|
Vršac Triptych
''Sowing and Harvesting and Market'', popularly referred to as the ''Vršac triptych'', is a three-panel oil painting by the Serbian Realism (art movement), realist Paja Jovanović. Painted around 1895, it shows the everyday interactions of the inhabitants of Vršac, a multi-ethnic and multi-religious town in the Banat region of Austria-Hungary of which Jovanović was a native. The painting was commissioned by the Vršac city council in 1895 for the following year's Budapest Millennium Exhibition. The triptych's centre panel measures and the two side panels measure each. The left panel is a market scene, the centre panel shows peasants harvesting grapes from a row of vines and the one to the right is an image of a farmer sharpening his scythe as two others labour in the background. The triptych was originally intended to be displayed alongside another one of Jovanović's paintings, ''Migration of the Serbs (painting), Migration of the Serbs'', which had been commissioned by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
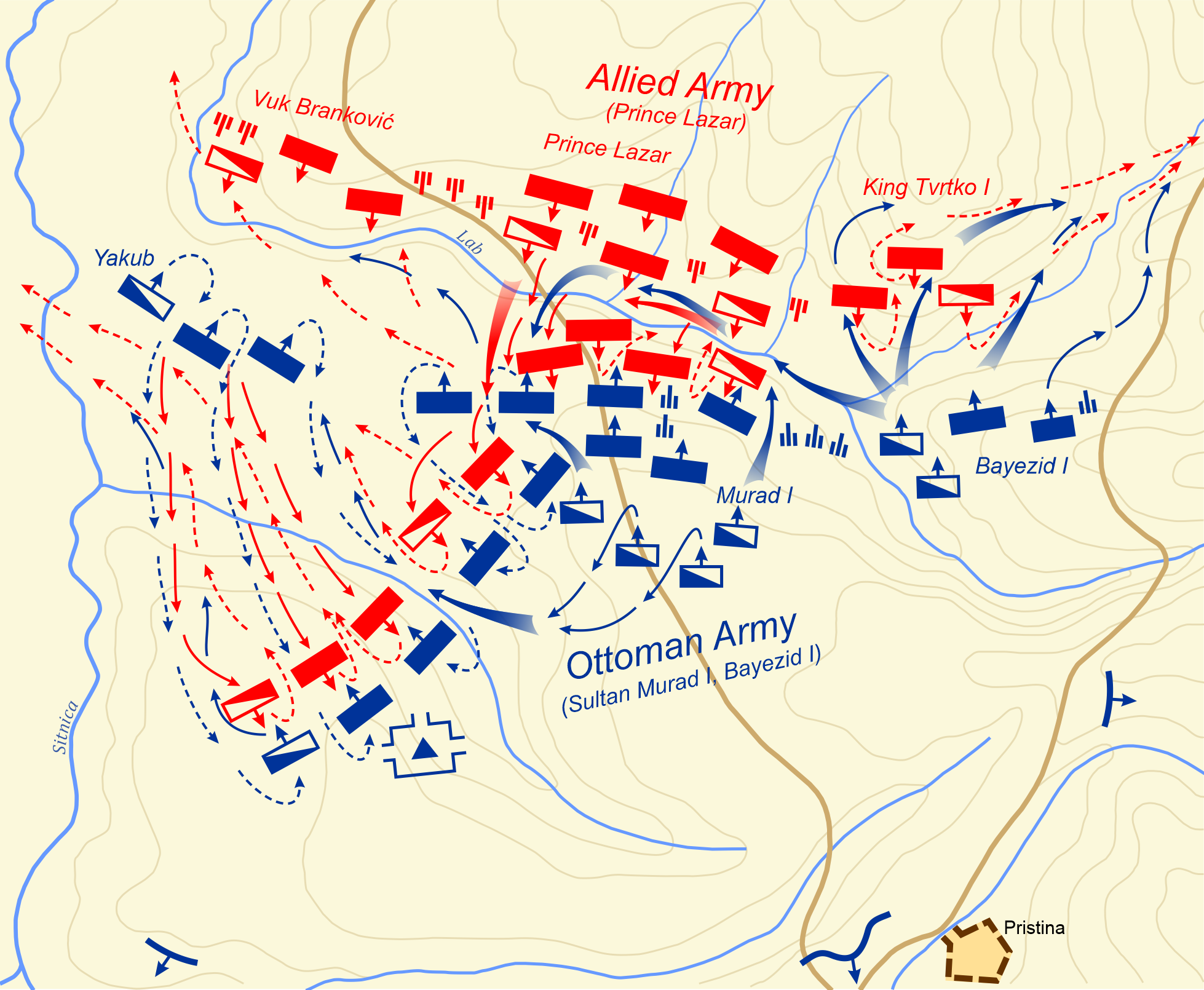
Battle Of Kosovo
The Battle of Kosovo took place on 15 June 1389 between an army led by the Serbian Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović and an invading army of the Ottoman Empire under the command of Sultan Murad I. It was one of the largest battles of the Late Middle Ages. The battle was fought on the Kosovo field in the territory ruled by Serbian nobleman Vuk Branković, in what is today Kosovo, about northwest of the modern city of Pristina. The army under Prince Lazar consisted mostly of his own troops, a contingent led by Branković, and a contingent sent from Bosnia by King Tvrtko I, commanded by Vlatko Vuković. Additionally, Lazar was also supported by a Christian coalition from various European ethnic groups. Prince Lazar was the ruler of Moravian Serbia and the most powerful among the Serbian regional lords of the time, while Branković ruled the District of Branković and other areas, recognizing Lazar as his overlord. Reliable historical accounts of the battle are scarce. The bulk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Takovo Uprising
''The Takovo Uprising'' is the title of two nearly identical oil paintings by the Serbian realist Paja Jovanović. They depict rebel leader Miloš Obrenović inciting his countrymen against the Ottoman Empire and initiating the Second Serbian Uprising. The first version, , was painted in Paris in 1894 and first exhibited in Belgrade the following year. The second, measuring , was composed specifically for King Alexander, who had also commissioned the first version. As part of his preparations, Jovanović studied authentic costumes and armaments from the time of the uprising, visited Takovo and sketched the church and large tree under which Obrenović incited the people. Jovanović also studied the facial features of locals and sketched them, and so some of their faces appear in the painting. Lithographic reproductions of the painting were soon made widely available, and distributed by the Serbian Ministry of Education in secondary schools, teachers' schools, and seminaries, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Painting
History painting is a genre in painting defined by its subject matter rather than any artistic style or specific period. History paintings depict a moment in a narrative story, most often (but not exclusively) Greek and Roman mythology and Bible stories, opposed to a specific and static subject, as in portrait, still life, and landscape painting. The term is derived from the wider senses of the word ''historia'' in Latin and ''histoire'' in French, meaning "story" or "narrative", and essentially means "story painting". Most history paintings are not of scenes from history, especially paintings from before about 1850. In modern English, "historical painting" is sometimes used to describe the painting of scenes from history in its narrower sense, especially for 19th-century art, excluding religious, mythological, and allegorical subjects, which are included in the broader term "history painting", and before the 19th century were the most common subjects for history paintings. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of the Western Sahara in the west, to Egypt and Sudan's Red Sea coast in the east. The most common definition for the region's boundaries includes Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia, and Western Sahara, the territory territorial dispute, disputed between Morocco and the list of states with limited recognition, partially recognized Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. The United Nations’ definition includes all these countries as well as Sudan. The African Union defines the region similarly, only differing from the UN in excluding the Sudan and including Mauritania. The Sahel, south of the Sahara, Sahara Desert, can be considered as the southern boundary of North Africa. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq. The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western European nations in the early 20th century as a replacement of the term Near East (both were in contrast to the Far East). The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions. Since the late 20th century, it has been criticized as being too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of West Asia, but without the South Caucasus. It also includes all of Egypt (not just the Sinai Peninsula, Sinai) and all of Turkey (including East Thrace). Most Middle Eastern countries (13 out of 18) are part of the Arab world. The list of Middle Eastern countries by population, most populous countries in the region are Egypt, Turkey, and Iran, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Musala, , in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria. The concept of the Balkan Peninsula was created by the German geographer August Zeune in 1808, who mistakenly considered the Balkan Mountains the dominant mountain system of southeastern Europe spanning from the Adriatic Sea to the Black Sea. In the 19th century the term ''Balkan Peninsula'' was a synonym for Rumelia, the parts of Europe that were provinces of the Ottoman E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orientalism
In art history, literature, and cultural studies, Orientalism is the imitation or depiction of aspects of the Eastern world (or "Orient") by writers, designers, and artists from the Western world. Orientalist painting, particularly of the Middle East, was one of the many specialties of 19th-century academic art, and Western literature was influenced by a similar interest in Oriental themes. Since the publication of Edward Said's ''Orientalism (book), Orientalism'' in 1978, much academic discourse has begun to use the term 'Orientalism' to refer to a general patronizing Western attitude towards Middle Eastern, Asian, and North African societies. In Said's analysis, 'the West' Essentialism, essentializes these societies as static and undeveloped—thereby fabricating a view of Oriental culture that can be studied, depicted, and reproduced in the service of Imperialism, imperial power. Implicit in this fabrication, writes Said, is the idea that Western society is developed, rational, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopold Müller (painter)
Leopold Carl Müller (9 December 1834 – 4 August 1892) was an Austrian genre painter noted for his Orientalist works. Biography Born in Dresden to Austrian parents, he was a pupil of Karl von Blaas and of Christian Ruben at the Academy in Vienna. Obliged to support his family after his father's death, he worked eight years as an illustrator for the Vienna ''Figaro''. Continuing his studies subsequently, he visited repeatedly Italy and Egypt, and made his name favorably known through a series of scenes from popular life in Italy and Hungary. In the late 1860s, he visited Paris, where he was inspired by the work of Eugene Fromentin and subsequently turned his attention to the Orientalist genre. In 1877 Müller took a position as professor at the Vienna Academy and later as a rector during 1890–91. Among his pupils were several orientalists such as Ludwig Deutsch, Paul Joanowitch, Jean Discart and Charles Wilda. His sisters were the painters Marie Müller and Bertha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Griepenkerl
Christian Griepenkerl (17 March 1839 – 22 March 1916) was a German painter and professor, best known for rejecting Adolf Hitler's application to train at the Academy of Fine Arts Vienna. Biography Griepenkerl was born to one of Oldenburg (city), Oldenburg's leading families. As a young man, he heeded the advice of his fellow countryman, the landscapist Ernst Willers, and went to Vienna in late 1855 in order to enroll at the private art school for the monumental paintings founded four years earlier by Carl Rahl. Rahl allowed several of his students to participate in drafting and carrying out his paintings and thereby shaped their individual artistic development. Griepenkerl's first painting – ''Œdipus, Led by Antigone'' – received Rahl's approval, and he was thereafter involved with Rahl and other students in painting frescos in the grand staircase of the Museum of Weapons (today's Heeresgeschichtliches Museum), in the Palais Todesco, and in the city palace of Simon Sinas. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy Of Fine Arts Vienna
The Academy of Fine Arts Vienna () is a public art school in Vienna, Austria. Founded in 1688 as a private academy, it is now a public university. The academy is also known for twice rejecting admission to a young Adolf Hitler in 1907 and 1908. History The Academy of Fine Arts Vienna was founded in 1688 as a private academy modelled on the Accademia di San Luca and the Parisien Académie de peinture et de sculpture by the court-painter Peter Strudel, who became the ''Praefectus Academiae Nostrae''. In 1701, he was ennobled by Emperor Joseph I as ''Freiherr'' (Baron) of the Empire. With his death in 1714, the academy temporarily closed. On 20 January 1725, Emperor Charles VI appointed the Frenchman Jacob van Schuppen as Prefect and Director of the academy, which was refounded as the ''k.k. Hofakademie der Maler, Bildhauer und Baukunst'' (Imperial and Royal Court Academy of painters, sculptors and architecture). Upon Charles's death in 1740, the academy at first declined, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
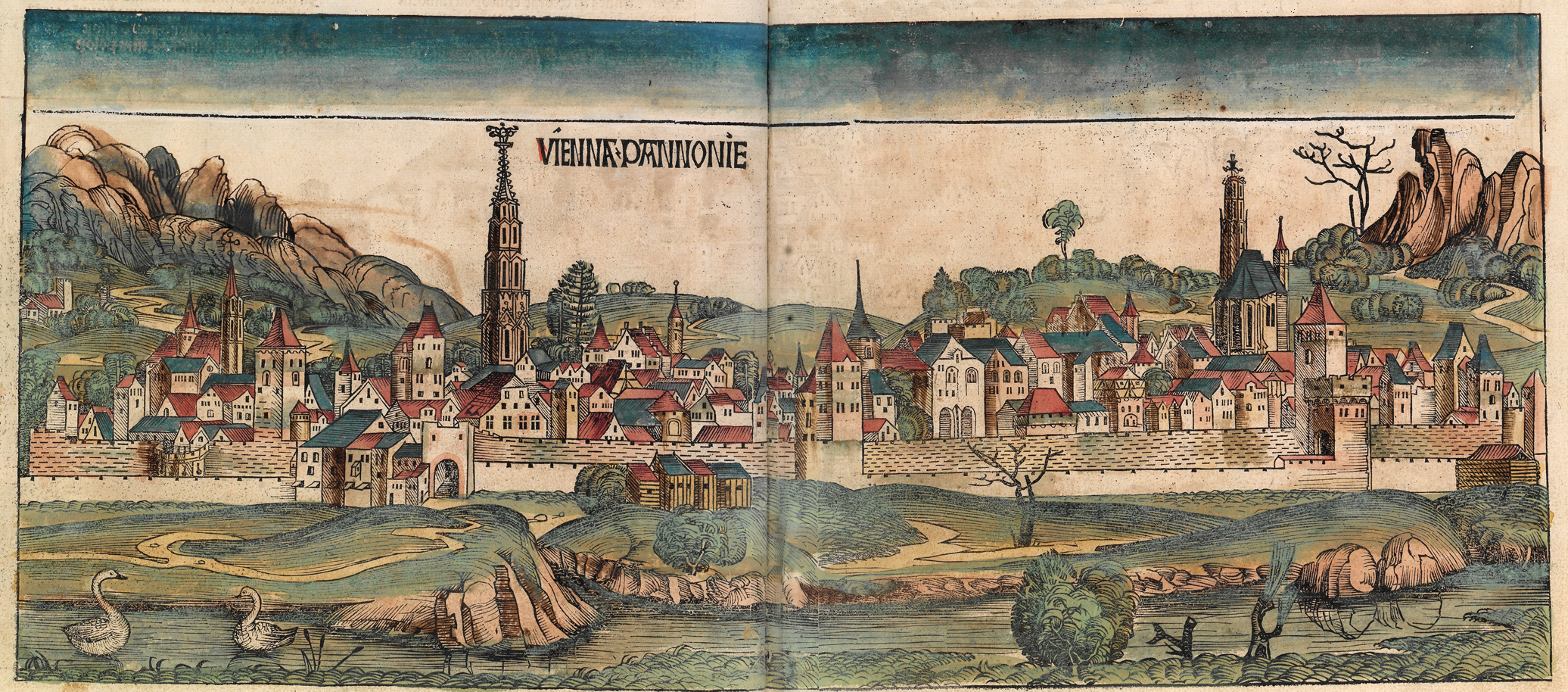
Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. Its larger metropolitan area has a population of nearly 2.9 million, representing nearly one-third of the country's population. Vienna is the Culture of Austria, cultural, Economy of Austria, economic, and Politics of Austria, political center of the country, the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, fifth-largest city by population in the European Union, and the most-populous of the List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. The city lies on the eastern edge of the Vienna Woods (''Wienerwald''), the northeasternmost foothills of the Alps, that separate Vienna from the more western parts of Austria, at the transition to the Pannonian Basin. It sits on the Danube, and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |