|
Wrocław Cathedral
The St. John the Baptist Archcathedral (, ) is the seat of the Archdiocese of Wrocław and a landmark of the city of Wrocław in Poland. The cathedral, located in the Cathedral Island, is a Gothic church with Neo-Gothic additions. The current standing cathedral is the fourth church to have been built on the site. Along with the Old Town of Wrocław, it is designated a Historic Monument of Poland. History A first church at the location of the present cathedral was built under Přemyslid rule in the mid-10th century, a fieldstone building with one nave about in length, including a distinctive transept and an apse. After the Polish conquest of Silesia and the founding of the Wrocław diocese under the Piast duke Bolesław I the Brave in 1000, this Bohemian church was replaced by a larger basilical structure with three naves, a crypt, and towers on its eastern side. The first cathedral was however soon destroyed, probably by the invading troops of Duke Bretislaus of Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathedral Island, Wrocław
The Cathedral Island (, , , ) is the oldest part of the city of Wrocław in south-western Poland. It was formerly an island (Old Polish: ) between branches of the Oder River. Today it is the city's popular tourist destination. The Cathedral Island in Wrocław is one of the few remaining places in Europe where a lamplighter lights the gas street lamps every evening. History Archaeological excavations have shown that the western part of the Cathedral Island, between the Church of St. Martin and the Holy Cross, was the first area to be inhabited. The first, wooden church (St. Martin), dating from the 10th century, was surrounded by defensive walls built on the banks of the river. The island had approximately 1,500 inhabitants at that time. The first constructions on the Cathedral Island were built in the 10th century by the Piast dynasty, and were made from wood. The first building from solid material was St. Martin's chapel, built probably at the beginning of the eleventh centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8,000,000. Silesia is split into two main subregions, Lower Silesia in the west and Upper Silesia in the east. Silesia’s culture reflects its complex history and diverse influences, blending Polish, Czech, and German elements. The region is known for its distinctive Silesian language (still spoken by a minority in Upper Silesia), richly decorated folk National costumes of Poland, costumes, hearty regional Silesian cuisine, cuisine, and a mix of Gothic, Baroque, and industrial-era Silesian architecture, architecture seen in its cities and towns. The largest city of the region is Wrocław. Silesia is situated along the Oder River, with the Sudeten Mountains extending across the southern border. The region contains many historical landmarks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
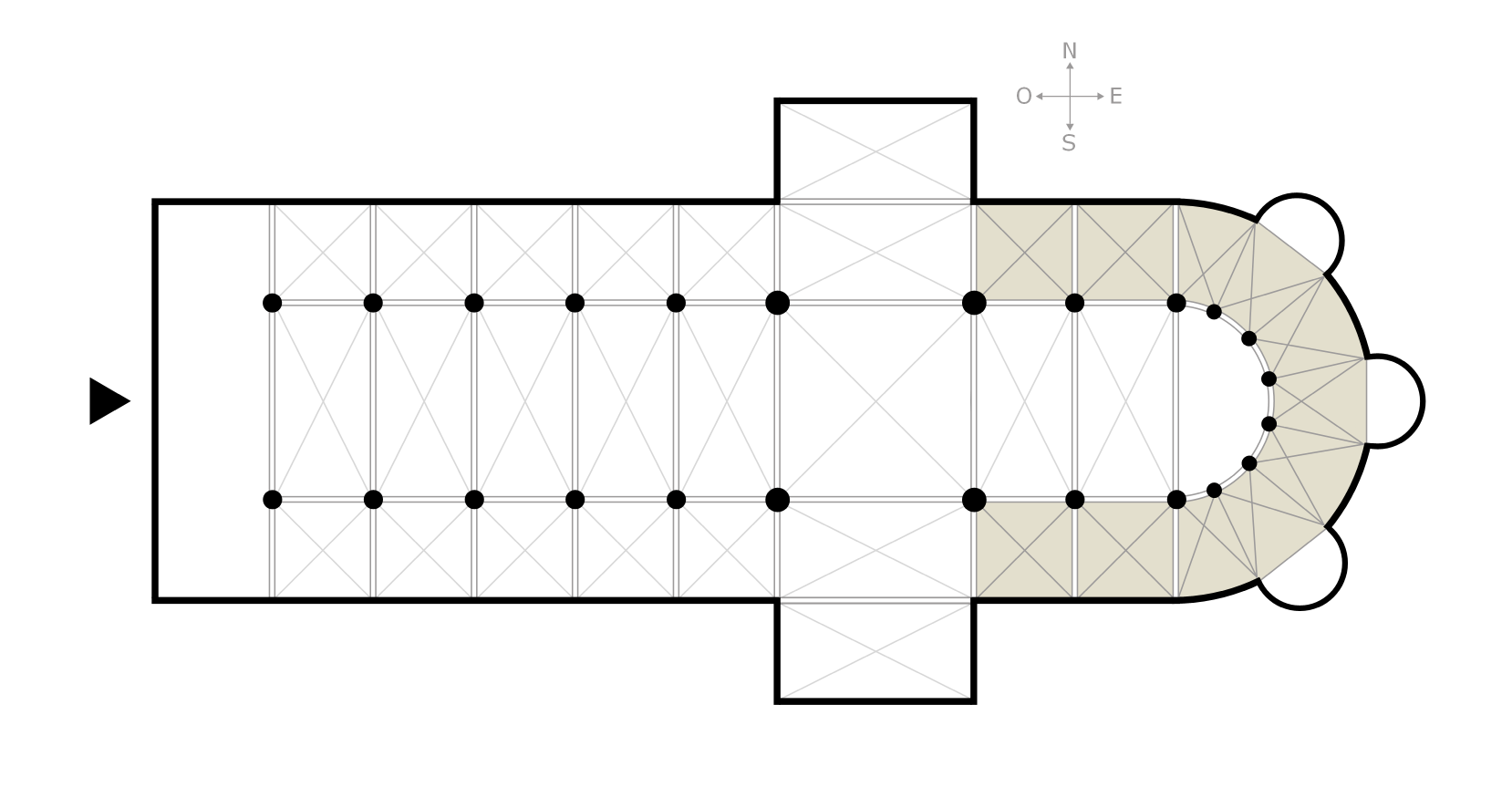
Ambulatory
The ambulatory ( 'walking place') is the covered passage around a cloister or the processional way around the east end of a cathedral or large church and behind the high altar. The first ambulatory was in France in the 11th century but by the 13th century ambulatories had been introduced in England and many English cathedrals were extended to provide an ambulatory. The same feature is often found in Indian architecture and Buddhist architecture generally, especially in older periods. Ritual circumambulation or parikrama around a stupa or cult image is important in Buddhism and Hinduism. Often the whole building was circumambulated, often many times. The Buddhist chaitya hall always allowed a path for this, and the Durga temple, Aihole (7th or 8th century) is a famous Hindu example. The term is also used to describe a garden feature in the grounds of a country house. A typical example is the one shown, which stands in the grounds of Horton Court in Gloucestershire, England. File:A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choir (architecture)
A choir, also sometimes called quire, is the area of a church or cathedral that provides seating for the clergy and church choir. It is in the western part of the chancel, between the nave and the sanctuary, which houses the altar and Church tabernacle. In larger medieval churches it contained choir-stalls, seating aligned with the side of the church, so at right-angles to the seating for the congregation in the nave. Smaller medieval churches may not have a choir in the architectural sense at all, and they are often lacking in churches built by all denominations after the Protestant Reformation, though the Gothic Revival revived them as a distinct feature. As an architectural term "choir" remains distinct from the actual location of any singing choir – these may be located in various places, and often sing from a choir-loft, often over the door at the liturgical western end. In modern churches, the choir may be located centrally behind the altar, or the pulpit. The place w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brick Gothic
Brick Gothic (, , ) is a specific style of Gothic architecture common in Baltic region, Northeast and Central Europe especially in the regions in and around the Baltic Sea, which do not have resources of standing rock (though Glacial erratic, glacial boulders are sometimes available). The buildings are essentially built using bricks. Buildings classified as Brick Gothic (using a strict definition of the architectural style based on the geographic location) are found in Belgium (and the very north of France), Netherlands, Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Kaliningrad oblast, Kaliningrad (former East Prussia), Switzerland, Denmark, Sweden and Finland. As the use of baked red brick arrived in Northwestern and Central Europe in the 12th century, the oldest such buildings are classified as the Brick Romanesque. In the 16th century, Brick Gothic was superseded by Brick Renaissance architecture. Brick Gothic is marked by lack of figurative architectural sculpture, widespr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Mongol Invasion Of Poland
The Mongol invasion of Poland from late 1240 to 1241 culminated in the Battle of Legnica, where the Mongols defeated an alliance which included forces from Testament of Bolesław III Wrymouth, fragmented Poland and their allies, led by Henry II the Pious, the Duke of Silesia and High Duke of Poland. The first invasion's intention was to secure the flank of the main Mongolian army attacking the Kingdom of Hungary. The Mongols neutralized any potential help to King Béla IV of Hungary, Béla IV being provided by the Poles or any military orders. Background The Mongol invasion of Europe, Mongols invaded Europe with three armies. One of the three armies was tasked with distracting Poland, before joining the main Mongol force invading Hungary. The Mongol general in charge, Subutai, did not want the Polish forces to be able to threaten his flank during the primary invasion of Hungary. Thus, the Mongol goal was to use a small detachment to prevent the Poles from assisting Hungary un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter (bishop Of Wrocław)
Walter was Bishop of Wrocław, Poland between 1149 and 1169. Little is known about his origins, career, or his episcopal work. He was a Walloon from the area of Namur. He came to Poland with his brother Aleksander of Malonne, who was appointed Bishop of Płock. During Walter's tenure as bishop, the Premonstratensians founded the St. Martin church, he also dedicated the St. Mary church, undertook some construction at Wrocław Cathedral The St. John the Baptist Archcathedral (, ) is the seat of the Archdiocese of Wrocław and a landmark of the city of Wrocław in Poland. The cathedral, located in the Cathedral Island, is a Gothic church with Neo-Gothic additions. The current ... and the castle in Wleń was built (1155). Bishops of Wrocław 12th-century Roman Catholic bishops in Poland People from Namur (province) Walloon emigrants {{Poland-bishop-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Płock Cathedral
Płock Cathedral (), or the Cathedral of the Blessed Virgin Mary of Masovia, is a Roman Catholic cathedral in the city of Płock, in central Poland. It is an example of 12th-century Romanesque architecture and is the oldest and most important historical monument in the city, which contains the tombs of several Polish monarchs. It is listed as a Historic Monument of Poland. History The bishopric in Płock was founded about 1075. The first definite reference to the cathedral is in 1102, when Władysław I Herman was buried there. The present Romanesque cathedral was built after 1129 by prince Bolesław III and Bishop Aleksander of Malonne. This was a rebuilding following a fire and took from 1136 until 1144. It was consecrated in 1144 as the Church of the Blessed Virgin Mary. The original bronze doors of the Romanesque cathedral (now in Velikiy Novgorod) have figurative bas-reliefs depicting the verses of the so-called "Roman Confession of Faith", and the figure of Alexander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casimir I The Restorer
Casimir I the Restorer (; 25 July 1016 – 19 March 1058), a member of the Piast dynasty, was the duke of Poland from 1040 until his death. Casimir was the son of Mieszko II Lambert and Richeza of Lotharingia. He is known as the Restorer because he managed to reunite parts of the Kingdom of Poland after a period of turmoil. He reincorporated Masovia and conquered Silesia and Pomerania. However, he failed to crown himself King of Poland, mainly because of internal and external threats to his rule. Biography Early years Relatively little is known of Casimir's early life. He must have spent his childhood at the royal court of Poland in Gniezno. In order to acquire a proper education, he was sent to one of the Polish monasteries in 1026. According to some older sources he initially wanted to have a career in the Church (it is probable that he held the post of oblate) and even asked for a dispensation to become a monk. This hypothesis, however, is not supported by modern historians. Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanesque Architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe that was predominant in the 11th and 12th centuries. The style eventually developed into the Gothic style with the shape of the arches providing a simple distinction: the Romanesque is characterized by semicircular arches, while the Gothic is marked by the pointed arches. The Romanesque emerged nearly simultaneously in multiple countries of Western Europe; its examples can be found across the continent, making it the first pan-European architectural style since Imperial Roman architecture. Similarly to Gothic, the name of the style was transferred onto the contemporary Romanesque art. Combining features of ancient Roman and Byzantine buildings and other local traditions, Romanesque architecture is known by its massive quality, thick walls, round arches, sturdy pillars, barrel vaults, large towers and decorative arcading. Each building has clearly defined forms, frequently of very regular, symmetrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bretislaus I, Duke Of Bohemia
Bretislav I (; 1002/1005 – 10 January 1055), known as the "Bohemian Achilles", of the Přemyslid dynasty, was Duke of Bohemia from 1034 until his death in 1055. Youth Bretislav was the son of Duke Oldřich and his low-born concubine Božena. As an illegitimate son who could not obtain a desirable wife by conventional means, he chose to kidnap Judith of Schweinfurt, a daughter of the Bavarian noble Henry of Schweinfurt, Margrave of Nordgau, in 1019 at Schweinfurt, and marry her. During his father's reign, in 1019 or 1029, Bretislav took back Moravia from Poland. About 1031, he invaded Hungary in order to prevent its expansion under king Stephen. The partition of Bohemia between Oldřich and his brother Jaromír in 1034 was probably the reason why Bretislav fled beyond the Bohemian border, only to come back to take the throne after Jaromír's abdication. Raid into Poland In 1035, Bretislav helped Holy Roman Emperor Conrad II in his war against the Lusatians. In 1039, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crypt
A crypt (from Greek κρύπτη (kryptē) ''wikt:crypta#Latin, crypta'' "Burial vault (tomb), vault") is a stone chamber beneath the floor of a church or other building. It typically contains coffins, Sarcophagus, sarcophagi, or Relic, religious relics. Originally, crypts were typically found below the main apse of a church, such as at the Abbey of Saint-Germain en Auxerre, but were later located beneath chancel, naves and transepts as well. Occasionally churches were raised high to accommodate a crypt at the ground level, such as St. Michael's Church, Hildesheim, St Michael's Church in Hildesheim, Germany. Etymology The word "crypt" developed as an alternative form of the Latin "vault" as it was carried over into Late Latin, and came to refer to the ritual rooms found underneath church buildings. It also served as a Bank vault, vault for storing important and/or sacred items. The word "crypta", however, is also the female form of ''crypto'' "hidden". The earliest known origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |