|
Upwind
In geography and seamanship, windward () and leeward () are directions relative to the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., along the direction towards which the wind is going. The side of a ship that is towards the leeward is its "lee side". If the vessel is heeling under the pressure of crosswind, the lee side will be the "lower side". During the Age of Sail, the term ''weather'' was used as a synonym for ''windward'' in some contexts, as in the '' weather gage''. Since it captures rainfall, the windward side of a mountain tends to be wetter than the leeward side it blocks. The drier leeward area is said to be in a rain shadow. Origin The term "windward" has roots in both Low German and Old English. The word "lee", which means a place without wind, comes from the Old Norse "hle" for "cover" and has been used in marine navigation in Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, Windsurfing, windsurfer, or Kitesurfing, kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (Land sailing, land yacht) over a chosen Course (navigation), course, which is often part of a larger plan of navigation. From prehistory until the second half of the 19th century, sailing craft were the primary means of maritime trade and transportation; exploration across the seas and oceans was reliant on sail for anything other than the shortest distances. Naval power in this period used sail to varying degrees depending on the current technology, culminating in the gun-armed sailing warships of the Age of Sail. Sail was slowly replaced by steam as the method of propulsion for ships over the latter part of the 19th century – seeing a gradual improvement in the technology of steam through a number of developmental steps. Steam allowed schedul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heeling (sailing)
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, windsurfer, or kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' ( land yacht) over a chosen course, which is often part of a larger plan of navigation. From prehistory until the second half of the 19th century, sailing craft were the primary means of maritime trade and transportation; exploration across the seas and oceans was reliant on sail for anything other than the shortest distances. Naval power in this period used sail to varying degrees depending on the current technology, culminating in the gun-armed sailing warships of the Age of Sail. Sail was slowly replaced by steam as the method of propulsion for ships over the latter part of the 19th century – seeing a gradual improvement in the technology of steam through a number of developmental steps. Steam allowed scheduled services that ran at higher average speeds than sailin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upwind Downwind Example
In geography and seamanship, windward () and leeward () are directions relative to the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., along the direction towards which the wind is going. The side of a ship that is towards the leeward is its "lee side". If the vessel is heeling (sailing), heeling under the pressure of crosswind, the lee side will be the "lower side". During the Age of Sail, the term ''weather'' was used as a synonym for ''windward'' in some contexts, as in the ''weather gage''. Since it captures rain, rainfall, the windward side of a mountain tends to be wetter than the leeward side it blocks. The drier leeward area is said to be in a rain shadow. Origin The term "windward" has roots in both Low German and Old English. The word "lee", which means a place without wind, comes from the Old Norse "hle" for "cover" and has been used in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square-rig
Square rig is a generic type of sail and rigging arrangement in which a sailing vessel's primary driving sails are carried on horizontal spars that are perpendicular (or square) to the median plane of the keel and masts of the vessel. These spars are called and their tips, outside the lifts, are called the . A ship mainly rigged so is called a square-rigger. In " Jackspeak" (Royal Navy slang), it also refers to the dress uniform of Junior Ratings. History Single sail square rigs were used by the ancient Egyptians, the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Romans, and the Celts. Later the Scandinavians, the Germanic peoples, and the Slavs adopted the single square-rigged sail, with it becoming one of the defining characteristics of the classic “Viking” ships.The Viking ship's single square-rigged sail. http://Longshipco.org/sail.html Retrieved 2018-8-20 See also * Glossary of nautical terms (A-L) Glossary of nautical terms may refer to: * Glossary of nautical terms (A–L) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
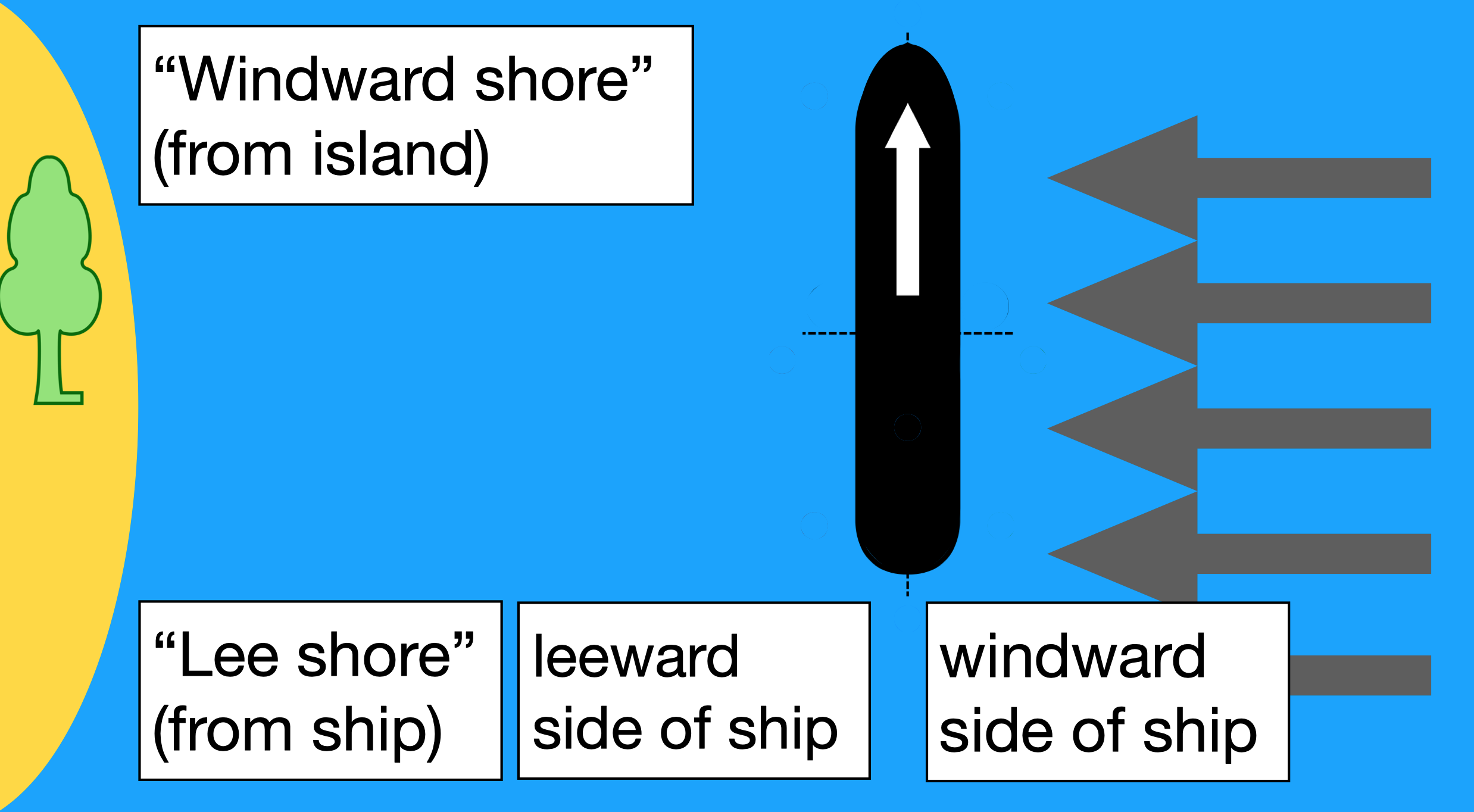
Lee Shore
A lee shore, sometimes also called a leeward ( shore, or more commonly ), is a nautical term to describe a stretch of shoreline that is to the Windward and leeward, lee side of a vessel—meaning the wind is blowing towards land. Its opposite, the shore on the windward side of the vessel, is called the weather or windward shore ( or, more commonly, ). Because of the danger of being driven aground on a lee shore it is essential seamanship to treat one with caution. This is particularly the case with sailing vessels, but a lee shore is an issue for powered vessels as well. Use of the terms "windward", "leeward", and "lee" Usage of the terms to describe shores in relation to an arbitrary point of view, including on land, can lead to ambiguity. The windward shore of an island is a lee shore from the perspective of a vessel travelling offshore. Although the terms are often confused, "the lee shore" is different from "a leeward shore" based on the reference point from which the sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
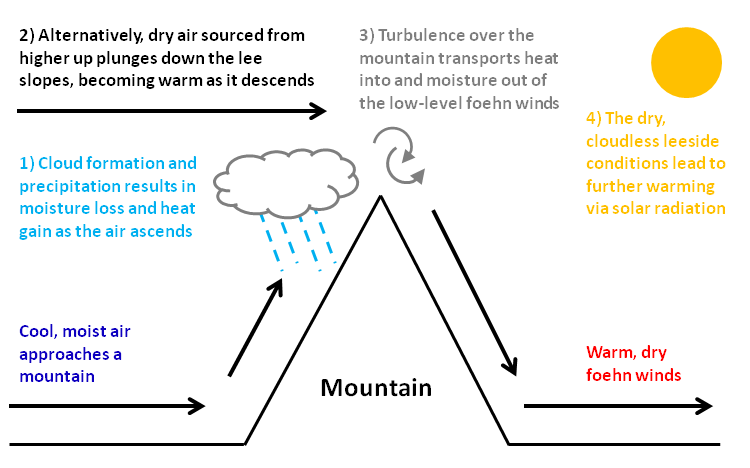
Foehn Wind
A Foehn, or Föhn (, , , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm downslope wind in the lee of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes (see orographic lift). As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes. Foehn winds can raise temperatures by as much as in just a matter of hours. Switzerland, southern Germany, and Austria have a warmer climate due to the Foehn, as moist winds off the Mediterranean Sea blow over the Alps. Etymology The name ''Foehn'' (, ) arose in the Alpine region. Originating from Latin , a mild west wind of which Favonius was the Roman personification and probably transmitted by or just , the term was adopted as . In the Southern Alps, the phenomenon is known as but also and in Serbo-Croatian and Slovene. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downstream And Upstream (hidrology)
In hydrology, a current in a water body is the flow of water in any one particular direction. The current varies spatially as well as temporally, dependent upon the flow volume of water, stream gradient, and channel geometry. In tidal zones, the current and streams may reverse on the flood tide before resuming on the ebb tide. On a global scale, wind and the rotation of the earth greatly influence the flow of ocean currents. In a stream or river there the current is influenced by gravity, the term ''upstream'' (or ''upriver'') refers to the direction towards the source of the stream (or river), i.e. against the direction of flow. Likewise, the term ''downstream'' or ''downriver'' describes the direction towards the mouth of the stream or river, in which the current flows. The term "left bank" and "right bank In geography, a bank is the land alongside a body of water. Different structures are referred to as ''banks'' in different fields of geography. In limnology (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Verde Islands
Cape Verde or Cabo Verde, officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country and archipelagic state of West Africa in the central Atlantic Ocean, consisting of ten volcanic islands with a combined land area of about . These islands lie between west of Cap-Vert, the westernmost point of continental Africa. The Cape Verde islands form part of the Macaronesia ecoregion, along with the Azores, the Canary Islands, Madeira and the Savage Isles. The Cape Verde archipelago was uninhabited until the 15th century, when Portuguese explorers colonized the islands, establishing one of the first European settlements in the tropics. Due to its strategic position, Cape Verde became a significant location in the transatlantic slave trade during the 16th and 17th centuries. The islands experienced economic growth during this period, driven by their role by the rapid emergence of merchants, privateers, and pirates. It declined economically in the 19th century, and many of its inh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sotavento Islands
Cape Verde (formally, the Republic of Cabo Verde) is a group of arid Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic islands which are home to distinct communities of plants, birds, and reptiles. Location and description The Cape Verde Islands are located in the mid-Atlantic Ocean some off the west coast of the continent of Africa. The landscape varies from dry plains to high active volcanoes with cliffs rising steeply from the ocean. The climate is arid. The total size is . The archipelago consists of ten islands and five islets, divided into the windward (Barlavento) and leeward (Sotavento) groups. The six islands in the Barlavento group, which sits in the trade winds, are Santo Antão, Cape Verde, Santo Antão, São Vicente, Cape Verde, São Vicente, Santa Luzia, Cape Verde, Santa Luzia, São Nicolau, Cape Verde, São Nicolau, Sal, Cape Verde, Sal, and Boa Vista, Cape Verde, Boa Vista. The total land mass is . [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barlavento Islands
Cape Verde (formally, the Republic of Cabo Verde) is a group of arid Atlantic islands which are home to distinct communities of plants, birds, and reptiles. Location and description The Cape Verde Islands are located in the mid-Atlantic Ocean some off the west coast of the continent of Africa. The landscape varies from dry plains to high active volcanoes with cliffs rising steeply from the ocean. The climate is arid. The total size is . The archipelago consists of ten islands and five islets, divided into the windward (Barlavento) and leeward (Sotavento) groups. The six islands in the Barlavento group, which sits in the trade winds, are Santo Antão, São Vicente, Santa Luzia, São Nicolau, Sal, and Boa Vista. The total land mass is .Valor simbólico do centro histórico da Praia Lourenço Conceição Gomes, Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Winds
The trade winds or easterlies are permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere, strengthening during the winter and when the Arctic oscillation is in its warm phase. Trade winds have been used by captains of sailing ships to cross the world's oceans for centuries. They enabled European colonization of the Americas, and trade routes to become established across the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. In meteorology, they act as the steering flow for tropical storms that form over the Atlantic, Pacific, and southern Indian oceans and cause rainfall in North America, Southeast Asia, and Madagascar and East Africa. Shallow cumulus clouds are seen within trade wind regimes and are capped from becoming taller by a trade wind inversion, which is caused by descending air aloft from within the subtropical ridge. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwealth usage), snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation; their water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate, so fog and mist do not fall. (Such a non-precipitating combination is a colloid.) Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated with water vapor: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called shower (p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |