|
Vadali, Gujarat
Vadali is a town in Vadali Taluka of Sabarkantha district of Gujarat, India. History Vadali is perhaps the O-cha-li or Vadari which Chinese traveller Xuanzang visited between Malwa and Valabhi circa 640 CE. In the eleventh century, Vadali was the centre of a large kingdom. It was formerly known as Vatapalli. ''Kharataragaccha-Gurvavali'' notes the Parshvanatha temple of Vadali dated to mid-12th century. Sahanapala, son of Haripala (a Pratihara of the Paramara king Dharavarsha) built the ''mandapa'' of the Vaidyanath temple at Vadali in Vikram Samvat 1264 (1208 CE). Demographics Vadali has a population of 23,000. Geography It's surrounded by mountains which are parts of the Aravali Range. Economy The chief source of income of people is agriculture. The villages surrounding Vadali grow large number of vegetables. It supplies vegetables to Sabarkantha district and as far as Ahmedabad, Surat and Rajasthan. Transport It is located thirteen kilometres north of Idar. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabarkantha District
Sabarkantha district is one of the 33 districts of Gujarat state of India and is located in the northeastern part of the state. The administrative headquarters of the district are located in Himatnagar. Geography Sabarkantha District is bounded by Rajasthan state to the north and northeast, Banaskantha district and Mehsana district to the west, Gandhinagar district to the south and Aravalli district to the southeast. It is spread across an area of 5390 km2. It has a gender ratio of 950 females per 1000 men, and the literacy rate for the district is 76.6%. History During the Western Satrap rule, the region was known as ''Shwabhra'' ( gu, શ્વભ્ર). The region was under rule of Satrap Rudradama in 150 A.D. as indicated in Ashoka's Major Rock Edicts at Junagadh. The river of the region is named as ''Shwabhravati'' which is now known as Sabarmati River. The region is also named in auxiliary text ''Gaṇapāṭha'' of Pāṇini's grammar work, ''Aṣṭādhyāyī''. Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state encompasses 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation (more than any other state). The most important sites are Lothal (the world's first dry dock), Dholavira (the fifth largest site), and Gola Dhoro (where 5 uncommon seals were found). Lothal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of his journey to India in 629–645 CE, his efforts to bring over 657 Indian texts to China, and his translations of some of these texts.Li Rongxi (1996), ''The Great Tang Dynasty Record of the Western Regions'', Bukkyo Dendo Kyokai and Numata Center for Buddhist Translation and Research, Berkeley, , pp. xiii-xiv Xuanzang was born on 6 April 602 in Chenliu, what is now Kaifeng municipality in Henan province. As a boy, he took to reading religious books, and studying the ideas therein with his father. Like his elder brother, he became a student of Buddhist studies at Jingtu monastery. Xuanzang was ordained as a '' śrāmaṇera'' (novice monk) at the age of thirteen. Due to the political and social unrest caused by the fall of the Sui dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malwa
Malwa is a historical region, historical list of regions in India, region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic plateau, volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also synonymous with the former state of Madhya Bharat which was later merged with Madhya Pradesh. At present the historical Malwa region includes districts of western Madhya Pradesh and parts of south-eastern Rajasthan. Sometimes the definition of Malwa is extended to include the Nimar region south of the Vindhyas. The Malwa region had been a separate political unit from the time of the ancient Malava Kingdom. It has been ruled by several kingdoms and dynasties, including the Avanti (India), Avanti Kingdom, The Maurya Empire, Mauryans, the Malavas, the Gupta Empire, Guptas, the Paramaras, the Delhi Sultanate, the Malwa Sultanate, Malwa sultans, the Mughal Empire, Mughals and the Maratha E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valabhi
Vallabhi (or Valabhi or Valabhipur, modern Vala; Devanāgarī: वल्लभी) is an ancient city located in the Saurashtra peninsula of Gujarat, near Bhavnagar in western India. It is also known as Vallabhipura and was the capital of the Suryavanshi Maitraka Dynasty. History Vallabhi was occupied as early as the Harappan period, and was later part of the Maurya Empire from about 322 BCE until 185 BCE. The Satavahana dynasty ruled the area, off and on, from the late second century BCE until the early third century CE. The Gupta Empire held the area from approximately 319 CE to 467 CE. The Great Council of Vallabhi, which codified the Śvētāmbaras Jain texts, was held there in 454 CE, during the decline of the Gupta Empire. In the fifth century (CE), the first two Maitraka rulers, Bhatarka and Dharasena I, only used the title of ''Senapati'' (general). The third ruler, Dronasimha (Dronasena ), declared himself ''Maharaja'' (literally "Great King").Roychaudhuri, H.C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parshvanatha
''Parshvanatha'' (), also known as ''Parshva'' () and ''Parasnath'', was the 23rd of 24 ''Tirthankaras'' (supreme preacher of dharma) of Jainism. He is the only Tirthankara who gained the title of ''Kalīkālkalpataru ( Kalpavriksha in this "Kali Yuga").'' Parshvanatha is one of the earliest ''Tirthankaras'' who are acknowledged as historical figures. He was the earliest exponent of Karma philosophy in recorded history. The Jain sources place him between the 9th and 8th centuries BCE whereas historians consider that he lived in the 8th or 7th century BCE. Parshvanatha was born 273 years before Mahavira. He was the spiritual successor of 22nd tirthankara Neminatha. He is popularly seen as a propagator and reviver of Jainism. Parshvanatha attained moksha on Mount Sammeda (Madhuban, Jharkhand) popular as Parasnath hill in the Ganges basin, an important Jain pilgrimage site. His iconography is notable for the serpent hood over his head, and his worship often includes Dharanendra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parmara Dynasty
Parmar is a Rajput clan found in Northern and Central India, especially in Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Kutch, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh and North Maharashtra Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te .... See also * Paramara Dynasty * Panwar Dynasty * Pawar * Panwar References {{Rajput Groups of India Rajput clans Agnivansha Rajput clans of Uttarakhand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vikram Samvat
Vikram Samvat ( IAST: ''Vikrama Samvat''; abbreviated VS) or Bikram Sambat B.S. and also known as the Vikrami calendar, is a Hindu calendar historically used in the Indian subcontinent. Vikram Samvat is generally 57 years ahead of Gregorian Calendar, except during January to April, when it is ahead by 56 years. Alongside Nepal Sambat, it is one of the two official calendars used in Nepal. In India, it is used in several states. The traditional Vikram Samvat calendar, as used in India, uses lunar months and solar sidereal years. The Nepali Bikram Sambat introduced in 1901 CE, also uses a solar sidereal year. History A number of ancient and medieval inscriptions used the Vikram Samvat. Although it was reportedly named after the legendary king Vikramaditya, the term "Vikrama Samvat" does not appear in the historical record before the 9th century; the same calendar system is found with other names, such as Krita and Malava. In colonial scholarship, the era was believed to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
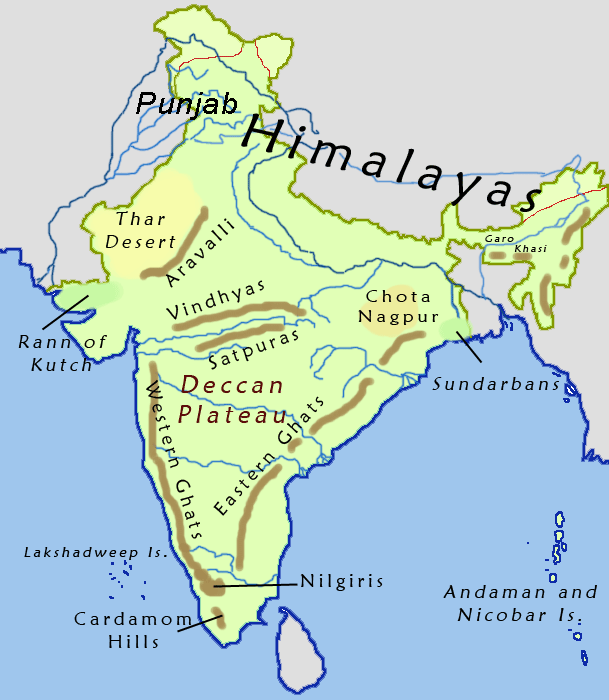
Aravali Range
The Aravalli Range (also spelled ''Aravali'') is a mountain range in North India, Northern-West India, Western India, running approximately in a south-west direction, starting near Delhi, passing through southern Haryana, Rajasthan, and ending in Ahmedabad Gujarat. The highest peak is Guru Shikhar on Mount Abu at . The Aravalli Range is arguably the oldest geological feature on Earth, having its origin in the Proterozoic era. The Aravalli Range is rich in natural resources and serves as check to the growth of the western desert. Etymology Aravalli, a composite Sanskrit word from the roots ''"ara"'' and ''"vali"'', literally means the ''"line of peaks"''. Natural history Geology The Aravalli Range, an eroded stub of ancient mountains, is believed to be the oldest range of fold mountains in India.Roy, A. B. (1990). Evolution of the Precambrian crust of the Aravalli Range. Developments in Precambrian Geology, 8, 327–347. The natural history of the Aravalli Range da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ; Gujarati: Amdavad ) is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 (per the 2011 population census) makes it the fifth-most populous city in India, and the encompassing urban agglomeration population estimated at 6,357,693 is the seventh-most populous in India. Ahmedabad is located near the banks of the Sabarmati River, from the capital of Gujarat, Gandhinagar, also known as its twin city. Ahmedabad has emerged as an important economic and industrial hub in India. It is the second-largest producer of cotton in India, due to which it was known as the ' Manchester of India' along with Kanpur. Ahmedabad's stock exchange (before it was shut down in 2018) was the country's second oldest. Cricket is a popular sport in Ahmedabad; a newly built stadium, called Narendra Modi Stadium, at Motera can accommodate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surat
Surat is a city in the western Indian state of Gujarat. The word Surat literally means ''face'' in Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of the river Tapti near its confluence with the Arabian Sea, it used to be a large seaport. It is now the commercial and economic center in South Gujarat, and one of the largest urban areas of western India. It has well-established diamond and textile industry, and is a major supply centre for apparels and accessories. About 90% of the world's diamonds supply are cut and polished in the city. It is the second largest city in Gujarat after Ahmedabad and the eighth largest city by population and ninth largest urban agglomeration in India. It is the administrative capital of the Surat district. The city is located south of the state capital, Gandhinagar; south of Ahmedabad; and north of Mumbai. The city centre is located on the Tapti River, close to Arabian Sea. Surat will be the world's fastest growing city from 2019 to 2035, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern side, where it comprises most of the wide and inhospitable Thar Desert (also known as the Great Indian Desert) and shares a border with the Pakistani provinces of Punjab to the northwest and Sindh to the west, along the Sutlej- Indus River valley. It is bordered by five other Indian states: Punjab to the north; Haryana and Uttar Pradesh to the northeast; Madhya Pradesh to the southeast; and Gujarat to the southwest. Its geographical location is 23.3 to 30.12 North latitude and 69.30 to 78.17 East longitude, with the Tropic of Cancer passing through its southernmost tip. Its major features include the ruins of the Indus Valley civilisation at Kalibangan and Balathal, the Dilwara Temples, a Jain pilgrimage site at Rajasthan's only hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |