|
Waterloo Town Hall, Merseyside
Waterloo Town Hall, also known as Crosby Town Hall (from 1937 to 1974), is a municipal building in Great George's Road in Waterloo, Merseyside, England. The building, which was the headquarters of Waterloo Urban District Council from 1863 to 1937 and then of Crosby Borough Council from 1937 to 1974, is a Grade II listed building. History In anticipation of the formation of the new urban district of Waterloo with Seaforth, which was formed out of Litherland in 1863, civic leaders decided to procure a dedicated town hall: the site they selected was open land just south of Waterloo railway station. The building, which was designed in the Italianate style by the council surveyor, F. S. Spencer Yates, opened in 1862. The design involved a symmetrical main frontage with three bays facing onto Great George's Road; the central section featured a portico with Tuscan order columns supporting a frieze with triglyphs; there was a stained glass pedimented window on the first floor, flanked b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterloo, Merseyside
Waterloo is an area of the Metropolitan Borough of Sefton, in Merseyside, England. Along with Seaforth the two localities make up the Sefton Ward of Church. The area is bordered by Crosby to the north, Seaforth to the south, the Rimrose Valley country park to the east, and to the west the Crosby Beach and Crosby Coastal Park. Crosby Beach begins in Waterloo at the Crosby Marine Park and stretches 3 miles up to Hightown and is the location of Antony Gormley's ''Another Place''. Waterloo is home to The Plaza Community Cinema, an award-winning volunteer ran cinema and host of local community public events. The area is connected to Liverpool in the south and Southport to the north by Merseyrail Northern line at Waterloo railway station. History Waterloo was historically part of Lancashire and originally an area of Crosby, named Crosby Seabank. At that time it consisted mostly of cottages, the beach front, sand-hills and fields. The area grew in popularity with wealthy visitors fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentil
A dentil (from Lat. ''dens'', a tooth) is a small block used as a repeating ornament in the bedmould of a cornice. Dentils are found in ancient Greek and Roman architecture, and also in later styles such as Neoclassical, Federal, Georgian Revival, Greek Revival, Renaissance Revival, Second Empire, and Beaux-Arts architecture. Dentillation refers to use of a course of dentils. History Origin The Roman architect Vitruvius (iv. 2) states that the dentil represents the end of a rafter (''asser''). It occurs in its most pronounced form in the Ionic temples of Asia Minor, the Lycian tombs and the porticoes and tombs of Persia, where it clearly represents the reproduction in stone of timber construction. The earliest example is found carved into the rock of the tomb of Darius, c. 500 BC, reproducing the portico of his palace. Its first employment in Athens is in the cornice of the caryatid portico of the Erechtheum (480 BC). When subsequently introduced into the bed-mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City And Town Halls In Merseyside
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Buildings Completed In 1862
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The major types of political systems in the modern era are democracies, monarchies, and authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and mixed gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Buildings In Great Crosby
Great Crosby, or Crosby, Merseyside, Crosby, is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Sefton in Merseyside, England. It contains 100 buildings that are recorded in the National Heritage List for England as designated listed buildings. Of these, two are listed at Grade II*, the middle of the three grades, and the others are at Grade II, the lowest grade. The list includes listed buildings in the districts of Seaforth, Merseyside, Seaforth and Waterloo, Merseyside, Waterloo, but not those in the districts of Blundellsands and Little Crosby. The area developed with the arrival of the railway in the middle of the 19th century, when the hamlet of Crosby Seabank was replaced by housing for the middle class. Most of the listed buildings are substantial private houses, many of them in the terraces of Beach Lawn, Adelaide Terrace, Marine Crescent, and Marine Terrace. The other listed buildings include churches and associated structures, schools, public buildings, publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bootle Town Hall
Bootle Town Hall is a municipal building in Oriel Road in Bootle, Merseyside, England. The building, which is the headquarters of Sefton Council, is a Grade II listed building. History After significant population growth in the later half of the 19th century, largely associated with Irish immigration attracted by work at the Liverpool docks, and following the incorporation of Bootle-cum-Linacre as a municipal borough in 1868, civic leaders decided to procure a dedicated town hall: the site they selected was open land north of Baliol Road. The foundation stone for the new building was laid by the mayor, John McArthur, on 8 July 1880. It was designed by John Johnson in the Renaissance style and was officially opened by the mayor, Alderman William Poulson, on 10 April 1882. The design involved an asymmetrical main frontage with eight bays facing onto Oriel Road; the left hand bay featured a large round headed window on the first floor with a pediment above, while the second bay fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atkinson Art Gallery And Library
The Atkinson is a building on the east side of Lord Street extending round the corner into Eastbank Street, Southport, Sefton, Merseyside, England. The building is a combination of two former buildings, the original Atkinson Art Gallery and Library that opened in 1878, and the adjacent Manchester and Liverpool District Bank that was built in 1879. These were combined in 1923–24 and the interiors have been integrated. The original building is in Neoclassical style, and the former bank is in Renaissance style. The art gallery and library has been integrated with the Southport Arts Centre and is now known as The Atkinson. The two former buildings are each recorded in the National Heritage List for England as designated Grade II listed buildings. History The Atkinson was built following a donation of £6,000 in 1875 by William Atkinson, a cotton manufacturer from Knaresborough, North Yorkshire, and a frequent visitor to Southport. The building was designed by Waddin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefton Council
Sefton Council is the governing body for the Metropolitan Borough of Sefton in the county of Merseyside, north-western England. The council was under no overall control from the 1980s until 2012 when the Labour Party took control. It is a constituent council of Liverpool City Region Combined Authority. History Sefton Council was created by the local government reorganisation of 1974, which created a two-tier system of government in the United Kingdom. It was a metropolitan district of the metropolitan county of Merseyside. Until 1986, the five metropolitan borough councils of Merseyside shared power with the central Merseyside County Council, but this was later abolished and its functions devolved solely to its districts. As a result, the borough is effectively a unitary authority within the ceremonial county of Merseyside. Sefton Council is not directly responsible for transport, waste-disposal and emergency services - these are administered by joint-boards of the five ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, around the top edge of a pedestal, or along the top of an interior wall. A simple cornice may be formed just with a crown, as in crown moulding atop an interior wall or above kitchen cabinets or a bookcase. A projecting cornice on a building has the function of throwing rainwater free of its walls. In residential building practice, this function is handled by projecting gable ends, roof eaves and gutters. However, house eaves may also be called "cornices" if they are finished with decorative moulding. In this sense, while most cornices are also eaves (overhanging the sides of the building), not all eaves are usually considered cornices. Eaves are primarily functional and not necessarily decorative, while cornices have a decorative aspect. A building's project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italianate Architecture
The Italianate style was a distinct 19th-century phase in the history of Classical architecture. Like Palladianism and Neoclassicism, the Italianate style drew its inspiration from the models and architectural vocabulary of 16th-century Italian Renaissance architecture, synthesising these with picturesque aesthetics. The style of architecture that was thus created, though also characterised as "Neo-Renaissance", was essentially of its own time. "The backward look transforms its object," Siegfried Giedion wrote of historicist architectural styles; "every spectator at every period—at every moment, indeed—inevitably transforms the past according to his own nature." The Italianate style was first developed in Britain in about 1802 by John Nash, with the construction of Cronkhill in Shropshire. This small country house is generally accepted to be the first Italianate villa in England, from which is derived the Italianate architecture of the late Regency and early Victorian e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
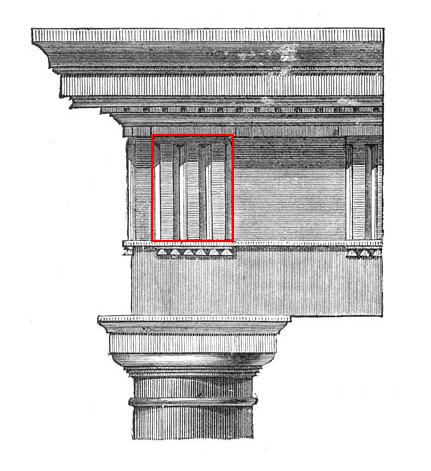
Triglyph
Triglyph is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture, so called because of the angular channels in them. The rectangular recessed spaces between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze are called metopes. The raised spaces between the channels themselves (within a triglyph) are called ''femur'' in Latin or ''meros'' in Greek. In the strict tradition of classical architecture, a set of guttae, the six triangular "pegs" below, always go with a triglyph above (and vice versa), and the pair of features are only found in entablatures of buildings using the Doric order. The absence of the pair effectively converts a building from being in the Doric order to being in the Tuscan order. The triglyph is largely thought to be a tectonic and skeuomorphic representation in stone of the wooden beam ends of the typical primitive hut, as described by Vitruvius and Renaissance writers. The wooden beams were notched in three separate pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frieze
In architecture, the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic or Doric order, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Paterae are also usually used to decorate friezes. Even when neither columns nor pilasters are expressed, on an astylar wall it lies upon the architrave ("main beam") and is capped by the moldings of the cornice. A frieze can be found on many Greek and Roman buildings, the Parthenon Frieze being the most famous, and perhaps the most elaborate. This style is typical for the Persians. In interiors, the frieze of a room is the section of wall above the picture rail and under the crown moldings or cornice. By extension, a frieze is a long stretch of painted, sculpted or even calligraphic decoration in such a position, normally above eye-level. Frieze decorations may depict scenes in a sequence of discrete panels. The material of which the frieze is made of may be plasterwork, carved wood or other decorative me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)