|
Undermining (chess)
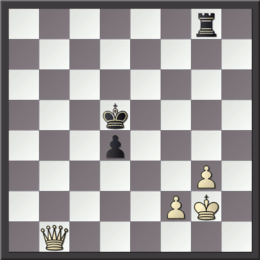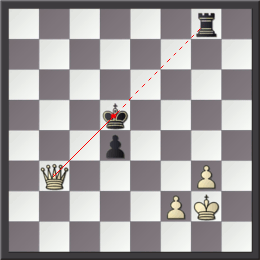
Undermining (also known as removal of the guard, or removing the defender) is a chess tactic in which a defensive piece is captured, leaving one of the opponent's pieces undefended or under-defended. The opponent has the unpalatable choice of recapturing or saving the undefended piece. A possible response is to sacrifice the piece whose defense was undermined before capturing the piece which just took the defender. Example Kramnik– Topalov in the seventh round of the 2004 Linares chess tournament reached the diagrammed position with White to play. The black knight on a4 is defended only by the black pawn on b5. White undermined the knight with 1. Bxb5. The game continued 1... Rxb5 2. Rxa4, with a net gain of a pawn for White. Black may attempt 1...Nxb2, disposing of the unguarded knight and hoping for 2.Kxb2 Rxb5+ to regain the lost pawn. After 2.Rb3, however, Black can only save the knight with 2...Rxb5 3.Rxb5, leaving White an exchange up instead of just a pawn. See a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Tactic
In chess, a tactic is a sequence of moves that each makes one or more immediate threats – a check, a threat, a checkmating sequence threat, or the threat of another tactic or otherwise forcing moves – that culminates in the opponent's being unable to respond to all of the threats without making some kind of concession. Most often, the immediate benefit takes the form of a material advantage or ; however, some tactics are used for defensive purposes and can salvage material that would otherwise be lost, or to induce stalemate in an otherwise lost position. Tactics are usually contrasted with strategy, whereby the individual moves by themselves do not make indefensible threats, and the cumulative advantage of them takes longer to capitalise. The dichotomy can be summarised as tactics concerning short-term play and strategy concerning long-term play. Examples of strategic advantages are in, compromised pawn structure in, and sustained pressure on, the opponent's position. Oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Kramnik
Vladimir Borisovich Kramnik (; born 25 June 1975) is a Russian Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster. He was the World Chess Champion#Split title (1993–2006), Classical World Chess Champion from 2000 to 2006, and the 14th undisputed World Chess Champion from 2006 to 2007. In 2000, Kramnik defeated Garry Kasparov and became the Classical World Chess Championship 2000, Classical World Chess Champion. He Classical World Chess Championship 2004, defended his title in 2004 against Peter Leko, and defeated the reigning World Chess Champion#Split title (1993–2006), FIDE World Champion Veselin Topalov in a World Chess Championship 2006, unification match in 2006. As a result, Kramnik became the first undisputed World Champion, holding both the FIDE and Classical titles, since Kasparov split from FIDE in 1993. In 2007, Kramnik lost the title to Viswanathan Anand, who won the World Chess Championship 2007 tournament ahead of Kramnik. He challenged Anand at the World Chess Championsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veselin Topalov
Veselin Aleksandrov Topalov (pronounced ; ; born 15 March 1975) is a Bulgarian Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster and former FIDE World Chess Championship, World Chess Champion. Topalov became FIDE World Chess Champion by winning the FIDE World Chess Championship 2005. He lost his title in the World Chess Championship 2006 against Vladimir Kramnik. He challenged Viswanathan Anand at the World Chess Championship 2010, losing 6½–5½. He won the 2005 Chess Oscar. He was ranked List of FIDE chess world number ones, world number one from April 2006 to January 2007. He regained the top ranking in October 2008 until January 2010. His peak rating was 2816 in July 2015, placing him joint-tenth on the list of List of chess players by peak FIDE rating, highest FIDE-rated players of all time. Topalov has competed at nine Chess Olympiads (1994–2000, 2008–2016), winning board one gold in 2014 and scoring best overall performance in 1994. He also won in Linares International Chess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linares Chess Tournament
The Linares International Chess Tournament (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Torneo Internacional de Ajedrez Ciudad de Linares'') was an annual chess tournament, usually played around the end of February, which takes its name from the city of Linares (Spain), Linares in the Jaén Province, Spain, Jaén province of Andalusia, Spain, in which it was held. It is sometimes described as the The Championships, Wimbledon, Wimbledon of chess, being one of the strongest annual tournaments held on the ''de facto'' chess tour, along with the Tata Steel Chess Tournament, Tal Memorial and Dortmund chess tournament, Dortmund events. The Linares tournament began in 1978 and was held annually from 1988 to 2010 (with the exception of 1996). Since 2010, the tournament has not been held for financial reasons. History The event, sponsored by Spanish businessman Luis Rentero, was first held in 1978. At that time it was not an elite event and was won by the relatively unknown Swede Jaan Eslon, on tie-bre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Exchange (chess)
In chess, the exchange is the difference of a rook for a (i.e. a bishop or knight). Having a rook for a minor piece is generally advantageous, since the rook is usually more valuable. A player who has a rook for a minor piece is said to be ''up the exchange'', and the other player is ''down the exchange''. A player who wins a rook for a minor piece is said to have ''won the exchange'', while the other player has ''lost the exchange''. The opposing captures often happen on consecutive moves, but this is not strictly necessary. Although it is generally detrimental to lose the exchange, one may occasionally find reason to purposely do so; the result is an ''exchange sacrifice''. "The exchange" differs from the more general " exchange" or "an exchange", which refers to the loss and subsequent gain of arbitrary pieces; for example, to "exchange queens" would mean that each side's queen is . The ''minor exchange'' is the exchange of a bishop for a knight. This term is rarely use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deflection (chess)
Deflection in chess is a tactic that forces an opposing piece to leave the square, rank or file it occupies, thus exposing the king or a valuable piece. It is typically used in the context of a combination or attack, where the deflected piece is critical to the defence. Deflection may be used as a gambit to cause an opponent's piece to move to a less suitable square. Deflections are often used as part of a combination which may involve other types of chess tactics as well. If the deflected piece happens to be an overworked piece then the opponent's defense instantly crumbles, making victory imminent to the one who employed the deflection. ''Chess Life'' Dana Mackenzie See also * Overl ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Tactics
In chess, a tactic is a sequence of moves that each makes one or more immediate threats – a check, a threat, a checkmating sequence threat, or the threat of another tactic or otherwise forcing moves – that culminates in the opponent's being unable to respond to all of the threats without making some kind of concession. Most often, the immediate benefit takes the form of a material advantage or ; however, some tactics are used for defensive purposes and can salvage material that would otherwise be lost, or to induce stalemate in an otherwise lost position. Tactics are usually contrasted with strategy, whereby the individual moves by themselves do not make indefensible threats, and the cumulative advantage of them takes longer to capitalise. The dichotomy can be summarised as tactics concerning short-term play and strategy concerning long-term play. Examples of strategic advantages are in, compromised pawn structure in, and sustained pressure on, the opponent's position. Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |