|
Yiğittaşı, Pasinler
Yiğittaşı is a (neighbourhood) in the municipality and district of Pasinler, Erzurum Province in Turkey. Its population is 294 (2022). Sos Höyük Sos Höyük is an archaeological mound that is located within the village ( :tr:Sos Höyük). The name of the mound comes from 'Sosköyü', the old name of the village. The settlement started from the Late Chalcolithic Age. The main excavations were carried out under the direction of Antonio Sagona between 1994 and 2000. The village is situated at an altitude of 1800m in the narrow Pasinler Valley, which represents a convenient route through the mountains of Eastern Anatolia to Western Turkey from Iran and the Caucasus. It is located in the highlands where the upper Araxes river and the upper Euphrates river come close together. In the late 4th millennium BC (Late Chalcolithic), Sos Höyük was initially settled by the representatives of Kura–Araxes culture, and they continued in this area through most of the Bronze Age. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
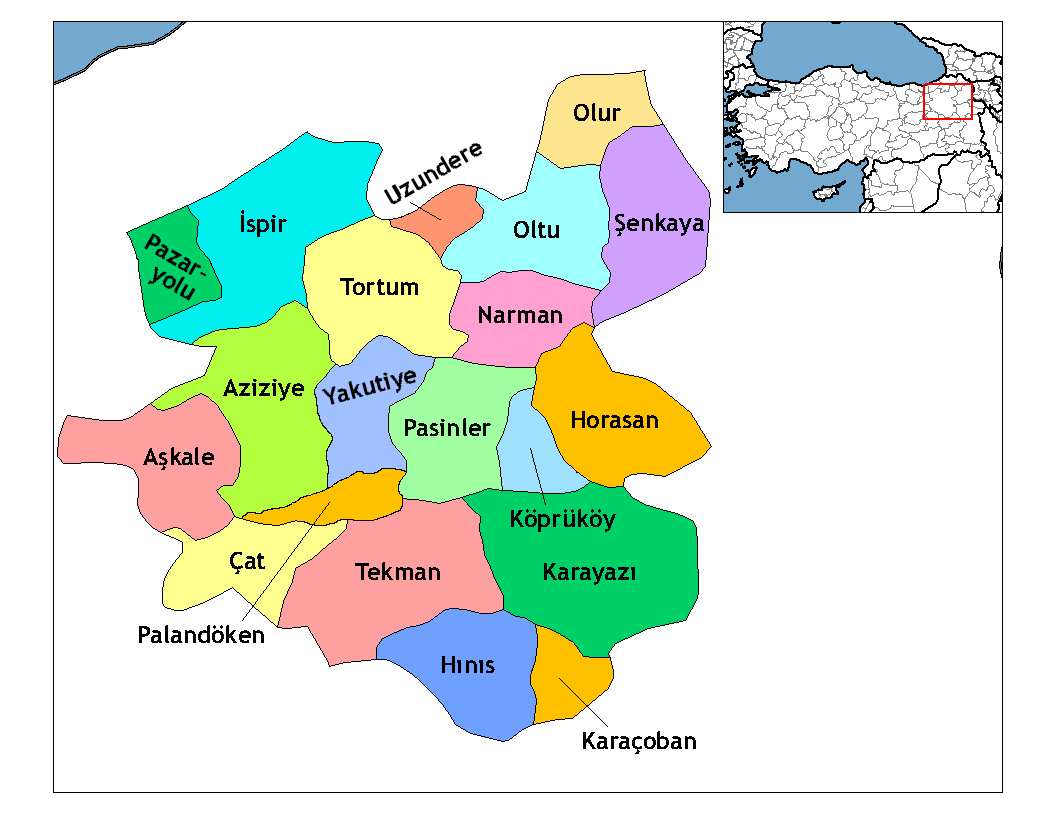
Pasinler
Pasinler or Basean (; ; ka, ბასიანი, tr; ; ; formerly Hasankale and Hesenqele 'the fortress of Hasan'), is a municipality and district of Erzurum Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,134 km2, and its population is 27,055 (2022). It lies on the Aras River. It is located east of the city of Erzurum and is the site of Hasankale Castle (sometimes called Pasinler Castle). It was the birthplace of the Ottoman poet Nef'i. The old name "Hasankale" may be based upon the Aq Qoyunlu ruler Uzun Hasan or upon Hasan the governor of the region in the 1330s or after Küçük Hasan, grandson of Coban, who attacked the town in 1340. History The first ancient kingdom that had a control of this territory was Urartu, when it was called Biani. One of the versions of the name Pasinler - it is derived from the ancient tribe called Phasians (Phazians). The name of this tribe seems to have survived in latter-day regional toponyms – Armenian ''Passen'', Greek ''Phasiane'', Georgian ''Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahalle
is an Arabic word variously translated as district, quarter, ward, or neighborhood in many parts of the Arab world, the Balkans, Western Asia, the Indian subcontinent, and nearby nations. History Historically, mahallas were autonomous social institutions built around familial ties and Islamic rituals. Today it is popularly recognised also by non-Muslims as a neighbourhood in large cities and towns. Mahallas lie at the intersection of private family life and the public sphere. Important community-level management functions are performed through mahalle solidarity, such as religious ceremonies, life-cycle rituals, resource management and conflict resolution. It is an official administrative unit in many Middle Eastern countries. The word was brought to the Balkans through Ottoman Turkish ''mahalle'', but it originates in Arabic محلة (''mähallä''), from the root meaning "to settle", "to occupy". In September 2017, a Turkish-based association referred to the historical mahalle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erzurum Province
Erzurum Province () is a province and metropolitan municipality in the Eastern Anatolia Region of Turkey. Its area is 25,006 km2, and its population is 749,754 (2022). The capital of the province is the city of Erzurum. It is the fourth largest province in all of Turkey. It is bordered by the provinces of Kars and Ağrı to the east, Muş and Bingöl to the south, Erzincan and Bayburt to the west, Rize and Artvin to the north and Ardahan to the northeast. The governor of the province is Mustafa Çiftçi, appointed in August 2023. The province has a Turkish majority. Geography The surface area of the province of Erzurum is the fourth biggest in Turkey. The majority of the province is elevated. Most plateaus are about above sea level, and the mountainous regions beyond the plateaus are and higher. Depression plains are located between the mountains and plateaus. The southern mountain ranges include the Palandöken Mountains (highest peak Büyük Ejder high) and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TÜİK
Turkish Statistical Institute (commonly known as TurkStat; or TÜİK) is the Turkish government agency commissioned with producing official statistics on Turkey, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It was founded in 1926 and headquartered in Ankara. Formerly named as the State Institute of Statistics (Devlet İstatistik Enstitüsü (DİE)), the institute was renamed as the Turkish Statistical Institute on November 18, 2005. See also * List of Turkish provinces by life expectancy References External linksOfficial website of the institute National statistical services Statistical Organizations established in 1926 Organizations based in Ankara {{Sci-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sos Höyük
SOS is a Morse code distress signal (), used internationally, originally established for maritime use. In formal notation SOS is written with an overscore line (), to indicate that the Morse code equivalents for the individual letters of "SOS" are transmitted as an unbroken sequence of three dots / three dashes / three dots, with no spaces between the letters. In International Morse Code three dots form the letter "S" and three dashes make the letter "O", so "S O S" became a common way to remember the order of the dots and dashes. IWB, VZE, 3B, and V7 form equivalent sequences, but traditionally SOS is the easiest to remember. SOS, when it was first agreed upon by the International Radio Telegraphic Convention in 1906, was merely a distinctive Morse code sequence and was initially not an abbreviation. Later a backronym was created for it in popular usage, and SOS became associated with mnemonic phrases such as "Save Our Souls" and "Save Our Ship". Moreover, due to its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio Sagona
Antonio (Tony) Giuseppe Sagona (1956 – 2017), was an archaeologist and classics professor who taught at the University of Melbourne in Victoria, Australia. Tony Sagona was born in Tripoli, Libya, on April 30, 1956. Accompanying his parents, Salvatore and Maria he migrated to Australia in 1960, initially settling in Williamstown, Victoria.Andrew Jamieso'Scholar brought the ancient world to life'Obituary, ''The Age'' 12 October 2017 Sagona received his education at Emmanuel College, Altona, completing his secondary education in 1973 and in the Humanities Department at the University of Melbourne. His PhD topic was the archaeology of the early Bronze Age Kura–Araxes culture of the Caucasus Region, which he completed in 1984. This was published as ''The Caucasian Region in the Early Bronze Age'' in 1984. Sagona tutored in the Humanities Department during his PhD candidature, and on the sudden death of his mentor and model, Bill Culican, he took over Culican's course and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araxes River
The Aras is a transboundary river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan, between Iran and both Azerbaijan and Armenia, and, finally, through Azerbaijan where it flows into the Kura river as a right tributary. It drains the south side of the Lesser Caucasus Mountains, while the Kura drains the north side of the Lesser Caucasus. The river's total length is and its watershed covers an area of . The Aras is one of the longest rivers in the Caucasus. Names In classical antiquity, the river was known to the Greeks as Araxes (). Its modern Armenian name is ''Arax'' or ''Araks'' (). Historically, it was called (, in modern pronunciation) by Armenians and its Old Georgian name is ''Rakhsi'' (). In Azerbaijani, the river's name is ''Araz''. In Persian, Kurdish and Turkish its name is (''Aras''). Geography The Aras is supported by the Kocagün stream, Dallı s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab in Iraq, which empties into the Persian Gulf. The Euphrates is the List of longest rivers of Asia, fifteenth-longest river in Asia and the longest in West Asia, at about , with a drainage area of that covers six countries. Etymology The term ''Euphrates'' derives from the Koine Greek, Greek ''Euphrátēs'' (), adapted from , itself from . The Elamite name is ultimately derived from cuneiform 𒌓𒄒𒉣; read as ''Buranun'' in Sumerian language, Sumerian and ''Purattu'' in Akkadian language, Akkadian; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word and an Akkadian word that mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kura–Araxes Culture
The Kura–Araxes culture (also named ''Kur–Araz culture, Mtkvari–Araxes culture, Early Transcaucasian culture, Shengavitian culture'') was an archaeological culture that existed from about 4000 BC until about 2000 BC, which has traditionally been regarded as the date of its end; in some locations it may have disappeared as early as 2600 or 2700 BC. The earliest evidence for this culture is found on the Ararat plain; it spread north in the Caucasus by 3000 BC. Altogether, the early Transcaucasian culture enveloped a vast area approximately 1,000 km by 500 km, and mostly encompassed the modern-day territories of the Armenia, eastern Georgia, Azerbaijan, northwestern Iran, the northeastern Caucasus, eastern Turkey, and as far as northern Syria.K. Kh. Kushnareva[The Southern Caucasus in Prehistory: Stages of Cultural and Socioeconomic Development from the Eighth to the Second Millennium B.C."UPenn Museum of Archaeology, 1 Jan. 1997. p 44Antonio Sagona, Paul Zimansky"A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transhumance
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or Nomad, nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and lower valleys in winter. Herders have a permanent home, typically in valleys. Generally only the herds travel, with a certain number of people necessary to tend them, while the main population stays at the base. In contrast, movement in plains or plateaus ''(horizontal transhumance)'' is more susceptible to disruption by climatic, economic, or political change. Traditional or fixed transhumance has occurred throughout the inhabited world, particularly Europe and western Asia. It is often important to pastoralist societies, as the dairy products of transhumance flocks and herds (milk, butter, yogurt and cheese) may form much of the diet of such populations. In many languages there are words for the higher summer pastures, and frequently these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
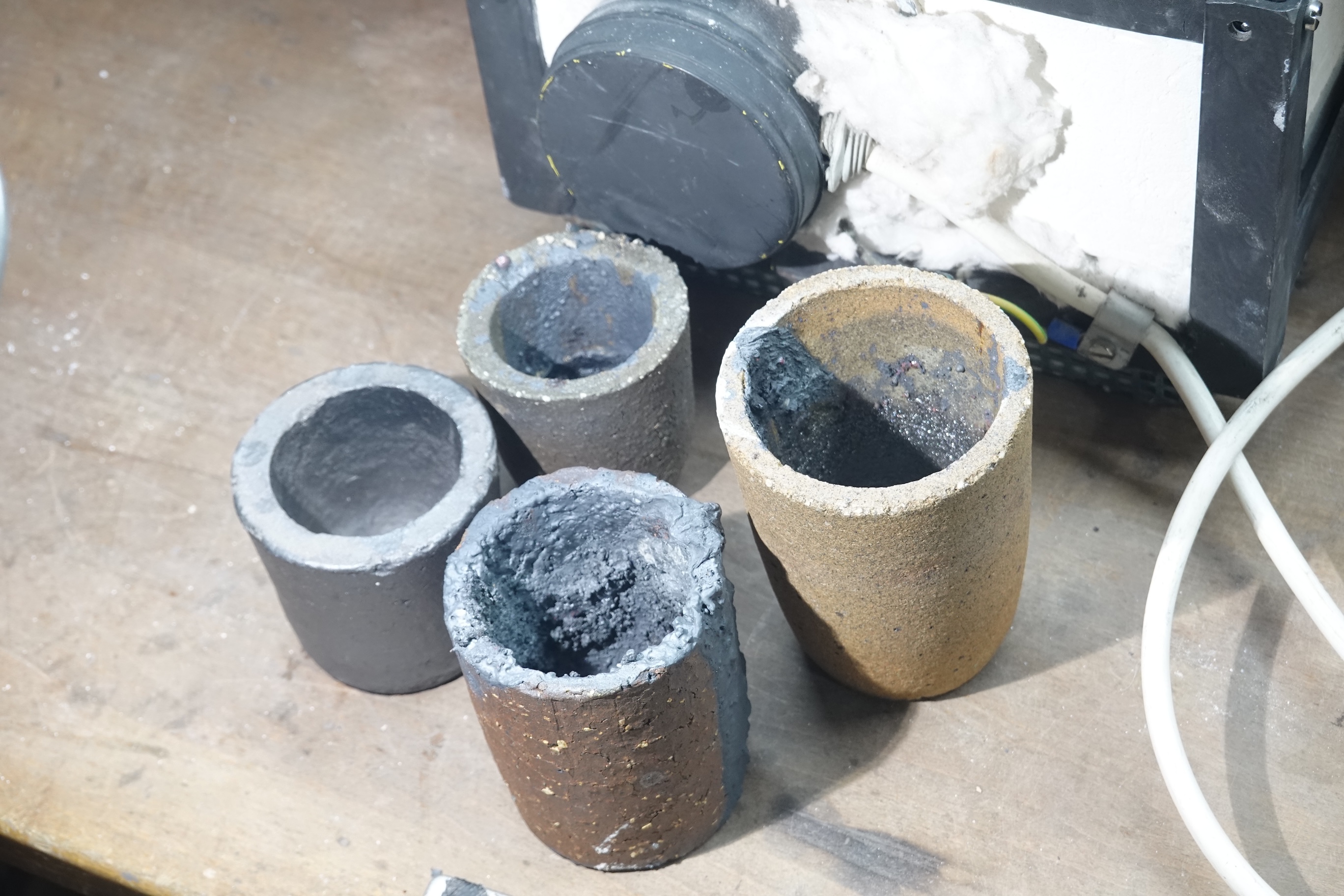
Crucible
A crucible is a container in which metals or other substances may be melted or subjected to very high temperatures. Although crucibles have historically tended to be made out of clay, they can be made from any material that withstands temperatures high enough to melt or otherwise alter its contents. History Typology and chronology The form of the crucible has varied through time, with designs reflecting the process for which they are used, as well as regional variation. The earliest crucible forms derive from the sixth/fifth millennium B.C. in Eastern Europe and Iran. Chalcolithic Crucibles used for copper smelting were generally wide shallow vessels made from clay that lacks refractory properties which is similar to the types of clay used in other ceramics of the time. During the Chalcolithic period, crucibles were heated from the top by using blowpipes.Hauptmann A., 2003, ''Developments in copper Metallurgy During the Fourth and Third Millennia B.C. at Feinan'', Jordan, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |