|
Overloading (chess)
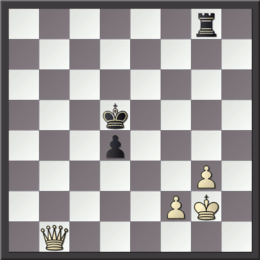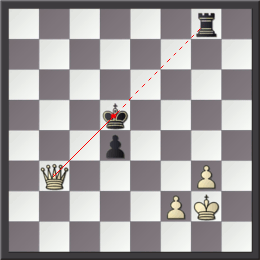
Overloading (also overworking) is a chess tactic in which a defensive piece is given an additional defensive assignment which it cannot complete without abandoning its original defensive assignment. Examples Krasenkow– Karpov, in the first round of the 2003 Corus chess tournament, reached the diagrammed position with Black to play. As the white rook on f1 is preventing the black queen from giving checkmate by capturing the pawn on f3, Black won immediately with :29... Re1 further pinning the white rook against the king and overloading the rook. White now cannot prevent the black queen from taking the f-pawn: if White tries to protect the rook with 30.Rxe1 or 30.Qc4, then 30...Qxf3. If White sacrifices the rook by playing 30.Kg2, then 30...Rxf1 31.Kxf1 Qxf3+ and loses the other rook with 32...Qxd5. In Liviu-Dieter Nisipeanu– Anish Giri (see diagram), Giri (Black) played :30... Bxh3 overloading the g2-pawn, as 31.gxh3 is met with 31...f3 32.Re3 Qg5+. After 31.Qc3 Bg4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chess Tactic
In chess, a tactic is a sequence of moves that each makes one or more immediate threats – a check, a threat, a checkmating sequence threat, or the threat of another tactic or otherwise forcing moves – that culminates in the opponent's being unable to respond to all of the threats without making some kind of concession. Most often, the immediate benefit takes the form of a material advantage or ; however, some tactics are used for defensive purposes and can salvage material that would otherwise be lost, or to induce stalemate in an otherwise lost position. Tactics are usually contrasted with strategy, whereby the individual moves by themselves do not make indefensible threats, and the cumulative advantage of them takes longer to capitalise. The dichotomy can be summarised as tactics concerning short-term play and strategy concerning long-term play. Examples of strategic advantages are in, compromised pawn structure in, and sustained pressure on, the opponent's position. Oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Michał Krasenkow
Michał Krasenkow (born 14 November 1963) is a Polish chess grandmaster, chess trainer and writer. He is one of the strongest Polish chess players since World War II. His playing style is aggressive and he has won many "best game" awards. Life and career He was born in Moscow (formerly Mikhail Vladimirovich Krasenkov, ). Master of applied mathematics (1985). His first notable successes date back to the 80s: he became a national master of the USSR in 1982, an International Master in 1988 and an International Grandmaster in 1989. He became Champion of Georgia in 1987 and team champion of the USSR (with " Tigran Petrosian Chess Club", Moscow) in 1990. In 1992 Krasenkow emigrated to Poland. Since 1996 he represents that country at international competitions. Two-times champion of Poland (2000, 2002). Krasenkow won Polish team championships 14 times: 1991, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1997, and 1998 with "Stilon" Gorzów Wielkopolski, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2009 with "P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anatoly Karpov
Anatoly Yevgenyevich Karpov (, ; born May 23, 1951) is a Russian and former Soviet Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster, former World Chess Championship, World Chess Champion, and politician. He was the 12th World Chess Champion from 1975 to 1985, a three-time FIDE World Champion (1993, 1996, 1998), twice World Chess champion as a member of the USSR team (1985, 1989), and a six-time winner of Chess Olympiad, Chess Olympiads as a member of the USSR team (1972, 1974, 1980, 1982, 1986, 1988). The International Association of Chess Press awarded him nine Chess Oscars (1973–77, 1979, 1980, 1981, 1984). Karpov's chess tournament successes include over 160 first-place finishes. He had a peak Elo rating system, Elo rating of 2780, and his 102 total months world number one is the third-longest of all time, behind Magnus Carlsen and Garry Kasparov. Karpov is also an elected Member of the State Duma in Russia. Since 2006, he has chaired the Commission for Ecological Safety and Envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Corus Chess Tournament
The Tata Steel Chess Tournament is an annual chess tournament held in January in Wijk aan Zee, the Netherlands. It was called the Hoogovens Tournament from its creation in 1938 until the sponsor Koninklijke Hoogovens merged with British Steel to form the Corus Group in 1999, after which the tournament was renamed the Corus Chess Tournament. Corus Group was taken over by the Tata Group and became Tata Steel Europe in 2007, with the tournament changing to its current name in 2011. It has also been referred to as "Wijk aan Zee" since the venue change from the town of Beverwijk to the town of Wijk aan Zee in 1968. Despite the name changes, the series is numbered sequentially from its Hoogovens beginnings; for example, the 2025 event was referred to as the 87th Tata Steel Chess Tournament. Top grandmasters compete in the tournament, but regular club players are welcome to play in the lower groups. The Masters group pits fourteen of the world's best players against each other i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Liviu-Dieter Nisipeanu
Liviu-Dieter Nisipeanu (born 1 August 1976) is a Romanian chess grandmaster. His peak FIDE rating was 2707 in October 2005, when he was ranked fifteenth in the world, and the highest rated Romanian player ever. Only in September 2022 his rating was overpassed by grandmaster Bogdan-Daniel Deac. Style His highly aggressive style of play has earned him a reputation of a modern-day Mikhail Tal. Career In 1999, Nisipeanu as a clear outsider made it to the semifinals of the FIDE World Chess Championship by beating Vasily Ivanchuk in round 4 and Alexei Shirov in the quarterfinals only to succumb to the eventual champion Alexander Khalifman. Nisipeanu won the European Individual Chess Championship 2005 in Warsaw with 10 points out of 13 games, half a point ahead of runner-up Teimour Radjabov from Azerbaijan. In April 2006, Nisipeanu played FIDE World Champion Veselin Topalov in a four-game match. Topalov won by a score of 3:1. The match was not for any official title. In Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anish Giri
Anish Kumar Giri (; ; born 28 June 1994) is a Dutch chess grandmaster. A chess prodigy Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves no hidden information and no elements of chance. It is played on a square board consisting of 64 squares arranged in an 8×8 grid. The players, referred to ..., he completed the requirements for the grandmaster title in 2009 at the age of 14 years, 7 months and 2 days. Giri is a five-time Dutch champion (2009, 2011, 2012, 2015, and 2023), and has represented the Netherlands at seven Chess Olympiads (39th Chess Olympiad, 2010, 40th Chess Olympiad, 2012, 41st Chess Olympiad, 2014, 42nd Chess Olympiad, 2016, 43rd Chess Olympiad, 2018, 44th Chess Olympiad, 2022, 45th Chess Olympiad, 2024). Giri is the No. 1 ranked player in the Netherlands, having switched from Russia in 2009. He has also won major international tournaments, most notably the Tata Steel Chess Tournament 2023, 2023 Tata Steel Chess Tourna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rotlewi Versus Rubinstein
Rotlewi versus Rubinstein is a game of chess played between Gersz Rotlewi and Akiba Rubinstein in Łódź, Poland on December 26, 1907. It features a brilliant queen and rook sacrifice by Rubinstein to . The game was dubbed Rubinstein's Immortal Game by Hans Kmoch. Garry Kasparov described the game as "Rubinstein's truly 'immortal' game" and "his most famous creation". The game White: Gersz Rotlewi Black: Akiba Rubinstein Opening: Tarrasch Defense, Symmetrical Variation ('' ECO'' D32) Łódź, Poland, December 1907 otes are based on ''The Big Book of Chess'' by Eric Schiller, and other referenced works. 1. d4 d5 2. Nf3 e6 3. e3 c5 4. c4 Nc6 5. Nc3 Nf6 6. dxc5 Bxc5 7. a3 a6 8. b4 Bd6 9. Bb2 0-0 10. Qd2 : Tartakower criticizes this as a loss of : "The queen will soon have to seek a better square. The most useful move is 10.Qc2." 10... Qe7 :This move sacrifices a pawn, but 11.cxd5 exd5 12.Nxd5? accepting the sacrifice allows 12...Nxd5 13.Qxd5 Rd8! with a strong attack. 11. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chess Tactics
In chess, a tactic is a sequence of moves that each makes one or more immediate threats – a check, a threat, a checkmating sequence threat, or the threat of another tactic or otherwise forcing moves – that culminates in the opponent's being unable to respond to all of the threats without making some kind of concession. Most often, the immediate benefit takes the form of a material advantage or ; however, some tactics are used for defensive purposes and can salvage material that would otherwise be lost, or to induce stalemate in an otherwise lost position. Tactics are usually contrasted with strategy, whereby the individual moves by themselves do not make indefensible threats, and the cumulative advantage of them takes longer to capitalise. The dichotomy can be summarised as tactics concerning short-term play and strategy concerning long-term play. Examples of strategic advantages are in, compromised pawn structure in, and sustained pressure on, the opponent's position. Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |