North Africa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
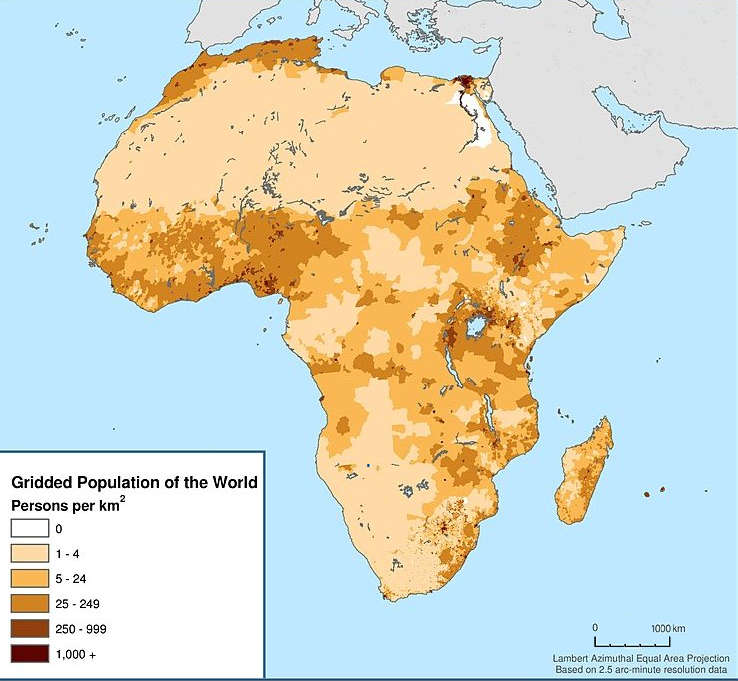 North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the
 Due to the
Due to the  Archaeological evidence has attested that population settlements occurred in Nubia as early as the Late
Archaeological evidence has attested that population settlements occurred in Nubia as early as the Late
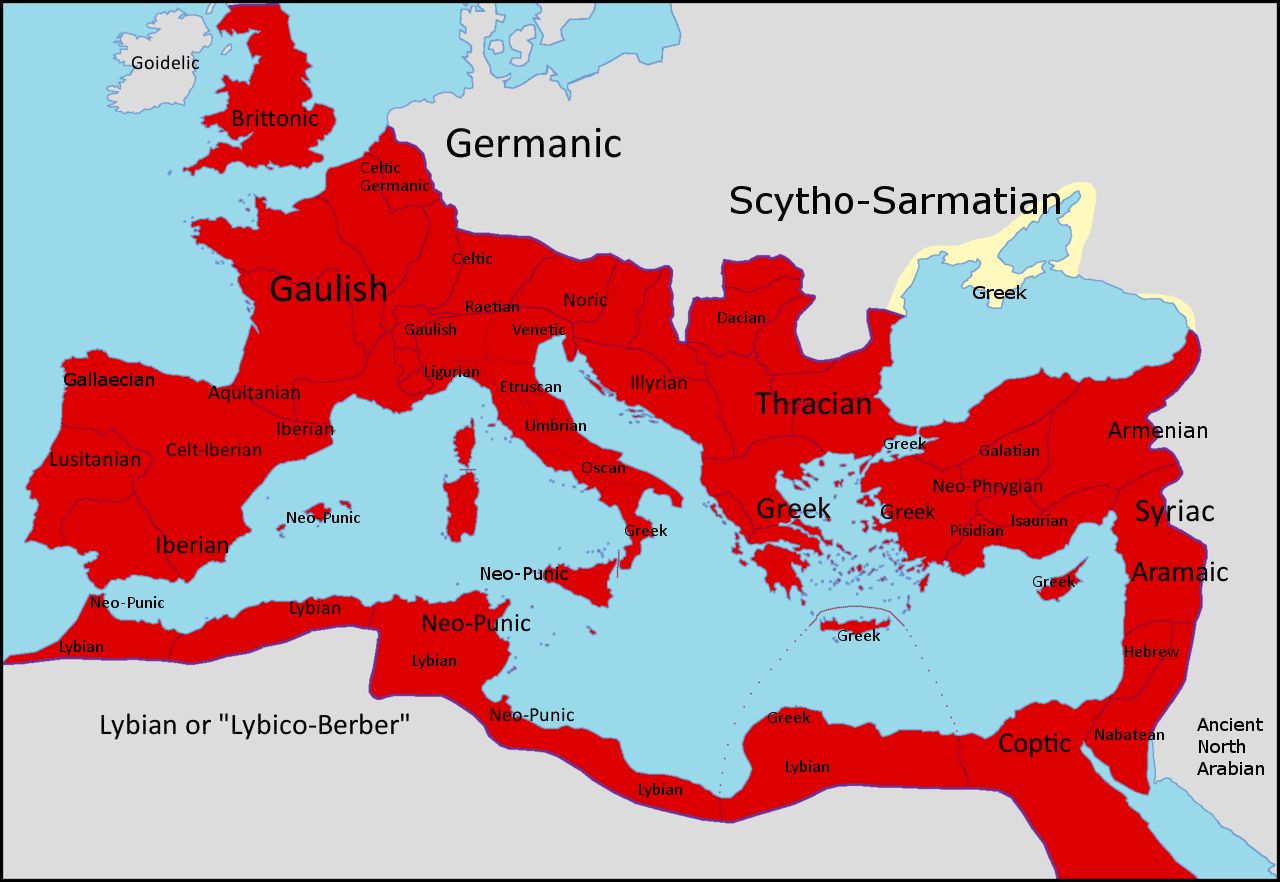
 The most notable nations of antiquity in western North Africa are
The most notable nations of antiquity in western North Africa are
 The
The  After the
After the
 North Africa has three main geographic features: the
North Africa has three main geographic features: the

 The majority of the people of the Maghreb and the Sahara regions speak
The majority of the people of the Maghreb and the Sahara regions speak
North Africa's Weather Forecasts and Weather Conditions
North Africa news and analysis
Africa Interactive Map
from the United States Army Africa (archived 17 January 2010) {{Authority control Geography of North Africa Regions of Africa
 North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
n continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of the Western Sahara
Western Sahara is a territorial dispute, disputed territory in Maghreb, North-western Africa. It has a surface area of . Approximately 30% of the territory () is controlled by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR); the remaining 70% is ...
in the west, to Egypt and Sudan's Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
coast in the east.
The most common definition for the region's boundaries includes Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
, Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
, Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
, and Western Sahara
Western Sahara is a territorial dispute, disputed territory in Maghreb, North-western Africa. It has a surface area of . Approximately 30% of the territory () is controlled by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR); the remaining 70% is ...
, the territory disputed between Morocco and the partially recognized Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
The Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR), also known as the Sahrawi Republic and Western Sahara, is a partially recognized state in the western Maghreb, which claims the non-self-governing territory of Western Sahara, but controls only ...
. The United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
’ definition includes all these countries as well as Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
. The African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the African Union. The b ...
defines the region similarly, only differing from the UN in excluding the Sudan and including Mauritania
Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Maghreb, Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to Mauritania–Western Sahara border, the north and northwest, ...
. The Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
, south of the Sahara Desert
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
, can be considered as the southern boundary of North Africa. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ) is an Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous city of Spain on the North African coast. Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Ceuta is one of th ...
and Melilla
Melilla (, ; ) is an autonomous city of Spain on the North African coast. It lies on the eastern side of the Cape Three Forks, bordering Morocco and facing the Mediterranean Sea. It has an area of . It was part of the Province of Málaga un ...
, and the plazas de soberanía
The (), meaning "strongholds of sovereignty", are a series of Spanish overseas territories scattered along the Mediterranean coast bordering Morocco, or that are closer to Africa than Europe. This term is used for those territories that have ...
. It can also be considered to include Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
, as well as other Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish regions such as Lampedusa and Lampione
Lampione (; ; ) is a small rocky island located in the Mediterranean Sea, which belongs geographically to the Pelagie Islands and administratively to the ''comune'' of Lampedusa e Linosa, Province of Agrigento, region of Sicily, Italy. It is abo ...
, Madeira
Madeira ( ; ), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (), is an autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous region of Portugal. It is an archipelago situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, in the region of Macaronesia, just under north of ...
, and the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
, which are all closer or as close to the African continent than Europe.
Northwest Africa has been inhabited by Berbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connec ...
since the beginning of recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world h ...
, while the eastern part of North Africa has been home to the Ancient Egyptians
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower ...
and Nubians
Nubians () ( Nobiin: ''Nobī,'' ) are a Nilo-Saharan speaking ethnic group indigenous to the region which is now northern Sudan and southern Egypt. They originate from the early inhabitants of the central Nile valley, believed to be one of th ...
. In the seventh and eighth centuries, Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
from the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
swept across the region during the early Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests (), also known as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the founder of Islam. He established the first Islamic state in Medina, Arabian Peninsula, Arabia that ...
. The Arab migrations to the Maghreb
The Arab migrations to the Maghreb involved successive waves of Human migration, migration and Settler, settlement by Arabs, Arab people in the Maghreb region of Africa, encompassing modern-day Algeria, Libya, Morocco and Tunisia. The process to ...
began immediately after, which started a long process of Islamization
The spread of Islam spans almost 1,400 years. The early Muslim conquests that occurred following the death of Muhammad in 632 CE led to the creation of the caliphates, expanding over a vast geographical area; conversion to Islam was boosted ...
and Arabization
Arabization or Arabicization () is a sociology, sociological process of cultural change in which a non-Arab society becomes Arabs, Arab, meaning it either directly adopts or becomes strongly influenced by the Arabic, Arabic language, Arab cultu ...
that has altered the demographic breakdown of the region and defined the cultural landscape of North Africa ever since. Many but not all Berbers and Ancient Egyptians gradually merged into Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
-Islamic culture
Islamic cultures or Muslim cultures refers to the historic cultural practices that developed among the various peoples living in the Muslim world. These practices, while not always religious in nature, are generally influenced by aspects of Islam ...
, and today, the Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
constitute the majority of the population in all North African countries.
The countries and people of North Africa share a large amount of their genetic, ethnic, cultural and linguistic identity and influence with the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
/West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
, a process that began with the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period in Afro-Eurasia from a lifestyle of hunter-gatherer, hunting and gathering to one of a ...
and pre Dynastic Egypt. The countries of North Africa are also a major part of the Arab world
The Arab world ( '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, comprises a large group of countries, mainly located in West Asia and North Africa. While the majority of people in ...
. The Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
ic and Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
influence in North Africa has remained dominant ever since, with the region being major part of the Muslim world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
. North Africa is associated with the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
in the realm of geopolitics
Geopolitics () is the study of the effects of Earth's geography on politics and international relations. Geopolitics usually refers to countries and relations between them, it may also focus on two other kinds of State (polity), states: ''de fac ...
to form the Middle East-North Africa region.
Countries and territories
History
Prehistory
 Due to the
Due to the recent African origin of modern humans
The recent African origin of modern humans or the "Out of Africa" theory (OOA) is the most widely accepted paleoanthropology, paleo-anthropological model of the geographic origin and Early human migrations, early migration of early modern h ...
, the history of Prehistoric North Africa is important to the understanding of pre-hominid and early modern human history in Africa.
Some researchers have postulated that North Africa rather than East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
served as the exit point for the modern humans who first trekked out of the continent in the Out of Africa
''Out of Africa'' is a memoir by the Danish people, Danish author Karen Blixen. The book, first published in 1937, recounts events of the eighteen years when Blixen made her home in Kenya, then called East Africa Protectorate, British East Africa ...
migration.
The earliest inhabitants of central North Africa have left behind significant remains: early remnants of hominid occupation in North Africa, for example, were found in Ain-Hnech in Setif dating back 2.6 million years, near Saïda (); in fact, more recent investigations have found signs of Oldowan
The Oldowan (or Mode I) was a widespread stone tool archaeological industry during the early Lower Paleolithic spanning the late Pliocene and the first half of the Early Pleistocene. These early tools were simple, usually made by chipping one ...
technology there, and indicate a date of up to 1.8 million BCE.
Recent finds in Jebel Irhoud in Morocco have been found to contain some of the oldest ''Homo sapiens'' remains; This suggests that, rather than arising only in East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
around 200,000 years ago, early ''Homo sapiens'' may already have been present across the length of Africa 100,000 years earlier. According to study author Jean-Jacques Hublin, "The idea is that early ''Homo sapiens'' dispersed around the continent and elements of human modernity appeared in different places, and so different parts of Africa contributed to the emergence of what we call modern humans today." Early humans may have comprised a large, interbreeding population dispersed across Africa whose spread was facilitated by a wetter climate that created a "green Sahara", around 330,000 to 300,000 years ago. The rise of modern humans may thus have taken place on a continental scale rather than being confined to a particular corner of Africa.
In September 2019, scientists reported the computerized determination, based on 260 CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
s, of a virtual skull shape of the last common human ancestor to modern human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s/''H. sapiens'', representative of the earliest modern humans, and suggested that modern humans arose between 260,000 and 350,000 years ago through a merging of populations in East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
and Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost region of Africa. No definition is agreed upon, but some groupings include the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations geoscheme, the intergovernmental Southern African Development Community, and ...
.
The cave paintings found at Tassili n'Ajjer, north of Tamanrasset, Algeria, and at other locations depict vibrant and vivid scenes of everyday life in central North Africa during the Neolithic Subpluvial period (about 8000 to 4000 BCE). Some parts of North Africa began to participate in the Neolithic revolution in the 6th millennium BCE, just before the rapid desertification of the Sahara around 3500 B.C. largely due to a tilt in the Earth's orbit. It was during this period that domesticated plants and animals were introduced in the region, spreading from the north and east to the southwest. There has been an inferred connection between areas of rapid drying and the introduction of livestock in which the natural (orbital) aridification was amplified by the spread of shrubs and open land due to grazing. Nevertheless, changes in northern Africa's ecology after 3500 BCE provided the backdrop for the formation of dynastic civilizations and the construction of monumental architecture such as the Pyramids of Giza
The Giza pyramid complex (also called the Giza necropolis) in Egypt is home to the Great Pyramid, the pyramid of Khafre, and the pyramid of Menkaure, along with their associated pyramid complexes and the Great Sphinx. All were built during th ...
.
 Archaeological evidence has attested that population settlements occurred in Nubia as early as the Late
Archaeological evidence has attested that population settlements occurred in Nubia as early as the Late Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
era and from the 5th millennium BC onwards, whereas there is "no or scanty evidence" of human presence in the Egyptian Nile Valley during these periods, which may be due to problems in site preservation. Several scholars have argued that the African origins of the Egyptian civilisation derived from pastoral communities which emerged in both the Egyptian and Sudanese regions of the Nile Valley in the fifth millennium BCE.
When Egypt entered the Bronze Age, the Maghreb remained focused on small-scale subsistence in small, highly mobile groups. Some Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
n and Greek colonies
Greek colonisation refers to the expansion of Archaic Greeks, particularly during the 8th–6th centuries BC, across the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea.
The Archaic expansion differed from the Iron Age migrations of the Greek Dark Ages ...
were established along the Mediterranean coast during the 7th century BCE.
Antiquity and ancient Rome

 The most notable nations of antiquity in western North Africa are
The most notable nations of antiquity in western North Africa are Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
, Numidia
Numidia was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia and Libya. The polity was originally divided between ...
and Mauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It extended from central present-day Algeria to the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, encompassing northern present-day Morocco, and from the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean in the ...
. The Phoenicians colonized much of North Africa including Carthage and parts of present-day Morocco (including Chellah, Essaouira
Essaouira ( ; ), known until the 1960s as Mogador (, or ), is a port city in the western Moroccan region of Marrakesh-Safi, on the Atlantic coast. It has 77,966 inhabitants as of 2014.
The foundation of the city of Essaouira was the work of t ...
and Volubilis
Volubilis (; ; ) is a partly excavated Berber-Roman city in Morocco, situated near the city of Meknes, that may have been the capital of the Kingdom of Mauretania, at least from the time of King Juba II. Before Volubilis, the capital of the kin ...
). The Carthaginians were of Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
n origin, with the Roman myth of their origin being that Dido
Dido ( ; , ), also known as Elissa ( , ), was the legendary founder and first queen of the Phoenician city-state of Carthage (located in Tunisia), in 814 BC.
In most accounts, she was the queen of the Phoenician city-state of Tyre (located ...
, a Phoenician princess, was granted land by a local ruler based on how much land she could cover with a piece of cowhide. She ingeniously devised a method to extend the cowhide to a high proportion, thus gaining a large territory. She was also rejected by the Trojan
Trojan or Trojans may refer to:
* Of or from the ancient city of Troy
* Trojan language, the language of the historical Trojans
Arts and entertainment Music
* '' Les Troyens'' ('The Trojans'), an opera by Berlioz, premiered part 1863, part 18 ...
prince Aeneas
In Greco-Roman mythology, Aeneas ( , ; from ) was a Troy, Trojan hero, the son of the Trojan prince Anchises and the Greek goddess Aphrodite (equivalent to the Roman Venus (mythology), Venus). His father was a first cousin of King Priam of Troy ...
according to Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; 15 October 70 BC21 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Rome, ancient Roman poet of the Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Augustan period. He composed three of the most fa ...
, thus creating a historical enmity between Carthage and Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
, as Aeneas would eventually lay the foundations for Rome. The Carthaginian Empire
Ancient Carthage ( ; , ) was an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic civilisation based in North Africa. Initially a settlement in present-day Tunisia, it later became a city-state, and then an empire. Founded by the Phoenicians ...
was a commercial power and had a strong navy, but relied on mercenaries for land soldiers. The Carthaginians developed an empire in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
, Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
, Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
, Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
and northwest Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, the latter being the cause of First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and grea ...
with the Romans.
Over a hundred years and more, all Carthaginian territory was eventually conquered by the Romans, resulting in the Carthaginian North African territories becoming the Roman province of Africa
Africa was a Roman province on the northern coast of the continent of Africa. It was established in 146 BC, following the Roman Republic's conquest of Carthage in the Third Punic War. It roughly comprised the territory of present-day Tunisi ...
in 146 B.C. This led to tension and eventually conflict between Numidia
Numidia was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia and Libya. The polity was originally divided between ...
and Rome. The Numidian wars are notable for launching the careers of both Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbrian War, Cimbric and Jugurthine War, Jugurthine wars, he held the office of Roman consul, consul an unprecedented seven times. Rising from a fami ...
, and Sulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (, ; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman people, Roman general and statesman of the late Roman Republic. A great commander and ruthless politician, Sulla used violence to advance his career and his co ...
, and stretching the constitutional burden of the Roman republic as Marius required a professional army, something previously contrary to Roman values, to overcome the talented military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
leader Jugurtha
Jugurtha or Jugurthen (c. 160 – 104 BC) was a king of Numidia, the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa. When the Numidian king Micipsa, who had adopted Jugurtha, died in 118 BC, Micipsa's two sons, Hiempsal and Adherbal ...
. Kingdom of Mauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It extended from central present-day Algeria to the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, encompassing northern present-day Morocco, and from the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean in the ...
remained independent until being annexed to the Roman Empire by Emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Ant ...
in 42 AD.
North Africa remained a part of the Roman Empire, producing notable citizens, including Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; ; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430) was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Africa. His writings deeply influenced the development of Western philosop ...
, until incompetent leadership from Roman commanders in the early fifth century allowed the Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of ...
, the Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vand ...
, to cross the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Europe from Africa.
The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical miles (14.2 kilometers, 8.9 miles) at its narrowest point. Fe ...
, whereupon they overcame the fickle Roman defense. The loss of North Africa is considered a pinnacle point in the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire, also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome, was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast ...
as Africa had previously been an important grain province that maintained Roman prosperity despite the barbarian incursions, and the wealth required to create new armies. The issue of regaining North Africa became paramount to the Western Empire, but was frustrated by Vandal victories. The focus of Roman energy had to be on the emerging threat of the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
. In 468 AD, the Romans made one last serious attempt to invade North Africa but were repelled. This perhaps marks the point of terminal decline for the Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
.
The last Roman emperor was deposed in 476 by the Heruli
The Heruli (also Eluri, Eruli, Herules, Herulians) were one of the smaller Germanic peoples of Late Antiquity, known from records in the third to sixth centuries AD.
The best recorded group of Heruli established a kingdom north of the Middle Danu ...
general Odoacer
Odoacer ( – 15 March 493 AD), also spelled Odovacer or Odovacar, was a barbarian soldier and statesman from the Middle Danube who deposed the Western Roman child emperor Romulus Augustulus and became the ruler of Italy (476–493). Odoacer' ...
. Trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over land or water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a singl ...
s between Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
and North Africa remained intact until the coming of Islam. Some Berbers were members of the Early African Church
The name early African church is given to the Christians, Christian communities inhabiting the region known politically as North Africa during Antiquity#Roman era, Roman Africa, and comprised geographically somewhat around the area of the Roman D ...
(but evolved their own Donatist doctrine), some were Berber Jews
Berber Jews are the Jewish communities of the Maghreb, in North Africa, who historically spoke Berber languages.
Between 1950 and 1970 most immigrated to France, Israel and the United States.
History Antiquity
Jews have settled in Maghreb since ...
, and some adhered to traditional Berber religion
The traditional Berber religion is the sum of ancient and native set of beliefs and deities adhered to by the Berbers. Originally, the Berbers seem to have believed in worship of the sun and moon, animism and in the afterlife, but interactions ...
. African pope Victor I served during the reign of Roman emperor Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; ; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through cursus honorum, the ...
. Furthermore, during the rule of the Romans, Byzantines, Vandals, Ottomans and Carthaginians the Kabyle people were the only or one of the few in North Africa who remained independent.
The Kabyle people were incredibly resistible so much so that even during the Arab conquest of North Africa they still had control and possession over their mountains.
Arab conquest to modern times
 The
The early Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests (), also known as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the founder of Islam. He established the first Islamic state in Medina, Arabian Peninsula, Arabia that ...
included North Africa by 640. By 700, most of North Africa had come under Muslim rule. Indigenous Berbers subsequently started to form their own polities in response in places such as Fez and Sijilmasa
Sijilmasa (; also transliterated Sijilmassa, Sidjilmasa, Sidjilmassa and Sigilmassa) was a medieval Moroccan city and trade entrepôt at the northern edge of the Sahara in Morocco. The ruins of the town extend for five miles along the River Ziz ...
. In the eleventh century, a reformist movement made up of members that called themselves the Almoravid dynasty
The Almoravid dynasty () was a Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire that stretched over the western Maghreb and Al-Andalus, starting in the 1050s and lasting until its fall to the Almo ...
expanded south into Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
.
North Africa's populous and flourishing civilization collapsed after exhausting its resources in internal fighting and suffering devastation from the invasion of the Banu Sulaym
The Banu Sulaym () is an Arab tribe that dominated part of the Hejaz in the pre-Islamic era. They maintained close ties with the Quraysh of Mecca and the inhabitants of Medina, and fought in a number of battles against the Islamic prophet Muha ...
and Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal () was a confederation of Arab tribes from the Najd region of the central Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to the Maghreb region of North Africa in the 11th century. They ruled the Najd, and campaigned in the borderlands between I ...
. Ibn Khaldun
Ibn Khaldun (27 May 1332 – 17 March 1406, 732–808 Hijri year, AH) was an Arabs, Arab Islamic scholar, historian, philosopher and sociologist. He is widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest social scientists of the Middle Ages, and cons ...
noted that the lands ravaged by Banu Hilal invaders had become completely arid desert.
 After the
After the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
much of the area was loosely under the control of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. The Barbary pirates
The Barbary corsairs, Barbary pirates, Ottoman corsairs, or naval mujahideen (in Muslim sources) were mainly Muslim corsairs and privateers who operated from the largely independent Barbary states. This area was known in Europe as the Barba ...
operated from the largely independent Barbary states
The Barbary Coast (also Barbary, Berbery, or Berber Coast) were the coastal regions of central and western North Africa, more specifically, the Maghreb and the Ottoman borderlands consisting of the regencies in Algiers, Tunis, and Tripoli, a ...
located on the coast of North Africa. The Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered ...
conquered several coastal cities between the 16th and 18th centuries. After the 19th century, the imperial and colonial presence of France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
and Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
left the entirety of the region under one form of European occupation.
In World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
from 1940 to 1943 the area was the setting for the North African Campaign
The North African campaign of World War II took place in North Africa from 10 June 1940 to 13 May 1943, fought between the Allies and the Axis Powers. It included campaigns in the Libyan and Egyptian deserts (Western Desert campaign, Desert Wa ...
. During the 1950s and 1960s all of the North African states gained independence. There remains a dispute over Western Sahara
Western Sahara is a territorial dispute, disputed territory in Maghreb, North-western Africa. It has a surface area of . Approximately 30% of the territory () is controlled by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR); the remaining 70% is ...
between Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
and the Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
n-backed Polisario Front
The Popular Front for the Liberation of Saguia el-Hamra and Río de Oro (Spanish language, Spanish: ; ), better known by its acronym Polisario Front, is a Sahrawi nationalism, Sahrawi nationalist liberation movement seeking to end the occupatio ...
.
The wider protest movement known as the Arab Spring
The Arab Spring () was a series of Nonviolent resistance, anti-government protests, Rebellion, uprisings, and Insurgency, armed rebellions that spread across much of the Arab world in the early 2010s. It began Tunisian revolution, in Tunisia ...
began with revolutions in Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
which ultimately led to the overthrow of their governments, as well as civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
in Libya. Large protests also occurred in Algeria and Morocco to a lesser extent. Many hundreds died in the uprisings.
Geography

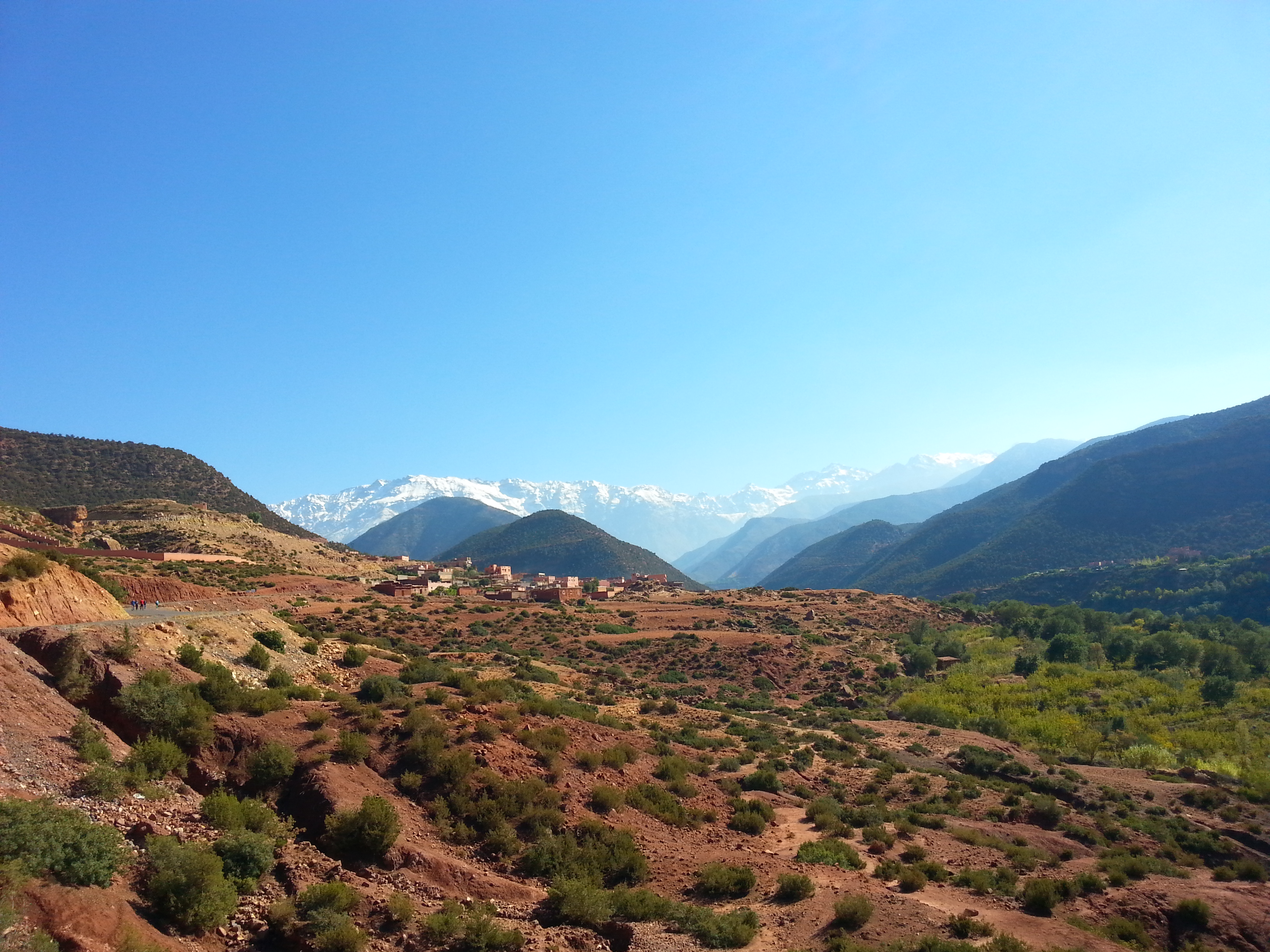
 North Africa has three main geographic features: the
North Africa has three main geographic features: the Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
desert in the south, the Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains are a mountain range in the Maghreb in North Africa. They separate the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; the name "Atlantic" is derived from the mountain range, which stretches around through M ...
in the west, and the Nile River
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river i ...
and delta in the east. The Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains are a mountain range in the Maghreb in North Africa. They separate the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; the name "Atlantic" is derived from the mountain range, which stretches around through M ...
extend across much of northern Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
, Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
, and Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
. These mountains are part of the fold mountain system that also runs through much of Southern Europe
Southern Europe is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, C ...
. They recede to the south and east, becoming a steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
landscape before meeting the Sahara desert, which covers more than 75 percent of the region. The tallest peaks are in the High Atlas range in south-central Morocco, which has many snow-capped peaks.
South of the Atlas Mountains is the dry and barren expanse of the Sahara desert, the largest sand desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
in the world. In places the desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
is cut by irregular watercourses called wadi
Wadi ( ; ) is a river valley or a wet (ephemerality, ephemeral) Stream bed, riverbed that contains water only when heavy rain occurs. Wadis are located on gently sloping, nearly flat parts of deserts; commonly they begin on the distal portion ...
s—streams that flow only after rainfall but are usually dry. The Sahara's major landforms include ergs, large seas of sand that sometimes form into huge dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, flat ...
s; the hammada, a level rocky plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; : plateaus or plateaux), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. ...
without soil or sand; and the reg, a desert pavement
A desert pavement, also called reg (in western Sahara), serir (in eastern Sahara), gibber (in Australia), or saï (in central Asia) is a desert surface covered with closely packed, interlocking angular or rounded rock fragments of pebble and ...
. The Sahara covers the southern part of Algeria, Morocco and Tunisia, and most of Libya. Only two regions of Libya are outside the desert: Tripolitania
Tripolitania (), historically known as the Tripoli region, is a historic region and former province of Libya.
The region had been settled since antiquity, first coming to prominence as part of the Carthaginian empire. Following the defeat ...
in the northwest and Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika (, , after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between the 16th and 25th meridians east, including the Kufra District. The coastal region, als ...
in the northeast. Most of Egypt is also desert, with the exception of the Nile River and the irrigated land along its banks. The Nile Valley forms a narrow fertile thread that runs along the length of the country.
Sheltered valleys in the Atlas Mountains, the Nile Valley and Delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier ...
, and the Mediterranean coast are the main sources of fertile farming land. A wide variety of valuable crops including cereals, rice and cotton, and woods such as cedar and cork, are grown. Typical Mediterranean crops, such as olives, figs, dates and citrus fruits, also thrive in these areas. The Nile Valley is particularly fertile and most of Egypt lives close to the river. Elsewhere, irrigation is essential to improve crop yields on the desert margins.
Economy
Science and technology
''Further information in the sections of History of science and technology in Africa:'' *Education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education als ...
* Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
* Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
* Metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
* Medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
* Agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
* Textiles
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. ...
* Maritime technology
* Architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
* Communication systems
A communications system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. Commun ...
* Warfare
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of State (polity), states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or betwe ...
* Commerce
Commerce is the organized Complex system, system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions that directly or indirectly contribute to the smooth, unhindered large-scale exchange (distribution through Financial transaction, transactiona ...
* By country
Demographics

Ethnic groups
The inhabitants of North Africa are roughly divided in a manner corresponding to the principal geographic regions of North Africa: theMaghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
, the Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
valley, and the Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
. The countries making up North Africa all have Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA) is the variety of Standard language, standardized, Literary language, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and in some usages al ...
as their official language. Additionally, Algeria and Morocco recognize Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
as a second official language after Arabic. French also serves as an administrative language in Algeria, Morocco and Tunisia. The most spoken dialects are Maghrebi Arabic
Maghrebi Arabic, often known as ''ad-Dārija'' to differentiate it from Literary Arabic, is a vernacular Arabic dialect continuum spoken in the Maghreb. It includes the Moroccan, Algerian, Tunisian, Libyan, Hassaniya and Saharan Arabic di ...
, a form of ancient Arabic dating back from the 8th century AD, and Egyptian Arabic
Egyptian Arabic, locally known as Colloquial Egyptian, or simply as Masri, is the most widely spoken vernacular Arabic variety in Egypt. It is part of the Afro-Asiatic language family, and originated in the Nile Delta in Lower Egypt. The esti ...
. The largest and most numerous ethnic group in North Africa are the Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
. In Algeria and Morocco, Berbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connec ...
are the second largest ethnic group after the Arab majority. Arabs constitute 70% to 80% of the population of Algeria, 92% to 97% of Libya, 67% to 70% of Morocco and 98% of Tunisia's population. The Berbers comprise 20% of Algeria, 10% of Libya, 35% of Morocco and 1% of Tunisia's population. The region is predominantly Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
with a Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
minority in Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
and Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
, and significant Christian minority—the Copts
Copts (; ) are a Christians, Christian ethnoreligious group, ethnoreligious group native to Northeast Africa who have primarily inhabited the area of modern Egypt since antiquity. They are, like the broader Egyptians, Egyptian population, des ...
—in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
, Morocco, Libya, and Tunisia. In 2001, the number of Christians in North Africa was estimated at 9 million, the majority of whom live in Egypt, with the remainder live in Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
countries.
The inhabitants of the Spanish Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
are of mixed Spanish and North African Berber ancestry, and the people of Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
are of primarily Southern Italian/Sicilian, as well as, to a lesser extent, North African and Middle Eastern ancestry and speak a derivative of Arabic. However, these areas are not generally considered part of North Africa, but rather Southern Europe, due to their proximity to mainland Europe and their European-based cultures and religion.
Historic movements
The Maghreb or western North Africa on the whole is believed to have been inhabited byBerbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connec ...
and their ancestors since at least 10,000 B.C., while the eastern part of North Africa or the Nile Valley
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river i ...
has mainly been home to the Egyptians
Egyptians (, ; , ; ) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian identity is closely tied to Geography of Egypt, geography. The population is concentrated in the Nile Valley, a small strip of cultivable land stretchi ...
and Nubians
Nubians () ( Nobiin: ''Nobī,'' ) are a Nilo-Saharan speaking ethnic group indigenous to the region which is now northern Sudan and southern Egypt. They originate from the early inhabitants of the central Nile valley, believed to be one of th ...
. Ancient Egyptians record extensive contact in their Western desert with people that appear to have been Berber or proto-Berber. As the Tassili n'Ajjer and other rock art findings in the Sahara have shown, the Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
also hosted various populations before its rapid desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.
The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This i ...
in 3500 B.C and even today continues to host small populations of nomadic trans-Saharan peoples. Laboratory examination of the Uan Muhuggiag
Uan Muhuggiag is an archaeological site in Libya that was occupied by pastoralists between the early Holocene and mid-Holocene; the Tashwinat mummy, which was found at Uan Muhuggiag, was dated to 5600 BP and presently resides in the Assaraya Al ...
child mummy and Tin Hanakaten child, suggested that the Central Saharan peoples from the Epipaleolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are someti ...
, Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
, and Pastoral
The pastoral genre of literature, art, or music depicts an idealised form of the shepherd's lifestyle – herding livestock around open areas of land according to the seasons and the changing availability of water and pasture. The target au ...
periods possessed dark skin complexions. The archaeological evidence from the Holocene period has shown that Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of around 210 African languages spoken by somewhere around 70 million speakers, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributari ...
speaking groups had populated the central and southern Sahara before the influx of Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
and Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
speakers, around 1500 years ago, who now largely populate the Sahara in the modern era.
After migrating to North Africa in the 1st millennium BC, Semitic Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
n settlers from the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
established over 300 coastal colonies throughout the region and built a powerful empire that controlled most of the region from the 8th century BC until the middle of the 2nd century BC.
Several waves of Arab migrations to the Maghreb
The Arab migrations to the Maghreb involved successive waves of Human migration, migration and Settler, settlement by Arabs, Arab people in the Maghreb region of Africa, encompassing modern-day Algeria, Libya, Morocco and Tunisia. The process to ...
began in the 7th century, including the migration of the Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal () was a confederation of Arab tribes from the Najd region of the central Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to the Maghreb region of North Africa in the 11th century. They ruled the Najd, and campaigned in the borderlands between I ...
and the Banu Sulaym
The Banu Sulaym () is an Arab tribe that dominated part of the Hejaz in the pre-Islamic era. They maintained close ties with the Quraysh of Mecca and the inhabitants of Medina, and fought in a number of battles against the Islamic prophet Muha ...
westward into the Maghreb in the eleventh century, which introduced Arab culture and language to the countryside. Historians mark their movement as a critical moment in the Arabization of North Africa. As Arab nomads spread, the territories of the local Berber tribes were moved and shrank. The Zenata
The Zenata (; ) are a group of Berber tribes, historically one of the largest Berber confederations along with the Sanhaja and Masmuda. Their lifestyle was either nomadic or semi-nomadic.
Society
The 14th-century historiographer Ibn Khaldun repo ...
were pushed to the west and the Kabyles were pushed to the north. The Berbers took refuge in the mountains whereas the plains were Arabized. This heavily shifted the demographics of the Maghreb.
The trans-Saharan slave trade
The trans-Saharan slave trade, also known as the Arab slave trade, was a Slavery, slave trade in which slaves Trans-Saharan trade, were mainly transported across the Sahara. Most were moved from sub-Saharan Africa to North Africa to be sold to ...
resulted in increased levels of sub-Saharan African ancestry in North Africa. The Haratin are commonly perceived as an endogamous group of former slaves
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
or descendants of slaves.
Genetic history
DNA studies of Iberomaurusian peoples atTaforalt
Taforalt, or Grotte des Pigeons, is a cave in the province of Berkane, Aït Iznasen region, Morocco, possibly the oldest cemetery in North Africa. It contained at least 34 Iberomaurusian adolescent and adult human skeletons, as well as young ...
, Morocco dating to around 15,000 years ago have found them to have a distinctive Maghrebi ancestry formed from a mixture of Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
ern and African ancestry, which is still found as a part of the genome of modern Northwest Africans. A 2025 study sequenced individuals from Takarkori (7,000 YBP) and discovered that most of their ancestry was from an unknown ancestral North African lineage, related to the African admixture component found in Iberomaurusians. According to the study, the Takarkori people were distinct from both contemporary sub-Saharan Africans and non-Africans/Eurasians. They had "only a minor component of non-African ancestry" but did "not carry sub-Saharan African ancestry, suggesting that, contrary to previous interpretations, the Green Sahara was not a corridor connecting Northern and sub-Saharan Africa."
Later during the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
, from around 7,500 years ago onwards, there was a migration into Northwest Africa of European Neolithic Farmers from the Iberian Peninsula (who had originated in Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
several thousand years prior), as well as pastoralists from the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
, both of whom also significantly contributed to the ancestry of modern Northwest Africans. The proto-Berber tribes evolved from these prehistoric communities during the late Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
- and early Iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
ages.
Culture

 The majority of the people of the Maghreb and the Sahara regions speak
The majority of the people of the Maghreb and the Sahara regions speak varieties of Arabic
Varieties of Arabic (or dialects or vernaculars) are the linguistic systems that Arabic speakers speak natively. Arabic is a Semitic languages, Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic family that originated in the Arabian P ...
and almost exclusively follow Islam. The Arabic and Berber languages are distantly related, both being members of the Afroasiatic language family. The Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym, depending on variety: ''Imuhaɣ'', ''Imušaɣ'', ''Imašeɣăn'' or ''Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group, traditionally nomadic pastoralists, who principally inhabit th ...
Berber languages are notably more conservative than those of the coastal cities.
Over the years, Berbers have been influenced by contact with other cultures: Egyptians
Egyptians (, ; , ; ) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian identity is closely tied to Geography of Egypt, geography. The population is concentrated in the Nile Valley, a small strip of cultivable land stretchi ...
, Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, Punic people
The Punic people, usually known as the Carthaginians (and sometimes as Western Phoenicians), were a Semitic people who migrated from Phoenicia to the Western Mediterranean during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' ...
, Romans, Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vand ...
, Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
, Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common ancestry, language, faith, historical continuity, etc. There are ...
, and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
ns. The cultures of the Maghreb and the Sahara therefore combines Arab, indigenous Berber and African elements. In the Sahara, the distinction between sedentary oasis
In ecology, an oasis (; : oases ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environmentBedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu ( ; , singular ) are pastorally nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia (Iraq). The Bedouin originated in the Sy ...
Arabs and Tuaregs is particularly marked.
Egyptians
Egyptians (, ; , ; ) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian identity is closely tied to Geography of Egypt, geography. The population is concentrated in the Nile Valley, a small strip of cultivable land stretchi ...
over the centuries have shifted their language from Egyptian
''Egyptian'' describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of year ...
(in its late form, varieties of Coptic) to modern Egyptian Arabic
Egyptian Arabic, locally known as Colloquial Egyptian, or simply as Masri, is the most widely spoken vernacular Arabic variety in Egypt. It is part of the Afro-Asiatic language family, and originated in the Nile Delta in Lower Egypt. The esti ...
while retaining a sense of national identity that has historically set them apart from other people in the region. Most Egyptians are Sunni Muslim
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Musli ...
, although there is a significant minority of Coptic Christians. The Copts are the largest Christian denomination in the Middle East and North Africa
The Middle East and North Africa (MENA), also referred to as West Asia and North Africa (WANA) or South West Asia and North Africa (SWANA), is a geographic region which comprises the Middle East (also called West Asia) and North Africa together ...
.
The Maghreb formerly had a significant Jewish population, almost all of whom emigrated to France or Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
when the North African nations gained independence. Prior to the modern establishment of Israel, there were about 500,000 Jews in Northern Africa, including both Sephardi Jews
Sephardic Jews, also known as Sephardi Jews or Sephardim, and rarely as Iberian Peninsular Jews, are a Jewish diaspora population associated with the historic Jewish communities of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) and their descendant ...
(refugees from Spain, France and Portugal from the Renaissance era) as well as indigenous Mizrahi Jews
Mizrahi Jews (), also known as ''Mizrahim'' () in plural and ''Mizrahi'' () in singular, and alternatively referred to as Oriental Jews or ''Edot HaMizrach'' (, ), are terms used in Israeli discourse to refer to a grouping of Jews, Jewish c ...
. Today, less than 3,000 remain in the region, almost all in Morocco and Tunisia, and are mostly part of a French-speaking urban elite. (See Jewish exodus from Arab and Muslim countries
The Jewish exodus from the Muslim world occurred during the 20th century, when approximately 900,000 Jews migrated, fled, or were expelled from Muslim-majority countries throughout Africa and Asia, primarily as a consequence of the establishme ...
.)
Architecture
''Further information in the sections of Architecture of Africa:'' * Prehistoric North African architecture * Ancient North African architecture * Medieval North African architectureSee also
*Culture of Egypt
The culture of Egypt has thousands of years of recorded history. A cradle of civilization, Ancient Egypt was among the earliest civilizations in the world. For millennia, Egypt developed strikingly unique, complex and stable cultures that influe ...
* Demographics of the Middle East and North Africa
* European Digital Archive on Soil Maps of the World
* List of modern conflicts in North Africa
* List of Roman Latin poets and writers from North Africa
References
Further reading
* Cesari, Jocelyne. ''The awakening of Muslim democracy: Religion, modernity, and the state'' (Cambridge University Press, 2014). * Fischbach, ed. Michael R. ''Biographical encyclopedia of the modern Middle East and North Africa'' (Gale Group, 2008). * Ilahiane, Hsain. ''Historical dictionary of the Berbers (Imazighen)'' (Rowman & Littlefield, 2017). * Issawi, Charles. ''An economic history of the Middle East and North Africa'' (Routledge, 2013). * Naylor, Phillip C. ''North Africa, Revised Edition: A History from Antiquity to the Present'' (University of Texas Press, 2015). *Willie Molesi, ''Black Africa versus Arab North Africa: The Great Divide'', *Willie Molesi, ''Relations Between Africans and Arabs: Harsh Realities'',External links
*North Africa's Weather Forecasts and Weather Conditions
North Africa news and analysis
Africa Interactive Map
from the United States Army Africa (archived 17 January 2010) {{Authority control Geography of North Africa Regions of Africa