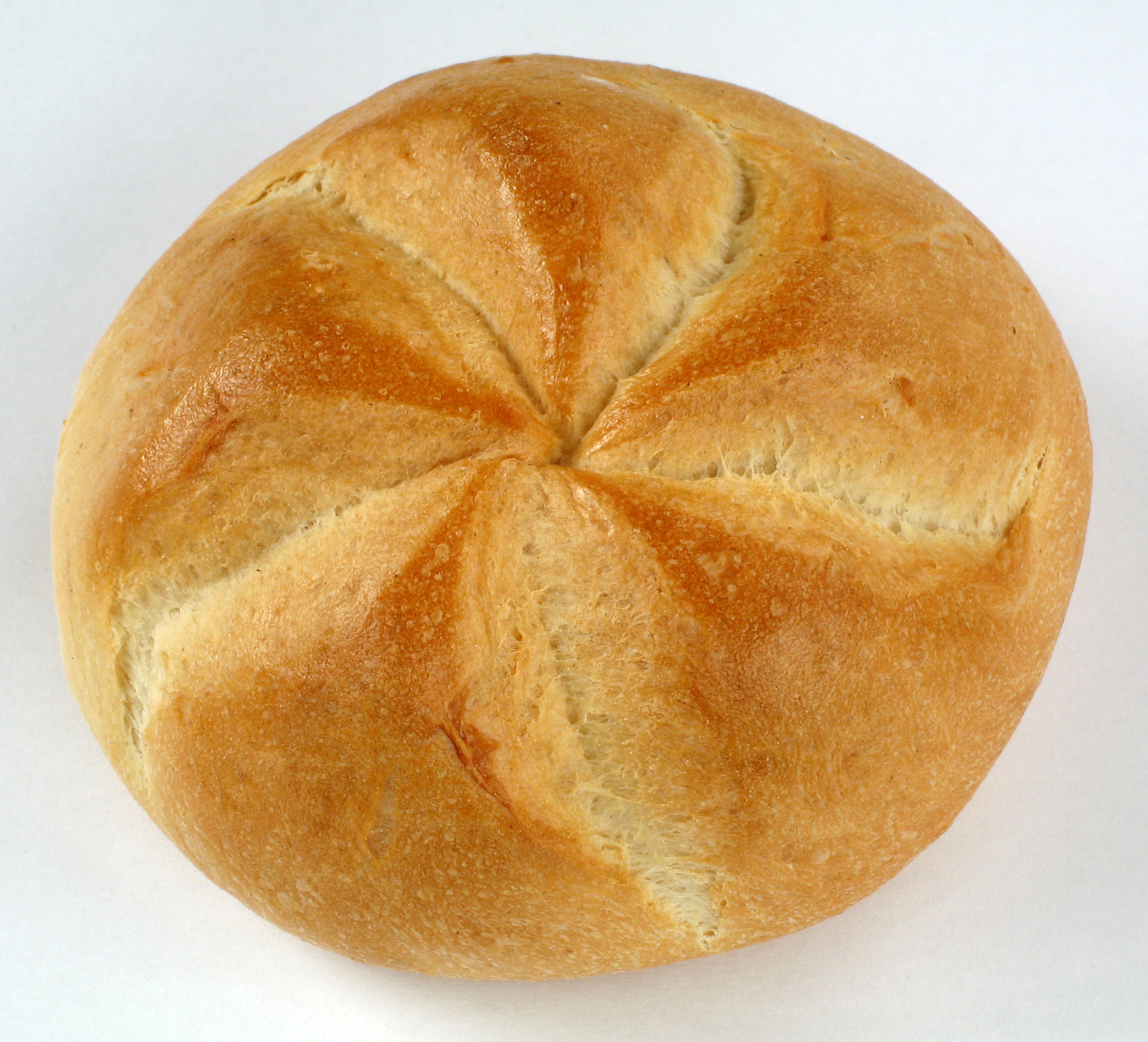
Bread Roll
A bread roll is a small, oblong individual loaf of bread served as a meal accompaniment (eaten plain or with butter). Rolls can be served and eaten whole or are also commonly cut and filled – the result of doing so is considered a '' sandwich'' in English. Europe Rolls are common throughout Europe. Even in the same languages, rolls are known by a variety of names. Some European languages have many local and dialectal terms for bread rolls. These include German language diminutives of ''Brot'' (bread) in most of western and central Germany (where they are called ''Brötchen'') and in Switzerland (where they are called ''Brötli''). Other German language terms include ''Rundstück'' ("round piece") in Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein; ''Weckerl'' or more specific ''Semmel'' in Austria, Saxony and southern Bavaria; ''Weck'' and ''Weckle'' in much of Baden-Württemberg, Franconia and Saarland; ''Schrippe'' in Berlin and parts of Brandenburg. Some of these names reappear in other E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zopf
Zopf (), Butterzopf () or Züpfe () ( in French and in Italian) is a type of Swiss, Austrian, and German bread made from white flour, milk, eggs, butter and yeast. The is typically brushed with egg yolk, egg wash, or milk before baking, lending it its golden crust. It is baked in the form of a plait and traditionally eaten on Sunday mornings. The German and French names are derived from the shape of the bread, meaning "braid" or "pigtail." Swiss Zopf differs from other braid-shaped breads such as Challah or Hefekranz by way of being unsweetened. See also * Cardamom bread * Panaret * Pulla * Vánočka ''Vánočka'' () is a plaited bread, baked in Czech Republic and Slovakia (in Slovak called ''vianočka'') traditionally at Christmas time. Such special festive Christmas bread made from white flour, either in the form of a wedge or of plait, wa ... References Braided egg breads Swiss breads Christmas food Austrian breads German breads {{Switzerland-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , ,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no #Conventions, defined orthography for any of them, many different spellings can be found. and others; ) is any of the Alemannic German, Alemannic dialects spoken in the German-speaking Switzerland, German-speaking part of Switzerland, and in some Alps, Alpine communities in Northern Italy bordering Switzerland. Occasionally, the Alemannic dialects spoken in other countries are grouped together with Swiss German as well, especially the dialects of Liechtenstein and Austrian Vorarlberg, which are closely associated to Switzerland's. Linguistically, Alemannic is divided into Low Alemannic German, Low, High Alemannic German, High and Highest Alemannic German, Highest Alemannic, varieties all of which are spoken both inside and outside Switzerland. The only exception within German-speaking Switzerland is the municipality of Samnaun, where a Bavarian language, Bavarian dialect is spoken. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Text Corpus
In linguistics and natural language processing, a corpus (: corpora) or text corpus is a dataset, consisting of natively digital and older, digitalized, language resources, either annotated or unannotated. Annotated, they have been used in corpus linguistics for statistical statistical hypothesis testing, hypothesis testing, checking occurrences or validating linguistic rules within a specific language territory. Overview A corpus may contain texts in a single language (''monolingual corpus'') or text data in multiple languages (''multilingual corpus''). In order to make the corpora more useful for doing linguistic research, they are often subjected to a process known as annotation. An example of annotating a corpus is part-of-speech tagging, or ''POS-tagging'', in which information about each word's part of speech (verb, noun, adjective, etc.) is added to the corpus in the form of ''tags''. Another example is indicating the Lemma (morphology), lemma (base) form of each word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rust (programming Language)
Rust is a General-purpose programming language, general-purpose programming language emphasizing Computer performance, performance, type safety, and Concurrency (computer science), concurrency. It enforces memory safety, meaning that all Reference (computer science), references point to valid memory. It does so without a conventional Garbage collection (computer science), garbage collector; instead, memory safety errors and data races are prevented by the "borrow checker", which tracks the object lifetime of references Compiler, at compile time. Rust does not enforce a programming paradigm, but was influenced by ideas from functional programming, including Immutable object, immutability, higher-order functions, algebraic data types, and pattern matching. It also supports object-oriented programming via structs, Enumerated type, enums, traits, and methods. It is popular for systems programming. Software developer Graydon Hoare created Rust as a personal project while working at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |